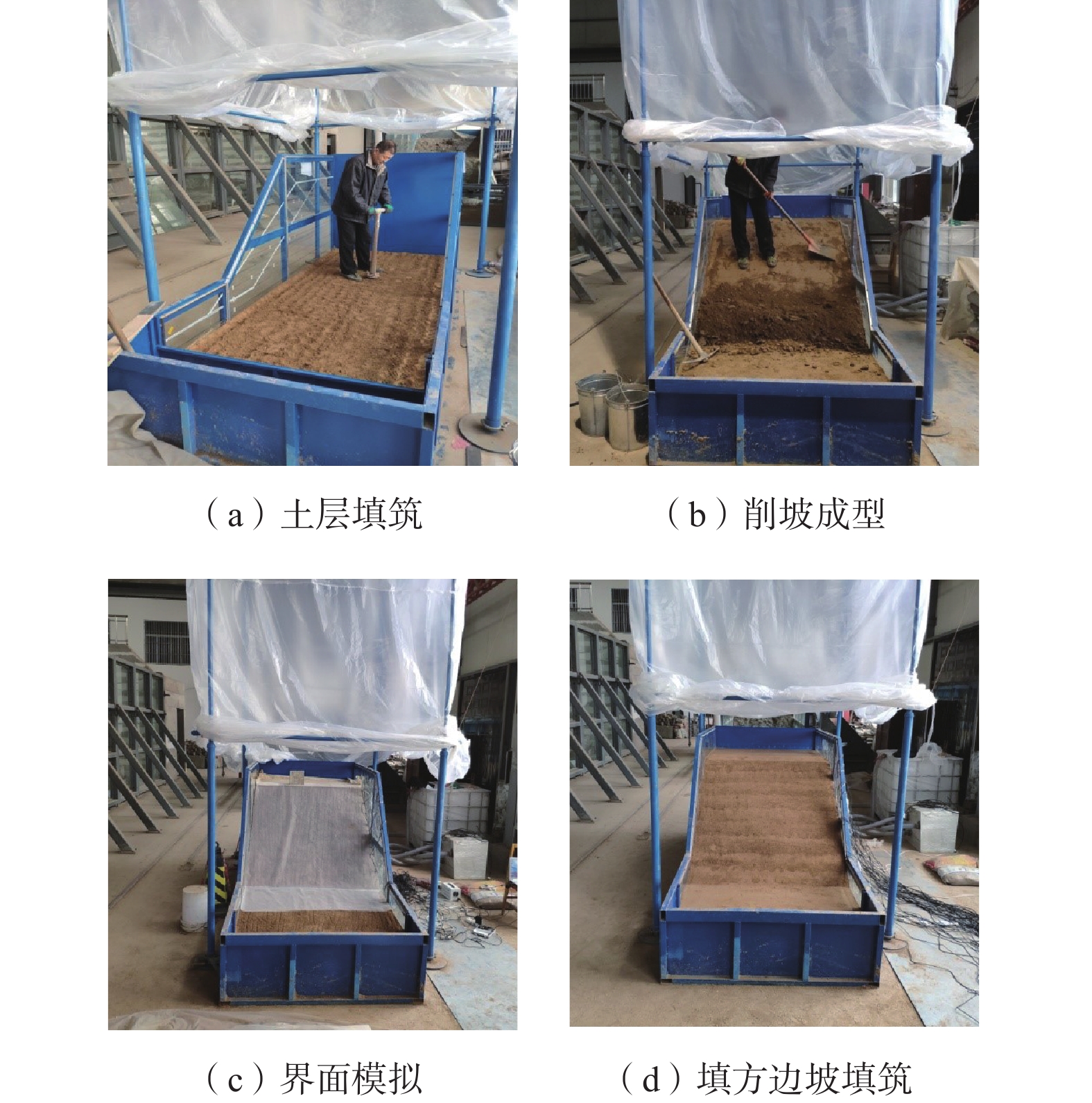
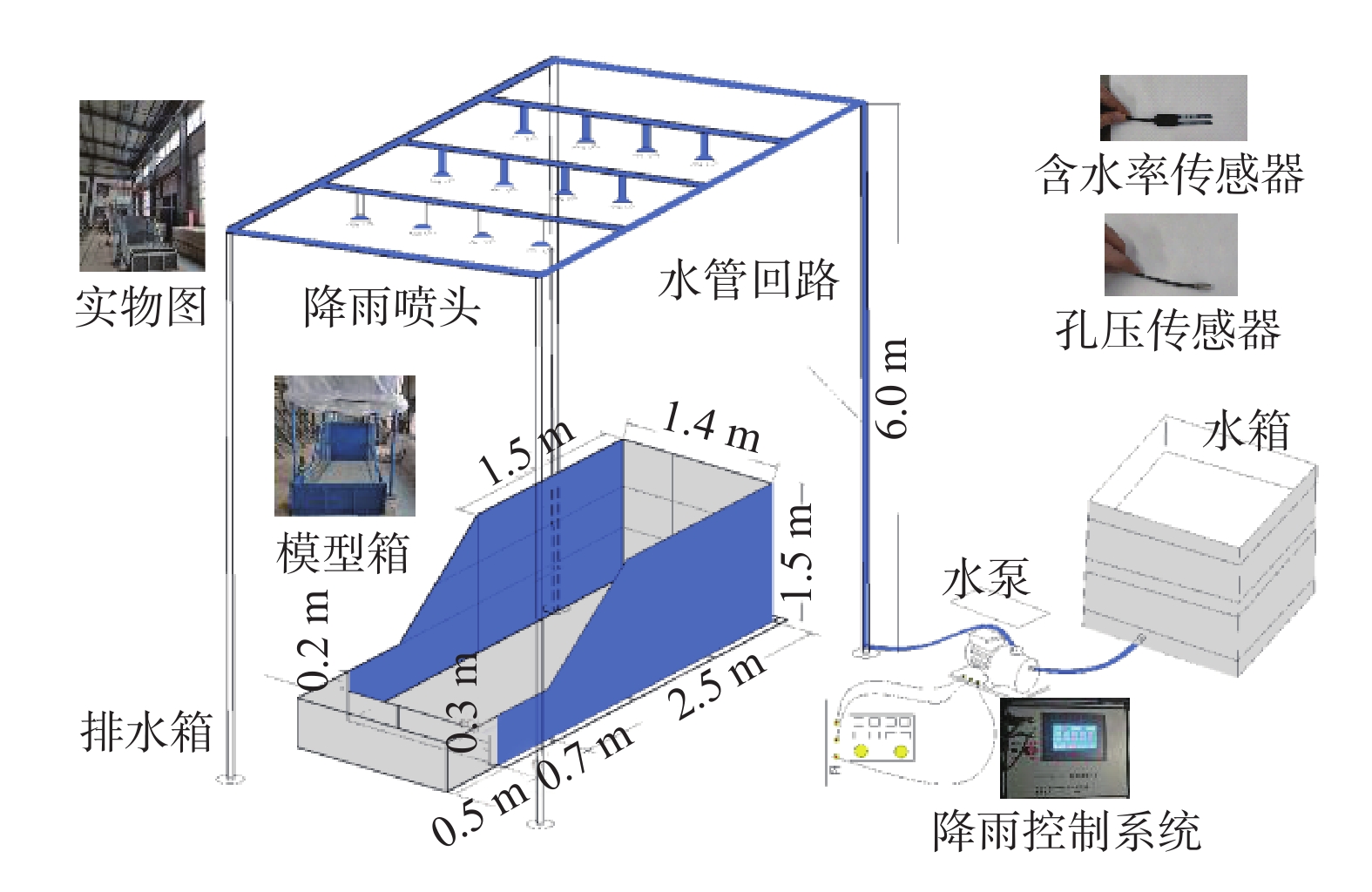
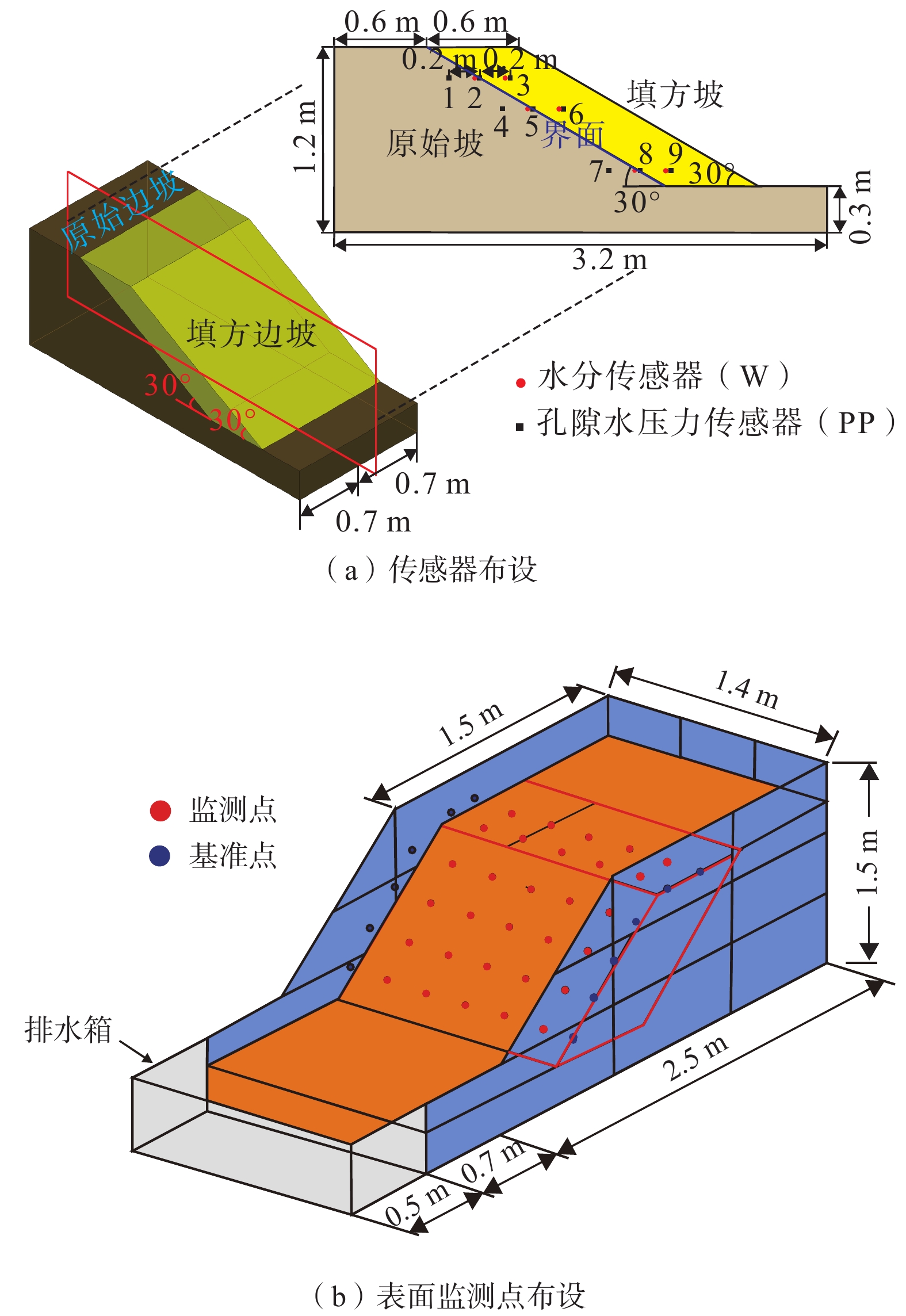
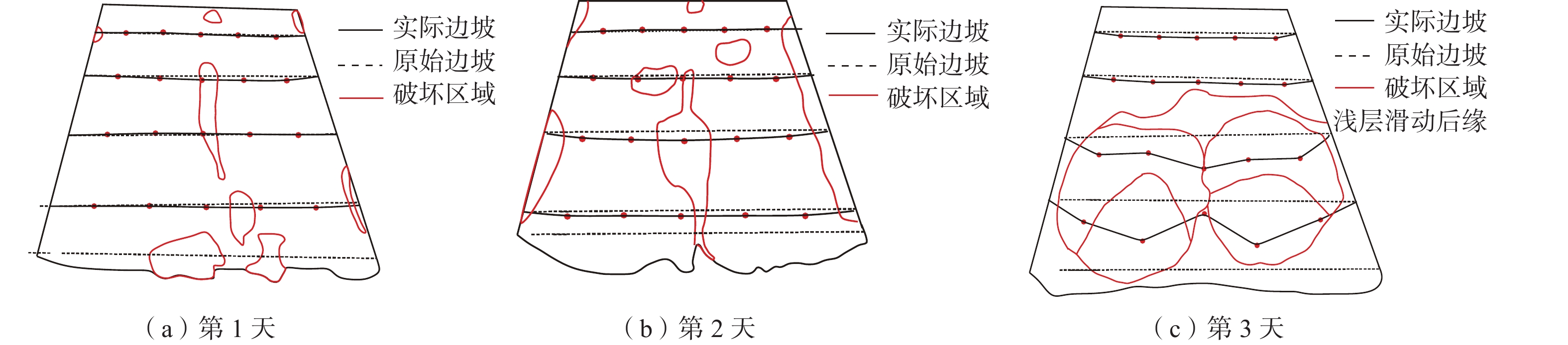
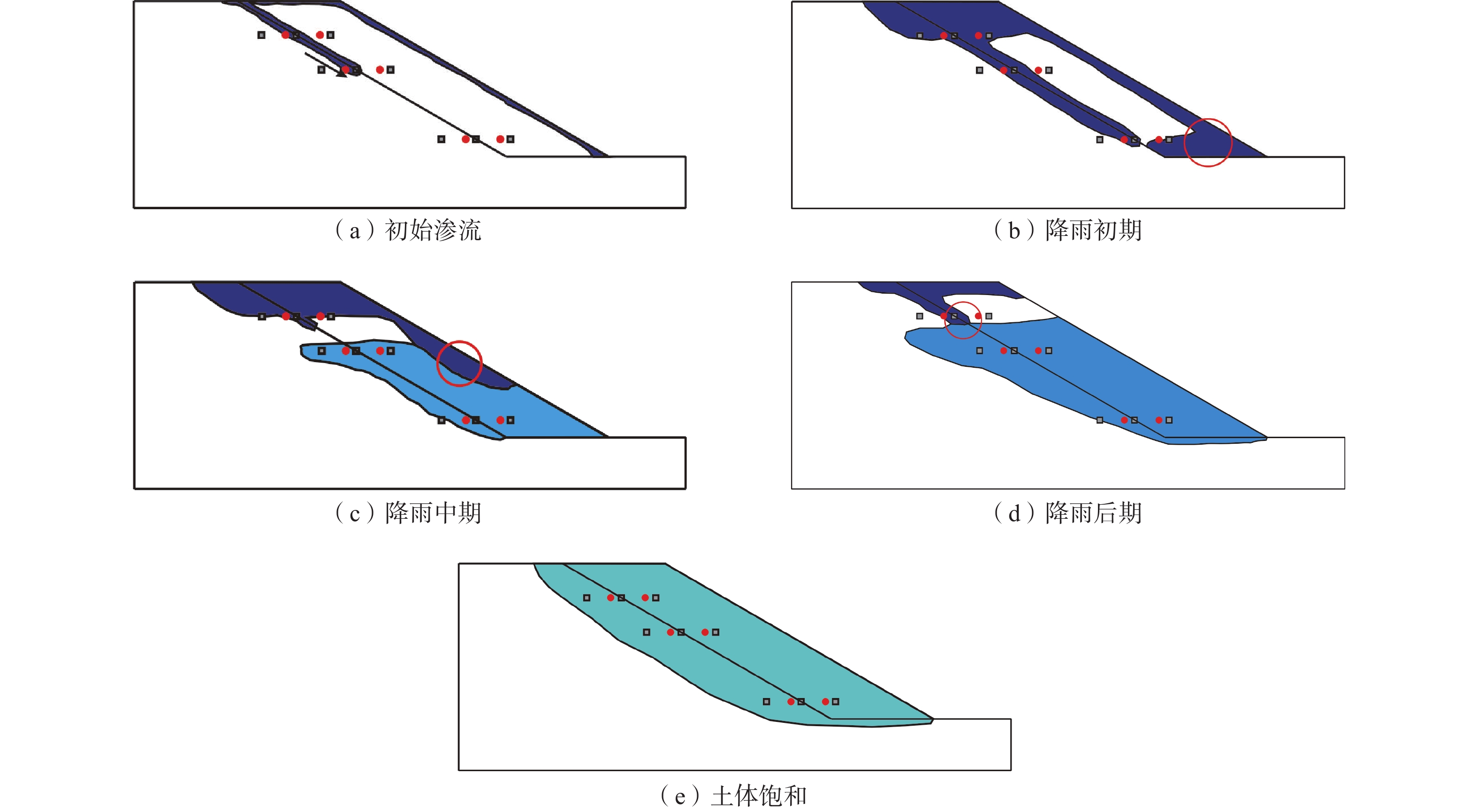
A model test study of the interface seepage and failure mechanism of loess-filled slope
-
摘要:
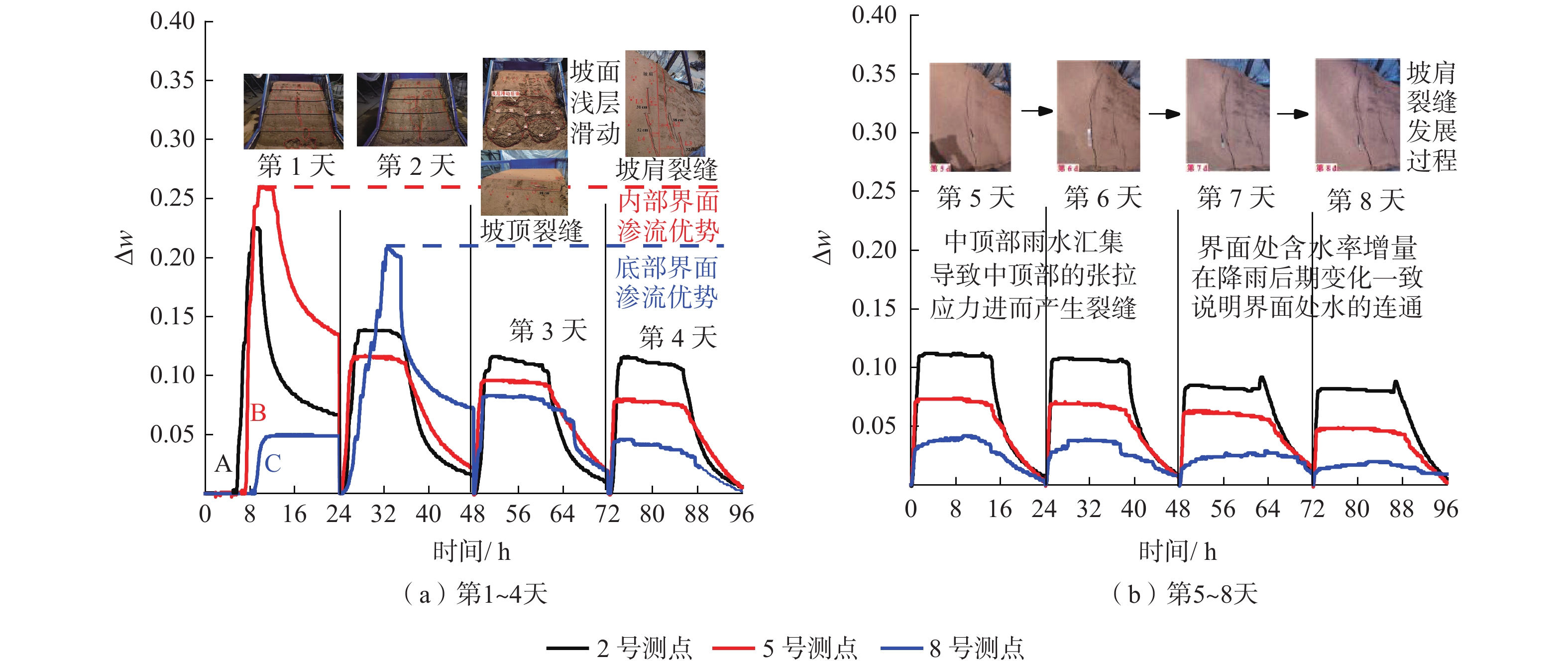
为了扩大可用耕地面积,延安地区开展了一系列的治沟造地工程,在填方坡体与原始坡体之间形成了接触界面,这类界面潜在影响着填方坡体的渗流变形破坏。针对延安地区治沟造地工程黄土填方边坡已有的和潜在的变形破坏问题,通过室内黄土边坡降雨模型试验,研究了界面对黄土填方坡体渗流特性与变形破坏的影响规律,揭示了界面渗流影响下填方边坡的破坏机制。结果表明:(1)界面是黄土填方边坡雨水入渗的优势渗流通道,雨水沿界面入渗至填方体中部和底部,界面入渗与坡面入渗雨水一并汇集于填方体中部,加速了填方体的饱和进程,改变了填方体的渗流场和有效应力场,坡顶与坡肩处产生张拉应力,诱发多条张拉裂缝萌生和扩展;(2)填方体坡脚中部先小范围侵蚀,随后中部产生大范围侵蚀破坏,进而触发填方体中部和底部产生较大规模的浅层滑动,加剧了填方体坡顶与坡肩裂缝的萌生和扩展,形成了多个优势渗流通道和复杂地质地貌条件,降低了填方体的局部稳定性。上述研究结果对黄土填方边坡稳定性评价和提高治沟造地工程使用寿命具有较好的指导意义。
Abstract:A series of Gully Reclamation Projects were carried out in Yan’an City to expand the area of available arable land. In these projects, contact interfaces formed between filled slope and original slope potentially influenced the seepage deformation and failure of the loess-filled slope. This paper aims to solve the deformation and failure of loess-filled slope in Yan’an City using the indoor rainfall model test. The influence of interface on seepage characteristics and deformation failure of loess-filled slope is analyzed, and the failure mechanism of loess-filled slope affected by the interface is revealed. The results show that: (1) the interface is a dominant seepage channel for rainwater infiltration in the loess-filled slope; along the seepage channel, rainwater infiltrates into the middle and bottom of the filling body and gathers in the middle of the filling body with the infiltration rainwater from slope surface; the process accelerates the saturation process of the filled slope, changes its seepage field and effective stress field, causes tensile stress at its top and shoulder, and induces the initiation and expansion of multiple tension cracks. (2) In the process, a small range of erosion occurs in the middle of the slope toe, and a large range of erosion damages in the middle of filled-slope surface; the erosion damage triggers a large-scale shallow sliding in the middle and bottom of the filled slope, and further intensifies the initiation and expansion of cracks at the top and shoulder of the filling body; finally, multiple dominant seepage channels and complex topographic feature are formed, and the local stability of loess-filled slope is gradually reduced. The research results are important for the stability evaluation of loess-filled slope and the service life of the Gully Reclamation Projects.
-
Key words:
- the Gully Reclamation Project /
- loess /
- slope /
- model test /
- interface seepage /
- failure mechanism
-

-
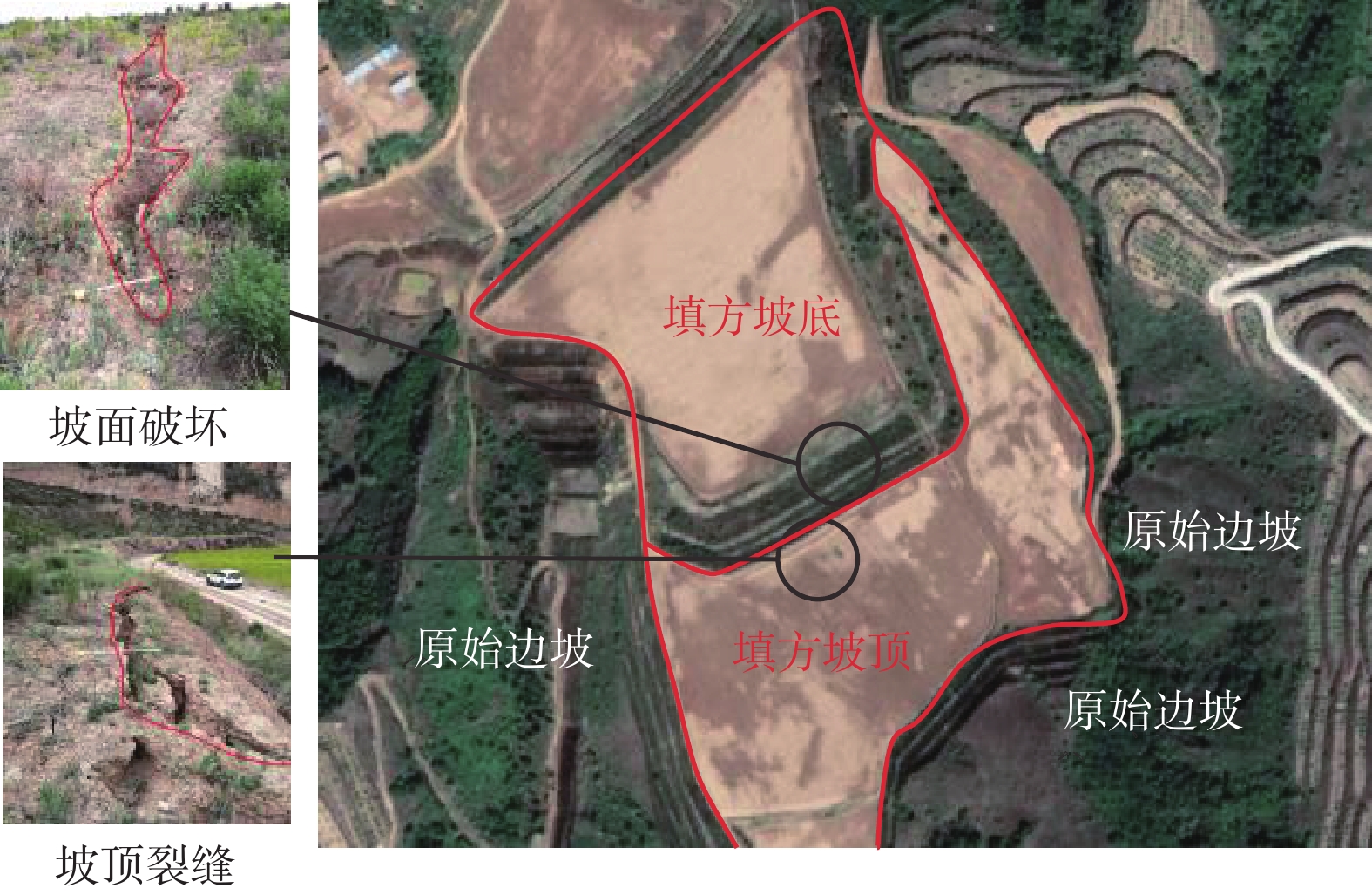
图 1 黄土填方边坡病害[24]
Figure 1.
表 1 土层参数
Table 1. Soil parameters
边坡 干密度/(g·cm−3) 含水率/% 重度/(kN·m−3) 原始边坡 1.63 13.5 18.53 填方边坡 1.58 10.0 17.38 表 2 每日降雨方案
Table 2. Rainfall schemes for one day
降雨次数 起止时间 降雨时间/min 降雨强度/(mm·h−1) 第1次 9:00—9:30 30 12.4 第2次 10:00—10:30 30 12.4 第3次 11:00—11:30 30 12.4 第4次 12:00—12:30 30 12.4 第5次 13:00—13:30 30 12.4 第6次 14:00—14:30 30 12.4 第7次 15:00—15:30 30 12.4 第8次 16:00—16:30 30 12.4 第9次 17:00—17:30 30 12.4 -
[1] 贺春雄. 延安治沟造地工程水毁成因及对策[J]. 陕西水利,2014(1):161 − 162. [HE Chunxiong. Causes and countermeasures of water damage in the Gully Reclamation Project of Yan’an[J]. Shaanxi Water Resources,2014(1):161 − 162. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9000.2014.01.077
[2] TANG D Q, PENG J B, WANG Q Y, et al. Lvliang typical loess landslide mechanism and characteristics[C]//ZHOU X J. Proceedings of the international conference on civil engineering and transportation (ICCET 2011). Jinan: Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2011: 1313 − 1317.
[3] ZHUANG J Q,PENG J B. A coupled slope cutting-a prolonged rainfall-induced loess landslide:A 17 October 2011 case study[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2014,73(4):997 − 1011. doi: 10.1007/s10064-014-0645-1
[4] 薛强,张茂省. 延安淹土安滑坡监测预警及变形特征[J]. 西北地质,2018,51(2):220 − 226. [XUE Qiang,ZHANG Maosheng. Monitoring,early warning and deformation characteristics of Yantu’an landslide in Yan’an[J]. Northwestern Geology,2018,51(2):220 − 226. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2018.02.029
[5] 徐盼盼. 重塑黄土渗透性变化的水-土作用机制研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021
XU Panpan. Study on water-soil interaction mechanism of permeability change of remolded loess[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2021. (in Chinese with Engiish abstract)
[6] ZHANG Y T,QIAN H,HOU K,et al. Investigating and predicting the temperature effects of permeability for loess[J]. Engineering Geology,2021,285:106050. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106050
[7] 张镇飞,倪万魁,王熙俊,等. 压实黄土水分入渗规律及渗透性试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):97 − 104. [ZHANG Zhenfei,NI Wankui,WANG Xijun,et al. An experimental study of water infiltration and hydraulic conductivity of the compacted loess[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):97 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.06.13
[8] WANG J D,LI P,MA Y,et al. Change in pore-size distribution of collapsible loess due to loading and inundating[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2020,15(5):1081 − 1094. doi: 10.1007/s11440-019-00815-9
[9] 李萍, 李同录, 王红, 等. 非饱和黄土土-水特征曲线与渗透系数Childs & Collis-Geroge模型预测[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(增刊2): 184 − 189
LI Ping, LI Tonglu, WANG Hong, et al. Soil-water characteristic curve and permeability perdiction on Childs & Collis-Geroge model of unsaturated loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(Sup2): 184 − 189. (in Chinese with Engiish abstract)
[10] TIAN K L,YANG A Q,NIE K Y,et al. Experimental study of steady seepage in unsaturated loess soil[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2020,15(9):2681 − 2689. doi: 10.1007/s11440-020-00948-2
[11] 梁燕,谢永利,刘保健,等. 非饱和黄土渗透性的试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2006,33(2):27 − 30. [LIANG Yan,XIE Yongli,LIU Baojian,et al. A test study of the permeability of unsaturated typical loess[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2006,33(2):27 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.02.007
[12] 颜斌,倪万魁,刘海松. 黄土边坡降水入渗规律及其稳定性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2009,36(3):77 − 81. [YAN Bin,NI Wankui,LIU Haisong. Research on rainfall infiltration law and stability of loess slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2009,36(3):77 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.03.016
[13] 李海亮,黄润秋,吴礼舟,等. 非均质土坡降雨入渗的耦合过程及稳定性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(4):70 − 76. [LI Hailiang,HUANG Runqiu,WU Lizhou,et al. Rainfall infiltration coupling process and stability analysis of a heterogeneous soil slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(4):70 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2013.04.009
[14] 林鸿州,于玉贞,李广信,等. 降雨特性对土质边坡失稳的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(1):198 − 204. [LIN Hungchou,YU Yuzhen,LI Guangxin,et al. Influence of rainfall characteristics on soil slope failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(1):198 − 204. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.01.026
[15] ALEOTTI P. A warning system for rainfall-induced shallow failures[J]. Engineering Geology,2004,73(3/4):247 − 265.
[16] TIMPONG S, ITOH K, TOYOSAWA Y. Geotechnical centrifuge modelling of slope failure induced by ground water table change[C]//MCINNES R, JAKEWAYS J, FAIRBANK H, et al. Proceedings of the international conference on landslides and climate change. London: Taylor & Francis Ltd, 2007: 107 − 112.
[17] TSAPARAS I,RAHARDJO H,TOLL D G,et al. Infiltration characteristics of two instrumented residual soil slopes[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2003,40(5):1012 − 1032. doi: 10.1139/t03-049
[18] RAHARDJO H,LEE T T,LEONG E C,et al. Response of a residual soil slope to rainfall[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2005,42(2):340 − 351. doi: 10.1139/t04-101
[19] LI C,YAO D,WANG Z,et al. Model test on rainfall-induced loess -mudstone interfacial landslides in Qingshuihe,China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(9):1 − 18.
[20] 胡黎明,濮家骝. 土与结构物接触面物理力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2001,23(4):431 − 435. [HU Liming,PU Jialiu. Experimental study on mechanical characteristics of soil-structure interface[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2001,23(4):431 − 435. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.04.010
[21] 王雷. 延安地区黄土-基岩接触面滑坡复活演化及机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018
WANG Lei. Study on resurrection evolution and mechanism of the loess-bedrock interface landside in Yan’an area[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2018. (in Chinese with Engiish abstract)
[22] 李绍红,朱建东,王少阳,等. 考虑降雨类型的基岩型浅层边坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):131 − 135. [LI Shaohong,ZHU Jiandong,WANG Shaoyang,et al. Stability analysis methods for the bedrock shallow slope considering rainfall types[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(2):131 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.02.20
[23] 贺春雄. 延安治沟造地工程的现状、特点及作用[J]. 地球环境学报,2015,6(4):255 − 260. [HE Chunxiong. The situation,characteristics and effect of the Gully Reclamation Project in Yan’an[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2015,6(4):255 − 260. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7515/JEE201504008
[24] 陈星. 黄土填方边坡界面效应及稳定性研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019
CHEN Xing. Study on interface effect and stability of loess fill slope[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2019. (in Chinese with Engiish abstract)
[25] 刘洪佳,门玉明,李寻昌,等. 采用不同滑面材料的滑坡模型试验研究[J]. 灾害学,2011,26(1):10 − 13. [LIU Hongjia,MEN Yuming,LI Xunchang,et al. Study on slip material in landslide model tests[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2011,26(1):10 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2011.01.003
[26] WEN B P,YAN Y J. Influence of structure on shear characteristics of the unsaturated loess in Lanzhou,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,168:46 − 58. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.10.023
[27] FREDLUND D G, RAHARDJO H. Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils[M]. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1993.
[28] GREEN W H,AMPT G A. Studies on soil physics I. —The flow of air and water through soils[J]. International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences & Numerical Simulation,2015,4(7/8):1 − 24.
[29] 陈林万,张晓超,裴向军,等. 降雨诱发直线型黄土填方边坡失稳模型试验[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):151 − 160. [CHEN Linwan,ZHANG Xiaochao,PEI Xiangjun,et al. Model test of the linear loess fill slope instability induced by rainfall[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):151 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202010041
[30] ZHANG S,ZHANG X C,PEI X J,et al. Model test study on the hydrological mechanisms and early warning thresholds for loess fill slope failure induced by rainfall[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,258:105135. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.05.012
[31] 石振明,赵思奕,苏越. 降雨作用下堆积层滑坡的模型试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):135 − 140. [SHI Zhenming,ZHAO Siyi,SU Yue. An experimental study of the deposit slope failure caused by rainfall[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):135 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2016.04.22
[32] 王健,马璠,张鹏辉,等. 干湿交替对黄土崩解速度的影响[J]. 土壤学报,2015,52(6):1273 − 1279. [WANG Jian,MA Fan,ZHANG Penghui,et al. Effect of wet-dry alternation on loess disintegration rate[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2015,52(6):1273 − 1279. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: