Comparative study on land subsidence monitoring and control in the Shandong Plain, China and the Greater Houston Area, USA
-
摘要:
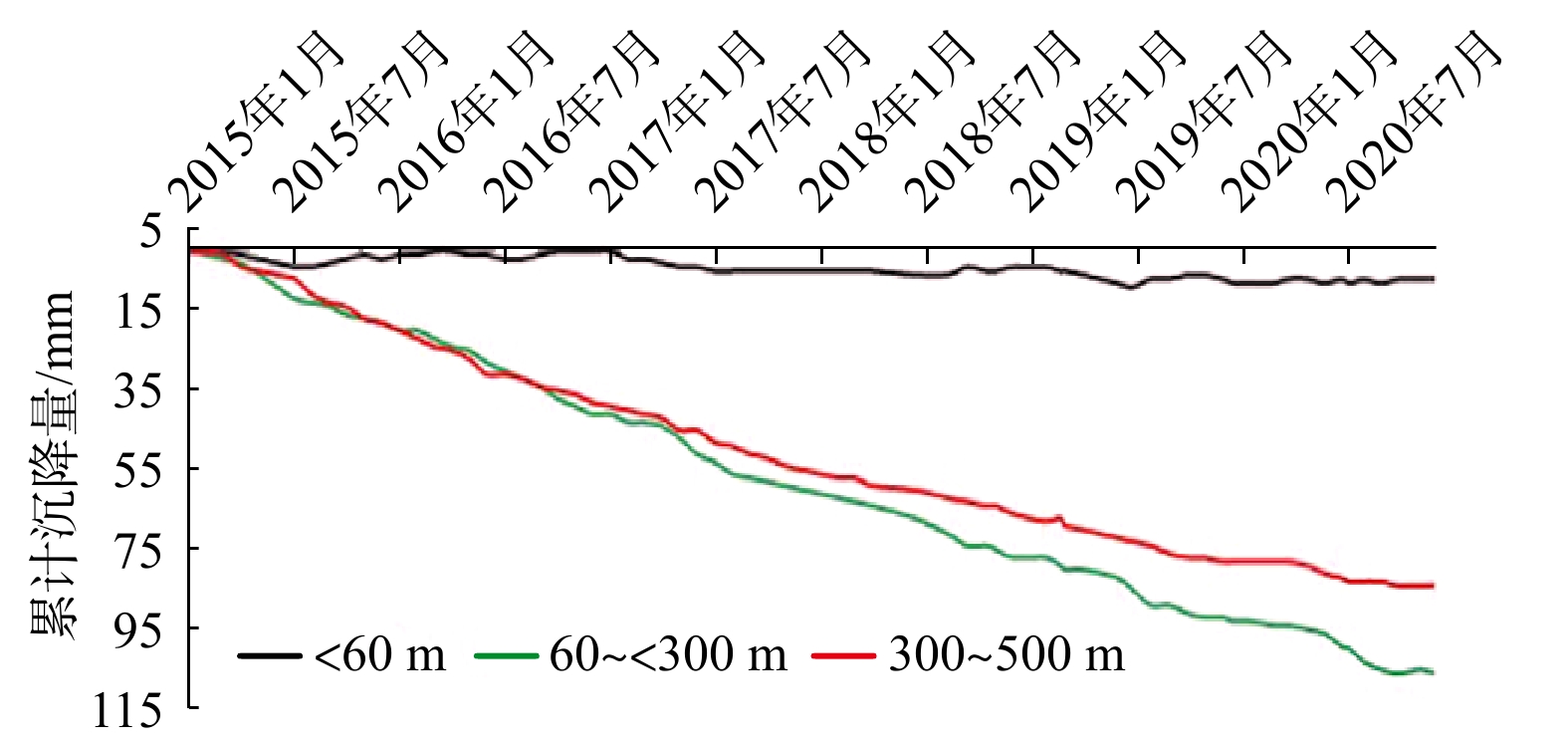
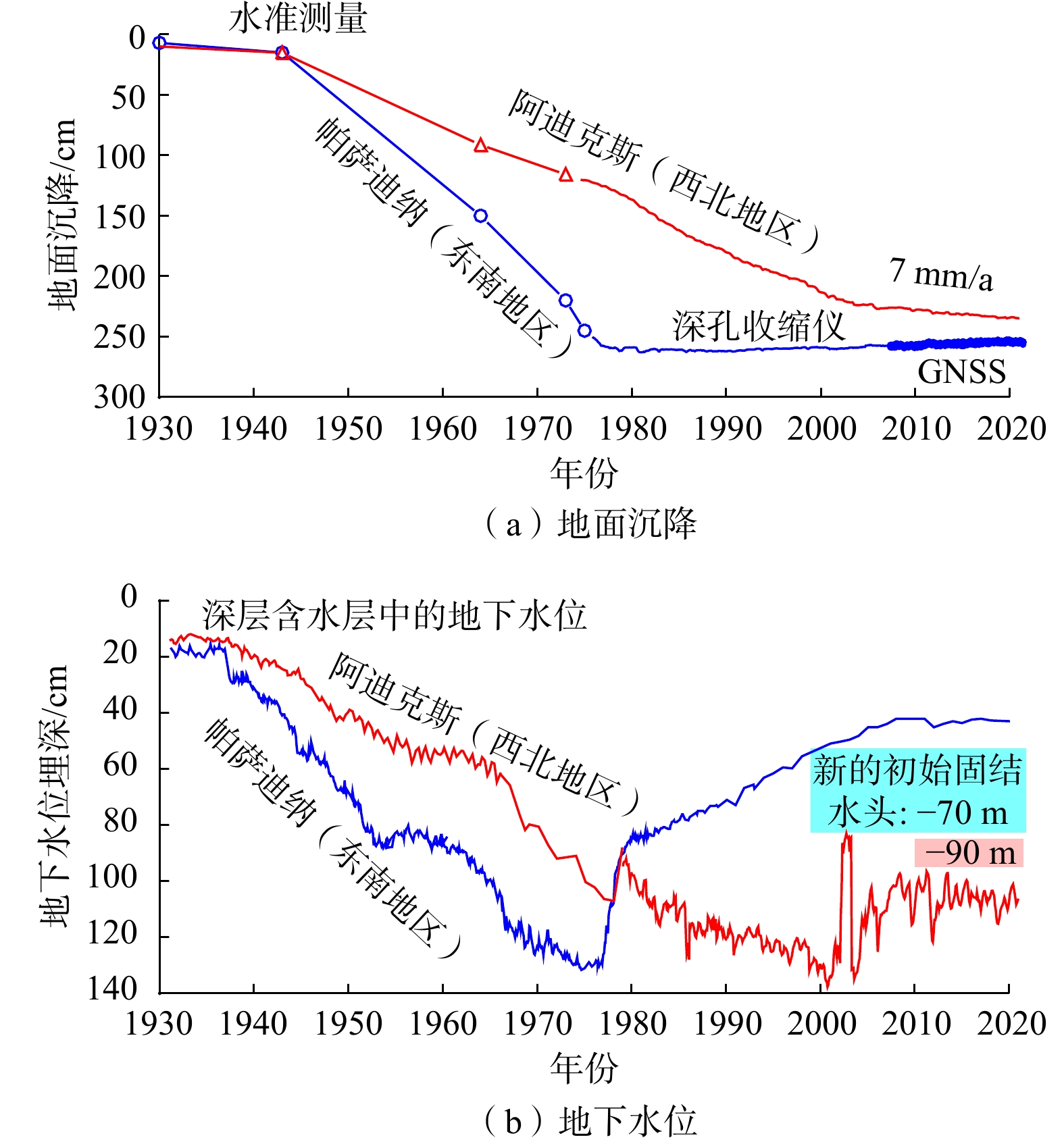
中国山东省平原区和美国大休斯顿地区都存在过量开采地下水引发的地面沉降问题,休斯顿积累了100多年的监测成果和50多年防控经验,与山东省平原区30多年来的地面沉降监测与防控经验具有一定的相似性。为进一步推动和加强山东省地面沉降监测与防治、地下水资源管理、数字赋能和数据共享,文章对两个地区的地面沉降成因、监测技术、地下水管理和地面沉降防控进行了对比分析。结果表明:过度抽取地下水是导致地面沉降的主要原因,两地都采取了以限制地下水开采为主的地面沉降管理措施,当前沉降面积和沉降速率都趋于减小;两地目前使用的监测方法和技术基本相同,主要使用精密水准测量、分层标或深孔伸缩仪、全球卫星定位系统和干涉合成孔径雷达技术,观测点的密度和监测频次都在逐步增加。然而,两地在观测数据的管理和共享方面存在很大差异。休斯顿地区的地面沉降管理部门主要负责采集数据和协调数据共享,不承担观测数据的处理和研究任务,所有的观测数据都向社会开放,基于观测数据的研究工作主要由美国地质调查局和大学的研究团体承担,研究成果公开发表;山东平原区的地面沉降和地下水位监测由自然资源和水利部门承担,下属的事业单位承担野外观测、数据保管、数据分析和研究,为制定地下水管理规章制度提供科技支撑,部门间的数据共享和整合存在一定困难,限制了对地面沉降的深入系统研究。
Abstract:Both the Shandong Plain in China and the Greater Houston Area in the United States have land subsidence problems that were caused by excessive groundwater pumping. Houston has accumulated more than 100 years of monitoring results and more than 50 years of prevention and control experience, which has certain similarities with the ground subsidence monitoring and control experience of Shandong Plain area in the past 30 years. To further promote and strengthen land subsidence monitoring and prevention, groundwater resource management, digital empowerment, and data sharing in Shandong Province, in this article a comparative study was conducted on the causes of land subsidence, monitoring techniques, groundwater management, and land subsidence prevention and control in the Shandong Plain and the Greater Houston Area. The results indicate that excessive extraction of groundwater is the main cause of land subsidence, and land subsidence management measures based on limiting groundwater extraction have been taken. Currently, the area and rate of subsidence are decreasing in both places. The monitoring methods and techniques used in two places are basically the same, mainly using precision leveling surveying, bench mark fixed on different stratum or borehole extensometers, Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), and Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) techniques, and the density and frequency of observations are gradually increasing. Meanwhile, the management and sharing of observation data is different. The land subsidence management administration agencies in the Houston area are mainly responsible for the collection and sharing of observation data, and do not undertake data processing and research tasks. All observation data are open to the public, and scientific researches based on observation data is mainly undertaken by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and universities. Research results are published on USGS reports or journal articles. Differently, land subsidence and groundwater level monitoring in Shandong Plain are undertaken by the Ministry of Natural Resources and the Ministry of Water Resources, and its affiliated institutions are responsible for field observation, data storage, data analysis and research, as well as formulating regulations for groundwater management. There are certain difficulties in data sharing and integration between departments, which limits in-depth and systematic research on land subsidence.
-
Key words:
- land subsidence /
- monitoring and prevention /
- groundwater /
- Shandong, China /
- Houston, USA
-

-
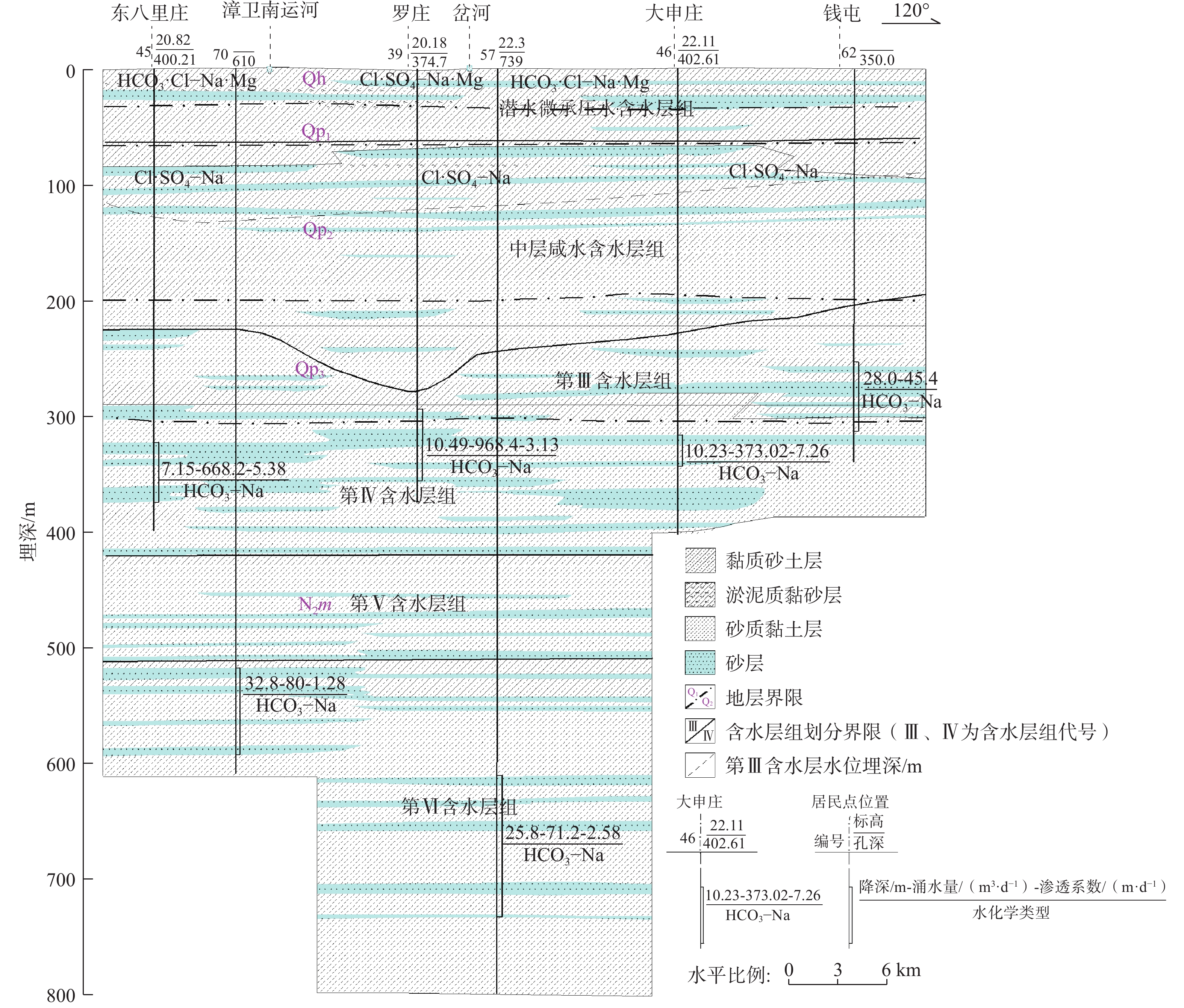
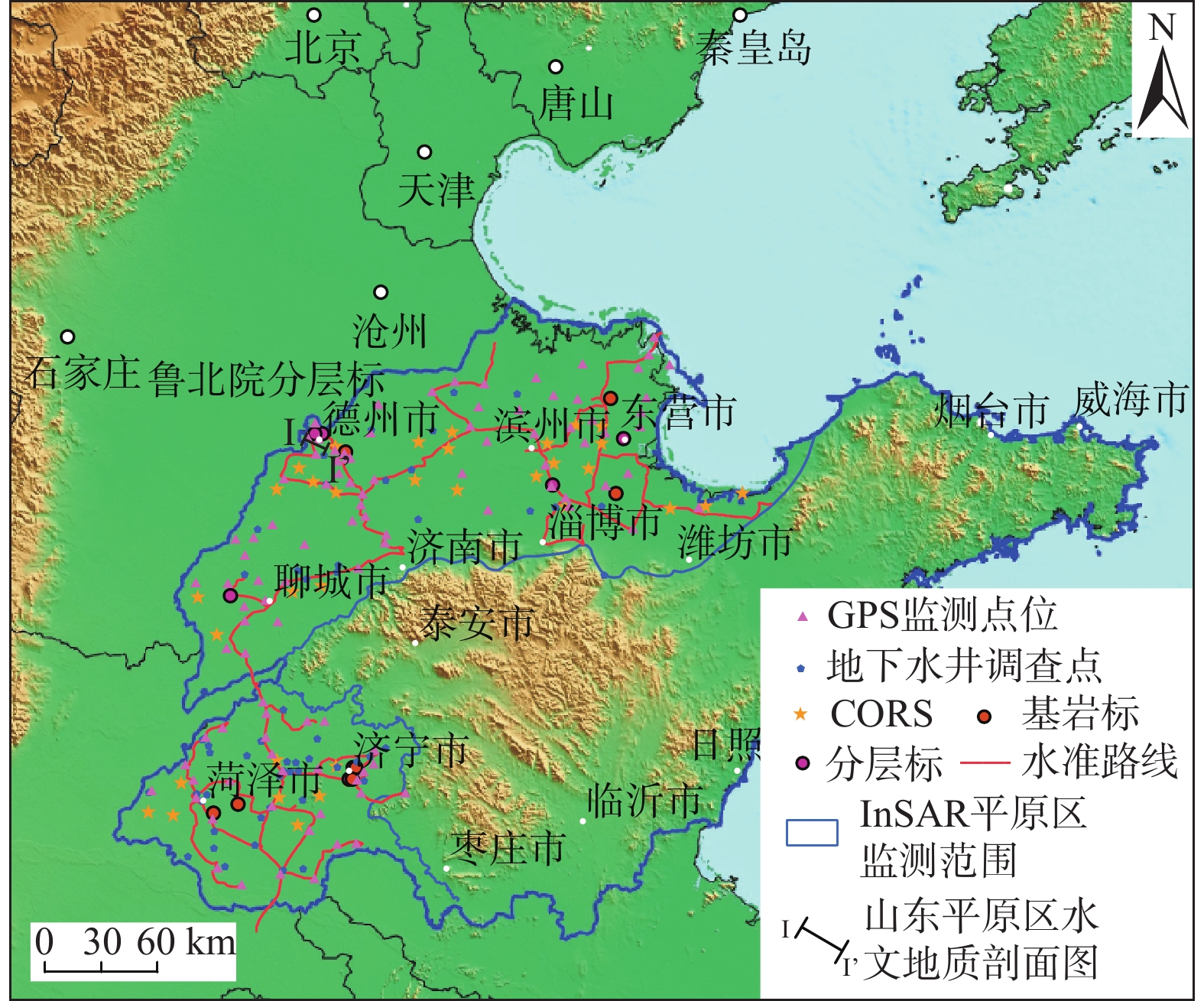
图 3 山东平原区的水文地质剖面图(根据文献[3]改编)
Figure 3.
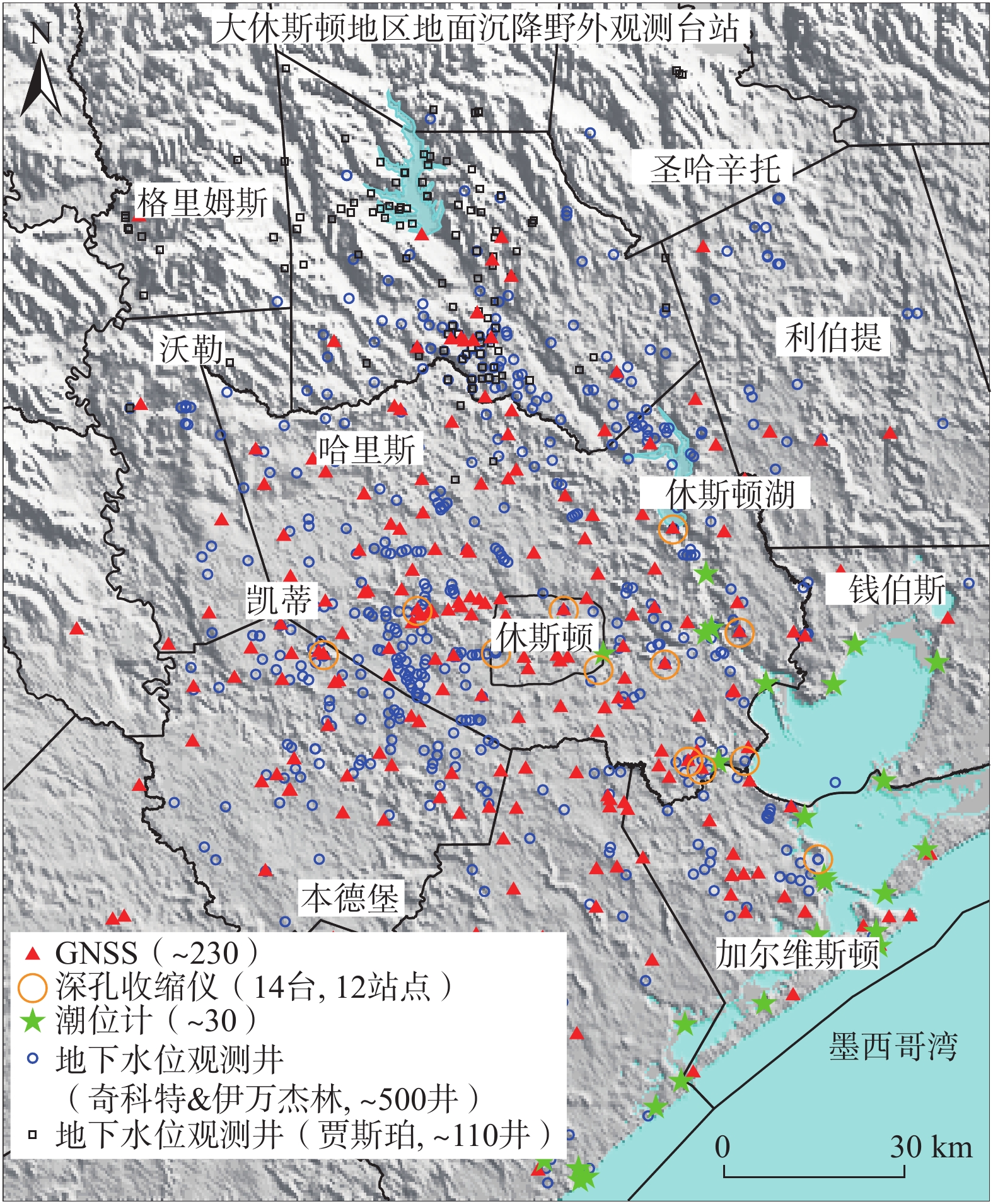
图 4 休斯顿地区含水层系统水文地质剖面(根据文献[14]改编)
Figure 4.
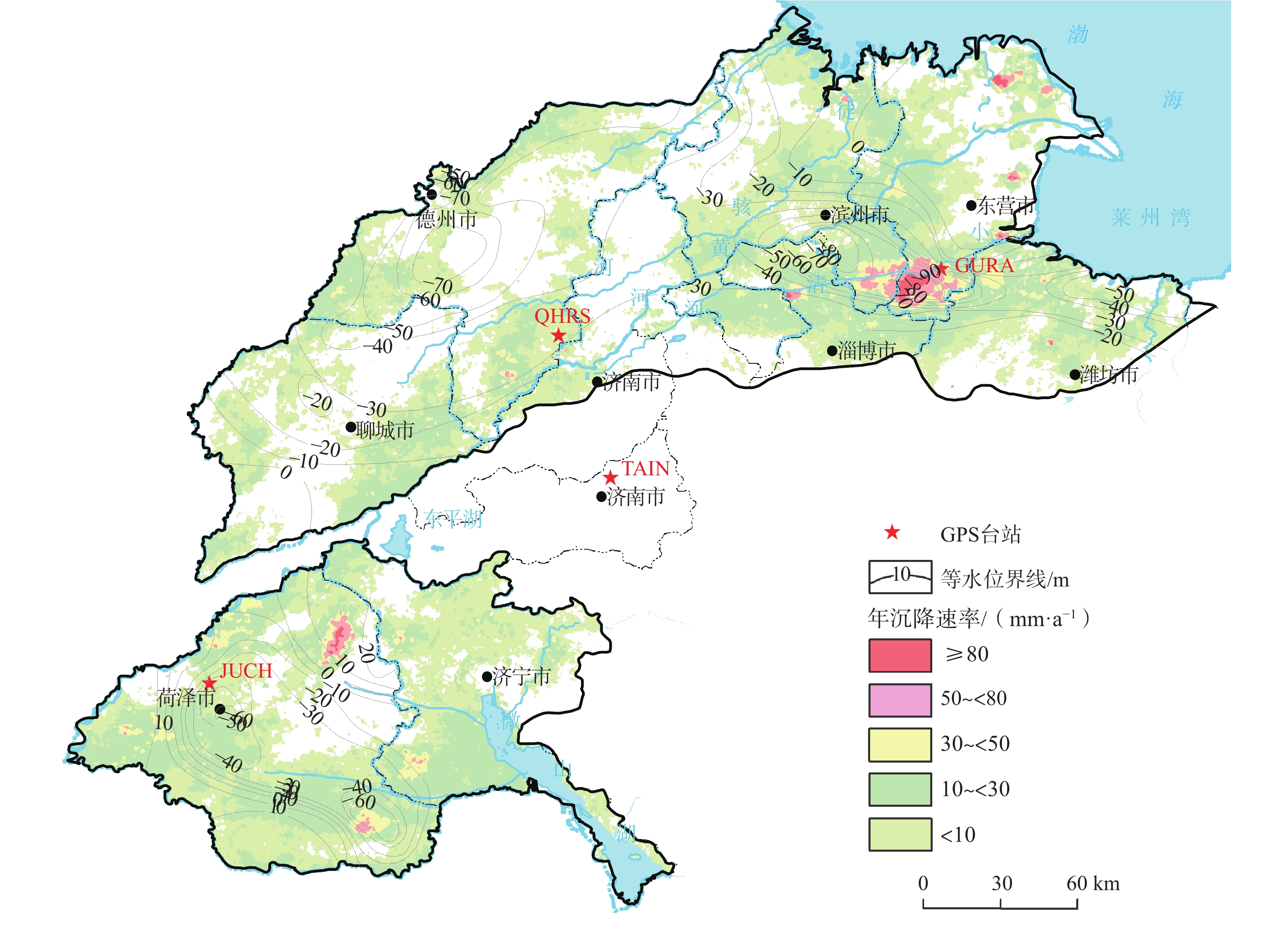
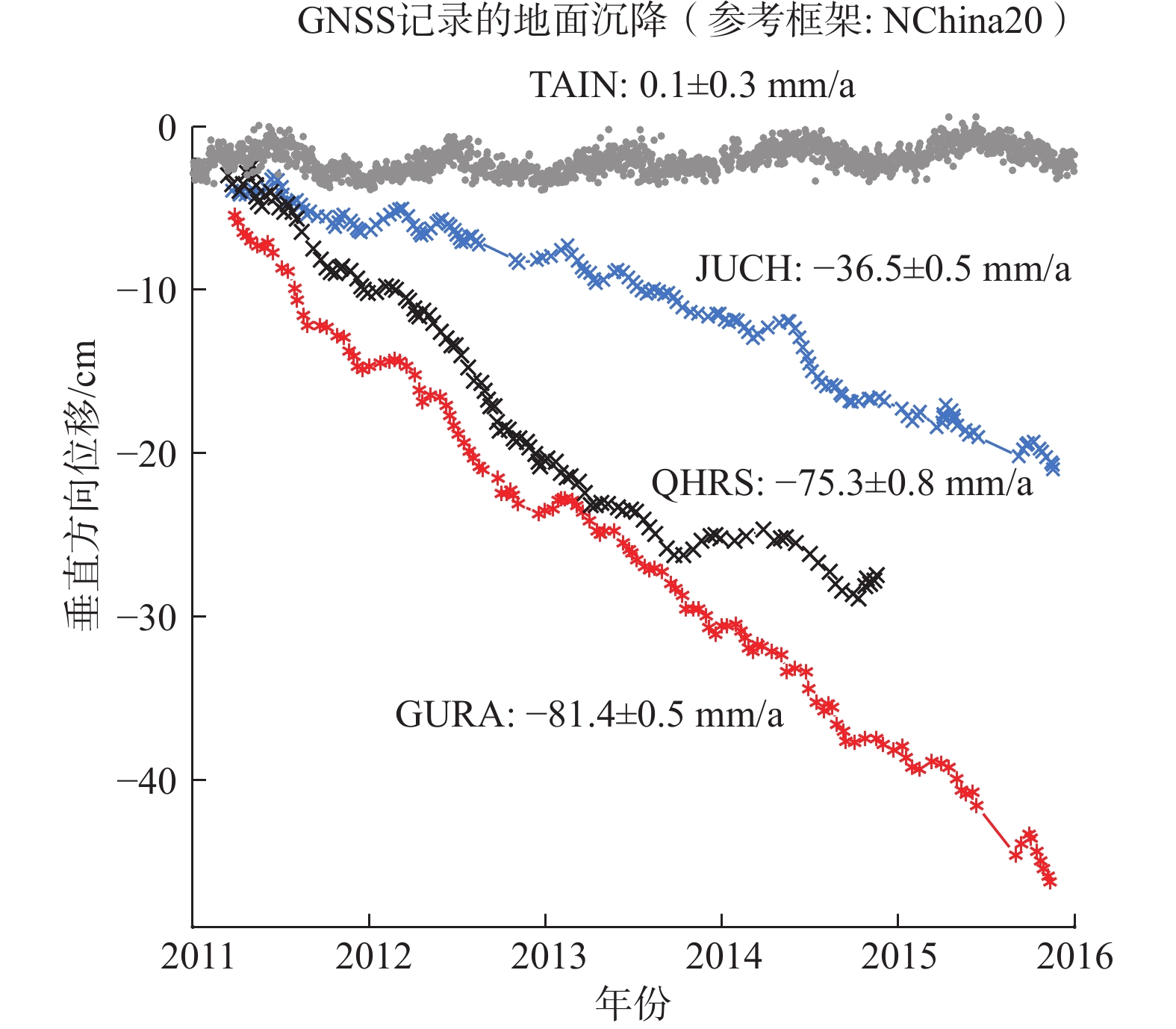
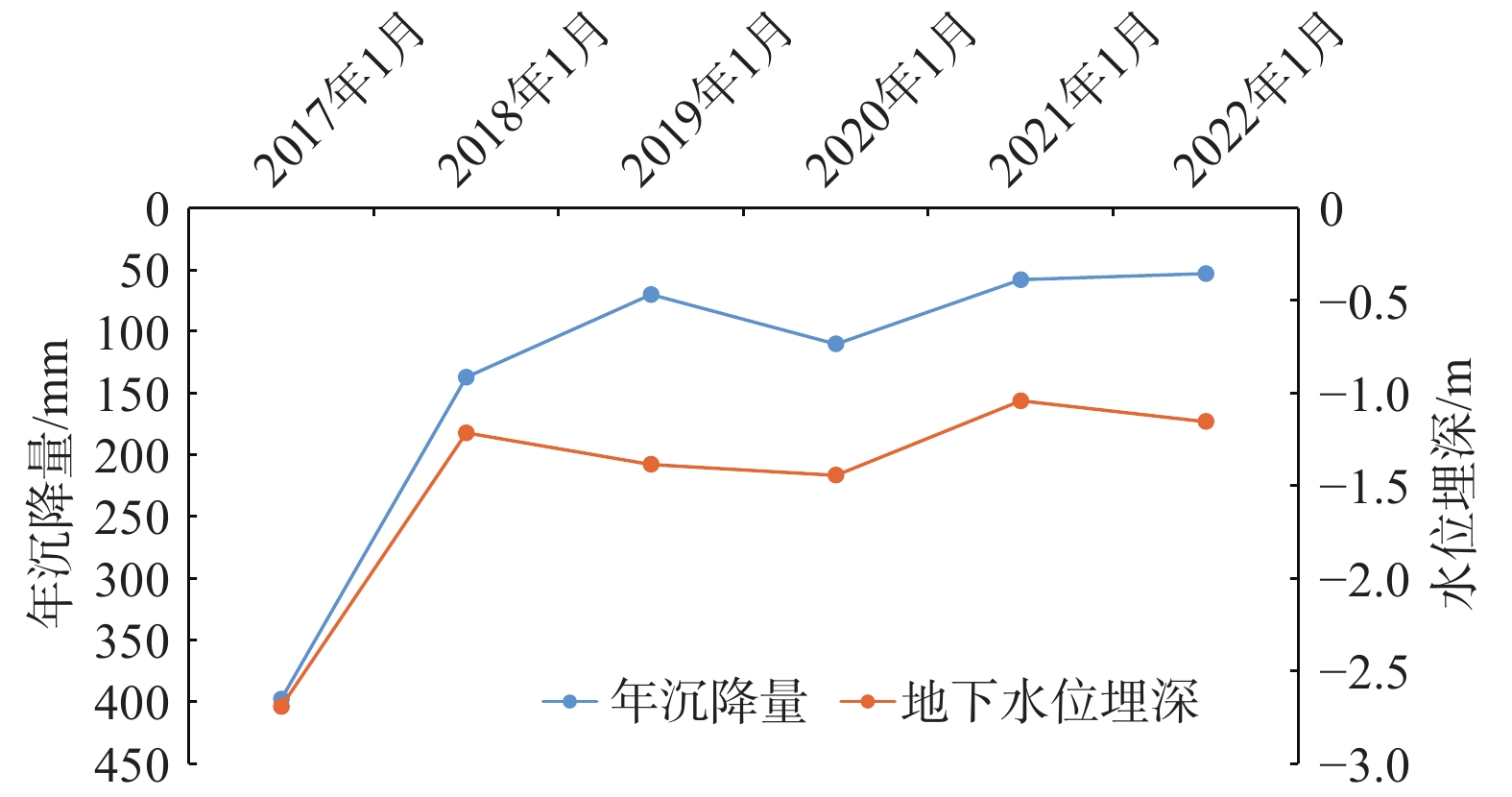
图 8 广饶县北面地面沉降年沉降量与承压含水层地下水水位历时曲线(根据文献[9]改编)
Figure 8.
-
[1] 郭海朋,李文鹏,王丽亚,等. 华北平原地下水位驱动下的地面沉降现状与研究展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):162 − 171. [GUO Haipeng,LI Wenpeng,WANG Liya,et al. Present situation and research prospects of the land subsidence driven by groundwater levels in the North China Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):162 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Haipeng, LI Wenpeng, WANG Liya, et al . Present situation and research prospects of the land subsidence driven by groundwater levels in the North China Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (3 ):162 −171 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 郭海朋,白晋斌,张有全,等. 华北平原典型地段地面沉降演化特征与机理研究[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(6):1115 − 1127. [GUO Haipeng,BAI Jinbin,ZHANG Youquan,et al. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain[J]. Geology in China,2017,44(6):1115 − 1127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Haipeng, BAI Jinbin, ZHANG Youquan, et al . The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain[J]. Geology in China,2017 ,44 (6 ):1115 −1127 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 张永伟. 华北平原德州地面沉降成生机理、监测预警与可控性研究[D]. 济南:山东大学,2014. [ZHANG Yongwei. Study on formation mechanism,monitoring and early warning and controllability of land subsidence in Dezhou,North China Plain[D]. Jinan:Shandong University,2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Yongwei. Study on formation mechanism, monitoring and early warning and controllability of land subsidence in Dezhou, North China Plain[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 张永伟,邵明,肖敏. 山东省地面沉降监测与防治工作进展[J]. 山东国土资源,2018,34(8):62 − 66. [ZHANG Yongwei,SHAO Ming,XIAO Min. Progress in monitoring and prevention of land subsidence in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,2018,34(8):62 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Yongwei, SHAO Ming, XIAO Min . Progress in monitoring and prevention of land subsidence in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,2018 ,34 (8 ):62 −66 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] WANG Guoquan. The 95% confidence interval for GNSS-derived site velocities[J]. Journal of Surveying Engineering,2022,148(1):04021030. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000390
[6] KASMAREK M C,GABRYSCH R K,JOHNSON M R. Estimated land-surface subsidence in Harris County,Texas,1915-17 to 2001[R]. Scientific Investigations Map-3097. Reston,VA:U. S. Geological Survey,2009.
[7] WANG Guoquan. New preconsolidation heads following the long-term hydraulic-head decline and recovery in Houston,texas[J]. Groundwater,2023,61(5):674 − 691. doi: 10.1111/gwat.13271
[8] BAKER E. Stratigraphic and hydrogeologic framework of part of the coastal plain of Texas[R]. Austin,TX:U. S. Geological Survey,1977
[9] 张永伟,杨培杰,梁浩,等,山东省地面沉降调查监测与防控报告[R]. 济南:山东省国土空间生态修复中心,2022. [ZHANG Yongwei,YANG Beijie,LIANG Hao,et al. Land subsidence investigation,monitoring and prevention and control report in Shandong Province[R]. JI Nan:Shandong Provincial Territorial Spatial Ecological Restoration Center,2022. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Yongwei, YANG Beijie, LIANG Hao, et al. Land subsidence investigation, monitoring and prevention and control report in Shandong Province[R]. JI Nan: Shandong Provincial Territorial Spatial Ecological Restoration Center, 2022. (in Chinese) [10] 刘贺, 罗勇, 雷坤超, 等. 北京新航城地区地面沉降演化规律及多源监测方法对比研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):398 − 406. [LIU He, LUO Yong, LEI Kunchao, et al. Evolution of land subsidence and comparative study on multi-source monitoring methods in New Airlines City of Beijing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):398 − 406.(in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU He, LUO Yong, LEI Kunchao, et al . Evolution of land subsidence and comparative study on multi-source monitoring methods in New Airlines City of Beijing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023 ,42 (1 ):398 −406 .[11] 刘蓉,曹国亮,赵勇,等. 地面沉降对含水层参数及给水能力的影响研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(3):47 − 54. [LIU Rong,CAO Guoliang,ZHAO Yong,et al. A study of the influence of land subsidence on hydraulic parameters and water supply capacity[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):47 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Rong, CAO Guoliang, ZHAO Yong, et al . A study of the influence of land subsidence on hydraulic parameters and water supply capacity[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019 ,46 (3 ):47 −54 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 纪洪磊,杨亚宾,张永伟,等. 鲁北平原第四纪沉积特征及地面沉降模式分析[J]. 地质学报,2019,93(增刊1):241-250. [JI Honglei,YANG Yabin,ZHANG Yongwei,et al. Quaternary sedimentary characteristics and land subsidence model in North Shandong Plain[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2019,93(Sup 1):241-250. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JI Honglei, YANG Yabin, ZHANG Yongwei, et al. Quaternary sedimentary characteristics and land subsidence model in North Shandong Plain[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(Sup 1): 241-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 骆勇,祝晓彬,郭飞,等. 不同方法求解疏排水引起的地面沉降对比研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(5):150 − 157. [LUO Yong,ZHU Xiaobin,GUO Fei,et al. A comparative study of land subsidence caused by drainage with different methods[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(5):150 − 157. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LUO Yong, ZHU Xiaobin, GUO Fei, et al . A comparative study of land subsidence caused by drainage with different methods[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018 ,45 (5 ):150 −157 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] ELLIS J,KNIGHT J E,WHITE J T,et al. Hydrogeology,land-surface subsidence,and documentation of the gulf coast land subsidence and groundwater-flow (GULF) model,southeast Texas ,1897–2018[R]. Austin,TX:U. S. Geological Survey,2023.
[15] YU Jiangbo,WANG Guoquan,KEARNS T J,et al. Is there deep-seated subsidence in the houston-galveston area?[J]. International Journal of Geophysics,2014,2014:1 − 11.
[16] 丁朋朋,贾超,韩瑶,等. 时序InSAR技术的潍北平原地面沉降分析[J]. 测绘科学,2021,46(8):135 − 140. [DING Pengpeng,JIA Chao,HAN Yao,et al. Analysis of land subsidence in Weibei plain based on time series InSAR method[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2021,46(8):135 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DING Pengpeng, JIA Chao, HAN Yao, et al . Analysis of land subsidence in Weibei plain based on time series InSAR method[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2021 ,46 (8 ):135 −140 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] HAN Yao,ZHAO Yang,ZHANG Yongwei,et al. Monitoring and analysis of land subsidence in modern Yellow River Delta using SBAS-InSAR Technology[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2021,643(1):012166. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/643/1/012166
[18] 狄胜同,贾超,张少鹏,等. 华北平原鲁北地区地下水超采导致地面沉降区域特征及演化趋势预测[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(5):1638 − 1654. [DI Shengtong,JIA Chao,ZHANG Shaopeng,et al. Regional characteristics and evolutionary trend prediction of land subsidence caused by groundwater over exploitation in North Shandong of the North China Plain[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(5):1638 − 1654. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DI Shengtong, JIA Chao, ZHANG Shaopeng, et al . Regional characteristics and evolutionary trend prediction of land subsidence caused by groundwater over exploitation in North Shandong of the North China Plain[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020 ,94 (5 ):1638 −1654 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] GABRYSCH B R K,PECK D L. Ground-water withdrawals and land-surface subsidence in the Houston-Galveston Region,Texas,1906-80[R]. Austin,TX:U. S. Geological Survey,1982.
[20] KEARNS T J,WANG Guoquan,BAO Yan,et al. Current land subsidence and groundwater level changes in the Houston metropolitan area (2005–2012)[J]. Journal of Surveying Engineering,2015,141(4):1 − 16.
[21] WANG Guoquan. Seasonal subsidence and heave recorded by borehole extensometers in Houston[J]. Journal of Surveying Engineering,2023,149(1):04022018. doi: 10.1061/JSUED2.SUENG-1369
[22] AGUDELO G,WANG Guoquan,LIU Yuhao,et al. GPS geodetic infrastructure for subsidence and fault monitoring in Houston,Texas,USA[J]. Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences,2020,382:11 − 18.
[23] LIU Yuhao,WANG Guoquan,YU Xiao,et al. Sentinel-1 InSAR and GPS-integrated long-term and seasonal subsidence monitoring in Houston,texas,USA[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,14(23):6184. doi: 10.3390/rs14236184
[24] BAWDEN G,JOHNSON M R,KASMAREK M C,et al. Investigation of land subsidence in the houston-galveston region of texas by using the global positioning system and interferometric synthetic aperture radar,1993-2000[R]. Reston,VA:U. S. Geological Survey,2014.
[25] 曲菲霏,杨成生,张勤. 基于MT-InSAR技术的城市活动断层定位与监测——以美国休斯顿地区为例[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2022,44(4):617 − 631. [QU Feifei,YANG Chengsheng,ZHANG Qin. Monitoring and identification of active faults in urban areas using MT-InSAR technology:A case of Houston area,USA[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2022,44(4):617 − 631. (in Chinese with English abstract)
QU Feifei, YANG Chengsheng, ZHANG Qin . Monitoring and identification of active faults in urban areas using MT-InSAR technology: A case of Houston area, USA[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2022 ,44 (4 ):617 −631 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[26] YU Xiao,WANG Guoquan,HU Xie,et al. Land subsidence in Tianjin,China:before and after the south-to-north water diversion[J]. Remote Sensing,2023,15(6):1647. doi: 10.3390/rs15061647
[27] GUO Chunxi,NIE Jianliang,TIAN Jie,et al. Vertical ground displacements in the Shandong Province derived from long-term GNSS and leveling surveying[J]. Advances in Space Research,2019,64(7):1388 − 1397. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2019.06.035
[28] 鲍艳,王国权,于笑,等. 华北稳定参考框架NChina20的建立及应用[J]. 中国地震,2020,36(4):788 − 805. [BAO Yan,WANG Guoquan,YU Xiao,et al. Establishment and application of stable North China reference frame:NChina20[J]. Earthquake Research in China,2020,36(4):788 − 805. (in Chinese with English abstract)
BAO Yan, WANG Guoquan, YU Xiao, et al . Establishment and application of stable North China reference frame: NChina20[J]. Earthquake Research in China,2020 ,36 (4 ):788 −805 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[29] JIA Chao,ZHANG Yongwei,HAN Jingmin,et al. Susceptibility area regionalization of land subsidence based on extenics theory[J]. Cluster Computing,2017,20(1):53 − 66. doi: 10.1007/s10586-016-0720-4
[30] WANG Guoquan,GREUTER A,PETERSEN C M,et al. Houston GNSS network for subsidence and faulting monitoring:data analysis methods and products[J]. Journal of Surveying Engineering,2022,148(4):04022008. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000399
-



 下载:
下载: