Mechanisms and stability analysis of the Jinjiling landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area based on Midas-GTS
-
摘要:
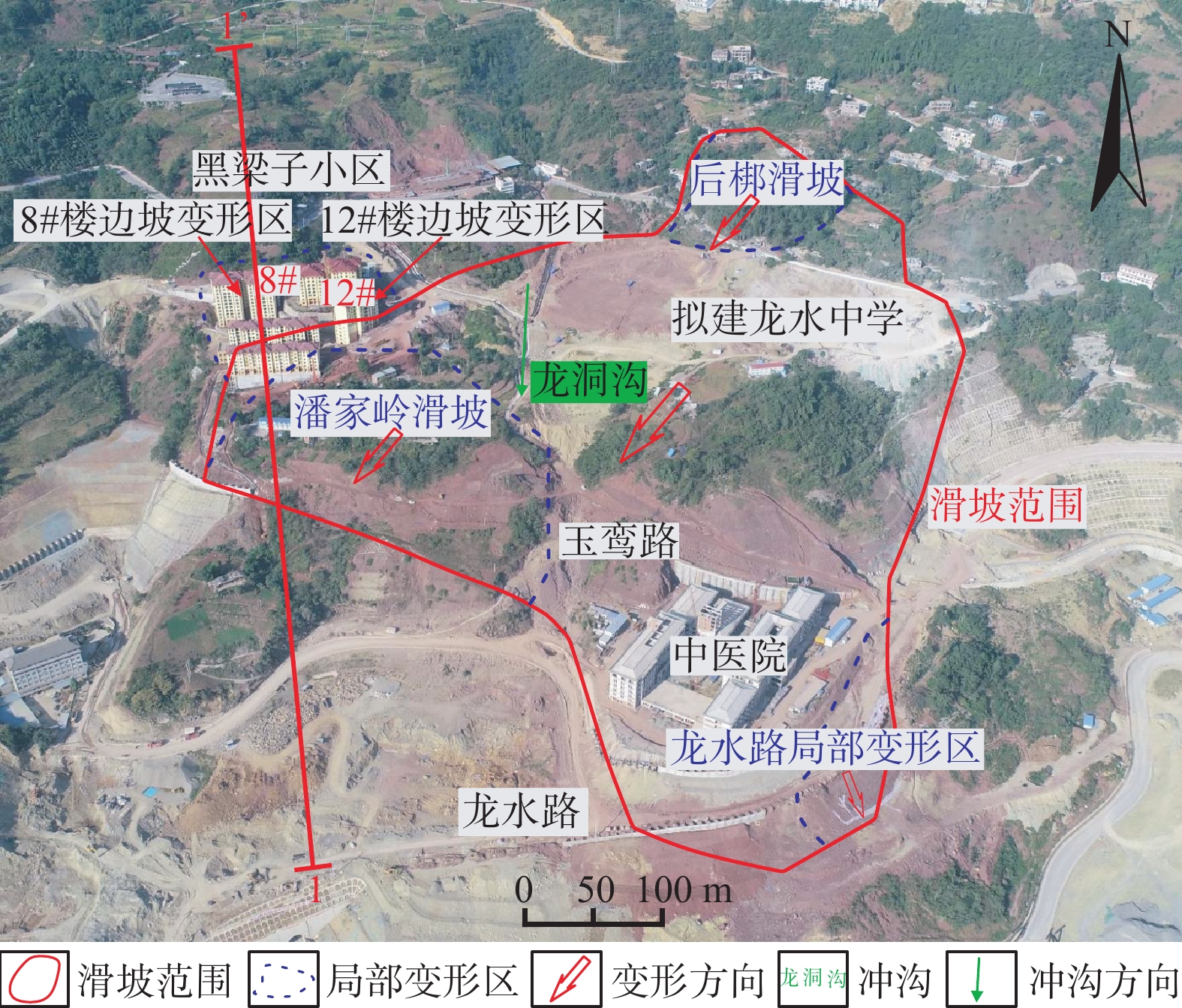
金鸡岭滑坡在暴雨后发生明显变形,通过现场勘察、钻探、物探、深部位移监测以及水平位移监测得出初步结论。为进一步查明该滑坡成因机制,通过解译现有勘察监测资料,结合Midas-GTS软件分析不同工况下滑坡的渗流场、位移场、稳定性计算,综合评价其成因机制。结果如下:(1)物探解译得出金鸡岭滑坡为岩土混合、含水滑坡,滑动面位于T2b1泥灰岩和T2b2泥岩分界线;(2)深部位移监测揭示该滑坡为浅表层土体在发生滑移,滑动面与物探解译得出的滑动面位置一致;(3)水平位移监测表明浅表分布的后梆滑坡和潘家岭滑坡变形速率较快,变形强烈;(4)数值模拟结果显示金鸡岭滑坡在现状工况下处于基本稳定状态;在排干地下水工况下处于基本稳定状态;在暴雨工况下处于欠稳定状态,可能产生整体滑移,其上的潘家岭滑坡及后梆滑坡产生土体次级滑移。(5)金鸡岭滑坡的地形地貌、地质构造、地层岩性、为滑坡的形成和发展提供了物源和场地条件,暴雨和人类工程活动作为诱发因素,进一步加剧滑坡变形。该研究成果将为三峡库区类似滑坡的成因机制与稳定性分析提供理论依据,对后期防治措施具有重要指导意义。
Abstract:The Jinjiling landslide was obviously deformed after the rainstorm, and preliminary conclusions were drawn through on-site investigation, drilling, geophysical prospecting, deep displacement monitoring and horizontal displacement monitoring. On this basis, in order to further find out the genesis mechanism of the landslide, this paper interprets the existing survey and monitoring data, combines the Midas-GTS software to analyze the seepage field, displacement field, and stability calculation of the landslide under different working conditions, and comprehensively evaluates its genesis mechanism. The results indicate that (1) geophysical interpretation shows that the Jinjiling landslide is a rock-soil mixed, water-bearing landslide, and the sliding surface is located at the boundary between T2b1 marlstone and T2b2 mudstone. (2) Deep displacement monitoring data reveals that the landslide occurs in a superficial soil mass, and the position of the slip surface is consistent with the location of the slip surface obtained by geophysical exploration. (3) The horizontal displacement monitoring shows that the superficially distributed Houbang landslide and Panjialing landslide have fast deformation rates and stronger deformation. (4) The numerical simulation results show that the Jinjiling landslide is currently in a basically stable state; it is in a basically stable state when the groundwater is drained; it is in a less stable state under heavy rain conditions, which may cause overall slippage, and the Panjialing and Houbang landslides produce secondary soil slippage. (5) The topography, geological structure, stratigraphic lithology of the Jinjiling landslide provide provenance and site conditions for the formation and development of the landslide. Torrential rain and human engineering activities are the inducing factors, which further aggravate the deformation of the landslide. The research results will provide a theoretical basis for the analysis of the genetic mechanism and stability of similar landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, and have important guiding significance for the later control measures.
-
Key words:
- Jinjiling landslide /
- Midas-GTS /
- numerical simulation /
- causal mechanisms /
- stability analysis
-

-
表 1 岩土体的物理参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of the rock and soil
岩土介质/参数 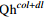 崩坡积物
崩坡积物T2b2泥岩 T2b1泥灰岩 天然重度/(kN·m−3) 23.3 25.5 24.9 饱和重度/(kN·m−3) 23.5 25.7 25.1 黏聚力/kPa 16.0 30.2 16.6 内摩擦角/(°) 15 36 38 弹性模量/MPa 26.76 5.46×103 8.18×104 泊松比 0.20 0.35 0.23 渗透系数/(cm·s−1) 3.47×10−4 2.31×10−4 5.0 饱和含水率/% 31 32 18 残余含水率/% 3.1 3.0 1.8 -
[1] 殷跃平. 三峡库区边坡结构及失稳模式研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2005,13(2):145 − 154. [YIN Yueping. Human-cutting slope structure and failure pattern at the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2005,13(2):145 − 154. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张富灵,邓茂林,周剑,等. 长江三峡库区谭家湾滑坡基本变形特征及机理分析[J]. 长江科学院院报,2021,38(1):78 − 83. [ZHANG Fuling,DENG Maolin,ZHOU Jian,et al. Basic deformation characteristics and mechanism of Tanjiawan landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021,38(1):78 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 张志兼,黄勋,蔡雨微,等. 三峡库区武隆段滑坡灾害驱动因子演变格局与人类活动的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):39 − 50. [ZHANG Zhijian,HUANG Xun,CAI Yuwei,et al. The evolution pattern and influence of human activities of landslide driving factors in Wulong section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):39 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 卫童瑶,殷跃平,高杨,等. 三峡库区巫山县塔坪H1滑坡变形机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):73 − 81. [WEI Tongyao,YIN Yueping,GAO Yang,et al. Deformation mechanism of the Taping H1 landslide in Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):73 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 薛阳,吴益平,苗发盛,等. 库水升降条件下考虑饱和渗透系数空间变异性的白水河滑坡渗流变形分析[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(5):1709 − 1720. [XUE Yang,WU Yiping,MIAO Fasheng,et al. Seepage and deformation analysis of Baishuihe landslide considering spatial variability of saturated hydraulic conductivity under reservoir water level fluctuation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(5):1709 − 1720. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 朱赛楠,殷跃平,王猛,等. 金沙江结合带高位远程滑坡失稳机理及减灾对策研究—以金沙江色拉滑坡为例[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(4):688 − 697. [ZHU Sainan,YIN Yueping,WANG Meng,et al. Instability mechanism and disaster mitigation measures of long-distance landslide at high location in Jinsha River junction zone:Case study of Sela landslide in Jinsha River,Xizang
J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(4):688 − 697. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 刘秋强,杜岩,郭富赟,等. 青藏高原东端甘肃舟曲牙豁口滑坡复活机理研究[J]. 灾害学,2021,36(2):113 − 117. [LIU Qiuqiang,DU Yan,GUO Fuyun,et al. Study on the reactivation mechanism of Yahuokou landslide at the eastern end of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau,Zhouqu County,Gansu Province,China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021,36(2):113 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 吴瑞安,马海善,张俊才,等. 金沙江上游沃达滑坡发育特征与堵江危险性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):120 − 128. [WU Ruian,MA Haishan,ZHANG Juncai,et al. Developmental characteristics and damming river risk of the Woda landslide in the upper reaches of the Jinshajiang River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):120 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 许强,汤明高,徐开祥,等. 滑坡时空演化规律及预警预报研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,6:1104 − 1112. [XU Qiang,TANG Minggao,XU Kaixiang,et al. Research on space-time evolution laws and early warning-prediction of landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,6:1104 − 1112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] ZHANG Chengcheng,ZHU Honghu,LIU Suping,et al. A kinematic method for calculating shear displacements of landslides using distributed fiber optic strain measurements[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,234:83 − 96. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.01.002
[11] 陶志刚, 罗森林, 朱淳, 等. 滑坡动态力学监测及破坏过程案例分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2022, 30(1): 177 − 186
TAO Zhigang, LUO Senlin, ZHU Chun, et al. Dynamic mechanical monitoring of landslide and case analysis of failure process[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(1): 177 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张海艳, 简文星, 杨涛, 等. 降雨作用下三峡库区秭归谭家湾滑坡监测预警研究[J]. 安全与环境程, 2022, 29(4): 129 − 138
ZHANG Haiyan, JIAN Wenxing, YANG Tao, et al. Monitoring and early warning of Tanjiawan landslide, Zigui, Three Gorges Reservoir region under rainfall effect[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(4): 129 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 周越,曾昭发,唐海燕,等. 公路勘察中滑坡体的地球物理特征与分析:以张榆线公路勘察为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(2):638 − 644. [ZHOU Yue, ZENG Zhaofa, TANG Haiyan, et al. Geophysical characteristics of landslide body in highway reconnaissance:A case study in highway prospecting of Zhangyu line[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(2):638 − 644. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 许超,吕义清,周泽文,等. 采动滑坡变形机理分析[J]. 煤炭技术,2017,36(11):164 − 166. [XU Chao,LYU Yiqing,ZHOU Zewen,et al. Mining landslide deformation mechanism analysis[J]. Coal Technology,2017,36(11):164 − 166. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 黄刚,肖洋,罗廷. 四川通江县袁家山滑坡特征与稳定性初步分析[J]. 人民长江,2020,51(增刊 2):75 − 78. [HUANG Gang,XIAO Yang,LUO Ting. Preliminary analysis on characteristics and stability of Yuanjiashan landslide in Tongjiang County,Sichuan[J]. Yangtze River,2020,51(Sup 2):75 − 78. (in Chinese)
[16] WANG Yetao,ZHU Guanyu,DING Linbo,et al. Numerical simulation of slope failure treatment of a tunnel portal section based on MIDAS GTS[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2021,1972(1):012026.
[17] 吕文斌,耿海深,魏赛拉加. 基于极限平衡法和Midas/GTS的张家湾滑坡稳定性[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(11):4369 − 4378. [LÜ Wenbin,GENG Haishen,WEI Sailajia. Stability of Zhangjiawan landslide based on limit equilibrium method and Midas/GTS[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(11):4369 − 4378. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 谭银龙,许万忠. 降雨入渗对裂隙岩质边坡稳定性影响分析[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2022,33(2):78 − 85. [TAN Yinlong,XU Wanzhong. Analysis of the influence of rainfall infiltration on the stability of fractured rock slopes[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2022,33(2):78 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 蒋先念, 浦磊, 范良刚, 等. 重庆市巫山县金鸡岭滑坡应急抢险勘查报告[R]. 重庆: 重庆市二零八勘察设计院, 2018
JIANG Xiannian, PU Lei, FAN Lianggang, et al. Investigation report on emergency rescue of Jinjiling landslide in Wushan County, Chongqing City[R]. Chongqing: Chongqing 208 Survey and Design Institute, 2018.(in Chinese)
[20] 赵尚毅,郑颖人,时卫民,等. 用有限元强度折减法求边坡稳定安全系数[J]. 岩土工程学报,2002,24(3):343 − 346. [ZHAO Shangyi,ZHENG Yingren,SHI Weimin,et al. Analysis on safety factor of slope by strength reduction FEM[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2002,24(3):343 − 346. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] EGELI I,PULAT H F. Mechanism and modelling of shallow soil slope stability during high intensity and short duration rainfall[J]. Scientia Iranica,2011,18(6):1179 − 1187. doi: 10.1016/j.scient.2011.09.010
[22] CHAI Bo,YIN Kunlong,DU Juan,et al. Correlation between incompetent beds and slope deformation at Badong Town in the Three Gorges Reservoir,China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2013,69(1):209 − 223. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1948-9
[23] DENG Qinglu,FU Min,REN Xingwei,et al. Precedent long-term gravitational deformation of large scale landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2017,221:170 − 183. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.02.017
-



 下载:
下载:





