An experimental study of spatial-temporal evolution of water-soil response and stability of a rainfall-induced accumulation landslide
-
摘要:
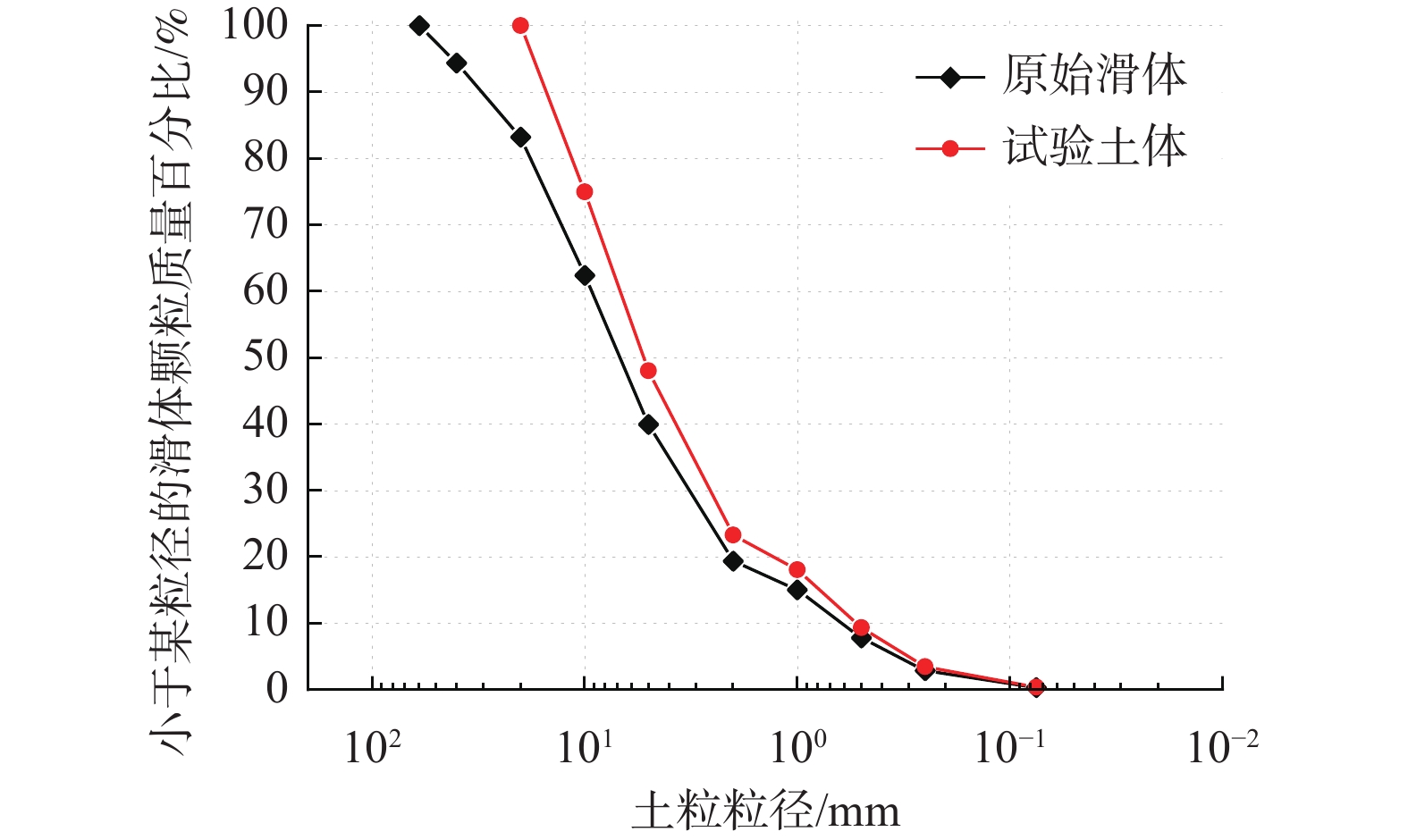
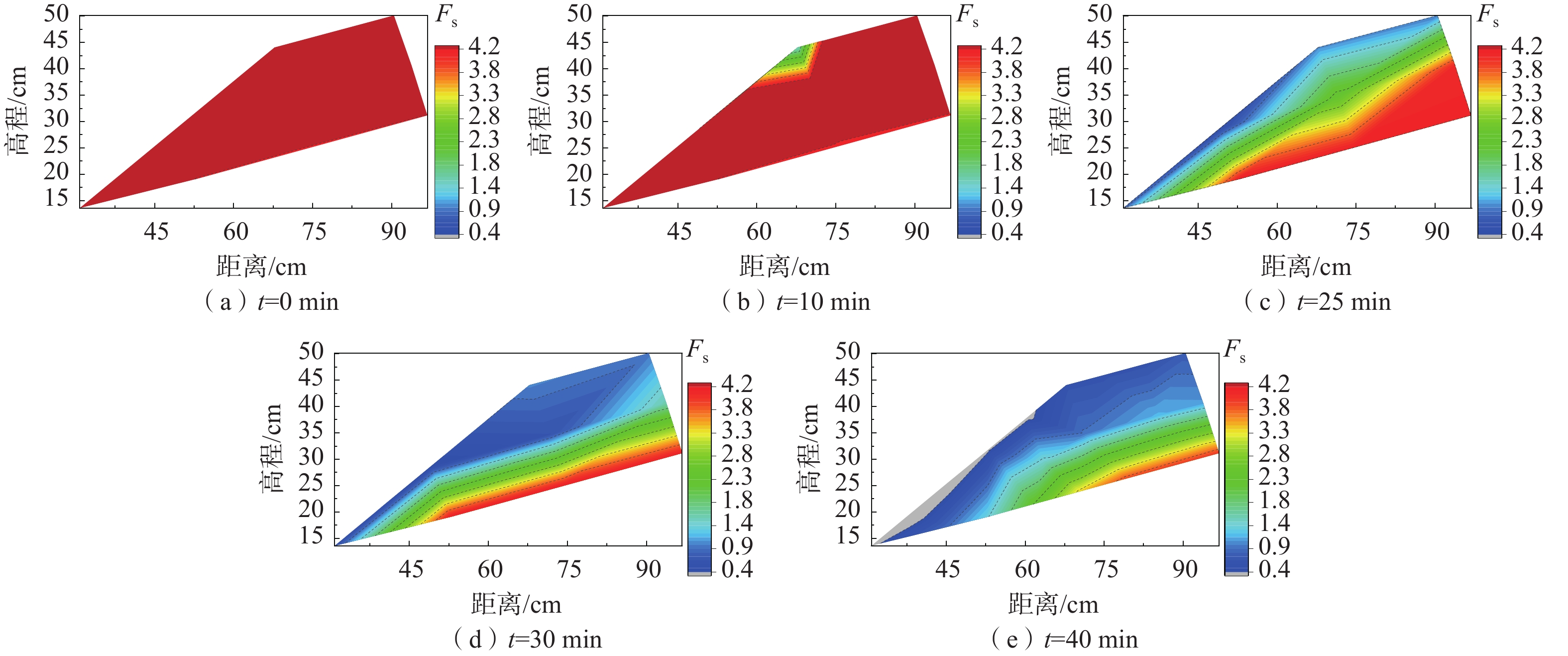
降雨在松散堆积土中入渗引起内部水土力学的变化是影响稳定性的关键。目前研究多侧重考虑颗粒粒径、含量等因素对斜坡破坏的影响,但是针对斜坡体内部水土响应及稳定性时空演化方面的研究存在不足。基于野外滑坡案例,通过室内降雨滑坡模型试验、土力学试验和理论分析手段,研究了降雨触发松散堆积体斜坡变形破坏过程及模式,采用Van Genuchten模型(VG模型)重构了土体的土-水特征曲线,重点探究了斜坡内部水土力学变化以及稳定性时空演化规律。结果表明:(1)堆积体斜坡破坏经历了微裂隙发育-局部破坏-整体破坏3个阶段,呈现出“初期拉裂-坡面坍塌-塑性滑动”的破坏模式;(2)入渗过程斜坡体积含水率以及孔隙水压力急速增加,而土颗粒之间基质吸力下降甚至消散,促进了斜坡破坏发展;(3)土体力学强度随体积含水率升高呈指数下降,体积含水率为36.3%时,有效黏聚力和有效内摩擦角仅为0.27 kPa、3.39°;(4)基于极限平衡理论和斜坡土水特征监测数据,构建了斜坡稳定性时空演化图谱,与模型试验破坏特征有较好的一致性。研究结果对降雨作用下的堆积层斜坡监测预警与防灾减灾提供理论支撑。
Abstract:The change of soil and water mechanics caused by rainfall infiltration in loose soil is the key to affect stability. At present, most studies focus on the influence of particle size, content and other factors on slope failure. However, the research on the internal water-soil response and spatial-temporal evolution of slope stability is insufficient. Based on a field landslide case, this study explores the deformation and failure processes and mode of loose accumulation slope triggered by rainfall through the flume test, soil mechanics test, and theoretical analysis. The Van Genuchten model (VG model) is used to reconstruct the soil-water characteristic curve of the soil, and the mechanical change of soil and water in the slope and the temporal and spatial evolution of stability are mainly explored. The results show that: (1) The failure processes of the accumulation slope emerge in three stages, that is, the micro-fracture development stage, local failure stage and complete collapse stage, presenting the failure mode of “initial cracking-slope collapsing-plastic sliding”. (2) The volumetric water content and pore water pressure of slope increase rapidly during infiltration, while the matric suction between soil particles decreases or even dissipates, which promotes the development of slope failure. (3) The mechanical strength of soil decreases exponentially with the increasing volumetric water content. When the volumetric water content is 36.3%, the effective cohesion and effective internal friction angle are only 0.27 kPa and 3.39°. (4) Based on the limit equilibrium theory and the monitoring data of slope soil-water characteristics, the spatio-temporal evolution map of slope stability is constructed, which is in good agreement with the failure characteristics of the model test. The research results provide theoretical support for monitoring and early warning of accumulation slope under rainfall and disaster prevention and mitigation.
-
Key words:
- accumulation slope /
- rainfall infiltration /
- flume test /
- stability analysis /
- hydrological response
-

-
表 1 斜坡稳定性分析土体参数(t=10 min)
Table 1. Soil parameters for slope stability analysis (t=10 min)
参数 Z/cm c'/kPa φ'/(°) γd/(kN·m−3) β/(°) θr/% θs/% 数值 5.06 3.14 28.74 11.86 25 3 49 12.47 3.33 12.83 3.34 15.00 3.37 25.27 3.45 -
[1] HUANG Runqiu,FAN Xuanmei. The landslide story[J]. Nature Geoscience,2013,6(5):325 − 326. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1806
[2] ZHANG S,ZHANG L M,CHEN H X. Relationships among three repeated large-scale debris flows at Pubugou Ravine in the Wenchuan earthquake zone[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2014,51(9):951 − 965. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2013-0368
[3] CUOMO S,DI P A,MARTINELLI M. Modelling the spatio-temporal evolution of a rainfall-induced retrogressive landslide in an unsaturated slope[J]. Engineering Geology,2021,294:106371. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106371
[4] GHOSH S,BORA A,NATH S,et al. Analysing the spatio-temporal evolution of an active debris slide in Eastern Himalaya,India[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India,2014,84(3):292 − 302. doi: 10.1007/s12594-014-0132-0
[5] 白永健,葛华,冯文凯,等. 乌蒙山区红层软岩滑坡地质演化及灾变过程离心机模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(增刊 1):3025 − 3035. [BAI Yongjian,GE Hua,FENG Wenkai,et al. Centrifugal tests on geological evolution and sliding process for red-bed soft rock landslide in Wumeng Mountain area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(Sup 1):3025 − 3035. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 冯文凯,胡云鹏,谢吉尊,等. 顺层震裂斜坡降雨触发灾变机制及稳定性分析—以三溪村滑坡为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(11):2197 − 2207. [FENG Wenkai,HU Yunpeng,XIE Jizun,et al. Disaster mechanism and stability analysis of shattered bedding slopes triggered by rainfall: A case study of Sanxicun landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(11):2197 − 2207. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] WANG G,SASSA K. Factors affecting rainfall-induced flowslides in laboratory flume tests[J]. Géotechnique,2001,51(7):587 − 599.
[8] 左自波,张璐璐,王建华. 降雨触发不同级配堆积体滑坡模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015,37(7):1319 − 1327. [ZUO Zibo,ZHANG Lulu,WANG Jianhua. Model tests on rainfall-induced colluvium landslides:Effects of particle-size distribution[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,37(7):1319 − 1327. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 涂国祥,邓辉,黄润秋. 水位变动速度对某库区岸坡堆积体稳定性的影响[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),2011,43(4):63 − 70. [TU Guoxiang,DENG Hui,HUANG Runqiu. Influence on a bank slope accumulation’ stability of the rising or falling speed of a reservoir water level[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2011,43(4):63 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] ORENSE R P,SHIMOMA S,MAEDA K,et al. Instrumented model slope failure due to water seepage[J]. Journal of Natural Disaster Science,2004,26(1):15 − 26. doi: 10.2328/jnds.26.15
[11] SASAHARA K. Prediction of the shear deformation of a sandy model slope generated by rainfall based on the monitoring of the shear strain and the pore pressure in the slope[J]. Engineering Geology,2017,224:75 − 86. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.05.003
[12] SASAHARA K,SAKAI N. Development of shear deformation due to the increase of pore pressure in a sandy model slope during rainfall[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,170(4):43 − 51.
[13] 李爱国,岳中琦,谭国焕,等. 土体含水率和吸力量测及其对边坡稳定性的影响[J]. 岩土工程学报,2003,25(3):278 − 282. [LI Aiguo,YUE Zhongqi,TAN Guohuan,et al. Soil moisture and suction measurement and its effect on slope stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2003,25(3):278 − 282. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] BORDONI M,MEISINA C,VALENTINO R,et al. Hydrological factors affecting rainfall-induced shallow landslides:From the field monitoring to a simplified slope stability analysis[J]. Engineering Geology,2015,193:19 − 37. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.04.006
[15] HU W,XU Q,VAN ASCH T W J,et al. Flume tests to study the initiation of huge debris flows after the Wenchuan earthquake in S-W China[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,182:121 − 129. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.04.006
[16] HU Wei,SCARINGI G,XU Qiang,et al. Internal erosion controls failure and runout of loose granular deposits:evidence from flume tests and implications for postseismic slope healing[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2018,45(11):5518 − 5527. doi: 10.1029/2018GL078030
[17] 张玉成,杨光华,张有祥,等. 古滑坡滑带土的力学特性与库水位变化对其稳定性影响及加固措施[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(增刊 2):43 − 52. [ZHANG Yucheng,YANG Guanghua,ZHANG Youxiang,et al. Influence of mechanical properties of sliding zone and water level changes on ancient landslide stability and its reinforcement measures[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2016,37(Sup 2):43 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 唐军峰,唐雪梅,周基,等. 滑坡堆积体变形失稳机制:以贵州剑河县东岭信滑坡为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(2):503 − 516. [TANG Junfeng, TANG Xuemei, ZHOU Ji, et al. Deformation and instability mechanism of landslide accumulation:A case study of donglingxin landslide accumulation in Jianhe County, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(2):503 − 516. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 杨宗佶,蔡焕,雷小芹,等. 非饱和地震滑坡堆积体降雨破坏水-力耦合行为试验[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(5):1869 − 1880. [YANG Zongji,CAI Huan,LEI Xiaoqin,et al. Experiment on hydro-mechanical behavior of unsaturated gravelly soil slope[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(5):1869 − 1880. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 蒋中明,曾铃,付宏渊,等. 极端久雨条件下软岩边坡动态稳定性分析[J]. 中国公路学报,2014,27(2):27 − 34. [JIANG Zhongming,ZENG Ling,FU Hongyuan,et al. Dynamic stability analysis of soft rock slope due to extremely prolonged rainfall[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2014,27(2):27 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 朱元甲,贺拿,钟卫,等. 间歇型降雨对堆积层斜坡变形破坏的物理模拟研究[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(12):4035 − 4044. [ZHU Yuanjia,HE Na,ZHONG Wei,et al. Physical simulation study of deformation and failure accumulation layer slope caused by intermittent rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(12):4035 − 4044. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 付宏渊,曾铃,王桂尧,等. 降雨入渗条件下软岩边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(8):2359 − 2365. [FU Hongyuan,ZENG Ling,WANG Guiyao,et al. Stability analysis of soft rock slope under rainfall infiltration[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(8):2359 − 2365. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张晨阳,张泰丽,张明,等. 东南沿海地区玄武岩残积土雨水运移特征及滑坡失稳数值模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):42 − 50. [ZHANG Chenyang,ZHANG Taili,ZHANG Ming,et al. Rainfall infiltration characteristics and numerical simulation of slope instability in the basalt residual soil in the coastal area of Southeast China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):42 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] BROOKS R H,COREY A T. Hydraulic properties of porous media[J]. Hydrol Pap,1964:1 − 27.
[25] VAN GENUCHTEN M T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1980,44(5):892 − 898. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
[26] FREDLUND D G,XING Anqing. Erratum: Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1994,31(6):1026 − 1026. doi: 10.1139/t94-120
[27] LU Ning, GODT J W. 斜坡水文与稳定 [M]. 简文星, 王菁莪, 侯龙, 译. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2014: 297-298.
LU Ning, GODT J W. Hillslope hydrology and stability [M]. JAN Wenxing, WANG Jing’e, HOU Long, tans. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2014: 297-298.
[28] 陈卫金,程东会,陶伟. van Genuchten模型参数的物理意义[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(6):147 − 153. [CHEN Weijin,CHENG Donghui,TAO Wei. Physical significance of the parameters in the van Genuchten model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(6):147 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 彭建平,邵爱军. 基于Matlab方法确定VG模型参数[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2006,33(6):25 − 28. [PENG Jianping,SHAO Aijun. Determination of the parameters of VG model based on Matlab[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2006,33(6):25 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: