Single well injection withdraw (SWIW) - based tracer test approach for in-situ permeability estimation in an enhanced geothermal system
-
摘要:
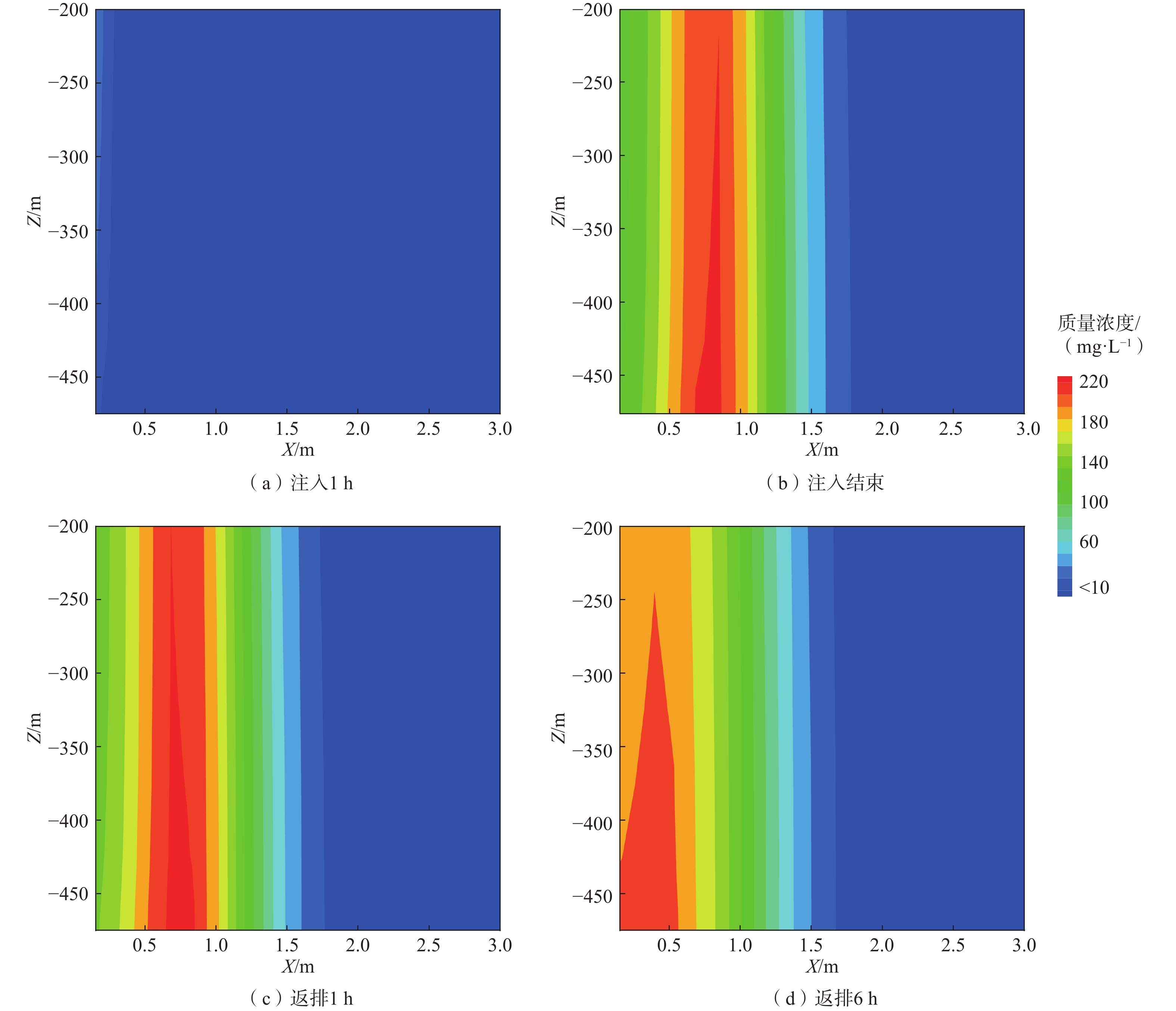
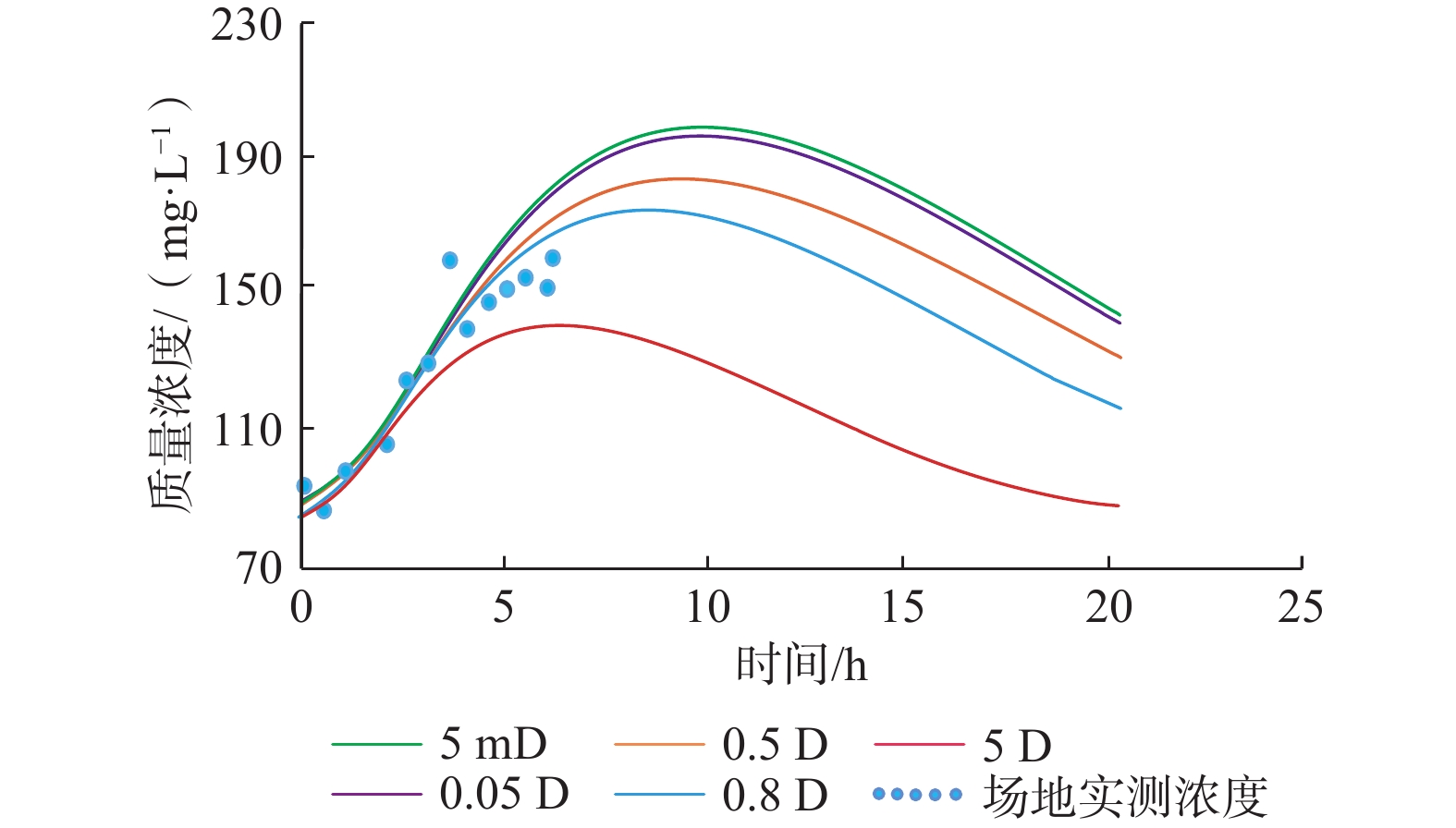
储层压裂阶段,对近井渗透率的高效评估是分析压裂效果、更新压裂方案的重要环节。但受技术或成本制约,目前仍然缺少深部储层近井渗透率原位测算方法。借助于压裂施工过程的间歇性注入和返排泄压环节,提出一种依托压裂施工过程的单井注抽示踪试验工艺,以及基于数值求解和解析解的2种渗透率估算方法,实现了低成本条件下深部储层渗透率原位测试。将该套方法体系应用于实际增强型地热系统场地,结果显示:在单井注抽试验示踪剂突破曲线不完备条件下,通过数值方法仍然能够合理地估算近井渗透率(0.8 D),但方法计算效率较低;而在示踪剂突破曲线相对完备条件下(即监测得到示踪剂浓度峰值),可采用解析法快速估算渗透率(0.25 D);但由于解析法中未能精确考虑井筒内部长距离示踪剂迁移过程和储层内部弥散作用对示踪剂突破曲线的影响,计算精度相对较低。然而,通过数值方法和解析方法估算近井渗透率处于同一数量级,表明解析法仍可以作为渗透率原位快速估算的一种有效手段。文章提出的单井注抽试验工艺和数据解释方法体系为深部储层渗透率原位测试提供了一种新的途径。
Abstract:Efficient estimation of near-wellbore permeability is critical for evaluating fracturing effect and updating fracturing plan. However, due to technical or cost constraints, there is still a lack of methods for in-situ testing and estimating near-wellbore permeability in deep geothermal reservoirs. Considering that the hydraulic fracturing is often associated with injection breaking and back drainage to control the reservoir pressure, this study proposes a single-well-injection-withdraw-based tracer test approach and two permeability interpretation methods based on numerical and analytical solutions, which allow in-situ permeability estimation at low cost. Implementation of the proposed method at a realistic enhanced geothermal system indicates that the numerical interpretation method can still reasonably estimate near-wellbore permeability under the condition of incomplete tracer breakthrough curve in the single well injection and withdraw test, but the computational efficiency is low. Once the tracer breakout curve is relatively complete (i.e. the peak tracer concentration is monitored), the analytical method can be used to quickly estimate the permeability. However, the analytical method cannot accurately consider the long-distance tracer migration process inside wellbore and the influence of dispersion on the tracer breakthrough curve, hence the accuracy is relatively low. The numerical and analytical permeability estimations are at the same order of magnitude. The results suggest that in addition to the numerical method, the analytical method can still be used as an effective method for in-situ rapid permeability estimation. The proposed methodology may provide a new tool for in-situ permeability estimation in deep geothermal reservoirs.
-

-
表 1 井储条件和示踪试验施工参数汇总表
Table 1. Well-reservoir conditions and parameters controlling the tracer test
类型 参数 数值 类型 参数 数值 井结构 进水段长度/m 500 示踪
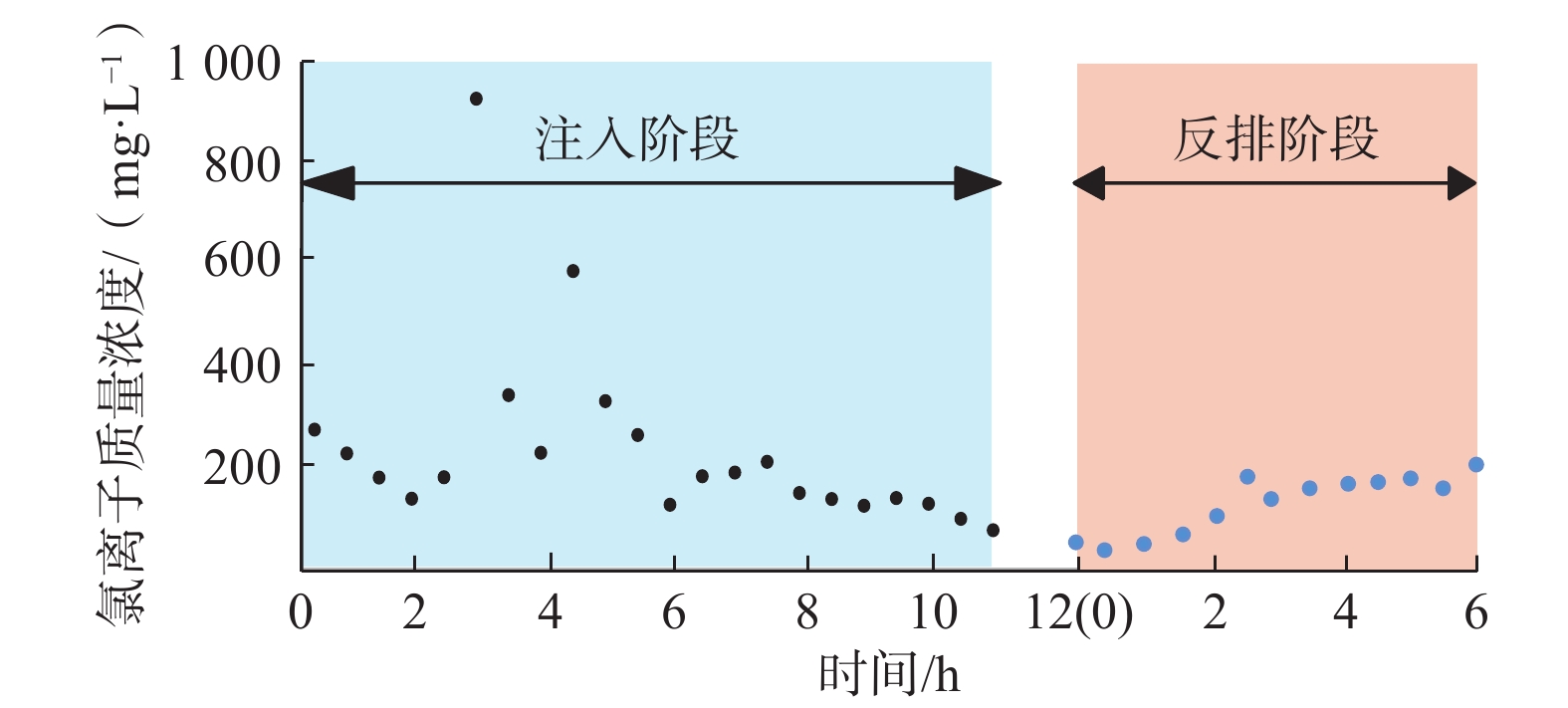
试验示踪剂用量/kg 200 进水段顶部埋深/m 3200 注入排量/(m3·h−1) 102 进水段井径/m 0.1~0.2 注入浓度 见图4 储层
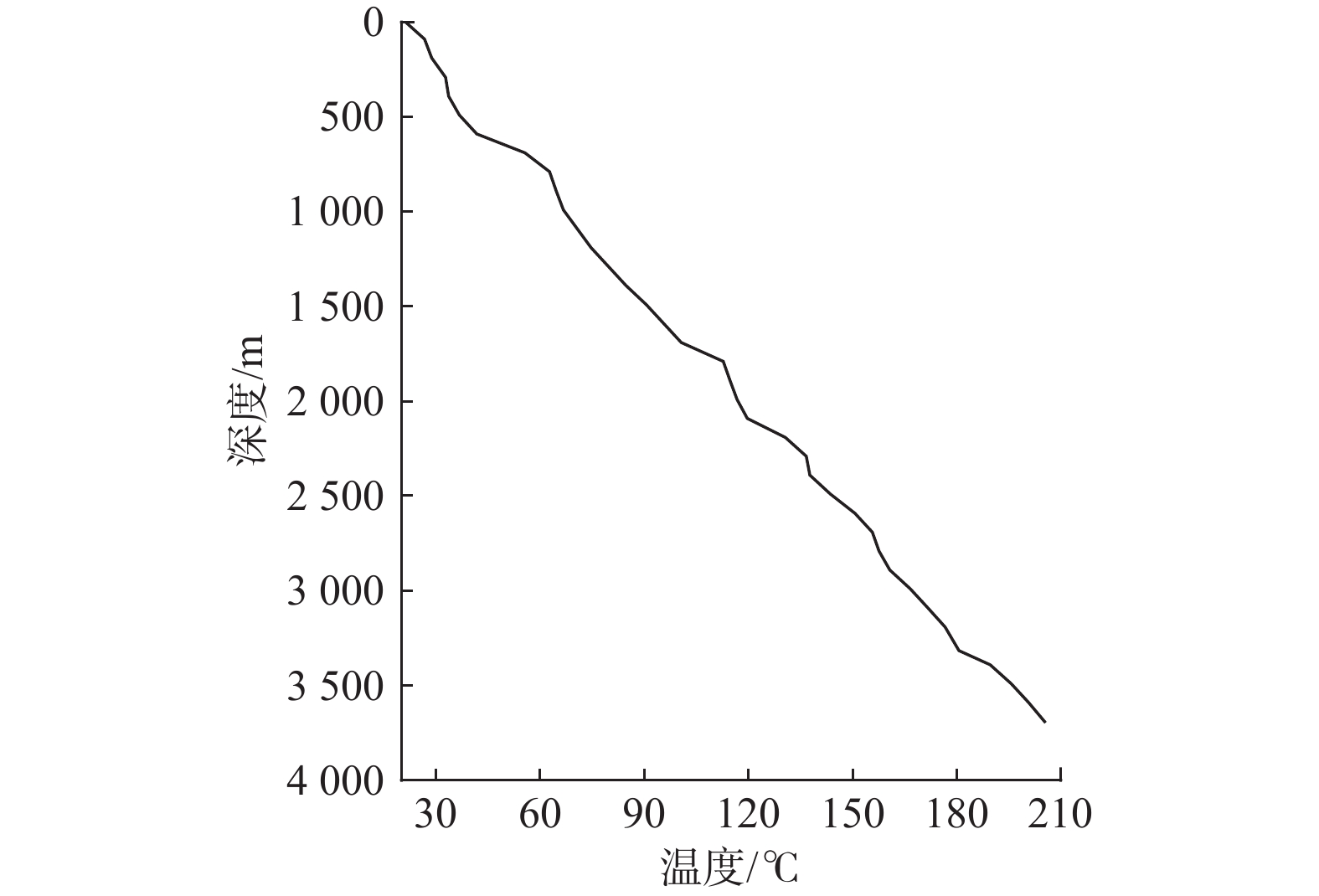
条件温度/°C 200 注入时长/h 10.5 导热系数/(W·m−1∙K−1) 2.51 返排时长/h 6 比热容/(J·kg−1∙°C−1) 920 返排流量/(m3·h−1) 51.5 岩性 花岗岩 返排时井口压力/MPa 40 -
[1] 王贵玲,张薇,梁继运,等. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报,2017,38(4):449 − 459. [WANG Guiling,ZHANG Wei,LIANG Jiyun,et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2017,38(4):449 − 459. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02
WANG Guiling, ZHANG Wei, LIANG Jiyun, et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4): 449-459. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02
[2] 蔺文静,刘志明,王婉丽,等. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质,2013,40(1):312 − 321. [LIN Wenjing,LIU Zhiming,WANG Wanli,et al. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Geology in China,2013,40(1):312 − 321. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021
LIN Wenjing, LIU Zhiming, WANG Wanli, et al. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(1): 312-321. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021
[3] OLASOLO P,JUÁREZ M C,MORALES M P,et al. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS):A review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2016,56:133 − 144. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.11.031
[4] 段云星,杨浩. 增强型地热系统采热性能影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2020,50(4):1161 − 1172. [DUAN Yunxing,YANG Hao. Analysis of influencing factors on heat extraction performance of enhanced geothermal system[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2020,50(4):1161 − 1172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DUAN Yunxing, YANG Hao. Analysis of influencing factors on heat extraction performance of enhanced geothermal system[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2020, 50(4): 1161-1172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 崔翰博,唐巨鹏,姜昕彤. 渗透率对干热岩开采过程储层变化规律的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):171 − 180. [CUI Hanbo,TANG Jupeng,JIANG Xintong. Influence of permeability on reservoir change during dry hot rock mining[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):171 − 180. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201811014
CUI Hanbo, TANG Jupeng, JIANG Xintong. Influence of permeability on reservoir change during dry hot rock mining[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(1): 171-180. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201811014
[6] O’MALLEY D,KARRA S,CURRIER R P,et al. Where does water go during hydraulic fracturing?[J]. Groundwater,2016,54(4):488 − 497. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12380
[7] LIU X, KITANIDIS P K. Large-scale inverse modeling with an application in hydraulic tomography[J]. Water Resources Research, 2011, 47(2): W02501.
[8] OWARE E K,IRVING J,HERMANS T. Basis-constrained Bayesian Markov-chain Monte Carlo difference inversion for geoelectrical monitoring of hydrogeologic processes[J]. Geophysics,2019,84(4):A37 − A42. doi: 10.1190/geo2018-0643.1
[9] YEH T C J,LIU Shuyun. Hydraulic tomography:Development of a new aquifer test method[J]. Water Resources Research,2000,36(8):2095 − 2105. doi: 10.1029/2000WR900114
[10] 刘莹. 基于电阻率与自然电位曲线的孔隙度与渗透率解释方法研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版),2013,10(32):80 − 82. [LIU Ying. Study on porosity and permeability interpretation method based on resistivity and spontaneous potential curve[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition),2013,10(32):80 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Ying. Study on porosity and permeability interpretation method based on resistivity and spontaneous potential curve[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 10(32): 80-82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 马建斌,唐新功,向葵. 利用电阻率求取岩石渗透率的方法研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版),2013,10(10):105 − 106. [MA Jianbin,TANG Xingong,XIANG Kui. Study on the method of calculating rock permeability by using resistivity[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition),2013,10(10):105 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MA Jianbin, TANG Xingong, XIANG Kui. Study on the method of calculating rock permeability by using resistivity[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 10(10): 105-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张志强,王猛,翁新伙. 基于时移电阻率资料的渗透率评价方法[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量,2021,41(12):7 − 8. [ZHANG Zhiqiang,WANG Meng,WENG Xinhuo. Permeability evaluation method based on time-lapse resistivity data[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality,2021,41(12):7 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2021.12.004
ZHANG Zhiqiang, WANG Meng, WENG Xinhuo. Permeability evaluation method based on time-lapse resistivity data[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2021, 41(12): 7-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2021.12.004
[13] 崔志文, 吕伟国, 谢树理, 等. 利用斯通利波衰减反演渗透率的方法改进[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(增刊1): 35 − 38
CUI Zhiwen, LYU Weiguo, XIE Shuli, et al. Improvement in inversion of permeability from attenuation of stoneley waves[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(Sup 1): 35 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 曹渊,牛冠毅,王铁良,等. 基于原位渗透率试验反演岩石孔隙度的新方法[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(1):272 − 276. [CAO Yuan,NIU Guanyi,WANG Tieliang,et al. A new method for rock porosity inversion based on in situ permeability test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(1):272 − 276. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.01.034
CAO Yuan, NIU Guanyi, WANG Tieliang, et al. A new method for rock porosity inversion based on in situ permeability test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(1): 272-276. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.01.034
[15] ALTMAN S J,MEIGS L C,JONES T L,et al. Controls of mass recovery rates in single-well injection-withdrawal tracer tests with a single-porosity,heterogeneous conceptualization[J]. Water Resources Research,2002,38(7):30-1 − 30-15.
[16] 顾昊琛,王全荣,詹红兵. 非完整井下单井注抽试验数值模拟方法改进[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(2):685 − 692. [GU Haochen,WANG Quanrong,ZHAN Hongbing. An improved approach in modeling injection-withdraw test of the partially penetrating well[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(2):685 − 692. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GU Haochen, WANG Quanrong, ZHAN Hongbing. An improved approach in modeling injection-withdraw test of the partially penetrating well[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(2): 685-692. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] TSANG C F, DOUGHTY C. Insight from simulations of single-well injection-withdrawal tracer tests on simple and complex fractures[R]. Berkeley, CA : Lawrence Berkeley National Lab(LBNL), 2009.
[18] CVETKOVIC V,CHENG H. Evaluation of single-well injection-withdrawal tests in Swedish crystalline rock using the Lagrangian travel time approach[J]. Water Resources Research,2011,47(2):W02527.
[19] NORDQVIST R, GUSTAFSSON E. Single-well injection-withdrawal tests (SWIW)— Literature review and scoping calculations for homogeneous crystalline bedrock conditions[R]. Stockholm, Sweden: Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co., 2002.
[20] HYMAN J D, RAJARAM H, SRINIVASAN S, et al. Matrix diffusion in fractured media: New insights into power law scaling of breakthrough curves[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46(23): 13785 − 13795.
[21] MACQUARRIE K T B, MAYER K U. Reactive transport modeling in fractured rock:A state-of-the-science review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2005,72(3/4):189 − 227.
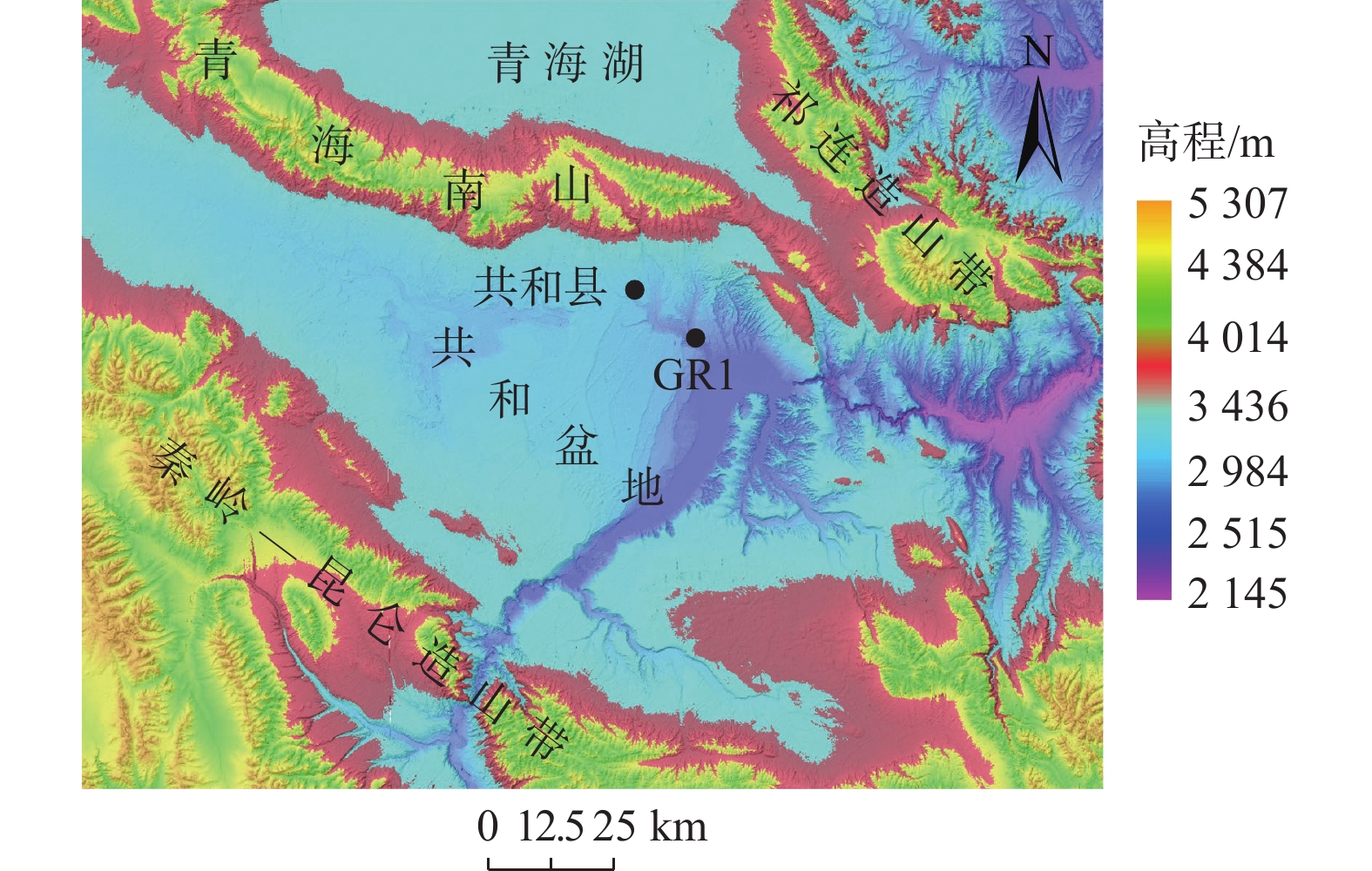
[22] 侯兆云. 基于流体渗流-化学(同位素)耦合模拟的共和—贵德地热储层特征分析[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019
HOU Zhaoyun. Characterizing the geothermal system in the Gonghe—Guide Basin by coupled fluid-heat-chemical (isotope) transport modeling[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 李佳琦. 基于示踪技术的增强型地热系统裂隙储层连通性及导热性评价[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015
LI Jiaqi. Evaluation of the fluid connectivity and heat exchange in a fractured reservoir of enhanced geothermal system based on the tracer technique[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 张盛生,张磊,田成成,等. 青海共和盆地干热岩赋存地质特征及开发潜力[J]. 地质力学学报,2019,25(4):501 − 508. [ZHANG Shengsheng,ZHANG Lei,TIAN Chengcheng,et al. Occurrence geological characteristics and development potential of hot dry rocks in Qinghai Gonghe Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2019,25(4):501 − 508. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.04.048
ZHANG Shengsheng, ZHANG Lei, TIAN Chengcheng, et al. Occurrence geological characteristics and development potential of hot dry rocks in Qinghai Gonghe Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(4): 501-508. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.04.048
[25] 张森琦,严维德,黎敦朋,等. 青海省共和县恰卜恰干热岩体地热地质特征[J]. 中国地质,2018,45(6):1087 − 1102. [ZHANG Senqi,YAN Weide,LI Dunpeng,et al. Characteristics of geothermal geology of the Qiabuqia HDR in Gonghe Basin,Qinghai Province[J]. Geology in China,2018,45(6):1087 − 1102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Senqi, YAN Weide, LI Dunpeng, et al. Characteristics of geothermal geology of the qiabuqia HDR in Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(6): 1087-1102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 孙知新,李百祥,王志林. 青海共和盆地存在干热岩可能性探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2011,38(2):119 − 124. [SUN Zhixin,LI Baixiang,WANG Zhilin. Exploration of the possibility of hot dry rock occurring in the Qinghai Gonghe Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2011,38(2):119 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.021
SUN Zhixin, LI Baixiang, WANG Zhilin. Exploration of the possibility of hot dry rock occurring in the Qinghai Gonghe Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(2): 119-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.021
-




 下载:
下载: