Numerical analysis for estimating residual DNAPL by single-well “push-pull” partitioning tracer tests
-
摘要:
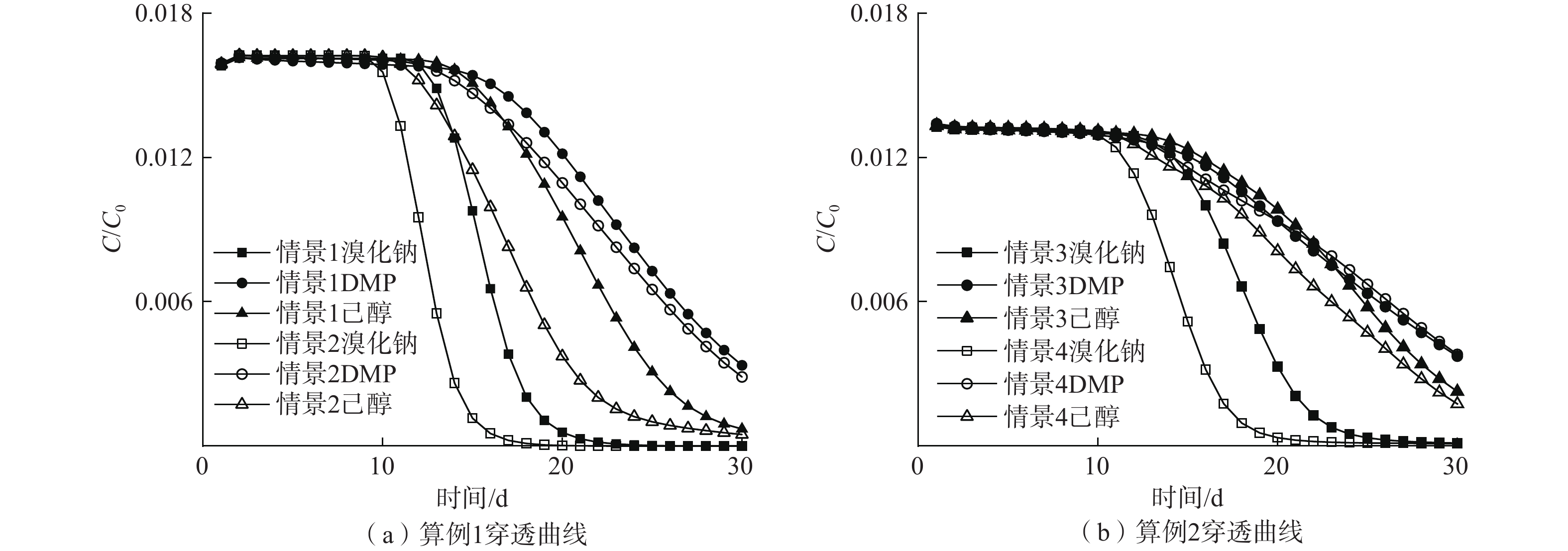
目前,刻画场地重非水相液体(dense non-aqueous phase liquid, DNAPL)污染常用的钻孔取样和井间分溶示踪试验方法成本高昂。相比而言,单井注抽试验节省经费,且对污染源区的扰动少,但该试验方法推估DNAPL残留量的准确性尚未得到定量验证。针对该问题,基于数值方法分析了示踪剂类型、注抽速率、污染源区结构等因素对单井注抽试验推估DNAPL残留量精度的影响。结果表明:(1)选用分溶系数比2,2-二甲基-3-戊醇(2,2-dimethyl-3-pentanol, DMP)低的己醇进行示踪,示踪剂回收更加充分,推估污染物残留量的平均精度增幅可达35.11%;(2)当注入速率从100 m3/d提高至130 m³/d、抽出速率从120 m3/d提高至150 m3/d,示踪剂接触的污染源区面积更大,均质源区对应的污染物残留量平均精度从42.45%提高到60.26%,非均质源区对应的平均精度从27.69%提高至48.72%;(3)污染源区结构复杂程度的增加会阻碍示踪剂的运移,非均质源区对应的平均精度比均质源区降低了13.15%;(4)单井注抽示踪试验更适用于离散状为主的污染源区,其平均精度比池状为主的源区增加了15.74%。单井注抽试验结合数值分析可有效推估残留非水相液体的分布,建议在DNAPL污染场地精细调查中使用,可为场地风险评估和修复方案的制定提供参考。
Abstract:The drilling methods and the partitioning inter-well tracer tests which are often used to characterize dense non-aqueous phase liquids (DNAPL) source zones cost a lot. Compared with common methods, the single- well “push-pull” partitioning tracer tests not only save money, but also reduce the disturbance to the contaminated site, which can be used to estimate the residual DNAPL. However, the accuracy of this method in estimating residue DNAPL has not been quantitatively verified. To solve the problem, this paper analyses the influence of several factors on estimating the accuracy of residual DNAPL based on the numerical method, including tracer type, the injection and pumping rate and contaminant source zone architectures. The results display that Hexanol with a smaller partition coefficient than DMP can be selected for tests, as the tracer are recovered more fully, which can result in the average accuracy of residue DNAPL estimated to increase by 35.11%. When the injection rate of the tests increases from 100 m³/d to 130 m³/d and the pumping rate increases from 120 m3/d to 150 m3/d, the tracer can expose to a larger contaminant source area so that the average accuracy of the homogeneous source zones increases from 42.45% to 60.26% while the average accuracy of the heterogeneous source zones increases from 27.69% to 48.72%. The increase of the complexity of the source zone architectures will hinder the tracer migration, and the average accuracy of the heterogeneous source zones is 13.15% lower than that of the homogeneous source zones. The single well “push-pull” partitioning tracer test is more suitable for the ganglia-dominated contaminant source zones, and the average accuracy of the ganglia-dominated contaminant source zones is 15.74% higher than that of the pool-dominated source zones. The single-well “push-pull” partitioning tracer tests combined with numerical analysis can effectively estimate the distribution of residual NAPL, and are recommended for use in the fine investigation of DNAPL contaminated sites, so as to provide a reference for the risk assessment and the site remediation.
-

-
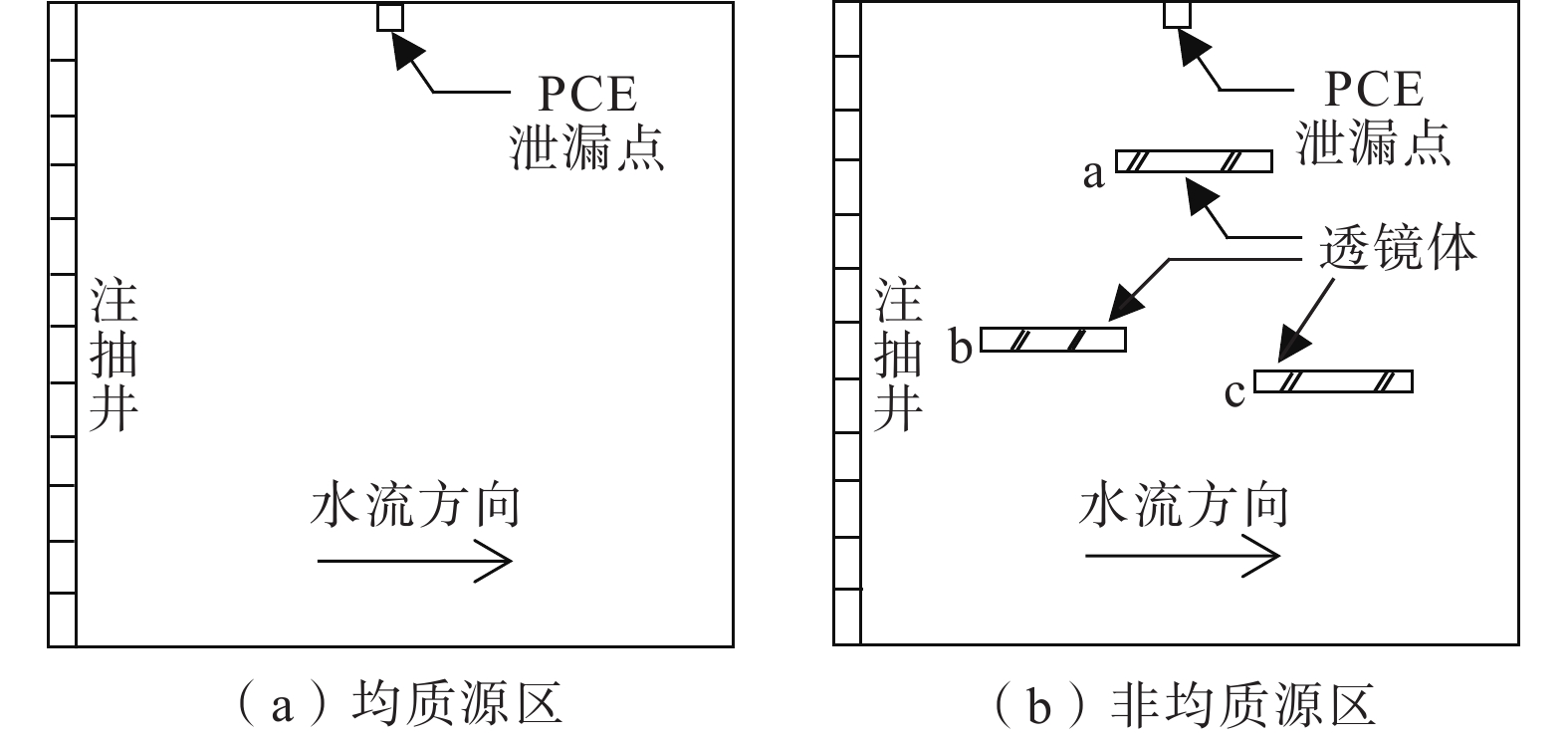
表 1 不同泄漏速率下生成的污染源区设置
Table 1. Cases of contaminant source zones with different leakage rates
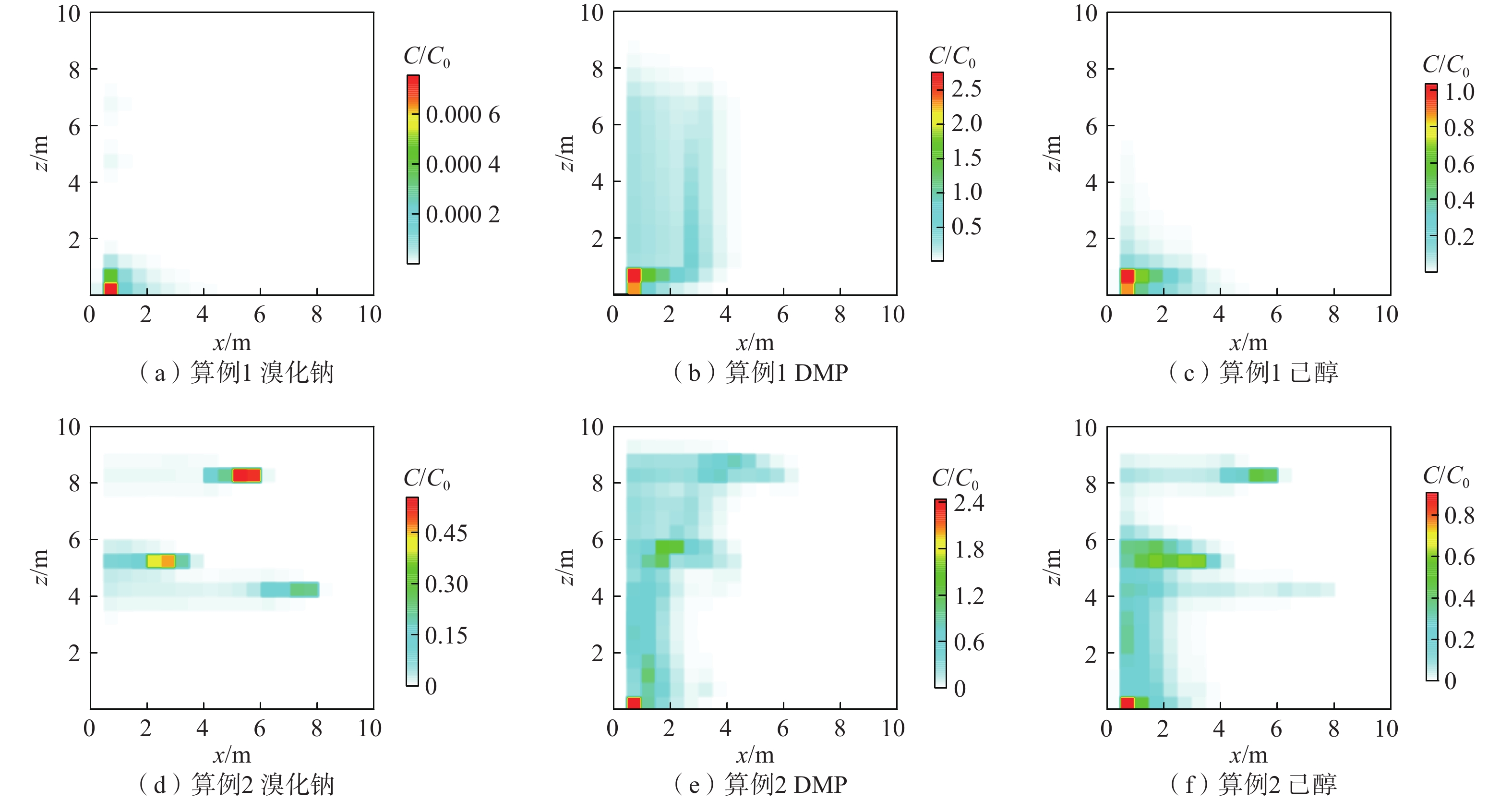
算例设置 污染源区结构 泄漏速率/(m3·d−1) 实际残留量/m3 GTP 算例1 均质 0.3 1.97 1.96 算例2 非均质 0.3 2.57 2.35 算例3 均质 0.9 3.02 0.90 算例4 非均质 0.9 3.49 0.71 表 2 模型参数
Table 2. Model parameters
研究区参数 取值 PCE的密度/(kg·m−3) 1.62 PCE的黏滞性/(mPa·S) 0.89 水力梯度 0.002 孔隙度 0.34 纵向弥散度/m 0.03 横向弥散度/m 0.009 DMP对PCE的分溶系数 27.5 己醇对PCE的分溶系数 8.5 表 3 毛管压力及相对渗透率参数
Table 3. Capillary pressure and relative permeability parameters
毛管压力模型
(Brooks-Corey)毛管压力
端点值C1 9.6 C2 19.9 毛管压力
指数λ1 −0.52 λ2 2 相对渗透率
模型
(Corey-Type)残余饱和度 Sw 0.24 So 0.2 端点相对
渗透率Pw 0.486 Po 0.65 相对渗透率指数 nw 2.85 no 2.7 注:下标1和2分别表示源区生成阶段和单井注抽阶段的参数;下标w和o分别代表水相和油相。 表 4 单井注抽示踪模拟设置
Table 4. The setting of single-well “push-pull” tracer simulation
模拟条件 注入阶段 抽取阶段 注入速率
/(m3·d−1)注入
天数/d抽取速率
/(m3·d−1)抽取
天数/d算例1、3 情景1 100 30 120 30 情景2 130 30 150 30 算例2、4 情景3 100 30 120 30 情景4 130 30 150 30 -
[1] 郑菲,高燕维,徐红霞,等. 非均质性对DNAPL污染源区结构特征影响的实验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(5):140 − 148. [ZHENG Fei,GAO Yanwei,XU Hongxia,et al. An experimental study of the influence of heterogeneity on the DNAPL source-zone architecture[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(5):140 − 148. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHENG Fei, GAO Yanwei, XU Hongxia, et al. An experimental study of the influence of heterogeneity on the DNAPL source-zone architecture[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(5): 140-148. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 赵科锋,王锦国,曹慧群. 含单裂隙非饱和带中轻非水相流体修复的数值模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):43 − 55. [ZHAO Kefeng,WANG Jinguo,CAO Huiqun. Numerical simulation of light non-aqueous phase liquids remediation in the unsaturated zone with single fractures[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):43 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Kefeng, WANG Jinguo, CAO Huiqun. Numerical simulation of light non-aqueous phase liquids remediation in the unsaturated zone with single fractures[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(5): 43-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 孙启明,高茂生,党显璋. 垃圾填埋场渗滤液变密度地下水溶质运移模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(4):1265 − 1274. [SUN Qiming,GAO Maosheng,DANG Xianzhang. Simulation of solute transport in variable-density groundwater for landfill leachate[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(4):1265 − 1274. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Qiming, GAO Maosheng, DANG Xianzhang. Simulation of solute transport in variable-density groundwater for landfill leachate[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2022, 52(4): 1265-1274. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] KUEPER B H,REDMAN D,STARR R C,et al. A field experiment to study the behavior of tetrachloroethylene below the water table:Spatial distribution of residual and pooled DNAPL[J]. Ground Water,1993,31(5):756 − 766. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1993.tb00848.x
[5] 卢文喜,罗建男,辛欣,等. 表面活性剂强化的DNAPLs污染含水层修复过程的数值模拟[J]. 地球科学,2012,37(5):1075 − 1081. [LU Wenxi,LUO Jiannan,XIN Xin,et al. Numerical simulation of surfactant enhanced aquifer remediation processes at DNAPLs contaminated aquifer[J]. Earth Science,2012,37(5):1075 − 1081. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LU Wenxi, LUO Jiannan, XIN Xin, et al. Numerical simulation of surfactant enhanced aquifer remediation processes at DNAPLs contaminated aquifer[J]. Earth Science, 2012, 37(5): 1075-1081. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 郭琼泽,张烨,姜蓓蕾,等. 表面活性剂增强修复地下水中PCE的砂箱实验及模拟[J]. 中国环境科学,2018,38(9):3398 − 3405. [GUO Qiongze,ZHANG Ye,JIANG Beilei,et al. Experiment and numerical simulation of surfactant-enhanced aquifer remediation in PCE contaminated laboratory sandbox[J]. China Environmental Science,2018,38(9):3398 − 3405. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Qiongze, ZHANG Ye, JIANG Beilei, et al. Experiment and numerical simulation of surfactant-enhanced aquifer remediation in PCE contaminated laboratory sandbox[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(9): 3398-3405. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 宋美钰,施小清,马春龙,等. 复杂DNAPL污染源区溶解相污染通量的升尺度计算[J]. 中国环境科学,2022,42(5):2095 − 2104. [SONG Meiyu,SHI Xiaoqing,MA Chunlong,et al. Upscaling dissolved phase mass flux for complex DNAPL source zones[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(5):2095 − 2104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SONG Meiyu, SHI Xiaoqing, MA Chunlong, et al. Upscaling dissolved phase mass flux for complex DNAPL source zones[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(5): 2095-2104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 周媛,杨盼瑞,郭会荣,等. 注入丁醇调节重非水液相密度的微空隙试验模拟[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(1):223 − 230. [ZHOU Yuan,YANG Panrui,GUO Huirong,et al. Injecting n-BuOH to achieve density conversion of dense non-aqueous phase liquid:Pore-scale experimental simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(1):223 − 230. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU Yuan, YANG Panrui, GUO Huirong, et al. Injecting n-BuOH to achieve density conversion of dense non-aqueous phase liquid: pore-scale experimental simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 223-230. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 郭琼泽,施小清,王慧婷,等. 井间分溶示踪估计重非水相污染物残留量的影响因素数值分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):165 − 172. [GUO Qiongze,SHI Xiaoqing,WANG Huiting,et al. Numerical analysis of the influencing factors for estimating DNAPL residual by the partitioning interwell tracer tests[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Qiongze, SHI Xiaoqing, WANG Huiting, et al. Numerical analysis of the influencing factors for estimating DNAPL residual by the partitioning interwell tracer tests[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(6): 165-172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘雪松, 张涛, 李敬杰. 污染场地调查技术综述[C]//中国环境科学学会. 2014中国环境科学学会学术年会论文集. 成都: 中国环境科学学会, 2014: 368 − 374
LIU Xuesong, ZHANG Tao, LI Jingjie. A review of contaminated site survey techniques[C]//Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences. Proceedings of 2014 annual meeting of Chinese society for environmental sciences. Chengdu: Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences, 2014: 6267 − 6273. (in Chinese)
[11] 王波,王宇,张贵,等. 滇东南泸江流域岩溶地下水质量及污染影响因素研究[J]. 地球学报,2021,42(3):352 − 362. [WANG Bo,WANG Yu,ZHANG Gui,et al. A study of quality and pollution factors of Karst groundwater in Lujiang River Basin in southeast Yunnan[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2021,42(3):352 − 362. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Bo, WANG Yu, ZHANG Gui, et al. A study of quality and pollution factors of Karst groundwater in Lujiang River Basin in southeast Yunnan[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(3): 352-362. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 马春龙,施小清,许伟伟,等. 基于自组织神经网络的污染场地多监测指标相关性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):191 − 202. [MA Chunlong,SHI Xiaoqing,XU Weiwei,et al. Correlation analysis of multiple monitoring indicators of contaminated site based on self-organizing map[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):191 − 202. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008001
MA Chunlong, SHI Xiaoqing, XU Weiwei, et al. Correlation analysis of multiple monitoring indicators of contaminated site based on self-organizing map[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(3): 191-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008001
[13] JIN Minquan,DELSHAD M,DWARAKANATH V,et al. Partitioning tracer test for detection,estimation,and remediation performance assessment of subsurface nonaqueous phase liquids[J]. Water Resources Research,1995,31(5):1201 − 1211. doi: 10.1029/95WR00174
[14] YOUNG C M,JACKSON R E,JIN M,et al. Characterization of a TCE DNAPL zone in alluvium by partitioning tracers[J]. Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation,1999,19(1):84 − 94.
[15] MORENO-BARBERO E,ILLANGASEKARE T H. Influence of dense nonaqueous phase liquid pool morphology on the performance of partitioning tracer tests:Evaluation of the equilibrium assumption[J]. Water Resources Research,2006,42(4):W04408.
[16] DRIDI L,POLLET I,RAZAKARISOA O,et al. Characterisation of a DNAPL source zone in a porous aquifer using the Partitioning Interwell Tracer Test and an inverse modelling approach[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2009,107(1/2):22 − 44.
[17] CHO I,JU Y,LEE S S,et al. Characterization of a NAPL-contaminated site using the partitioning behavior of noble gases[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2020,235:103733. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2020.103733
[18] ISTOK J D,FIELD J A,SCHROTH M H,et al. Single-well “Push−Pull” partitioning tracer test for NAPL detection in the subsurface[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2002,36(12):2708 − 2716.
[19] HEBIG K H,ZEILFELDER S,ITO N,et al. Study of the effects of the chaser in push-pull tracer tests by using temporal moment analysis[J]. Geothermics,2015,54:43 − 53. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.11.004
[20] WANG Quanrong,ZHAN Hongbin,WANG Yanxin. Single-well push-pull test in transient Forchheimer flow field[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2017,549:125 − 132. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.03.066
[21] 李旭,苏世林,文章,等. 单井注抽试验测算地下水流速的数值分析[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(2):633 − 641. [LI Xu,SU Shilin,WEN Zhang,et al. Numerical analysis of estimating groundwater velocity through single-well push-pull test[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(2):633 − 641. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Xu, SU Shilin, WEN Zhang, et al. Numerical analysis of estimating groundwater velocity through single-well push-pull test[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(2): 633-641. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] GELHAR L W,COLLINS M A. General analysis of longitudinal dispersion in nonuniform flow[J]. Water Resources Research,1971,7(6):1511 − 1521. doi: 10.1029/WR007i006p01511
[23] HALL S H,LUTTRELL S P,CRONIN W E. A method for estimating effective porosity and ground-water velocity[J]. Ground Water,1991,29(2):171 − 174. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1991.tb00506.x
[24] HAGGERTY R,SCHROTH M H,ISTOK J D. Simplified method of “push-pull” test data analysis for determining in situ reaction rate coefficients[J]. Ground Water,1998,36(2):314 − 324. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1998.tb01097.x
[25] ISTOK J D,FIELD J A,SCHROTH M H,et al. Laboratory and field investigation of surfactant sorption using single-well,“push-pull” tests[J]. Ground Water,1999,37(4):589 − 598. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1999.tb01146.x
[26] SCHROTH M H,ISTOK J D,HAGGERTY R. In situ evaluation of solute retardation using single-well push-pull tests[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2000,24(1):105 − 117. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1708(00)00023-3
[27] TOMICH J F,DALTON R L,DEANS H A,et al. Single-well tracer method to measure residual oil saturation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology,1973,25(2):211 − 218. doi: 10.2118/3792-PA
[28] HUANG Junqi,CHRIST J A,GOLTZ M N. Analytical solutions for efficient interpretation of single-well push-pull tracer tests[J]. Water Resources Research,2010,46(8):W08538.
[29] DAVIS B M,ISTOK J D,SEMPRINI L. Push-pull partitioning tracer tests using radon-222 to quantify non-aqueous phase liquid contamination[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2002,58(1/2):129 − 146.
[30] DAVIS B M,ISTOK J D,SEMPRINI L. Numerical simulations of radon as an in situ partitioning tracer for quantifying NAPL contamination using push-pull tests[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2005,78(1/2):87 − 103.
[31] AL-SHALABI E W,LUO Haishan,DELSHAD M,et al. Single-well chemical-tracer modeling of low-salinity-water injection in carbonates[J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering,2017,20(1):118 − 133.
[32] 陈梦佳,吴剑锋,孙晓敏,等. 地下水典型非水相液体污染运移模拟的尺度提升研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):11 − 18. [CHEN Mengjia,WU Jianfeng,SUN Xiaomin,et al. Upscaling of PCE transport modeling based on UTCHEM in heterogeneous porous media[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):11 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201901032
CHEN Mengjia, WU Jianfeng, SUN Xiaomin, et al. Upscaling of PCE transport modeling based on UTCHEM in heterogeneous porous media[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(1): 11-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201901032
[33] ARIS R. On the dispersion of linear kinematic waves[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A Mathematical and Physical Sciences,1958,245:268 − 277.
[34] CUNNINGHAM J A,ROBERTS P V. Use of temporal moments to investigate the effects of nonuniform grain-size distribution on the transport of sorbing solutes[J]. Water Resources Research,1998,34(6):1415 − 1425. doi: 10.1029/98WR00702
[35] 张国俊,孟洪,薛峰,等. TCE/PCE的DNAPL污染及零价铁墙防治技术[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备,2006(4):12 − 18. [ZHANG Guojun,MENG Hong,XUE Feng,et al. TCE/PCE DNAPL pollution and zero-valent iron technology[J]. Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control,2006(4):12 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Guojun, MENG Hong, XUE Feng, et al. TCE/PCE DNAPL pollution and zero-valent iron technology[J]. Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control, 2006(4): 12-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 程洲,吴吉春,徐红霞,等. DNAPL在透镜体及表面活性剂作用下的运移研究[J]. 中国环境科学,2014,34(11):2888 − 2896. [CHENG Zhou,WU Jichun,XU Hongxia,et al. Investigation of the migration characteristic of DNAPL in aquifer with lenses and under the action of surfactant flushing[J]. China Environmental Science,2014,34(11):2888 − 2896. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHENG Zhou, WU Jichun, XU Hongxia, et al. Investigation of the migration characteristic of DNAPL in aquifer with lenses and under the action of surfactant flushing[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(11): 2888-2896. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: