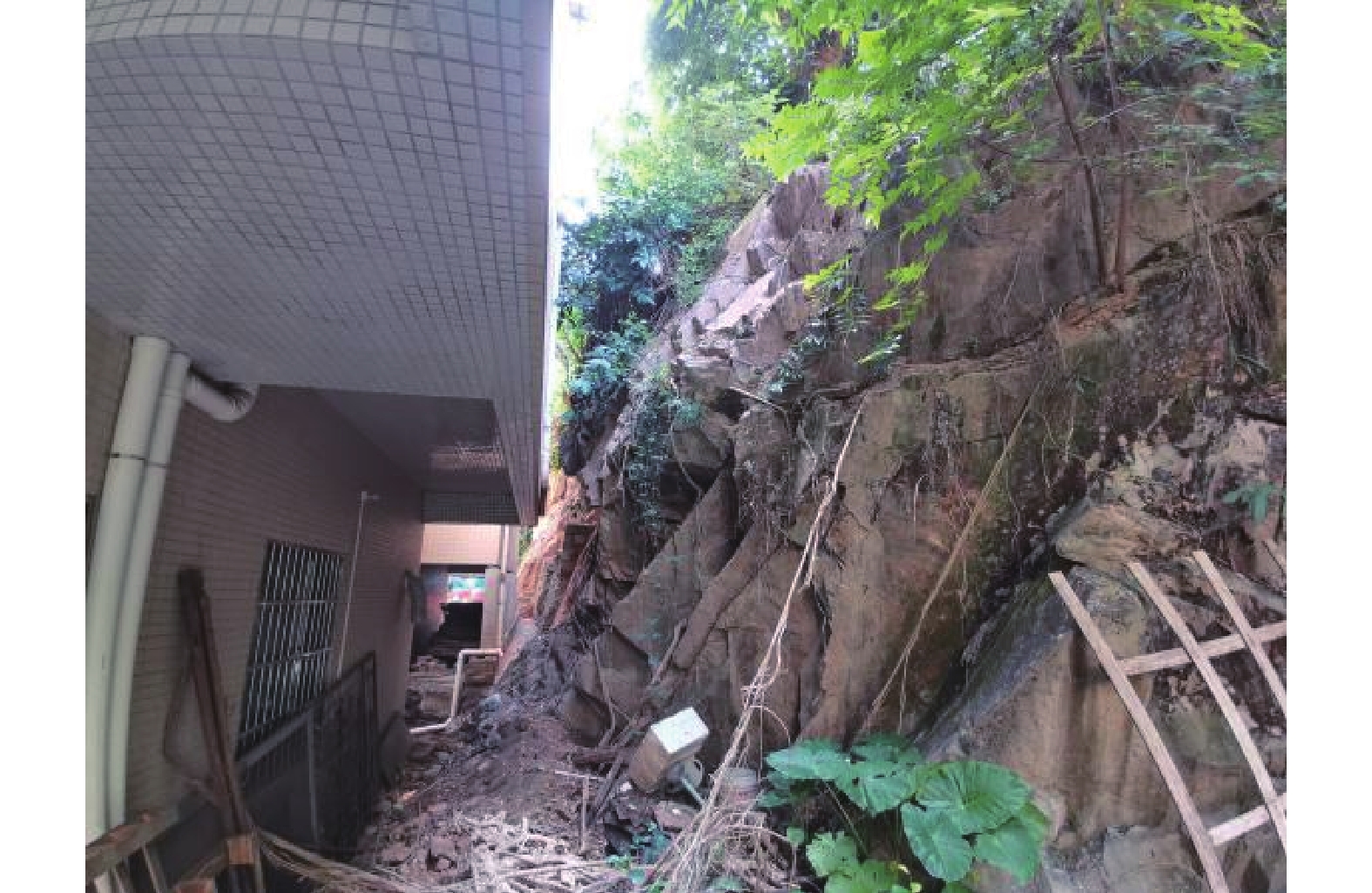
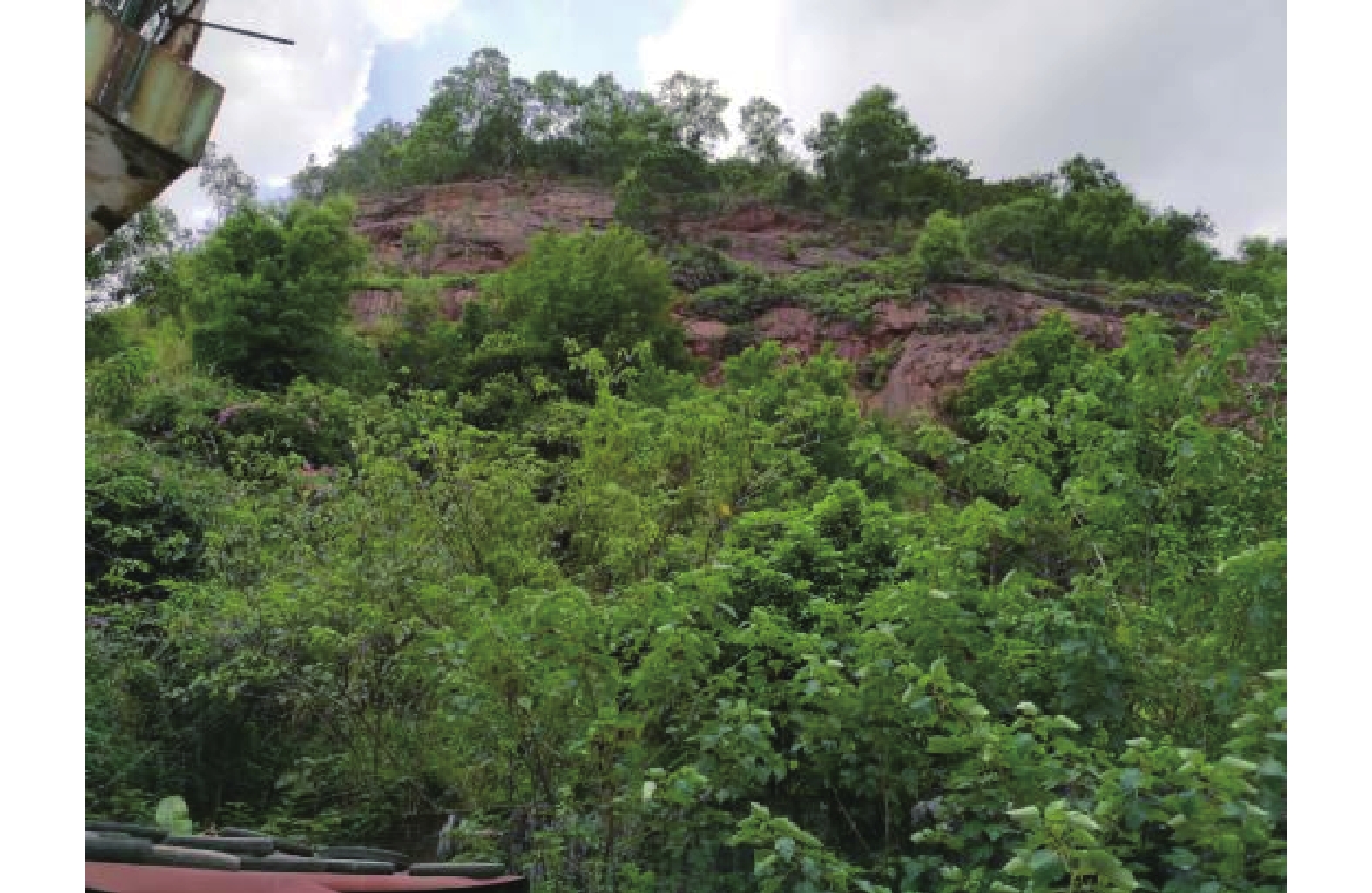
Calculation methods of the collapse influence range of a simple rock slope in the Guangzhou area
-
摘要:
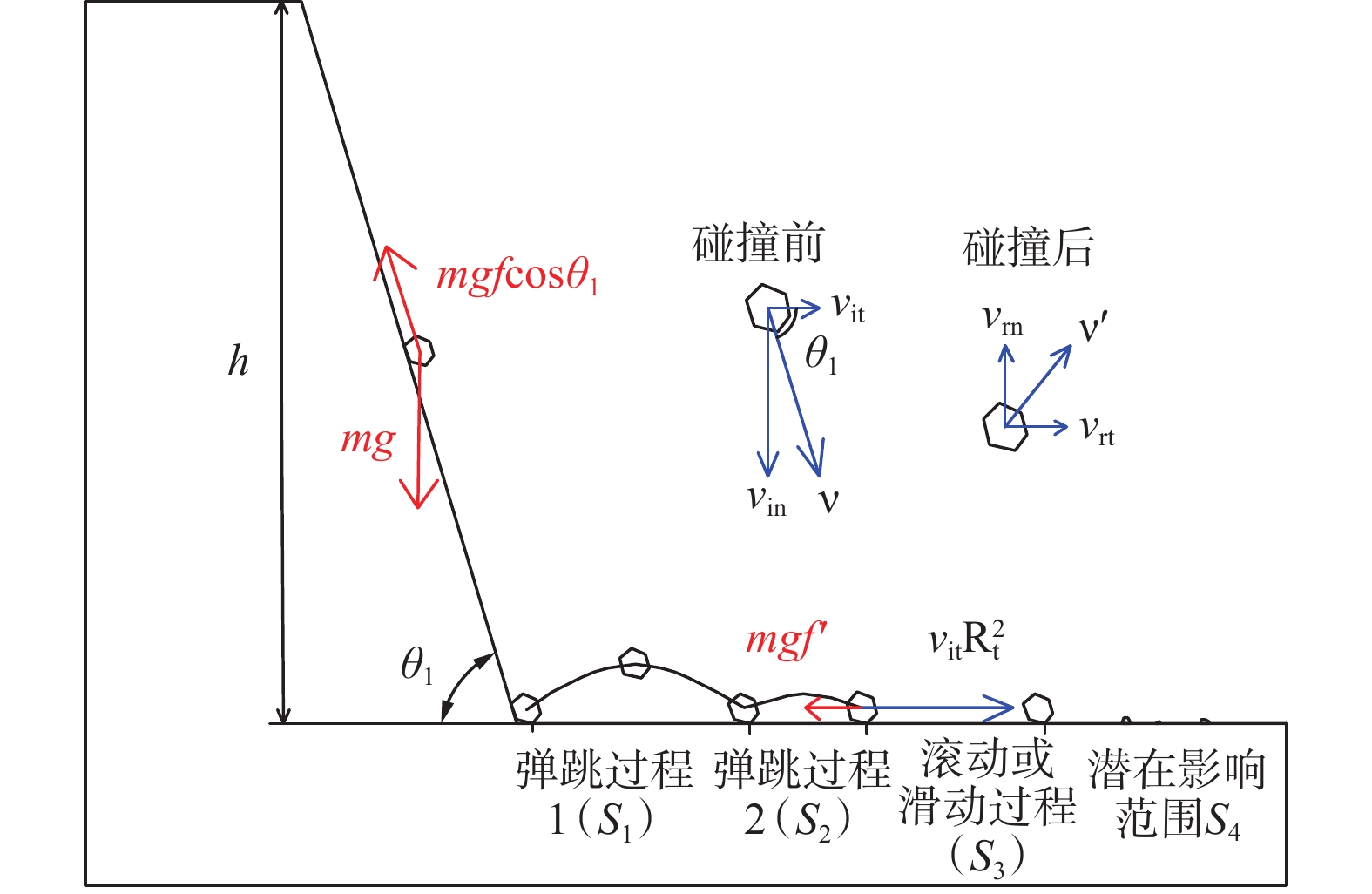
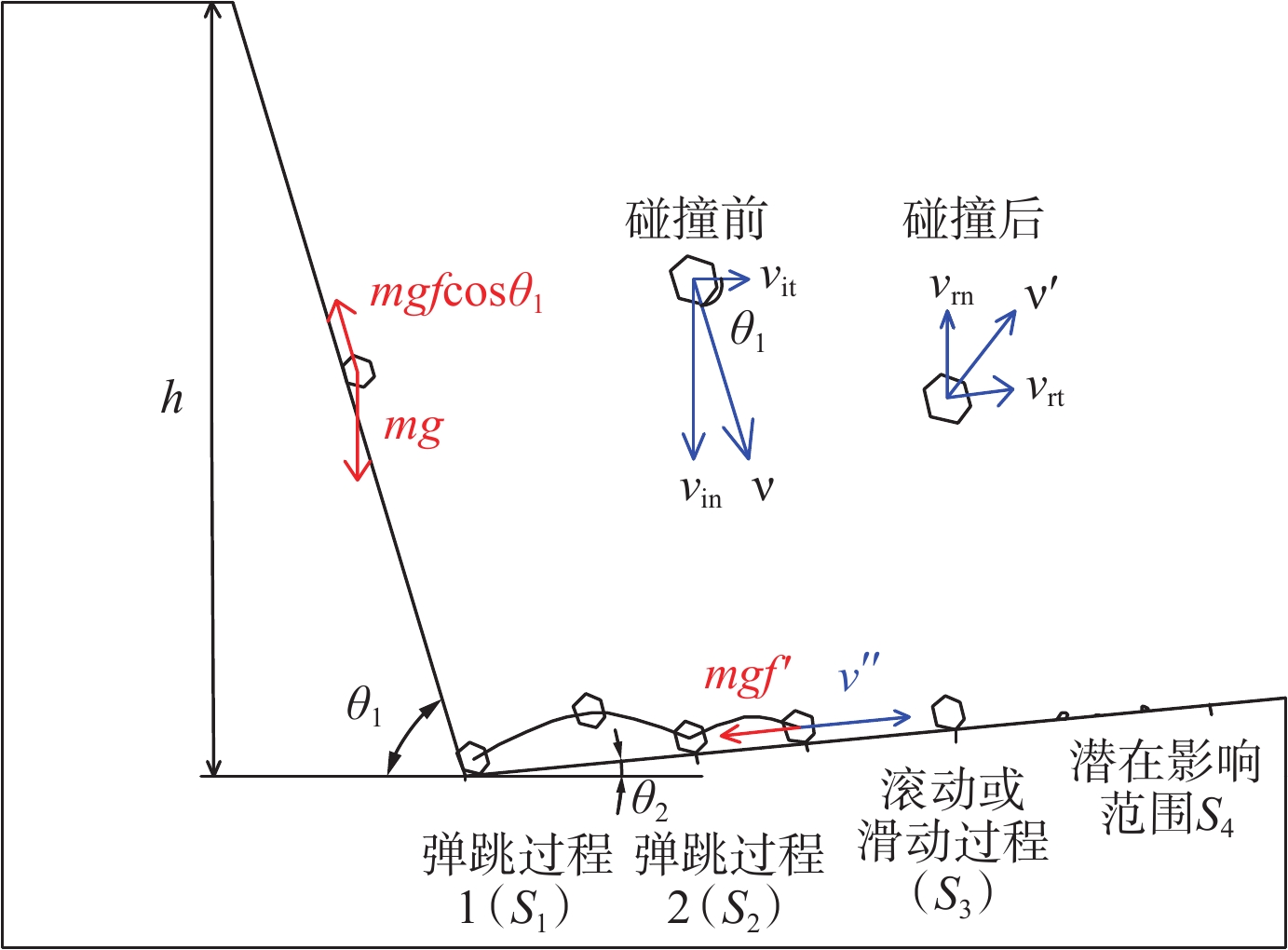
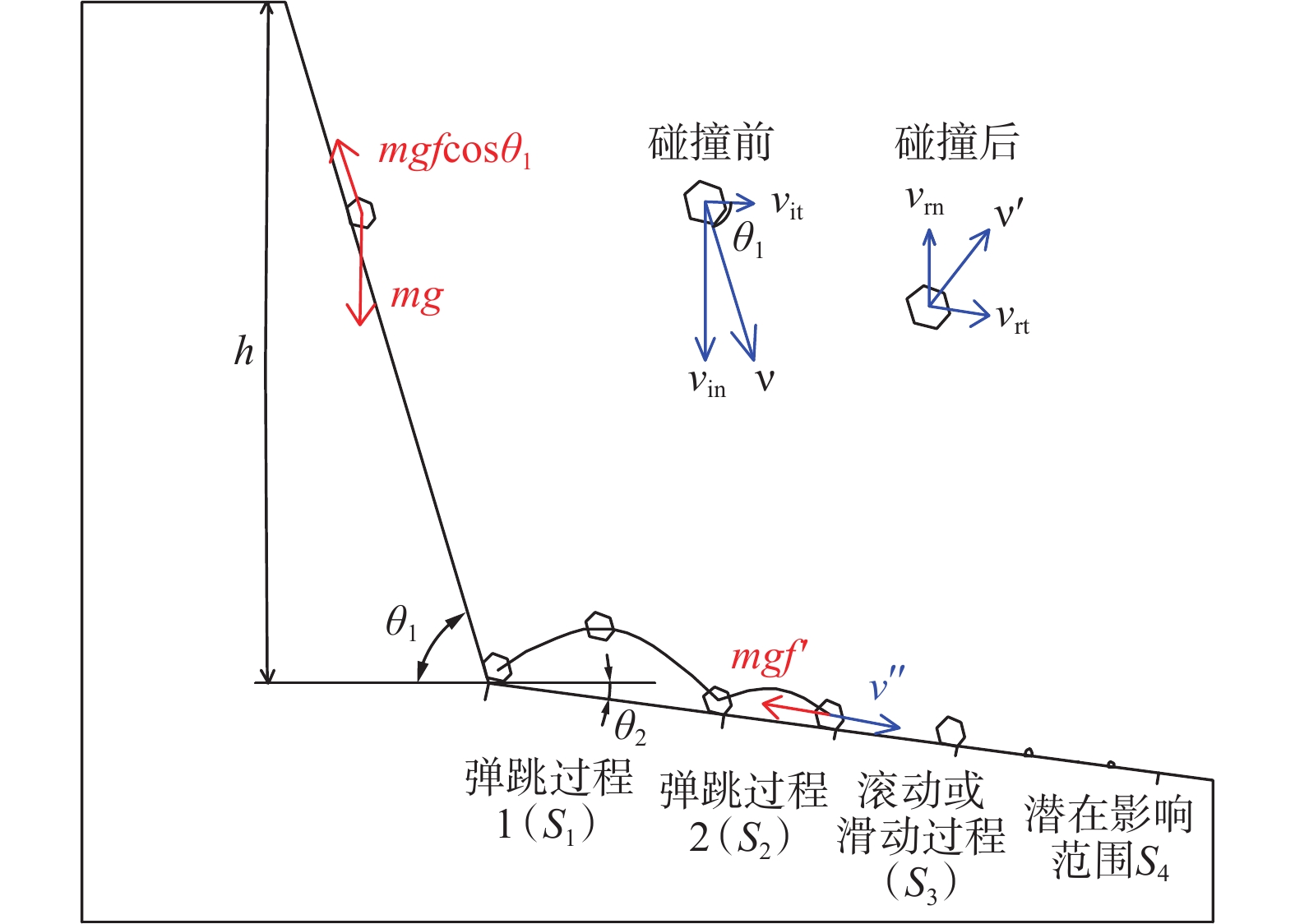
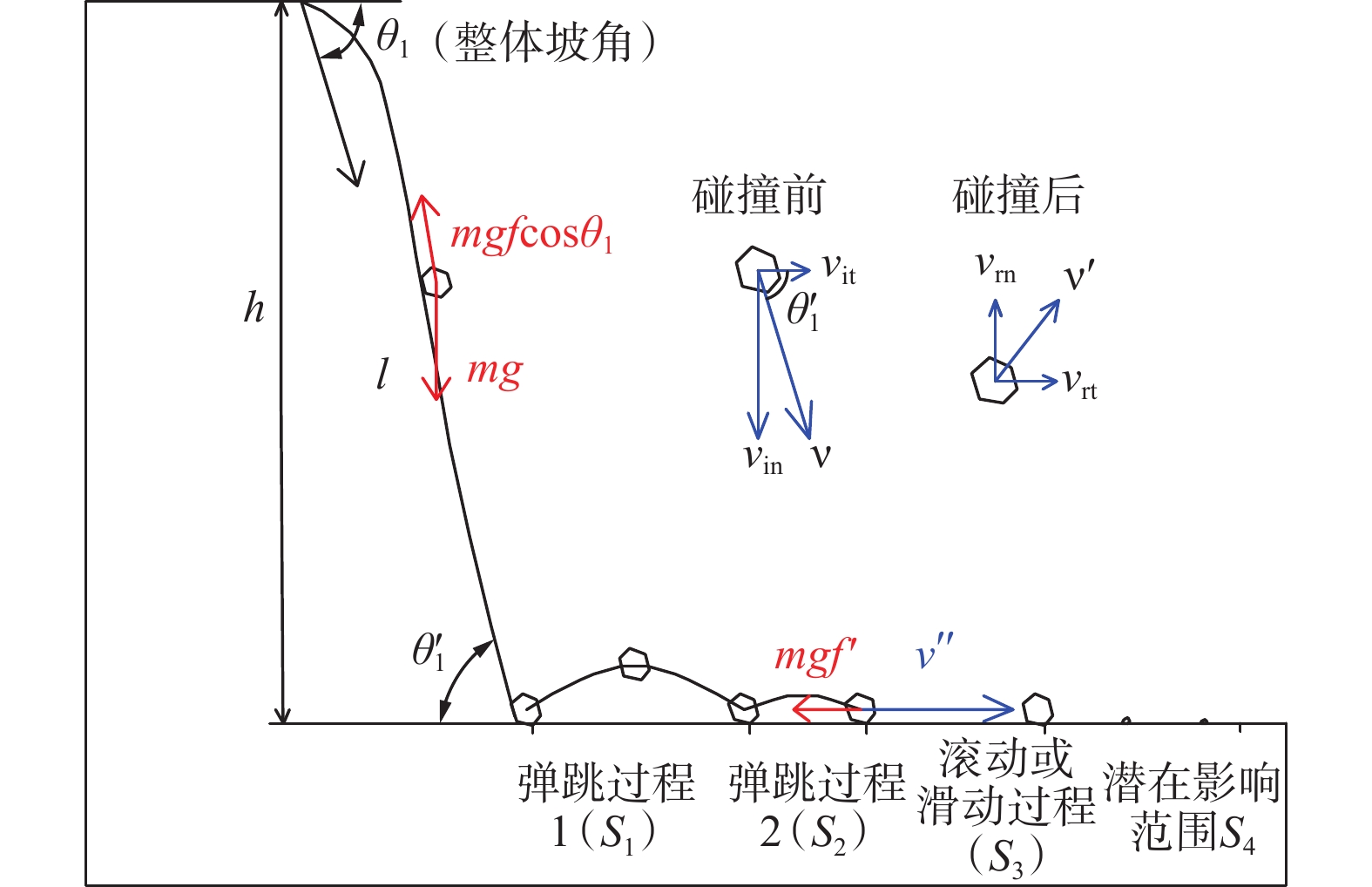
边坡危岩体产生的岩质崩塌灾害突发性强、破坏能力强,是一种危害极大的地质灾害。防治边坡危岩体的关键在于划定危岩体的影响范围,准确评估边坡危岩体影响范围,提升边坡危岩体灾害防治能力,降低崩塌威胁,目前亟需完善边坡危岩体影响范围的计算模型。依据广州市危岩体调查成果归纳出常见边坡危岩体的类型和坡形特征,分类建立危岩体影响范围物理几何模型,综合考虑坡面摩擦力、块体碰撞、弹跳、碎裂、接触面覆盖物性质和恢复系数、地形条件、地震等崩塌运动过程的主要影响因素,通过概化运动过程要素建立起直线型、曲线型边坡在不同坡度条件下崩塌影响范围的计算模型,并根据地震力对崩塌体动能的影响求得地震工况下崩塌影响范围的扩大系数。该模型在前人研究基础上进一步归纳出坡形分类形成几何模型,依据运动过程推求出常见工况不同地形条件下边坡危岩体最大影响范围的计算模型,获取坡高、坡度和地表特征后可依据该模型计算得出危岩体影响范围。通过实际案例验证比对,计算结果相对误差较小,且能预留一定的安全距离,可用于常见坡形边坡危岩体影响范围评价,为边坡危岩体防治提供依据。
Abstract:The rock collapse disaster caused by the dangerous rock mass of slope is a geological disaster with strong sudden occurrence and destructive ability. The key to prevent and control the dangerous rock mass of slope is to delineate the influence range of the dangerous rock mass. In order to accurately assess the influence range of the dangerous rock mass of slope, improve the disaster prevention ability of the dangerous rock mass of slope and reduce the collapse threat, it is urgent to improve the calculation model of the influence range of the dangerous rock mass of slope. Based on the survey results of dangerous rock mass in Guangzhou, the types and slope shape characteristics of common dangerous rock mass in slope are summarized, and the physical and geometric model of the influence range of dangerous rock mass is established. The main factors affecting the collapse movement process, such as slope friction, block collision, bounce, fragmentation, properties of contact surface covering and coefficient of restitution, terrain conditions and earthquake, are comprehensively considered. The calculation model of collapse influence range of linear and curved slope under different slope conditions is established by generalized motion process elements, and the expansion coefficient of collapse influence range under earthquake conditions is obtained according to the influence of earthquake force on the kinetic energy of collapse body. On the basis of previous studies, this model further summarizes the geometric model of slope shape classification and formation, and calculates the calculation model of the maximum influence range of dangerous rock mass under common working conditions and different terrain conditions according to the movement process. After obtaining the slope height, slope and surface characteristics, the influence range of dangerous rock mass can be calculated according to this model. Through the verification and comparison of actual cases, the relative error of calculation results is small, and a certain safety distance can be reserved, which can be used for the evaluation of the influence range of dangerous rock mass in common slope slope, and provide a basis for the prevention and control of dangerous rock mass in slope.
-
Key words:
- rock collapse /
- movement distance /
- scope of influence /
- coefficient of restitution
-

-
表 1 常见坡面岩块滚动摩擦系数
Table 1. Rolling friction coefficients of common slope blocks
坡面特征 滚动摩擦系数 光滑岩面、混凝土表面 0.30~0.60 软岩面、强风化硬岩面 0.40~0.60 块石堆积坡面 0.55~0.70 密实碎石堆积坡面、硬土坡面、(植被灌木从)发育 0.55~0.85 密实碎石堆积坡面、硬土坡面、植被不发育或少量杂草 0.50~0.75 松散碎石坡面、软土坡面、植被(灌木丛为主)发育 0.50~0.85 软土坡面、植被不发育或少量杂草 0.50~0.85 表 2 崩塌防治工程勘察规范推荐岩块恢复系数
Table 2. Block springback coefficient recommended by the investigation code of collapse prevention engineering
碰撞系数 地面岩性 硬岩 软岩 硬土 普通土 松土 ${R}_{{\rm{n}}}$ 0.4 0.35 0.30 0.26 0.22 ${R}_{{\rm{t}}}$ 0.86 0.84 0.81 0.75 0.65 表 3 铁道部运输局推荐岩块恢复系数
Table 3. Rock springback coefficient recommended by the Transportation Bureau of the Ministry of Railways
坡面特征 ${{R} }_{\rm{n} }$ 光滑而坚硬的表面和铺砌面,如人行道或光滑的基岩面 0.37~0.42 多数为基岩和砾岩区的斜面 0.33~0.37 硬土边坡 0.30~0.33 软土边坡 0.28~0.30 坡面特征 ${{R} }_{\rm{t} }$ 光滑而坚硬的表面和铺砌面,如人行道或光滑的基岩面 0.87~0.92 多数为基岩和无植被覆盖的斜坡 0.83~0.87 多数为有少量植被的斜坡 0.82~0.85 植被覆盖的斜坡和有稀少植被覆盖的土质边坡 0.80~0.83 灌木林覆盖的土质边坡 0.78~0.82 表 4 不同计算方法所得影响范围对照表
Table 4. Comparison of the influence range obtained with different calculation methods
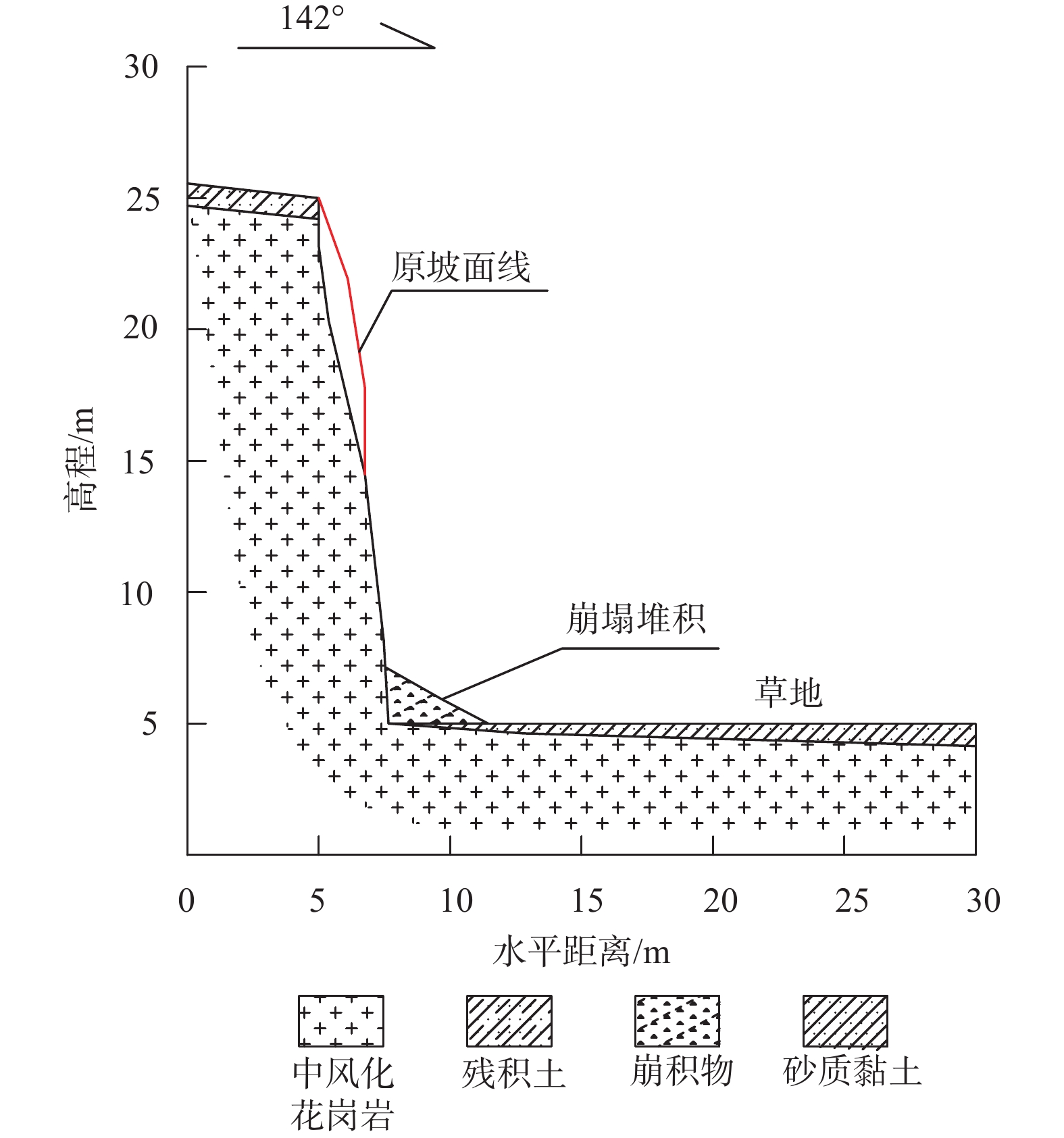
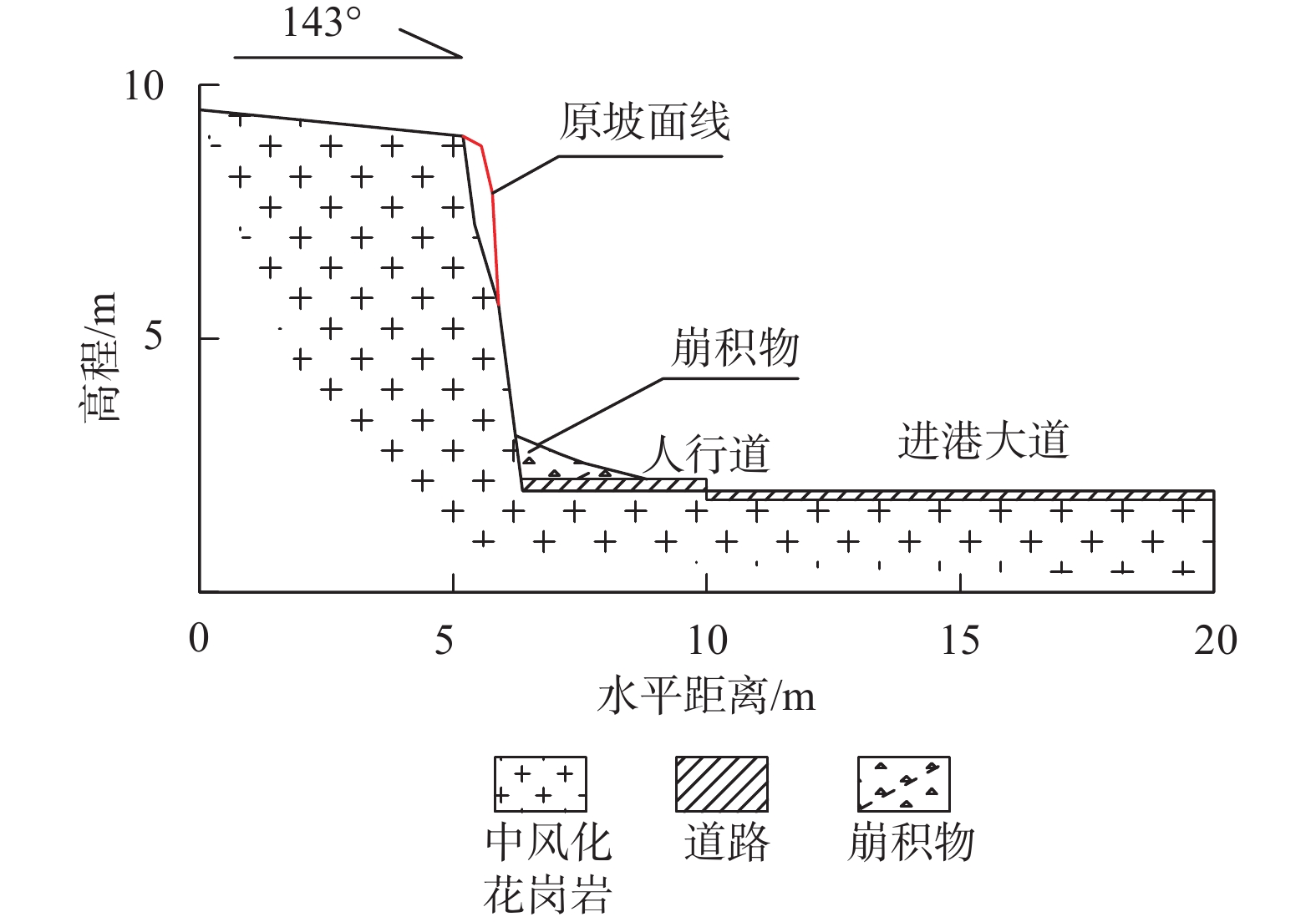
边坡名称 南沙区大角一路北侧 南沙进港大道北侧 模型计算运动距离/m 1.54 2.32 模型计算影响范围/m 5.52 3.7 RocFall模型影响范围/m 4.65 8.9 实际崩塌体堆积范围/m 3.65 2.6 -
[1] 胡厚田. 崩塌落石研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2005, 22(增刊1): 387 − 391
HU Houtian. Research on the collapse and falling stone[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2005, 22(Sup 1): 387 − 391. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 刘传正. 中国崩塌滑坡泥石流灾害成因类型[J]. 地质论评,2014,60(4):858 − 868. [LIU Chuanzheng. Genetic types of landslide and debris flow disasters in China[J]. Geological Review,2014,60(4):858 − 868. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2014.04.017
LIU Chuanzheng. Genetic types of landslide and debris flow disasters in China[J]. Geological Review, 2014, 60(4): 858-868. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2014.04.017
[3] 亚南,王兰生,赵其华,等. 崩塌落石运动学的模拟研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,1996,7(2):25 − 32. [YA Nan,WANG Lansheng,ZHAO Qihua,et al. Simulation study of rockfall kinematics[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Enveronment Preservation,1996,7(2):25 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YA Nan, WANG Lansheng, ZHAO Qihua, et al. Simulation study of rockfall kinematics[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Enveronment Preservation, 1996, 7(2): 25-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 肖智勇. 高陡边坡崩塌危岩体运动轨迹及冲击能量分析[J]. 路基工程,2021(2):187 − 192. [XIAO Zhiyong. Analysis of movement trajectory and impact energy of dangerous rock mass in high and steep slope collapse[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2021(2):187 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.202011017
XIAO Zhiyong. Analysis of movement trajectory and impact energy of dangerous rock mass in high and steep slope collapse[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2021(2): 187-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.202011017
[5] 廖俊展. 地质灾害治理设计中崩塌落石的运动特征分析[J]. 山西建筑,2021,47(19):72 − 75. [LIAO Junzhan. Analysis on the motion characteristic of rockfall in the designing about geological disaster treatment[J]. Shanxi Architecture,2021,47(19):72 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13719/j.cnki.1009-6825.2021.19.027
LIAO Junzhan. Analysis on the motion characteristic of rockfall in the designing about geological disaster treatment[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2021, 47(19): 72-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13719/j.cnki.1009-6825.2021.19.027
[6] 王伟才. 崩塌落石运动特征评判及量化分析[J]. 西部探矿工程,2021,33(8):15 − 18. [WANG Weicai. Evaluation and quantitative analysis of the characteristics of rockfall movement[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering,2021,33(8):15 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2021.08.005
WANG Weicai. Evaluation and quantitative analysis of the characteristics of rockfall movement[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2021, 33(8): 15-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2021.08.005
[7] 李娟,何亮,荀晓慧. 强震作用下崩塌滚石冲击耗能损伤演化分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):157 − 163. [LI Juan,HE Liang,XUN Xiaohui. An evolution analysis of the impact energy damage of collapsed rolling stones under strong earthquakes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):157 − 163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Juan, HE Liang, XUN Xiaohui. An evolution analysis of the impact energy damage of collapsed rolling stones under strong earthquakes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 157-163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] WANG Xing,XIA Yongxu,ZHOU Tianyue. Theoretical analysis of rockfall impacts on the soil cushion layer of protective structures[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2018,2018:1 − 18.
[9] 王林峰,刘丽,唐芬,等. 基于落石棚洞冲击试验的落石冲击力研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2018,38(6):973 − 979. [WANG Linfeng,LIU Li,TANG Fen,et al. Study on impact force of rockfall impact experiment on shed tunnel[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2018,38(6):973 − 979. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.2018.06.011
WANG Linfeng, LIU Li, TANG Fen, et al. Study on impact force of rockfall impact experiment on shed tunnel[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2018, 38(6): 973-979. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.2018.06.011
[10] 吴建利,胡卸文,梅雪峰,等. 落石冲击混凝土板与缓冲层组合结构的动力响应[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):78 − 87. [WU Jianli,HU Xiewen,MEI Xuefeng,et al. Dynamic response of RC slab with cushion layer composed of sandy soil to rockfall impact[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):78 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202004029
WU Jianli, HU Xiewen, MEI Xuefeng, et al. Dynamic response of RC slab with cushion layer composed of sandy soil to rockfall impact[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(1): 78-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202004029
[11] ZHU Chun,WANG Dongsheng,XIA Xing,et al. The effects of gravel cushion particle size and thickness on the coefficient of restitution in rockfall impacts[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2018,18(6):1811 − 1823. doi: 10.5194/nhess-18-1811-2018
[12] ZHANG Yulong,LIU Zaobao,SHI Chong,et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of block shape irregularity and its effects on block impacts using an energy-based approach[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2018,51(4):1173 − 1191. doi: 10.1007/s00603-017-1385-x
[13] CAVIEZEL A,DEMMEL S E,RINGENBACH A,et al. Reconstruction of four-dimensional rockfall trajectories using remote sensing and rock-based accelerometers and gyroscopes[J]. Earth Surface Dynamics,2019,7(1):199 − 210. doi: 10.5194/esurf-7-199-2019
[14] AZZONI A,LA BARBERA G,ZANINETTI A. Analysis and prediction of rockfalls using a mathematical model[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics,1995,32(7):709 − 724.
[15] CROSTA G B,AGLIARDI F. A methodology for physically based rockfall hazard assessment[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2003,3(5):407 − 422. doi: 10.5194/nhess-3-407-2003
[16] HUNGR O,EVANS S G,BOVIS M J,et al. A review of the classification of landslides of the flow type[J]. Environmental and Engineering Geoscience,2001,7(3):221 − 238. doi: 10.2113/gseegeosci.7.3.221
[17] BOURRIER F,LAMBERT S,BAROTH J. A reliability-based approach for the design of rockfall protection fences[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2015,48(1):247 − 259. doi: 10.1007/s00603-013-0540-2
[18] DORREN L, BERGER F. New approaches for 3D rockfall modelling with or without the effect of forest in Rockyfor3D[C]//EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts. 2010.
[19] 彭卫平,刘伟. 广州城市地质研究与城市可持续发展[J]. 城市勘测,2005(6):51 − 53. [PENG Weiping,LIU Wei. Guangzhou urban geological research and urban sustainable development[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2005(6):51 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PENG Weiping, LIU Wei. Guangzhou urban geological research and urban sustainable development[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2005(6): 51-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 曾志林. 广东省广州市黄埔区保利林语山庄会所后山崩塌地质灾害勘查报告[R]. 广州: 广东省有色矿山地质灾害防治中心, 2019
Zeng Zhilin. Geological disaster investigation report of the collapse of the back mountain of the Baoli Linyu Villa Club in Huangpu District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province[R]. Guangzhou: Guangdong non-ferrous mine geological disaster prevention center, 2019. (in Chinese)
[21] 吕庆,孙红月,翟三扣,等. 边坡滚石运动的计算模型[J]. 自然灾害学报,2003,12(2):79 − 84. [吕庆LÜ Qing,SUN Hongyue,ZHAI Sankou,et al. Evaluation models of rockfall trajectory[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2003,12(2):79 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2003.0214
吕庆LÜ Qing, SUN Hongyue, ZHAI Sankou, et al. Evaluation models of rockfall trajectory[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2003, 12(2): 79-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2003.0214
[22] 韩振华,陈鑫,王学良,等. 四川罗家青杠岭崩塌风险的定量评价研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(2):520 − 530. [HAN Zhenhua,CHEN Xin,WANG Xueliang,et al. Risk assessment for luojiaqinggangling rockfall[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(2):520 − 530. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.02.032
HAN Zhenhua, CHEN Xin, WANG Xueliang, et al. Risk assessment for luojiaqinggangling rockfall[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(2): 520-530. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.02.032
[23] 中国地质灾害防治工程行业协会. 崩塌防治工程勘查规范: TCAGHP011-2018[S]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2018.
China Geological Disaster Prevention Engineering Industry Association. Exploration specification for collapse prevention project: TCAGHP011-2018[S]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2018. (in Chinese)
[24] 程强,苏生瑞. 汶川地震崩塌滚石坡面运动特征[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(3):772 − 776. [CHENG Qiang,SU Shengrui. Movement characteristics of collapsed stones on slopes induced by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(3):772 − 776. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2014.03.011
CHENG Qiang, SU Shengrui. Movement characteristics of collapsed stones on slopes induced by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(3): 772-776. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2014.03.011
[25] 于帅印. 河南省山地丘陵区地质灾害风险评价[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018
YU Shuaiyin. Risk assessment of geological disasters in mountainous and hilly areas of Henan Province[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 陆明. 危岩崩塌运动数值模拟及治理措施研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2017
LU Ming. Study on numerical simulation of dangerous rock collapse movement and control measures[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 王颂,张路青,周剑,等. 青藏铁路设兴村段崩塌特征分析与运动学模拟[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(4):784 − 792. [WANG Song,ZHANG Luqing,ZHOU Jian,et al. Characteristic analysis and kinematic simulation of rockfall along shexing village section of Qinghai-Xizang railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(4):784 − 792. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-519
WANG Song, ZHANG Luqing, ZHOU Jian, et al. Characteristic analysis and kinematic simulation of rockfall along shexing village section of Qinghai-Xizang railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(4): 784-792. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-519
-
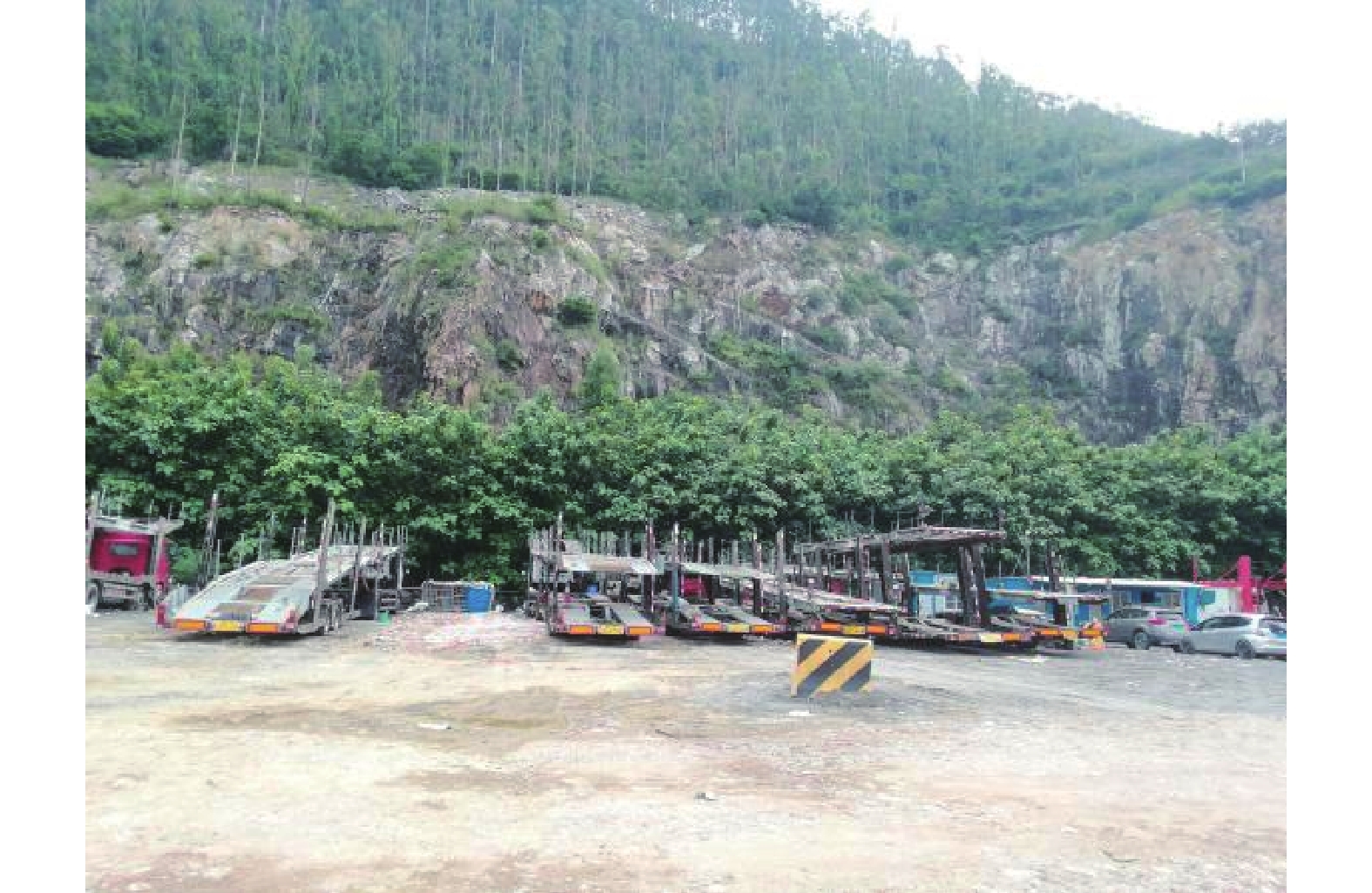




 下载:
下载: