Spatial distribution and sources of PAHs in topsoil in the Beiyun River Basin (Beijing section)
-
摘要:
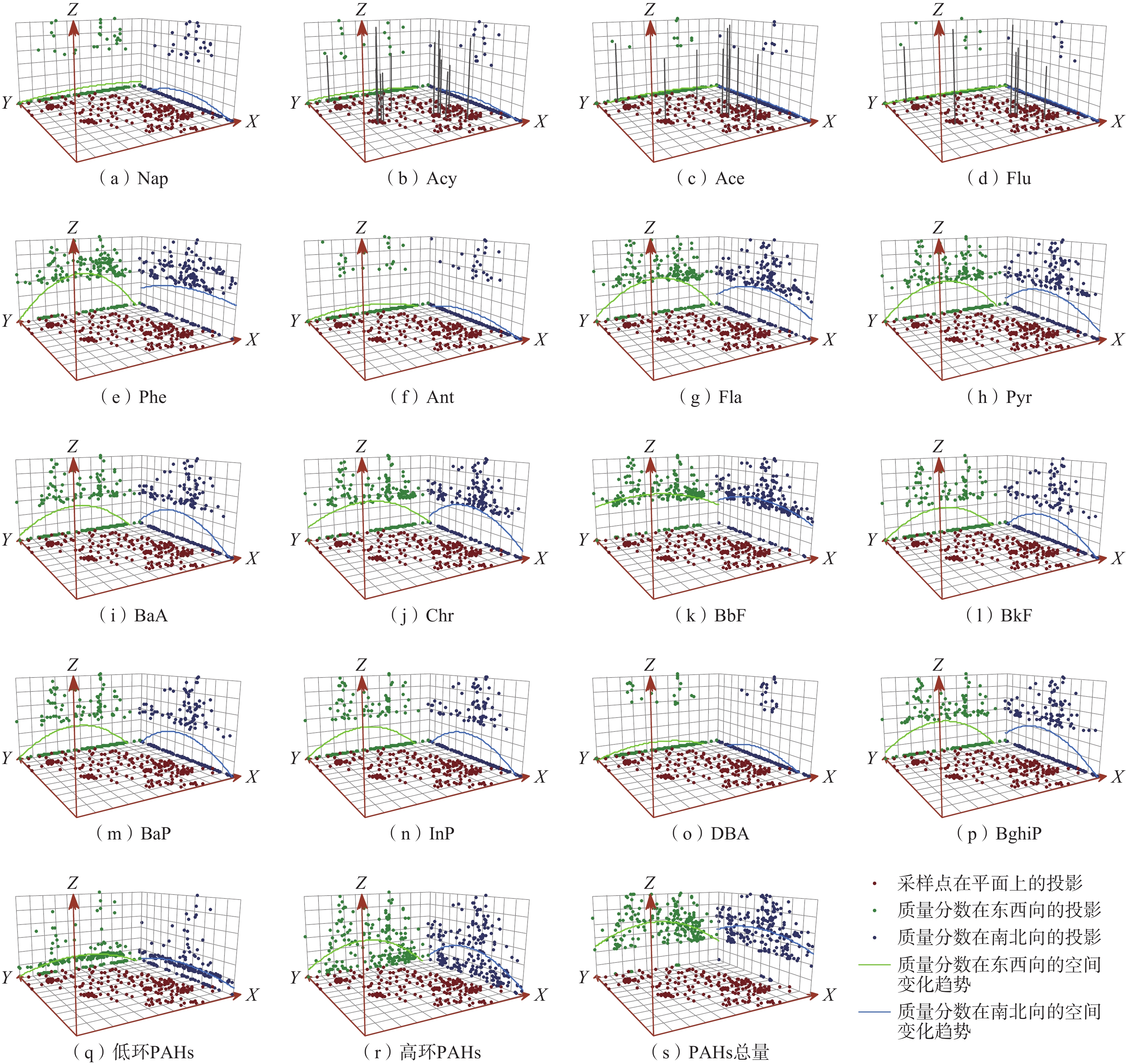
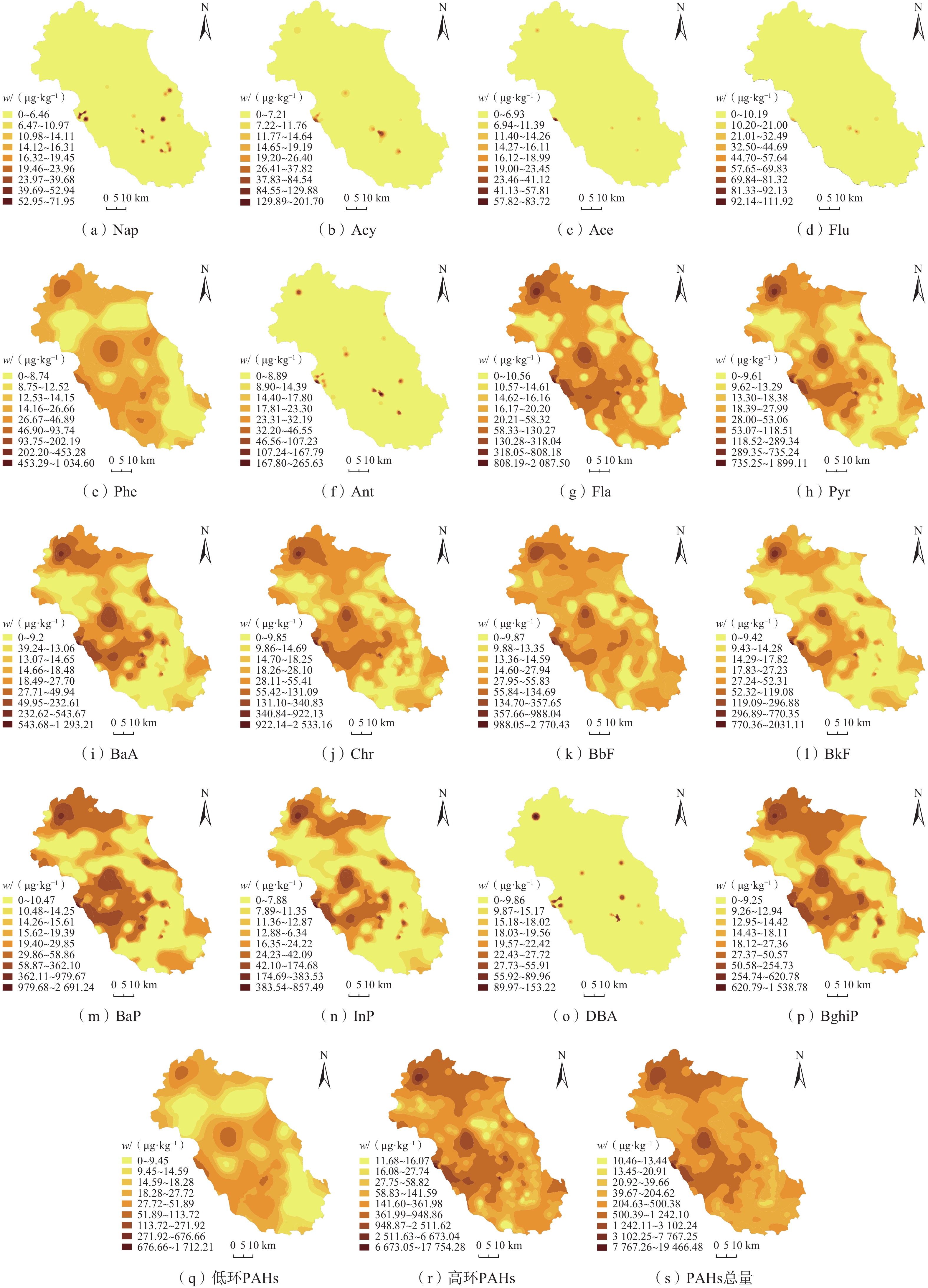
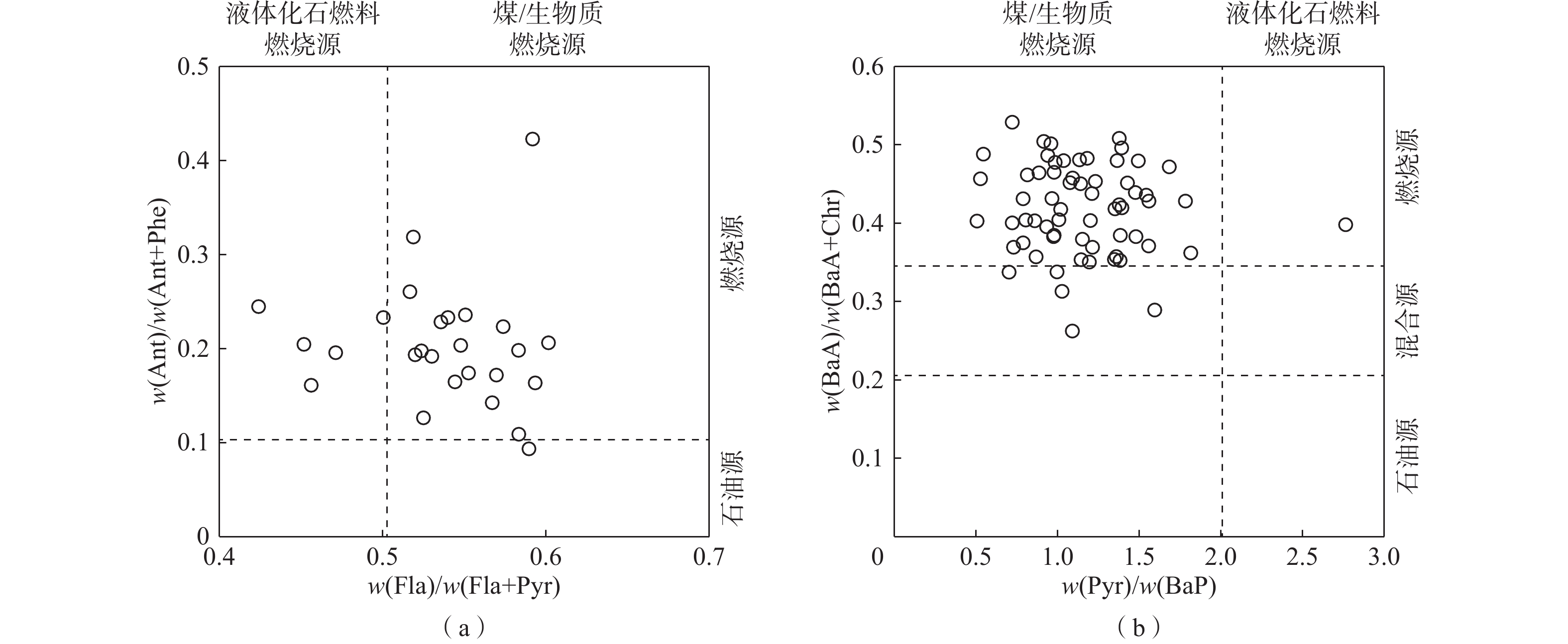
土壤中的多环芳烃(PAHs)会威胁人类健康和生态环境安全。为掌握北运河流域(北京段)土壤中PAHs的分布特征及其形成机制,采用克里格插值、主成分分析-多元线性回归等多元统计方法,结合同分异构体比值法对该区域表层土壤中16种优控PAHs的质量分数、分布趋势、空间分布特征及其污染来源进行了研究。结果表明:(1)研究区216件土壤样品中16种PAHs均被检出,且主要为高环PAHs(4~6环),总PAHs的质量分数范围在10.5~19466.5 μg/kg,受污染土壤样品占29.63% ;(2)表层土壤中的PAHs在东西及南北方向上均呈现出中部高、两端低的趋势,在空间分布上总体表现为北部区域及中部城区含量较高、其他地区相对较低的特征,且由于人为活动影响导致个别点位PAHs富集,存在点源污染或局部污染;(3)PAHs同分异构体比值法及主成分分析法研究表明,研究区内PAHs的来源为以煤/生物质燃烧及交通燃烧为主、石油泄漏等石油化工源为辅的混合源,多元线性回归方法分析后得到 2 者的贡献率分别为89%和11%。研究结果可为研究区的污染防控、土地质量评价和国土空间规划等工作提供有力支撑。
Abstract:Organic pollution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in topsoil has threatened human health and ecological environment. In order to understand the distribution and pollution characteristics of PAHs in topsoil in the Beiyun River Basin in Beijing, an investigation is carried out to examine the contents, distribution trends, spatial distribution and pollution sources of 16 optimal PAHs in topsoil of the study area by means of multivariate statistical methods including the Kriging interpolation, principal component analysis-multiple linear regression and the concentration ratio among certain components. The results are as follows (1) all 16 PAHs are detected, and most of them are high loop PAHs (4−6 rings). The total contents of PAHs in topsoil range from 10.5 to 19466.5 μg/kg, about 29.63% of the samples are polluted in the study area. (2) The PAHs contents in topsoil show a trend of higher in the middle and lower at ends in both east-west and south-north direction. In terms of spatial distribution, the PAHs contents in topsoil are higher in the northern region and the central urban area, while the PAHs contents are lower in other areas. Due to the accumulation of PAHs caused by human activities at some points, point source pollution or local pollution exist. (3)The ratio of specific PAHs components and principal component analysis indicate that the sources of 16 PAHs in the study area are mainly coal, biomass combustion and traffic combustion. Multiple linear regression shows that the contribution rates of the two are 89% and 11% respectively. The research results can provide strong support for pollution prevention and control, land quality evaluation and territorial space planning in the study area.
-
Key words:
- Beiyun River Basin /
- topsoil /
- PAHs /
- spatial distribution /
- pollution sources
-

-
表 1 土壤PAHs质量分数统计
Table 1. Statistic of soil PAHs
指标 环数 最小值/
(μg·kg−1)最大值/
(μg·kg−1)平均值/
(μg·kg−1)中值/
(μg·kg−1)检出
率/%Nap 2 ND 213.0 36.6 24.2 12.90 Acy 3 ND 201.7 46.6 27.1 7.41 Ace 3 ND 83.7 28.6 19.4 5.09 Flu 3 ND 111.9 52.1 34.0 4.17 Phe 3 ND 1034.6 60.1 24.4 69.44 Ant 3 ND 265.6 53.5 25.3 12.04 Fla 4 ND 2087.5 85.9 22.5 66.20 Pyr 4 ND 1899.1 87.6 23.4 54.17 BaA 4 ND 1293.2 75.2 21.9 44.44 Chr 4 ND 2533.2 80.0 21.6 61.11 BbF 5 ND 2770.4 69.7 19.8 87.50 BkF 5 ND 2031.1 92.7 25.6 37.96 BaP 5 ND 2691.2 112.8 32.0 38.89 DBA 5 ND 153.2 43.6 33.4 10.65 InP 6 ND 857.5 70.0 27.1 34.26 BghiP 6 ND 1538.8 73.9 23.3 48.15 低环
PAHs2~3 ND 1712.2 82.6 24.8 72.69 高环
PAHs4~6 ND 17754.3 424.4 72.0 92.13 PAHs
总量— 10.5 19466.5 451.0 83.5 100.00 注:ND表示未检出。 表 2 土壤PAHs污染标准
Table 2. Pollution standard of soil PAHs
PAHs 筛选值/
(103 μg·kg−1)管制值/
(103 μg·kg−1)PAHs 筛选值/
(103 μg·kg−1)管制值/
(103 μg·kg−1)Nap 25 255 BkF 55 550 BaA 5.5 55 BaP 0.55 5.5 Chr 490 4900 InP 5.5 55 BbF 5.5 55 DBA 0.55 5.5 表 3 土壤PAHs质量分数半变异函数理论模型及参数
Table 3. Theoretical model and parameters of the soil PAHs semivariogram
PAHs 理论模型 块金值 基台值 块金系数 变程/km R2 RSS Nap 球状 0.037 0.079 0.462 9.75 0.197 0.0055 Acy 线性 0.559 0.559 1.000 38.96 0.317 0.0376 Ace 球状 0.029 0.336 0.086 15.25 0.248 0.7040 Flu 高斯 0.096 0.450 0.213 29.22 0.141 0.0843 Phe 线性 0.043 0.124 0.347 16.82 0.332 0.2290 Ant 球状 0.094 0.489 0.192 7.21 0.119 0.4370 Fla 线性 0.552 1.080 0.511 45.94 0.868 0.0562 Pyr 指数 0.009 0.052 0.169 9.15 0.672 2.84E-04 BaA 线性 0.037 0.037 1.000 41.92 0.252 3.09E-05 Chr 线性 0.780 1.460 0.530 45.99 0.714 0.2450 BbF 线性 0.489 1.210 0.404 48.31 0.838 0.1320 BkF 高斯 0.034 0.068 0.499 10.48 0.255 0.0031 BaP 指数 0.002 0.010 0.235 12.60 0.499 2.05E-05 DBA 球状 0.010 0.085 0.112 3.36 0.213 0.0143 InP 线性 0.368 0.368 1.000 36.45 0.236 0.5350 BghiP 线性 0.679 0.945 0.719 42.11 0.413 0.1330 低环PAHs 球状 0.139 1.120 0.124 11.90 0.752 0.9590 高环PAHs 高斯 1.521 3.043 0.500 48.67 0.773 0.9890 PAHs总量 高斯 1.221 2.566 0.476 48.28 0.896 0.2790 表 4 土壤PAHs质量分数比值及其来源
Table 4. Mass fraction ratio and sources of soil PAHs
比值 比值范围 来源 w(低环PAHs)/w(高环PAHs) <1 燃烧源 >1 石油源 w(Ant)/w(Ant+Phe) <0.1 石油源 >0.1 燃烧源 w(Fla)/w(Fla+Pyr) <0.4 石油源 0.4~0.5 液体化石燃料燃烧源 >0.5 煤/生物质燃烧源 w(BaA)/w(BaA+Chr) <0.2 石油源 0.2~0.35 混合源 >0.35 燃烧源 w(Pyr)/w(BaP) <2 煤/生物质燃烧源 2~6 液体化石燃料燃烧源 表 5 土壤PAHs主成分因子旋转载荷矩阵
Table 5. Rotation load matrix of the principal component factors of soil PAHs
PAHs 主成分1 主成分2 Nap 0.850 −0.026 Acy 0.744 0.562 Ace 0.716 0.563 Flu 0.761 0.406 Phe 0.900 0.339 Ant 0.903 0.019 Fla 0.990 −0.047 Pyr 0.985 0.042 BaA 0.973 −0.168 Chr 0.960 −0.250 BbF 0.955 −0.277 BkF 0.954 −0.278 BaP 0.960 −0.232 DBA 0.965 −0.180 InP 0.885 0.059 BghiP 0.958 −0.231 方差贡献率 82.42% 8.16% 累计方差贡献率 82.42% 90.58% -
[1] 安永龙,黄勇,孙朝,等. 北京通州某改造区土壤中PAHs的来源分析及风险评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(5):112 − 120. [AN Yonglong,HUANG Yong,SUN Zhao,et al. Source apportionment and risk assessment of PAHs in soil from a renewal area in the Tongzhou District of Beijing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(5):112 − 120. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 郭娜,王金生,翟远征,等. 北京市平原区土壤中PAHs分布特征与来源分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(6):110 − 115. [GUO Na,WANG Jinsheng,ZHAI Yuanzheng,et al. Distribution and source analysis of PAHs in the surface soil in the Beijing Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(6):110 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 卢晓丽,康翔,魏宇宸,等. 城乡结合带农田土壤多环芳烃空间分布特征及来源解析—以南京市周岗镇为例[J]. 土壤通报,2021,52(2):286 − 296. [LU Xiaoli,KANG Xiang,WEI Yuchen,et al. Spatial distribution and sources of PAHs in farmland soil of peri-urban areas:A case study of Zhougang,Nanjing[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2021,52(2):286 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘增俊,滕应,黄标,等. 长江三角洲典型地区农田土壤多环芳烃分布特征与源解析[J]. 土壤学报,2010,47(6):1110 − 1117. [LIU Zengjun,TENG Ying,HUANG Biao,et al. Distribution and sources analysis of pahs in farmland soils in areas typical of the Yangtze River Delta,China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2010,47(6):1110 − 1117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 黄勇,王安婷,袁国礼,等. 北京市表层土壤中PAHs含量特征及来源分析[J]. 岩矿测试,2022,41(1):54 − 65. [HUANG Yong,WANG Anting,YUAN Guoli,et al. The content characteristics and source analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in topsoil of Beijing City[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,2022,41(1):54 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张秀秀,卢晓丽,魏宇宸,等. 城郊农田土壤多环芳烃污染特征及风险评价[J]. 环境科学,2021,42(11):5510 − 5518. [ZHANG Xiuxiu,LU Xiaoli,WEI Yuchen,et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a suburban farmland soil[J]. Environmental Science,2021,42(11):5510 − 5518. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 刘洋. “引温济潮”实现区域性水资源跨流域回补[J]. 北京规划建设,2010(2):71 − 74. [LIU Yang. “Divert water from Wenyu River into Chaobai River” to realize regional water resources recharge across river basins[J]. Beijing Planning Review,2010(2):71 − 74. (in Chinese)
[8] 荆红卫,张志刚,郭婧. 北京北运河水系水质污染特征及污染来源分析[J]. 中国环境科学,2013,33(2):319 − 327. [JING Hongwei,ZHANG Zhigang,GUO Jing. Water pollution characteristics and pollution sources of Bei Canal River system in Beijing[J]. China Environmental Science,2013,33(2):319 − 327. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 杨颖,孙文,刘吉宝,等. 北运河流域沙河水库沉积物重金属分布及生态风险评估[J]. 环境科学学报,2021,41(1):217 − 227. [YANG Ying,SUN Wen,LIU Jibao,et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Shahe Reservoir in Northern Canal Basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2021,41(1):217 − 227. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 陈永娟,庞树江,耿润哲,等. 北运河水系主要污染物通量特征研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2015,35(7):2167 − 2176. [CHEN Yongjuan,PANG Shujiang,GENG Runzhe,et al. Fluxes of the main contaminant in Beiyun River[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2015,35(7):2167 − 2176. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张家铭,李炳华,毕二平,等. 北运河流域(北京段)沉积物中PAHs污染特征与风险评估[J]. 环境科学研究,2019,32(11):1852 − 1860. [ZHANG Jiaming,LI Binghua,BI Erping,et al. Pollutant characteristics and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediment of the North Canal Basin(Beijing section)[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2019,32(11):1852 − 1860. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] ZHANG Shiwei,LI Binghua,ZHANG Dasheng,et al. Distribution and risk assessment of PAHs in river water and groundwater in North Canal Basin of Beijing[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2021,19(1):179 − 190.
[13] 薛源. 北运河流域(北京段)多环芳烃的空间分布和逸度模拟[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2015
XUE Yuan. Spatial distribution and multimedia fugacity environment behavior of PAHs in Beiyun River Basin of Beijing[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 丁淮剑. 北运河流域沉积物重金属污染状况分析[D]. 北京: 首都师范大学, 2009
DING Huaijian. Study of heavy meatal pollution of the sediment in Beiyunhe River in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Capital Normal University, 2009.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 孙久虎,刘晓萌,李佑钢,等. 北运河地区植被覆盖的遥感估算及变化分析[J]. 水土保持研究,2006,13(6):97 − 99. [SUN Jiuhu,LIU Xiaomeng,LI Yougang,et al. Estimation of vegetation fraction in Beiyunhe District by remote sensing[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2006,13(6):97 − 99. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2006.06.030
[16] 田林锋,罗桂林,姜文娟,等. 基于多元统计的宁夏典农河水质演替特征探究[J]. 中国环境监测,2023,39(1):128 − 136. [TIAN Linfeng,LUO Guilin,JIANG Wenjuan,et al. Water quality succession of Diannong River in Ningxia based on multiple statistics[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China,2023,39(1):128 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 王昱,卢世国,冯起,等. 黑河上中游水质时空分异特征及污染源解析[J]. 中国环境科学,2019,39(10):4194 − 4204. [WANG Yu,LU Shiguo,FENG Qi,et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics and source identification of water pollutants in the upper and middle reachers of Heihe River[J]. China Environmental Science,2019,39(10):4194 − 4204. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 宋旭,高灯州,曾从盛,等. 基于GIS地统计学的海坛岛农田养分变异研究[J]. 实验室科学,2017,20(1):25 − 28. [SONG Xu,GAO Dengzhou,ZENG Congsheng,et al. Spatial variation of soil nutrient of the Haitan Island based on GIS and Geo-statistic[J]. Laboratory Science,2017,20(1):25 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 安永龙,万利勤,李霞,等. 承德市土壤重金属空间结构与分布特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):119 − 131. [AN Yonglong,WAN Liqin,LI Xia,et al. Spatial structure and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in the soil in Chengde[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):119 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 安永龙,杜子图,黄勇,等. 基于地统计学和GIS 技术的北京市大兴区礼贤镇土壤养分空间变异性研究[J]. 现代地质,2018,32(6):1311 − 1321. [AN Yonglong,DU Zitu,HUANG Yong,et al. Spatial variation analysis of soil nutrients in Lixian Town of Daxing District in Beijing based on geostatistics and GIS[J]. Geoscience,2018,32(6):1311 − 1321. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 陈静,王学军,胡俊栋,等. 多环芳烃(PAHs)在砂质土壤中的吸附行为[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2005,24(1):69 − 73. [CHEN Jing,WANG Xuejun,HU Jundong,et al. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sand soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science,2005,24(1):69 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2005.01.016
[22] 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局.土壤环境质量—建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准: GB36600—2018[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2018
Ministry of Ecology and Environment, State Administration for Market Regulation. Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of development land: GB36600—2018[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2018. (in Chinese)
[23] EDWARDS N T. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the terrestrial environment :A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality,1983,12(4):427 − 441.
[24] MALISZEWSKA-KORDYBACH B,SMRECZAK B,KLIMKOWICZ-PAWLAS A,et al. Monitoring of the total content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in arable soils in Poland[J]. Chemosphere,2008,73(8):1284 − 1291. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.009
[25] 陈卫锋,倪进治,杨红玉,等. 闽江福州段沉积物中多环芳烃的空间分布异质性研究[J]. 环境科学,2012,33(5):1687 − 1692. [CHEN Weifeng,NI Jinzhi,YANG Hongyu,et al. Spatial heterogeneity and autocorrelation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediment of Minjiang River in Fuzhou City[J]. Environmental Science,2012,33(5):1687 − 1692. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2012.05.046
[26] 马瑾,邱兴华,周永章,等. 东莞市农业土壤多环芳烃污染及其空间分布特征研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),2011,47(1):149 − 158. [MA Jin,QIU Xinghua,ZHOU Yongzhang,et al. PAHs pollution and spatial distribution in agricultural soils of Dongguan[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,2011,47(1):149 − 158. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 李秀梅,周时学,罗胜军,等. 地统计学在生态学中的应用[J]. 现代农业科技,2014(13):245. [LI Xiumei,ZHOU Shixue,LUO Shengjun,et al. Application of geostatistics in ecology[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2014(13):245. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 蔡婷. 土壤类型对多环芳烃吸附性能的影响[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017
CAI Ting. The influence of soil type on PAHs adsorption properties[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 李随云,杨飞,杨载熙,等. 京山市钱场—新市两镇表层土壤有机质含量分布及影响因素[J]. 资源环境与工程,2021,35(2):179 − 181. [LI Suiyun,YANG Fei,YANG Zaixi,et al. Distribution of topsoil organic matter content in Qianchang − Xinshi Towns in Jingshan City and its influencing factors[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2021,35(2):179 − 181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 孙军亚. 多环芳烃在藏东南森林土壤中的分布、迁移及其生态风险评价[D]. 天津: 天津理工大学, 2019
SUN Junya. Distribution and migration and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in forest soils in southeast Xizang[D]. Tianjin : Tianjin University of Technology, 2019.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 吴萌,段永红,何佳璘,等. 北方地区表层土壤中PAHs的含量及来源分析[J]. 山西农业科学,2021,49(3):311 − 317. [WU Meng,DUAN Yonghong,HE Jialin,et al. Content and source analysis of PAHs in surface soil of Northern China[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2021,49(3):311 − 317. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 赵振华, 全文熠, 田德海, 等. 多环芳烃的环境健康化学[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 1993
ZHAO Zhenhua, QUAN Wenyi, TIAN Dehai, et al. Environmental health chemistry of PAHs[M]. Beijing: Science and technology of China press, 1993. (in Chinese)
[33] MCCREADY S,SLEE D J,BIRCH G F,et al. The distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surficial sediments of Sydney Harbour,Australia[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2000,40(11):999 − 1006. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00044-8
[34] SIMCIK M F,EISENREICH S J,LIOY P J. Source apportionment and source/sink relationships of PAHs in the coastal atmosphere of Chicago and Lake Michigan[J]. Atmospheric Environment,1999,33(30):5071 − 5079. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00233-2
[35] LARSEN R K,BAKER J E. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urban atmosphere:A comparison of three methods[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2003,37(9):1873 − 1881.
[36] JIANG Yufeng,WANG Xuetong,WANG Fei,et al. Levels,composition profiles and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soil of Shanghai,China[J]. Chemosphere,2009,75(8):1112 − 1118. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.01.027
[37] MURAKAMI M,NAKAJIMA F,FURUMAI H. Size- and density-distributions and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban road dust[J]. Chemosphere,2005,61(6):783 − 791. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.04.003
[38] BOONYATUMANOND R,WATTAYAKORN G,TOGO A,et al. Distribution and origins of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in riverine,estuarine,and marine sediments in Thailand[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2006,52(8):942 − 956. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.12.015
[39] 江淼华,徐素云,许辰森,等. 城市绿地表层土壤中PAHs的来源及风险评估—以福州市鼓楼区为例[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报,2015,10(3):11 − 16. [JIANG Miaohua,XU Suyun,XU Chensen,et al. Sources and risk assessment of PAHs in surface soil from urban green lands:A case of Gulou District,Fuzhou,China[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment,2015,10(3):11 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[40] 刘芬芬,孙小华,丁力,等. 搬迁企业原址场地土壤挥发性有机物污染特征—以北京某搬迁化工厂为例[J]. 城市地质,2021,16(1):18 − 24. [LIU Fenfen,SUN Xiaohua,DING Li,et al. Characteristics of soil volatile organic compound pollution in the original site of relocated enterprises:A case study of a relocated chemical plant in Beijing[J]. Urban Geology,2021,16(1):18 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] 北京市统计局, 国家统计局北京调查总队. 北京统计年鉴-2021[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022
Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics, Survey Office of the National Bureau of Statistics in Beijing. Beijing statistical yearbook-2021[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2022. (in Chinese)
[42] 段海静. 路域环境多介质PAHs污染与综合健康风险分析——以G310和G30郑开段为例[D]. 开封: 河南大学, 2016
DUAN Haijing. Pollution and comprehensive health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in roadside multiple medias: A case study of 310th national highway and 30th highway[D]. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: