A study of simulation and optimization of the production-reinjection scheme of a geothermal water system: A case study of the geothermal space heating demonstration area in northern Jiangsu countryside
-
摘要:
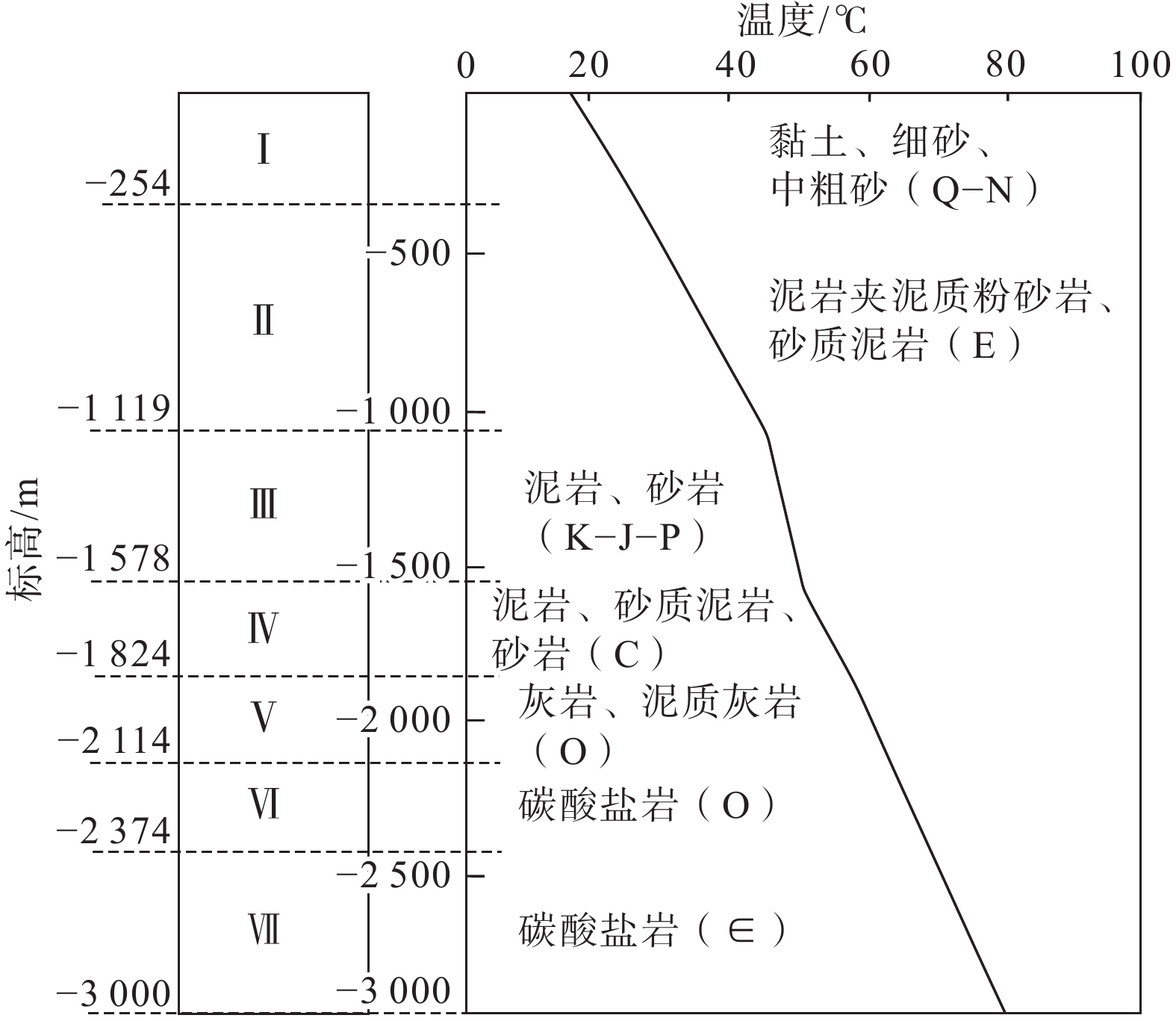
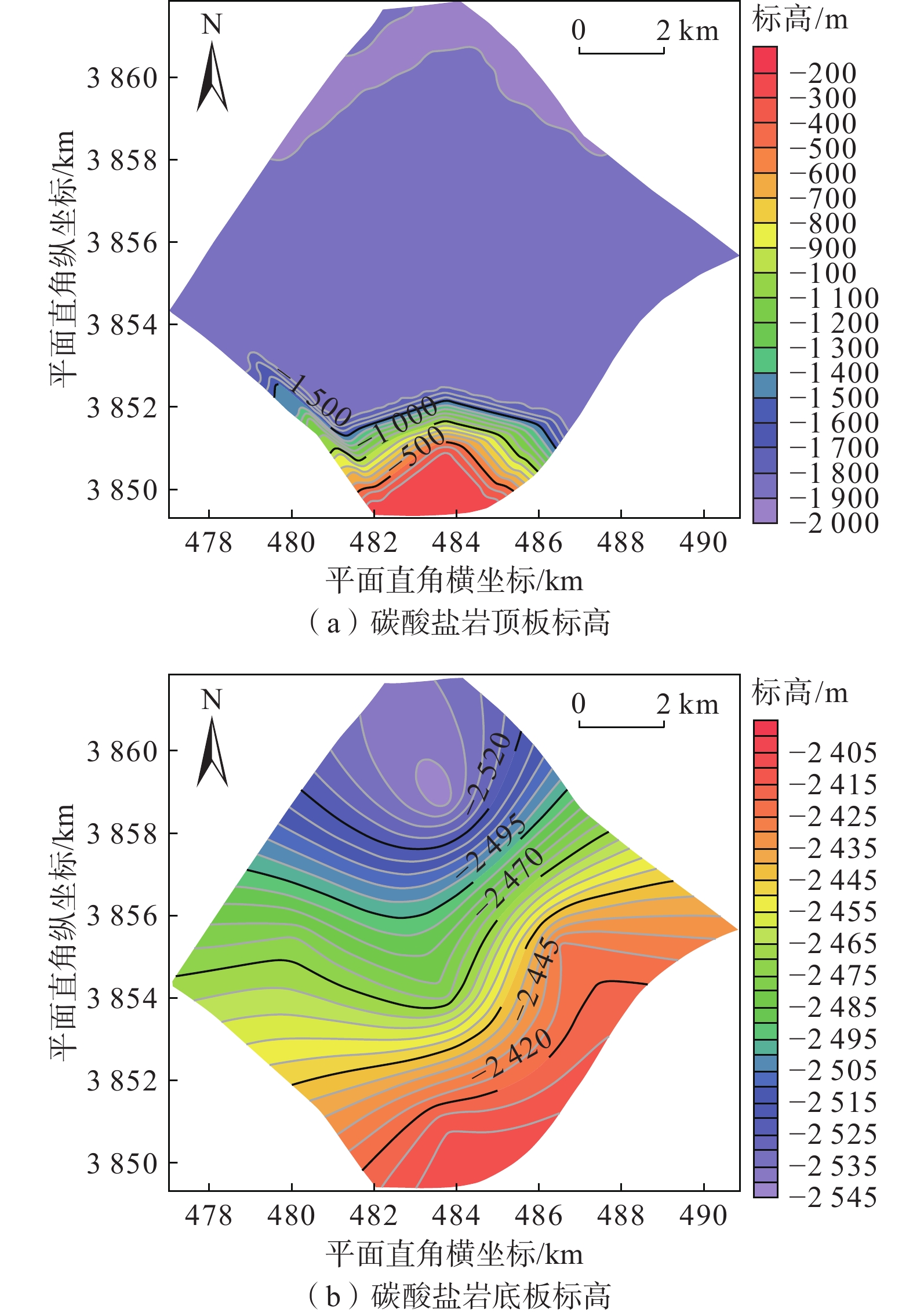
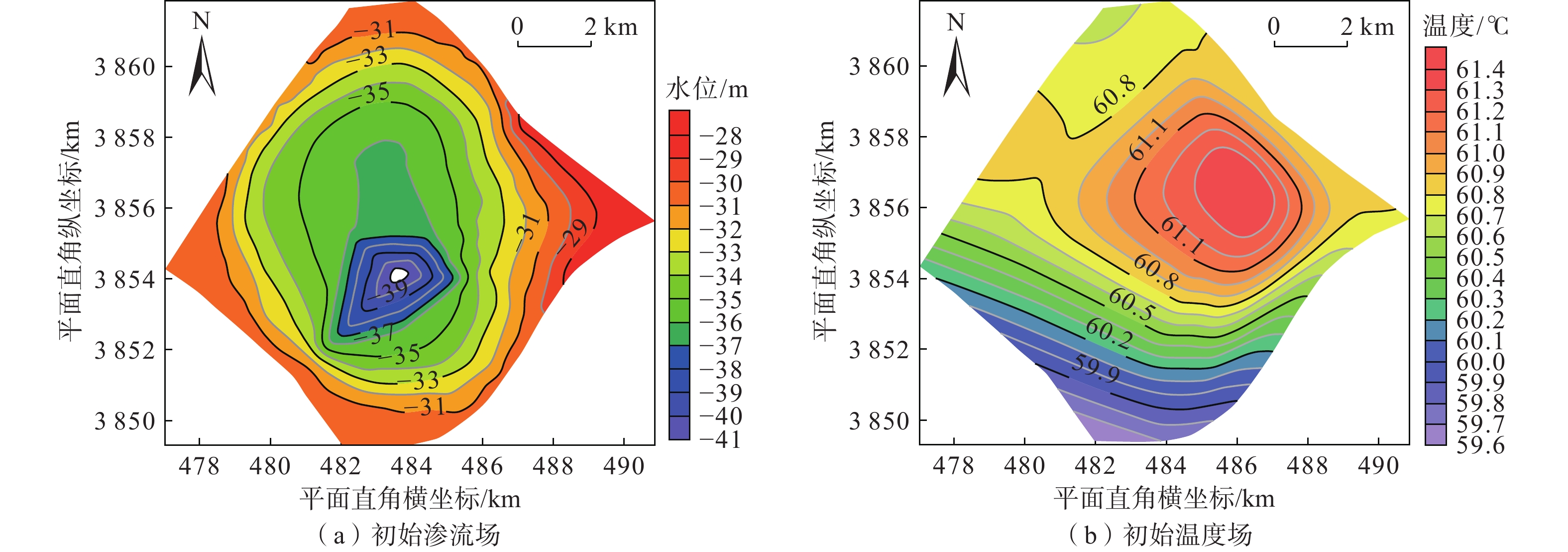
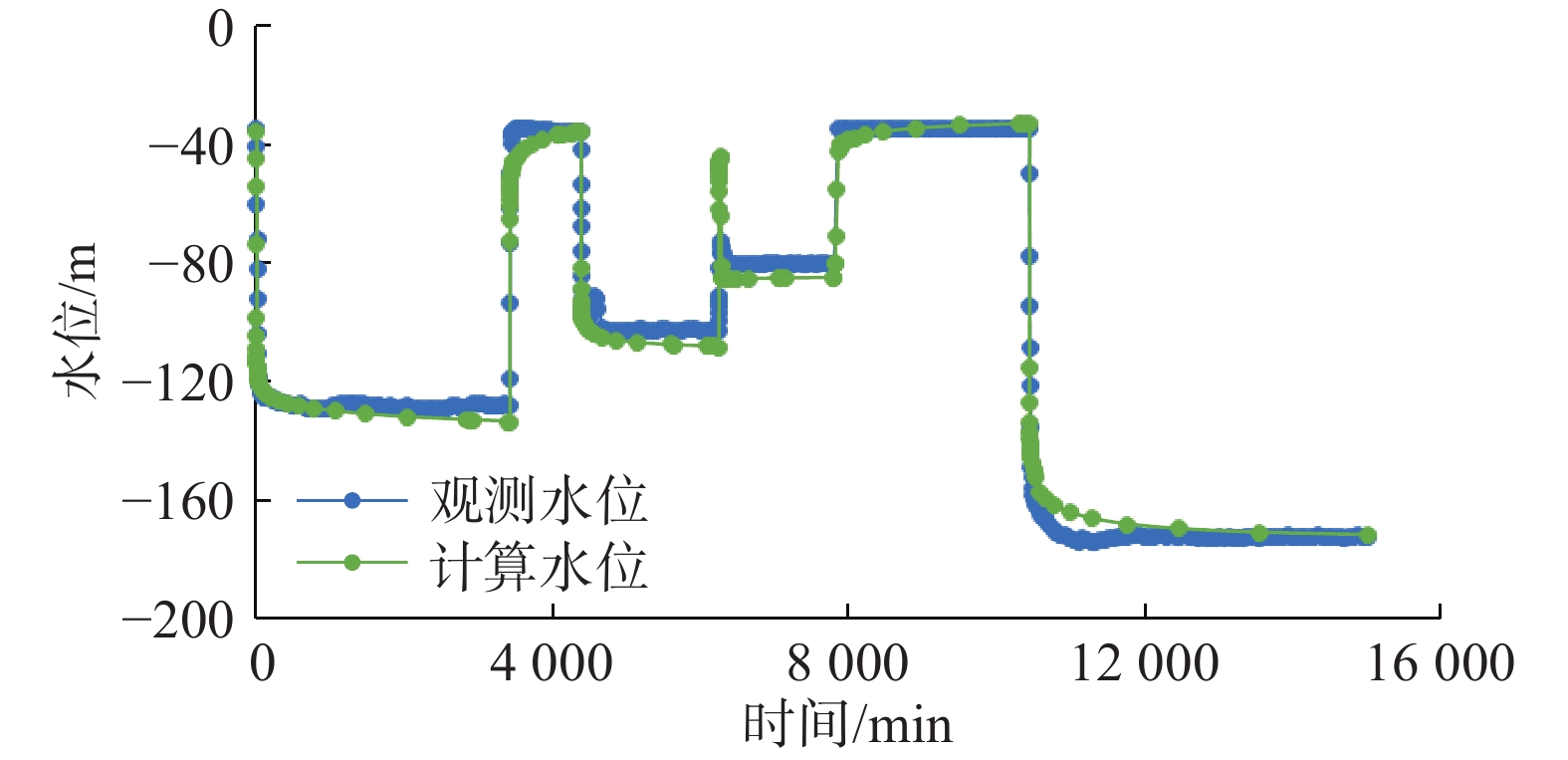
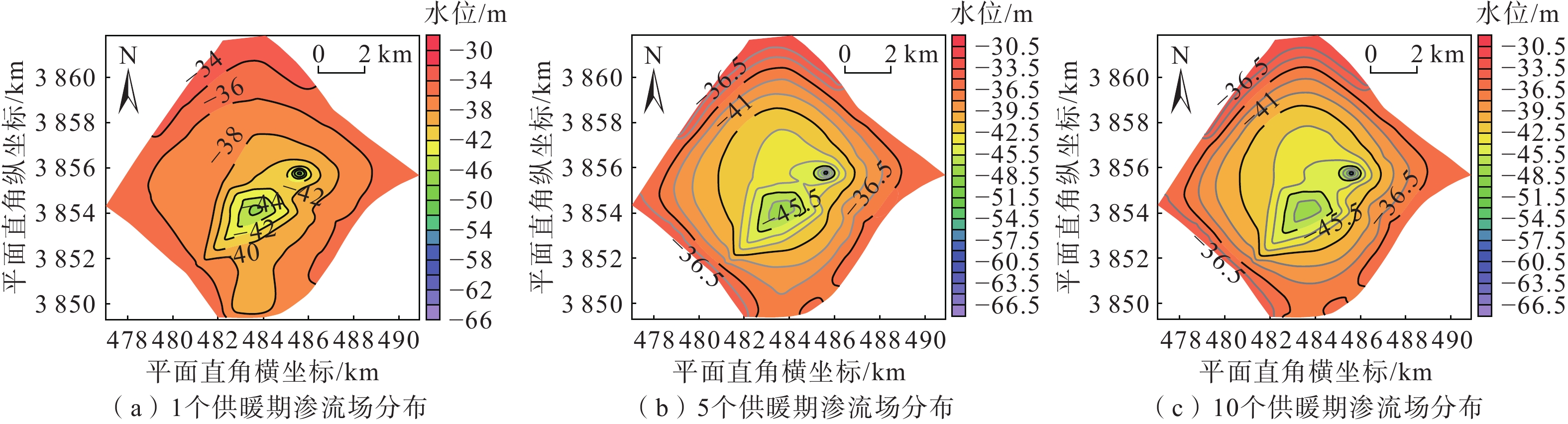
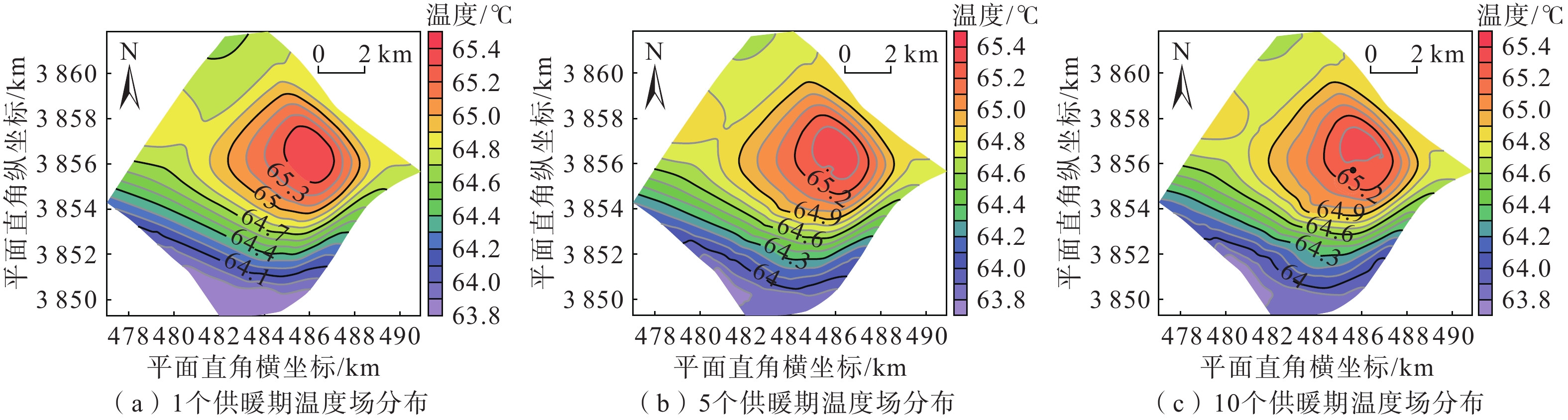
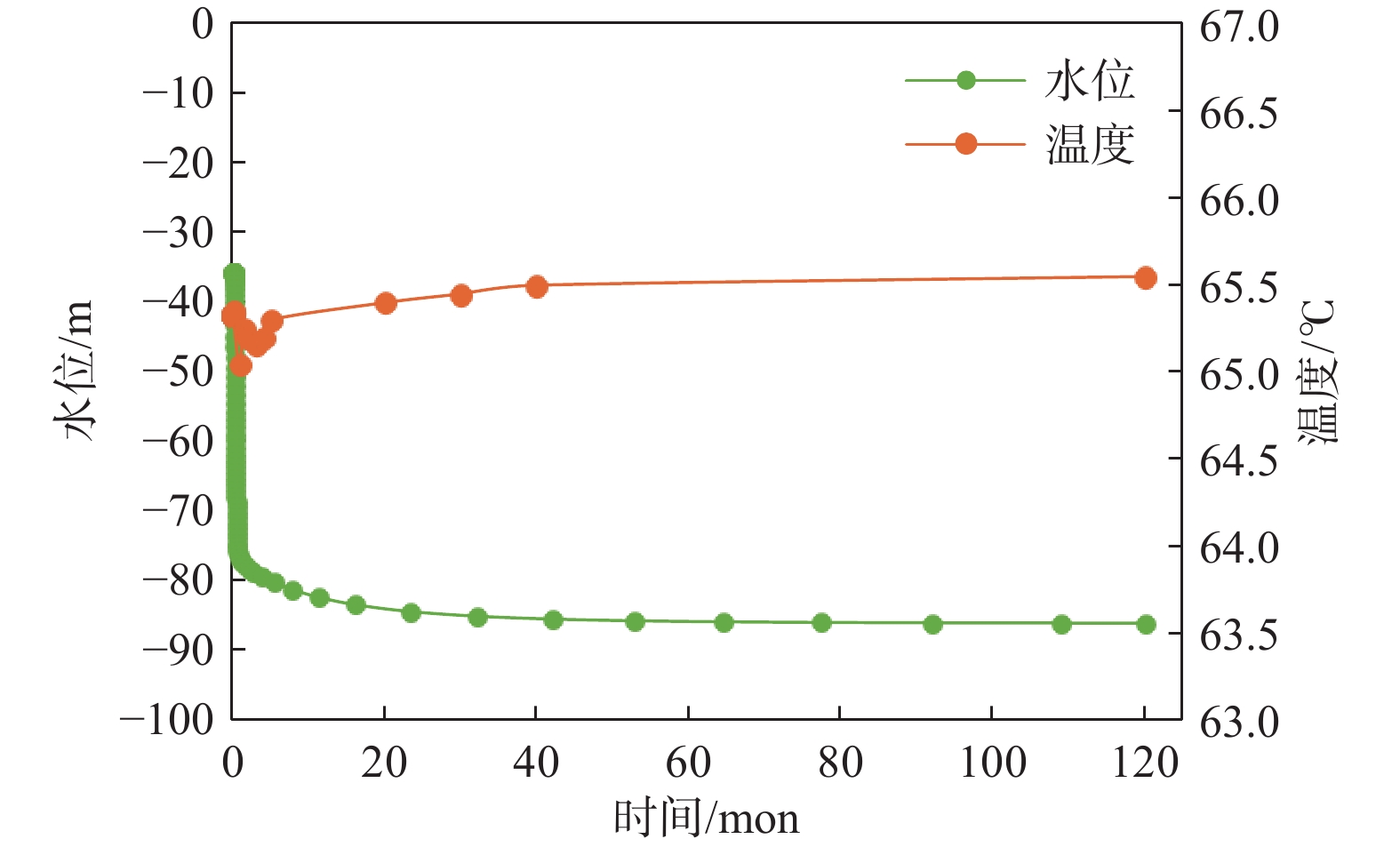
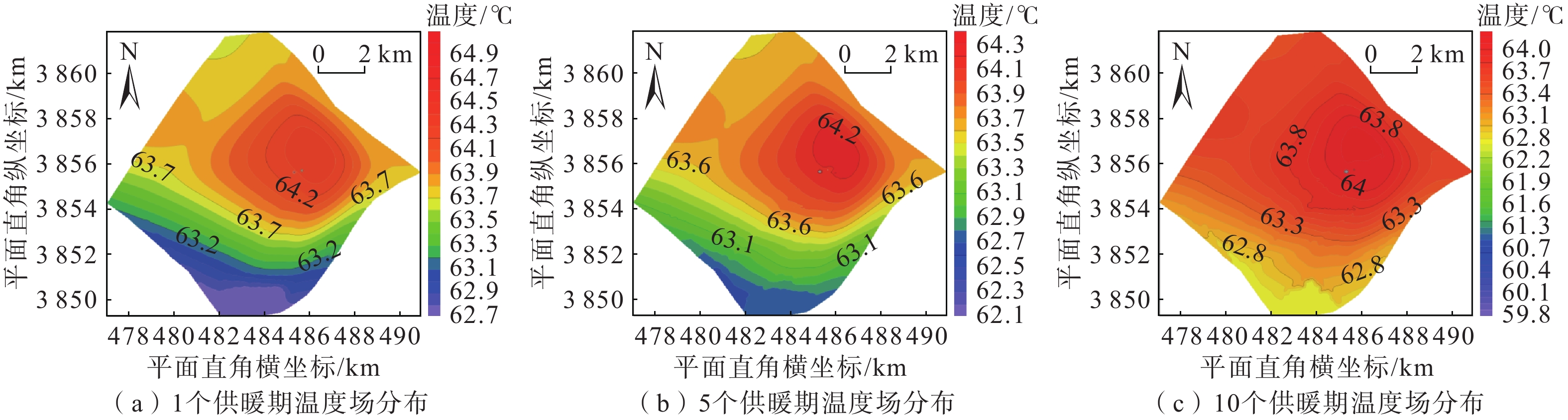
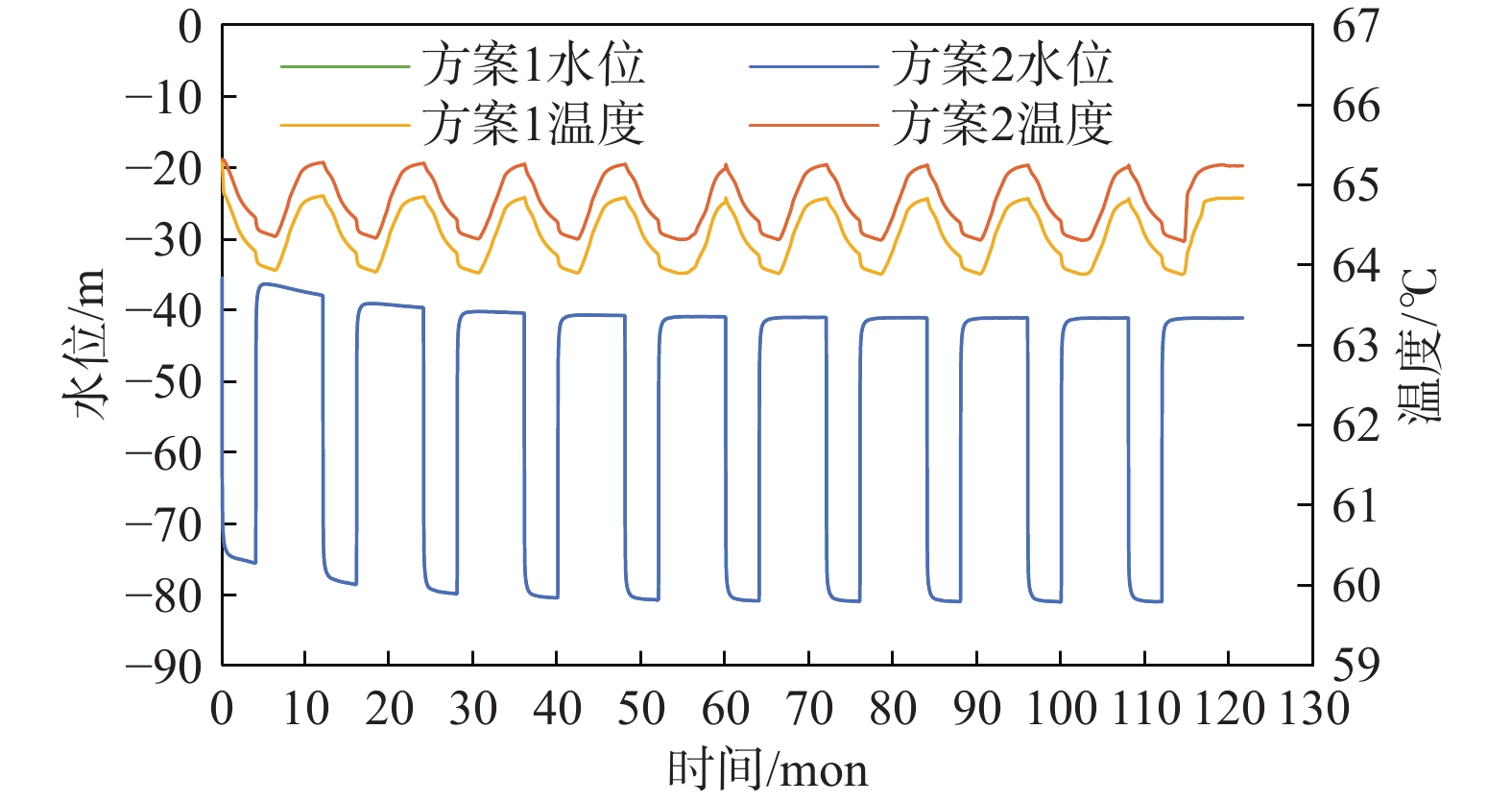
在地热资源开发利用过程中,热储温度、压力会随开采量和时间的增加而降低,地热尾水的排放也会对环境造成热污染,热储回灌可以成为解决这些问题的有效措施。在进行地热开发利用之前,科学合理地规划采灌井的布局方式,探索避免采灌井过早发生热突破、实现地热资源高效利用的最优采灌方案,有利于延长地热井的使用寿命。江苏沛县安国镇所在的丰沛盆地为古近纪以来发育的新生代断陷盆地,岩溶裂隙型热储分布较为广泛,以奥陶系灰岩为主。文章在安国镇地热资源勘查成果的基础上,基于地热井抽水试验、回灌试验获取的采灌井间距、灌采比等重要参数,利用Feflow6.2软件建立了地下热水渗流与热量运移三维耦合数值模型,模拟预测了奥陶系灰岩热储层中地热水的可开采资源量,进行了采灌井开发利用方案的模拟优选。研究结果表明:RPX01开采井与RPX02回灌井合理井底间距为389 m;地热井的灌采比为1.29,确定了一抽一灌的方式进行可持续开发利用;水位降深稳定在50.61 m时,开采井可开采资源量为1000 m3/d;开采量为1000 m3/d、回灌量1000 m3/d,回灌温度40 °C时,10个供暖期后开采井水位下降45.49 m,温度降低1.44 °C,是本次模拟方案中的最佳循环开发利用方案。上述结果为苏北农村清洁能源供暖示范区建设提供了科学决策依据。
Abstract:During the process of developing and utilizing geothermal resources, various challenges are encountered. One such challenge is the decrease in temperature and pressure of the geothermal reservoir as a result of the increasing geothermal exploitation and duration. In addition, the discharge of geothermal tail water poses a risk of thermal pollution, leading to environmental concerns. To address these issues effectively, reinjection of geothermal fluids into the reservoir can be implemented as a viable solution. Prior to initiating the geothermal development and utilization, it is crucial to conduct scientifical and rational planning of the layout of production and reinjection wells. This involves exploring optimal strategies for the production-reinjection scheme that prevents the premature thermal breakthrough and maximize the efficient utilization of geothermal resources, thereby extending the lifespan of the geothermal reservoir. The Fengpei Basin, a Cenozoic rift basin that developed since the Paleogene period, exhibits a widespread distribution of geothermal reservoirs, primarily composed of the Ordovician limestone with karst and fracture characteristics. Building upon the geothermal resource exploration results in the Anguo Town in Peixian County in Jiangsu Province, this study utilizes key parameters obtained from pumping tests and reinjection experiments, such as well spacing and the reinjection-to-production ratio. This paper establishes a 3D coupled numerical model of geothermal water seepage and heat transfer by using the Feflow6.2 software. The recoverable reserves of geothermal fluid within the geothermal reservoir are simulated and predictd, specifically the Ordovician limestone formation. Furthermore, a simulated optimization of the development and utilization scheme for the production-reinjection wells is conducted. The results reveal that an appropriate well spacing of 389 m between the producing well (RPX01) and the reinjection well (RPX02) is recommended. Moreover, the reinjection-to-production ratio, namely the ratio of average aquifer hydraulic conductivity, is determined to be 1.29, supporting a sustainable approach of one-for-one pumping and reinjection. With a stabilized drawdown of 50.61 m, the production well has a capacity to recover 1000 m3/d of geothermal resources. Under the conditions of a production rate and a reinjection rate of 1000 m3/d, as well as a reinjection temperature of 40 °C, the simulation predicts a decrease in groundwater level by 45.49 m and a temperature reduction of 1.44 °C after ten heating seasons. This represents the optimal cyclic development and utilization scheme among the simulated scenarios. The above results provide a scientific basis for decision-making in the construction of the clean energy heating demonstration area in rural northern Jiangsu. They contribute to the establishment of a scientifically sound and sustainable approach for utilizing geothermal resources, while considering the challenges associated with the thermal breakthrough and the environmental impact of geothermal tail water discharge.
-

-
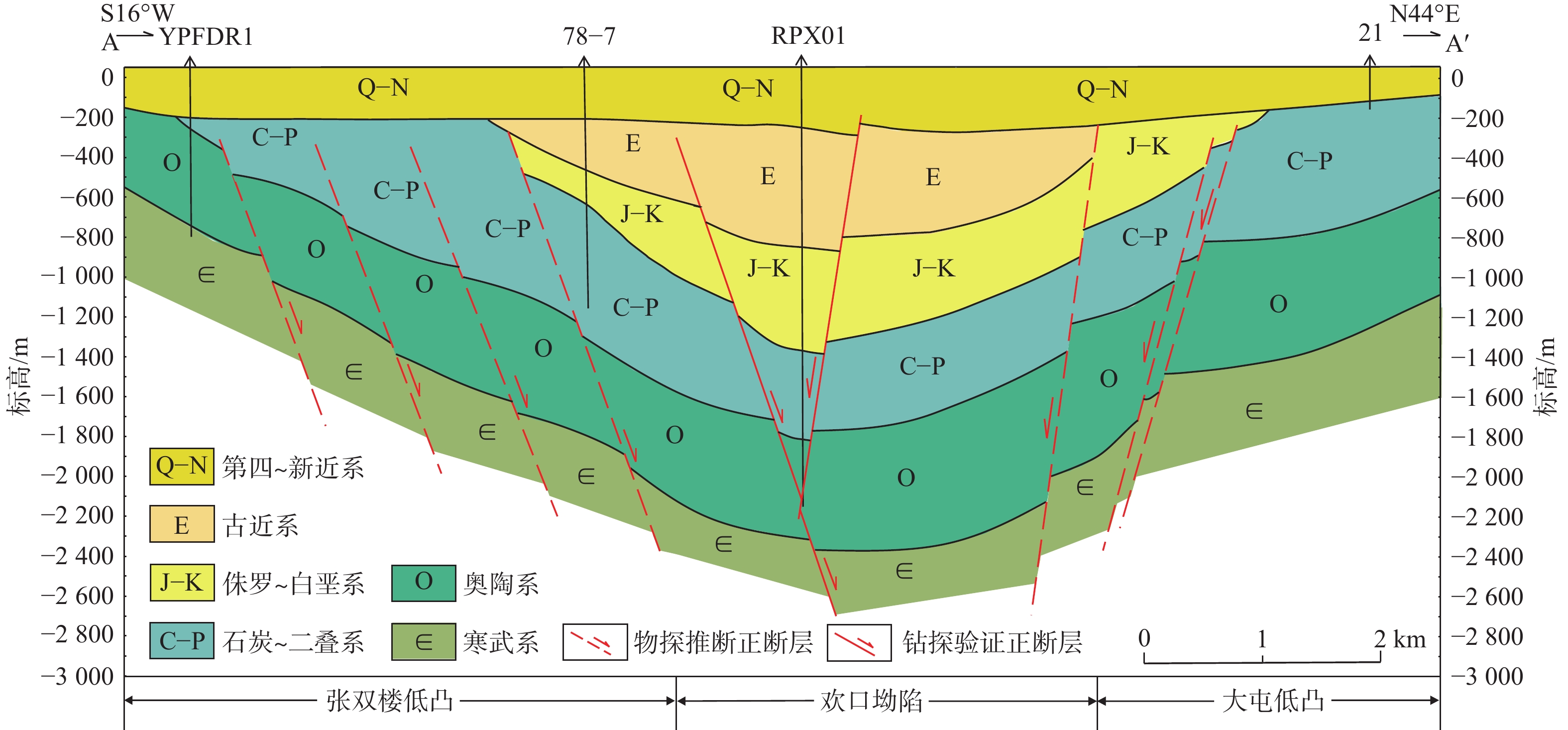
表 1 丰沛地区地热井热储层类型与出水量统计
Table 1. Statistics of the geothermal well reservoir type and water yield in Feng County and Pei County
井名 成井
时间井深/m 热储层 出水层段/m 水温/℃ 大降深水量
/(m3·d−1)燕牌坊地热井(YPFDR1) 2015年 851 奥陶系灰岩 491~851 35 800 丰参1井 1987年 3 946 白垩系、侏罗系砂岩 1 680~2 132 43 463 安国镇地热开采井(RPX01) 2021年 2 200 奥陶系灰岩 1 860~2 200 65 1 940 安国镇地热回灌井
(RPX02)2021年 2 000 奥陶系灰岩 1 928~2 000 52 422 注:丰参1井原为油气井,1987年完井,2020年对其进行地热井改造,成功出水。 表 2 不同采、灌方案设计一览表
Table 2. Different geothermal exploitation and reinjection schemes
方案编号 开采量/(m3·d−1) 回灌水量/(m3·d−1) 回灌
温度/°C方案编号 开采量/(m3·d−1) 回灌水量/(m3·d−1) 回灌
温度/°C方案编号 开采量/(m3·d−1) 回灌水量/(m3·d−1) 回灌
温度/°C1 1 000 1 000.00 50 9 1500 1 500.00 50 17 2000 2 000.00 50 2 1 000.00 40 10 1 500.00 40 18 2 000.00 40 3 666.67 50 11 1 000.00 50 19 1 333.33 50 4 666.67 40 12 1 000.00 40 20 1 333.33 40 5 500.00 50 13 750.00 50 21 1 000.00 50 6 500.00 40 14 750.00 40 22 1 000.00 40 7 333.33 50 15 500.00 50 23 666.67 50 8 333.33 40 16 500.00 40 24 666.67 40 无回灌开采 无回灌开采 无回灌开采 表 3 不同采、灌方案水位、水温模拟结果统计表
Table 3. Simulation results of groundwater level and water temperature in different exploitation and reinjection schemes
方案编号 水位/m 水温/℃ 10个供暖期后 水位下降 10个供暖期后 水温
变化1/2 −81.04 45.49 64.11/63.89 −1.22/−1.44 3/4 −82.56 47.01 64.18/64.09 −1.15/−1.24 5/6 −83.35 47.8 64.28/64.22 −1.05/−1.11 7/8 −84.13 48.58 64.38/64.33 −0.95/−1.00 无回灌开采 −86.73 51.18 65.55 0.22 9/10 −100.88 65.33 63.27/63.09 −2.06/−2.24 11/12 −103.19 67.64 63.38/63.31 −1.95/−2.02 13/14 −104.36 68.81 63.51/63.50 −1.82/−1.83 15/16 −105.57 70.02 63.77/64.22 −1.56/−1.11 无回灌开采 −109.51 73.96 65.62 0.29 17/18 −120.79 85.24 63.01/62.66 −2.32/−2.67 19/20 −123.88 88.33 63.23/63.14 −2.10/−2.19 21/22 −125.44 89.89 63.66/63.43 −1.67/−1.90 23 −126.98 91.43 64.18/64.10 −1.15/−1.23 无回灌开采 −132.29 96.74 65.65 0.32 -
[1] LUND J W,TOTH A N. Direct utilization of geothermal energy 2020 worldwide review[J]. Geothermics,2021,90:1 − 31.
[2] 王贵玲,刘彦广,朱喜,等. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘,2020,27(1):1 − 9. [WANG Guiling,LIU Yanguang,ZHU Xi,et al. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2020,27(1):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2020.1.1
WANG Guiling, LIU Yanguang, ZHU Xi, et al. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(1): 1–9. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2020.1.1
[3] 陈宗宇. 天津市塘沽低温热储回灌的水-岩相互作用地球化学模拟[J]. 地球科学,1998(5):79 − 84. [CHEN Zongyu. Modeling water-rock interaction of geothermal reinjection in the Tanggu low-temperature field,Tianjin[J]. Earth Earth Science,1998(5):79 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Zongyu. Modeling water-rock interaction of geothermal reinjection in the tanggu low-temperature field, Tianjin [J]. Earth Earth Science, 1998, (5): 79–84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 何满潮,刘斌,姚磊华,等. 地热水对井回灌渗流场理论研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2004(3):11 − 14. [HE Manchao,LIU Bin,YAO Leihua,et al. Study on theory of seepage field around geothermal production-reinjection doublets wells[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2004(3):11 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HE Manchao, LIU Bin, YAO Leihua, et al. Study on theory of seepage field around geothermal production-reinjection doublets wells [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2004, (3): 11–14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 申建梅,陈宗宇,张古彬. 地热开发利用过程中的环境效应及环境保护[J]. 地球学报,1998(4):67 − 73. [SHEN Jianmei,CHEN Zongyu,ZHANG Gubin. Environmental protection and environmental impact of geothermal development and utilization[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,1998(4):67 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SHEN Jianmei, CHEN Zongnyu, ZHANG Gubin. Environmental protection and environmental impact of geothermal development and utilization [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 1998, (4): 67–73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] BAKKE S, VIK E A, GRÜNER H, et al. Produced water reinjection (PWRI) [M]// REED M, JOHNSEN S. Produced water 2: Environmental issues and mitigation technologies. Boston, MA: Springer, 1996 : 447-458.
[7] AXELSSON G,GUNNLAUGSSON E,JÓNASSON T,et al. Low-temperature geothermal utilization in Iceland–Decades of experience[J]. Geothermics,2010,39(4):329 − 338. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2010.09.002
[8] CAPPETTI G, PARISI L, RIDOLFI A, et al. Fifteen years of reinjection in the Larderello-Valle Secolo area: Analysis of the production data[C]// Proceedings World Geothermal Congress, 1995 : 18 − 31.
[9] KENNEDY B M, PRUESS K, LIPPMANN M J, et al. A history of geothermal energy research and development in the United States: Reservoir Engineering 1976—2006[R]. Washington, DC : Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), 2010.
[10] UNGEMACH P, ANTICS M, PAPACHRISTOU M. Sustainable geothermal reservoir management[C]//Proceedings World Geothermal Congress, 2005 : 24 − 29.
[11] 刘久荣. 地热回灌的发展现状[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2003,30(3):100 − 104. [LIU Jiurong. The status of geothermal reinjection[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2003,30(3):100 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.03.025
LIU Jiurong. The status of geothermal reinjection [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2003, 30(3): 100–104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.03.025
[12] 曾梅香,田光辉,赵越波,等. 采灌条件下中低温热储温度场动态特征初探[J]. 中国地质,2010,37(1):191 − 197. [ZENG Meixiang,TIAN Guanghui,ZHAO Yuebo,et al. A tentative discussion on dynamic characteristics of the low-medium temperature geothermal reservoir field under the condition of exploitation-reinjection[J]. Geology in China,2010,37(1):191 − 197. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZENG Meixiang, TIAN Guanghui, ZHAO Yuebo, et al. A tentative discussion on dynamic characteristics of the low-medium temperature geothermal reservoir field under the condition of exploitation-reinjection [J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(1): 191–197. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 宋先知,李根生,王高升,等. 中深层地热能取热技术研究进展[J]. 科技导报,2022,40(20):42 − 51. [SONG Xianzhi,LI Gensheng,WANG Gaosheng,et al. Research progress on heat extraction technology for developing medium-deep geothermal energy[J]. Science & Technology Review,2022,40(20):42 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SONG Xianzhi, LI Gensheng, WANG Gaosheng, et al. Research progress on heat extraction technology for developing medium-deep geothermal energy [J]. Science & Technology Review, 2022, 40(20): 42–51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 高楠安, 汪新伟, 梁海军, 等. 山东临清坳陷大名次凹陷地热系统成因模式[J]. 中国地质, 2021: 1–19
GAO Nan’an, WANG Xinwei, LIANG Haijun, et al. Genetic mechanism of geothermal system in Daming sag, Linqing depression, Linqing, Shangdong [J]. Geology in China, 2021: 1–19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘润川,任战利,叶汉青,等. 地热资源潜力评价—以鄂尔多斯盆地部分地级市和重点层位为例[J]. 地质通报,2021,40(4):565 − 576. [LIU Runchuan,REN Zhanli,YE Hanqing,et al. Potential evaluation of geothermal resources:Exemplifying some municipalities and key strata in Ordos Basin as a study case[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021,40(4):565 − 576. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Runchuan, REN Zhanli, YE Hanqing, et al. Potential evaluation of geothermal resources: exemplifying some municipalities and key strata in Ordos Basin as a study case [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40( 4): 565-576. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 刘东林,李义曼,庞忠和,等. 碳酸盐岩热储对湖水回灌的响应[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):178 − 183. [LIU Donglin,LI Yiman,PANG Zhonghe,et al. Geochemical responses of carbonate reservoir to untreated lake water reinjecition doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-064
J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):178 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-064
[17] WANG Shufang,LIU Jiurong,SUN Ying,et al. Study on the geothermal production and reinjection mode in Xiong County[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2018,5(3):178 − 186.
[18] WANG Guiling,ZHANG Wei,MA Feng,et al. Overview on hydrothermal and hot dry rock researches in China[J]. China Geology,2018,1(2):273 − 285. doi: 10.31035/cg2018021
[19] STEFANSSON V. Geothermal reinjection experience[J]. Geothermics,1997,26(1):99 − 139. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6505(96)00035-1
[20] KAMILA Z,KAYA E,ZARROUK S J. Reinjection in geothermal fields:An updated worldwide review 2020[J]. Geothermics,2021,89:1 − 88.
[21] 阮传侠,沈健,李立亮,等. 天津市滨海新区东丽湖地区基岩热储回灌研究[J]. 地质通报,2017,36(8):1439 − 1449. [RUAN Chuanxia,SHEN Jian,LI Liliang,et al. Researches on the reinjection of Dongli Lake bedrock reservoir in Binhai New Area,Tianjin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2017,36(8):1439 − 1449. (in Chinese with English abstract)
RUAN Chuanxia, SHEN Jian, LI Liliang, et al. Researches on the reinjection of Dongli Lake bedrock reservoir in Binhai New Area, Tianjin [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(8): 1439-1449. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 赵振,秦光雄,罗银飞,等. 西宁盆地地热水特征及回灌结垢风险[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):193 − 204. [ZHAO Zhen,QIN Guangxiong,LUO Yinfei,et al. Characteristics of geothermal water in the Xining Basin and risk of reinjection scaling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):193 − 204. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202103058
ZHAO Zhen, QIN Guangxiong, LUO Yinfei, et al. Characteristics of geothermal water in the Xining Basin and risk of reinjection scaling [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 193–204. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202103058
[23] 马峰, 王贵玲, 刘桂宏, 等. 雄安新区容城地热田碳酸盐岩热储采灌数值模拟[J/OL]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), (2022-12-27)[2023-01-30]. https://doi.org/10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20220004.
MA Feng, WANG Guiling, LIU Guihong, et al. Numerical simulation of exploitation and reinjection of carbonate geothermal reservoir in Rongcheng geothermal field, Xiongan New Area[J/OL]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), (2022-12-27)[2023-01-30].(in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] ZARROUK S J, O’SULLIVAN M J, CROUCHER A E, et al. Optimized numerical modeling of production from the poihipi dry steam zone: Wairakei geothermal system[C]//Proceedings of 31 workshop on geothermal reservoir engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California. 2006.
[25] ROMAGNOLI P,ARIAS A,BARELLI A,et al. An updated numerical model of the Larderello–Travale geothermal system,Italy[J]. Geothermics,2010,39(4):292 − 313.
[26] 杨亚军,丁桂伶,徐巍,等. 基于示踪试验及动态数据的北京小汤山地区地热资源量评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):196 − 200. [YANG Yajun,DING Guiling,XU Wei,et al. Tracer test and geothermal resource quantity evaluation based on dynamic data in the Xiaotangshan area of Beijing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):196 − 200. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201808029
YANG Yajun, DING Guiling, XU Wei, et al. Tracer test and geothermal resource quantity evaluation based on dynamic data in the Xiaotangshan area of Beijing [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(5): 196–200. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201808029
[27] 杜建国, 王彩会, 孔刚, 等. 苏北农村住房条件改善清洁能源供暖示范区(沛县)地热资源勘查报告[R]. 南京: 江苏省地质调查研究院, 2022
DU Jianguo, WANG Caihui, KONG Gang, et al. Report of geothermal resources exploration in the clean energy heating demonstration area of rural housing improvement in Northern Jiangsu (Peixian County)[R]. Nanjing: Geological Survey of Jiangsu Province, 2022. (in Chinese)
[28] 梅玲, 王健呈, 张华哲. 江苏省沛县朱寨镇燕牌坊地热资源勘查报告[R]. 南京: 江苏长江地质勘查院, 2015
MEI Ling, WANG Jiancheng, ZHANG Huazhe. Geothermal resources exploration report of Yanpaifang, Zhuzhai Town, Peixian County, Jiangsu Province [R]. Nanjing: Jiangsu Yangtze River Geological Exploration Institute, 2015. (in Chinese)
[29] SU Yujuan,YANG Fengtian,WANG Bing,et al. Reinjection of cooled water into sandstone geothermal reservoirs in China:A review[J]. Geosciences Journal,2018,22(1):199 − 207. doi: 10.1007/s12303-017-0019-3
[30] WANG Guiling,WANG Wanli,ZHANG Wei,et al. The status quo and prospect of geothermal resources exploration and development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China[J]. China Geology,2020,3(1):173 − 181. doi: 10.31035/cg2020013
[31] 王钧, 黄尚瑶, 黄歌山, 等. 中国地温分布的基本特征[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1990
WANG Jun, HUANG Shangyao, HUANG Geshan, et al. Basic characteristics of geothermal distribution in China [M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1990. (in Chinese)
[32] 江苏省地质矿产局. 江苏省及上海市区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1984: 612 − 616
Jiangsu Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration. Monograph on the regional geology of Jiangsu Province and Shanghai City[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1984: 612 − 616. (in Chinese)
[33] 吕雅馨,骆祖江,徐成华. 南京汤山地区地热水资源评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2020,50(6):1844 − 1853. [LǙ Yaxin,LUO Zujiang,XU Chenghua. Evaluation of geothermal water resources in Tangshan area,Nanjing[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition),2020,50(6):1844 − 1853. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LǙ Yaxin, LUO Zujiang, XU Chenghua. Evaluation of geothermal water resources in Tangshan are, Nanjing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2020, 50(6): 1844–1853. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 中国地质调查局. 水文地质手册[M]. 2 版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012: 445 − 461. [China Geological Survey. Handbook of hydrogeology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Geology Press, 2012: 445 − 461. (in Chinese)]
[35] 宾德智, 刘延忠, 郑克棪, 等. 地热资源地质勘查规范: GB/T 11615—2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011
BIN Dezhi, LIU Yanzhong, ZHENG Keyan, et al. Geologic exploration standard of geothermal resources: GB/T 11615—2010[S]. Beijing: Standard Press of China, 2021. (in Chinese)
[36] 曹剑峰, 迟宝明, 王文科, 等. 专门水文地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006
CAO Jianfeng, CHI Baoming, Wang Wenke, et al. Applied hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[37] 王贵玲, 李曼, 张明燕, 等. 地热资源评价方法及估算规程: DZ/T 0331—2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020
WANG Guiling, LI Man, ZHANG Mingyan, et al. Specification for estimation and evaluation of geothermal resources: DZ/T 0331—2020[S]. Beijing: Standard Press of China, 2020. (in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: