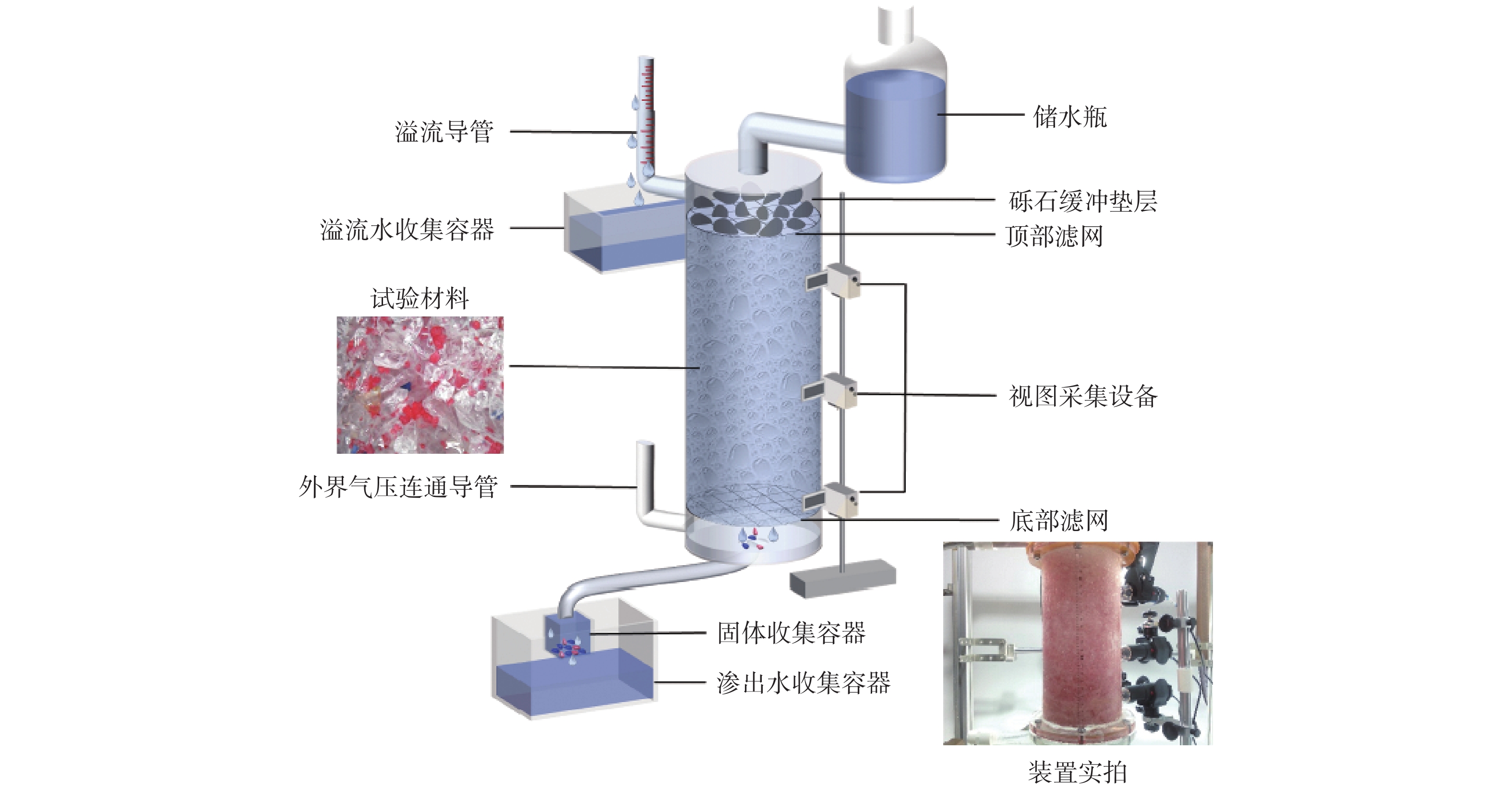
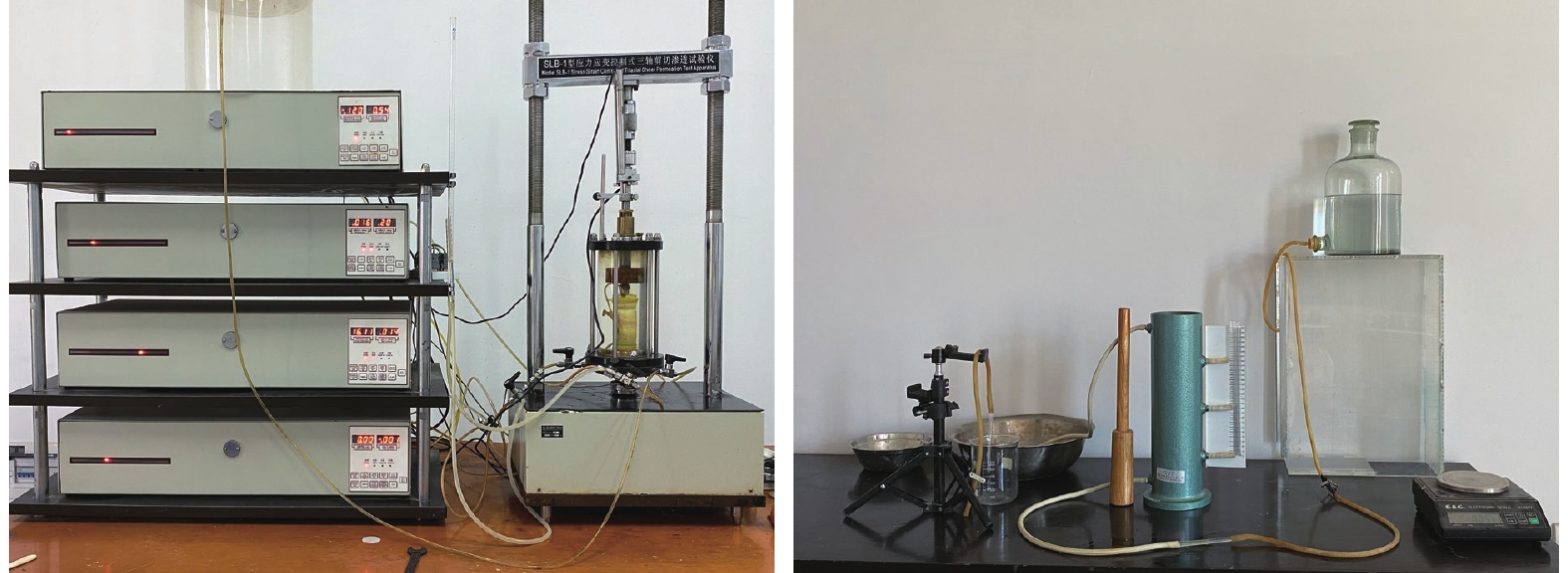
Critical physical and hydraulic condition for fine grains migration, deposition and self-dredging in seepage erosion of gravel soil
-
摘要:
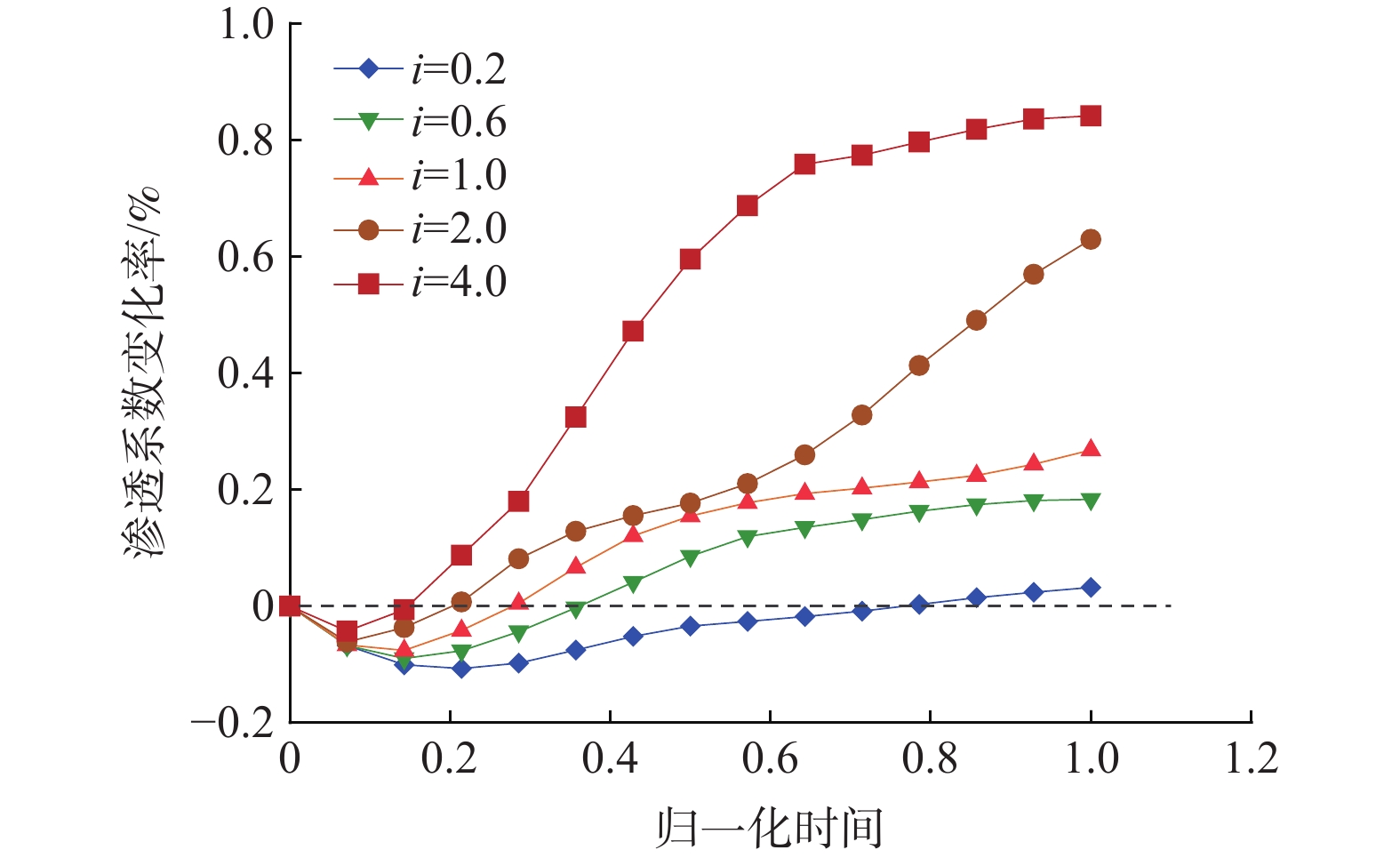
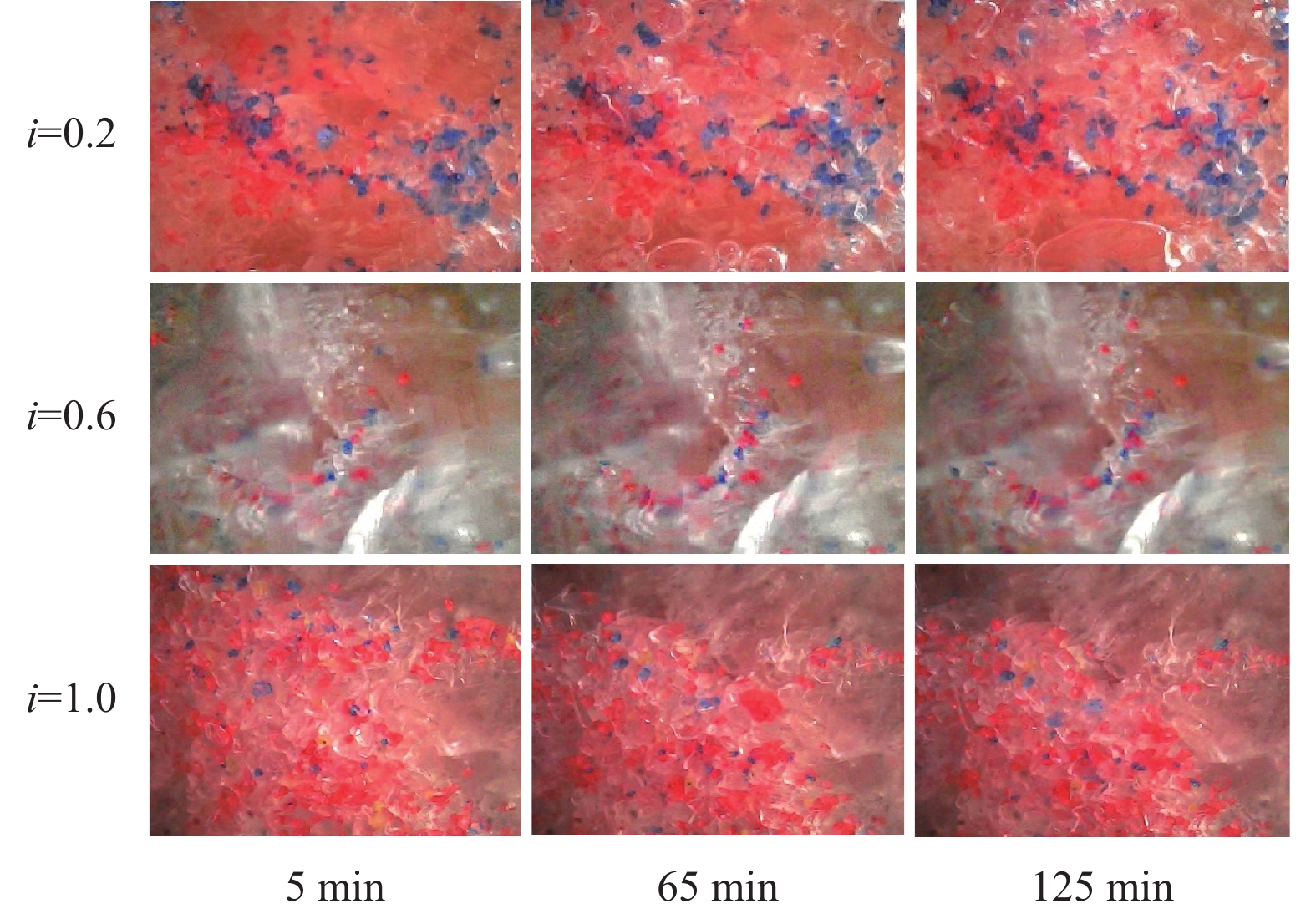
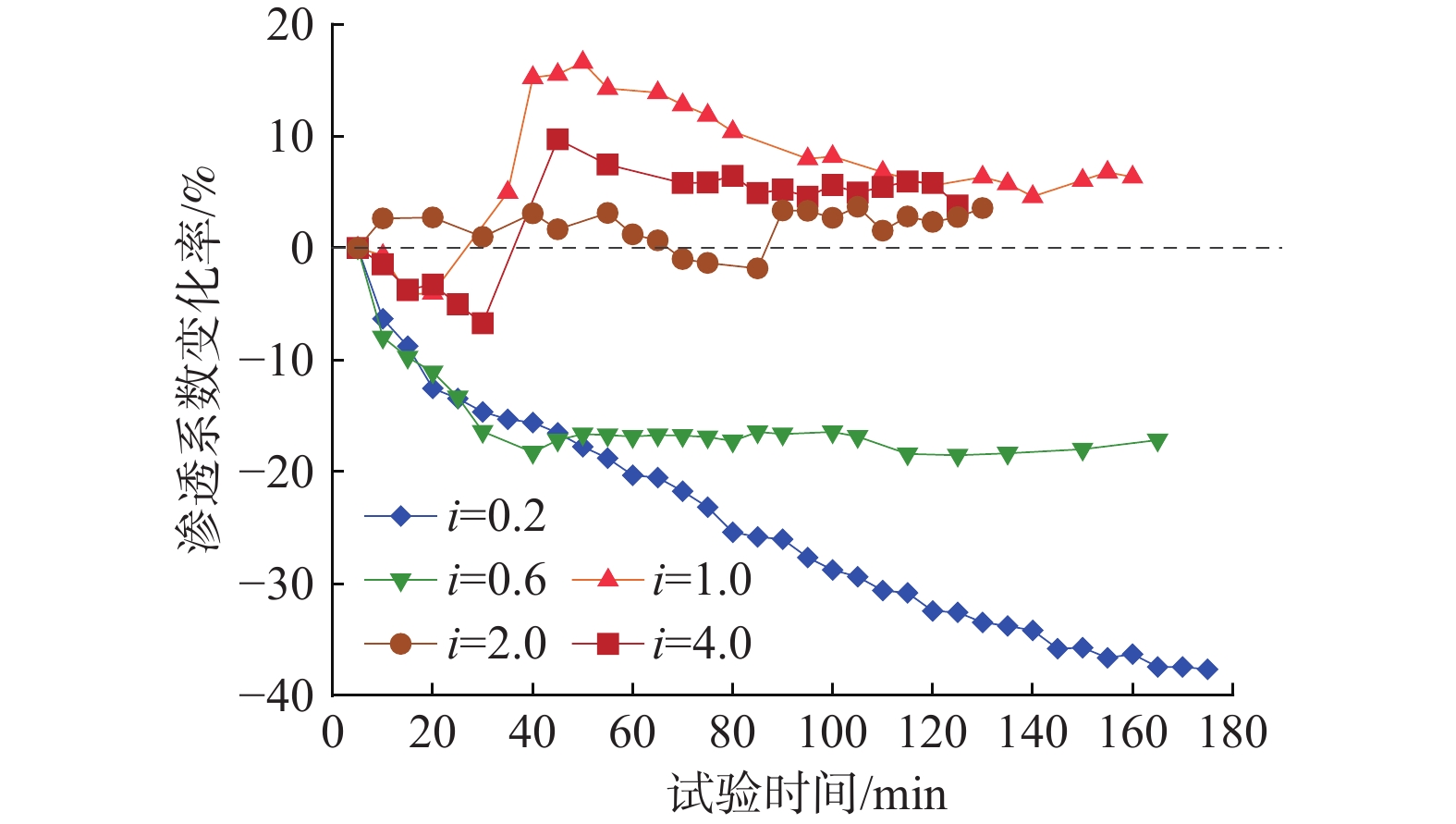
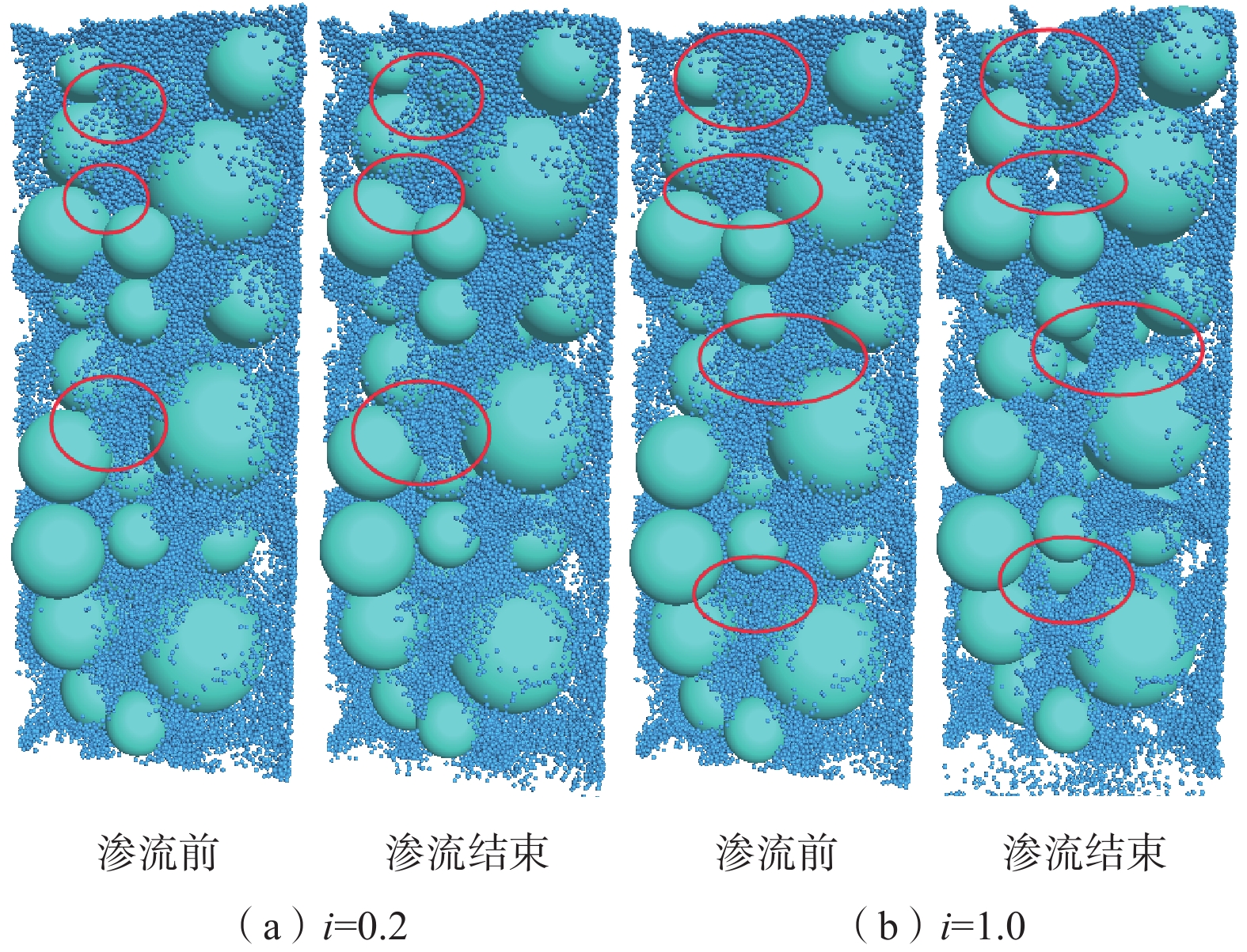
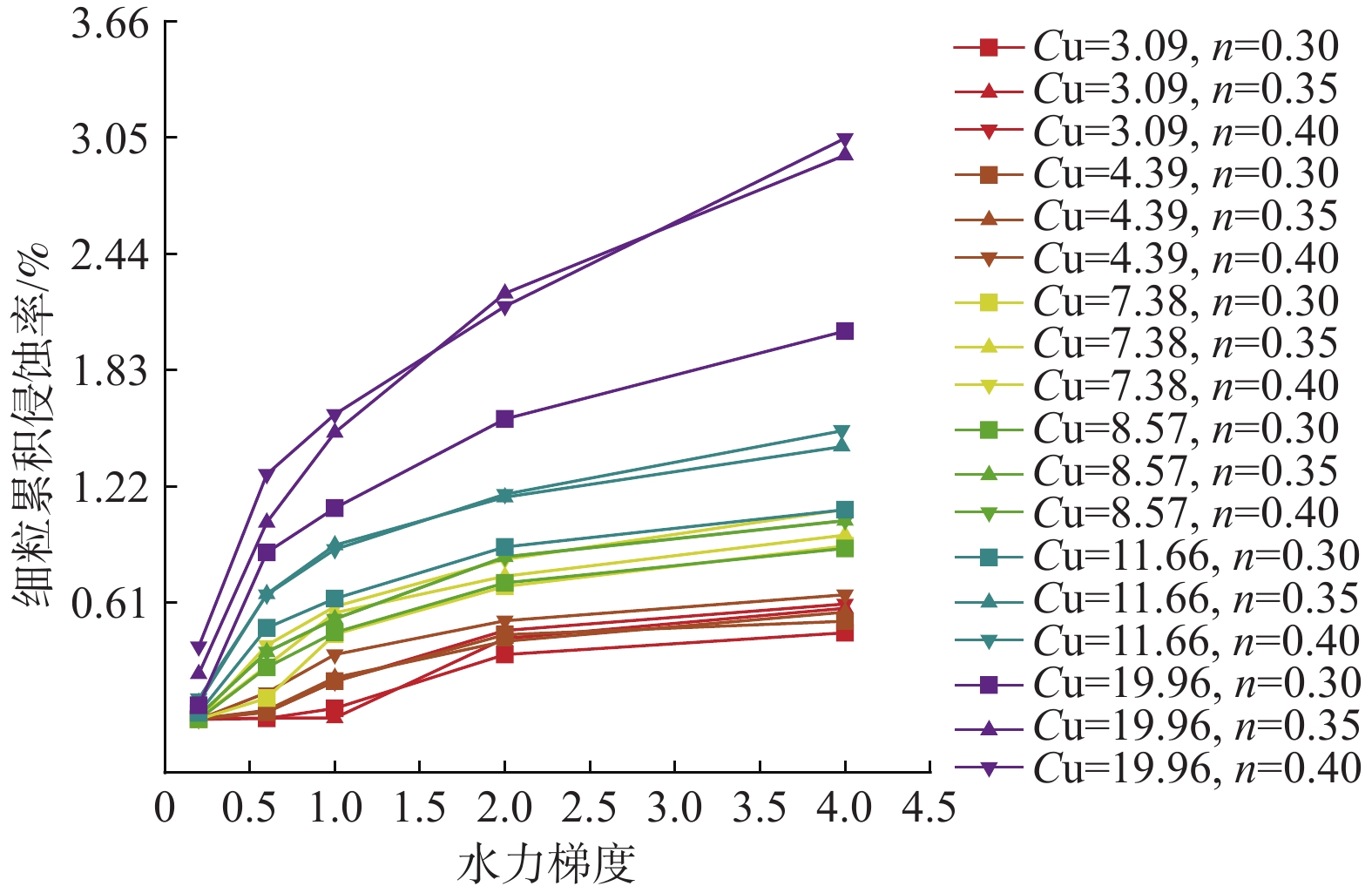
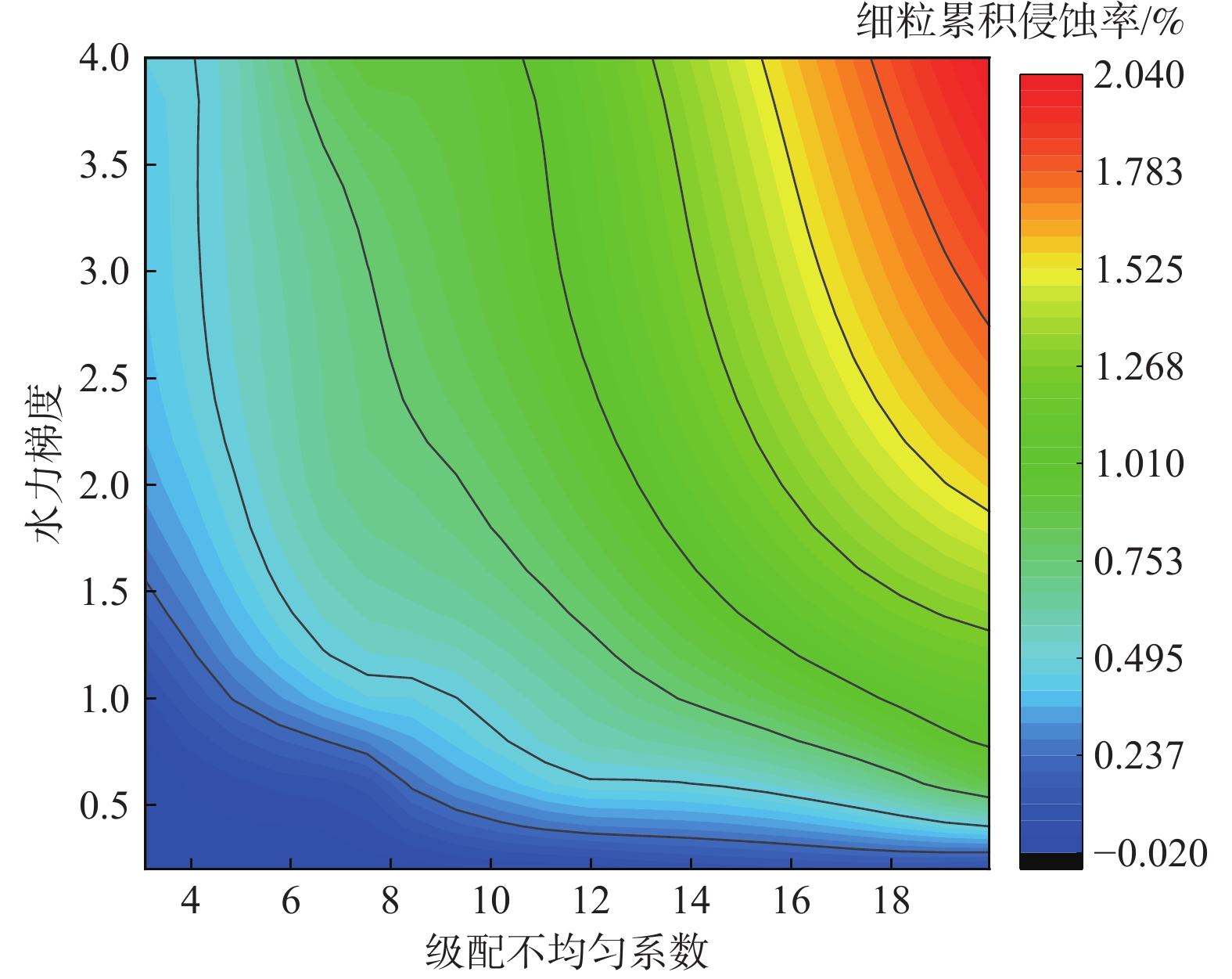
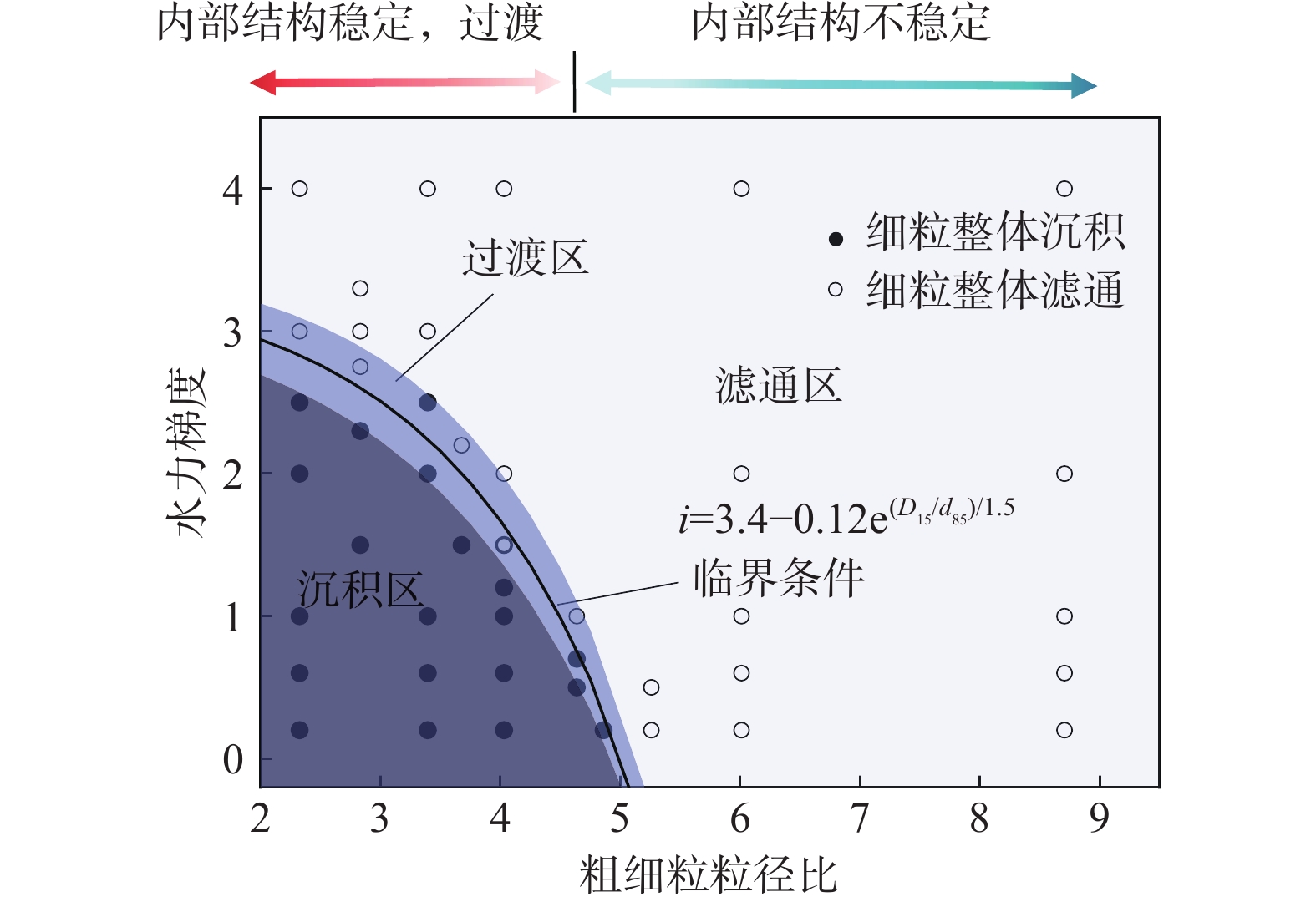
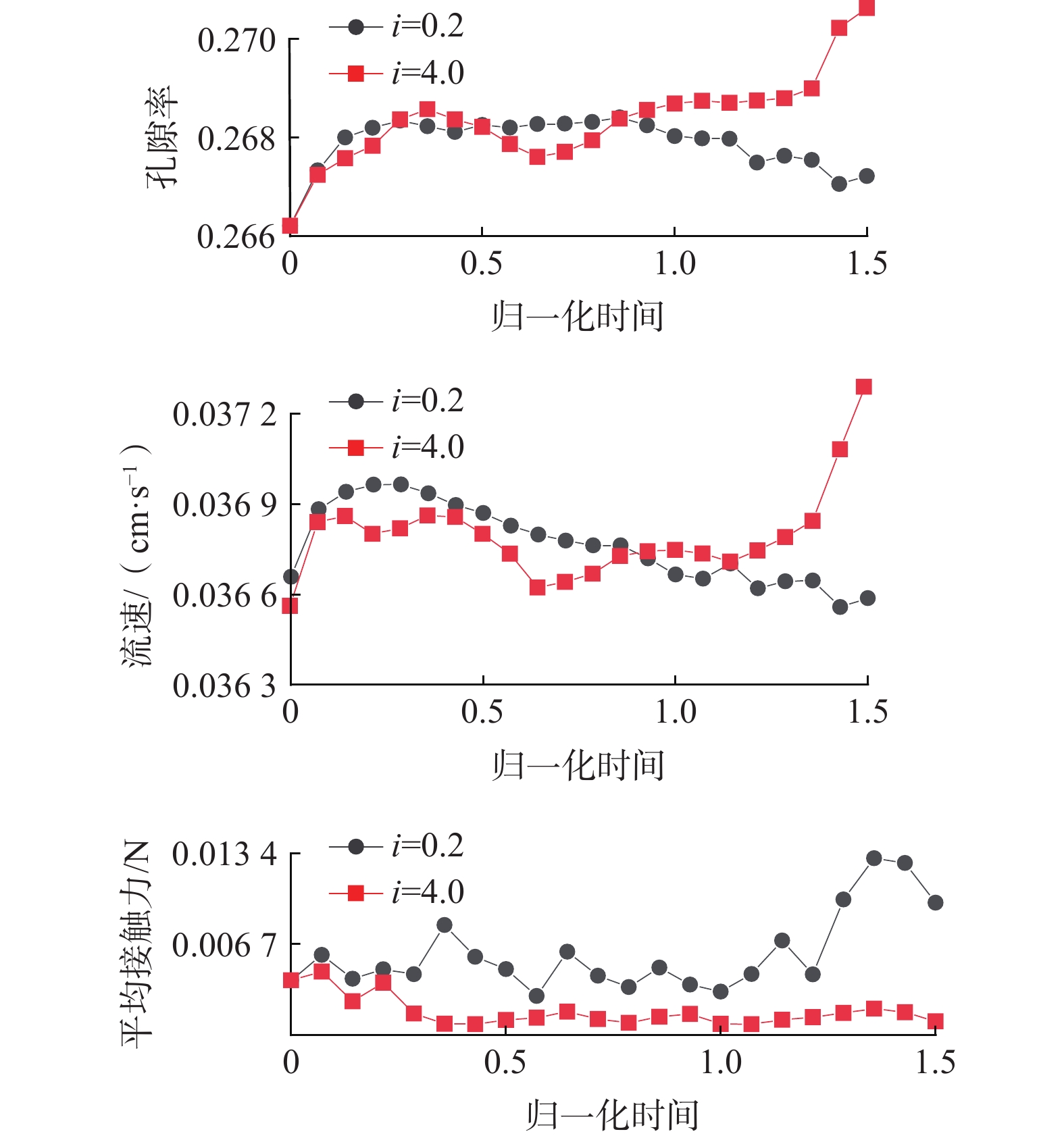
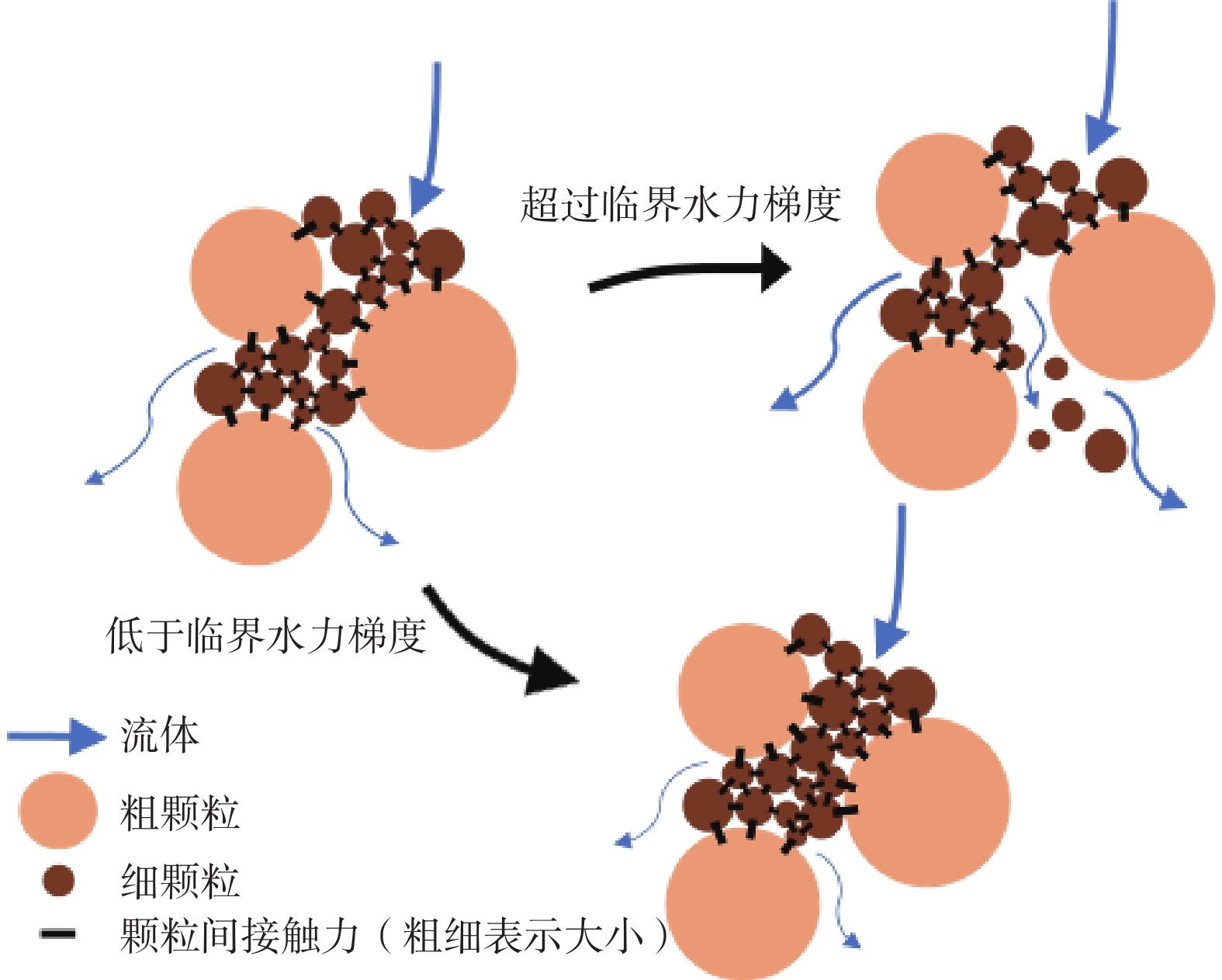
细粒迁移机制是理解砂砾土渗流侵蚀过程的基础与关键,对研究砂砾土斜坡雨水侵蚀过程的细观致灾机制具有重要意义。目前其运移模式及运移状态发生转变的临界条件并不清晰,不同物理水力条件下的细粒运动类型有所不同。为掌握砂砾土侵蚀过程中细粒的整体运动类型及其发生改变的临界条件,采用可视圆柱入渗试验和离散元数值模拟,分析了细粒迁移的影响因素和内部机理。结果表明:(1)细粒迁移受级配和水力梯度影响显著,而受初始孔隙率影响不显著,且级配的影响大于水力梯度;(2)水力作用下细粒整体运动状态可分为沉积和滤通2种模式,内部结构不稳定的砂砾土细粒运动处于滤通状态,内部结构稳定和稳定性过渡型砂砾土随水力梯度升高细粒的运动状态从整体沉积转变为整体滤通;(3)细粒运动状态在粒径比和水力梯度共同作用下存在明显界限,最终得到细粒沉积-滤通转变的临界条件为$ i = 3.4 - $$ 0.12{{\text{e}}^{\left( {{D_{15}}/{d_{85}}} \right)/1.5}} $。研究可为砂砾土斜坡渗蚀失稳防护提供理论指导。
Abstract:The mechanism of fine grains migration is the basis and key to understand the seepage erosion process of gravel soil, which is significance to study the disaster-caused mesomechanism of rain erosion process on sandy gravel slopes. However, the migration mode and critical condition for the transition of migration state are unclear. The migration types of fine grains differ from different physical and hydraulic conditions. To reveal the overall movement characteristics of fine grains and the critical conditions for the change of their motion state during the process of gravel soil erosion, this study adopted the visual cylindrical infiltration test and discrete element numerical simulation to analyze the influencing factors and mechanism of the fine grains migration, deposition, and self-dredging. The results show that: 1) the migration of fine grains is significantly affected by the gradation and hydraulic gradient but not by the initial porosity. The gradation has a greater effect than the hydraulic gradient. 2) The overall motion of fine grains under hydraulic forces can be divided into two states: deposition and self-dredging. The fine grains of gravel soil with unstable internal structure are in the self-dredging state, and that with stable and transitional internal structure will change from deposition to self-dredging with the increase of hydraulic gradient. 3) The motion state of fine grains has an obvious boundary under the combined effects of grain size ratio and hydraulic gradient, and the critical condition for fine grains transition from deposition to self-dredging is obtained to be $ i = 3.4 - 0.12{{\text{e}}^{\left( {{D_{15}}/{d_{85}}} \right)/1.5}} $.
-
Key words:
- gravel soil /
- seepage erosion /
- fine grains migration /
- migration mode /
- critical condition
-

-
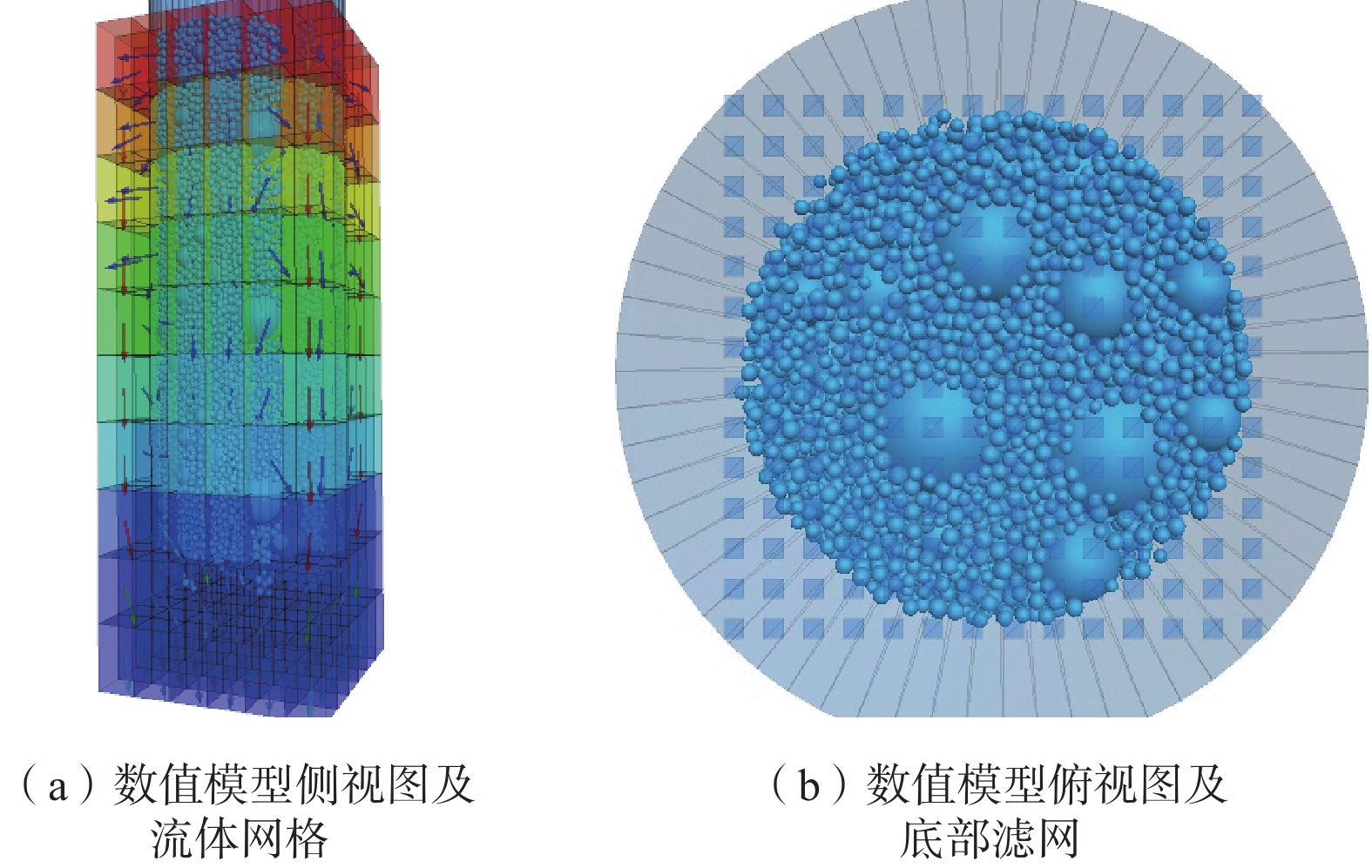
表 1 数值模型相关参数
Table 1. Related parameters of numerical model
固体 流体 密度/ ${\text{(kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{)}}$ 弹性模量
/$ {\text{(N}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{ - 2}}{\text{)}} $ 刚度比 摩擦
系数密度/ ${\text{(kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{)}}$ 黏滞系数/
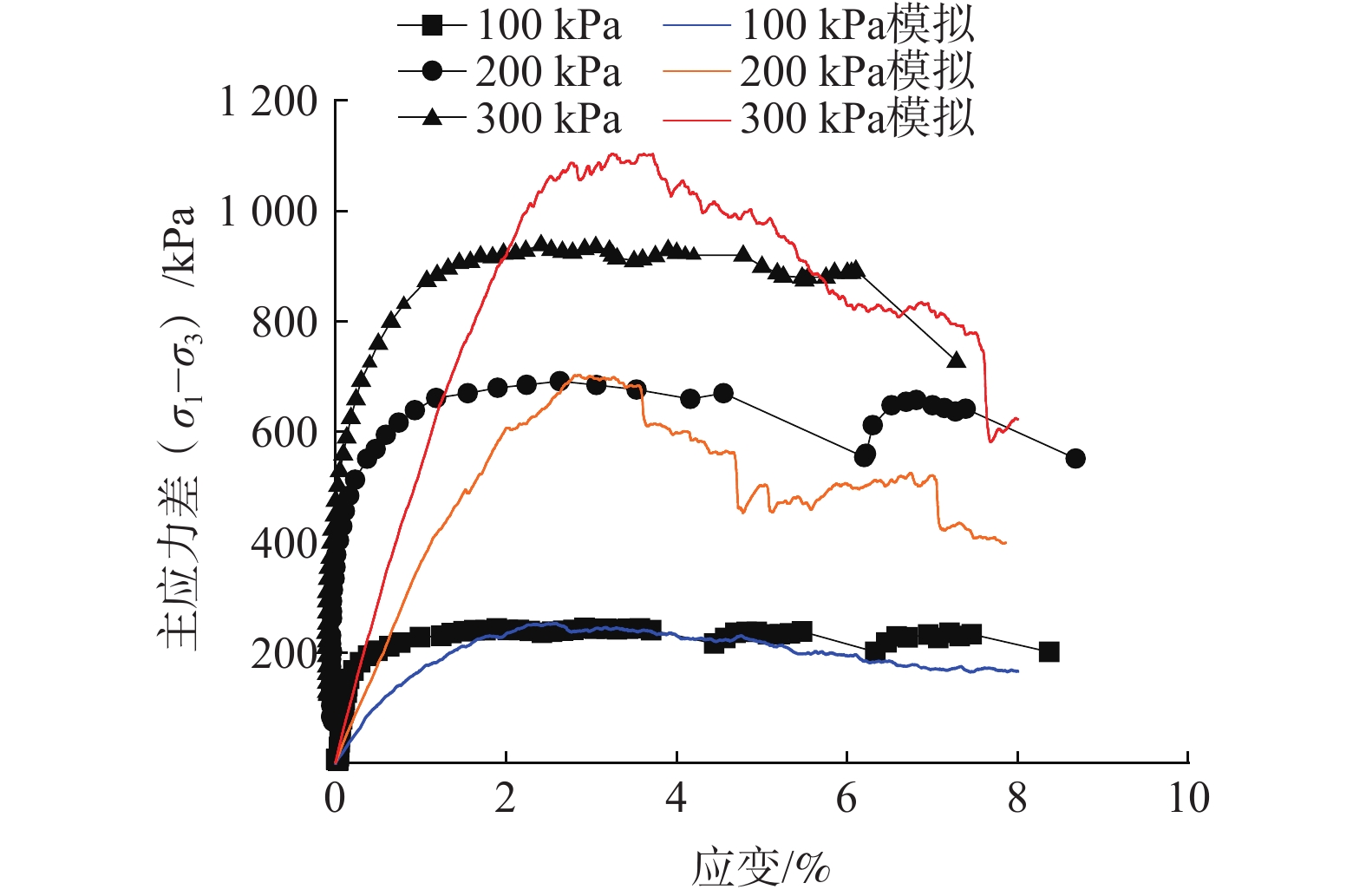
(Pa·s)2500 5×108 1.5 0.8 1000 1×10−3 表 2 三种应力水平下峰值应力误差平均值与内摩擦角误差
Table 2. Average value of peak stress error and internal friction angle error under three stress levels
参数 计算公式 B1数值模拟与A1
试验结果比对/%B6数值模拟与A6
试验比对结果/%应力误差
平均值$ \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\Delta {\sigma _{100}}}}{{{\sigma _{100}}}} + \dfrac{{\Delta {\sigma _{200}}}}{{{\sigma _{200}}}} + \dfrac{{\Delta {\sigma _{300}}}}{{{\sigma _{300}}}}}}{3} $ 5.6 −9.6 内摩擦角
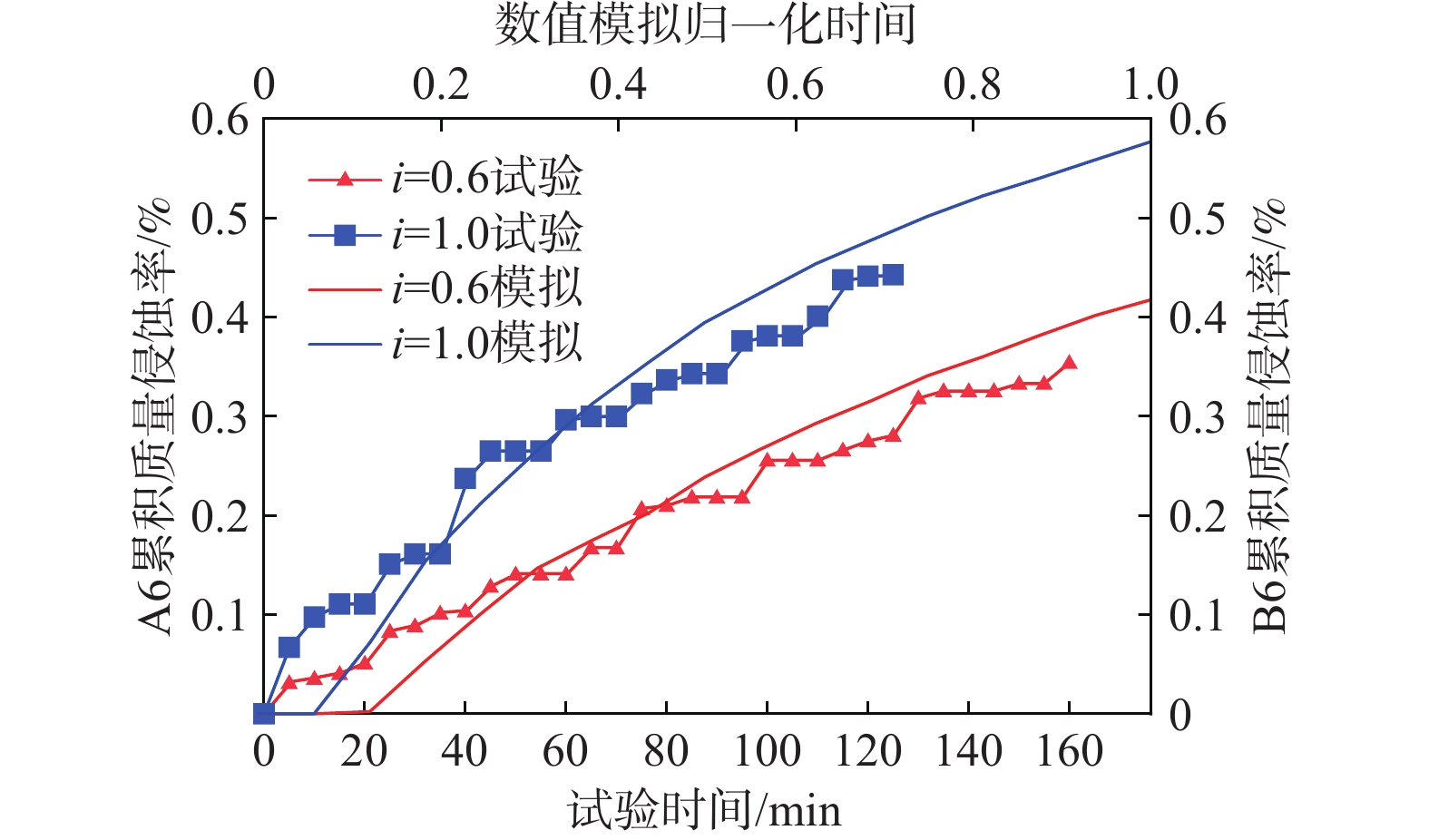
误差$ \dfrac{\Delta \varphi }{{\varphi }_{试验}} $ 8.6 −1.3 表 3 渗透试验与数值模拟得到的渗透系数
Table 3. Comparison of hydraulic conductivity measured by test and simulation
试验和
模拟类型试验次数 常水头试验结果/(cm·s−1) 数值模拟
结果/(cm·s−1)试验值 平均值 A6与B6 第1次 0.0557 0.0562 0.0529 第2次 0.0627 第3次 0.0501 A1与B1 第1次 0.0112 0.0107 0.0083 第2次 0.0100 第3次 0.0110 表 4 数值模型粒径组成
Table 4. Particle size composition in the numerical model
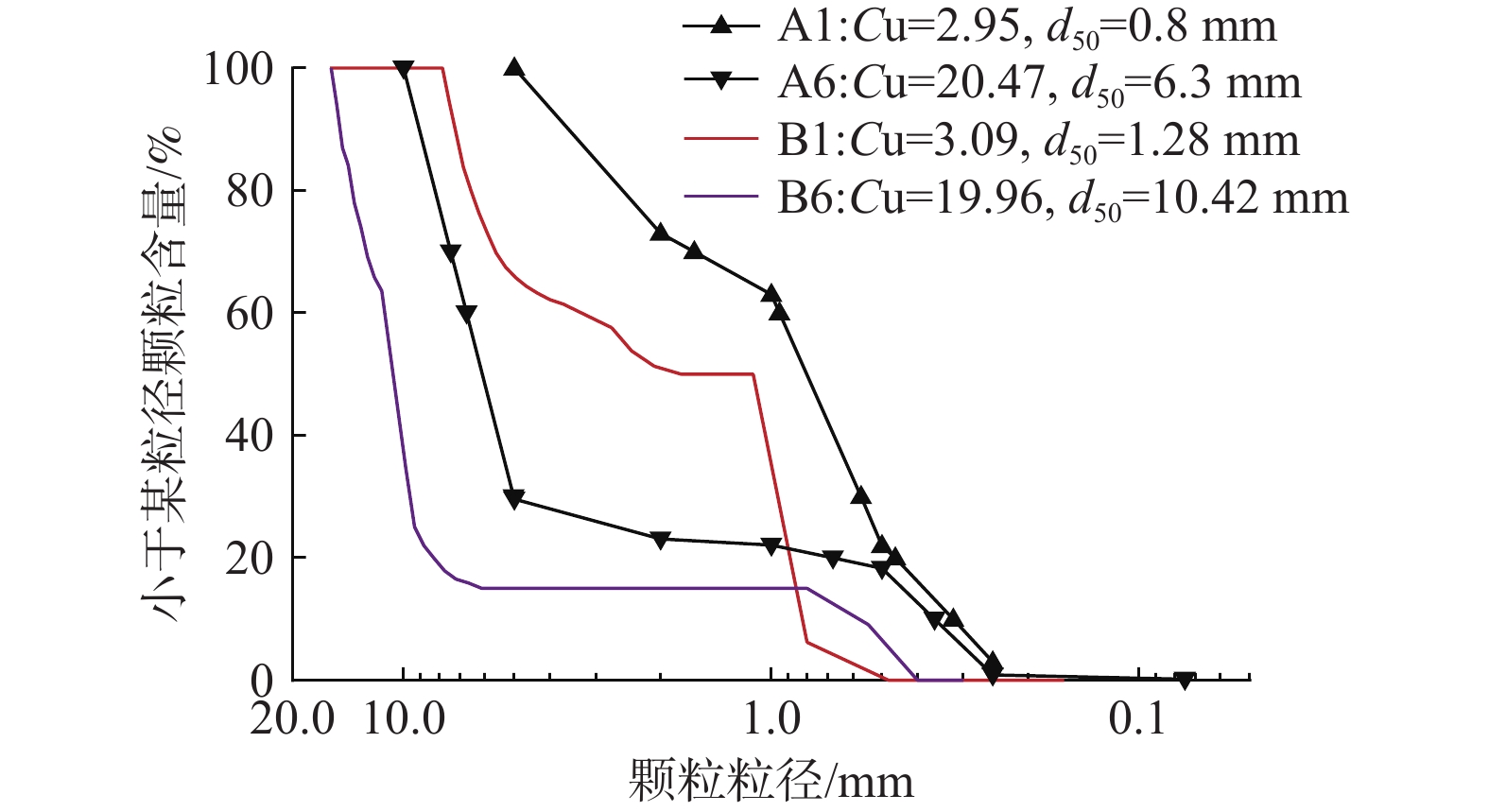
级配编号 级配数量/种 d50/mm Cu $\dfrac{{{D_{15}}}}{{{d_{85}}}}$ 颗粒图像 级配编号 级配数量/种 d50/mm Cu $\dfrac{{{D_{15}}}}{{{d_{85}}}}$ 颗粒图像 B1 2 1.28 3.09 2.33 
B4 4 7.20 8.57 6.01 
B2 4 2.20 4.39 3.39 
B5 4 9.99 11.66 8.71 
B3 4 4.80 7.38 4.03 
B6 2 10.42 19.96 16.23 
注:D15表示粗粒组中颗粒的累计粒度分布百分数达到15%时所对应的粒径;d85表示细粒组中颗粒的累计粒度分布百分数达到85%时所对应的粒径。 表 5 土体内部稳定性判定准则及其判定结果和数值模拟结果
Table 5. Results of soil internal stability criterion and numerical simulation
判定准则 结构稳定判定指标 Cu=3.09 Cu=4.39 Cu=7.38 Cu=8.57 Cu=11.66,19.96 Istonima准则 Cu≤10 S S S S T Burenkova法 0.76lgh″+1<h′<1.86lgh″+1 S S U S U Wan & Fell法 30/lg(d90/d60)<80
或15/lg(d20/d15)>22S S S S S Beriram准则 D15/d85≤6且D15/d15≤9 S S S U U Kenndy & Lau法 $ {f}_{4d}\geqslant 2.3{f}_{d},{f}_{d}\leqslant \left\{\begin{array}{l}0.3,C{\mathrm{u}}\leqslant 3\\ 0.2,C{\mathrm{u}} < 3\end{array} \right.$ S S T U U 数值模拟结果 kki<0 S S T U U 注:S代表稳定;U代表不稳定;T代表稳定性过渡;fd和f4d分别为粒径小于d和小于4d的颗粒质量百分比;h′为d90/d60;h″为d90/d15;d15表示细粒组中颗粒的累计粒度分布百分数达到15%时所对应的粒径。 -
[1] 李涛,付宏渊,周功科,等. 降雨入渗条件下粗粒土路堤暂态饱和区发展规律及稳定性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40 (5) :74 − 80. [LI Tao,FU Hongyuan,ZHOU Gongke,et al. A study of development law and stability of transient saturated areas of coarsegrained soil embankment under rainfall infiltration[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(5) :74 − 80. ( in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Tao, FU Hongyuan, ZHOU Gongke, et al. A study of development law and stability of transient saturated areas of coarsegrained soil embankment under rainfall infiltration[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(5) : 74 − 80. ( in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 梁劲, 王强, 胡新丽, 等. 渗流-应力耦合下侏罗系红砂岩力学及渗透特性试验研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):52 − 61. [LIANG Jin, WANG Qiang, HU Xinli, et al. Experimental study on mechanics and permeability characteristics of Jurassic red sandstone under hydro-mechanical coupling[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):52 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIANG Jin, WANG Qiang, HU Xinli, et al . Experimental study on mechanics and permeability characteristics of Jurassic red sandstone under hydro-mechanical coupling[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023 ,42 (1 ):52 −61 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] WANG Xiukai,TANG Yao,HUANG Bo,et al. Review on numerical simulation of the internal soil erosion mechanisms using the discrete element method[J]. Water,2021,13(2):169. doi: 10.3390/w13020169
[4] XU Y,ZHANG L M. Breaching parameters for earth and rockfill dams[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2009,135(12):1957 − 1970. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000162
[5] 郭朝旭,崔鹏. 宽级配弱固结土体内细颗粒迁移规律研究评述[J]. 山地学报,2017,35(2):179 − 186. [GUO Chaoxu,CUI Peng. Fine particle migration in wide grading and poorly consolidated soil:An overview[J]. Mountain Research,2017,35(2):179 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Chaoxu, CUI Peng . Fine particle migration in wide grading and poorly consolidated soil: An overview[J]. Mountain Research,2017 ,35 (2 ):179 −186 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] ISTOMINA V. Filtration stability of soils[J]. Gostroizdat,1957:15.
[7] BURENKOVA V V. Assessment of suffusion in non-cohesive and graded soils[J]. Filters in Geotechnical and Hydraulic Engineering,1993:357 − 360.
[8] WAN C F,FELL R. Assessing the potential of internal instability and suffusion in embankment dams and their foundations[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2008,134(3):401 − 407. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2008)134:3(401)
[9] KENNEY T C,LAU D. Internal stability of granular filters[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1985,22(2):215 − 225. doi: 10.1139/t85-029
[10] 宋宜祥,管景华,李彦奇,等. 反粒序砂土体内侵蚀及渗流特性变化规律试验研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(3):16 − 27. [SONG Yixiang, GUAN Jinghua, LI Yanqi, et al. Experimental study on the change law of internal erosion and seepage characteristics of inverse grading sand accumulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(3):16 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SONG Yixiang, GUAN Jinghua, LI Yanqi, et al . Experimental study on the change law of internal erosion and seepage characteristics of inverse grading sand accumulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023 ,42 (3 ):16 −27 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 刘杰,谢定松. 反滤层设计原理与准则[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(4):609 − 616. [LIU Jie,XIE Dingsong. Design principles and guidelines of filters[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(4):609 − 616. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Jie, XIE Dingsong . Design principles and guidelines of filters[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017 ,39 (4 ):609 −616 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] TO H D,SCHEUERMANN A,GALINDO-TORRES S A. Probability of transportation of loose particles in suffusion assessment by self-filtration criteria[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2016,142(2):04015078. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001403
[13] MOFFAT R A,FANNIN R J. A large permeameter for study of internal stability in cohesionless soils[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal,2006,29(4):273 − 279.
[14] KE Lin,TAKAHASHI A. Experimental investigations on suffusion characteristics and its mechanical consequences on saturated cohesionless soil[J]. Soils & Foundations,2014,54(4):713 − 730.
[15] CHANG D S,ZHANG L M. Critical hydraulic gradients of internal erosion under complex stress states[J]. Journal of Geotechnical & Geoenvironmental Engineering,2013,139(9):1454 − 1467.
[16] 丁瑜,饶云康,倪强,等. 颗粒级配与孔隙比对粗粒土渗透系数的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(3):108 − 116. [DING Yu,RAO Yunkang,NI Qiang,et al. Effects of gradation and void ratio on the coefficient of permeability of coarse-grained soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):108 − 116. ( in Chinese with English abstract
DING Yu, RAO Yunkang, NI Qiang, et al . Effects of gradation and void ratio on the coefficient of permeability of coarse-grained soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019 ,46 (3 ):108 −116 . ( in Chinese with English abstract[17] 蔡袁强,张志祥,曹志刚,等. 不均匀级配砂土渗蚀过程的细观数值模拟[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版,2019,50(5):1144 − 1153. [CAI Yuanqiang,ZHANG Zhixiang,CAO Zhigang,et al. Mesoscopic numerical simulation for suffusion process of gap-graded sandy soil[J] Journal of Zhongnan University:Natural Sciences,2019,50(5):1144 − 1153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CAI Yuanqiang, ZHANG Zhixiang, CAO Zhigang, et al. Mesoscopic numerical simulation for suffusion process of gap-graded sandy soil[J] Journal of Zhongnan University: Natural Sciences, 2019, 50(5): 1144 − 1153. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 魏婕,魏玉峰,黄鑫. 颗粒形状对粗粒土剪切变形影响的细观研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):114 − 122. [WEI Jie,WEI Yufeng,HUANG Xin. A meso-scale study of the influence of particle shape on shear deformation of coarse-grained soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):114 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202002017
WEI Jie, WEI Yufeng, HUANG Xin . A meso-scale study of the influence of particle shape on shear deformation of coarse-grained soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (1 ):114 −122 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] 李伟一,钱建固,尹振宇,等. 间断级配砂土渗流侵蚀现象的计算流体力学-离散元耦合模拟[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(11):3191 − 3201. [LI Weiyi,QIAN Jiangu,YIN Zhenyu,et al. Simulation of seepage erosion in gap graded sand soil using CFD-DEM[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(11):3191 − 3201. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Weiyi, QIAN Jiangu, YIN Zhenyu, et al . Simulation of seepage erosion in gap graded sand soil using CFD-DEM[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021 ,42 (11 ):3191 −3201 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[20] LIU Y,WANG L,HONG Y,et al. A coupled CFD‐DEM investigation of suffusion of gap graded soil:Coupling effect of confining pressure and fines content[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,2020,44(18):2473 − 2500. doi: 10.1002/nag.3151
[21] XIONG H,YIN Z Y,ZHAO J,et al. Investigating the effect of flow direction on suffusion and its impacts on gap-graded granular soils[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2021,16:399 − 419. doi: 10.1007/s11440-020-01012-9
[22] WANG Xiukai,HUANG Bo,TANG Yao,et al. Microscopic mechanism and analytical modeling of seepage-induced erosion in bimodal soils[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2022,141:104527. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104527
[23] SHIRE T,O’SULLIVAN C. Micromechanical assessment of an internal stability criterion[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2013,8(1):81 − 90. doi: 10.1007/s11440-012-0176-5
[24] SIBILLE L,MAROT D,SAIL Y. A description of internal erosion by suffusion and induced settlements on cohesionless granular matter[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2015,10(6):735 − 748. doi: 10.1007/s11440-015-0388-6
[25] 张升,高峰,陈琪磊,等. 砂-粉土混合料在列车荷载作用下细颗粒迁移机制试验[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(5):1591 − 1598. [ZHANG Sheng,GAO Feng,CHEN Qilei,et al. Experimental study of fine particles migration mechanism of sand-silt mixtures under train load[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(5):1591 − 1598. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Sheng, GAO Feng, CHEN Qilei, et al. Experimental study of fine particles migration mechanism of sand-silt mixtures under train load[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(5): 1591 − 1598. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] 高岳. 化学注浆扩散机理的透明土试验研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2016. [GAO Yue. Experimental investigations on the mechanisms of chemical grouting in transparent soil[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GAO Yue. Experimental investigations on the mechanisms of chemical grouting in transparent soil[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 屈智炯. 对粗粒土渗透变形研究的进展[J]. 水电站设计,2008,24(1):48 − 55. [QU Zhijiong. Progress in study on coarse grained soil seepage deformation[J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station,2008,24(1):48 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
QU Zhijiong . Progress in study on coarse grained soil seepage deformation[J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station,2008 ,24 (1 ):48 −55 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[28] CUNDALL P A,STRACK O D L. Discussion:A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies[J]. Géotechnique,1980,30(3):331 − 336.
[29] Itasca Consulting Group Inc. PFC 5.0 Documentation[M]. Minneapolis:Itasca Consulting Group Inc,2016:2363 − 2364.
[30] 蒋中明,袁涛,刘德谦,等. 粗粒土渗透变形特性的细观数值试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(4):752 − 758. [JIANG Zhongming,YUAN Tao,LIU Deqian,et al. Mesoscopic numerical tests on seepage failure characteristics of coarse grained soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018,40(4):752 − 758. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIANG Zhongming, YUAN Tao, LIU Deqian, et al . Mesoscopic numerical tests on seepage failure characteristics of coarse grained soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018 ,40 (4 ):752 −758 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[31] 刘先珊,刘洋. 考虑流固耦合效应的饱和砂土渗透破坏数值模拟[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2013,49(5):633 − 638. [LIU Xianshan,LIU Yang. Numerical simulation of seepage failure of saturated sand with consideration of fluid-solid coupling efect[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2013,49(5):633 − 638. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Xianshan, LIU Yang . Numerical simulation of seepage failure of saturated sand with consideration of fluid-solid coupling efect[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2013 ,49 (5 ):633 −638 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[32] SKEMPTON A W,BROGAN J M. Discussion:Experiments on piping in sandy gravels[J]. Géotechnique,1995,45(3):565 − 567.
[33] ZHOU Wei,MA Qirui,MA Gang,et al. Microscopic investigation of internal erosion in binary mixtures via the coupled LBM-DEM method[J]. Powder Technology,2020,376:31 − 41. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.07.099
-




 下载:
下载: