Study on the spatial vriability of hydraulic conductivity of underground reservoir in Fuping section of Shichuan River
-
摘要:
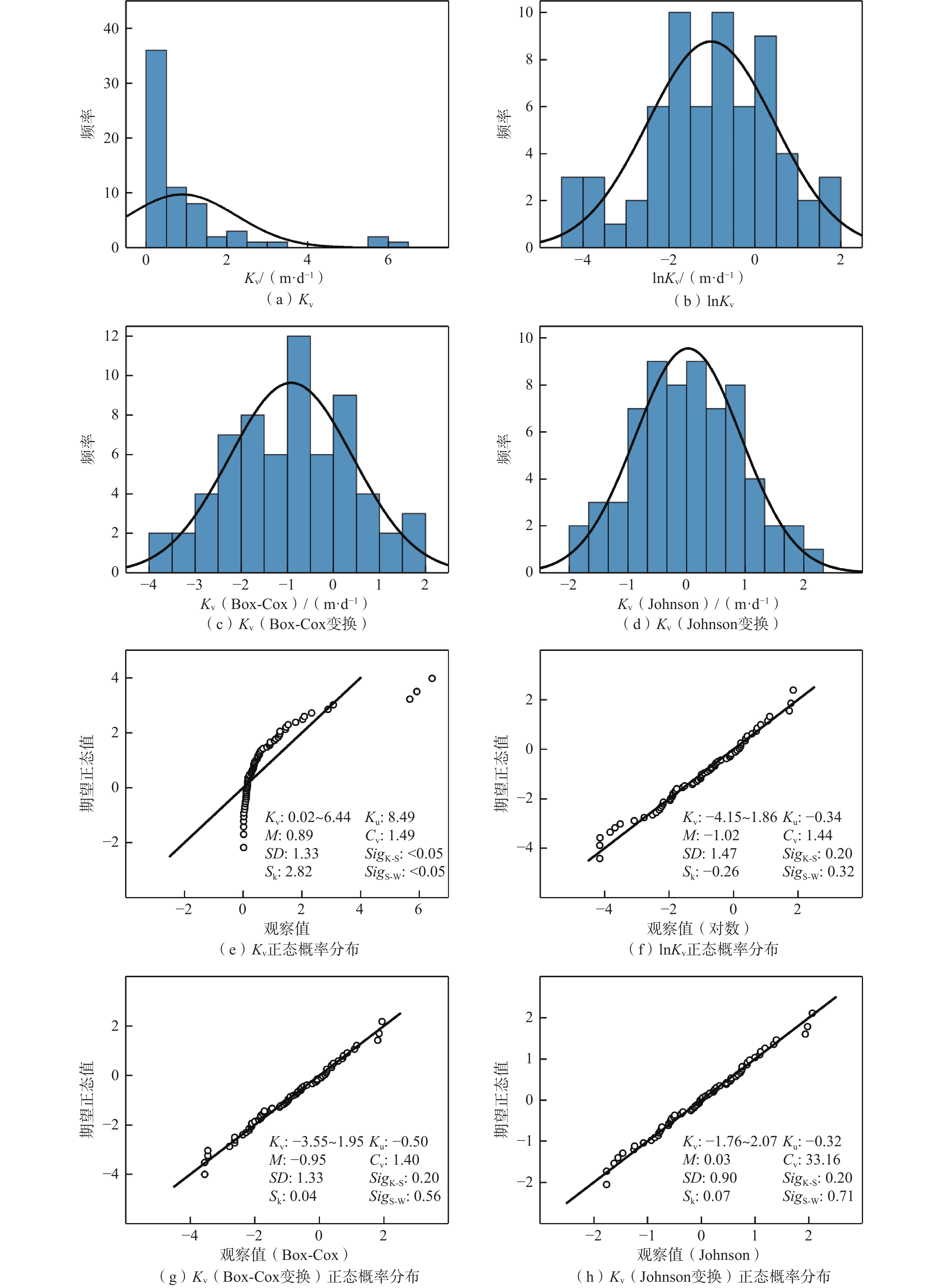
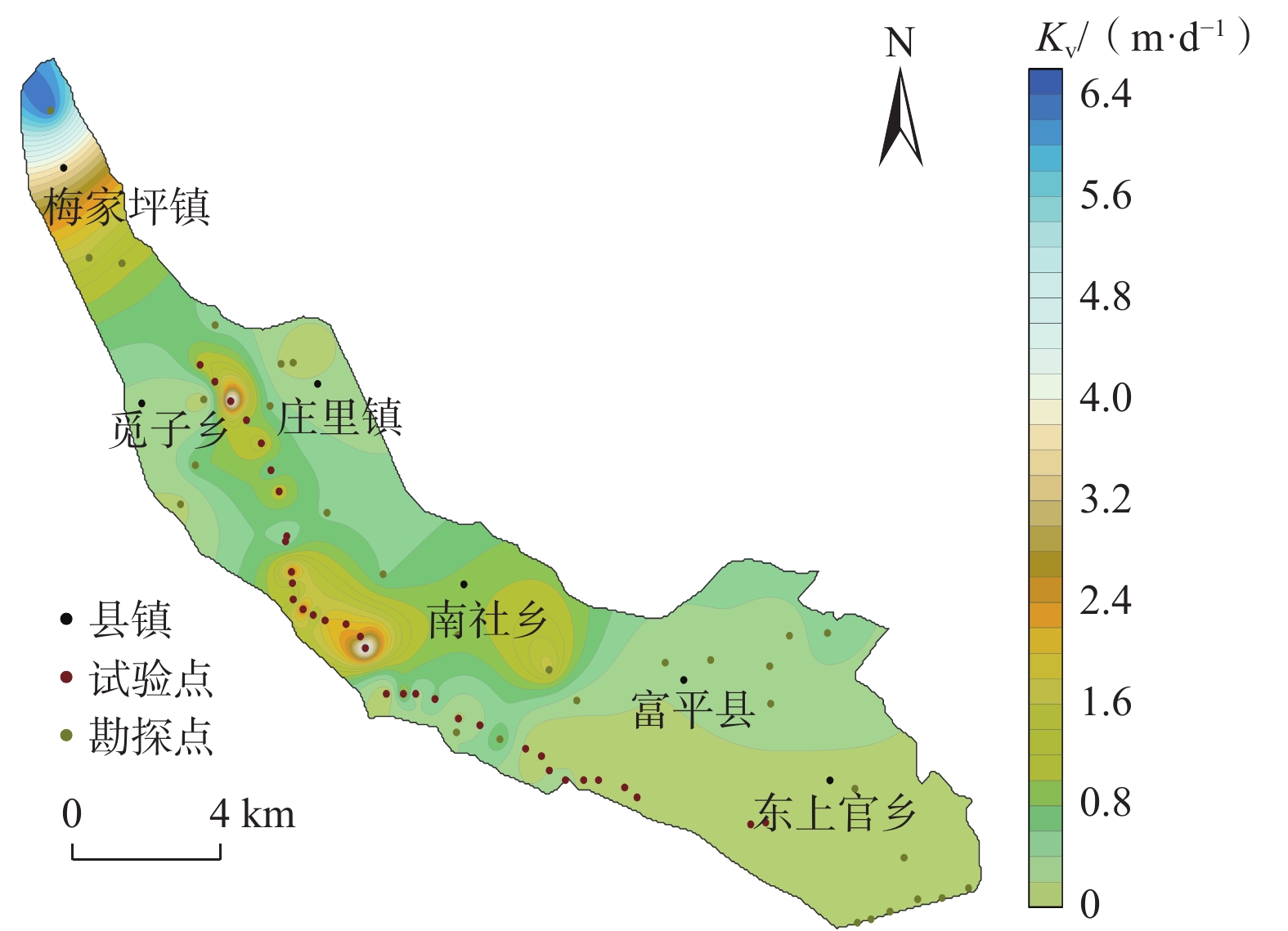
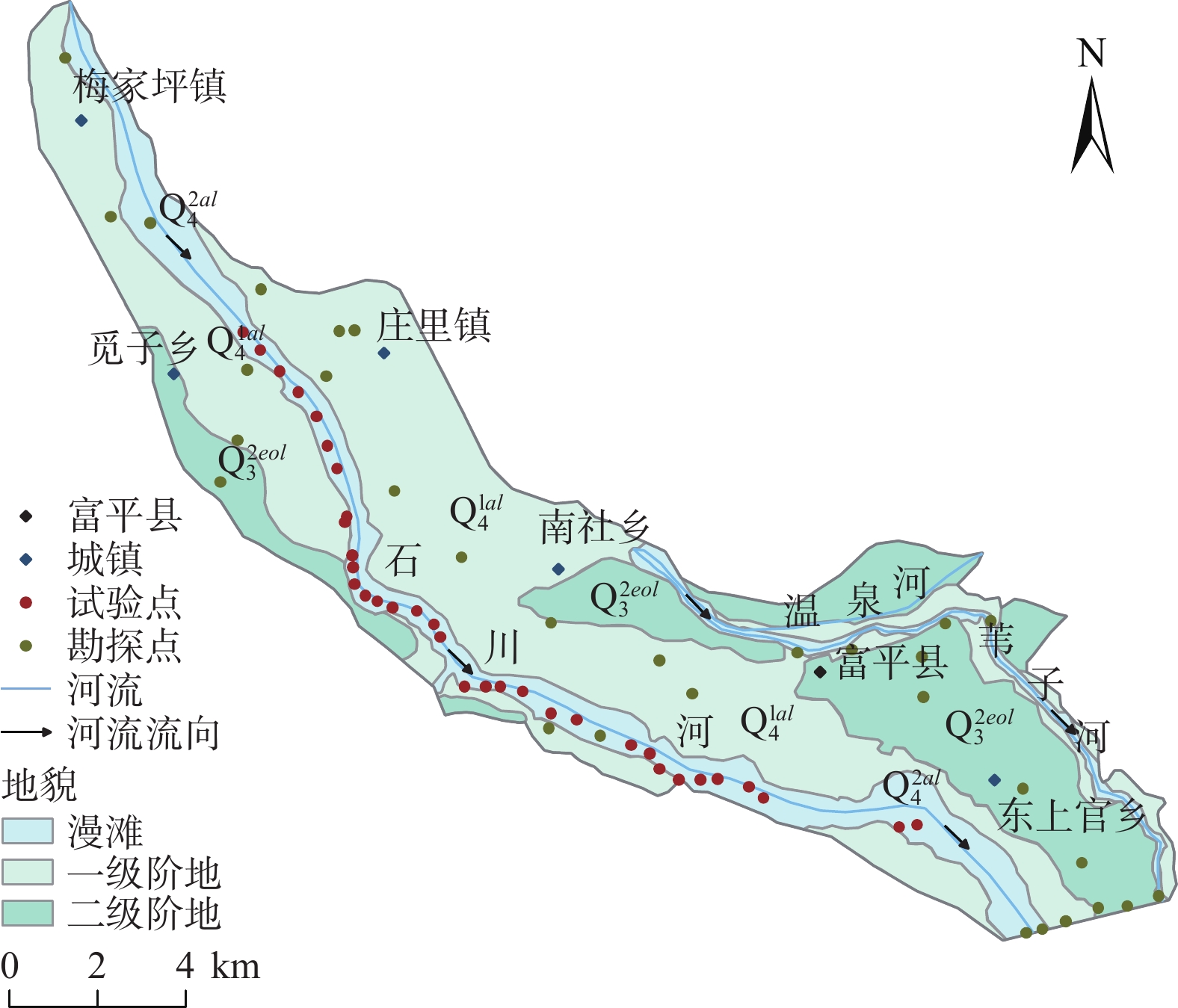
渗透系数的空间变异性研究是进行地下水库人工回灌的基础。为研究石川河富平地下水库渗透系数的空间变化规律,引入Box-Cox变换及Johnson变换对库区65组野外双环渗水试验及勘探孔数据进行预处理,并以变异函数为工具,运用传统统计学和地统计学方法分析渗透系数的空间变异性。结果表明:库区等效渗透系数变化范围为0.02~6.44 m/d,既服从对数正态分布也服从Box-Cox变换的正态分布。渗透系数空间相关程度中等,最优拟合模型为高斯模型。基于最优模型,渗透系数插值结果整体上呈现西北方向较大、东南方向较小的特点,在梅家坪镇及南社乡附近最大,范围为2.84~6.44 m/d,空间变异尺度小;在觅子乡、庄里镇附近变化明显,空间变异尺度大;在东上官乡南部最小,均小于0.2 m/d,变异尺度小。空间变异受地形、地貌、地层岩性、水文气象条件、试验点及勘探点分布、人类活动等因素的综合影响。回灌位置应选择在梅家坪镇等渗透系数大,空间变异尺度小及受人为扰动影响小的地段。研究结果可为地下水库建设提供理论参考。
Abstract:The study on the spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity is the basis for artificial recharge of groundwater reservoir. In order to study the spatial variability of the hydraulic conductivity of underground reservoirs in Fuping section of Shichuan River, Box-Cox transform and Johnson transform were introduced to preprocess the field double-loop percolation test and exploration hole data. Traditional statistical methods and geostatistical methods were applied to analyze the hydraulic conductivity of the reservoir area with the variation function as a tool. The results show that the hydraulic conductivity of the reservoir area varies from 0.02 m/d to 6.44 m/d and obeys both logarithmic normal distribution and Box-Cox transformation normal distribution, the spatial correlation of the hydraulic conductivity is medium, and the best fitting model is Gaussian model. The Kriging interpolation results based on the optimal model show that the hydraulic conductivity as a whole is larger in the northwest and smaller in the southeast. The hydraulic conductivity is the largest near Meijiaping Township and Nanshe Township, ranging from 2.84 m/d to 6.44 m/d, with small spatial variation scale. It varies significantly near Mizi Township and Zhuangli Township, with large spatial variation scale. It is the smallest in the south of Dongshangguan Township, all less than 0.2 m/d, with small variation scale. The spatial variation is influenced by the combination of topography, geomorphology, distribution of stratigraphic lithology, hydro-meteorological conditions, distribution of test sites and exploration sites, human activities and other factors. The location of recharge should be chosen in Meijiaping town and other locations with large hydraulic conductivity, small spatial variation scale and low influence by human disturbance. The research results can provide theoretical references for the construction of underground reservoirs.
-

-
表 1 各点位岩层厚度及等效渗透系数
Table 1. Statistical results of rock thickness and hydraulic conductivity at each point
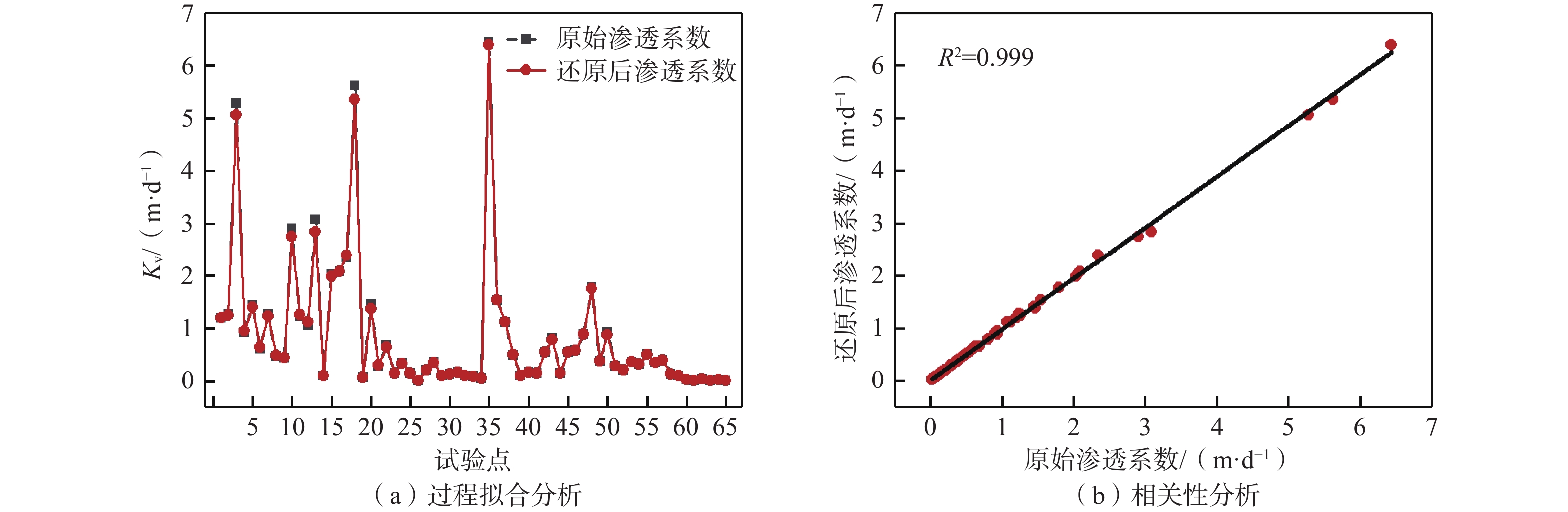
编号 岩层厚度/m 等效渗透系数/(m·d−1) 编号 岩层厚度/m 等效渗透系数/(m·d−1) 编号 岩层厚度/m 等效渗透系数/(m·d−1) S-1 41.50 1.20 S-23 38.50 0.15 11 56.20 0.56 S-2 46.00 1.26 S-24 36.00 0.34 12 52.70 0.58 S-3 39.10 5.68 S-25 24.90 0.16 13 53.30 0.90 S-4 47.20 0.93 S-26 14.80 0.02 14 59.15 1.79 S-5 54.10 1.45 S-27 17.00 0.22 15 39.00 0.39 S-6 54.70 0.62 S-28 23.50 0.37 16 31.90 0.93 S-7 44.00 1.26 S-29 21.00 0.11 17 59.70 0.29 S-8 55.10 0.48 S-30 20.20 0.14 18 31.60 0.21 S-9 54.40 0.44 S-31 15.00 0.17 19 40.60 0.37 S-10 51.30 2.90 S-32 18.00 0.10 20 57.50 0.32 S-11 52.80 1.24 S-33 36.00 0.09 21 59.00 0.51 S-12 53.80 1.07 S-34 37.20 0.06 22 56.04 0.36 S-13 53.90 3.08 1 23.80 6.44 23 56.04 0.40 S-14 44.30 0.10 2 28.80 1.54 24 65.20 0.14 S-15 52.70 2.03 3 31.00 1.12 25 63.80 0.11 S-16 53.00 2.09 4 39.60 0.50 26 15.10 0.03 S-17 46.10 2.34 5 43.50 0.11 27 26.30 0.02 S-18 38.30 5.92 6 39.00 0.17 28 36.90 0.05 S-19 38.80 0.08 7 52.20 0.15 29 48.10 0.02 S-20 42.50 1.46 8 53.20 0.56 30 39.50 0.03 S-21 44.00 0.28 9 53.10 0.81 31 41.90 0.02 S-22 32.50 0.68 10 54.20 0.15 表 2 变换函数类型
Table 2. Transformation function type
一般公式 分布类型 
X服从Johnson SL分布(即对数分布) 
X服从Johnson SB分布 
X服从Johnson SU分布 表 3 变异函数理论模型
Table 3. Theoretical model of variation function
变异函数理论模型 一般公式 变程 球状模型 
a 指数模型 
3a 高斯模型 

注:C0为块金值;C表示空间变量最大的变异程度;C0+C为基台值;h为步长;a为变程,表示最大自相关距离,当距离大于a时,变量相互独立。 -
[1] 姜秋香,付强,王子龙. 空间变异理论在土壤特性分析中的应用研究进展[J]. 水土保持研究,2008,15(1):250 − 253. [JIANG Qiuxiang,FU Qiang,WANG Zilong. Research progress of the spatial variability theory in application to soil characteristic analysis[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2008,15(1):250 − 253. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] HATCH E C,FISHER T A,RUEHL R C,et al. Spatial and temporal variations in streambed hydraulic conductivity quantified with time-series thermal methods[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2010,389(3/4):276 − 288.
[3] ZHANG Nan,LI Lin,JIANG Hong,et al. Study on variation rule of permeability coefficient in unsaturated zone along the WeiHe River in the intertidal area[J]. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science,2018,208(1):71 − 78.
[4] 李金荣,韩新正,万红友,等. 渗透系数的空间变异研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2011(2):11 − 13. [LI Jinrong,HAN Xinzheng,WAN Hongyou,et al. Research on the spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2011(2):11 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 王开丽,黄冠华. 二维强非均质含水层中渗透系数空间变异对污染物迁移的影响[J]. 水利学报,2010,41(4):437 − 445. [WANG Kaili,HUANG Guanhua. Effect of hydraulic conductivity on contaminant transport in highly heterogeneous two-dimensional aquifers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2010,41(4):437 − 445. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] CHEN Xunhong,SONG Jinxi,WANG Wenke. Spatial variability of specific yield and vertical hydraulic conductivity in a highly permeable alluvial aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2010,388(3/4):379 − 388.
[7] CHENG Cheng,SONG Jinxi,CHEN Xunhong,et al. Statistical distribution of streambed vertical hydraulic conductivity along the Platte River,Nebraska[J]. Water Resources Management,2011,25(1):265 − 285. doi: 10.1007/s11269-010-9698-5
[8] 施小清,吴吉春,袁永生. 渗透系数空间变异性研究[J]. 水科学进展,2005,16(2):210 − 215. [SHI Xiaoqing,WU Jichun,YUAN Yongsheng. Study on the spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity[J]. Advances in Water Science,2005,16(2):210 − 215. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2005.02.010
[9] 陈宝辉,王文科,段磊,等. 巴音河下游河床渗透系数空间变异性研究[J]. 水利水电技术,2019,50(1):52 − 57. [CHEN Baohui,WANG Wenke,DUAN Lei,et al. Spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity of riverbed sediment in the lower reaches of Bayin River[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2019,50(1):52 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2019.01.007
[10] 沈鹏云. 渭河河床沉积物渗透系数空间变异性研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2012
SHEN Pengyun. Study on the spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity of riverbed sediment in the Weihe River[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 米海存,Chen X H,何红曼,等. 渭河河漫滩沉积物渗透性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(4):19 − 23. [MI Haicun,CHEN X H,HE Hongman,et al. Determination of hydraulic conductivity of the floodplain in the Weihe River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(4):19 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2014.04.007
[12] 葛佳亮,严婷,吕敬,等. 渭河临潼段漫滩沉积物渗透系数分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2018,29(2):201 − 204. [GE Jialiang,YAN Ting,LV Jing,et al. Analysis of floodplain sediments saturated hydraulic conductivity in Lintong section of Weihe River[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering,2018,29(2):201 − 204. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2018.02.33
[13] 吕敬,柯贤敏,张小筱,等. 泾阳南塬黄土边坡饱和渗透系数变异性分析[J]. 水土保持通报,2017,37(3):254 − 257. [LV Jing,KE Xianmin,ZHANG Xiaoxian,et al. Variability of saturated permeability coefficient of loess slopes in South Jingyang Tableland[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2017,37(3):254 − 257. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2017.03.043
[14] 刘波,林晓宁,马红亮,等. 黄河三角洲沉积物及其渗透系数空间分布特征[J]. 人民黄河,2018,40(5):1 − 6. [LIU Bo,LIN Xiaoning,MA Hongliang,et al. Spatial distribution of particle size and hydraulic conductivity of shallow surface sediments in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Yellow River,2018,40(5):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 宋扬. 灞河橡胶坝库区沉积物渗透系数空间变异及河水—地下水交互作用研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2017
SONG Yang. Spatial variability of sediment permeability coefficient and river-groundwater interaction in Bahe rubber dam area[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王超,束龙仓,鲁程鹏. 渗透系数空间变异性对低渗透地层中地下水溶质运移的影响[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2014,42(2):137 − 142. [WANG Chao,SHU Longcang,LU Chengpeng. Impacts of spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity on solute transport in groundwater of low-permeability stratum[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences),2014,42(2):137 − 142. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2014.02.008
[17] 何满潮,刘斌,姚磊华,等. 地下热水回灌过程中渗透系数研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2002(4):374 − 377. [HE Manchao,LIU Bin,YAO Leihua. Study on hydraulic conductivity during geothermal reinjection[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2002(4):374 − 377. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] CUI Ruifei,ZHU Yaguang,ZHANG Huan,et al. BoxCox multi-output linear regression for 10.7 cm solar radio flux prediction[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics,2021,21(4):149 − 158.
[19] 常浩浩,宋松柏,吴海江,等. 基于Johnson分布的年降水量频率分析[J]. 水力发电学报,2021,40(3):76 − 83. [CHANG Haohao,SONG Songbai,WU Haijiang,et al. Frequency analysis of annual precipitation based on Johnson distribution[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering,2021,40(3):76 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20210307
[20] 蔡国涛,乔长录. 基于正态变换的玛纳斯河水文频率研究[J]. 人民黄河,2022,44(3):21 − 25. [CAI Guotao,QIAO Changlu. Study on hydrological frequency with Manas River based on normal transform[J]. Yellow River,2022,44(3):21 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2022.03.005
[21] 薛佩佩,文章,梁杏. 地质统计学在含水层参数空间变异研究中的应用进展与发展趋势[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(1):209 − 222. [XUE Peipei,WEN Zhang,LIANG Xing. Application and development trend of geostatistics in the research of spatial variation of aquifer parameters[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(1):209 − 222. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 荆永滨,王公忠,毕林. 矿山离散钻孔样品变异函数模型计算与拟合[J]. 矿冶工程,2017,37(4):19 − 22. [JING Yongbin,WANG Gongzhong,BI Lin. Calculating and fitting variogram models for dispersed mine drill samples[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering,2017,37(4):19 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2017.04.005
[23] 王友年,李升,余斌. 阿克苏河流域渗透系数空间变异性分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2021(1):64 − 70. [WANG Younian,LI Sheng,YU Bin. Spatial variability analysis of permeability coefficient in Aksu River Basin[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2021(1):64 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2021.01.013
[24] NALDER A I,WEIN W R. Spatial interpolation of climatic Normals:Test of a new method in the Canadian boreal forest[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,1998,92(4):211 − 225. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(98)00102-6
[25] 李海涛,邵泽东. 空间插值分析算法综述[J]. 计算机系统应用,2019,28(7):1 − 8. [LI Haitao,SHAO Zedong. Review of spatial interpolation analysis algorithm[J]. Computer Systems & Applications,2019,28(7):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.006988
[26] 杨洁荣,宋向东,明喆. Johnson转换与Box-Cox转换相比的优越性[J]. 佳木斯大学学报(自然科学版),2010,28(3):449 − 452. [YANG Jierong,SONG Xiangdong,MING Zhe. The superiority of Johnson transformation to Box-Cox transformation[J]. Journal of Jiamusi University (Natural Science Edition),2010,28(3):449 − 452. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1402.2010.03.038
[27] 郭志奇. 陕西省富平县石川河河道渗透性能分析[J]. 地下水,2021,43(6):82 − 85. [GUO Zhiqi. Analysis of the infiltration performance of the Shichuan River in Fuping County,Shaanxi Province[J]. Ground Water,2021,43(6):82 − 85. (in Chinese)
[28] 刘卫岗. 陕西省石川河流域地下水调蓄研究报告[R]. 西安: 陕西省工程勘察研究院, 2015
LIU Weigang. Study on groundwater storage in Shichuan River Basin of Shaanxi Province[R]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Engineering Investigation and Research Institute, 2015. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: