Influence of stratified heterogeneity on the recharge from surface water to groundwater
-
摘要:
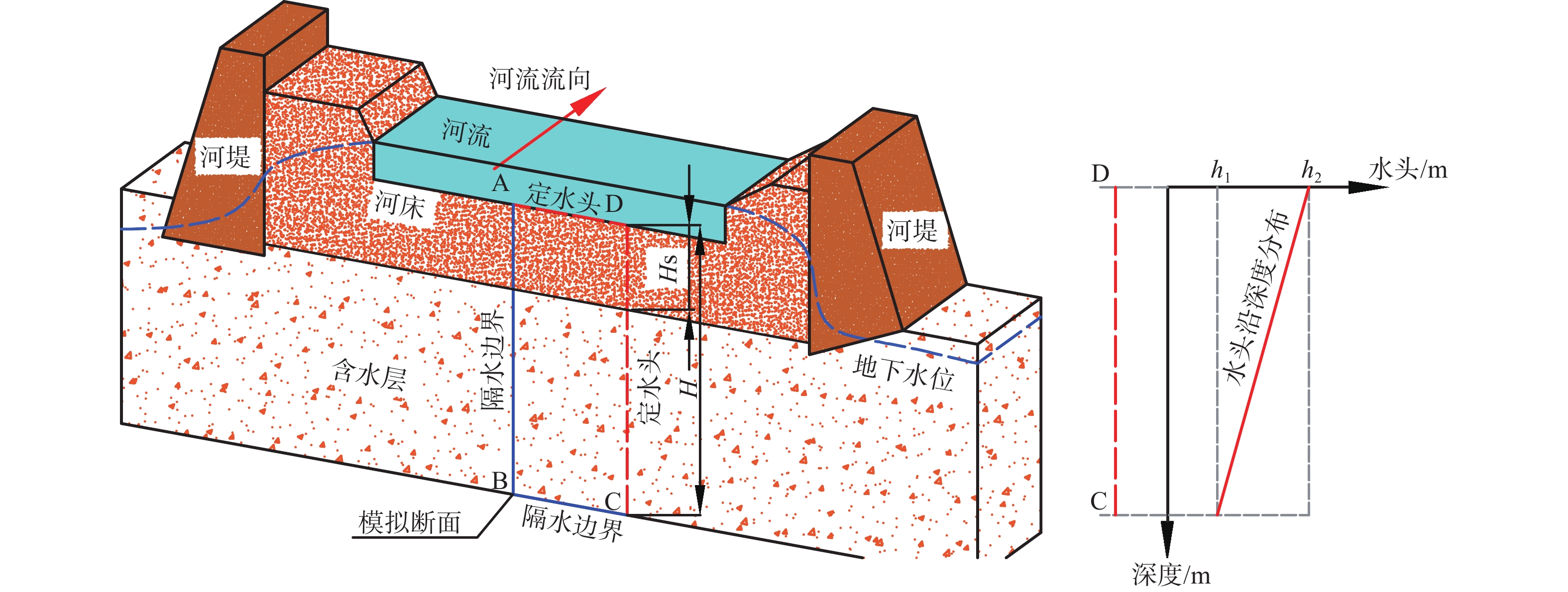
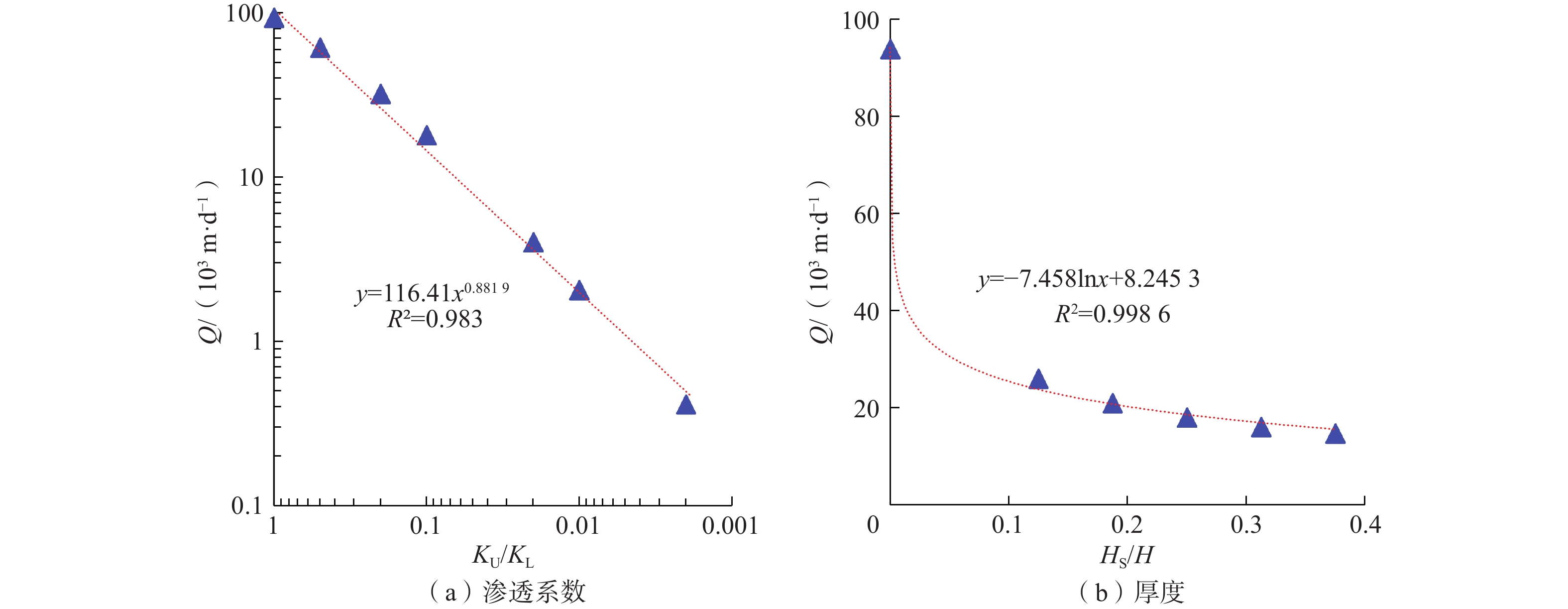
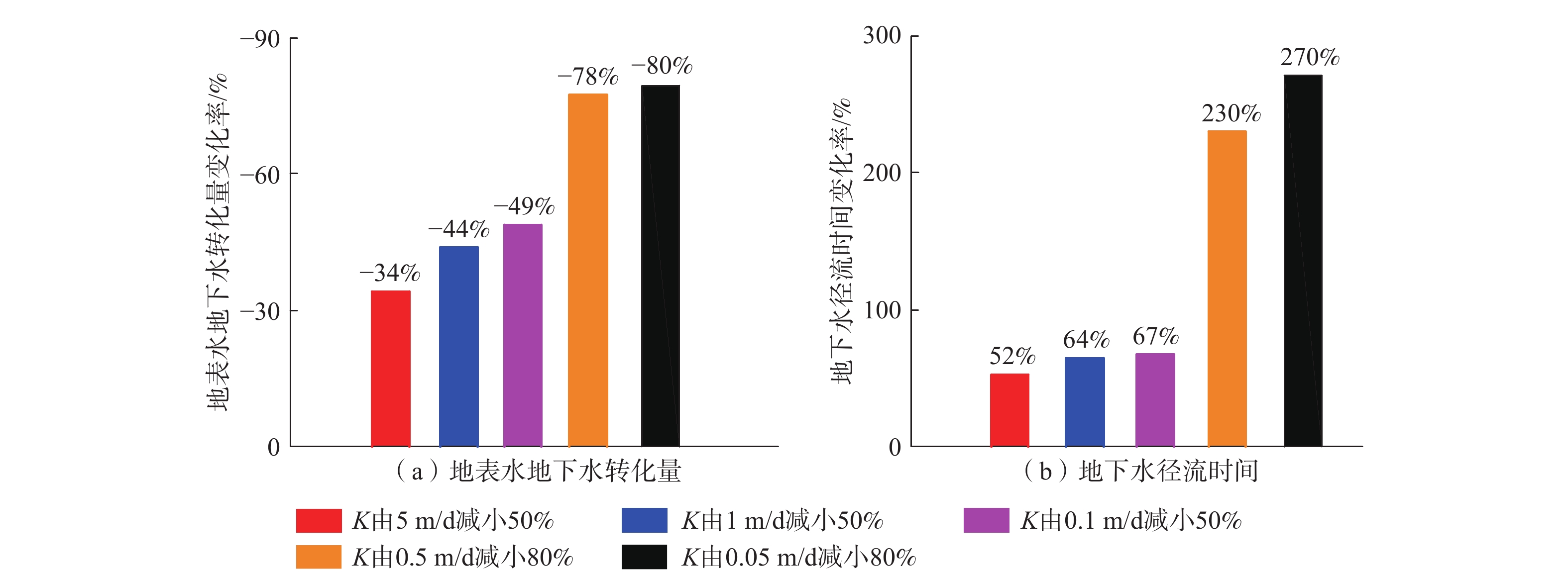
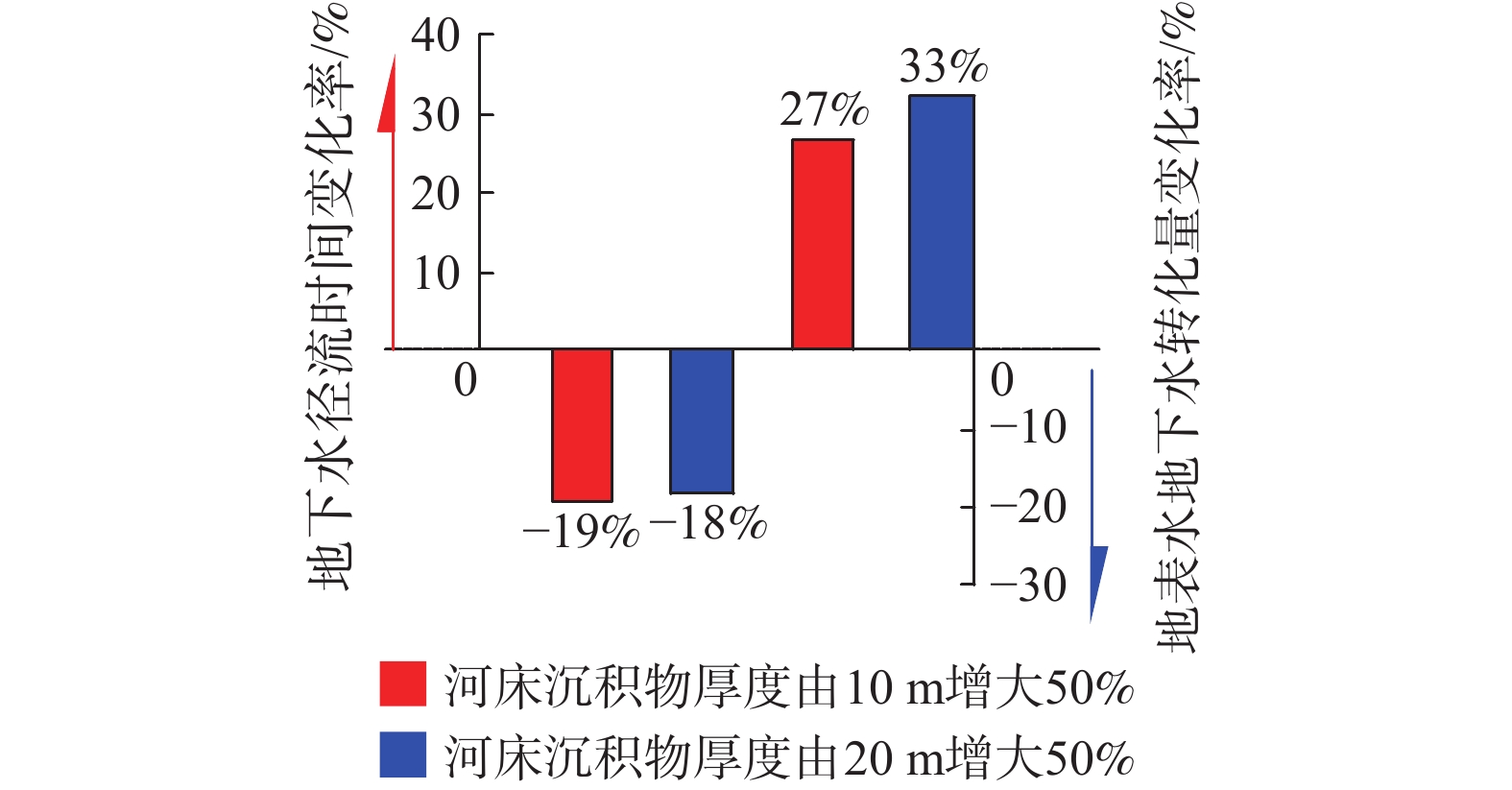
河流对地下水的补给过程研究是科学认识水循环规律及地下水资源可持续管理的基础。河床沉积层与其下伏潜水含水层岩性差异是河流下伏含水层的主要结构特征,也是控制河流对地下水补给过程的主要因素。为揭示含水介质分层结构特征影响下河流对地下水的补给过程,基于黄河干流河南段野外试验结果,建立了地表水地下水相互作用概念模型,并以地下水流路径为对象,精细刻画了地表水地下水的相互作用过程。结果表明:(1)河流对地下水的补给量主要受河床沉积层渗透性影响,河床沉积层厚度变化对河流向地下水的补给量影响不大。即:河床低渗透性沉积物的存在是河流向地下水补给量降低的主要原因,当河床沉积层与其下伏含水层厚度比(HS/H)由0增大为0.125时,河流向地下水补给量的减小幅度达72%。(2)与均质条件相比,河床沉积层渗透性及其厚度变化均明显改变了河水向地下水补给的水流路径及径流时间。随着河床沉积物与下伏含水层渗透系数比KU/KL的增大,河水向地下水补给的水流路径穿透深度增大,径流时间延长。(3)河流对地下水的补给量及地下水径流时间对低渗透性河床沉积层渗透系数的敏感性随渗透系数的减小而增大,同时,地下水径流时间对低渗透性河床沉积层的厚度变化较为敏感,且随着厚度的增大,敏感性增强。研究成果可为地下水资源管理及可持续开发提供参考依据。
Abstract:Knowledge of the recharge from surface water to groundwater is the basement of the scientific understanding of water cycle and the sustainable management of groundwater resources. Meanwhile, the layered heterogeneity is the main structural feature of riverbed sediments (i.e., the lithologic difference between riverbed sediments and the underlying aquifer) and the main factor that controlling the recharge from surface water to groundwater. To reveal the influence mechanism of layered structure of pore media on the recharge from surface water to groundwater, a conceptual model of surface water and groundwater interaction is established based on the field test results of Henan reaches of the Yellow River, and the process of the recharge from surface water to groundwater interaction is described using flow path as the object. The results show that the exchange flux of surface water and groundwater is mainly affected by hydraulic conductivity of riverbed sediments, and the change of the thickness of riverbed sediments has little effect on the exchange flux between surface water and groundwater. That is, the increase of the ratio of the thickness of the sediments to that of the underlying aquifer (HS/H) from 0 to 0.125 leads to the interaction flux decreased by 72%, indicating that the existence of the low permeability layer is the main reason that decreases the interaction flux between surface water and groundwater. The change of the permeability and the thickness of riverbed sediments has obviously changed the flow path from surface water to groundwater and the travel time. Specifically, the increase in KU/KL leads to a lager penetration depth of groundwater flow and lager travel times. The sensitivity of exchange flux between surface water and groundwater and groundwater travel time to the hydraulic conductivity of riverbed sediments increases with the decreasing hydraulic conductivity. At the same time, the groundwater travel time is more sensitive to the change of the thickness of the low permeability riverbed sediments, and the sensitivity increases with the increasing thickness. The research results can provide reference for groundwater resource management and sustainable development.
-

-
表 1 不同试验断面不同点位渗透系数竖管试验结果
Table 1. Standpipe test results of hydraulic conductivity at different points in different test sections
/(m·d−1) 断面 测点编号1 测点编号2 测点编号3 测点编号4 测点编号5 测点编号6 桃花峪 4.500 2.800 3.400 0.014 6.000 2.400 4.800 2.700 3.800 0.010 5.800 2.100 4.000 1.800 3.000 0.012 4.900 2.500 3.400 2.000 4.000 0.009 6.400 1.800 平均值 4.175 2.325 3.550 0.011 5.775 2.200 花园口 2.400 1.780 2.530 2.180 1.720 0.240 2.140 1.690 2.320 2.980 0.980 0.190 1.980 2.010 2.510 2.570 1.540 0.540 2.070 1.750 1.890 1.690 1.210 0.810 平均值 2.148 1.808 2.313 2.355 1.363 0.445 柳园口 1.570 0.021 0.140 0.001 1.210 0.850 1.280 0.009 0.009 0.001 1.080 0.940 1.370 0.021 0.014 0.005 0.970 0.090 2.150 0.050 0.021 0.008 0.520 0.120 平均值 1.593 0.025 0.046 0.004 0.945 0.500 -
[1] BOUCHEZ C,COOK P G,PARTINGTON D,et al. Comparison of surface water-groundwater exchange fluxes derived from hydraulic and geochemical methods and a regional groundwater model[J]. Water Resources Research,2021,57(3):e2020WR029137.
[2] BOANO F,HARVEY J W,MARION A,et al. Hyporheic flow and transport processes:Mechanisms,models,and biogeochemical implications[J]. Reviews of Geophysics,2014,52(4):603 − 679. doi: 10.1002/2012RG000417
[3] SAHA G C,LI Jianbing,THRING R W,et al. Temporal dynamics of groundwater-surface water interaction under the effects of climate change:A case study in the Kiskatinaw River Watershed,Canada[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2017,551:440 − 452. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.008
[4] SEDGHI M M,ZHAN Hongbin. Groundwater dynamics due to general stream fluctuations in an unconfined single or dual-porosity aquifer subjected to general areal recharge[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2019,574:436 − 449. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.04.052
[5] FERENCZ S B,CARDENAS M B,NEILSON B T. Analysis of the effects of dam release properties and ambient groundwater flow on surface water-groundwater exchange over a 100-km-long reach[J]. Water Resources Research,2019,55(11):8526 − 8546. doi: 10.1029/2019WR025210
[6] 廖福,罗新,谢月清,等. 氡(222Rn)地下水-地表水相互作用中的应用研究进展[J]. 地学前缘(中国地质大学(北京); 北京大学),2022,29(3):76 − 87. [LIAO Fu,LUO Xin,XIE Yueqing,et al. Advances in 222Rn application in the study of groundwater-surface water interactions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2022,29(3):76 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] LAMONTAGNE S,TAYLOR A,COOK P,et al. Field assessment of surface water-groundwater connectivity in a semi-arid river basin (Murray-Darling,Australia)[J]. Hydrological Processes,2014,28(4):1561 − 1572. doi: 10.1002/hyp.9691
[8] CONSTANTZ J. Heat as a tracer to determine streambed water exchanges[J]. Water Resources Research,2008,44(4):W00D10.
[9] RAUTIO A,KORKKA N K. Chemical and isotopic tracers indicating groundwater/surface-water interaction within a boreal lake catchment in Finland[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2015,23(4):687 − 705. doi: 10.1007/s10040-015-1234-5
[10] 杨艳林,靖晶,赵永波,等. 基于氢氧稳定同位素的武汉北部新城地表水-地下水转换关系研究[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(3):706 − 715. [YANG Yanlin,JING Jing,ZHAO Yongbo,et al. Conversion relationship between surface water and groundwater based on stable isotopes of D and 18O of new town in the northern Wuhan, Hubei[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(3):706 − 715. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 鲁程鹏,束龙仓,陈洵洪. 河床地形影响潜流交换作用的数值分析[J]. 水科学进展,2012,23(6):789 − 795. [LU Chengpeng,SHU Longcang,CHEN Xunhong. Numerical analysis of the impacts of bedform on hyporheic exchange[J]. Advances in Water Science,2012,23(6):789 − 795. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2012.06.018
[12] 鲁程鹏,张颖,朱静思,等. 基于热追踪方法的河流横断面潜流交换时空非均质特征研究[J]. 第四纪研究,2014,34(5):1094 − 1105. [LU Chengpeng,ZHANG Ying,ZHU Jingsi,et al. Temporal spatial patterns of hyporheic exchange along a river transect of dawen river through the heat tracing method[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2014,34(5):1094 − 1105. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.05.18
[13] 文广超,王文科,段磊,等. 基于水化学和稳定同位素定量评价巴音河流域地表水与地下水转化关系[J]. 干旱区地理,2018,41(4):734 − 743. [WEN Guangchao,WANG Wenke,DUAN Lei,et al. Quantitatively evaluating exchanging relationship between river water and groundwater in Bayin River Basin of northwest China using hydrochemistry and stable isotope[J]. Arid Land Geography,2018,41(4):734 − 743. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2018.04.08
[14] CARDENAS M B. Surface water-groundwater interface geomorphology leads to scaling of residence times[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2008,35(8):307 − 315.
[15] 束龙仓,宫荣,栾佳文,等. 地下水与地表水水量交换识别及交换量计算—以新汴河宿州段为例[J]. 水科学进展,2022,33(1):57 − 67. [SHU Longcang,GONG Rong,LUAN Jiawen,et al. A integrated method to quantify flow exchanges between surface water and groundwater:Take Suzhou section of the Xinbian River as an example[J]. Advances in Water Science,2022,33(1):57 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] HUANG Peng,CHUI T F M. Hyporheic exchange in a straight stream with alternate bars[J]. Water Resources Research,2022,58(10):e2022WR032221.
[17] 束龙仓,殷晓然,袁亚杰,等. 三江平原典型区河水与地下水水量交换的时空变化规律分析[J]. 水利学报,2021,52(10):1151 − 1162. [SHU Longcang,YIN Xiaoran,YUAN Yajie,et al. Temporal and spatial variation of water quantity exchange between surface water and groundwater in typical district of Sanjiang Plain[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2021,52(10):1151 − 1162. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.20210509
[18] DRUMMOND J D,AQUINO T,DAVIES C R J,et al. Modeling contaminant microbes in rivers during both baseflow and stormflow[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2022,49(8):e2021GL096514.
[19] 李刚,马佰衡,周仰效,等. 白洋淀湖岸带地表水与地下水垂向交换研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):48 − 54. [LI Gang,MA Baiheng,ZHOU Yangxiao,et al. A study of vertical exchange between surface water and groundwater around the banks of Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):48 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008004
[20] JASECHKO S,SEYBOLD H,PERRONE D,et al. Widespread potential loss of streamflow into underlying aquifers across the USA[J]. Nature,2021,591(7850):391 − 395. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03311-x
[21] 雷米,周金龙,张杰,等. 新疆博尔塔拉河流域平原区地表水与地下水水化学特征及转化关系[J]. 环境科学,2022,43(4):1873 − 1884. [LEI Mi,ZHOU Jinlong,ZHANG Jie,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and transformation relationship of surface water and groundwater in the plain area of Bortala River Basin,Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Science,2022,43(4):1873 − 1884. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] TÓTH J. Groundwater as a geologic agent:An overview of the causes,processes,and manifestations[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,1999,7(1):1 − 14. doi: 10.1007/s100400050176
[23] JIANG Qihao,JIN Guangqiu,TANG Hongwu,et al. Density-dependent solute transport in a layered hyporheic zone[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2020,142:103645. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2020.103645
[24] 吴佩鹏,束龙仓,鲁程鹏,等. 三峡水库蓄水前后下游河床沉积物渗透系数的变化分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(6):98 − 102. [WU Peipeng,SHU Longcang,LU Chengpeng,et al. An analysis of the changes in the riverbed sediment hydraulic conductivity in the downstream channel before and after the Three Gorges Reservoir impoundment[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(6):98 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2014.06.018
[25] WU Peipeng,SHU Longcang,COMTE J C,et al. The effect of typical geological heterogeneities on the performance of managed aquifer recharge:physical experiments and numerical simulations[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2021,29(6):2107 − 2125. doi: 10.1007/s10040-021-02375-3
[26] 陈孝兵,郑春阳,袁越. 河床沉积物非均质性影响下的潜流交换数值模拟[J]. 水科学进展,2019,30(2):220 − 229. [CHEN Xiaobing,ZHENG Chunyang,YUAN Yue. Modeling the impacts of streambed sediment heterogeneity on hyporheic exchange[J]. Advances in Water Science,2019,30(2):220 − 229. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2019.02.007
[27] 赵云章, 邵景力, 闫振鹏, 等. 黄河下游影响带地下水资源评价及可持续开发利用[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2002
ZHAO Yunzhang, SHAO Jingli, YAN Zhenpeng, et al. Evaluation and sustainable exploitation of groundwater resources in the influenced zone of the lower Yellow River[M]. Beijing: China Land Press, 2002. (in Chinese)
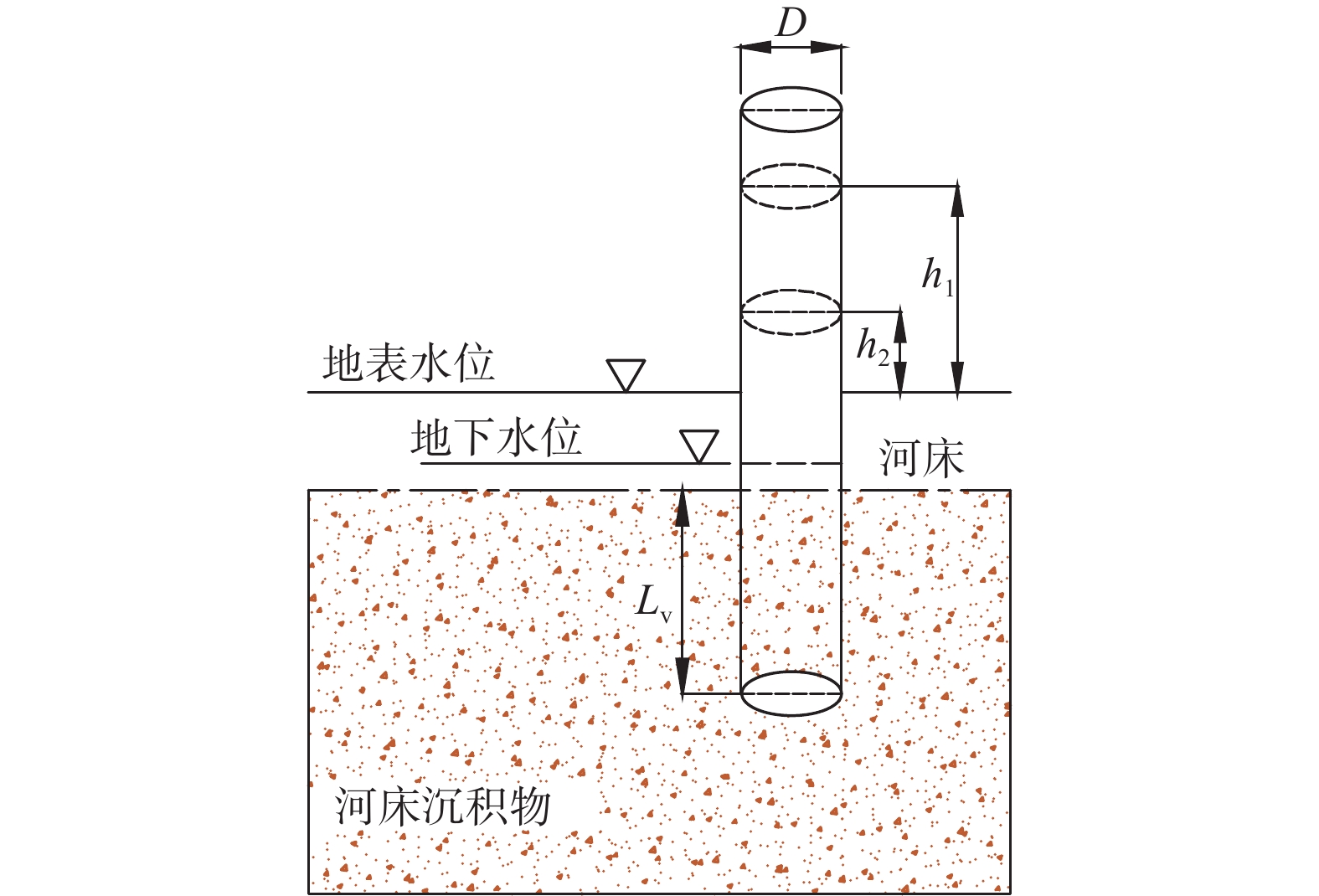
[28] 束龙仓. 美国内布拉斯加州普拉特河河床沉积物渗透系数的现场测定[J]. 水科学进展,2002,13(5):629 − 633. [SHU Longcang. Measurement in situ of streambed hydraulic conductivities in the Platte River,Nebraska[J]. Advances in Water Science,2002,13(5):629 − 633. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2002.05.017
[29] ANDERSON M P, WOESSNER W W, HUNT R J. Applied groundwater modeling: Simulation of flow and advective transport[M]. 2nd ed. London: Academic Press, 2015.
[30] WU Guangdong,SHU Longcang,LU Chengpeng,et al. Variations of streambed vertical hydraulic conductivity before and after a flood season[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2015,23(7):1603 − 1615. doi: 10.1007/s10040-015-1275-9
[31] 童坤,束龙仓,黄修东,等. 雨洪水回灌过程中堵塞滤层特征试验[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2011,31(4):52 − 55. [TONG Kun,SHU Longcang,HUANG Xiudong,et al. Characteristics of mechanical clogging in rain-flood infiltration system[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources,2011,31(4):52 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1006-7647.2011.04.012
[32] WANG Wenke,LI Junting,FENG Xizhou,et al. Evolution of stream-aquifer hydrologic connectedness during pumping experiment[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2011,402(3/4):401 − 414.
-




 下载:
下载: