An experimental study of the relationship between water content and strength of unsaturated expansive soil on canal slope
-
摘要:
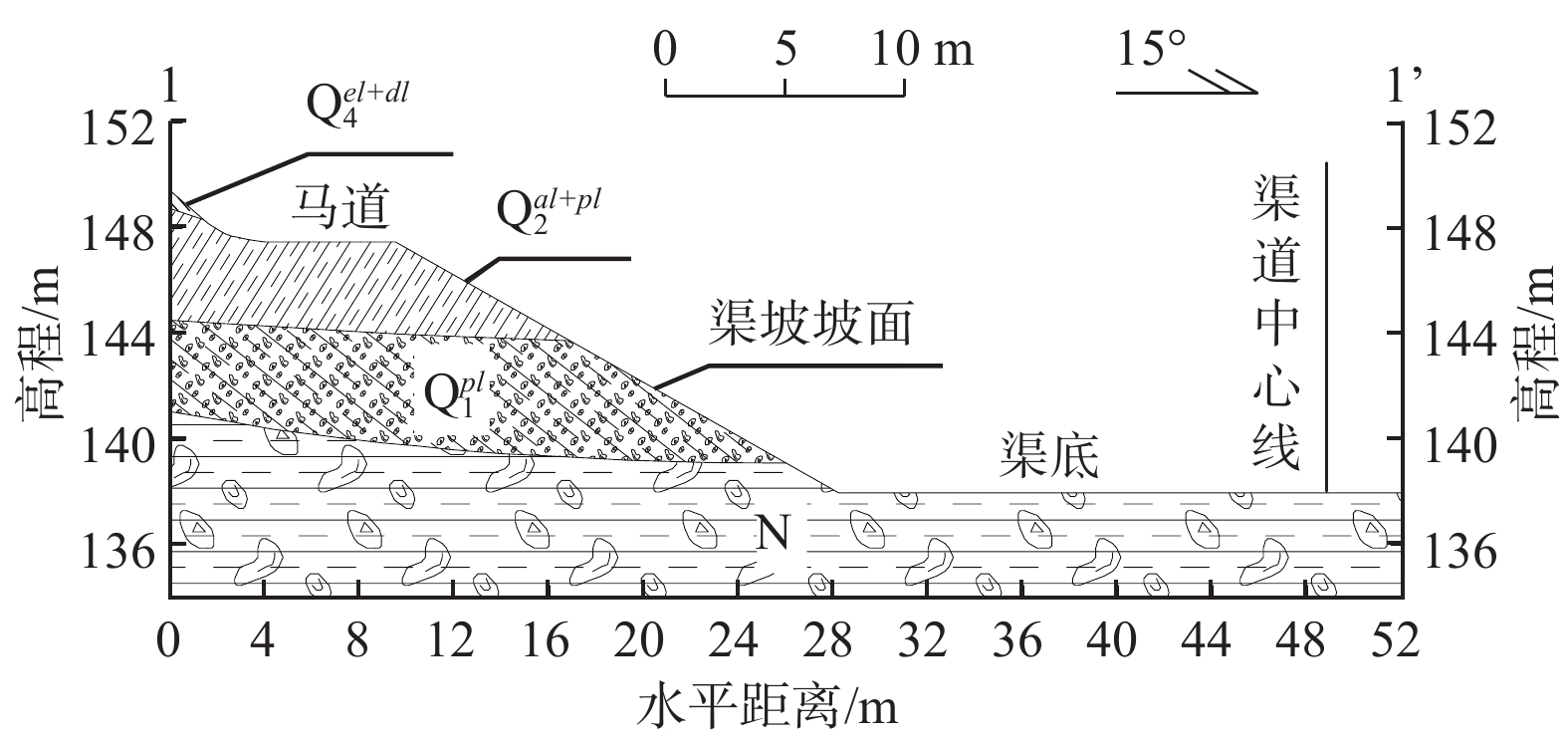
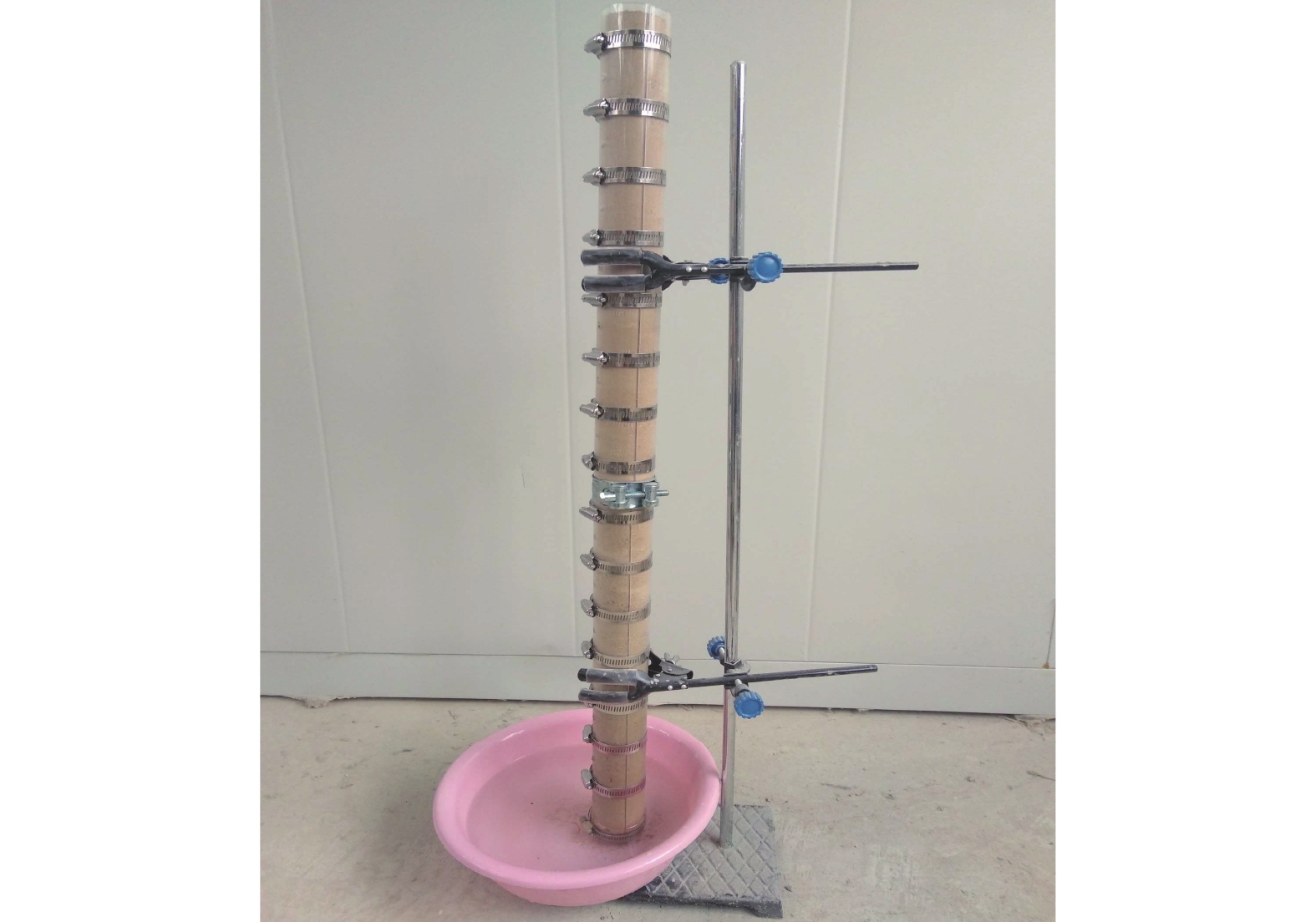
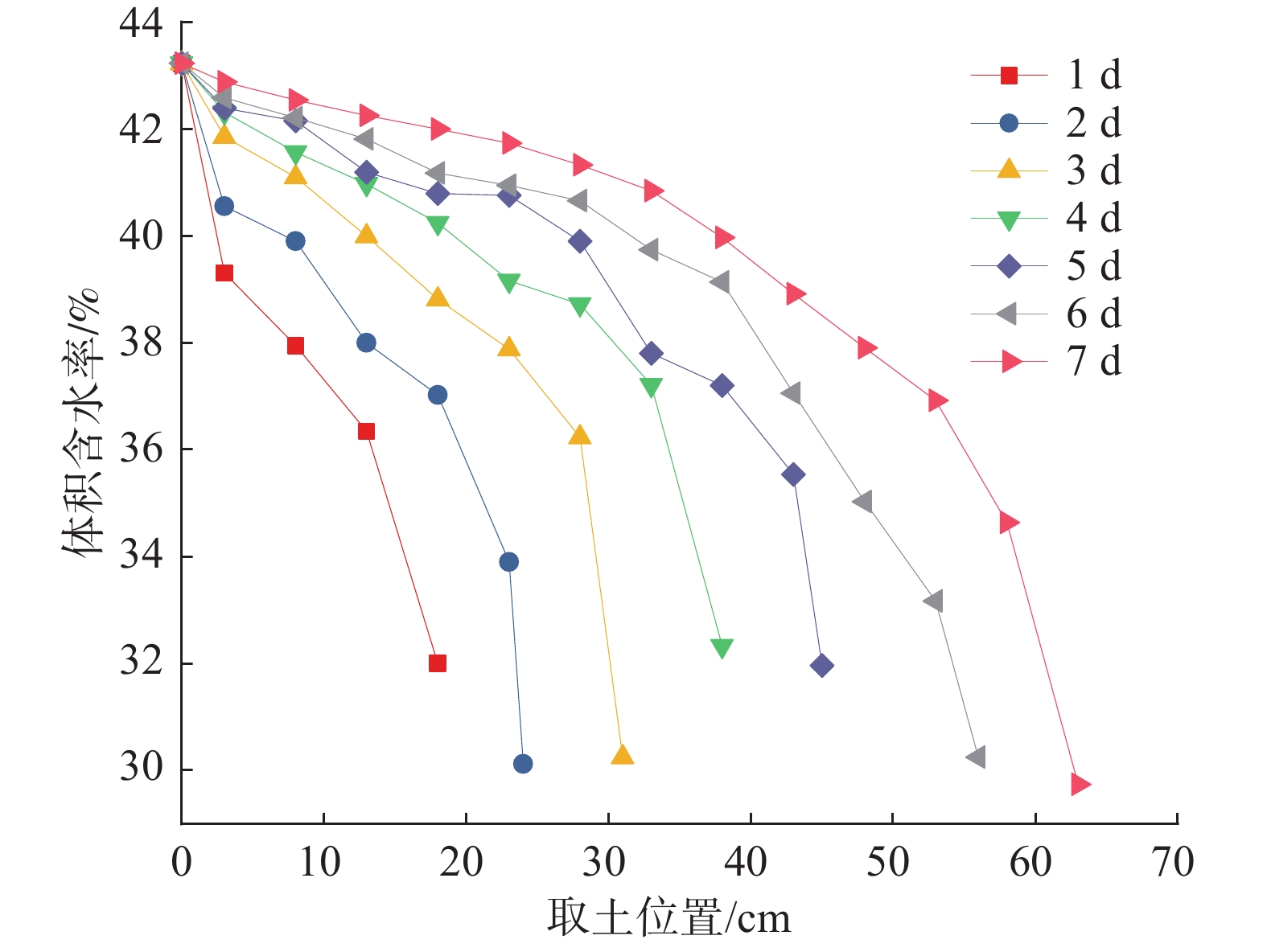
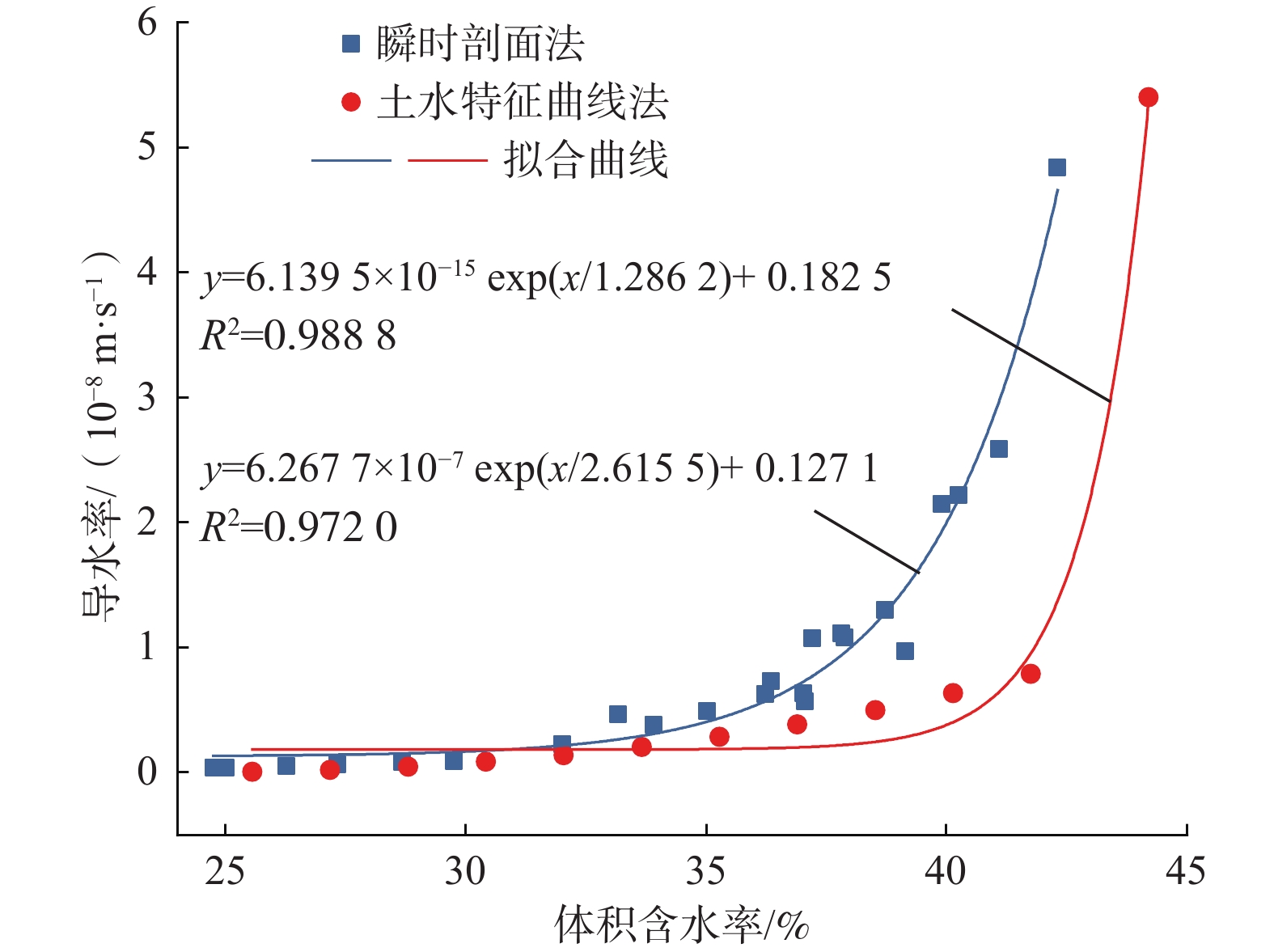
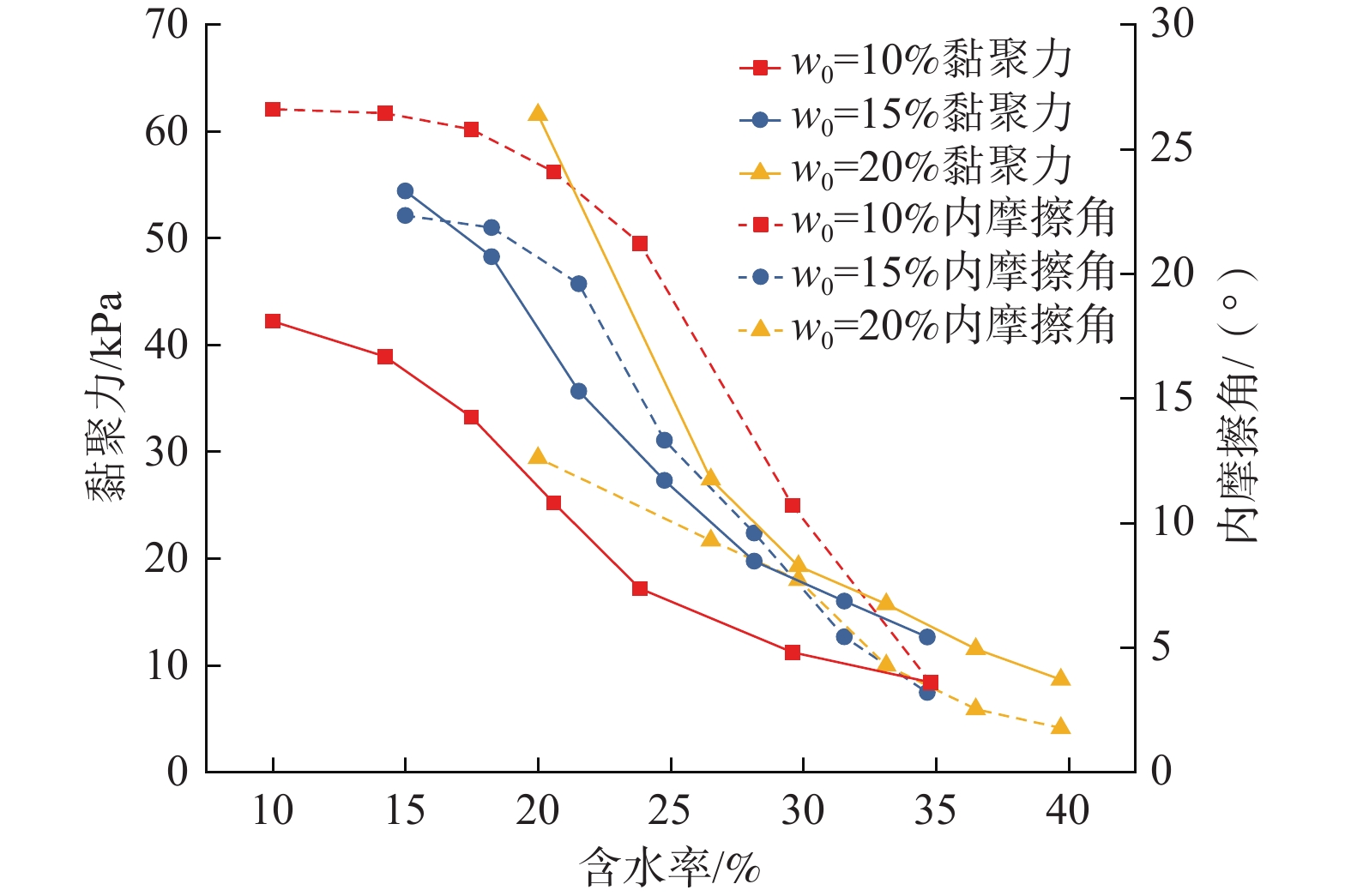
南水北调中线渠首段渠坡土主要为膨胀土,渠坡膨胀土含水率的变化会影响坡体稳定性。为了探究含水率变化对渠坡稳定性影响的具体特征,对采集自南水北调中线渠首段的渠坡膨胀土进行了滴定直剪试验,获得了渠坡膨胀土抗剪强度指标与含水率的关系曲线,试验结果表明:抗剪强度随含水率增加而明显衰减,衰减过程先快后慢;试样初始含水率越低,黏聚力下降越慢,内摩擦角下降越快,不同初始含水率试样的抗剪强度均在增湿至30%左右时产生拐点,此时衰减速率降低并趋于稳定。设计进行了土-水特征曲线法和瞬时剖面法导水率测试试验,获得了非饱和渠坡膨胀土导水率随含水率变化的曲线,试验结果表明:含水率越低,导水率越小,导水率变化速率越快;反之,导水率变化速率越慢,土体含水率趋于稳定。研究成果可用于膨胀土渠坡稳定性与坡体地下水位关系的定量分析,应用在实际工程中可以更有效地获取渠坡非饱和土体中含水率和抗剪强度的分布特征,并获得含水率和抗剪强度随时间的变化规律,为引入土体空间动态抗剪强度分析,建立更准确的膨胀土渠坡稳定性评价模型奠定基础。
Abstract:The soil layer in the canal first section of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project (MR-SNWTP) is mainly composed of expansive soil, and changes in water content of the expansive soil affect the stability of the slope. In order to make a reasonable assessment of the stability of expansive soil canal slopes, it is necessary to test and analyze the relevant physical and mechanical properties of the expansive soil on canal slopes at different water content. In this paper, titration-direct shear tests are carried out on the expansive soil collected from the canal first section of MR-SNWTP to obtain the relationship between the shear strength parameters and water content of the expansive soil. The test results show that the shear strength decreases significantly with increasing water content, and the decay process starts fast and then slows down. The lower the initial water content of the sample is, the slower the cohesion decreases, and the faster the angle of the internal friction decreases, and the shear strengths of the sample with different initial water content all show an inflection point when the water content increases to about 30%, when the decay rate decreases and becomes stable. Hydraulic conductivity tests based on soil-water characteristic curve method and instantaneous profile method are designed to obtain the hydraulic conductivity-water content curve of unsaturated expansive soil. The test results show that the lower the water content is, the smaller the hydraulic conductivity is and the faster the change rate of hydraulic conductivity is. Conversely, the slower the change rate of hydraulic conductivity is, and the more stable the soil water content tends to be. The research results of this paper can be used for quantitative analysis of the relationship between the stability of the expansive soil canal slopes and the groundwater level of the slopes. In practical applications, they can also be used to effectively obtain the distribution characteristics of water content and shear strength in the unsaturated soil of the canal slope, and to obtain the time variation laws of water content and shear strength, and a more accurate stability evaluation model is established based on spatial dynamic shear strength analysis of the expansive soil of the canal slopes.
-

-
表 1 物理指标与强度指标值
Table 1. Values of physical and strength indicators
指标 含水率/% 干密度/(g·cm−3) 孔隙比 饱和度/% 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 取值 22.9 1.65 0.76 83 13~23 15~16 -
[1] 贾文聪, 李永红, 党进谦, 等. 膨胀土强度特性的试验研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(5): 217—221.
JIA Wencong, LI Yonghong, DANG Jinqian, et al. Strength characteristics of expansive soil[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(5): 217—221. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 杨和平,曲永新,郑健龙. 宁明膨胀土研究的新进展[J]. 岩土工程学报,2005,27(9):981 − 987. [YANG Heping,QU Yongxin,ZHENG Jianlong. New development in studies on Ningming expansive soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2005,27(9):981 − 987. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.09.002
[3] ESCARIO V,SAEZ J. The shear strength of partly saturated soils[J]. Geotechnique,1986,36(3):453 − 456. doi: 10.1680/geot.1986.36.3.453
[4] 郭倩怡, 谷天峰, 吴熠哲. 永靖非饱和黄土抗剪强度试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2015, 42(6): 103 − 107
GUO Qianyi, GU Tianfeng, WU Yizhe. A test study of shear strength of unsaturated loess in Yongjing County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(6): 103 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 缪林昌,殷宗泽. 非饱和土的剪切强度[J]. 岩土力学,1999,20(3):1 − 6. [MIAO Linchang,YIN Zongze. Shear strength of unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,1999,20(3):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.1999.03.018
[6] 吕海波,曾召田,赵艳林,等. 胀缩性土强度衰减曲线的函数拟合[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013(增刊2):157 − 162. [LYU Haibo,ZENG Zhaotian,ZHAO Yanlin,et al. Function fitting on strength attenuation curve of swell-shrining soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013(Sup2):157 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 郭永春,陈伟乐,赵海涛. 膨胀土吸水过程的试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):108 − 112. [GUO Yongchun,CHEN Weile,ZHAO Haitao. Experimental research of water-uptake process of the expansive soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):108 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2016.04.18
[8] 崔颖,缪林昌. 非饱和压实膨胀土渗透特性的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(7):2007 − 2012. [CUI Ying,MIAO Linchang. Testing study of permeability characteristics of unsaturated compacted expansive soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2011,32(7):2007 − 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.07.015
[9] 舒志乐,孙启明,廖智伟,等. 干湿循环下膨胀土应力-应变行为及强度分析[J]. 中国科技论文,2021,16(8):825 − 829. [SHU Zhile,SUN Qiming,LIAO Zhiwei,et al. Stress-strain behavior and strength study of expansive soil under dry-wet cycles[J]. China Sciencepaper,2021,16(8):825 − 829. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2021.08.005
[10] 张琦,杨忠年,时伟,等. 冻融循环下初始含水率对非饱和膨胀土剪切特性试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(5):1544 − 1550. [ZHANG Qi,YANG Zhongnian,SHI Wei,et al. Experiment on shear characteristics of unsaturated expansive soil with initial moisture content under freezing-thawing cycles[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition),2021,51(5):1544 − 1550. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 杨庆,张慧珍,栾茂田. 非饱和膨胀土抗剪强度的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004(3):420 − 425. [YANG Qing,ZHANG Huizhen,LUAN Maotian. Testing study on shear strength of unsaturated expansive soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004(3):420 − 425. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.03.011
[12] 陈善雄,陈守义. 考虑降雨的非饱和土边坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 岩土力学,2001,22(4):447 − 450. [CHEN Shanxiong,CHEN Shouyi. Analysis of stability of unsaturated soil slope due to permeation of rainwater[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2001,22(4):447 − 450. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2001.04.019
[13] 陈亮胜,韦秉旭,廖欢,等. 膨胀土边坡非饱和渗流及渐进性破坏耦合分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):132 − 140. [CHEN Liangsheng,WEI Bingxu,LIAO Huan,et al. A coupling analysis of unsaturated seepage and pro-gressive failure of an expansive soil slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201910045
[14] 饶鸿,王金淑,赵志明,等. 基于有限元软件自定义本构模型的膨胀土边坡降雨入渗分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):154 − 162. [RAO Hong,WANG Jinshu,ZHAO Zhiming,et al. An analysis of rainfall infiltration of expansive soil slope based on the finite element software custom constitutive model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):154 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202002020
[15] 陈善雄, 冷星火, 赵旻, 等. 强膨胀土渠坡破坏机理及处理技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 24 − 29
CHEN Shanxiong, LENG Xinghuo, ZHAO Min, et al. Damage mechanism and treatment technology for strongly expansive soil drainage slope[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 24 − 29. (in Chinese)
[16] 夏蒙. 膨胀土非饱和特性试验研究及其在边坡稳定性分析中的应用[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2013
XIA Meng. Unsaturated expansive soils characteristics experimental study and its application in slope stability analysis[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 肖夺. 宁明膨胀土渗透特性的试验研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2006
XIAO Duo. Testing research on permeability of Ningming expansive soils[D]. Changsha: Changsha University of Science & Technology, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李萍,李同录,王红,等. 非饱和黄土土-水特征曲线与渗透系数Childs & Collis-Geroge 模型预测[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(2):184 − 189. [LI Ping,LI Tonglu,WANG Hong,et al. Soil-water characteristic curve and permeability perdiction on Childs & Collis-Geroge model of unsaturated loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(2):184 − 189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 李雄威,张鹤年,张勇. 膨胀土渗透性室内试验与非饱和渗透系数预测[J]. 四川建筑科学研究,2011,37(5):115 − 118. [LI Xiongwei,ZHANG Henian,ZHANG Yong. Lab test and unsaturated coefficient prediction of expansive soil permeability[J]. Sichuan Building Science,2011,37(5):115 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1933.2011.05.030
[20] 戴张俊,陈善雄,罗红明,等. 非饱和膨胀土/岩持水与渗透特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(1):134 − 141. [DAI Zhangjun,CHEN Shanxiong,LUO Hongming,et al. Experimental study of water-holding and permeability characteristics of unsaturated expansive soils and rocks[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(1):134 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2013.s1.066
[21] 杨毅凡. 一种非饱和膨胀土渗透性试验技术的研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016
YANG Yifan. Study on a kind of permeability test technology of unsaturated expansive soil[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 贺雷,王志俭,曹玲,等. 不同干密度下的非饱和膨胀土渗透特性试验研究[J]. 中国水运,2015,15(5):300 − 304. [HE Lei,WANG Zhijian,CAO Ling,et al. Experimental study on permeability characteristics of unsaturated expansive soils under different dry densities[J]. China Water Transport,2015,15(5):300 − 304. (in Chinese)
[23] 谢定义. 非饱和土土力学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015: 152 − 160
XIE Dingyi. Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2015: 152 − 160. (in Chinese)
[24] 肖正. 膨胀土基坑水位变化对坑壁荷载影响研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019
XIAO Zheng. Study on the influence of water level change of expansive soil foundation pit on pit wall load[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 严神通. 平顶山市西湖明珠膨胀土深基坑坑底浸水条件下土钉支护研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019
YAN Shentong. Study on soil nailing support for deep foundation pit in pearl expansive soil of Xihumingzhu in Pingdingshan City[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: