An early prediction model of regional landslide disasters in Fujian Province based on convolutional neural network
-
摘要:
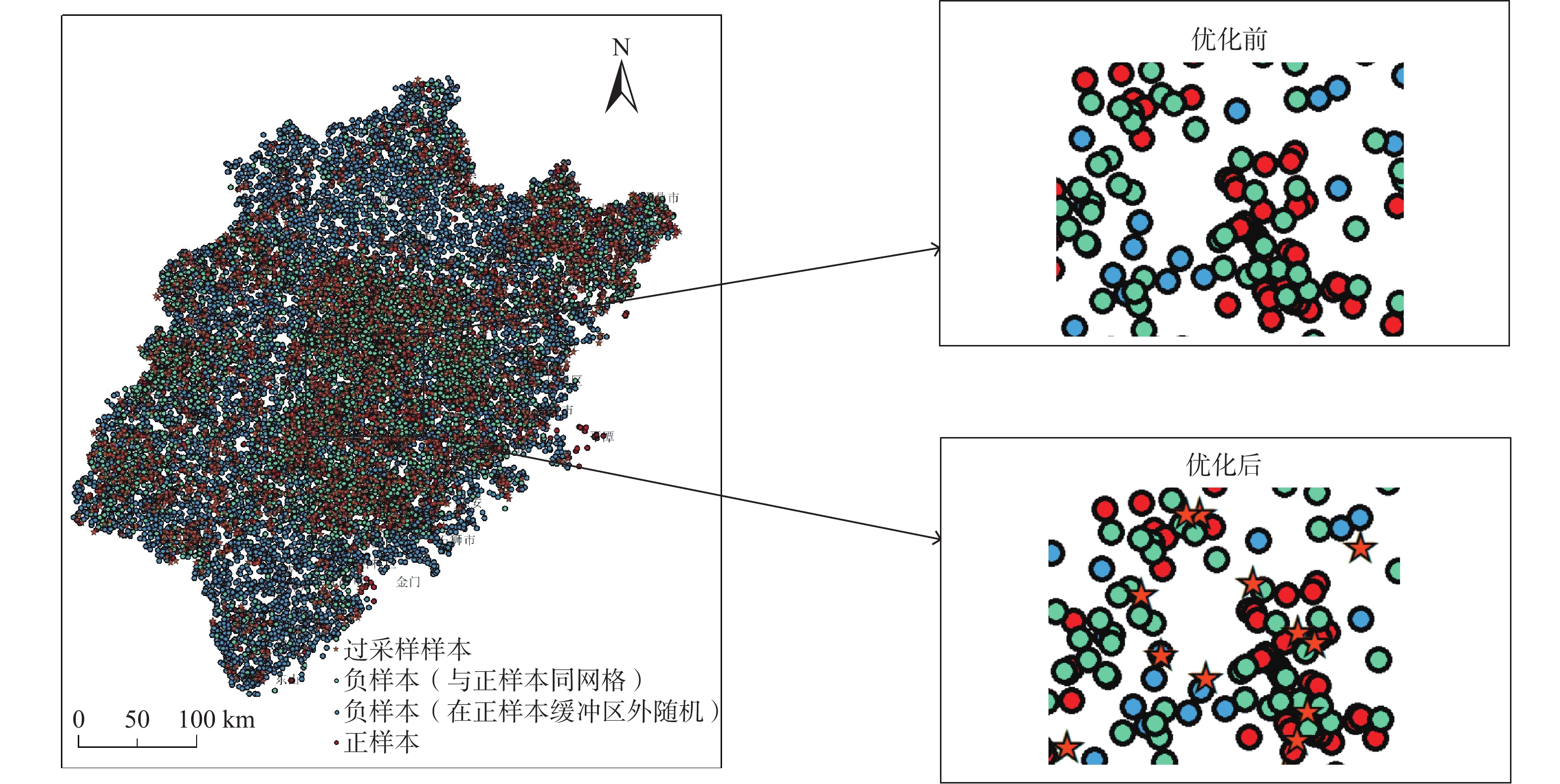
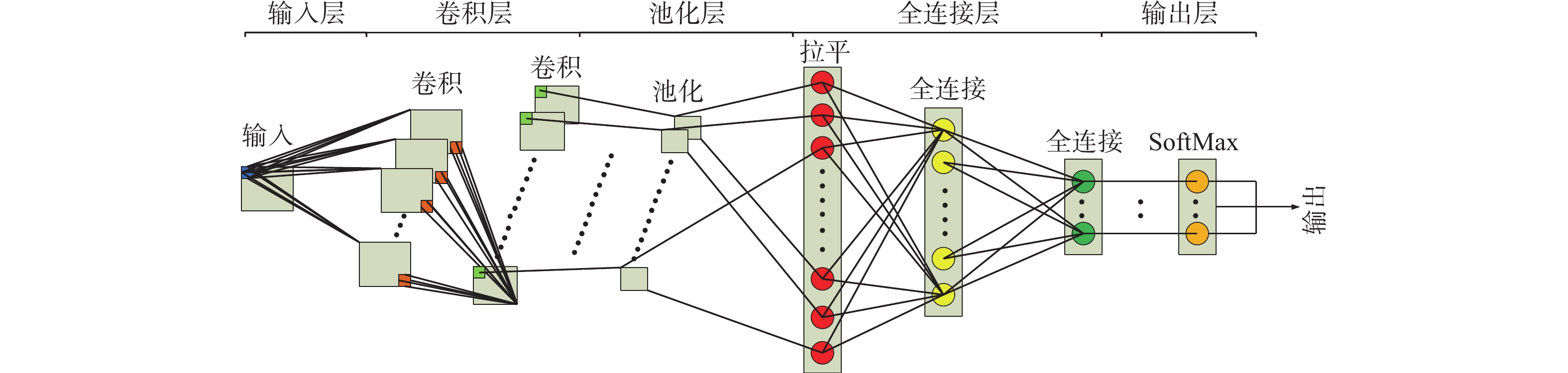
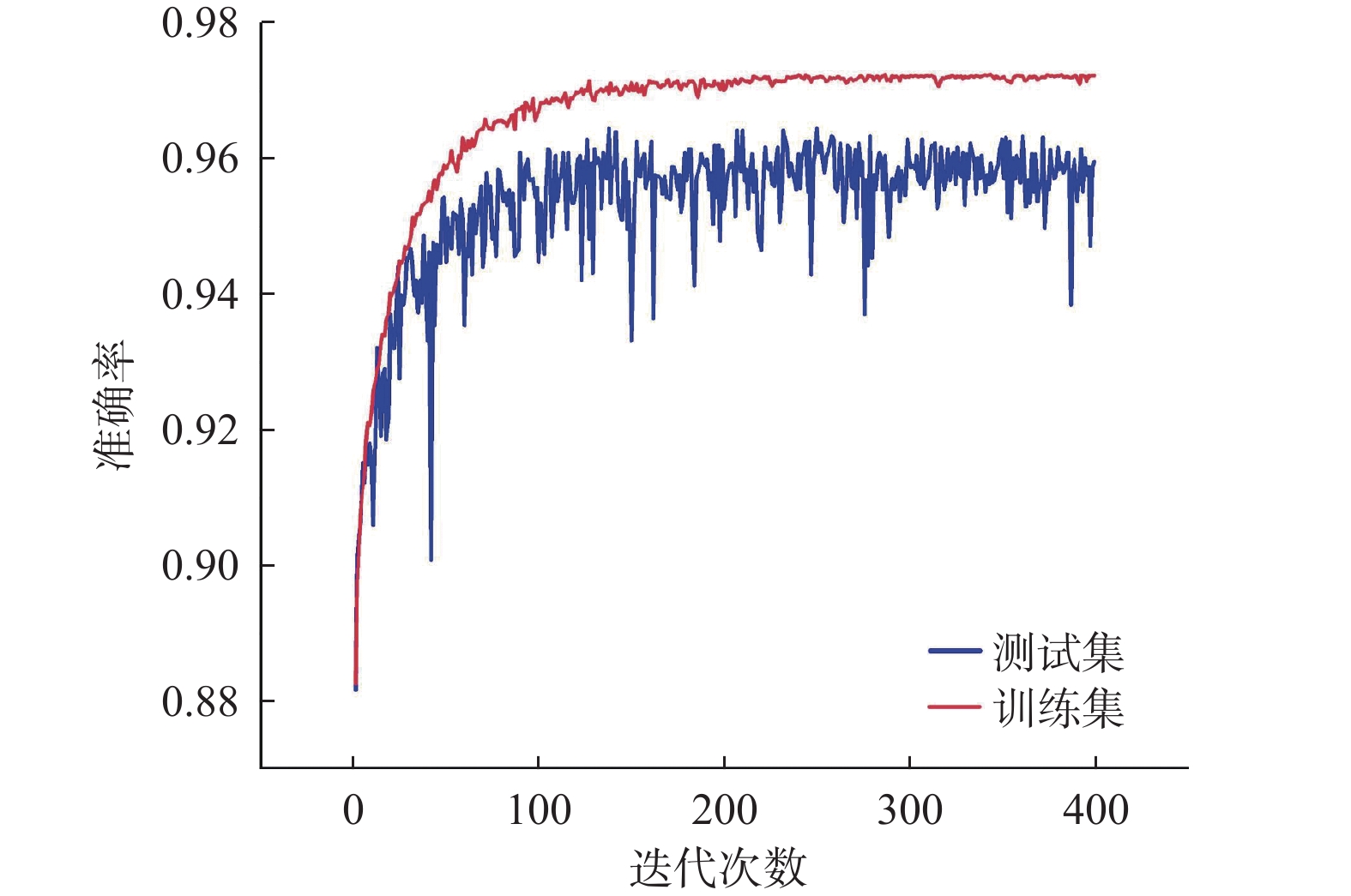
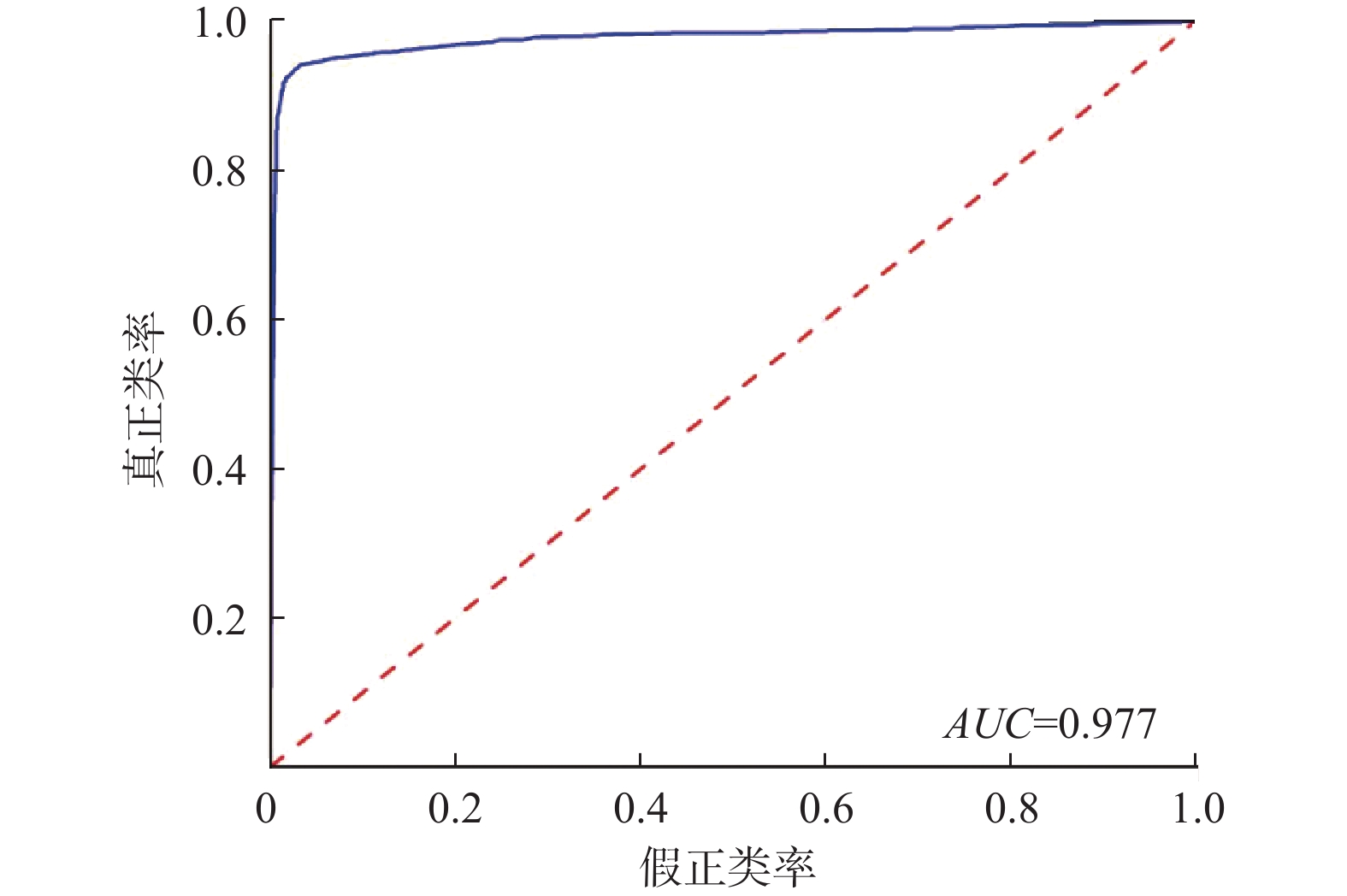
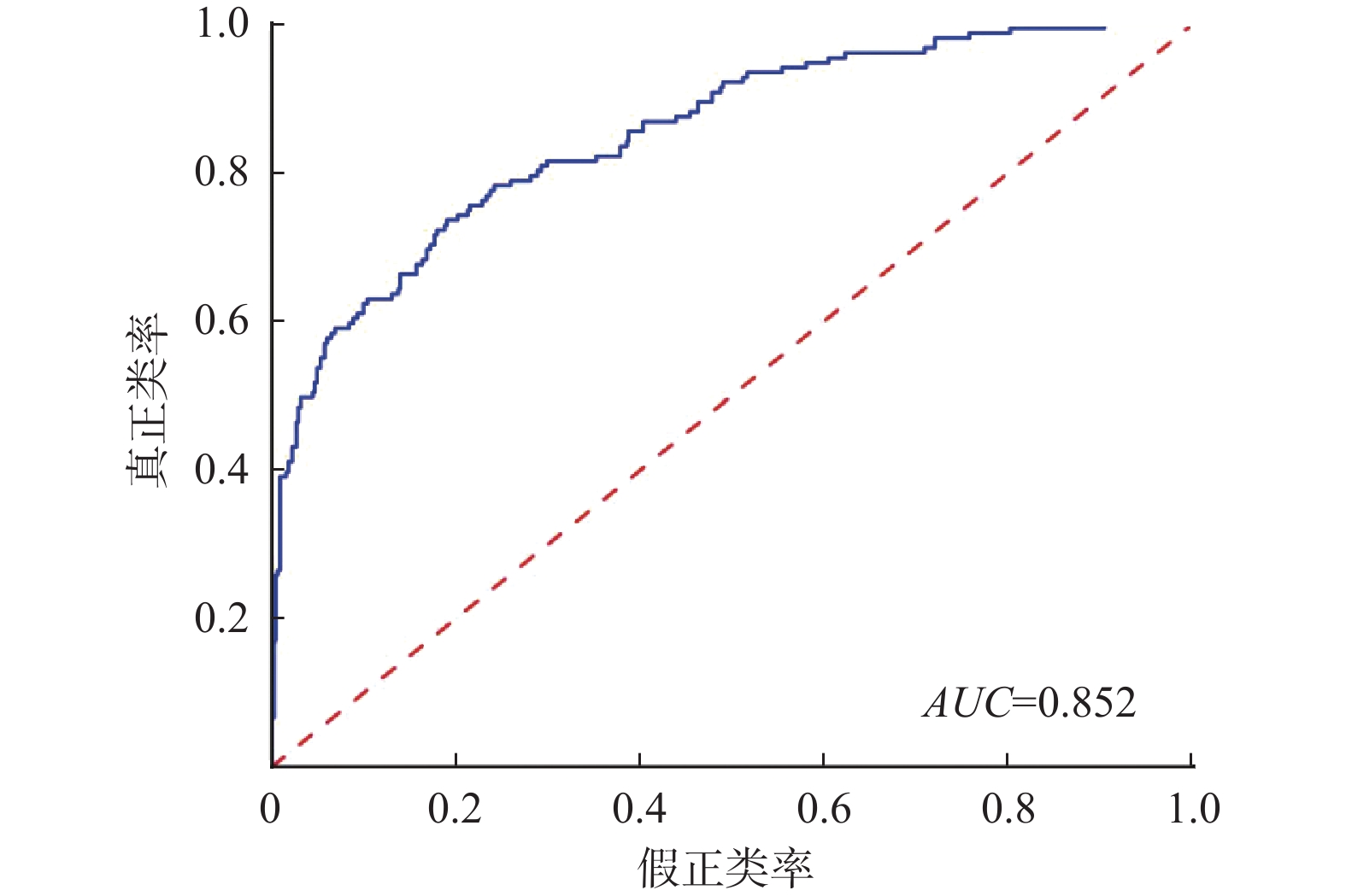
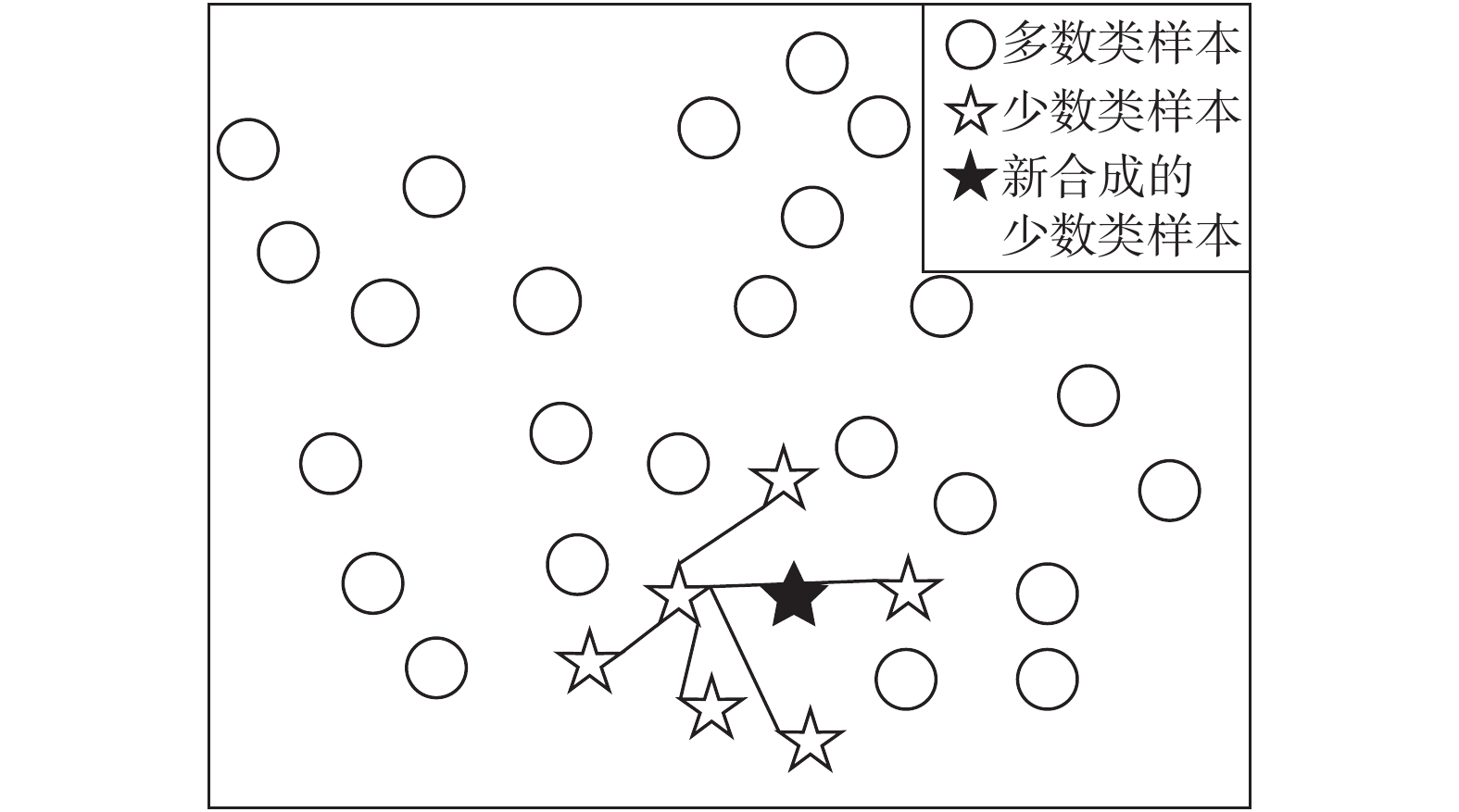
福建省滑坡灾害频发,开展区域尺度上的滑坡灾害预警是防灾减灾的重要手段,但由于滑坡成灾机理复杂,传统的区域滑坡预警方法存在精度不足等问题。深度学习是指通过构建神经网络模型进行特征的提取、抽象、表示与学习的技术,是机器学习的一种。卷积神经网络作为一种经典的深度学习算法,具有比传统机器学习更强大的分类能力与表征能力。文章以福建省为研究区,将卷积神经网络引入滑坡灾害预警领域,构建福建省区域滑坡预警模型,过程及结果如下:(1)采用SMOTE优化算法对2010—2018年福建省滑坡灾害样本库进行优化,扩充正样本的个数,将正负样本比例从1∶3.4扩充到1∶2,样本总量达到18040个;(2)构建卷积神经网络模型结构,模型结构包括一个输入层、两个卷积层、两个最大池化层和一个全连接层以及一个输出层;(3)使用卷积神经网络对优化后的样本(2010—2018年样本的80%作为训练集)进行训练,并用贝叶斯优化算法优化模型超参数,得到福建省区域滑坡预警模型;(4)以2010—2018年样本的20%作为测试集对模型进行测试,采用混淆矩阵、ROC曲线进行模型测试,结果显示模型准确度为0.96~0.97,AUC值达到0.977,模型精度与泛化能力良好;(5)以2019年汛期滑坡灾害实况作为正样本,通过时空采样的方法采集负样本,构建2019年区域滑坡样本校验集(样本数603个),对模型进行进一步实况校验,采用混淆矩阵、ROC曲线进行模型校验,结果显示模型准确度为0.75~0.85,AUC值为0.852。虽然仅用了2019年汛期的滑坡实况样本进行校验,但也达到较好的效果。将卷积神经网络算法应用到区域滑坡预警中,为建立区域滑坡预警模型提供了一种新的途径,初步校验表明,模型效果良好,今后将在福建省对模型进行进一步的应用与校验。
Abstract:Landslide disasters occur frequently in Fujian Province, and early warning of landslide disasters on a regional scale is an important means of effective disaster prevention and mitigation. Due to the complex mechanism of landslide disasters, the traditional regional landslide early warning methods have such problems as insufficient accuracy. Deep learning mainly refers to the technology of feature extraction, abstraction, representation and learning by constructing the neural network model, which is a kind of machine learning. As a classical deep learning algorithm, convolutional neural network has more powerful classification and representation ability than traditional machine learning. Taking Fujian Province as the research area, this paper introduces the convolution neural network into the field of landslide disaster early warning and constructs a regional landslide early warning model of Fujian Province. The process is as follows: (1) The SMOTE optimization algorithm is used to optimize the sample database of landslide disasters in Fujian Province from 2010 to 2018, enlarging the number of positive samples and expanding the proportion of positive and negative samples from 1∶3.4 to 1∶2, and the total number of samples reaches 18040. (2) Construct a convolution neural network model structure, which includes an input layer, two convolution layers, two maximum pooling layers, a full connection layer and an output layer. (3) Use the convolution neural network to train the optimized samples (80% of the samples from 2010 to 2018 as the training set), and use the Bayesian optimization algorithm to optimize the model parameters to obtain the regional landslide early warning model of Fujian Province. (4) The model is tested with 20% of the samples from 2010 to 2018 as the test set, and the confusion matrix and ROC curve are used to test the model. The results show that the accuracy of the model ranges from 0.96 to 0.97, the AUC value is 0.977, indicating that the model accuracy and generalization ability are good. (5) The actual situation of the landslide disaster in the flood season of 2019 is taken as a positive sample, negative samples are collected through the method of time-space sampling, and the 2019 regional landslide sample verification set (603 samples) is constructed. The model is further verified by using the confusion matrix and ROC curve. The results show that the accuracy of the model ranges from 0.75 to 0.85, and the AUC value is 0.852. Although only the actual landslide samples in the flood season of 2019 is used for verification, good results is also achieved. In this paper, the convolution neural network algorithm is applied to the regional landslide early warning, which provides a new way to establish the regional landslide early warning model. The preliminary verification shows that the model is effective and will be further applied and verified in Fujian Province in the future.
-
Key words:
- landslide disaster /
- early warning model /
- deep learning /
- convolutional neural network /
- model building
-

-
表 1 CNN模型超参数设置
Table 1. Hyperparameter settings of the CNN models
超参数 意义 优化后参数 units1
units2
dropout rate
activation1
activation2
activation3
lr第一层卷积核的大小
第二层卷积核的大小
每层神经元丢弃率
第一层激活函数
第二层激活函数
全连接层激活函数
学习率512 $ \times 1 $
32$ \times 1 $
0.1
relu
relu
elu
0.002表 2 不同阈值下的 CNN分类结果混淆矩阵
Table 2. Confuse matrix of the results of the CNN classification under different thresholds
阈值 实际值 非滑坡 滑坡 预测值 非滑坡 2325 72 特异度:0.969 0.25 滑坡 73 1138 灵敏度:0.939 假正类率:0.969 真正类率:0.941 准确率:0.960 预测值 非滑坡 2344 53 特异度:0.978 0.50 滑坡 78 1133 灵敏度:0.935 假正类率:0.967 真正类率:0.955 准确率:0.964 预测值 非滑坡 2353 44 特异度:0.982 0.75 滑坡 86 1125 灵敏度:0.929 假正类率:0.964 真正类率:0.962 准确率:0.964 表 3 2019年样本CNN模型校验结果的混淆矩阵
Table 3. Confusion matrix of the 2019 sample CNN model verification results
阈值 实际值 非滑坡 滑坡 预测值 非滑坡 434 76 特异度:0.851 0.25 滑坡 18 75 灵敏度:0.806 假正类率:0.960 真正类率:0.497 准确率:0.844 预测值 非滑坡 450 120 特异度:0.789 0.50 滑坡 2 31 灵敏度:0.939 假正类率:0.996 真正类率:0.205 准确率:0.798 预测值 非滑坡 452 151 特异度:0.750 0.75 滑坡 0 0 灵敏度:0 假正类率:1 真正类率:0 准确率:0.750 表 4 福建省预警模型评价对比
Table 4. Comparison of early warning model evaluation in Fujian Province
人工智能模型 ACC AUC 卷积神经网络 0.964 0.977 随机森林(过采样) 0.945 0.980 随机森林 0.953 0.954 注:随机森林评价数据摘自文献[29]。 -
[1] KAVZOGLU T,SAHIN E K,COLKESEN I. Landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis,support vector machines,and logistic regression[J]. Landslides,2014,11(3):425 − 439. doi: 10.1007/s10346-013-0391-7
[2] HUANG Lu,XIANG Luyang. Method for meteorological early warning of precipitation-induced landslides based on deep neural network[J]. Neural Processing Letters,2018,48(2):1243 − 1260. doi: 10.1007/s11063-017-9778-0
[3] 何永金. 福建省主要地质灾害的特点、成因及其对策[J]. 福建地质,1995,14(4):263 − 271. [HE Yongjin. Characteristics and mechanism of major geological hazards in Fujian Province and protection and controlling method against them[J]. Geology of Fujian,1995,14(4):263 − 271. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HE Yongjin. Characteristics and mechanism of major geological hazards in Fujian Province and protection and controlling method against them[J]. Geology of Fujian, 1995, 14(4): 263-271. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] CANNON S H, ELLEN S D. Rainfall conditions for abundant debris avalanches, San Francisco Bay region, California[J]. California Geology. 1985, 38(12): 267–272
[5] 兰恒星,周成虎,王苓涓,等. 地理信息系统支持下的滑坡-水文耦合模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2003,22(8):1309 − 1314. [LAN Hengxing,ZHOU Chenghu,WANG Lingjuan,et al. GIS based landslide stability and hydrological distribution coupled model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2003,22(8):1309 − 1314. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.08.015
LAN Hengxing, ZHOU Chenghu, WANG Lingjuan, et al. GIS based landslide stability and hydrological distribution coupled model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(8): 1309-1314. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.08.015
[6] 史中发. 哀牢山地区典型降雨型滑坡稳定性研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014
SHI Zhongfa. Stability analysis of a rainfall-induced landslide in the area of ailao mountain[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李媛. 区域降雨型滑坡预报预警方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2005
LI Yuan. Method for the warning of precipitation-induced landslides[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘传正,李铁锋,程凌鹏,等. 区域地质灾害评价预警的递进分析理论与方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2004,31(4):1 − 8. [LIU Chuanzheng,LI Tiefeng,CHENG Lingpeng,et al. A method by to analyses four parameters for assessment and early warning on the regional geo-hazards[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2004,31(4):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2004.04.001
LIU Chuanzheng, LI Tiefeng, CHENG Lingpeng, et al. A method by to analyses four parameters for assessment and early warning on the regional geo-hazards[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2004, 31(4): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2004.04.001
[9] CAINE N. The rainfall intensity - duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows[J]. Geografiska Annaler:Series A,Physical Geography,1980,62(1/2):23 − 27.
[10] BRAND E W, PREMCHITT J, PHILLIPSON H B. Relationship between rainfall and landslides in Hong Kong[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Landslides. Toronto: Canadian Geotechnical Society, 1984, 1(1): 276 − 284.
[11] HONG Yong,HIURA H,SHINO K,et al. The influence of intense rainfall on the activity of large-scale crystalline schist landslides in Shikoku Island,Japan[J]. Landslides,2005,2(2):97 − 105. doi: 10.1007/s10346-004-0043-z
[12] 刘传正,刘艳辉,温铭生,等. 中国地质灾害气象预警实践:2003—2012[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(1):1 − 8. [LIU Chuanzheng,LIU Yanhui,WEN Mingsheng,et al. Early warning for regional geo-hazards during 2003-2012,China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(1):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Chuanzheng, LIU Yanhui, WEN Mingsheng, et al. Early warning for regional geo-hazards during 2003-2012, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2015, 26(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] PENNINGTON C, DASHWOOD C, FREEBOROUGH K. The National Landslide Database and GIS for Great Britain: construction, development, data acquisition, application and communication[C]//EGU General Asse-mbly Conference Abstracts. 2014: 3638.
[14] 陈香,王俪儒. 福建省滑坡灾害气象预警的研究[J]. 防灾科技学院学报,2015,17(4):68 − 75. [CHEN Xiang,WANG Liru. A study on landslide hazard meteorological early warning in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention,2015,17(4):68 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2015.04.011
CHEN Xiang, WANG Liru. A study on landslide hazard meteorological early warning in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention, 2015, 17(4): 68-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2015.04.011
[15] 方然可,刘艳辉,苏永超,等. 基于逻辑回归的四川青川县区域滑坡灾害预警模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):181 − 187. [FANG Ranke,LIU Yanhui,SU Yongchao,et al. A early warning model of regional landslide in Qingchuan County,Sichuan Province based on logistic regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):181 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201911034
FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, SU Yongchao, et al. A early warning model of regional landslide in Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province based on logistic regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(1): 181-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201911034
[16] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归-信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang,YANG Zhihua,YUAN Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Xizang traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Xizang traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 102-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] Paraskevas,Tsangaratos. Comparison of a logistic regression and Naïve Bayes classifier in landslide susceptibility assessments:the influence of models complexity and training dataset size[J]. CATENA,2016,145:164 − 179. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2016.06.004
[18] YOUSSEF A M,POURGHASEMI H R,POURTAGHI Z S,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest,boosted regression tree,classification and regression tree,and general linear models and comparison of their performance at Wadi Tayyah Basin,Asir Region,Saudi Arabia[J]. Landslides,2016,13(5):839 − 856. doi: 10.1007/s10346-015-0614-1
[19] CHEN Wei,XIE Xiaoshen,WANG jiale,et al. A comparative study of logistic model tree,random forest,and classification and regression tree models for spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility[J]. CATENA,2017,151:147 − 160. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.032
[20] 冉光静,李晓,陈刚. 福建省滑坡发育强度分布规律及影响因素分析[J]. 西部探矿工程,2009,21(2):20 − 22. [RAN Guangjing,LI Xiao,CHEN Gang. Distribution law and influencing factors of landslide development intensity in Fujian Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering,2009,21(2):20 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2009.02.009
RAN Guangjing, LI Xiao, CHEN Gang. Distribution law and influencing factors of landslide development intensity in Fujian Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2009, 21(2): 20-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2009.02.009
[21] 刘艺梁,殷坤龙,刘斌. 逻辑回归和人工神经网络模型在滑坡灾害空间预测中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(5):92 − 96. [LIU Yiliang,YIN Kunlong,LIU Bin. Application of logistic regression and artificial neural networks in spatial assessment of landslide hazards[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(5):92 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.05.017
LIU Yiliang, YIN Kunlong, LIU Bin. Application of logistic regression and artificial neural networks in spatial assessment of landslide hazards[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(5): 92-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.05.017
[22] 刘福臻,王灵,肖东升. 机器学习模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):98 − 106. [LIU Fuzhen,WANG Ling,XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):98 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Fuzhen, WANG Ling, XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 98-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 方然可,刘艳辉,黄志全. 基于机器学习的区域滑坡危险性评价方法综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):1 − 8. [FANG Ranke,LIU Yanhui,HUANG Zhiquan. A review of the methods of regional landslide hazard assessment based on machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, HUANG Zhiquan. A review of the methods of regional landslide hazard assessment based on machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(4): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 刘艳辉,方然可,苏永超,等. 基于机器学习的区域滑坡灾害预警模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(1):116 − 124. [LIU Yanhui,FANG Ranke,SU Yongchao,et al. Machine learning based model for warning of regional landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(1):116 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-533
LIU Yanhui, FANG Ranke, SU Yongchao, et al. Machine learning based model for warning of regional landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(1): 116-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-533
[25] 王毅,方志策,牛瑞卿,等. 基于深度学习的滑坡灾害易发性分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2021,23(12):2244 − 2260. [WANG Yi,FANG Zhice,NIU Ruiqing,et al. Landslide susceptibility analysis based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2021,23(12):2244 − 2260. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.210057
WANG Yi, FANG Zhice, NIU Ruiqing, et al. Landslide susceptibility analysis based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2021, 23(12): 2244-2260. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.210057
[26] 王毅,方志策,牛瑞卿. 融合深度神经网络的三峡库区滑坡灾害易发性预测[J]. 资源环境与工程,2021,35(5):652 − 660. [WANG Yi,FANG Zhice,NIU Ruiqing. Prediction of landslide susceptibility in Three Gorges Reservoir area based on integrating deep neural network[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2021,35(5):652 − 660. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16536/j.cnki.issn.1671-1211.2021.05.013
WANG Yi, FANG Zhice, NIU Ruiqing. Prediction of landslide susceptibility in Three Gorges Reservoir area based on integrating deep neural network[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2021, 35(5): 652-660. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16536/j.cnki.issn.1671-1211.2021.05.013
[27] WANG Yi,FANG Zhice,HONG Haoyuan. Comparison of convolutional neural networks for landslide susceptibility mapping in Yanshan County,China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,666:975 − 993. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.263
[28] 林经纬. 福建省滑坡灾害特征及驱动因素分析[J]. 莆田学院学报,2015,22(5):83 − 88. [LIN Jingwei. Characteristics and driving factors of landslide hazard in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Putian University,2015,22(5):83 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIN Jingwei. Characteristics and driving factors of landslide hazard in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Putian University, 2015, 22(5): 83-88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 刘艳辉,黄俊宝,肖锐铧,等. 基于随机森林的福建省区域滑坡灾害预警模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(3):944 − 955. [LIU Yanhui,HUANG Junbao,XIAO Ruihua,et al. Study on early warning model for regional landslides based on random forest in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(3):944 − 955. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0625
LIU Yanhui, HUANG Junbao, XIAO Ruihua, et al. Study on early warning model for regional landslides based on random forest in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(3): 944-955. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0625
[30] 刘艳辉, 肖锐铧, 陈春利, 等. 区域滑坡预警中训练样本集的构建方法、系统及存储介质: 20201082-9816.0[P]
LIU Yanhui, XIAO Ruihua, CHEN Chunli, et al. Construction method system and storage medium of training sample set in regional landslide early warning: 202010829816.0[P]. 2020-08-18. (in Chinese)
[31] CHAWLA N V,BOWYER K W,HALL L O,et al. SMOTE:synthetic minority over-sampling technique[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research,2002,16:321 − 357. doi: 10.1613/jair.953
[32] LECUN Y,BOSER B,DENKER J S,et al. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition[J]. Neural Computation,1989,1(4):541 − 551.
[33] GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, COURVILLE A. Deep learning[M]. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press, 2016
[34] SNOEK J, LAROCHELLE H, ADAMS R P. Practical Bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems-Volume 2. December 3 − 6, 2012, Lake Tahoe, Nevada. New York: ACM, 2012: 2951 − 2959.
[35] SAMEEN M I,PRADHAN B,LEE S. Application of convolutional neural networks featuring Bayesian optimization for landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. CATENA,2020,186:104249. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.104249
[36] 李亭,田原,邬伦,等. 基于随机森林方法的滑坡灾害危险性区划[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2014,30(6):25 − 30. [LI Ting,TIAN Yuan,WU Lun,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science,2014,30(6):25 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2014.06.006
LI Ting, TIAN Yuan, WU Lun, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2014, 30(6): 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2014.06.006
-



 下载:
下载: