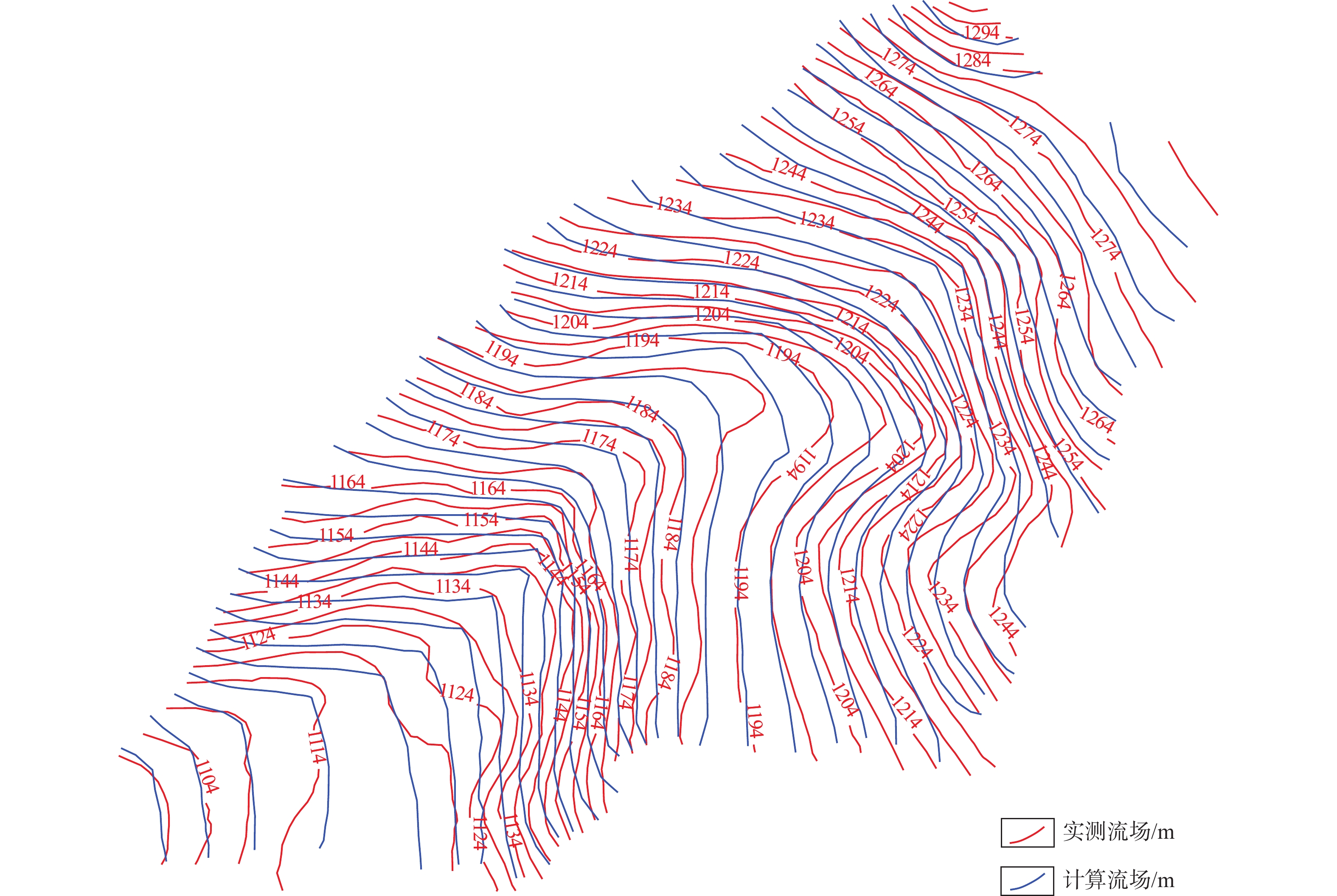
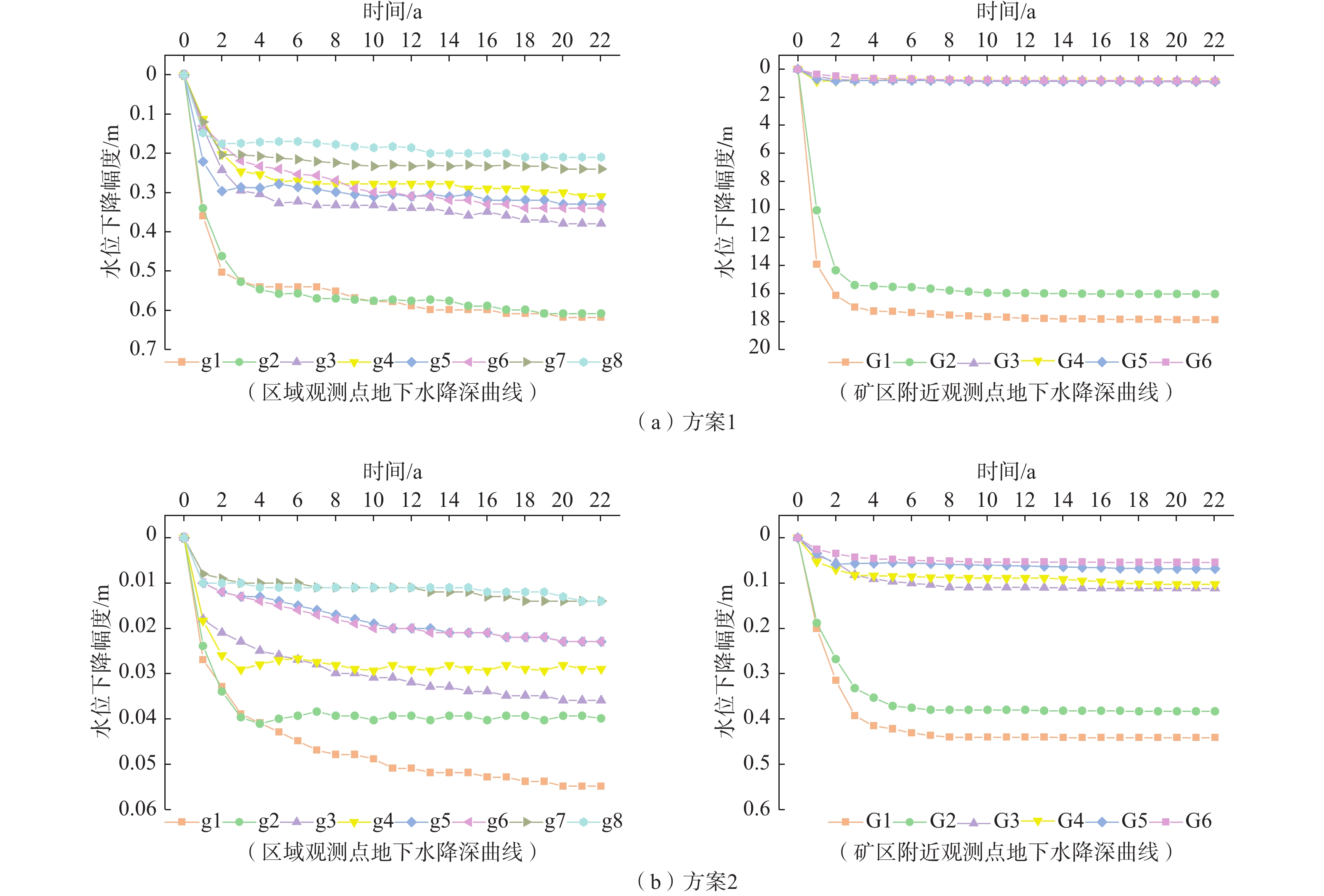
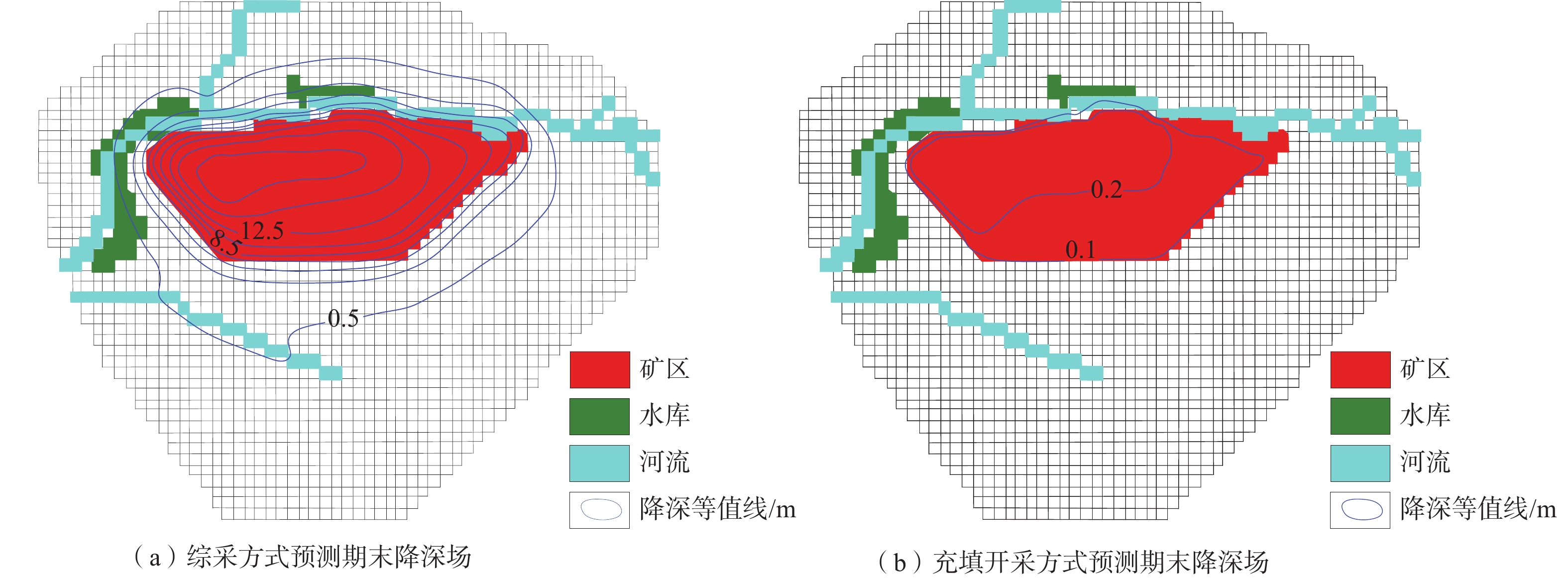
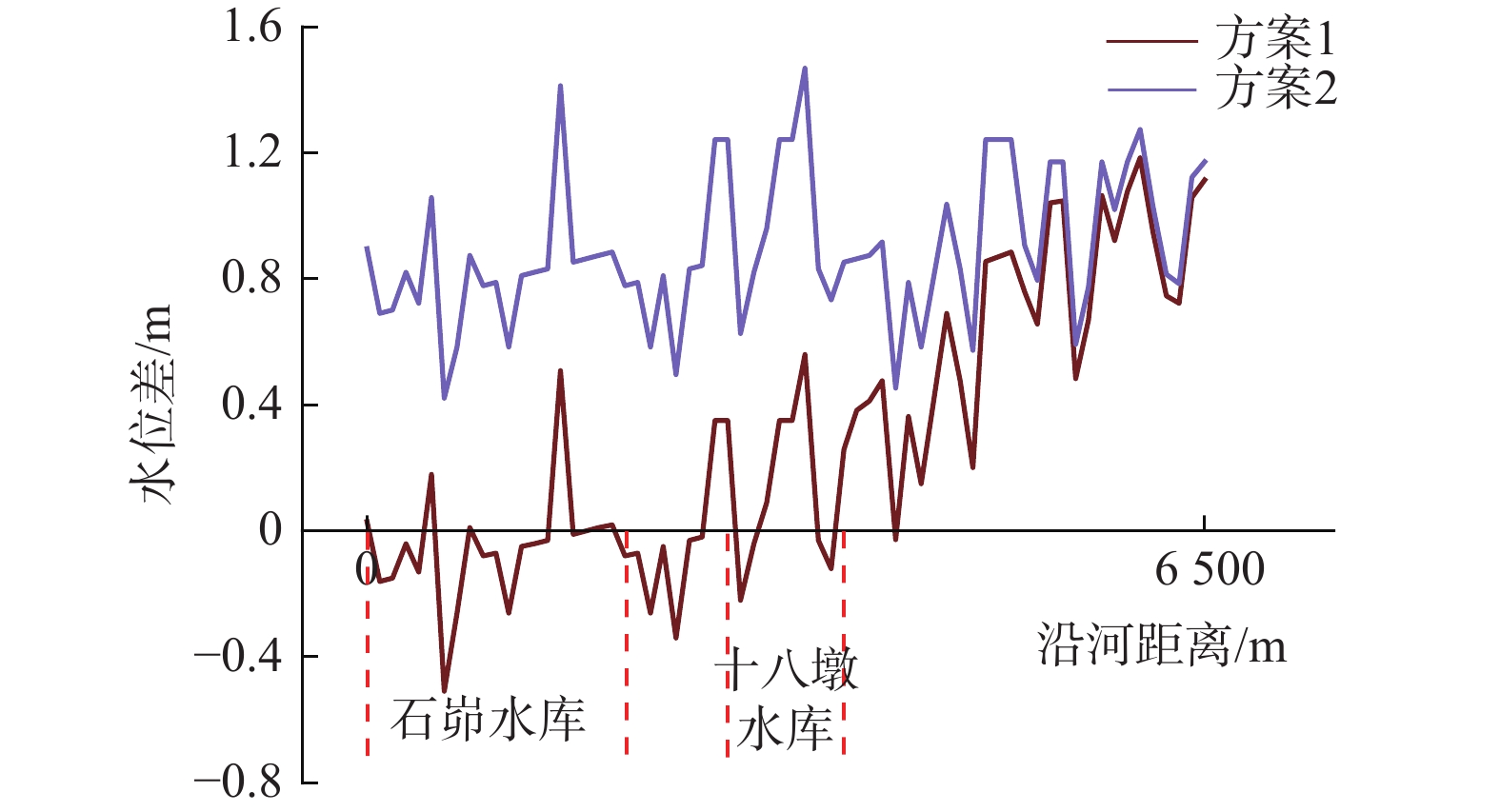
Prediction of coal mine water inflow by different mining methods and environment impact analyses
-
摘要:
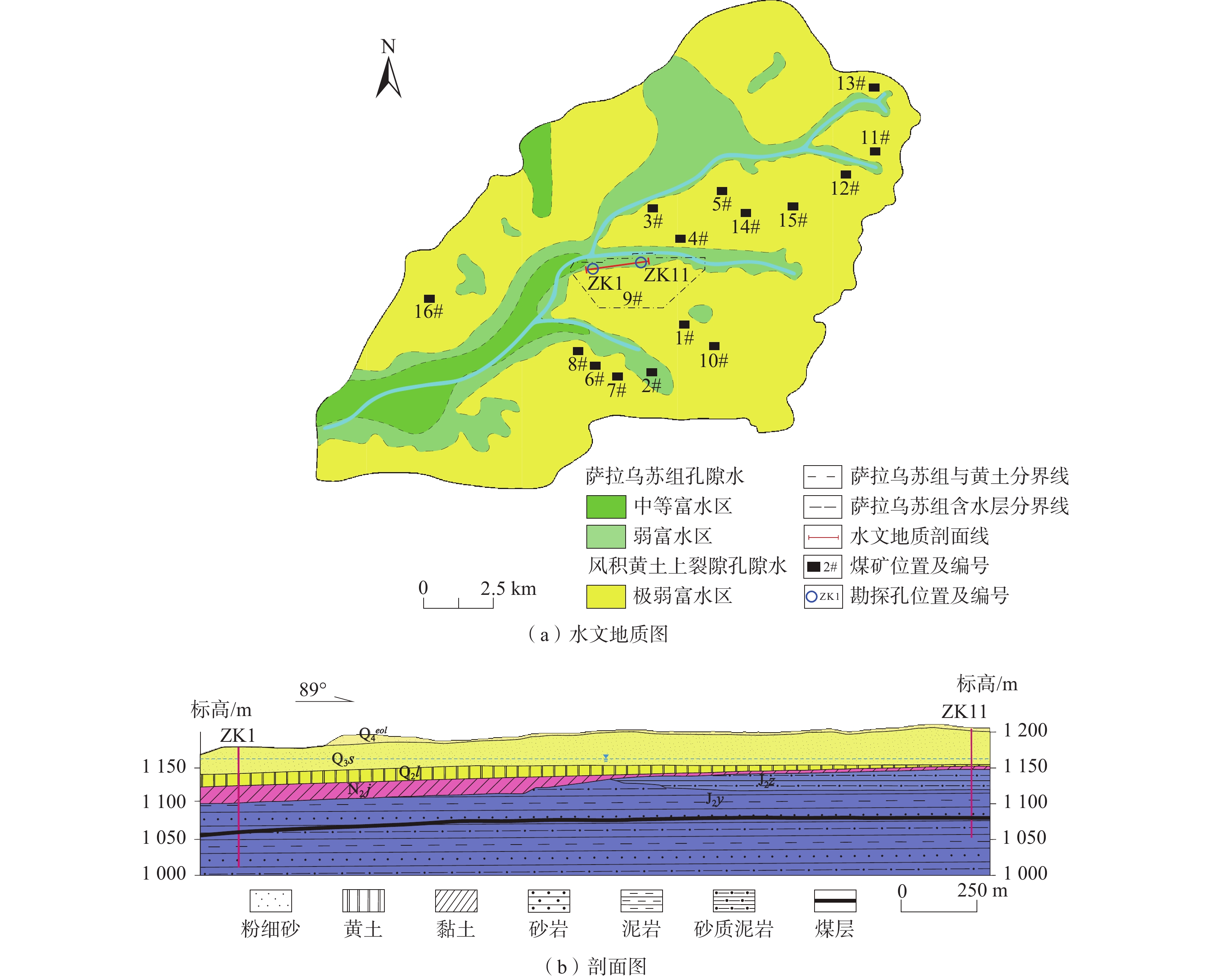
煤矿开采不当会对水资源与水环境造成破坏,尤其在生态环境相对脆弱地区更是如此。针对目前矿井涌水量预测大多以单一工作面或煤矿为评价单元,对沟域内煤矿群同时长期开采的地下水环境影响重视不够。选择头道河则沟域为研究区,以地下水勘查、井田勘探资料为依据,构建了头道河则完整沟域的地下水三维非稳定流数值模型,根据地下水、地表水监测数据和煤矿群开采涌水量的长观资料进行模型的识别与验证,以9#煤矿为典型矿区,分析综采和条带充填2种不同开采方式下矿井涌水量及其对水环境的影响。研究结果表明:(1)综采状态下,矿井涌水量增加0.70×104 m3/d,导致地下水溢出量减少0.20×104 m3/d,引发矿区及区域地下水水位下降0.21~17.92 m;条带充填开采状态下,矿井涌水量增加0.11×104 m3/d,导致地下水溢出量减少0.04×104 m3/d,引发矿区及区域地下水水位下降0.01~0.44 m。(2)煤矿按综采方式开采,导水裂隙带高度大,将大面积导通第四系潜水含水层,矿井涌水对水环境影响较大;若按条带充填方式开采,导水裂隙带高度大幅变小,不会导通第四系潜水含水层,矿井涌水对水环境影响较小。煤矿企业在煤层上覆岩层厚度较薄的地段采煤时,宜采取条带充填开采的方式。研究结果可为研究区或类似煤田开采方案制定、科学处理好煤炭资源开采与生态环境保护关系等提供依据或参考。
Abstract:Improper mining of coal mines can cause damage to water resources and the water environment, especially in areas with relatively fragile ecological environment. At present, the prediction of mine water inflow mainly focuses on the single working face or mining area, and enough attention has not been paid to the influence of long-term mining of coal groups in the gully on groundwater environment. The Toudaoheze gully is selected as the study area. Based on the data of groundwater exploration and coal field investigation, a 3D numerical model of groundwater unsteady flow of the whole gully is constructed. The model is identified and verified with the monitoring data of groundwater and surface water and the long-term data of mine water inflow in coal groups. Taking 9# coal mine as a typical area, the mine water inflow and its influence on water environment under the fully mechanized mining and strip filling mining methods are analyzed. The main results show that (1) under the fully mechanized mining method, the increase of mine water inflow is 0.70×104 m3/d, resulting in the reduction of groundwater overflow of 0.20×104 m3/d and causing groundwater level to drop between 0.21 and 17.92 m in the mining area and region. Under the strip filling mining method, the increase of mine water inflow is 0.11×104 m3/d, resulting in the reduction of groundwater overflow is 0.04×104 m3/d and causing groundwater level to drop between 0.01 and 0.44 m in mining area and region. (2) The water-conducting fracture zone connects with a large area of the Quaternary phreatic aquifer under the fully mechanized mining method, and mine water inflow has a great impact on water environment. If the strip filling method is carried out, the height of the water-conducting fracture zone will be greatly reduced, and the Quaternary phreatic aquifer will not be connected, and mine water inflow will have less impact on water environment. The filling mining method can be adopted when coal mining in the area has small thickness of strata above the coal seam. The results can provide a basis or reference for the formulation of mining schemes in the study area or other similar coal fields, and for scientifically handling the relationship between coal resource mining and ecological environmental protection.
-

-
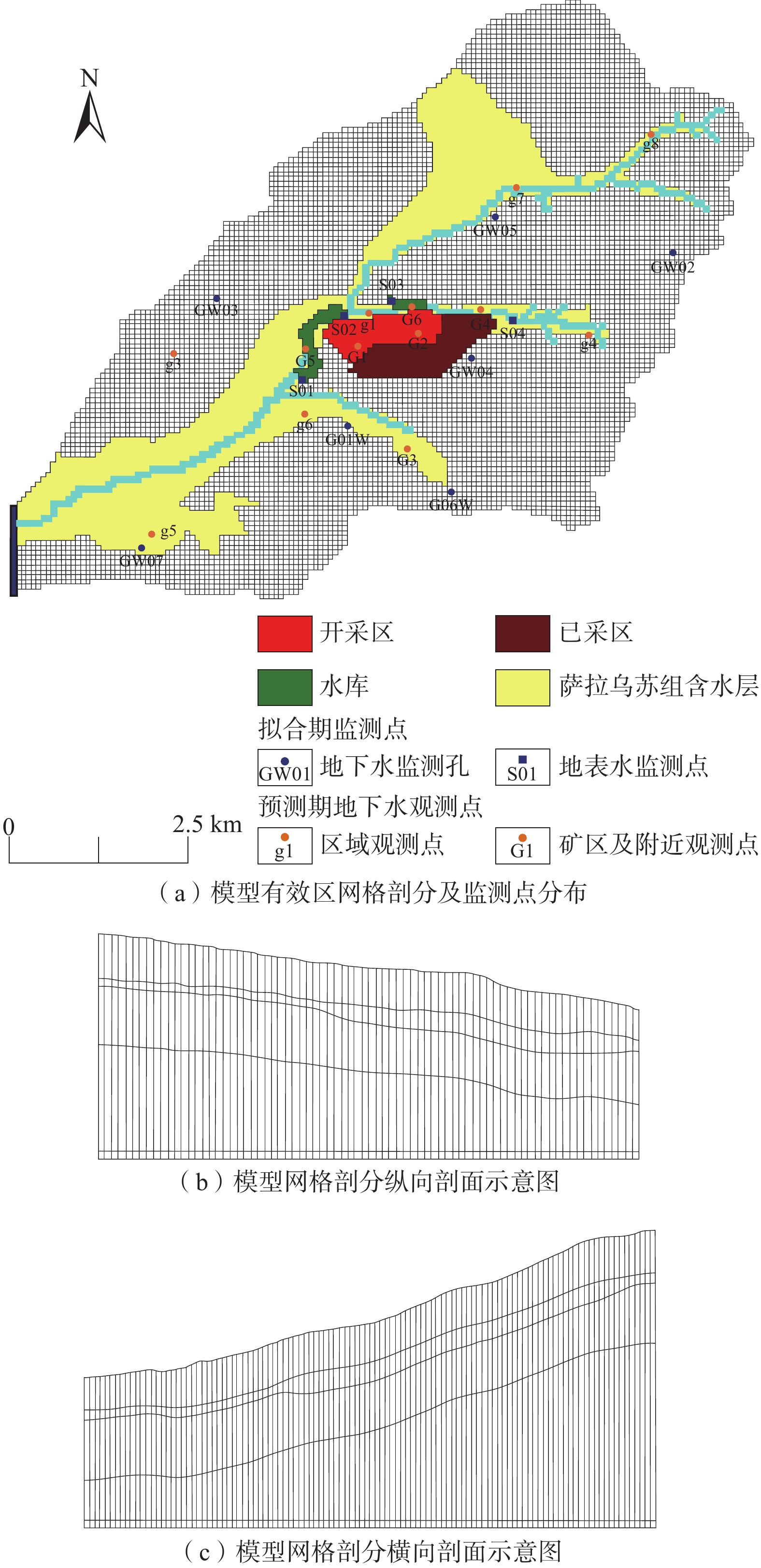
表 1 模型区水文地质参数分区与参数值
Table 1. Hydrogeological parameter partition and parameter values in the model area
分层 分区编号 地层 渗透系数/(m·d−1) 给水度 弹性
释水率
/m−1备注 水平 垂直 一层 Ⅰ 河谷区砂土层 1.5 1 0.15 Ⅱ 萨拉乌苏组砂层 1.85 1.85 0.17 Ⅲ 萨拉乌苏组/黄土 0.93 0.05 0.12 上部萨拉乌苏组,下部黄土 Ⅳ 黄土层 0.015 0.025 0.05 二层 Ⅰ 新近系岩层 1×10−5 1×10−5 1×10−20 Ⅱ 侏罗系岩层 0.051 0.00009 1×10−5 侏罗系原岩层 三层 全区 侏罗系岩层 0.051 0.00009 1×10−5 导水裂隙带之上原岩层 四层 Ⅰ 侏罗系岩层 35 55 1×10−5 导水裂隙带 Ⅱ 侏罗系岩层 0.051 0.00009 1×10−5 导水裂隙带的两侧原岩层 五层 Ⅰ 侏罗系煤层 — — 1×10−5 采空区 Ⅱ 侏罗系煤层 0.08 0.0005 1×10−5 采空区的两侧原煤层 注:—表示无此数据。 表 2 各方案的地下水补排量预测成果
Table 2. Prediction results of groundwater recharge and discharge of each scheme
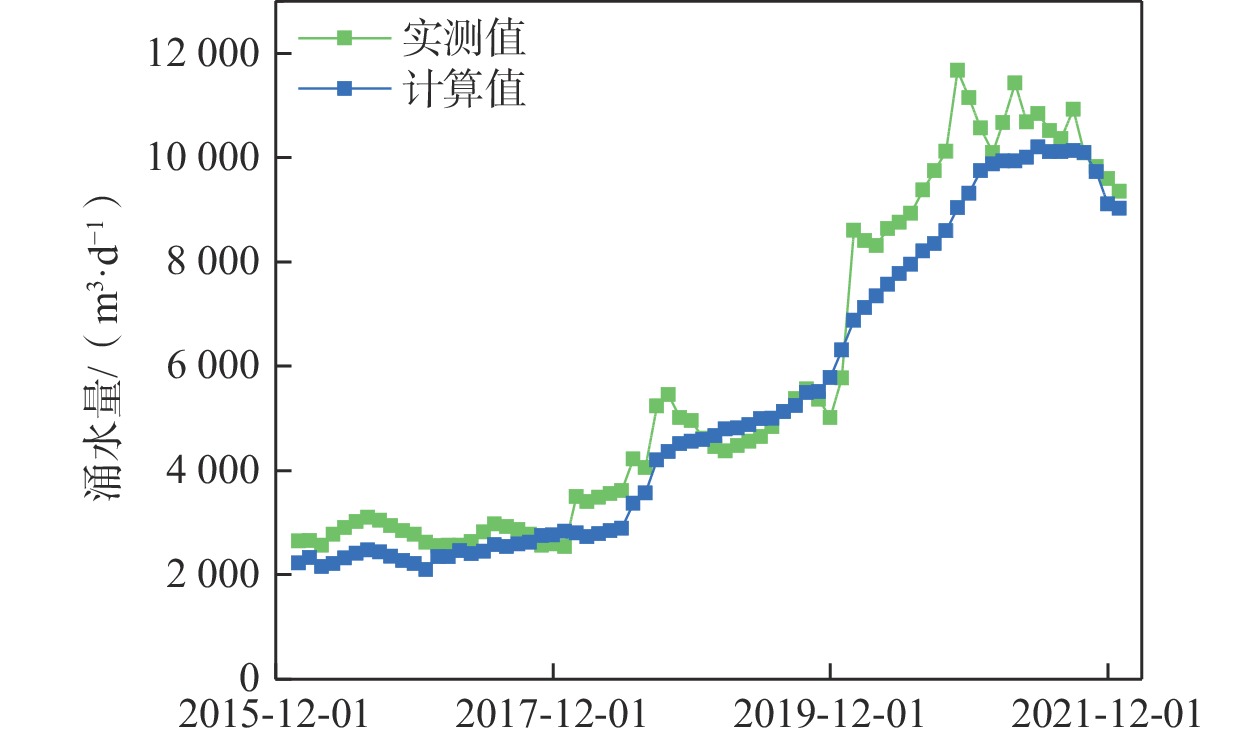
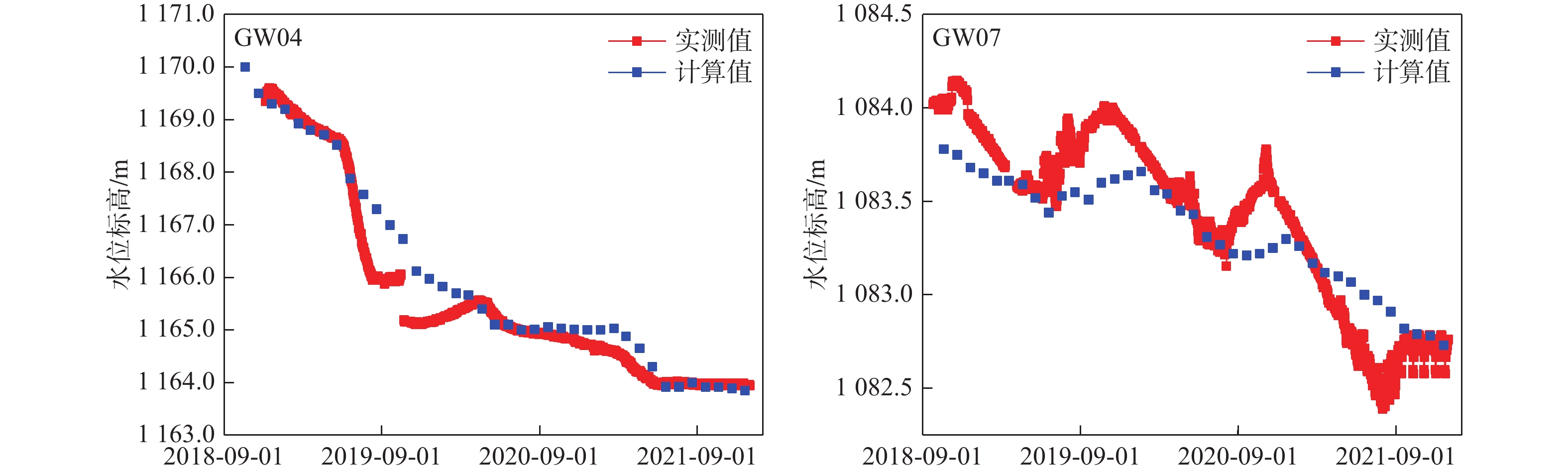
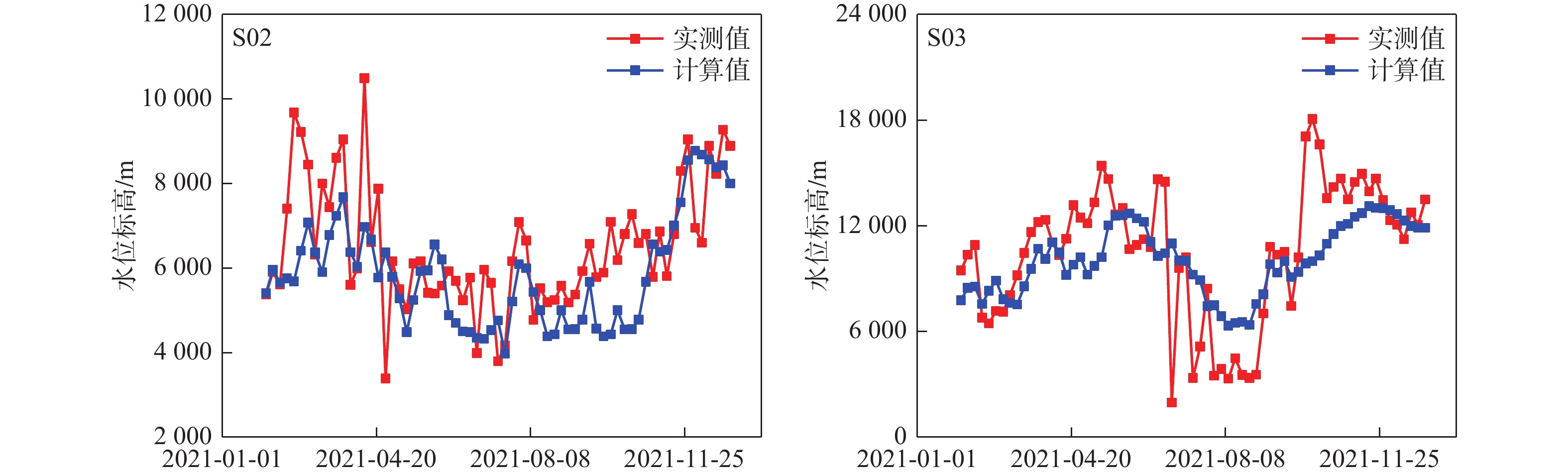
/(104 m3·d−1) 补排项 天然状态 预测期初 预测期末 变化量 方案1 方案2 方案1 方案2 补给项 大气降水入渗补给量 4.49 4.32 4.49 4.49 0.17 0.17 凝结水全年平均补给量 0.09 0.09 0.09 0.09 0 0 农灌回归量 0.27 0.27 0.27 0.27 0 0 地表积水入渗 0 0.16 0 0 −0.16 −0.16 激发河库水入渗补给量 0 0 0.0988 0 0.0988 0 合计 4.85 4.84 4.95 4.85 0.11 0.01 排泄项 地下水蒸发量 0.67 0.51 0.41 0.49 −0.1 −0.02 地下水溢出量 3.83 1.37 1.17 1.33 −0.20 −0.04 地下水开采量(农业) 0.36 0.36 0.36 0.36 0 0 矿坑涌水量(9#煤矿) 0 0.843 1.5391 0.9577 0.6961 0.1147 矿坑涌水量(头道河则其它煤矿) 0 3.07 3.07 3.07 0 0 地下水径流流出量 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.02 0 0 合计 4.90 6.17 6.57 6.23 0.40 0.05 均衡差 −0.05 −1.33 −1.62 −1.38 表 3 预测期末煤矿综采与充填开采预测结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of fully mechanized mining and filling mining at the end of the prediction period
项目 煤矿涌水量
增加量/(m3·d−1)溢出量减少量
/(m3·d−1)矿区及附近地下
水水位下降/m区域地下水
水位下降/m综采
(方案1)6961 2000 0.84~17.92 0.21~0.62 充填开采
(方案2)1147 400 0.05~0.44 0.01~0.06 -
[1] 康宁,武强,曾一凡,等. 毛乌素沙漠南缘煤矿开采涌水及其对浅层地下水影响的预测分析[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),2018,48(6):867 − 874. [KANG Ning,WU Qiang,ZENG Yifan,et al. Prediction of water yield from coal mining and its influence on shallow groundwater on the southern edge of Mu Us Desert[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),2018,48(6):867 − 874. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 苏贺. 榆神矿区煤矿开采矿井涌水量预测及其环境影响分析: 以小保当1、2号井田为例[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2014
SU He. Forecasting research of mine inflow of coal mining of Yushen coal zone and its environment impact analysis[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 彭捷,李成,向茂西,等. 榆神府区采动对潜水含水层的影响及其环境效应[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(2):156 − 162. [PENG Jie,LI Cheng,XIANG Maoxi,et al. Influence of coal mining on phreatic aquifer and its environmental effects in Yulin-Shenmu-Fugu Area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2018,46(2):156 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 虎维岳,闫丽. 对矿井涌水量预测问题的分析与思考[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(1):13 − 18. [HU Weiyue,YAN Li. Analysis and consideration on prediction problems of mine water inflow volume[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2016,44(1):13 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 杜敏铭,邓英尔,许模. 矿井涌水量预测方法综述[J]. 四川地质学报,2009,29(1):70 − 73. [DU Minming,DENG Yinger,XU Mo. Review of methodology for prediction of water yield of mine[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan,2009,29(1):70 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 华解明. 矿井涌水量计算的非稳定流解析法[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2010,22(10):38 − 40. [HUA Jieming. Unsteady flow analytic method in mine inflow computation[J]. Coal Geology of China,2010,22(10):38 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 高召宁,孟祥瑞,王向前. 矿井涌水量时间序列的长程相关性分析及分维数估算[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(3):31 − 35. [GAO Zhaoning,MENG Xiangrui,WANG Xiangqian. Analysis of long-range correlation and fractal dimension estimation of time series of mining water inflow[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(3):31 − 35. (in Chinese)
[8] 马秀媛,李逸凡,张立,等. 数值方法在矿井涌水量预测中的应用[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版),2011,41(5):86 − 91. [MA Xiuyuan,LI Yifan,ZHANG Li,et al. Numerical methods in predicting mine discharge[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Edition),2011,41(5):86 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 凌成鹏,孙亚军,杨兰和,等. 基于BP神经网络的孔隙充水矿井涌水量预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2007,34(5):55 − 58. [LING Chengpeng,SUN Yajun,YANG Lanhe,et al. Prediction of inrush water of mine with pore water yield based on BP artificial neural network[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2007,34(5):55 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 陈酩知,刘树才,杨国勇. 矿井涌水量预测方法的发展[J]. 工程地球物理学报,2009,6(1):68 − 72. [CHEN Mingzhi,LIU Shucai,YANG Guoyong. The development of mining water inflow predict method[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics,2009,6(1):68 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李超峰,虎维岳. 回采工作面顶板复合含水层涌水量时空组成及过程预测方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(3):1 − 13. [LI Chaofeng,HU Weiyue. Prediction method of mine water inflow regime from a layered extra-thick aquifer[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(3):1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 黄欢. 矿井涌水量预测方法及发展趋势[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44(增刊1): 127 − 130
HUANG Huan. Prediction method of mine inflow and its development[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(Sup 1): 127 − 130. (in Chinese)
[13] 侯恩科, 席慧琴, 文强, 等. 基于GMS的隐伏火烧区下煤层开采工作面涌水量预测[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(5): 2482 − 2492.
HOU Enke, XI Huiqin, WEN Qiang, et al. Prediction of water inflow volume in coal mining workface below the concealed fire area based on GMS[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(5): 2482 − 2492. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 刘基,王强民,杨建. 基于Visual Modflow的矿井涌水量模拟和动态预测研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2018,49(3):190 − 193. [LIU Ji,WANG Qiangmin,YANG Jian. Mine inflow simulation and dynamic prediction based on Visual Modflow[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2018,49(3):190 − 193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 宫厚健,刘守强,李哲,等. 基于Visual Modflow的矿井涌水量数值模拟预测研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2018,37(8):155 − 157. [GONG Houjian,LIU Shouqiang,LI Zhe,et al. Prediction of numerical simulation for mine water inflow based on visual modflow[J]. Coal Technology,2018,37(8):155 − 157. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 胡炳南. 我国煤矿充填开采技术及其发展趋势[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2012,40(11):1 − 5. [HU Bingnan. Backfill mining technology and development tendency in China coal mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2012,40(11):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李叔磊,冯涛,李石林. 条带膏体充填开采地表沉陷研究[J]. 采矿技术,2012,12(6):9 − 11. [LI Shulei,FENG Tao,LI Shilin. Study on surface subsidence of strip paste filling mining[J]. Mining Technology,2012,12(6):9 − 11. (in Chinese)
[18] 缪协兴,巨峰,黄艳利,等. 充填采煤理论与技术的新进展及展望[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2015,44(3):391 − 399. [MIAO Xiexing,JU Feng,HUANG Yanli,et al. New development and prospect of backfilling mining theory and technology[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2015,44(3):391 − 399. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 屈稚林. 麻黄梁煤矿CT301工作面窄条带膏体充填开采技术研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019.
QU Zhilin. Research on narrow strip paste filling mining technology at CT301 working face of Mahuangliang coal mine[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 范立民. 陕北地区采煤造成的地下水渗漏及其防治对策分析[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2007(5):62 − 64. [FAN Limin. Analysis of groundwater seepage caused by coal mining in northern Shaanxi and its prevention and control measures[J]. Mining Safety and Environmental Protection,2007(5):62 − 64. (in Chinese)
[21] 范立民,王国柱. 萨拉乌苏组地下水及采煤影响与保护[J]. 采矿技术,2006(3):422 − 425. [FAN Limin,WANG guozhu. Groundwater and coal mining impact and protection in the Salausu Formation[J]. Mining Technology,2006(3):422 − 425. (in Chinese)
[22] 张茂省,卢娜,陈劲松. 陕北能源化工基地地下水开发的植被生态效应及对策[J]. 地质通报,2008,27(8):1299 − 1312. [ZHANG Maosheng,LU Na,CHEN Jinsong. Ecological effects of vegetations during groundwater exploitation in the Northern Shaanxi Energy & Chemical Industry Base,China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2008,27(8):1299 − 1312. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: