High-level collapse risk identification based on oblique photography and InSAR technology
-
摘要:
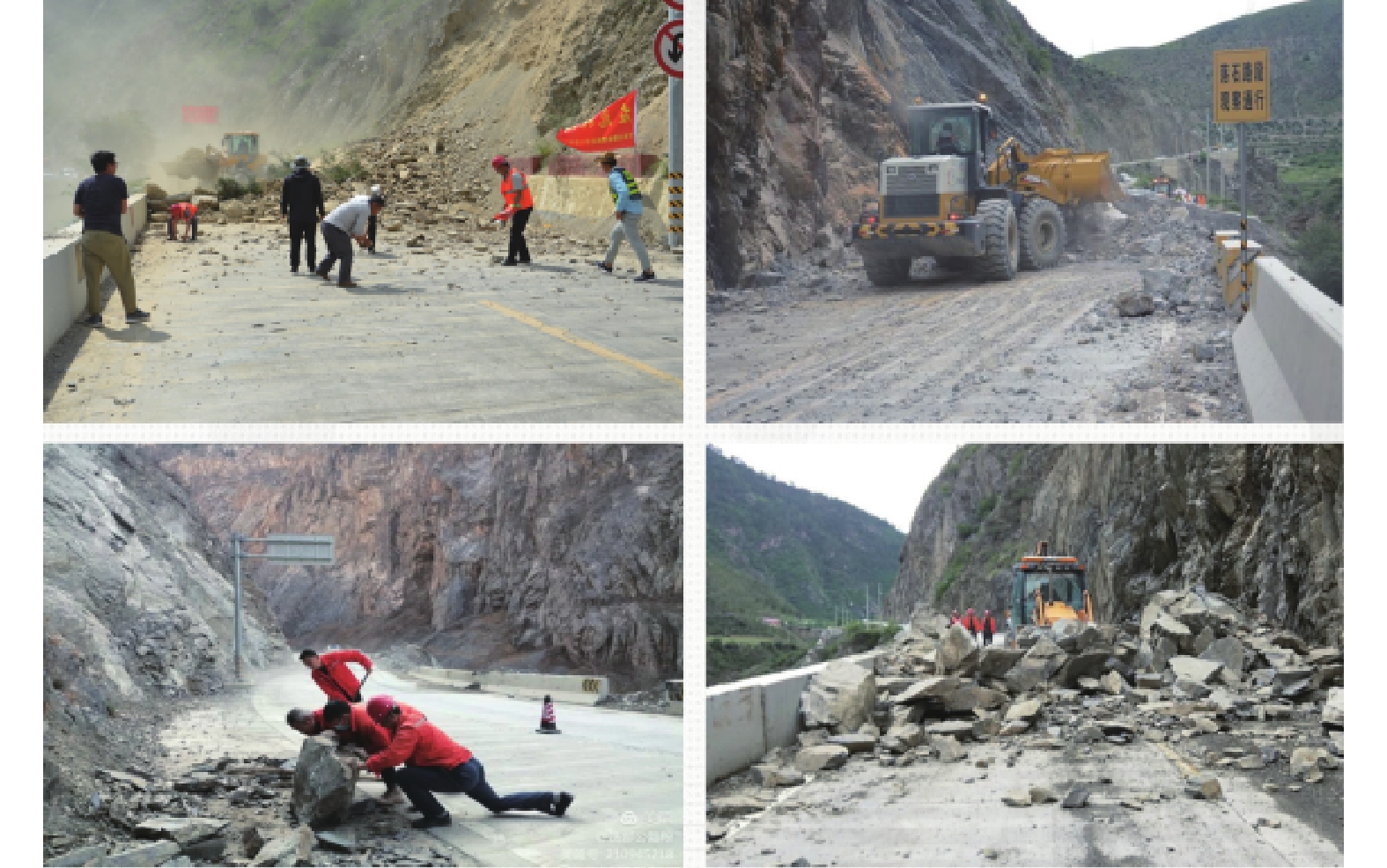
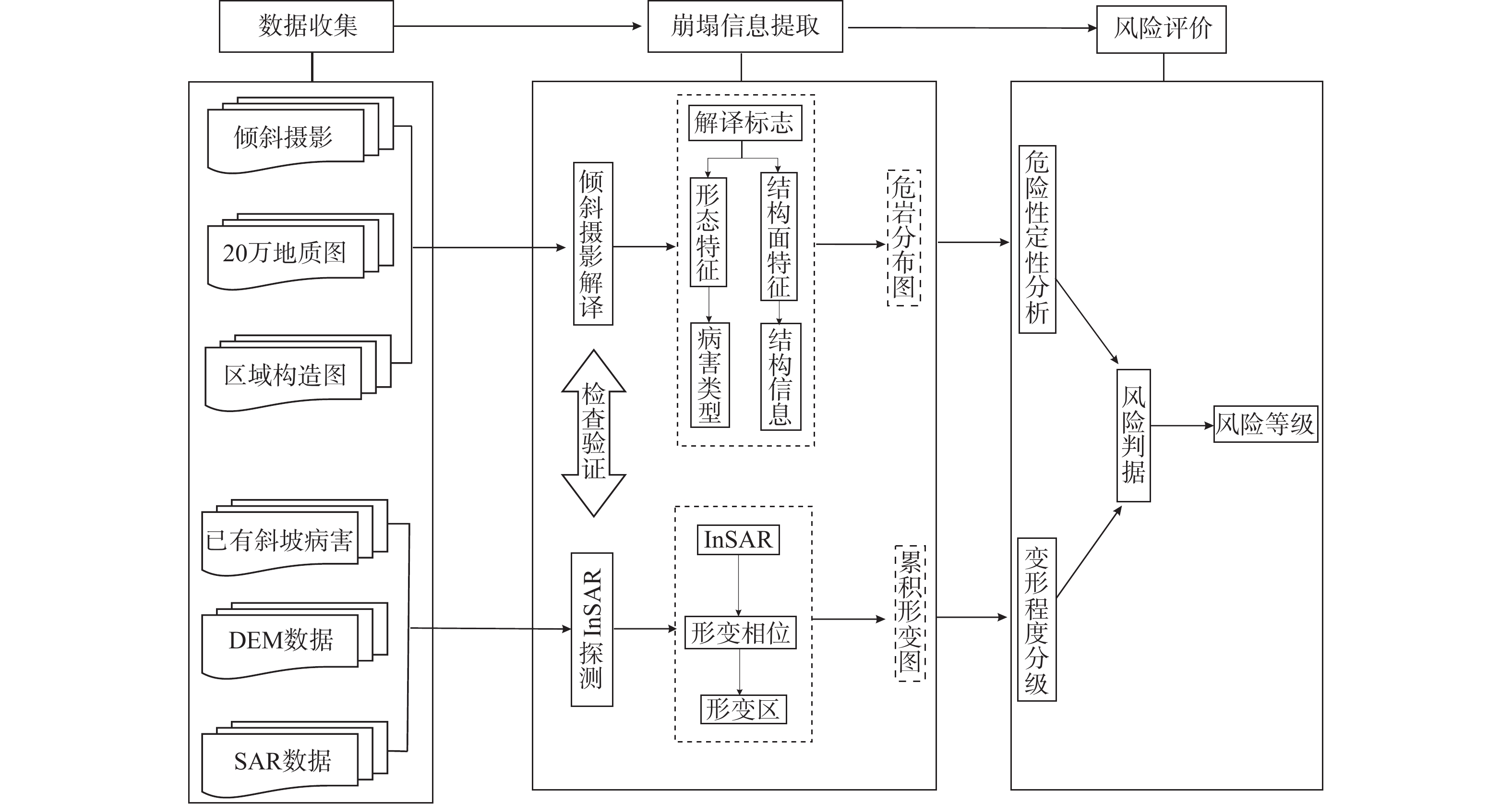
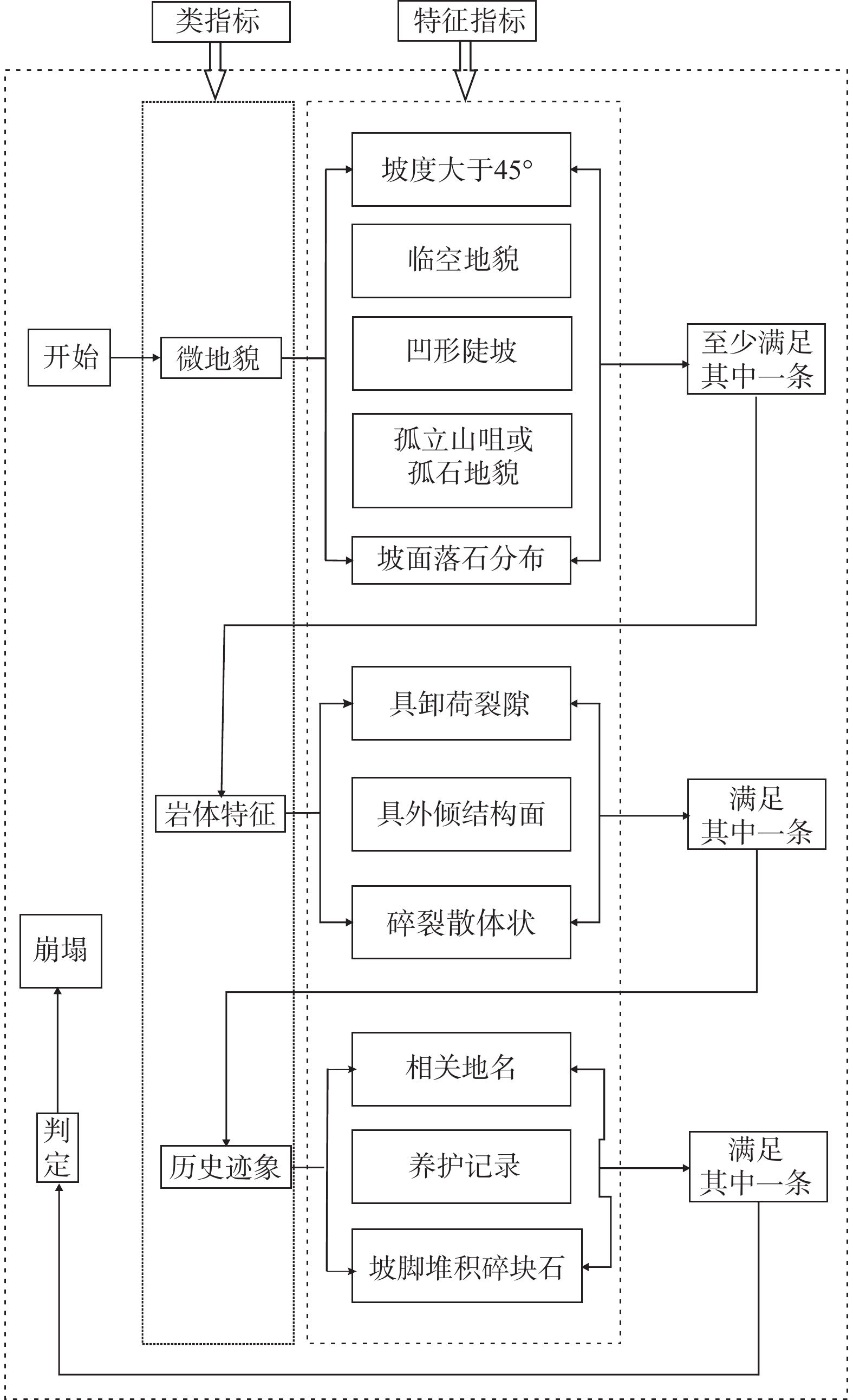
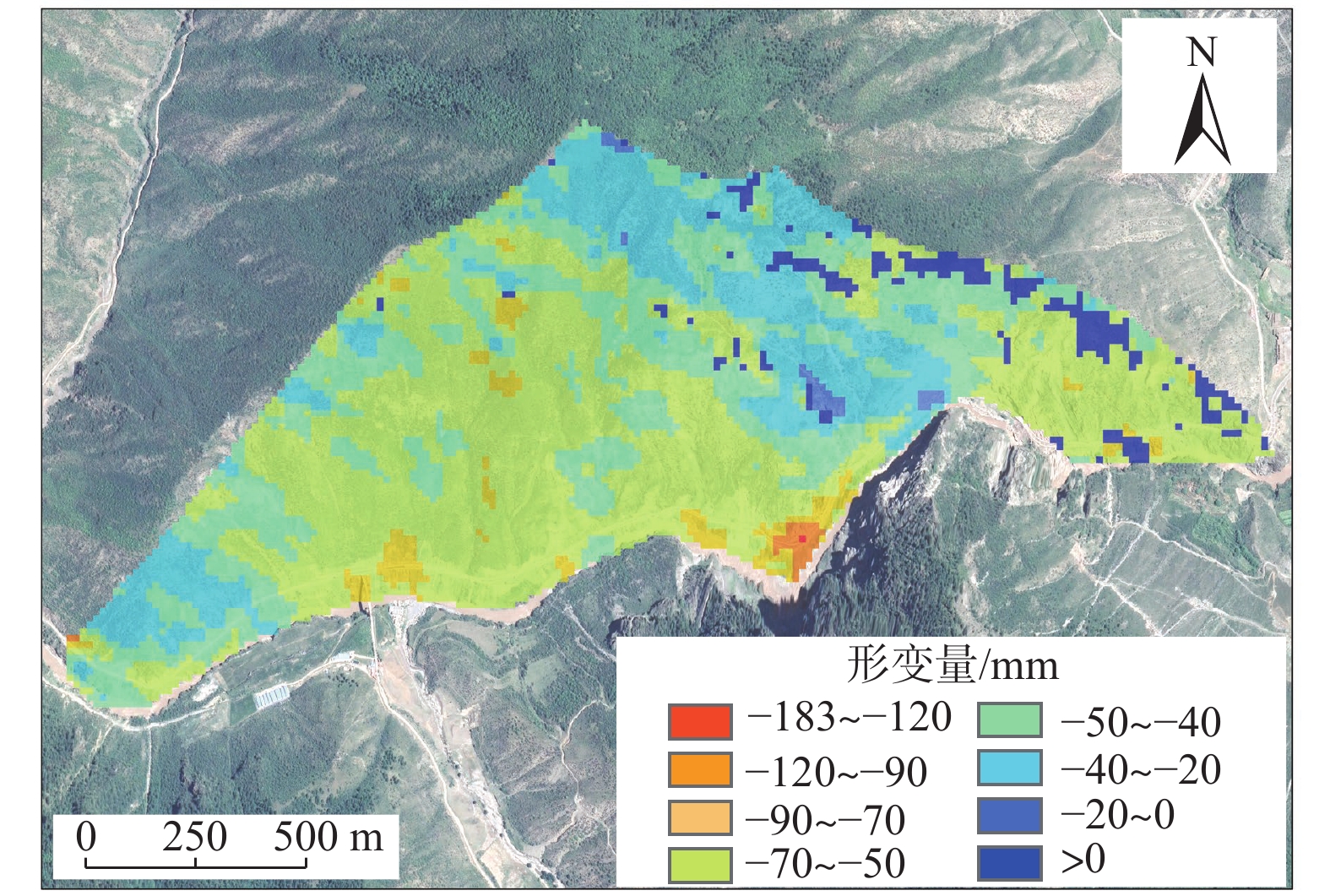
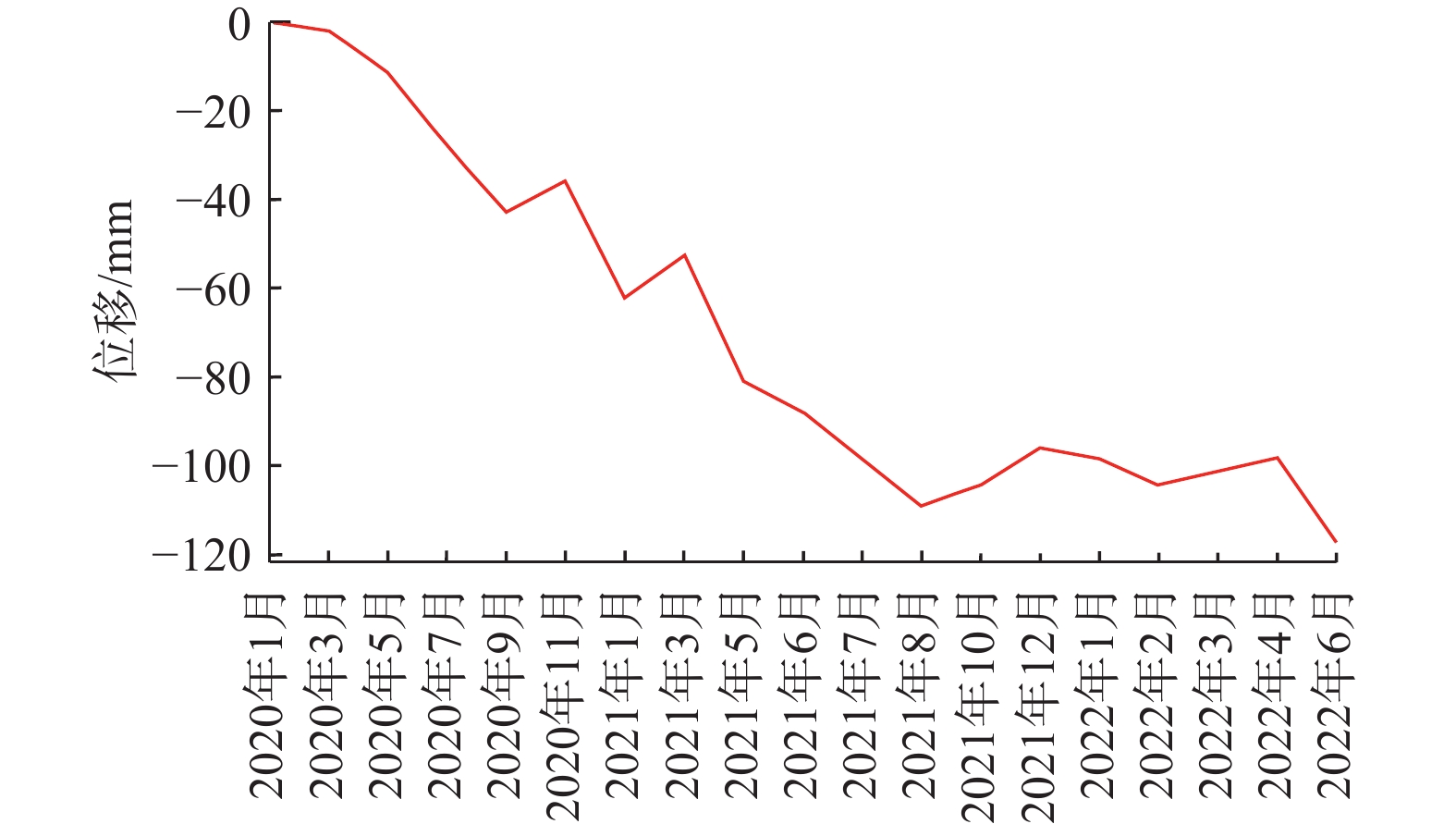
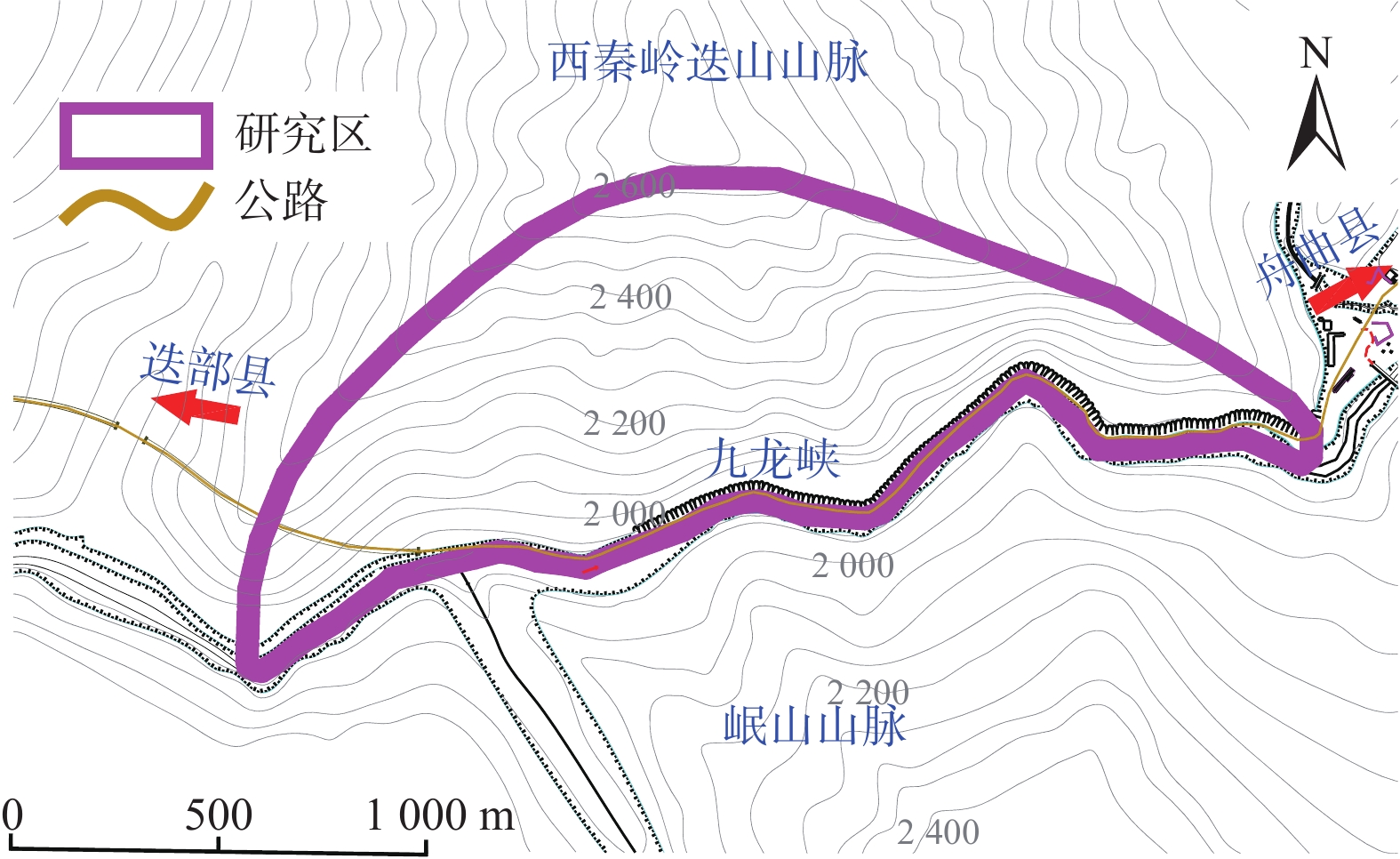
崩塌风险识别是崩塌灾害防治的基础。高位崩塌一般具有突发性、隐蔽性、高差大等特点,给信息采集、灾害识别和风险评估等工作带来了极大的挑战。针对这一工程难题,以白龙江流域九龙峡高位斜坡为例,基于倾斜摄影三维模型,确定高位崩塌识别指标,探索结构面信息提取方法,提出赤平投影定性分析与InSAR定量分析相结合的崩塌风险评估模型,形成了崩塌识别、稳定性分析和形变监测三者相结合的高位崩塌识别与风险评价的全过程模式。结果显示:(1)2020年1月—2022年6月,研究区斜坡最大累积变形量为120 mm,研究区东侧斜坡、西侧坡脚、南侧突出山咀变形较为强烈,变形等级以一、二级为主,灾害危险等级较高。(2)研究区共有崩塌危岩体22处(高风险7处,占32%;中风险11处,占50%;低风险4处,占18%),分布高度在37~640 m之间,高风险危岩主要集中在南侧突出的山咀、东侧斜坡以及西侧坡脚地带。分析结果与公路灾害养护历史资料相吻合,验证了倾斜摄影和InSAR技术在高位崩塌风险识别方面的可行性,为该技术在崩塌灾害防治方面的应用提供了依据和借鉴。
Abstract:Collapse risk identification is the basis of collapse disaster prevention. High level collapse is characterized by sudden, hidden and large height difference, which brings great challenges to information collection, disaster identification and risk assessment. In order to solve this engineering problem, this paper takes the Jiulongxia high slope in the Bailong River basin as an example, Based on the 3D model of oblique photography, the establishment of high-level collapse identification index and its structural plane information extraction method, proposes a collapse risk assessment model combining stereographic projection qualitative analysis and InSAR quantitative analysis, and forms a whole process model of high level collapse identification and risk assessment combining collapse identification, stability analysis and deformation monitoring. The results show that there are 22 collapse dangerous rocks in the study area (including 7 high risk rocks, accounting for 32%, 11 medium risk rocks, accounting for 50%, and 4 low risk rocks, accounting for 18%), with a distribution height of 37 m – 640 m. High risk dangerous rocks are mainly concentrated in the prominent mountain mouth in the south, the eastern slope and the western slope toe. These analysis results are consistent with the historical data of highway disaster maintenance, which verifies the feasibility of tilt photography and InSAR technology in high level collapse risk identification. The results provide a basis and reference for the application of this technology in collapse disaster prevention.
-
Key words:
- high level slope /
- collapse /
- tilt photography /
- InSAR /
- risk identification
-

-
表 1 边坡稳定性分级评价表
Table 1. Slope stability classification and evaluation index
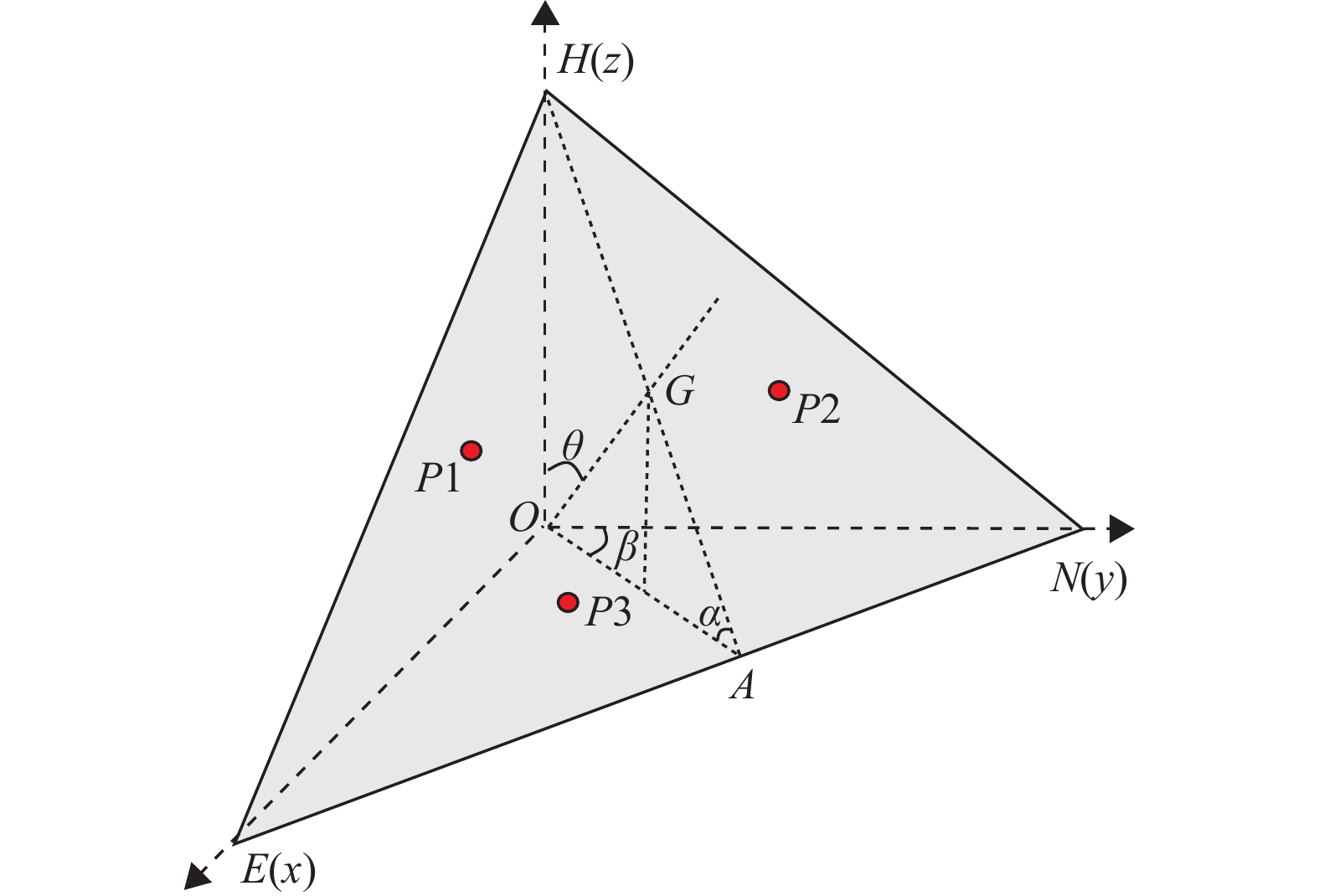
稳定性分级 评 价 指 标 稳定 结构面倾角或交棱倾角≤15°
结构面倾角或交棱倾角≥边坡角
结构面倾向或交棱倾向与坡向夹角≥60°基本稳定 结构面倾向或交棱倾向与坡向夹角<45°,
15°≤结构面倾角或交棱倾角<25°45°<结构面倾向或交棱倾向与坡向夹角≤60°,
15°≤结构面倾角或交棱倾角<边坡角欠稳定 结构面倾向或交棱倾向与坡向夹角<25°,
25°≤结构面倾角或交棱倾角<40°25°<结构面倾向或交棱倾向与坡向夹角≤45°,
25°≤结构面倾角或交棱倾角<边坡角不稳定 结构面倾向或交棱倾向与坡向夹角≤25°,
40°≤结构面倾角或交棱倾角<边坡角表 2 崩塌危岩体风险评价指标
Table 2. Risk assessment index of collapse dangerous rock mass
一级指标 二级指标 等级划分 分值 权重(R) 评分 稳定性评价 见表1 不稳定 40~50 0~1 K1 欠稳定 30~40 0~1 K2 基本稳定 20~30 0~1 K3 稳定 10~20 0~1 K4 InSAR
变形等级>90 mm 一级 40~50 0~1 S1 90~50 mm 二级 30~40 0~1 S2 50~20 mm 三级 20~30 0~1 S3 <20 mm 四级 10~20 0~1 S4 表 3 崩塌危岩风险判据
Table 3. Criteria for risk identification of dangerous rock collapse
评判值 <50 50~75 >75 级别 低风险 中风险 高风险 注:该评判标准与发生概率相对应。 表 4 崩塌识别解译表
Table 4. Interpretation for collapse recognition
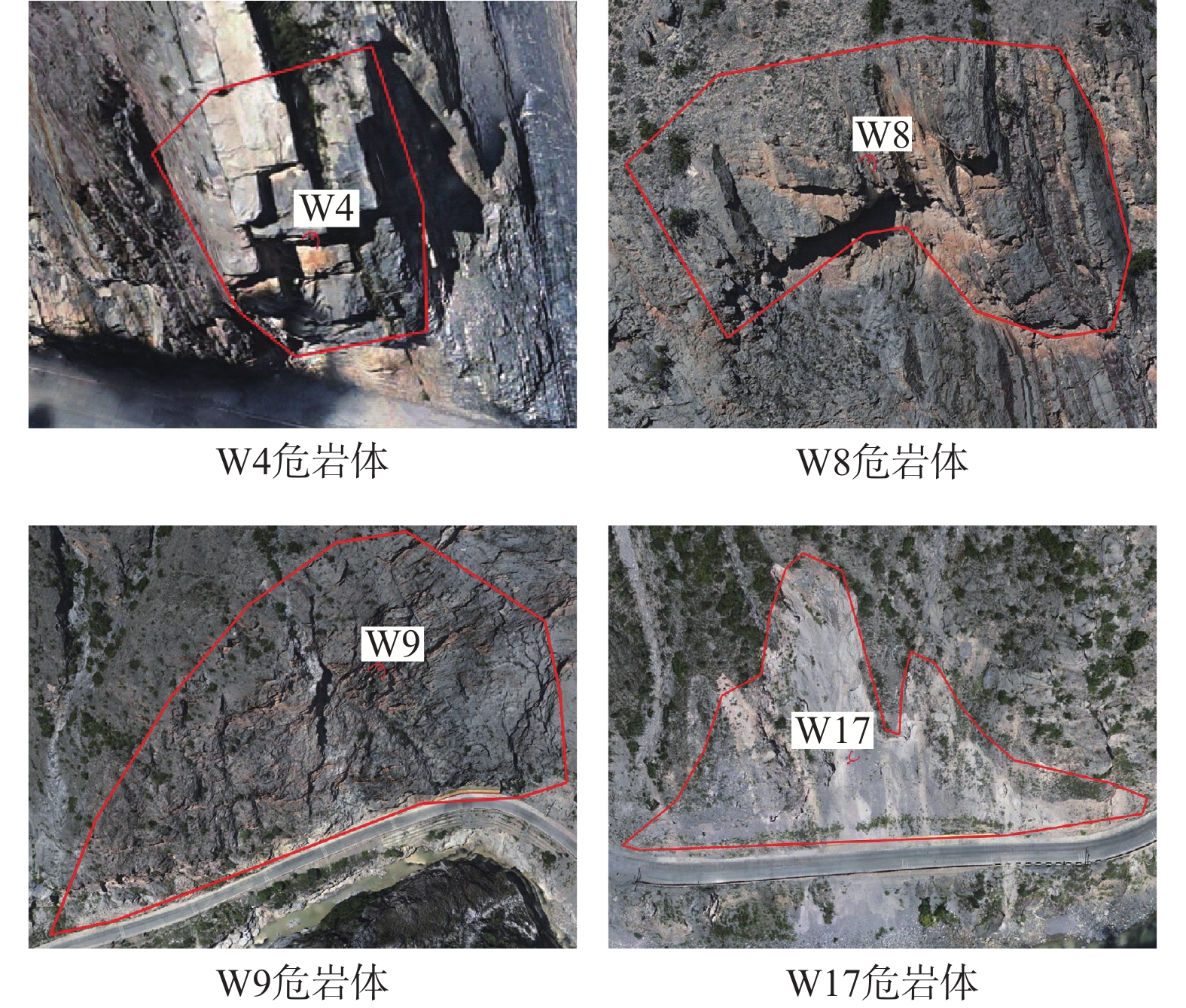
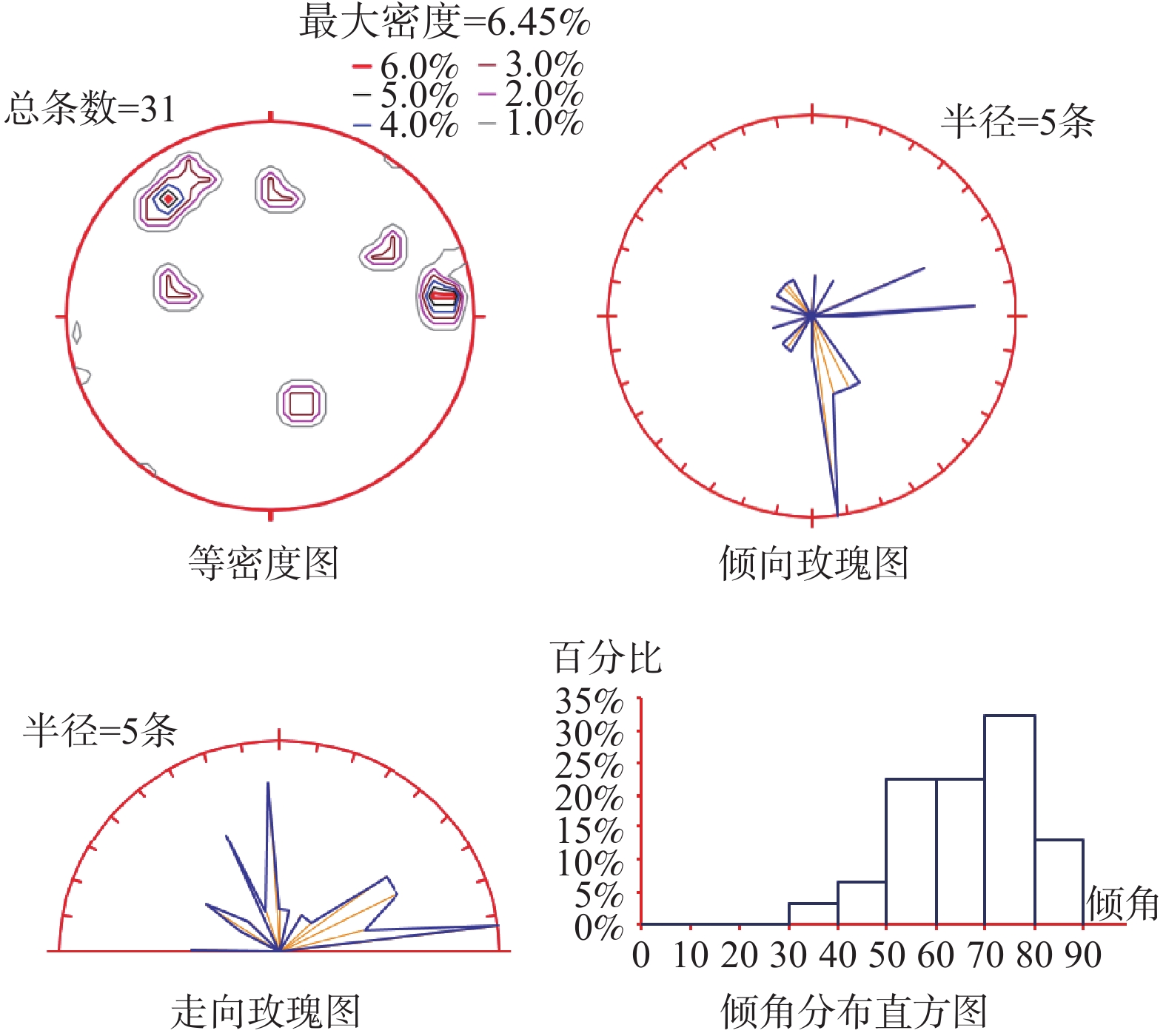
代表区域 崩塌类型 岩性 坡体结构 岩体特征 结构面发育情况 距离路面高度/m 是否直接威胁公路 W1、W17、W18、W19 土质 碎块石土 土质、类土质坡体结构 石夹土状 160、70、39、45 是 W2、W3、W4、W9、
W13、W15岩质 灰岩夹板岩 层状斜向结构 薄-中厚层状 具外倾结构面、
卸荷裂隙发育80、110、37、
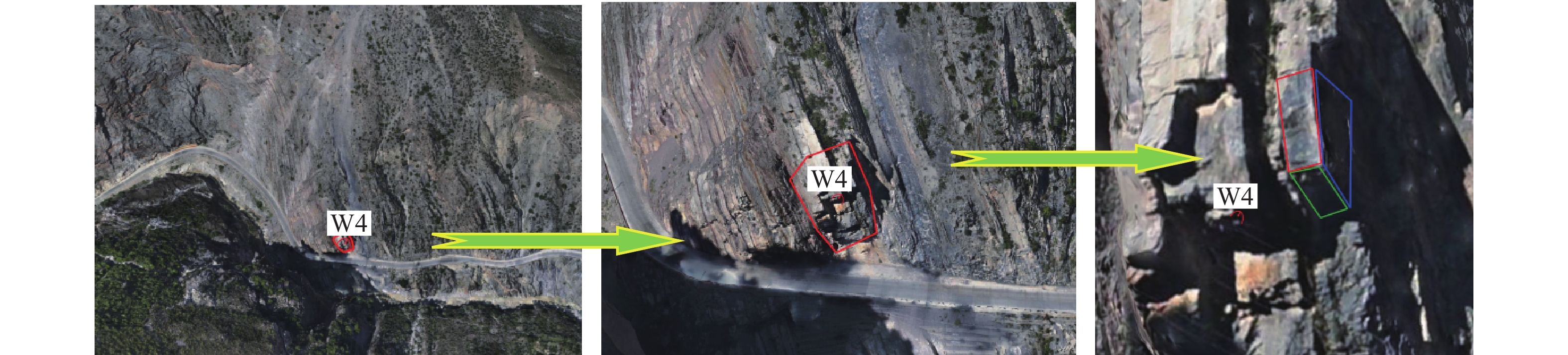
161、76、45是 W12、W20、W21、W22 岩质 灰岩 碎裂结构 碎裂镶嵌结构状 构造裂隙密集 165、160、175、195 是 W7、W8 岩质 灰岩 层状斜向结构 薄-中厚层状 底部悬空 165、235 是 W5 岩质 千枚岩、板岩 碎裂结构 碎裂镶嵌结构状 构造风化裂隙密集 197 否 W6、W10 岩质 千枚岩、板岩 反倾-斜向结构 薄层状、板状 风化裂隙发育 310、640 否 W11、W14、W16 岩质 灰岩 层状斜向结构 薄-中厚层状 具外倾结构面、卸荷裂隙发育 345、235、345 否 表 5 边坡优势结构面信息及破坏评价(W4、W7为例)
Table 5. Slope dominant structural plane information and damage evaluation (W4 and W7 as examples)
代表区域 结构面编号 产状 形态 填充
特性间距/cm 张开度/mm 稳定性评价 失稳模式 W4 P0 187°∠55° 不稳定 滑移 S0 69°∠74° 平直 钙泥质胶结 100 J1 168°∠48° 平直 岩屑断续填充 100 3 J2 333°∠77° 平直 岩屑断续填充 150 5 W7 P0 170°∠53° 稳定 坠落式 S0 30°∠49° 平直 钙泥质胶结 130 J1 180°∠62° 平直 岩屑断续填充 50 2 J2 300°∠53 平直 岩屑断续填充 50 2 注:P为坡面,S为岩层层面,J为岩体节理。 表 6 危岩风险等级评价表
Table 6. Risk level evaluation of dangerous rocks
编号 稳定性评价 稳定性得分 变形等级 变形得分 威胁对象 权重 总分 风险等级 W1 不稳定 40 二级 30 公路 1 70 中风险 W2 不稳定 45 二级 35 公路 1 80 高风险 W3 欠稳定 35 一级 40 公路 1 75 中风险 W4 不稳定 50 四级 15 公路 1 65 中风险 W5 不稳定 45 二级 35 公路 1 80 高风险 W6 不稳定 45 二级 30 公路 1 75 中风险 W7 稳定 20 三级 30 公路 1 50 中风险 W8 稳定 20 三级 30 公路 1 50 中风险 W9 不稳定 50 三级 25 公路 1 75 中风险 W10 欠稳定 30 三级 20 沟谷 0.5 25 低风险 W11 欠稳定 30 三级 25 沟谷 0.5 27.5 低风险 W12 不稳定 50 二级 30 公路 1 80 高风险 W13 不稳定 50 一级 45 公路 1 95 高风险 W14 欠稳定 30 二级 30 沟谷 0.5 30 低风险 W15 不稳定 40 二级 30 公路 1 70 中风险 W16 欠稳定 35 三级 25 沟谷 0.5 30 低风险 W17 不稳定 40 二级 35 公路 1 75 中风险 W18 不稳定 40 二级 35 公路 1 75 中风险 W19 不稳定 40 一级 45 公路 1 85 高风险 W20 不稳定 45 二级 35 公路 1 80 高风险 W21 不稳定 50 三级 30 公路 1 80 高风险 W22 不稳定 50 三级 25 公路 1 75 中风险 -
[1] 许强,董秀军,李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957 − 966. [XU Qiang,DONG Xiujun,LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957-966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 葛大庆,戴可人,郭兆成,等. 重大地质灾害隐患早期识别中综合遥感应用的思考与建议[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):949 − 956. [GE Daqing,DAI Keren,GUO Zhaocheng,et al. Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies:Thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):949 − 956. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GE Daqing, DAI Keren, GUO Zhaocheng, et al. Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies: thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 949-956. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 许强,陆会燕,李为乐,等. 滑坡隐患类型与对应识别方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2022,47(3):377 − 387. [XU Qiang,LU Huiyan,LI Weile,et al. Types of potential landslide and corresponding identification technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2022,47(3):377 − 387. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU Qiang, LU Huiyan, LI Weile, et al. Types of potential landslide and corresponding identification technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(3): 377-387. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘传正. 崩塌滑坡灾害风险识别方法初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):88 − 97. [LIU Chuanzheng. Analysis methods on the risk identification of landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):88 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Chuanzheng. Analysis methods on the risk identification of landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(1): 88-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 罗刚,程谦恭,沈位刚,等. 高位高能岩崩研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(3):913 − 934. [LUO Gang,CHENG Qiangong,SHEN Weigang,et al. Research status and development trend of the high-altitude extremely-energetic rockfalls[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(3):913 − 934. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.3.dqkx202203013
LUO Gang, CHENG Qiangong, SHEN Weigang, et al. Research status and development trend of the high-altitude extremely-energetic rockfalls[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(3): 913-934. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.3.dqkx202203013
[6] 刘传正. 地质灾害防治研究的认识论与方法论[J]. 工程地质学报,2015,23(5):809 − 820. [LIU Chuanzheng. Epistemology and methodology on geo-hazard research[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2015,23(5):809 − 820. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Chuanzheng. Epistemology and methodology on geo-hazard research[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(5): 809-820. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 俊豪,魏云杰,梅傲霜,等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影的黄土滑坡信息多维提取与应用分析[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(2):388 − 401. [WANG Junhao,WEI Yunjie,MEI Aoshuang,et al. Multidimensional extraction of UAV tilt photography-based information of loess landslide and its application[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(2):388 − 401. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[WANG Junhao, WEI Yunjie, MEI Aoshuang, et al. Multidimensional extraction of UAV tilt photography-based information of loess landslide and its application[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(2): 388-401.(in Chinese with English abstract)]
[8] 周福军. 高原复杂山区铁路无人机倾斜摄影勘察技术应用研究[J]. 铁道标准设计,2021,65(6):1 − 5. [ZHOU Fujun. Application of unmanned aerial vehicle oblique photography survey technology for railway in complex plateau mountain area[J]. Railway Standard Design,2021,65(6):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU Fujun. Application of unmanned aerial vehicle oblique photography survey technology for railway in complex plateau mountain area[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2021, 65(6): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 潘文明,王德高. 基于无人机低空航摄的典型地质灾害识别研究—以滑坡、泥石流、崩塌为例[J]. 宿州学院学报,2021,36(12):53 − 57. [PAN Wenming,WANG Degao. Identification of typical geological hazards based on low altitude aerial photography by unmanned aerial vehicles:Taking landslide,debris flow and collapse as examples[J]. Journal of Suzhou University,2021,36(12):53 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PAN Wenming, WANG Degao. Identification of typical geological hazards based on low altitude aerial photography by unmanned aerial vehicles: taking landslide, debris flow and collapse as examples[J]. Journal of Suzhou University, 2021, 36(12): 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 梁京涛,铁永波,赵聪,等. 基于贴近摄影测量技术的高位崩塌早期识别技术方法研究[J]. 中国地质调查,2020,7(5):107 − 113. [LIANG Jingtao,TIE Yongbo,ZHAO Cong,et al. Technology and method research on the early detection of high-level collapse based on the nap-of-the-object photography[J]. Geological Survey of China,2020,7(5):107 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIANG Jingtao, TIE Yongbo, ZHAO Cong, et al. Technology and method research on the early detection of high-level collapse based on the nap-of-the-object photography[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2020, 7(5): 107-113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 廖斌,杨根兰,覃乙根,等. 基于无人机技术的高陡危岩体参数获取及稳定性评价[J]. 路基工程,2021(4):24 − 29. [LIAO Bin,YANG Genlan,QIN Yigen,et al. Parameter acquisition and stability evaluation of high steep and dangerous rock mass based on UAV[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2021(4):24 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIAO Bin, YANG Genlan, QIN Yigen, et al. Parameter acquisition and stability evaluation of high steep and dangerous rock mass based on UAV[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2021(4): 24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张欢,巨能攀,陆渊,等. 基于无人机的滑坡地形快速重建与稳定性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):171 − 179. [ZHANG Huan,JU Nengpan,LU Yuan,et al. Rapid remodeling of three-dimensional terrain and stability analyses of landslide based on UAV[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):171 − 179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Huan, JU Nengpan, LU Yuan, et al. Rapid remodeling of three-dimensional terrain and stability analyses of landslide based on UAV[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 171-179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 吕权儒,曾斌,孟小军,等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影技术的崩塌隐患早期识别及影响区划分方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(6):313 − 325. [LÜ Quanru,ZENG Bin,MENG Xiaojun,et al. Early identification and influence range division method of collapse hazards based on UAV oblique photography technology[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(6):313 − 325. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LÜ Quanru, ZENG Bin, MENG Xiaojun, et al. Early identification and influence range division method of collapse hazards based on UAV oblique photography technology[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 313-325. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 宋珺敏. 基于多源数据的岩体结构面智能识别方法与信息解译研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2016
SONG Junmin. Research on intelligent identification method and information interpretation of rock mass structural plane based on multi-source data[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 宣程强,章杨松,许文涛. 基于数字表面模型的岩体结构面产状获取[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(1):75 − 83. [XUAN Chengqiang,ZHANG Yangsong,XU Wentao. Extraction of the discontinuity orientation from a digital surface model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(1):75 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XUAN Chengqiang, ZHANG Yangsong, XU Wentao. Extraction of the discontinuity orientation from a digital surface model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(1): 75-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 宋来臣,庞凤波,李秀娟. SBAS-InSAR干涉技术在滑坡早期识别中的应用研究[J]. 现代矿业,2022,38(5):234 − 236. [SONG Laichen,PANG Fengbo,LI Xiujuan. Study on application of SBAS-InSAR interference technolgy in early landslide identification[J]. Modern Mining,2022,38(5):234 − 236. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SONG Laichen, PANG Fengbo, LI Xiujuan. Study on application of SBAS-InSAR interference technolgy in early landslide identification[J]. Modern Mining, 2022, 38(5): 234-236. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 吴东霖,葛伟鹏,魏聪敏,等. 黄河流域刘家峡—兰州段滑坡灾害的InSAR识别及成因分析[J]. 地震工程学报,2021,43(3):607 − 614. [WU Donglin,GE Weipeng,WEI Congmin,et al. Identification and cause analysis of potential landslides in Liujiaxia-Lanzhou section of the Yellow River Basin with InSAR technique[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2021,43(3):607 − 614. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Donglin, GE Weipeng, WEI Congmin, et al. Identification and cause analysis of potential landslides in Liujiaxia-Lanzhou section of the Yellow River Basin with InSAR technique[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2021, 43(3): 607-614. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李梦华,张路,董杰,等. 四川茂县岷江河谷区段滑坡隐患雷达遥感识别与形变监测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(10):1529 − 1537. [LI Menghua,ZHANG Lu,DONG Jie,et al. Detection and monitoring of potential landslides along Minjiang River valley in Maoxian County,Sichuan using radar remote sensing[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(10):1529 − 1537. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Menghua, ZHANG Lu, DONG Jie, et al. Detection and monitoring of potential landslides along Minjiang River valley in Maoxian County, Sichuan using radar remote sensing[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(10): 1529-1537. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 韩旭东,付杰,李严严,等. 舟曲江顶崖滑坡的早期判识及风险评估研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):180 − 186. [HAN Xudong,FU Jie,LI Yanyan,et al. A study of the early identification and risk assessment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):180 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HAN Xudong, FU Jie, LI Yanyan, et al. A study of the early identification and risk assessment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 180-186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 赵富萌,张毅,孟兴民,等. 基于小基线集雷达干涉测量的中巴公路盖孜河谷地质灾害早期识别[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):142 − 152. [ZHAO Fumeng,ZHANG Yi,MENG Xingmin,et al. Early identification of geological hazards in the Gaizi valley near the Karakoran Highway based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):142 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Fumeng, ZHANG Yi, MENG Xingmin, et al. Early identification of geological hazards in the Gaizi valley near the Karakoran Highway based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(1): 142-152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 李振洪,朱武,余琛,等. 雷达影像地表形变干涉测量的机遇、挑战与展望[J]. 测绘学报,2022,51(7):1485 − 1519. [LI Zhenhong,ZHU Wu,YU Chen,et al. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar for deformation mapping:Opportunities,challenges and the outlook[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2022,51(7):1485 − 1519. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Zhenhong, ZHU Wu, YU Chen, et al. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar for deformation mapping: opportunities, challenges and the outlook[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 1485-1519. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王颂,张路青,周剑,等. 青藏铁路设兴村段崩塌特征分析与运动学模拟[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(4):784 − 792. [WANG Song,ZHANG Luqing,ZHOU Jian,et al. Characteristic analysis and kinematic simulation of rockfall along Shexing village section of Qinghai-Xizang railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(4):784 − 792. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Song, ZHANG Luqing, ZHOU Jian, et al. Characteristic analysis and kinematic simulation of rockfall along shexing village section of Qinghai-Xizang railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(4): 784-792. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 刘帅,陈建华,王峰,等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影的数字露头实景三维模型构建[J]. 地质科学,2022,57(3):945 − 957. [LIU Shuai,CHEN Jianhua,WANG Feng,et al. Construction of a 3D model of digital outcrop real scene based on UAV oblique photography[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica),2022,57(3):945 − 957. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Shuai, CHEN Jianhua, WANG Feng, et al. Construction of a 3D model of digital outcrop real scene based on UAV oblique photography[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 2022, 57(3): 945-957. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 徐国良,张振飞,裴伦培,等. 用有限元强度折减法评价节理岩质边坡稳定性[J]. 山东国土资源,2021,37(5):59 − 66. [XU Guoliang,ZHANG Zhenfei,PEI Lunpei,et al. Slope stability evaluation of the rock mass by using finite element strength reduction method[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,2021,37(5):59 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[XU Guoliang, ZHANG Zhenfei, PEI Lunpei, et al. slope stability evaluation of the rock mass by using finite element strength reduction method[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2021, 37(5): 59-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
[25] 葛云峰,夏丁,唐辉明,等. 基于三维激光扫描技术的岩体结构面智能识别与信息提取[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017,36(12):3050 − 3061. [GE Yunfeng,XIA Ding,TANG Huiming,et al. Intelligent identification and extraction of geometric properties of rock discontinuities based on terrestrial laser scanning[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2017,36(12):3050 − 3061. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GE Yunfeng, XIA Ding, TANG Huiming, et al. Intelligent identification and extraction of geometric properties of rock discontinuities based on terrestrial laser scanning[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(12): 3050-3061. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 杨洪. 水电工程高陡边坡小型危岩体动力分析及治理[J]. 水电站设计,2017,33(1):36 − 39. [YANG Hong. Dynamic analysis and treatment of small dangerous rock mass on high and steep slope of hydropower project[J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station,2017,33(1):36 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Hong. Dynamic analysis and treatment of small dangerous rock mass on high and steep slope of hydropower project[J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station, 2017, 33(1): 36-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 卢达. 基于赤平投影法的岩质边坡稳定性分析[J]. 铁道建筑,2010,50(11):69 − 71. [LU Da. Stability analysis of rock slope based on stereographic projection method[J]. Railway Engineering,2010,50(11):69 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LU Da. Stability analysis of rock slope based on stereographic projection method[J]. Railway Engineering, 2010, 50(11): 69-71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 龙海涛. 用CAD绘制赤平投影图进行边坡稳定性分析程序[J]. 南方国土资源,2009(8):35 − 36. [LONG Haitao. Program for slope stability analysis by drawing stereographic projection with CAD[J]. Nanfang Guotu Ziyuan,2009(8):35 − 36. (in Chinese)
LONG Haitao. Program for slope stability analysis by drawing stereographic projection with CAD[J]. Nanfang Guotu Ziyuan, 2009(8): 35-36. (in Chinese)
[29] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑边坡工程技术规范: GB 50330—2013[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2014.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for building slope engineering: GB 50330—2013[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
[30] 董佳慧,牛瑞卿,亓梦茹,等. InSAR技术和孕灾背景指标相结合的地灾隐患识别[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):187 − 196. [DONG Jiahui,NIU Ruiqing,QI Mengru,et al. Identification of geological hazards based on the combination of InSAR technology and disaster background indicators[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):187 − 196. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DONG Jiahui, NIU Ruiqing, QI Mengru, et al. Identification of geological hazards based on the combination of InSAR technology and disaster background indicators[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 187-196. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] FELL R, HO K K S, LACASSE S, et al. A framework for landslide risk assessment and management[C]//EBERHARDT E, HUNGR O, FELL R, et al. Landslide risk management. Vancouver: Taylor & Francis, 2005: 3 − 25.
[32] 张奇华,胡惠华,张煜,等. 块体稳定分析中传统赤平投影与全空间赤平投影对比研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2022,44(6):1148 − 1155. [ZHANG Qihua,HU Huihua,ZHANG Yu,et al. Comparison of traditional and whole-space stereographic projections in block stability analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2022,44(6):1148 − 1155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Qihua, HU Huihua, ZHANG Yu, et al. Comparison of traditional and whole-space stereographic projections in block stability analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(6): 1148-1155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 杜岩,霍磊晨,张洪达,等. 岩块体崩塌灾害遥感监测预警试验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2022,51(6):1201 − 1208. [DU Yan,HUO Leichen,ZHANG Hongda,et al. Experimental study on remote sensing monitoring and early warning of rock block collapse disaster[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2022,51(6):1201 − 1208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DU Yan, HUO Leichen, ZHANG Hongda, et al. Experimental study on remote sensing monitoring and early warning of rock block collapse disaster[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022, 51(6): 1201-1208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 党杰,董吉,何松标,等. 机载LiDAR与地面三维激光扫描在贵州水城独家寨崩塌地质灾害风险调查中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):106 − 113. [DANG Jie,DONG Ji,HE Songbiao,et al. Application of airborne LiDAR and ground 3D laser scanning in geological hazard risk investigation of Dujiazhai collapse in Shuicheng,Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):106 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DANG Jie, DONG Ji, HE Songbiao, et al. Application of airborne LiDAR and ground 3D laser scanning in geological hazard risk investigation of Dujiazhai collapse in Shuicheng, Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 106-113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 许强,朱星,李为乐,等. “天-空-地”协同滑坡监测技术进展[J]. 测绘学报,2022,51(7):1416 − 1436. [XU Qiang,ZHU Xing,LI Weile,et al. Technical progress of space-air-ground collaborative monitoring of landslide[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2022,51(7):1416 − 1436. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU Qiang, ZHU Xing, LI Weile, et al. Technical progress of space-air-ground collaborative monitoring of landslide[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 1416-1436. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路路基设计规范: JTG D30—2015[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2015.
Specifications for Design of Highway Subgrades: JTG D30—2015[S]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: