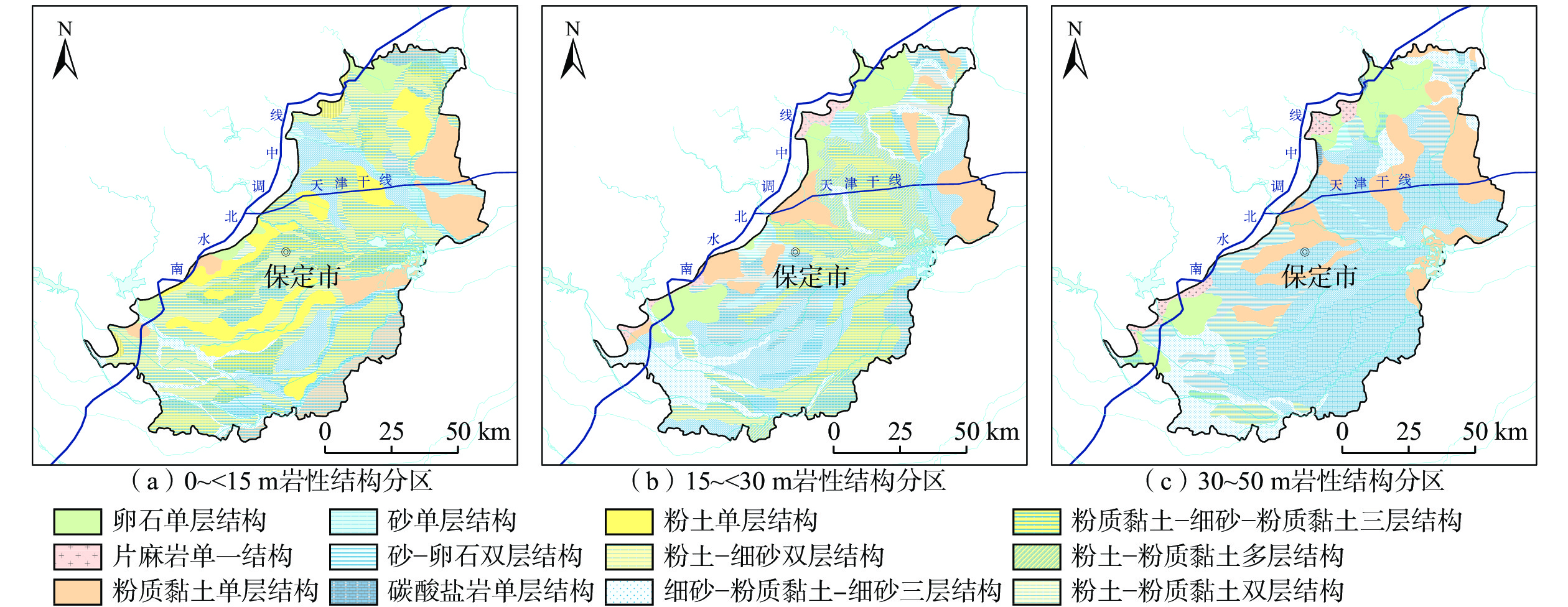
Spatial variability of free porosity in the groundwater level fluctuation zone in the Baoding Plain area
-
摘要:
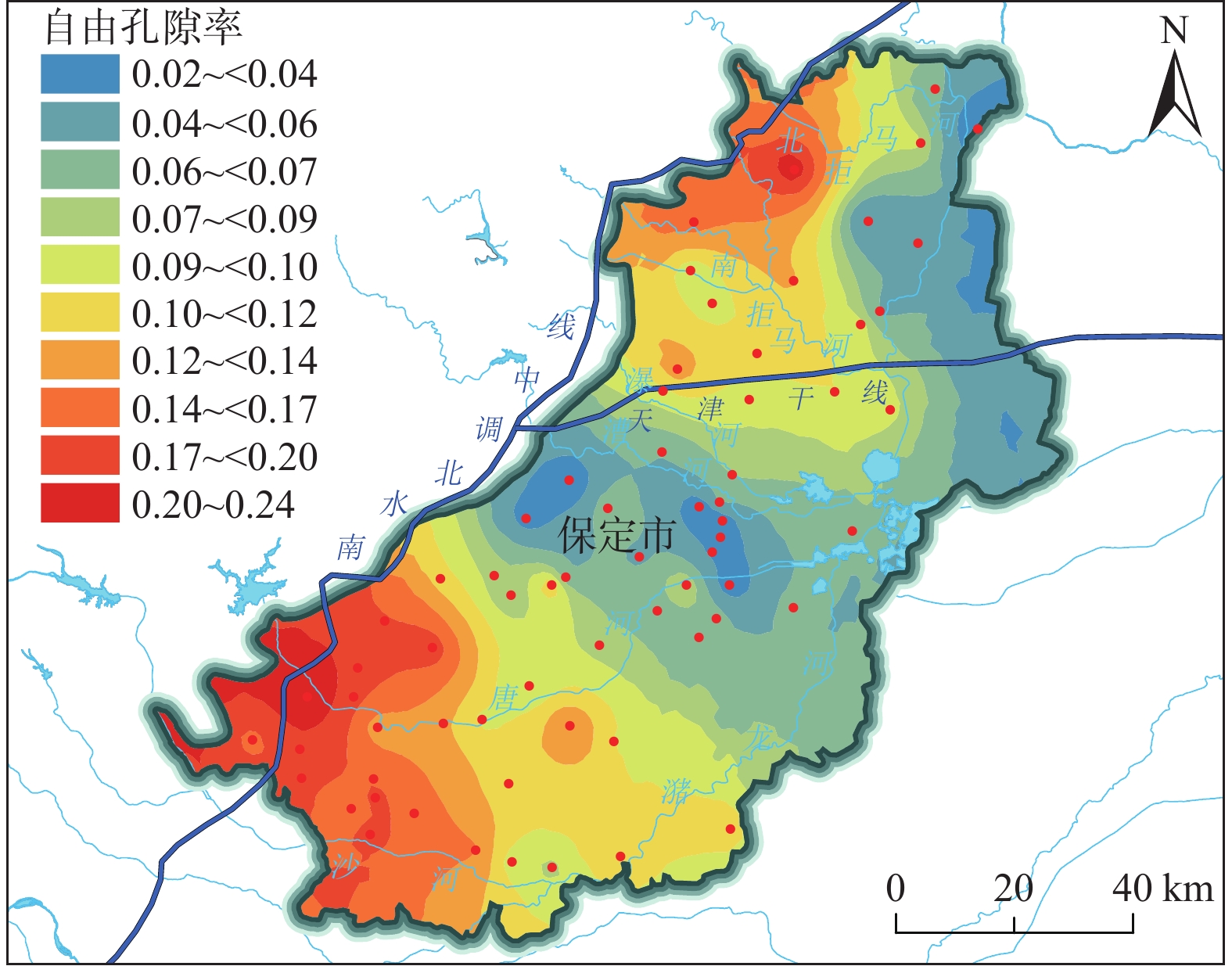
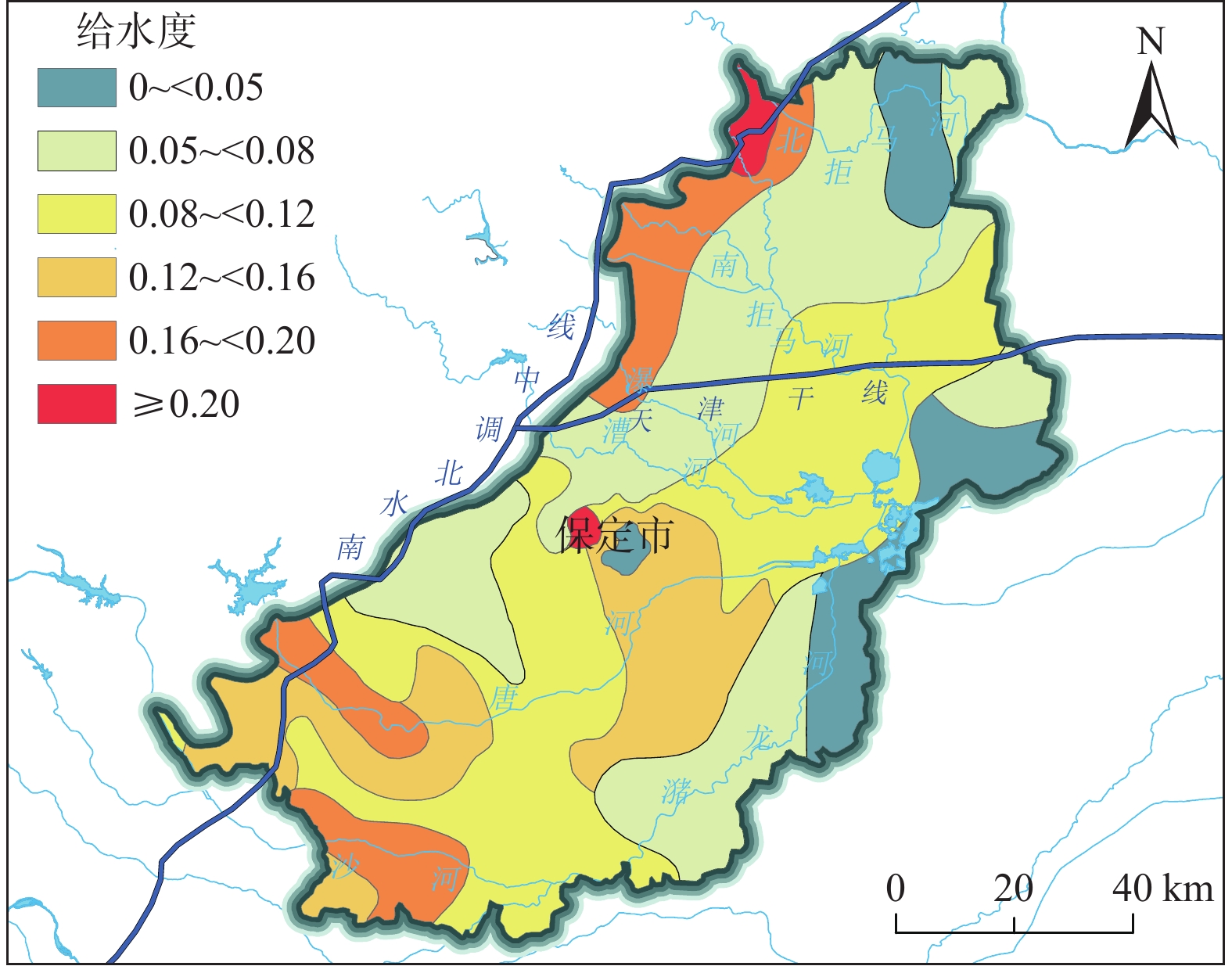
科学确定地下水水位变幅带的地学参数是水资源评价与管理中的重要环节。保定平原近40年来强烈开采地下水,水位持续下降形成规模巨大的厚包气带层,南水北调工程通水后,随着河湖生态补水与地下水压采工作的推进,保定平原局部地区地下水水位止跌回升。回补水量与水位变化的定量关系成为超采治理的一个重要科学问题,但水位回升条件下的计算中仍用表示释水过程的给水度参数将造成结果偏差,因此表述水位恢复过程的自由孔隙率参数研究是解决这一问题的重点所在。文章基于保定平原区67个工程地质钻孔采样数据,确定水位变幅带的综合自由孔隙率,通过趋势分析和结果交叉验证方法遴选半变异函数模型,结合普通克里金插值方法对未知点进行无偏最优估计。结果显示:(1)保定平原区水位变幅带综合自由孔隙率的最优半变异函数模型为一阶趋势效应指数模型。数据具有强空间自相关性,主要受变幅带空间位置、地层类型等结构性因素影响。(2)综合自由孔隙率分布表现为西南、西北为高值区,极值可达0.25,数值向中部及东部逐步降低,最小降至0.02。(3)与惯用给水度值进行对比,自由孔隙率值在南北部地区整体升高约0.03,约为惯用给水度的1.2倍。在中部地区降低了约0.06,变为惯用给水度值的一半左右。研究成果对南水北调受水区生态补水与水资源调控具有重要研究价值和借鉴意义。
Abstract:Scientific determination of geological parameters of the groundwater level fluctuation zone is an important step for water resources evaluation and management. In the past 40 years, over-exploitation of groundwater in the Baoding Plain led to a serious deficit of aquifers, thus forming a huge deep vadose zone. After the South-to-North Water Diversion Project was put into operation, with the progress of ecological water supplement of rivers and lakes and groundwater limited-over-exploitation, the groundwater levels in some areas of the Baoding Plain stopped falling and rose. The quantitative relationship between the amount of water supplement and the change of groundwater levels has become an important scientific issue in the management of over-exploitation of groundwater. However, under the condition of groundwater level recovery, the calculation results will be deviated if the specific yield parameter of water release process is still used. Therefore, the free porosity parameter study of groundwater level recovery process is the key to solve this problem. Based on 67 engineering geological boreholes in the Baoding Plain, the comprehensive free porosity during groundwater level recovery is determined according to the lithologic characteristic parameters of the groundwater level fluctuation zone. The semi-variogram model is selected by the trend analysis and cross validation, and the spatial unknown points are interpolated by the Ordinary Kriging interpolation. The results show that (1) the best semi-variogram model of the comprehensive free porosity in the groundwater level fluctuation zone of the Baoding Plain is the 1 order index model. The spatial autocorrelation of the data is obvious, which is mainly affected by structural factors such as spatial location of the groundwater level fluctuation zone and stratigraphic type. (2) The comprehensive free porosity distribution shows that the southwest and northwest are the high value areas, and the extreme value can reach 0.25. The parameter gradually decreases to the central and eastern regions, and the minimum value is 0.02. (3) Compared with the value of the conventional specific yield, the value of the free porosity increases by about 0.03 in the north and south regions, which is about 1.2 times that of the conventional specific yield. In the central region, it is reduced by about 0.06, which is about half that of the conventional specific yield value. The research results are of important research value and great significance for ecological water supplement and water resources regulation in the benefited regions of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project.
-
Key words:
- free porosity /
- specific yield /
- unsaturated zone /
- geostatistics /
- spatial variability /
- Baoding Plain area
-

-
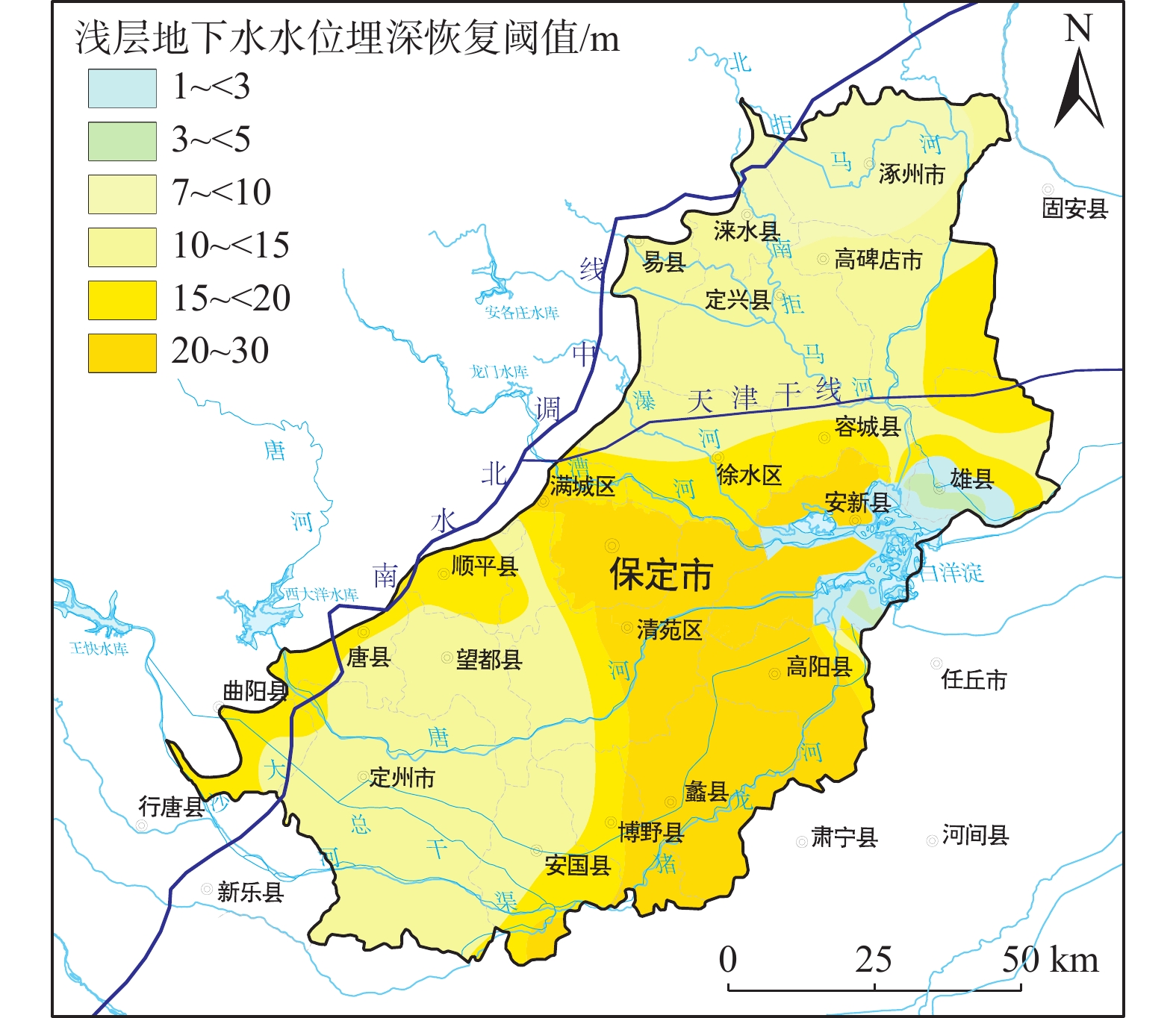
图 4 浅层地下水水位恢复阈值图(据文献[25]改)
Figure 4.
图 8 浅层地下水给水度分布图(据文献[36]改)
Figure 8.
表 1 地下水水位恢复阈值指标体系
Table 1. Groundwater level recovery threshold index system
地下水层位 考虑要素 目标水位埋深 浅层 大规模开采对地下水水位影响 20世纪80年代水位埋深 地下水水位降落漏斗区水位恢复 20世纪80年代水位埋深 大中型城市地下空间利用安全性 20~30 m 有利于降水入渗补给、地下水调蓄 10~15 m 地裂缝防控 7~10 m 盐渍化防控 3~4 m 表 2 变异函数理论模型
Table 2. Theoretical models of the variation function
模型 公式 变程 块金值 基台值 球状模型 



指数模型 



高斯模型 



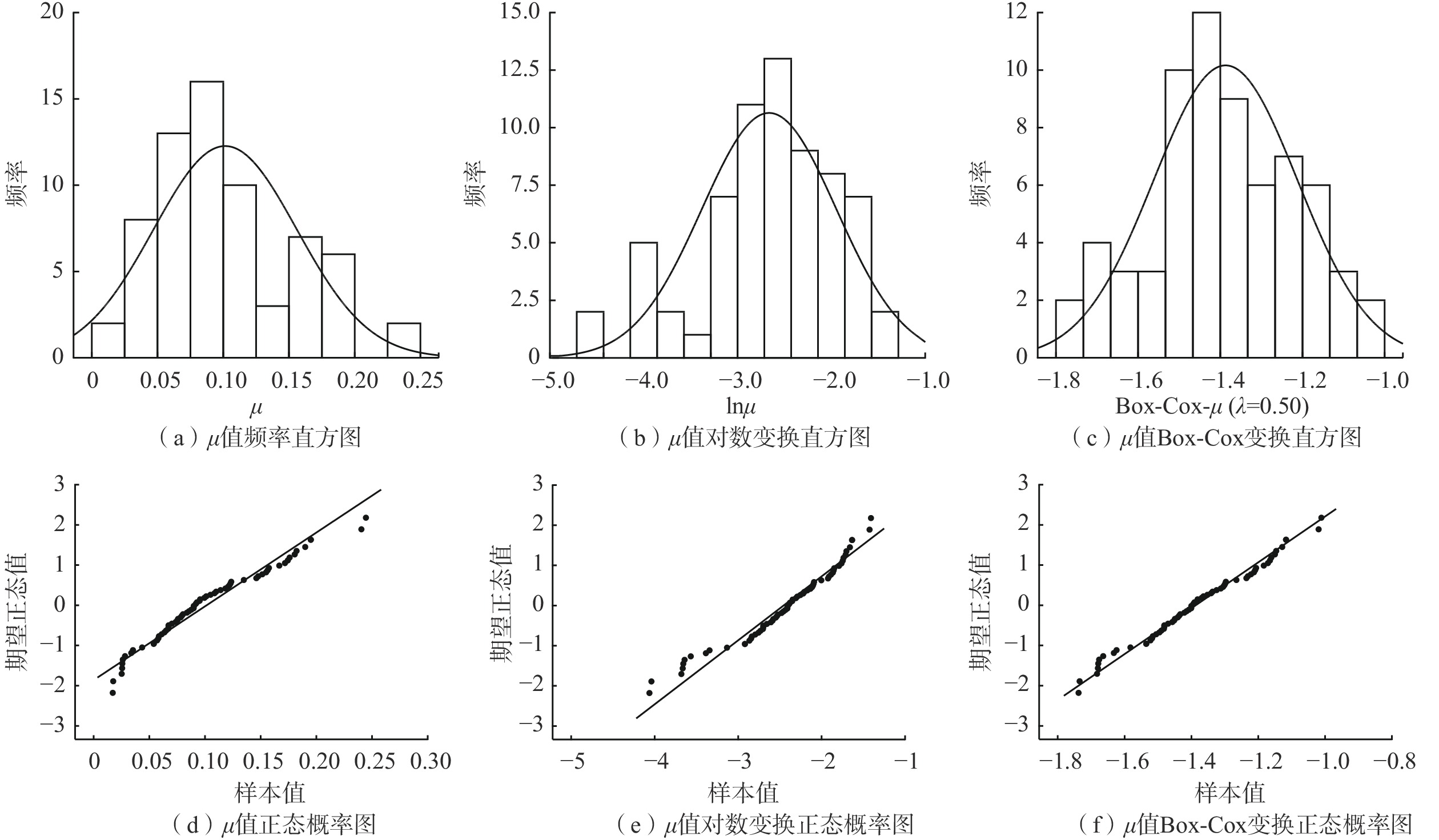
表 3 综合自由孔隙率统计特征表
Table 3. Statistical characteristics of the comprehensive free porosity
数据 中值 平均值 标准差 变异系数 偏度 峰度 偏度标准误差 峰度标准误差 偏度Z评分 峰度Z评分 µ 0.090 0.101 0.054 53.7 0.6066 −0.1638 0.293 0.578 2.071 −0.283 lnµ −2.408 −2.456 0.628 −25.6 −0.7103 0.1331 0.293 0.578 −2.426 0.230 Box-Cox −1.400 −1.387 0.175 −12.6 0.0025 −0.5078 0.293 0.578 −0.008 −0.879 注:Box-Cox变换中λ=0.50。 表 4 综合自由孔隙率正态性检验结果
Table 4. Normality test results of the comprehensive free porosity
数据 K-S检验 S-W检验 统计 样本 Sig 统计 样本 Sig µ 0.110 67 0.043 0.956 67 0.018 lnµ 0.081 67 0.200 0.949 67 0.008 Box-Cox 0.060 67 0.200 0.981 67 0.418 表 5 不同趋势阶数插值误差比较
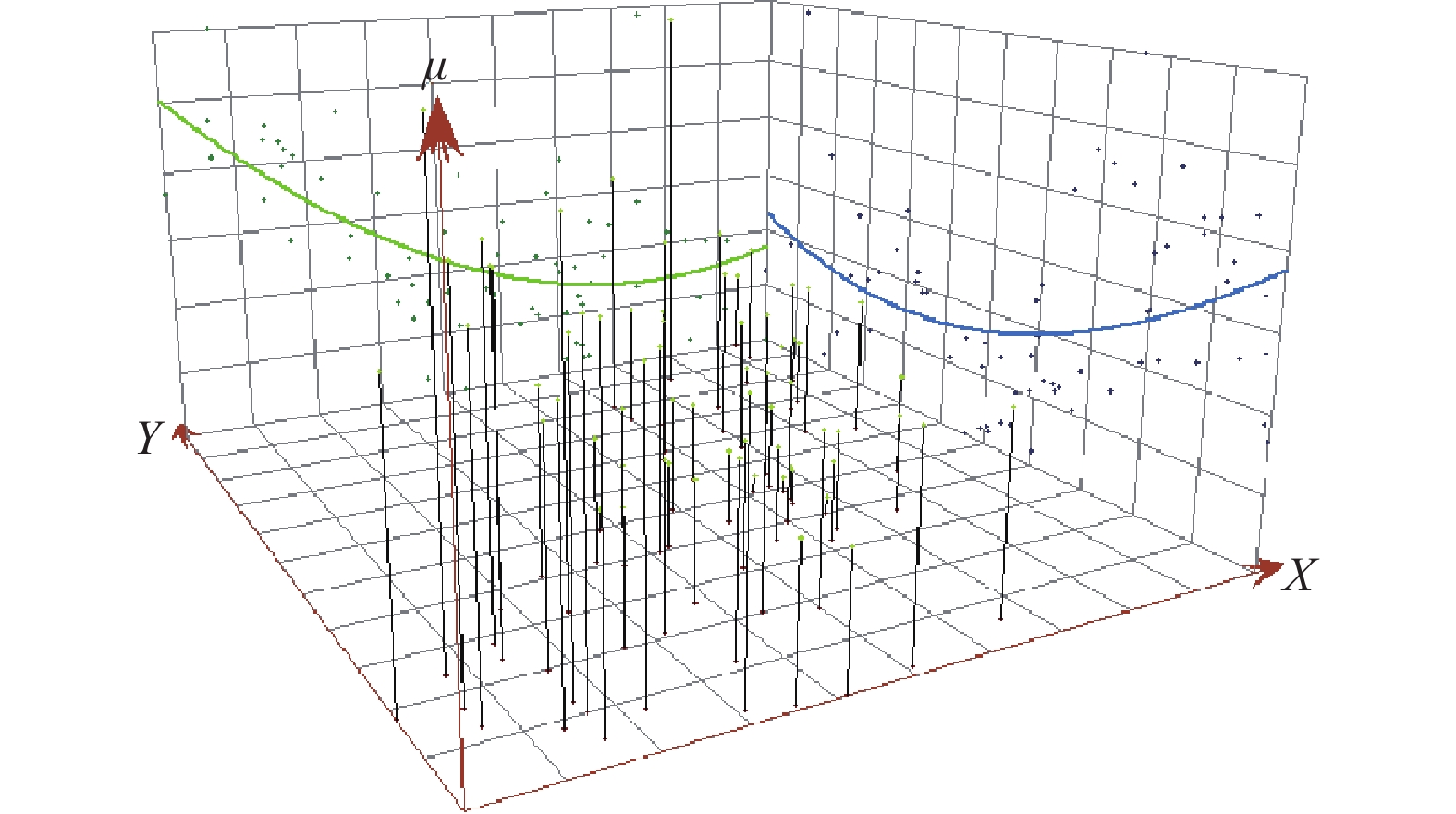
Table 5. Comparison of interpolation errors of different trend orders
趋势 模型 预测误差 阶数 类型 平均误差 均方根误差 平均标准误差 标准化均方根误差 平均标准误差 0 球状 −0.00045 0.0345 −0.0231 1.0753 0.0333 指数 −0.00164 0.0348 −0.0497 0.9871 0.0368 高斯 −0.00031 0.0351 −0.0254 1.1676 0.0309 1 球状 −0.00113 0.0349 −0.0479 1.1160 0.0322 指数 −0.00112 0.0345 −0.0425 1.0093 0.0355 高斯 −0.00126 0.0352 −0.0481 1.1152 0.0320 2 球状 0.00063 0.0349 −0.0106 1.0842 0.0332 指数 0.00050 0.0354 −0.0175 1.0402 0.0347 高斯 0.00040 0.0347 −0.0169 1.0874 0.0328 表 6 半变异函数类型及模型参数
Table 6. Types of the semi-variation function and model parameters
模型类型 趋势效应 变程/m 各向异性系数 块金值 基台值 块金效应/% 长轴 短轴 指数模型 一阶 24936.15 21944.23 1.14 0.0001 0.0166 0.60 -
[1] 李文鹏,王龙凤,杨会峰,等. 华北平原地下水超采状况与治理对策建议[J]. 中国水利,2020(13):26 − 30. [LI Wenpeng,WANG Longfeng,YANG Huifeng,et al. The groundwater over exploitation status and counter measure suggestions of the North China Plain[J]. China Water Resources,2020(13):26 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2020.13.017
[2] SHI J S,WANG Z,ZHANG Z J,et al. Assessment of deep groundwater over-exploitation in the North China Plain[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2011,2(4):593 − 598. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2011.07.002
[3] SU G L,WU Y Q,ZHAN W,et al. Spatio temporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence caused by groundwater depletion in the North China plain during the past six decades[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,600:126678.
[4] 曹文庚,杨会峰,高媛媛,等. 南水北调中线受水区保定平原地下水质量演变预测研究[J]. 水利学报,2020,51(8):924 − 935. [CAO Wengeng,YANG Huifeng,GAO Yuanyuan,et al. Prediction of groundwater quality evolution in the Baoding Plain of the SNWDP benefited regions[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2020,51(8):924 − 935. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] ZHANG C, DUAN Q Y, YEH P J-F, et al. Sub-regional groundwater storage recovery in North China Plain after the South-to-North water diversion project[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 597: 126156.
[6] 杨会峰,曹文庚,支传顺,等. 近40年来华北平原地下水位演变研究及其超采治理建议[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(4):1142 − 1155. [YANG Huifeng,CAO Wengeng,ZHI Chuanshun,et al. Evolution of groundwater level in the North China Plain in the past 40 years and suggestions on groundwater over exploitation treatment[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(4):1142 − 1155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 裴源生. 地下水水位匀速升降条件下土壤水分运动和给水度的研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1983(4):1 − 7. [PEI Yansheng. Study on soil water movement and specific yield under the condition of uniform rise and fall of groundwater level[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1983(4):1 − 7. (in Chinese)
[8] 张蔚榛,张瑜芳. 土壤的给水度和自由空隙率[J]. 灌溉排水,1983(2):1 − 16+47. [ZHANG Weizhen,ZHANG Yufang. Specific yield and free porosity of soil[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,1983(2):1 − 16+47. (in Chinese)
[9] 蔡树英. 土壤储水过程及自由孔隙率的初步研究[J]. 武汉水利电力学院学报,1988(2):104 − 108. [CAI Shuying. A study of the water storage procedure and free porosity of soil[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University,1988(2):104 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] XUE P P,WEN Z,ZHAO D J,et al. Determination of hydraulic conductivity and its spatial variability in the Jianghan Plain using a multi-format,multi-method approach[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,594:125917. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125917
[11] CHERIF K,YAMINA B,BILAL B,et al. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Wadi Saida Watershed of NW-Algeria using remote sensing,geographic information system-based AHP techniques and geostatistical analysis[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2021,9(1):45 − 64.
[12] MEHDI B,ELMIRA K,ELAHE K. Spatial variation assessment of groundwater quality using multivariate statistical analysis (Case Study:Fasa Plain,Iran)[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2020,8(3):230 − 243.
[13] 高瑞忠,朝伦巴根,贾德彬,等. 神经网络模型在根系带土壤水力特征参数空间变异性研究中的应用[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2004(4):13 − 16. [GAO Ruizhong,CHAO Lunbagen,JIA Debin,et al. Research on the spatial variance of the soil hydraulic parameters based on the artificial neutral network[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2004(4):13 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-643X.2004.04.003
[14] 董勤各,许迪,章少辉,等. 考虑灌溉参数空间变异的区域畦灌模拟与验证[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(9):1 − 9. [DONG Qinge,XU Di,ZHANG Shaohui,et al. Simulation and validation for regional border irrigation considering spatial variability of irrigation parameters[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2017,33(9):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 方萍,吕成文,朱艾莉. 分形方法在土壤特性空间变异研究中的应用[J]. 土壤,2011,43(5):710 − 713. [FANG Ping,LV Chengwen,ZHU Aili. Applied studies of fractal theory on spatial variability of soil properties:A review[J]. Soils,2011,43(5):710 − 713. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] WANG T,LIU Y Q,WANG J Z,et al. Assessment of spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity of seasonally frozen ground in Northeast China[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,274:105741.
[17] 宋浩,张琛,刘明,等. 基于地统计学的伊犁-巩乃斯河谷渗透系数空间变异性研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2019,30(1):97 − 103. [SONG Hao,ZHANG Chen,LIU Ming,et al. The spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity based on geostatistics in Ili-Kunes valley[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2019,30(1):97 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 薛佩佩,文章,梁杏. 地质统计学在含水层参数空间变异研究中的应用进展与发展趋势[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(1):209 − 222. [XUE Peipei,WEN Zhang,LIANG Xing. Application and development trend of geostatistics in the research of spatial variation of aquifer parameters[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(1):209 − 222. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] WANG W,WANG Y,SUN Q M,et al. Spatial variation of saturated hydraulic conductivity of a loess slope in the South Jingyang Plateau,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,236:70 − 78. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.08.002
[20] FU T G,CHEN H S,ZHANG W,et al. Spatial variability of surface soil saturated hydraulic conductivity in a small karst catchment of southwest China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2015,74(3):2381 − 2391. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4238-5
[21] 刘泓志,肖长来,张岩祥,等. 基于地统计学的降水入渗补给系数的空间变异特征分析[J]. 节水灌溉,2014(6):54 − 56. [LIU Hongzhi,XIAO Changlai,ZHANG Yanxing,et al. Spatial variation characteristics analysis of precipitation infiltration recharge coefficient based on geostatistics[J]. Water Saving Irrigation,2014(6):54 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4929.2014.06.016
[22] 钱永. 开采条件下华北平原浅层地下水系统演变研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2007
QIAN Yong. Research on evolvement of shallow groundwater system impacted by exploiting in North China Plain[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Geological Sciences, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 靳博文,王文科,段磊,等. 保定平原区地下水生态水位阈值的探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):166 − 175. [JIN Bowen,WANG Wenke,DUAN Lei,et al. Discussion on ecological water level threshold of groundwater in Baoding Plain area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):166 − 175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 刘鹏飞,张光辉,崔尚进,等. 旱区湿地周边盐渍化农田生态水位阈值与“水位-水量”双控技术[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):42 − 51. [LIU Pengfei,ZHANG Guanghui,CUI Shangjin,et al. Threshold value of ecological water table and dual control technology of the water table and its quantity in the salinized farmland around wetland in arid areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):42 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] YANG H F,MENG R F,BAO X L,et al. Assessment of water level threshold for groundwater restoration and over-exploitation remediation the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2022,10(2):113 − 127.
[26] 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 等. 水文地质学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011
ZHANG Renquan, LIANG Xing, JIN Menggui, et al. Fundamentals of hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Geological publishing house, 2011. (in Chinese)
[27] 陈南祥. 给水度与饱和差关系的初步研究[J]. 河海大学学报,1998(4):112 − 115. [CHEN Nanxiang. Study on the relation between specific yield and saturation deficiency[J]. Journal of Hohai University,1998(4):112 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 张仁铎. 空间变异理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005
ZHANG Renduo. Spatial variation theory and its application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005. (in Chinese)
[29] 赵鑫,王存国,魏永霞. 坡耕地主要土壤参数的空间变异特征[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2014(1):11 − 14. [ZHAO Xin,WANG Cunguo,WEI Yongxia. Spatial statistic properties of soil parameters at slope[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2014(1):11 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2014.01.003
[30] VIEIRA S R,DECASTRO O M,TOPP G C. Spatial variability of some soil physical properties in three soils of Sao-Paulo,Brazil[J]. Pesquisa Agropecuaria Brasileira,1992,27,(2):333 − 341.
[31] 顾晓敏,崔亚莉,肖勇,等. 昌平区山前平原地下水位空间变异性特征分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(2):10 − 15. [GU Xiaomin,CUI Yali,XIAO Yong,et al. Spatial variability of groundwater levels of piedmont in the Changping District[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(2):10 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 张经泾,魏传江,申晓晶,等. 基于GIS的吉林市区地下水埋深空间异质性分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2018,29(2):97 − 103. [ZHANG Jingjing,WEI Chuanjiang,SHEN Xiaojing,et al. Spatial variability of groundwater depth based on GIS in Jilin Urban Area[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2018,29(2):97 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2018.02.16
[33] CAMBARDELLA C A,MOORMAN T B,NOVAK J M,et al. Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1994,58(5):1501 − 1511. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800050033x
[34] JONES D R. A taxonomy of global optimization methods based on response surfaces[J]. Journal of Global Optimization,2001,21(4):345 − 383. doi: 10.1023/A:1012771025575
[35] 张涛,吴剑锋,林锦,等. 变异函数模型对渗透系数克里格插值的影响研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):1 − 7. [ZHANG Tao,WU Jianfeng,LIN Jin,et al. A comparative study of the ordinary kriging applied to hydraulic conductivity interpolation based on different variogram models[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 张兆吉, 费宇红. 华北平原地下水可持续利用图集[M]. 北京: 中国地图出版社, 2009, 72 − 72
ZHANG Zhaoji, FEI Yuhong. Atlas of groundwater sustainable utilization in North China Plain[M]. Beijing: China Cartographic Publishing House, 2009, 72 − 72. (in Chinese)
[37] 林丹. 包气带变化及其对地下水补给的影响[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2014
LIN Dan. The change of vadose zone and its impact on groundwater recharge[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: