Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of soil moisture in the non-freezing period under the bare land and vegetation cover in the Mu Us desert
-
摘要:
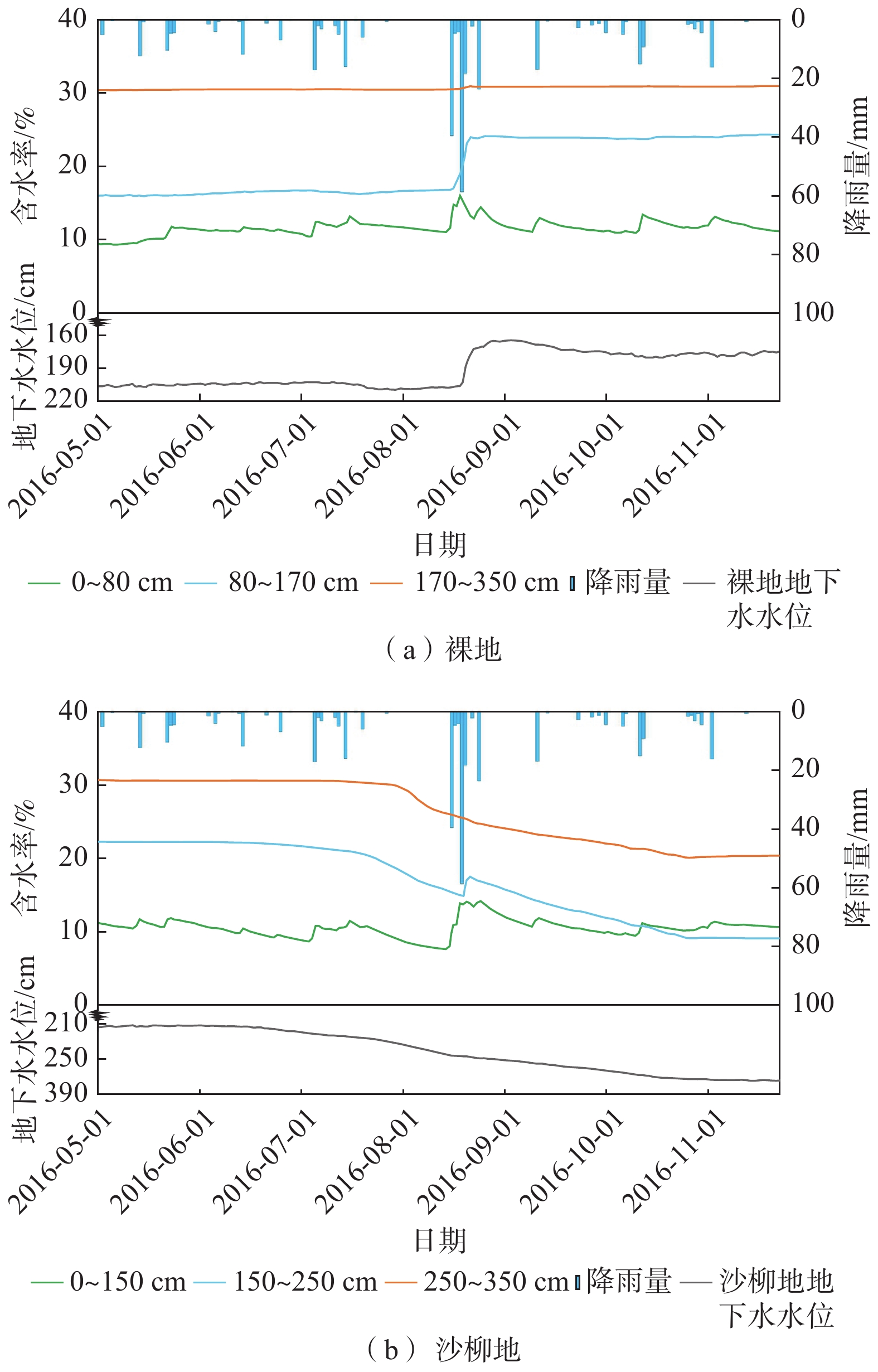
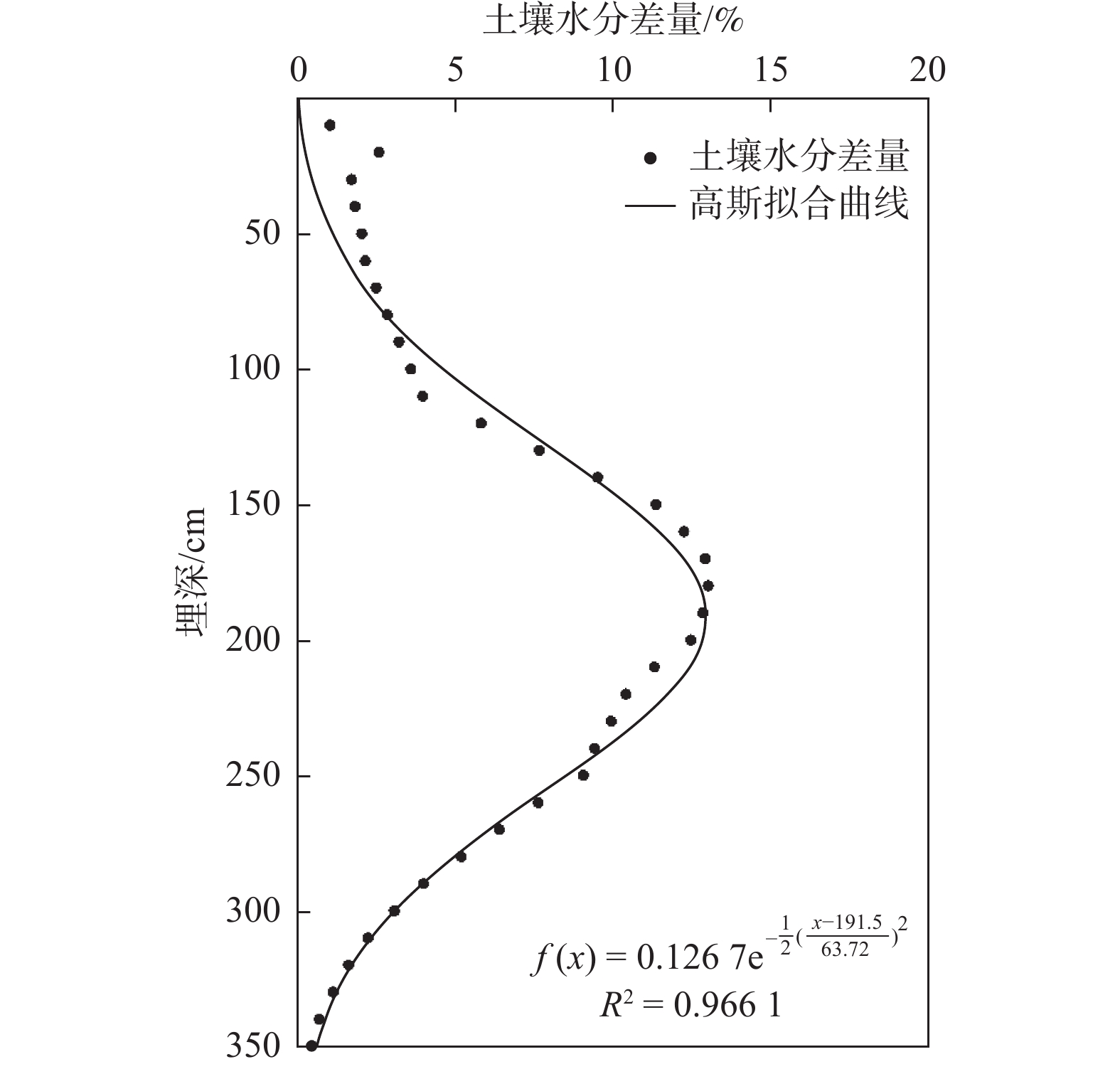
在水资源短缺的沙地生态系统中,土壤水分是植被恢复和水资源管理的主要控制因子,正确认识沙地土壤水分的分布特征及时空变化规律是促进沙地水资源可持续发展的基础。以毛乌素沙地为研究区,利用原位试验观测、经典统计学分析和聚类分析相结合的方法,揭示了有无植被覆盖下的土壤剖面水分时空变化特征,探讨了植物生长对土壤水分布的影响。结果表明:在2016年非冻结期内,地下水水位埋深较浅时,裸地与植被覆盖情况下土壤平均含水率均随土壤深度的增加而增大,可将0~350 cm土层划分为气候影响层、过渡层与地下水影响层。裸地剖面平均含水率为23.59%,变异系数为4.24%,属于弱变异,剖面含水率在观测期间明显上升,并在8月中旬强降雨时上升速率达到最大;植被覆盖下土壤剖面平均含水率为17.74%,变异系数为15.61%,属于中等变异,剖面含水率在观测期间显著下降,在8月沙柳发育成熟后剖面含水率下降最快。在垂向深度上,植被对土壤剖面含水率的影响近似呈高斯曲线变化,对过渡层含水率的影响最大,占总影响的50%以上,对气候影响层与地下水影响层的影响相对较小,且随着植物生长,气候影响层受到的相对影响逐渐减弱,地下水影响层受到的相对影响逐渐增强。研究成果可为半干旱区毛乌素沙地合理的水资源调控以及沙地生态系统的稳定发展提供参考依据。
Abstract:In the sandy land ecosystem with water shortage, soil moisture is the main controlling factor for vegetation restoration and water resources management. Therefore, a correct understanding of the distribution characteristics and spatial-temporal variation of soil moisture in the sandy land is the basis for promoting the sustainable development of sandy land water resources. The Mu Us desert is taken as the study area, in-situ experimental observations, classical statistical analysis and hierarchical clustering analysis methods are used to reveal the spatial and temporal changes of soil profile moisture with or without vegetation cover, and the effect of plant growth on soil water distribution are discussed in this paper. The results show that in the non-freezing period of 2016, when the groundwater depth was relatively shallow, the average soil moisture content increased with the increasing soil depth under the bare land and vegetation coverage. The soil layer of 0−350 cm thick can be divided into the climate-influencing layer, transition layer and groundwater-influencing layer. The average moisture content of the bare soil profile is 23.59%, and the coefficient of variation is 4.25%, which belongs to weak variation. The profile moisture content increased significantly during the observation period, and the rate of increase reached the maximum when the heavy rainfall event occurred in mid-August. The average moisture content of the soil profile under the vegetation cover is 17.74%, and the coefficient of variation is 15.61%, which is a medium variation. The water content of the profile dropped significantly during the observation period, and it dropeds the fastest in August after the Salix matures. At the vertical depth, the influence of vegetation on the soil profile moisture content approximates a Gaussian curve, and has the greatest influence on the moisture content of the transition layer, accounting for more than 50% of the total influence. The impact on climate-influencing layer and groundwater-influencing layer is relatively small. As plants grow, the relative influence on the climate-influencing layer gradually weakens, and the relative influence on the groundwater-influencing layer gradually increases. The research results can provide references for the rational regulation of water resources in the semi-arid Mu Us Sandy Land and the stable development of the sandy land ecosystem.
-
Key words:
- soil moisture /
- spatial and temporal distribution /
- bare land /
- vegetation cover /
- Mu Us desert
-

-
表 1 均质风积沙的物理参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of the homogeneous aeolian sand measured in the laboratory
土壤容重
/(g·cm−3)残余含水率
/(cm3·cm−3)饱和含水率
/(cm3·cm−3)渗透系数
/(m·d−1)1.45±0.005 0.014±0.002 0.31±0.009 6.2±0.6 表 2 裸地和沙柳地不同土层土壤含水率和变异系数
Table 2. Soil moisture content and coefficient of variationin different soil layers in the bare land and Salix land
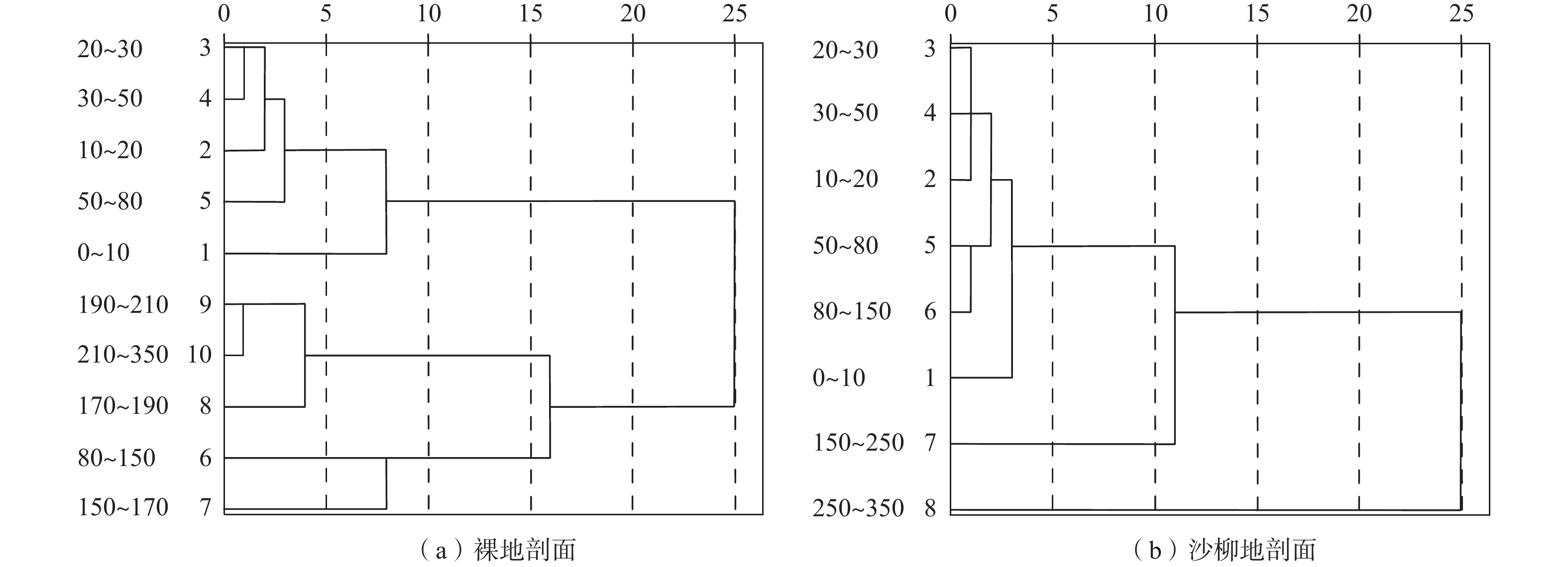
土地类型 土层/cm 平均值/% 标准差SD/% 变异系数CV/% 裸地 0~80 11.65 1.05 9.01 80~170 19.97 3.77 18.88 170~350 30.71 0.21 0.68 0~350 23.59 1.00 4.24 沙柳地 0~150 10.55 1.21 11.47 150~250 18.43 6.36 34.51 250~350 27.82 3.28 11.79 0~350 17.74 2.77 15.61 表 3 沙柳不同生长阶段各土层的土壤水分差量占比
Table 3. Δθ proportions of each soil layer at different growth stages of Salix
/% 土层 发芽期 生长期 成熟期 枯萎期 休眠期 0~150 cm 36.71 42.53 30.28 22.37 19.93 150~250 cm 56.23 53.40 58.29 56.00 55.55 250~350 cm 7.06 4.07 11.43 21.63 24.52 -
[1] BERNDTSSON R, NODOMI K, YASUDA H, et al. Soil water and temperature patterns in an arid desert dune sand[J]. Journal of Hydrology,1996,185(1/2/3/4):221 − 240.
[2] BUTTAFUOCO G, CASTRIGNANÒ A, BUSONI E, et al. Studying the spatial structure evolution of soil water content using multivariate geostatistics[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2005,311(1/2/3/4):202 − 218.
[3] HU W, SHAO M A, WANG Q J, et al. Time stability of soil water storage measured by neutron probe and the effects of calibration procedures in a small watershed[J]. Catena,2009,79(1):72 − 82. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2009.05.012
[4] 王文科, 宫程程, 张在勇, 等. 旱区地下水文与生态效应研究现状与展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2018,33(7):702 − 718. [WANG Wenke, GONG Chengcheng, ZHANG Zaiyong, et al. Research status and prospect of the subsurface hydrology and ecological effect in arid regions[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2018,33(7):702 − 718. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.07.0702
[5] 刘凯, 高磊, 彭新华, 等. 半干旱区科尔沁沙地土壤水分时空特征研究[J]. 土壤,2015,47(4):765 − 772. [LIU Kai, GAO Lei, PENG Xinhua, et al. Spatio-temporal variability of soil moisture in horqinsandy land[J]. Soils,2015,47(4):765 − 772. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 杨丽萍,苏志强,侯成磊,等. 基于随机森林的干旱区全极化SAR土壤含水量反演[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(4):1255 − 1264. [YANG Liping, SU Zhiqiang, HOU Chenglei, et al. Soil moisture content retrieval in arid area based on Random Forest using Polarimetric SAR data[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(4):1255 − 1264. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 洪光宇, 王晓江, 王少昆, 等. 沙地土壤水分时空动态研究进展[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(3):390 − 398. [HONG Guangyu, WANG Xiaojiang, WANG Shaokun, et al. Research progress on spatiotemporal dynamics of soil moisture in sandy land[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,28(3):390 − 398. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张进虎, 贺康宁, 段玉玺, 等. 毛乌素沙地西南缘不同植被下的土壤水分时空变化研究[J]. 水土保持研究,2008,15(1):96 − 99. [ZHANG Jinhu, HE Kangning, DUAN Yuxi, et al. Study on the spacial and temporal change of soil water content under different plant coverage on the southwestern edge of maowususandy land[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2008,15(1):96 − 99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 伍永秋, 张健枫, 杜世松, 等. 毛乌素沙地南缘不同活性沙丘土壤水分时空变化[J]. 中国沙漠,2015,35(6):1612 − 1619. [WU Yongqiu, ZHANG Jianfeng, DU Shisong, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of soil moisture in dunes with different vegetation coverage in southern margin of the mu us sandy land[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2015,35(6):1612 − 1619. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2014.00157
[10] 贺帅, 张成福, 洪光宇, 等. 毛乌素沙地土壤水分研究进展[J]. 北方园艺,2020(10):138 − 144. [HE Shuai, ZHANG Chengfu, HONG Guangyu, et al. Research progress of soil moisture in Mu Us Sandy Land[J]. Northern Horticulture,2020(10):138 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 陈洪松, 邵明安. 黄土区坡地土壤水分运动与转化机理研究进展[J]. 水科学进展,2003,14(4):413 − 420. [CHEN Hongsong, SHAO Ming’an. Review on hillslope soil water movement and transformation mechanism on the loess plateau[J]. Advances in Water Science,2003,14(4):413 − 420. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 殷地迟, 王立, 蔡国军, 等. 半干旱黄土丘陵区不同植被类型的土壤水分特征及其稳定性[J]. 水土保持通报,2020,40(1):65 − 71. [YIN Dichi, WANG Li, CAI Guojun, et al. Soil moisture characteristics and stability of different vegetation types in semi-arid loess hilly region[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,40(1):65 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王海燕, 刘廷玺, 王力, 等. 科尔沁沙地坨甸交错区土壤水分的空间变异规律[J]. 干旱区研究,2013,30(3):438 − 443. [WANG Haiyan, LIU Tingxi, WANG Li, et al. Spatial variation of soil moisture content in the dune-meadow ecotone in the horqin sandy land[J]. Arid Zone Research,2013,30(3):438 − 443. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] YU X N, HUANG Y M, LI E G, et al. Effects of rainfall and vegetation to soil water input and output processes in the Mu Us Sandy Land, northwest China[J]. Catena,2018,161:96 − 103. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.023
[15] 易小波, 贾小旭, 邵明安, 等. 黄土高原区域尺度土壤干燥化的空间和季节分布特征[J]. 水科学进展,2017,28(3):373 − 381. [YI Xiaobo, JIA Xiaoxu, SHAO Ming’an, et al. Regional spatial and seasonal characteristics of soil desiccation on the Loess Plateau[J]. Advances in Water Science,2017,28(3):373 − 381. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 周宏飞, 肖祖炎, 姚海娇, 等. 古尔班通古特沙漠树枝状沙丘土壤水分时空变异特征[J]. 水科学进展,2013,24(6):771 − 777. [ZHOU Hongfei, XIAO Zuyan, YAO Haijiao, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of soil moisture in dendritic sand dune over Gurbantunggut Desert in central Eurasia[J]. Advances in Water Science,2013,24(6):771 − 777. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 王宇祥, 刘廷玺, 段利民, 等. 科尔沁不同类型沙丘土壤水分时空变化特征及其环境影响因子[J]. 水土保持学报,2020,34(6):125 − 134. [WANG Yuxiang, LIU Tingxi, DUAN Limin, et al. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of soil moisture and environmental impact factors in different types of dunes in horqin[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,34(6):125 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 符超峰, 赵景波. 毛乌素沙地东南缘不同类型沙丘土壤水分分布特征[J]. 干旱区研究,2011,28(3):377 − 383. [FU Chaofeng, ZHAO Jingbo. Distribution of soil moisture content in different types of sand dunes in the southeastern marginal zone of the Mu Us Sandy Land[J]. Arid Zone Research,2011,28(3):377 − 383. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王翔宇, 张进虎, 丁国栋, 等. 沙地土壤水分特征及水分时空动态分析[J]. 水土保持学报,2008,22(6):222 − 227. [WNAG Xiangyu, ZHANG Jinhu, DING Guodong, et al. Study on the temporal and spacial change of soil water content and soil moisture characteristics of sandy land[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2008,22(6):222 − 227. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2008.06.047
[20] 石莎, 冯金朝, 邹学勇. 不同地形条件对沙漠植物生长和沙地土壤水分的影响[J]. 干旱区地理,2007,30(6):846 − 851. [SHI Sha, FENG Jinchao, ZOU Xueyong. Effects of the fixed dune topography on soil water and plant growth[J]. Arid Land Geography,2007,30(6):846 − 851. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 张友焱, 周泽福, 程金花, 等. 毛乌素沙地不同沙丘部位几种灌木地土壤水分动态[J]. 东北农业大学学报,2010,41(6):73 − 78. [ZHANG Youyan, ZHOU Zefu, CHENG Jinhua, et al. Soil moisture characteristics of several types of shrubs in different anchored dune positions in Maowusu sandy land[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University,2010,41(6):73 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2010.06.014
[22] 潘颜霞, 王新平, 苏延桂, 等. 荒漠人工固沙植被区土壤水分的时空变异性[J]. 生态学报,2009,29(2):993 − 1000. [PAN Yanxia, WANG Xinping, SU Yangui, et al. Temporal and spatial variability of surface soil moisture in a re-vegetation desert area in Shapotou[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2009,29(2):993 − 1000. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.02.055
[23] HU W, SHAO M, REICHARDT K. Using a new criterion to identify sites for mean soil water storage evaluation[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,2010,74(3):762 − 773. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2009.0235
[24] 侯琼, 苗百岭, 王英舜, 等. 水分胁迫对半干旱典型草原土壤水分变化特征的影响[J]. 干旱气象,2020,38(6):987 − 993. [HOU Qiong, MIAO Bailing, WANG Yingshun, et al. Effects of water stress on soil moisture in semiarid typical steppe[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology,2020,38(6):987 − 993. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 余优森. 人工草地土壤水分垂直变化规律的实验研究[J]. 水科学进展,1991,2(4):271 − 276. [YU Yousen. An experimental study on vertical variation of soil moisture in the artificial sward[J]. Advances in Water Science,1991,2(4):271 − 276. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.1991.04.009
[26] 蔺鹏飞, 朱喜, 何志斌, 等. 土壤水分时间稳定性研究进展[J]. 生态学报,2018,38(10):3403 − 3413. [LIN Pengfei, ZHU Xi, HE Zhibin, et al. Research progress on soil moisture temporal stability[J]. Acta EcologicaSinica,2018,38(10):3403 − 3413. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] DARDANELLI J L, RITCHIE J T, CALMON M, et al. An empirical model for root water uptake[J]. Field Crops Research,2004,87(1):59 − 71. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2003.09.008
[28] NEPSTAD D C, CARVALHO C D, DAVIDSON E A, et al. The role of deep roots in the hydrological and carbon cycles of Amazonian forests and pastures[J]. Nature,1994,372(6507):666 − 669. doi: 10.1038/372666a0
[29] 刘深思, 徐贵青, 李彦, 等. 5种沙地灌木对地下水埋深变化的响应[J]. 生态学报,2021,41(2):615 − 625. [LIU Shensi, XU Guiqing, LI Yan, et al. Difference and consistency of responses of five sandy shrubs to changes in groundwater level in the Hailiutu River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(2):615 − 625. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] GRIBOVSZKI Z, SZILÁGYI J, KALICZ P. Diurnal fluctuations in shallow groundwater levels and streamflow rates and their interpretation:A review[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2010,385(1/2/3/4):371 − 383.
[31] WANG Y Q, SHAO M A, SHAO H B. A preliminary investigation of the dynamic characteristics of dried soil layers on the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2010,381(1/2):9 − 17.
[32] CAO S X, CHEN L, SHANKMAN D, et al. Excessive reliance on afforestation in China’s arid and semi-arid regions:Lessons in ecological restoration[J]. Earth Science Reviews,2011,104(4):240 − 245.
[33] FU B J, ZHAO W W, CHEN L D, et al. Assessment of soil erosion at large watershed scale using RUSLE and GIS:A case study in the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Land Degradation & Development,2005,16(1):73 − 85.
[34] WEI F, HUANG M, GALLICHAND J, et al. Optimization of plant coverage in relation to water balance in the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Geoderma,2012,173/174:134 − 144. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.12.016
[35] ZHANG Z Y, WANG W K, GONG C C, et al. Salix psammophilaafforestations can cause a decline of the water table, prevent groundwater recharge and reduce effective infiltration[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2021,780(9):146336.
[36] ZHAO M, WANG W K, WANG Z F, et al. Water use of Salix in the variably unsaturated zone of a semiarid desert region based on insitu observation[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,591(3):125579.
-



 下载:
下载: