Visualization experimental investigation into the dissolution processes in rough fracture under gravity conditions
-
摘要:
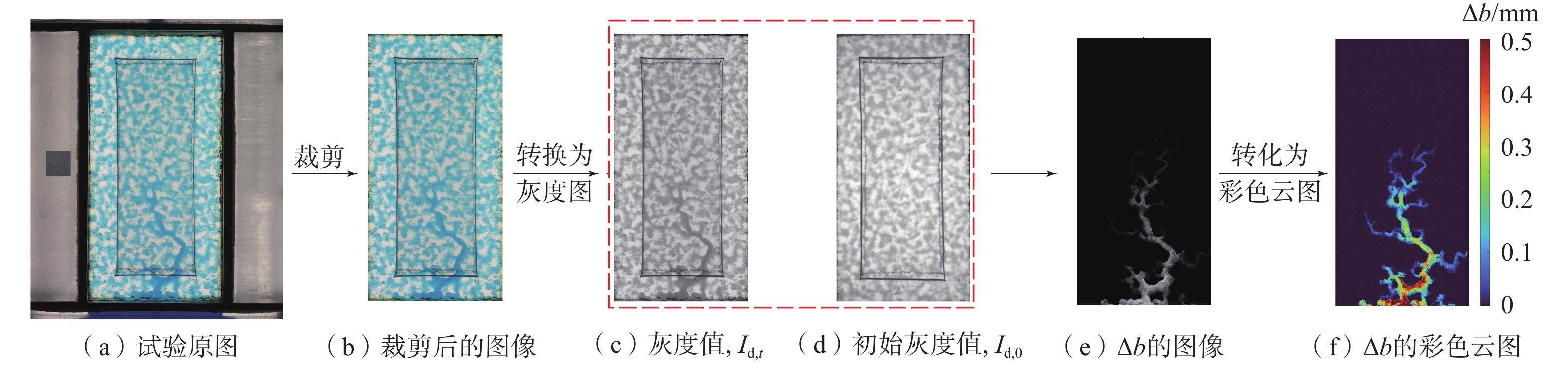
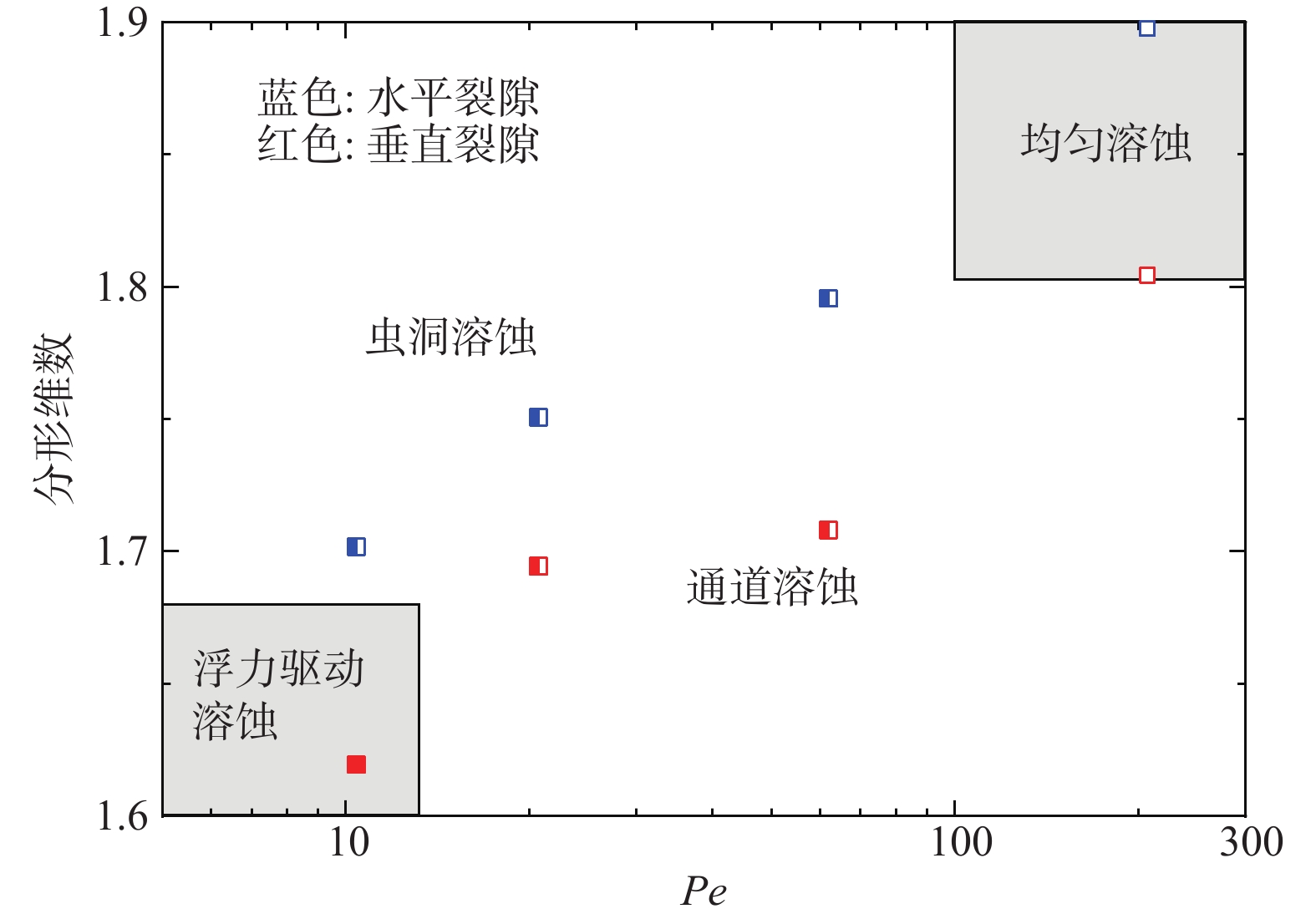
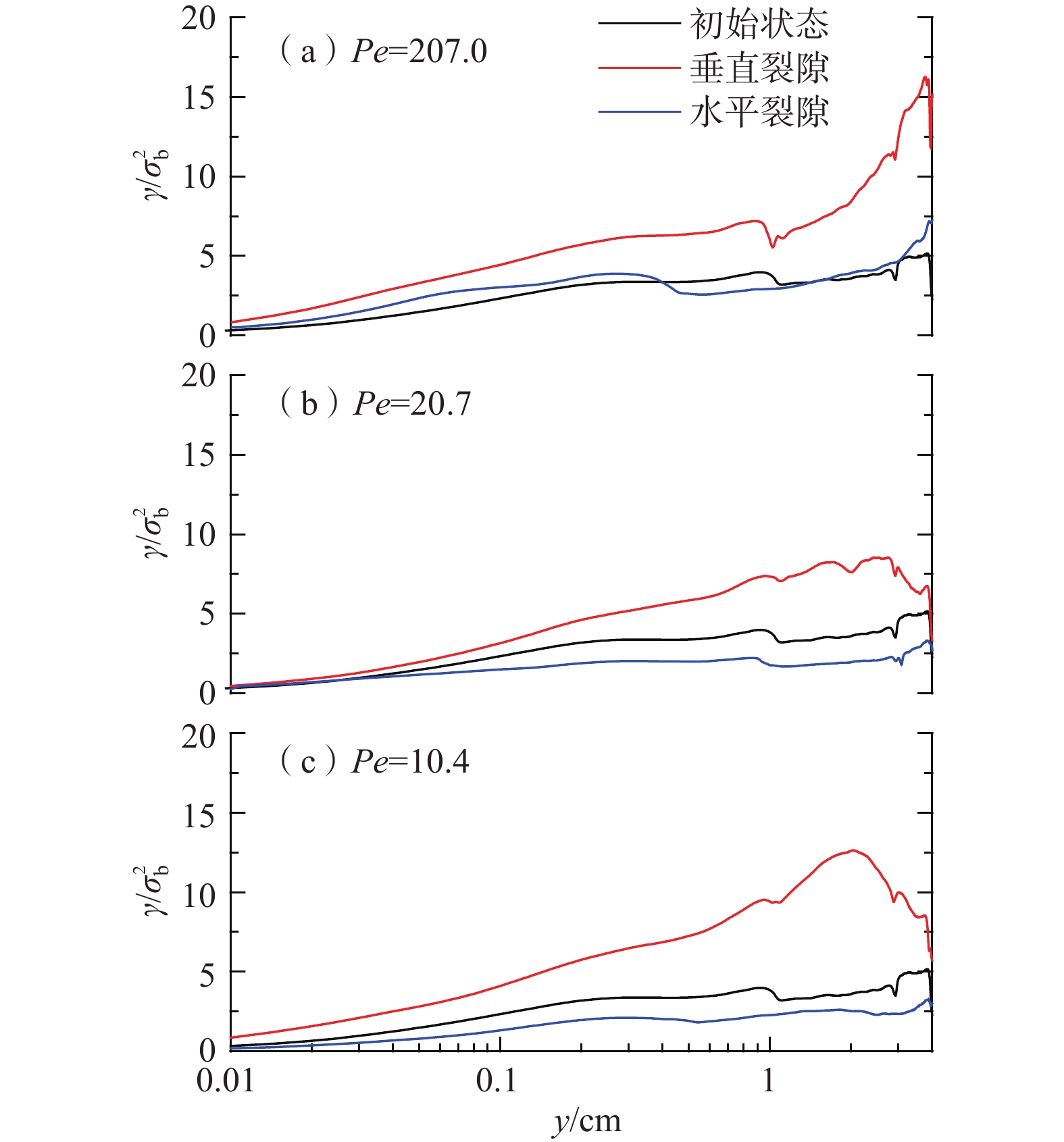
岩体裂隙的溶蚀现象广泛存在于自然过程和工程实践,重力对溶蚀过程具有重要作用。可视化观测技术是研究粗糙裂隙溶蚀机理的关键手段,然而传统的可视化技术存在裂隙粗糙壁面难以复制、溶蚀过程难以实时观测等问题。通过自主研发的粗糙裂隙溶蚀过程可视化试验平台,开展了垂直裂隙和水平裂隙在4种流量条件(0.05,0.1,0.3,1 mL/min)下的溶蚀可视化实验,研究了重力效应对溶蚀模式和溶蚀形态的影响,采用分形维数量化了不同溶蚀模式的形态学特征,最终确定了不同佩克莱数(Pe)条件下的突破时注液量。试验结果表明:在Pe≤62.1范围内,重力效应对溶蚀模式具有重要影响,垂直裂隙中的溶蚀发育为浮力主导模式和通道模式,重力效应将诱发单一、集中的溶蚀通道;而水平裂隙则统一发育为开度演变均匀、宽度较大的通道,即经典的虫洞溶蚀模式;在Pe数较大时(Pe=207.0)时,垂直裂隙和水平裂隙中的溶蚀均发育为均匀溶蚀。试验结果还证实了垂直裂隙更易发育为贯通的溶蚀通道,从而加速溶蚀突破;Pe=20.7时为最优注入条件,垂直裂隙的突破时注液量最小。在此条件下,垂直裂隙的突破时注液量仅为水平裂隙的1/4。建议重点关注重力效应对溶蚀过程的影响,研究结果对CO2地质封存等工程实践具有重要意义。
Abstract:Dissolution of rock fractures is common in natural processes and engineering practices, in which gravity plays an important role. Visual observation technology is a key means to study the mechanism of dissolution in rough fractures. However, the traditional visualization technologies have some problems, such as difficult to reproduce the rough wall of fractures and difficult to observe the dissolution process in real time. In this work, a flow-visualization system for dissolution processes in rough fractures is developed, on which flow-through experiments are conducted on four flow rates (0.05, 0.1, 0.3, and 1 mL/min) for vertical and horizontal fractures, and the gravity effect is evaluated on dissolution patterns and dissolution morphologies, which are characterized by fractal dimension and other morphological parameters. The pore volumes at breakthrough are calculated for each Peclet number (Pe). The experimental results show that the gravity effect significantly influences the dissolution patterns for Pe≤62.1. The dissolution morphologies exhibit buoyancy-dominated patterns and channeling patterns for vertical fractures, and the gravity effect will induce a single and concentrated channel. For horizontal fractures, the dissolution forms dissolution channels with relatively uniform aperture evolution and large width, which are classical wormhole patterns. When the Peclet number is large (Pe=207.0), dissolution in both the vertical and horizontal fractures develops into uniform dissolution. The experimental results also confirm that the dissolution in vertical fractures is more likely to develop channels through the inlet to the outlet to accelerate the breakthrough; Pe=20.7 is the optimal injection condition, which means that the amount of injected liquid is the minimum when breakthrough takes place in vertical fractures. Under this condition, the pore volumes at breakthrough in vertical fractures are only 1/4 of the horizontal fractures. The results in this paper are of great significance to engineering practice such as CO2 geological storage, indicating that the effect of gravity on the dissolution process should be greatly taken into account.
-

-
表 1 试验条件
Table 1. Experimental conditions
裂隙倾角/(°) 试验组 Q/(mL·min−1) Pe 90 V1 1 207.0 V2 0.3 62.1 V3 0.1 20.7 V4 0.05 10.4 0 H1 1 207.0 H2 0.3 62.1 H3 0.1 20.7 H4 0.05 10.4 -
[1] 陈崇希. 岩溶管道-裂隙-孔隙三重空隙介质地下水流模型及模拟方法研究[J]. 地球科学,1995,20(4):361 − 366. [CHEN Chongxi. Groundwater flow model and simulation method in triple media of karstic tube-fissure-pore[J]. Earth Science,1995,20(4):361 − 366. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 陈旺光,曾成,龚效宇,等. 贵州深切峡谷区典型岩溶地下河水文水化学特征—以贵州三塘地下河为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(4):19 − 29. [CHEN Wangguang,ZENG Cheng,GONG Xiaoyu,et al. Hydrological and hydrochemical regime of a typical subterraneous river in a deep canyon Karst area:A case study in the Santang underground river, Guizhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(4):19 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] ZHANG Cheng,WORAKUL M,WANG Jinliang,et al. Hydrogeochemical features of Karst in the western Thailand[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2014(2):18 − 26.
[4] 陈友智, 姜伏伟, 于宁, 等. 湘渝黔红色岩溶地貌形成的地质条件及成因分析[J/OL]. 地球化学. (2021-11-15)[2022-09-24].https://doi.org/10.19700/j.0379-1726.2021.04.009.
CHEN Youzhi, JIANG Fuwei, YU Ning, et al. Analysis on the geological conditions and genesis of red karst landform in Hu’nan-Chongqing-Guizhou[J]. Geochimica. (2021-11-15)[2022-09-24]. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] LI Sanbai,KANG Zhijiang,FENG Xiating,et al. Three-dimensional hydrochemical model for dissolutional growth of fractures in Karst aquifers[J]. Water Resources Research,2020,56(3):e2019WR025631.
[6] 钟祖良,高国富,刘新荣,等. 地下采动下含深大裂隙岩溶山体变形响应特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):97 − 106. [ZHONG Zuliang,GAO Guofu,LIU Xinrong,et al. Deformation response characteristics of Karst Mountains with deep and large fissures under the condition of underground mining[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):97 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003051
[7] 李向全,马剑飞,张春潮,等. 川藏铁路格聂山和察雅段构造岩溶发育规律及岩溶地下水循环模式研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):34 − 45. [LI Xiangquan,MA Jianfei,ZHANG Chunchao,et al. Evolution regularity of the plateau tectonic karst and the relevant karst groundwater circulation mode in Mount Genie and Zaya sections along the Sichuan—Xizang railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):34 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202104005
[8] 张良喜,赵其华,胡相波,等. 某地区白云岩室内溶蚀试验及微观溶蚀机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(4):576 − 584. [ZHANG Liangxi,ZHAO Qihua,HU Xiangbo,et al. Laboratory dissolution test on dolomite and its micro-dissolution mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(4):576 − 584. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.04.014
[9] 张强. 金沙江观音岩电站红层钙质砂岩类岩溶发育特征及渗透稳定性研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2010
ZHANG Qiang. Semi-Karst development characteristics and engineering seepage stability of the calcareous sandstone red beds of Guanyinyan hydropower, Jinsha River[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘海燕,伍法权,祁生文,等. 三峡库区泥质灰岩溶蚀作用与边坡岩体破坏[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2006,34(4):37 − 41. [LIU Haiyan,WU Faquan,QI Shengwen,et al. The dissolution process and the rock mass breakage of marlite slope in Three Gorges Reservoir Region[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2006,34(4):37 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2006.04.011
[11] 马瑾. 地质封存条件下超临界二氧化碳运移规律研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2013
MA Jin. Researches on the migration of supercritical CO2 on geological storage conditions[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] ELKHOURY J E,AMELI P,DETWILER R L. Dissolution and deformation in fractured carbonates caused by flow of CO2-rich brine under reservoir conditions[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2013,16:S203 − S215. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.02.023
[13] CARROLL S A,IYER J,WALSH S D C. Influence of chemical,mechanical,and transport processes on wellbore leakage from geologic CO2 storage reservoirs[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research,2017,50(8):1829 − 1837. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00094
[14] ZHANG Liwei,WANG Yan,MIAO Xiuxiu,et al. Geochemistry in geologic CO2 utilization and storage:A brief review[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research,2019,3(3):304 − 313. doi: 10.26804/ager.2019.03.08
[15] FREDD C N,FOGLER H S. Optimum conditions for wormhole formation in carbonate porous media:Influence of transport and reaction[J]. SPE Journal,1999,4(3):196 − 205. doi: 10.2118/56995-PA
[16] HUANG Zhaoqin,XING Hongchuan,ZHOU Xu,et al. Numerical study of vug effects on acid-rock reactive flow in carbonate reservoirs[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research,2020,4(4):448 − 459. doi: 10.46690/ager.2020.04.09
[17] KIANI S,JAFARI S,APOURVARI S N,et al. Simulation study of wormhole formation and propagation during matrix acidizing of carbonate reservoirs using a novel in-situ generated hydrochloric acid[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research,2021,5(1):64 − 74. doi: 10.46690/ager.2021.01.07
[18] 武亚遵,林云,万军伟,等. 碳酸盐岩单裂隙渗流-溶蚀耦合模型及其参数敏感性分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2016,35(1):81 − 86. [WU Yazun,LIN Yun,WAN Junwei,et al. Coupled fluid flow and dissolution model and associated parameter sensitivity analysis in a single carbonate rock fracture[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2016,35(1):81 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11932/karst20160112
[19] SZYMCZAK P,LADD A J C. Wormhole formation in dissolving fractures[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,2009,114:B06203.
[20] SZYMCZAK P,LADD A J C. Reactive-infiltration instabilities in rocks. Fracture dissolution[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2012,702:239 − 264. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2012.174
[21] LADD A J C,SZYMCZAK P. Reactive flows in porous media:challenges in theoretical and numerical methods[J]. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,2021,12:543 − 571. doi: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-092920-102703
[22] DETWILER R L. Experimental observations of deformation caused by mineral dissolution in variable-aperture fractures[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2008, 113: B08202.
[23] MENKE H P,REYNOLDS C A,ANDREW M G,et al. 4D multi-scale imaging of reactive flow in carbonates:Assessing the impact of heterogeneity on dissolution regimes using streamlines at multiple length scales[J]. Chemical Geology,2018,481:27 − 37. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.01.016
[24] DENG Hang,MOLINS S,TREBOTICH D,et al. Pore-scale numerical investigation of the impacts of surface roughness:Upscaling of reaction rates in rough fractures[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2018,239:374 − 389. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.08.005
[25] DETWILER R L,GLASS R J,BOURCIER W L. Experimental observations of fracture dissolution:The role of Peclet number on evolving aperture variability[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2003,30(12):1648.
[26] XU Le,SZYMCZAK P,TOUSSAINT R,et al. Dissolution phase diagram in radial geometry[J]. Frontiers in Physics,2020,8:369. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2020.00369
[27] WANG Ting,HU Ran,YANG Zhibing,et al. Transitions of dissolution patterns in rough fractures[J]. Water Resources Research,2022,58:e2021WR030456.
[28] HU Ran,WANG Ting,YANG Zhibing,et al. Dissolution hotspots in fractures[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2021,48:e2021GL094118.
[29] BOUQUAIN J,MEHEUST Y,DAVY P. Horizontal pre-asymptotic solute transport in a plane fracture with significant density contrasts[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2011,120-121:184 − 197. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2010.08.002
[30] DIJK P E,BERKOWITZ B. Buoyancy-driven dissolution enhancement in rock fractures[J]. Geology,2000,28(11):1051 − 1054. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<1051:BDEIRF>2.0.CO;2
[31] DIJK P E,BERKOWITZ B,YECHIELI Y. Measurement and analysis of dissolution patterns in rock fractures[J]. Water Resources Research,2002,38(2):1013.
[32] CHAUDHURI A,RAJARAM H,VISWANATHAN H,et al. Buoyant convection resulting from dissolution and permeability growth in vertical limestone fractures[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2009,36(3):L03401.
[33] PHILIPPI J,BERHANU M,DERR J,et al. Solutal convection induced by dissolution[J]. Physical Review Fluids,2019,4(10):103801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevFluids.4.103801
[34] SLIM A C,BANDI M M,MILLER J C,et al. Dissolution-driven convection in a hele-shaw cell[J]. Physics of Fluids,2013,25(2):024101. doi: 10.1063/1.4790511
[35] SNIPPE J,GDANSKI R,OTT H. Multiphase modelling of wormhole formation in carbonates by the injection of CO2[J]. Energy Procedia,2017,114:2972 − 2984. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1426
[36] OLTÉAN C,GOLFIER F,BUÈS M A. Numerical and experimental investigation of buoyancy-driven dissolution in vertical fracture[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2013,118(5):2038 − 2048. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50188
[37] AHOULOU A W A,TINET A J,OLTÉAN C,et al. Experimental insights into the interplay between buoyancy,convection,and dissolution reaction[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2020,125(11):e2020JB020854.
[38] DETWILER R L,RAJARAM H. Predicting dissolution patterns in variable aperture fractures:Evaluation of an enhanced depth-averaged computational model[J]. Water Resources Research,2007,43:W04403.
[39] DETWILER R L. Permeability alteration due to mineral dissolution in partially saturated fractures[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,2010,115(B9):B09210.
[40] XU Le,SZYMCZAK P,TOUSSAINT R,et al. Experimental observation of dissolution finger growth in radial geometry[J]. Frontiers in Physics,2019,7:96. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2019.00096
[41] 林云,任华鑫,武亚遵,等. 不同赋存环境下碳酸盐岩溶蚀过程试验模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):15 − 26. [LIN Yun,REN Huaxin,WU Yazun,et al. Experimental simulation of the carbonate dissolution process under different occurrence conditions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):15 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202002001
[42] DENG Hang,FITTS J P,CRANDALL D,et al. Alterations of fractures in carbonate rocks by CO2-acidified brines[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(16):10226 − 10234.
[43] MCDUFF D,JACKSON S,SHUCHART C,et al. Understanding wormholes in carbonates:Unprecedented experimental scale and 3D visualization[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology,2010,62(10):78 − 81. doi: 10.2118/129329-JPT
[44] 胡冉,陈益峰,万嘉敏,等. 超临界CO2-水两相流与CO2毛细捕获:微观孔隙模型实验与数值模拟研究[J]. 力学学报,2017,49(3):638 − 648. [HU Ran,CHEN Yifeng,WAN Jiamin,et al. Supercritical CO2-water displacements and CO2 capillary trapping:Micromodel experiment and numerical simulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2017,49(3):638 − 648. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-16-237
[45] 魏鹳举,胡冉,廖震,等. 湿润性对孔隙介质两相渗流驱替效率的影响[J]. 力学学报,2021,53(4):1008 − 1017. [WEI Guanju,HU Ran,LIAO Zhen,et al. Effects of wettability on displacement efficiency of two-phase flow in porous media[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2021,53(4):1008 − 1017. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-20-403
[46] CHEN Yifeng,FANG Shu,WU Dongsheng,et al. Visualizing and quantifying the crossover from capillary fingering to viscous fingering in a rough fracture[J]. Water Resources Research,2017,53(9):7756 − 7772. doi: 10.1002/2017WR021051
[47] FORD D C, WILLIAMS P. Karst hydrogeology and geomorphology[M]. Chichester: Wiley, 2007.
[48] 郭静芸,毕鑫涛,方然可,等. 可溶岩化学溶蚀试验方法研究综述[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):24 − 34. [GUO Jingyun,BI Xintao,FANG Ranke,et al. Advances in the chemical dissolution methods of soluble rocks[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):24 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003054
[49] SZYMCZAK P,LADD A J C. Interacting length scales in the reactive-infiltration instability[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2013,40(12):3036 − 3041. doi: 10.1002/grl.50564
[50] 朱欣月,李三百,冯夏庭,等. 基于数值法的三维缝洞溶蚀演化主控因素研究[J]. 中国岩溶,2021,40(6):943 − 951. [ZHU Xinyue,LI Sanbai,FENG Xiating,et al. Numerical investigation on the main controlling factors of the dissolution evolution of three-dimensional fracture-cavity reservoirs[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2021,40(6):943 − 951. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[51] 余逍逍,史文兵,王小明,等. 基于数字图像处理技术的溶蚀岩体细观变形破坏机制模拟研究[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(3):409 − 416. [YU Xiaoxiao,SHI Wenbing,WANG Xiaoming,et al. Simulation on mesoscopic deformation and failure mechanism of dissolved rock mass using digital image processing technology[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020,39(3):409 − 416. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: