Roughness coefficient of rock discontinuities based on random forest regression analyses
-
摘要:
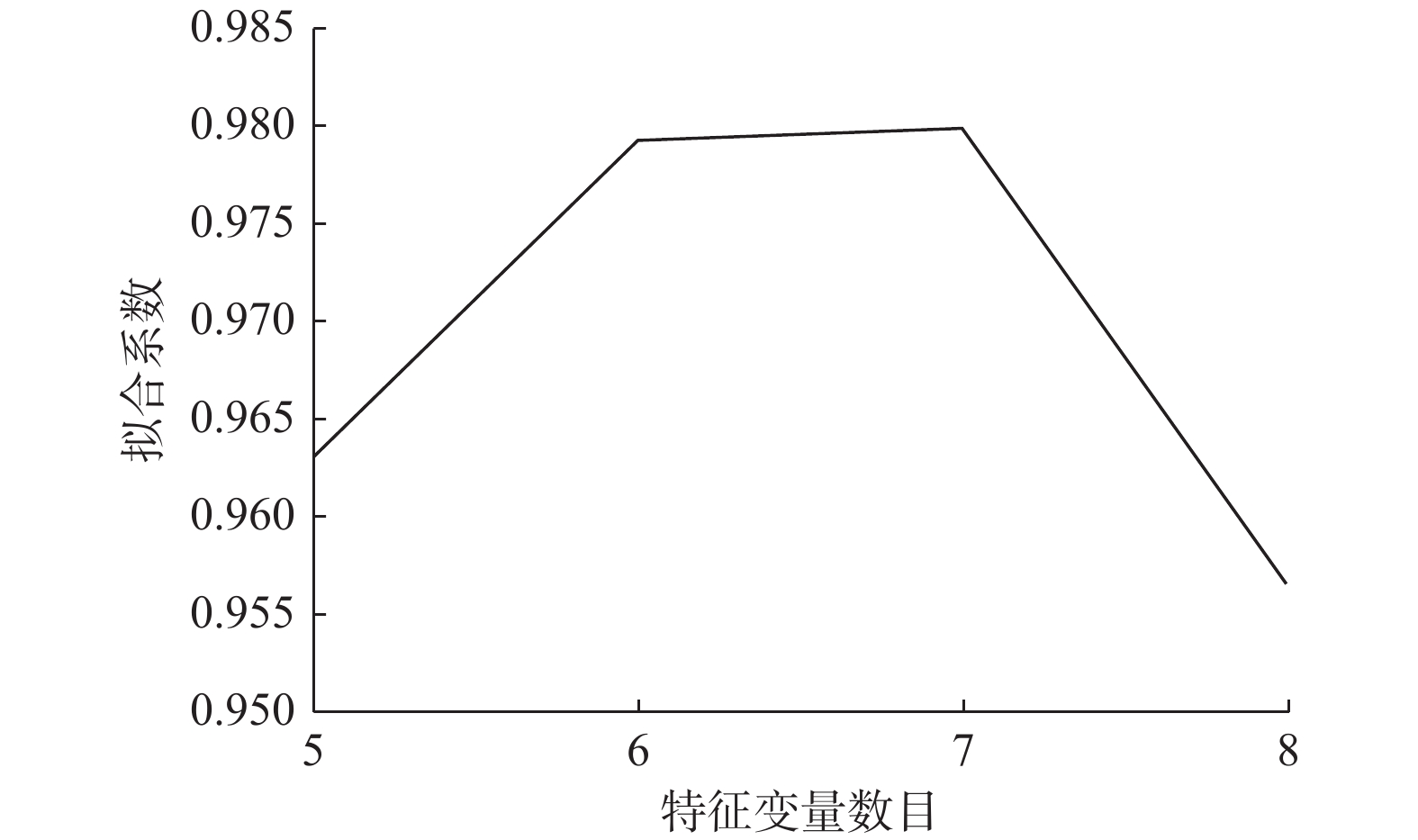
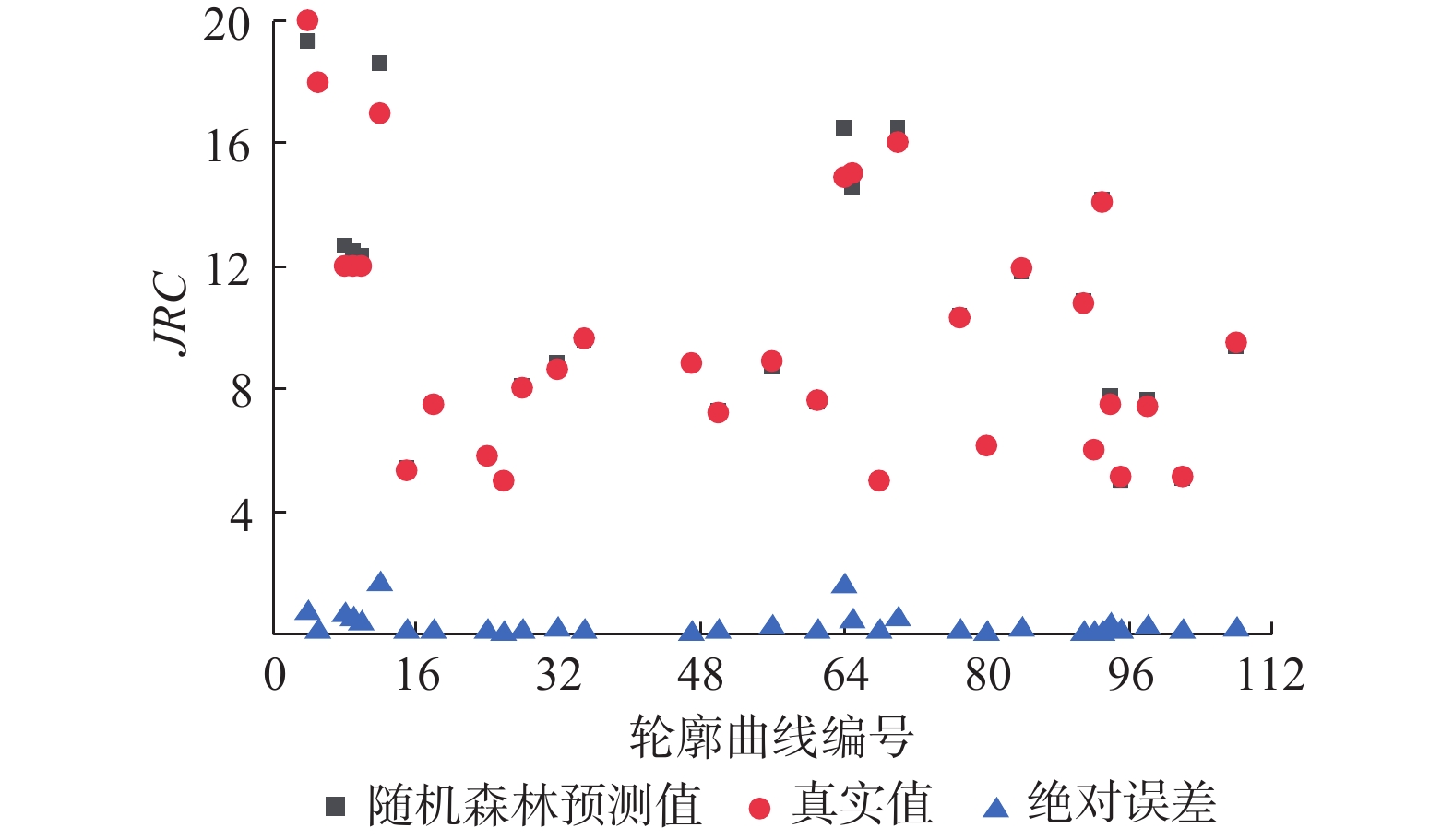
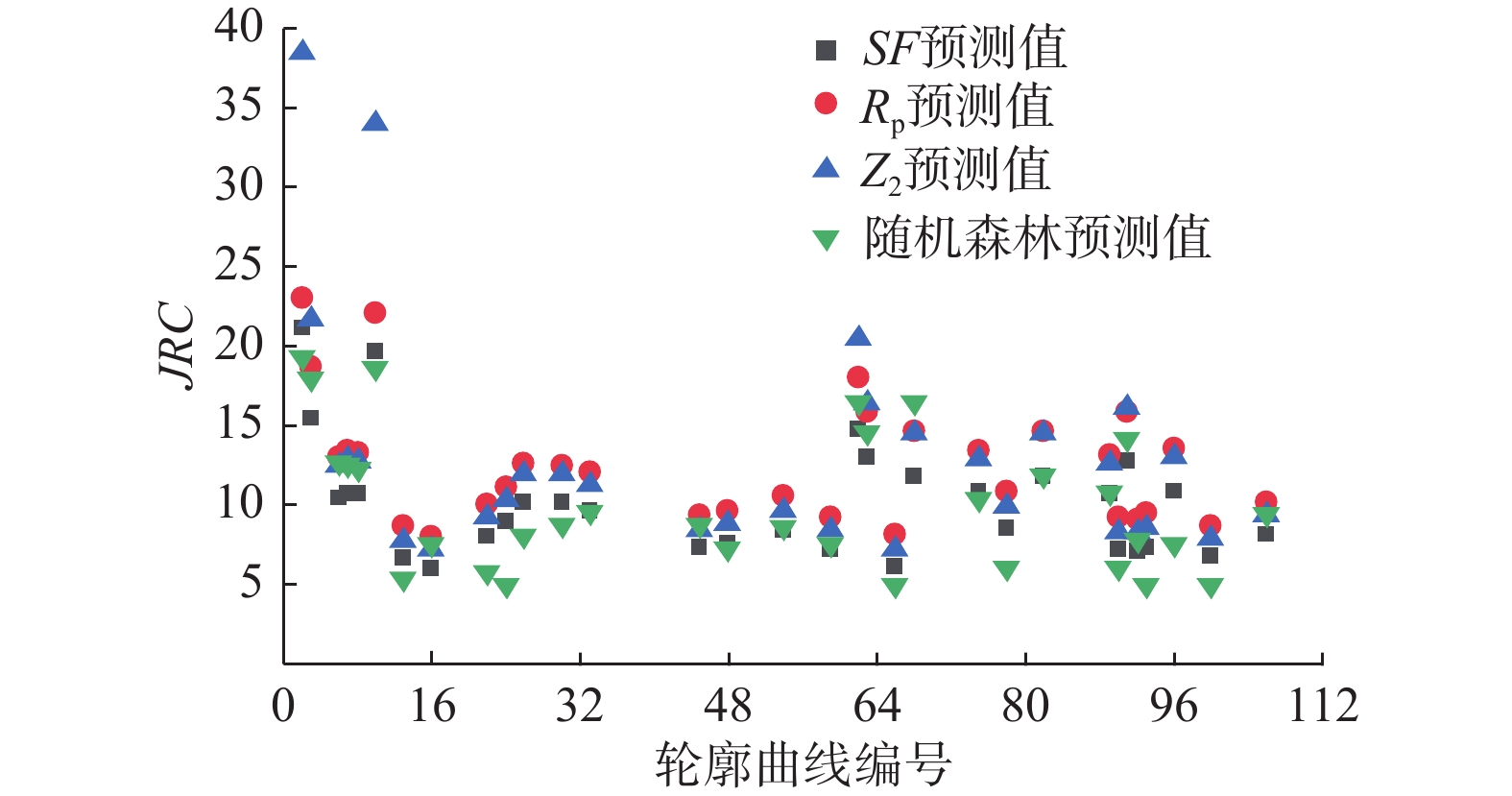
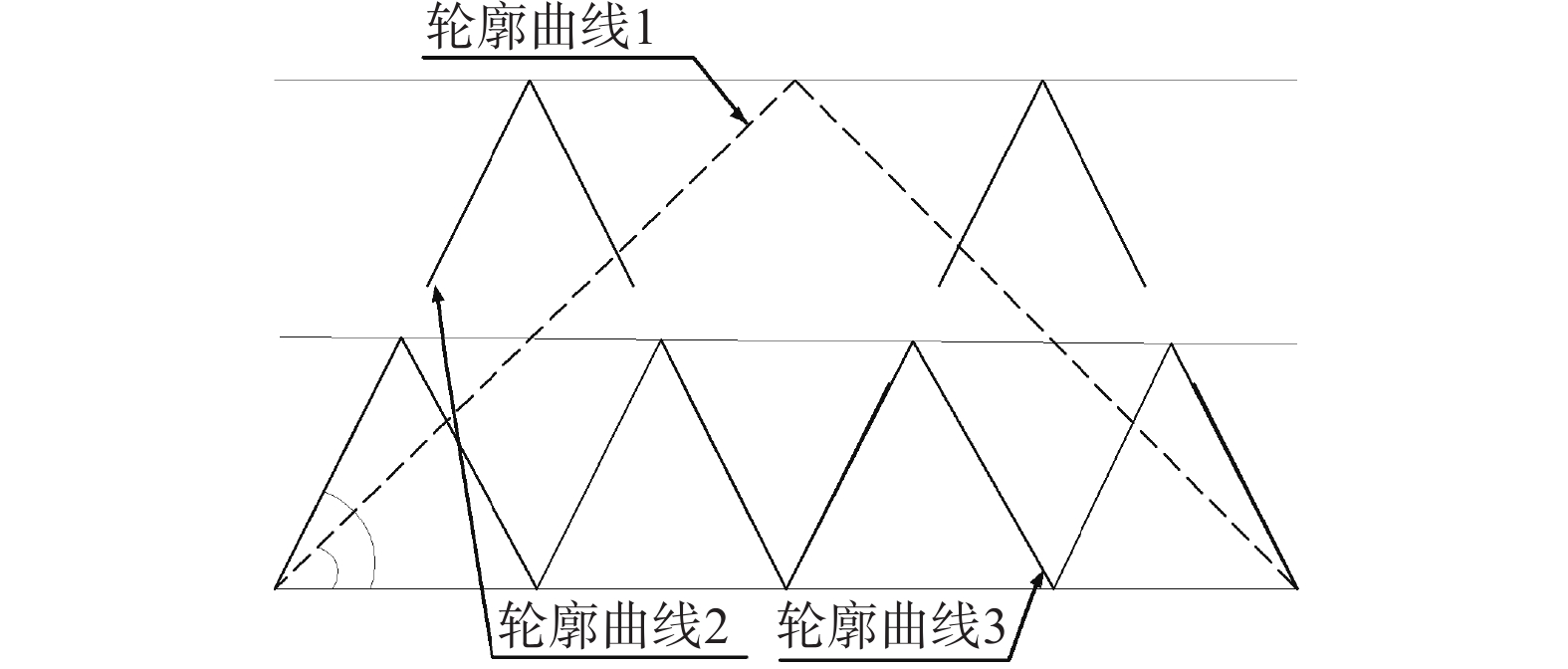
岩体结构面粗糙度系数是快速估算结构面峰值抗剪强度的重要参数。但是结构面轮廓曲线复杂,单一统计参数无法量化表征粗糙度。为解决这一问题,收集了112条结构面轮廓曲线起伏角、起伏度、迹线长度3方面的8项统计参数,利用随机森林回归模型交叉验证的方法评估统计参数的重要性。结果表明:最大起伏度、起伏高度标准偏差、平均起伏角、起伏角标准差、平均相对起伏度及粗糙度剖面指数等6项统计参数重要性占比达到93.2%,且回归拟合系数趋于平稳,基于重要性评估结果建立最优超参数决策树数目(ntree)为400、参与节点分割的数目(mtry)为2的随机森林回归模型,模型预测结果拟合优度高达98.1%。与基于坡度均方根、结构函数及粗糙度剖面指数等传统线性回归结果对比,随机森林回归模型结果精度更高,误差更小,拟合优度提高6%以上,表明随机森林回归模型更适用于结构面粗糙度反演。
Abstract:The peak shear strength of the discontinuities can be estimated quickly by the roughness of the discontinuities. However, it is difficult to quantify the roughness of the structural surface using the single statistical parameter. In order to improve the prediction accuracy of the standard discontinuities roughness, eight statistical parameters in the aspects of undulating degree and trace length of 112 structural profile curves are collected, and the method of cross-validation of random forest regression model is used to evaluate the importance of statistical parameters. The evaluation results show that the importance of six statistical parameters, including the maximum undulation, undulation height standard deviation, mean undulating angle, undulating angle standard deviation, mean relative undulation rave and roughness profile index, accounts for 93.2%, and the regression fitting coefficient tends to be stable. Based on the importance assessment results, a random forest regression model is established. The model prediction results fitting excellence is up to 98.1%, showing the excellent prediction results. Compared with the traditional linear regression results, such as the results of the slope-based mean square root, structural function and roughness profile index, the random forest regression model has higher accuracy, smaller error and better fit. The random forest regression model is more suitable for structural roughness inversion.
-
Key words:
- random forest /
- roughness /
- rock structure surface /
- statistical parameters /
- importance assessment
-

-
表 1 结构面粗糙度统计参数重要性评分
Table 1. The importance score of the discontinuity roughness statistical parameters
变量 Rmax SDh iave SDi Rave Rp SF Z2 重要性评分 0.323 0.270 0.159 0.069 0.066 0.044 0.041 0.027 表 2 各模型预测精度
Table 2. Predictive accuracy for each mode
模型精度 RF SF RP Z2 R2/% 98.1 92.1 91.7 91.3 MSE 0.219 3.363 6.366 13.974 RMSE 0.502 1.227 1.623 1.781 -
[1] BARTON N. Review of a new shear-strength criterion for rock joints[J]. Engineering Geology,1973,7(4):287 − 332. doi: 10.1016/0013-7952(73)90013-6
[2] BARTON N,CHOUBEY V. The shear strength of rock joints in theory and practice[J]. Rock Mechanics,1977,10(1/2):1 − 54.
[3] BARTON N. Suggested methods for the quantitative description of discontinuities in rock masses[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences and Geomechanics Abstracts,1978,15(6):319-368.
[4] 邓华锋,熊雨,肖瑶,等. 基于单试件法的节理岩体抗剪强度参数分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2020,42(8):1509 − 1515. [DENG Huafeng,XIONG Yu,XIAO Yao,et al. Shear strength parameters of jointed rock mass based on single test sample method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2020,42(8):1509 − 1515. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] TSE R,CRUDEN D M. Estimating joint roughness coefficients[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1979,16(5):303 − 307.
[6] YANG Z Y,LO S C,DI C C. Reassessing the joint roughness coefficient (JRC) estimation using Z_2[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2001,34(3):243 − 251. doi: 10.1007/s006030170012
[7] YU Xianbin,VAYSSADE B. Joint profiles and their roughness parameters[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1991,28(4):333 − 336.
[8] 孙辅庭,佘成学,万利台. Barton标准剖面JRC与独立于离散间距的统计参数关系研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(增刊 2):3539 − 3544. [SUN Futing,SHE Chengxue,WAN Litai. Research on relationship between JRC of Barton’s standard profiles and statistic parameters independent of sampling interval[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(Sup 2):3539 − 3544. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] ZHANG Guangcheng,KARAKUS M,TANG Huiming,et al. A new method estimating the 2D Joint Roughness Coefficient for discontinuity surfaces in rock masses[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2014,72:191 − 198. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.09.009
[10] 吉峰. 硬性结构面粗糙度系数量化确定及其工程应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(3):84 − 86,101. [JI Feng. Quantization research and project application of roughness coefficient of a rigid structure plane[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(3):84 − 86,101. (in Chinese)
[11] 李化,黄润秋. 岩石结构面粗糙度系数JRC定量确定方法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(增刊 2):3489 − 3496. [LI Hua,HUANG Runqiu. Method of quantitative determination of joint roughness coefficient[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(Sup 2):3489 − 3496. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 徐光黎. 岩石结构面几何特征的分形与分维[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1993,20(2):20 − 22. [XU Guangli. Fractal analysis for rock mass joint geometry[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,1993,20(2):20 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 谢和平. 岩石节理的分形描述[J]. 岩土工程学报,1995,17(1):18 − 23. [XIE Heping. Fractal description of rock joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1995,17(1):18 − 23. (in Chinese)
[14] 杜时贵,陈禹,樊良本. JRC修正直边法的数学表达[J]. 工程地质学报,1996,4(2):36 − 43. [DU Shigui,CHEN Yu,FAN Liangben. Mathematical expression of JRC modified straight edge[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,1996,4(2):36 − 43. (in Chinese)
[15] BARTON, BANDIS S. Effects of block size on the shear behavior of jointed rock[C]// The 23rd US Symposium on Rock Mechanics. 1982: 739-760.
[16] 胡越,罗东阳,花奎,等. 关于深度学习的综述与讨论[J]. 智能系统学报,2019,14(1):1 − 19. [HU Yue,LUO Dongyang,HUA Kui,et al. Overview on deep learning[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems,2019,14(1):1 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李欣海. 随机森林模型在分类与回归分析中的应用[J]. 应用昆虫学报,2013,50(4):1190 − 1197. [LI Xinhai. Using “random forest” for classification and regression[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology,2013,50(4):1190 − 1197. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning,2001,45(1):5 − 32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324
[19] 李扬,祁乐,聂佩芸. 大规模数据的随机森林算法[J]. 统计与信息论坛,2020,35(6):24 − 33. [LI Yang,QI Le,NIE Peiyun. A distributed random forest algorithm for massive data[J]. Statistics & Information Forum,2020,35(6):24 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 刘新荣,邓志云,刘永权,等. 岩石节理峰前循环直剪试验颗粒流宏细观分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(7):2103 − 2115. [LIU Xinrong,DENG Zhiyun,LIU Yongquan,et al. Macroscopic and microscopic analysis of particle flow in pre-peak cyclic direct shear test of rock joint[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(7):2103 − 2115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 黄曼,洪陈杰,杜时贵,等. 岩石结构面形貌分级方法及两级粗糙特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(6):1153 − 1164. [HUANG Man,HONG Chenjie,DU Shigui,et al. Study on morphological classification method and two-order roughness of rock joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(6):1153 − 1164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 陈世江,赵自豪,王超. 基于修正线粗糙度法的岩石节理粗糙度估值[J]. 金属矿山,2012(6):22 − 25. [CHEN Shijiang,ZHAO Zihao,WANG Chao. Estimation of rock joint roughness based on modified line-roughness[J]. Metal Mine,2012(6):22 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] LI Yanrong,ZHANG Yongbo. Quantitative estimation of joint roughness coefficient using statistical parameters[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2015,77:27 − 35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.03.016
-



 下载:
下载: