Lithospheric thermo-rheological structure of the Huangshadong geothermal field in Huizhou of Guangdong and its heat-sources implications
-
摘要:
岩石圈热-流变结构研究是揭示岩石圈范围内热状态的有效手段,开展地热异常区的岩石圈热-流变结构研究可以对热源贡献进行有效约束。东南沿海地区是我国地热资源重要分布区,地表出露大量天然温泉,地热钻探揭露深部具有较高的地温梯度,然而关于其热源机制尚未有定论,且深部是否赋存干热岩资源亦不清楚。以广东惠州黄沙洞地热田为研究对象,分析岩石圈尺度温度分布和流变强度,探讨黄沙洞地热田的热源构成,分析浅部水热系统的热影响,并对干热岩资源前景进行分析。结果表明:(1)黄沙洞地热田水热活动影响下地表热通量为130.3 mW/m2,地壳热流与地幔热流值相近,表现为温壳温幔型岩石圈热结构,此外,构造活动相关热流达到了30.5~60.3 mW/m2;(2)岩石圈流变结构显示中地壳存在韧性流变层,上地壳与下地壳以脆性破裂为主,下地壳与地幔表现出流变结构耦合,为相对稳固的地壳底界;(3)黄沙洞地热田的热源以地壳构造活动产生的热源为主,地幔热源和放射性生热是主要的热源组成部分,构造热作用的主要方式包括区域深断裂的热聚敛和水热系统循环换热,两者可能通过“接力式”热传递携带热量至浅表;(4)区域深断裂的热聚敛在构造热作用中的占比是影响干热岩资源前景的关键因素。本项研究可为后续东南沿海同类型地区的干热岩资源勘查与靶区选址提供参考。
Abstract:The thermo-rheological structure of the lithosphere is an effective method to reveal the thermal state within the lithosphere. Studies of the thermo-rheological structure of the lithosphere in geothermal anomaly areas can effectively constrain the contribution of heat sources. The southeastern China is an important distribution region for geothermal resources, with a large number of natural hot springs emerging on the land surface. Boreholes in this region have identified high geothermal gradients at depth. However, the mechanism of the heat sources is still controversial, and whether the hot dry rock resources exists is not clear. In this study, we take the Huangshadong geothermal field in Huizhou of Guangdong as the research target. We analyze the temperature distribution and rheological strength of the lithosphere, discuss the heat sources of the Huangshadong geothermal field, examine the thermal influence of shallow hydrothermal systems, and predict the prospects of dry hot rock resources. The results show that the heat flux under the influence of hydrothermal systems in the Huangshadong geothermal field is 130.3 mW/m2, and the crustal heat flow is similar to the mantle heat flow, showing a warm-crust-warm-mantle lithospheric thermal structure. In addition, the structural heat flux reaches 30.5–60.3 mW/m2. The rheological structure of the lithosphere shows that the middle crust has a ductile rheological layer, the upper crust and the lower crust are mainly controlled by brittle failure, and the lower crust and the lithosphere mantle show coupling in the rheological structure, which indicates a relatively stable crustal bottom boundary. The heat sources of the Huangshadong geothermal field is dominated by the tectonic heat source, and the mantle heat source and radiogenic heat production are the main heat source components. The main parts of tectonic heat source include the heat accumulation in regional deep faults and cyclic heat transfer in hydrothermal systems, both of which may carry heat to the surface through “relay” heat transfer. The proportion of heat accumulation of regional deep faults in the tectonic heat source is the key factor affecting the prospects of dry hot rock resources.
-
Key words:
- thermal-rheological structure /
- heat source /
- Huangshadong /
- hot dry rock /
- heat flow
-

-
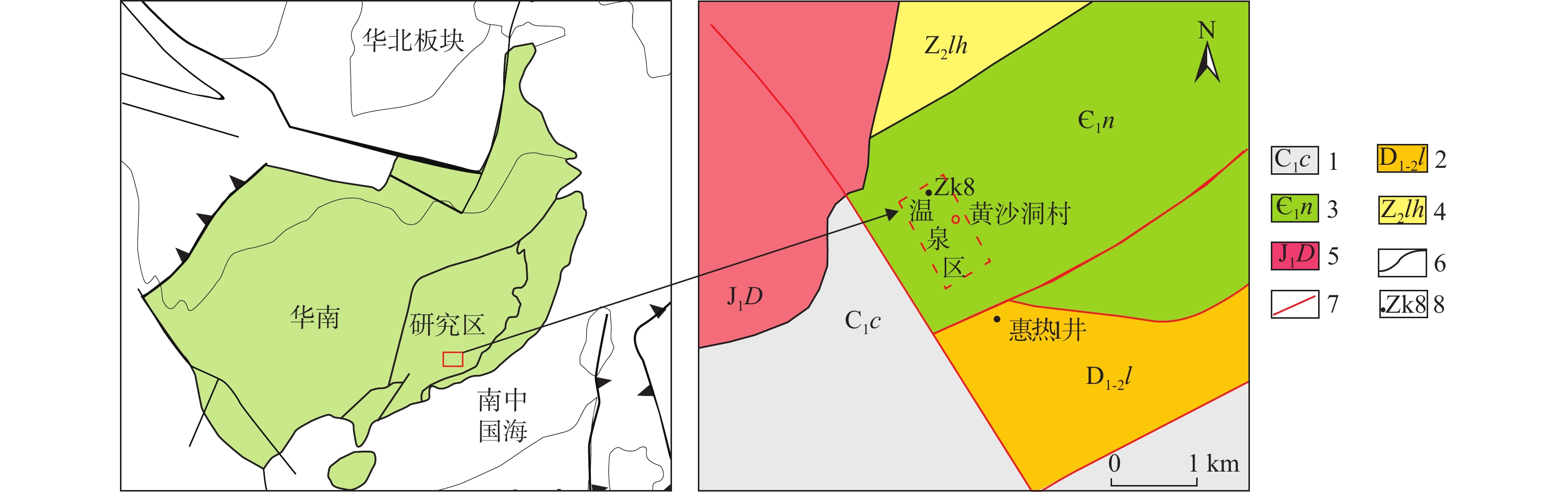
图 1 黄沙洞地热田地质构造简图(大地构造位置简图修改自文献[39])
Figure 1.
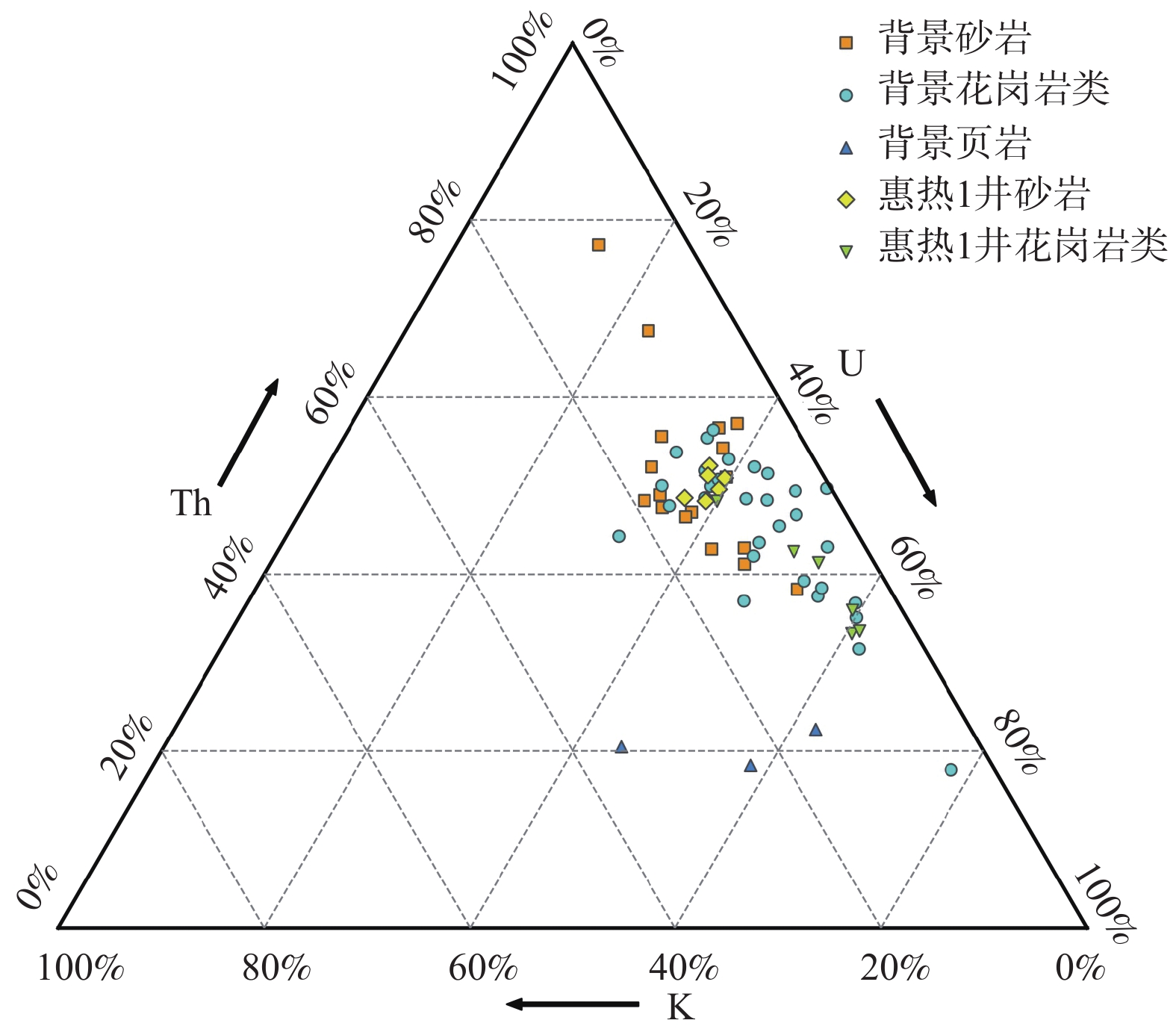
表 1 惠州及周边区域不同岩性放射性生热率统计表
Table 1. Radiogenic heat production of different rock types in Huizhou and surrounding area
编号 岩性 CK
/%CTh
/(μg∙g−1)CU
/(μg∙g−1)ρ
/(kg∙m−3)A
/(μW∙m−3)CHA026D 砂岩 1.97 28.00 4.95 2.49 3.13 CHA036D 3.22 13.80 3.01 2.43 1.83 CHA058D 6.08 24.40 5.34 2.26 3.04 CHA038D 0.22 1.27 0.47 2.44 0.21 CHA040D 5.58 19.45 3.56 2.48 2.56 CHB092D 4.34 18.90 3.09 2.53 2.35 CHB156D 5.64 22.10 4.14 2.24 2.59 CHA044D 2.41 28.60 1.39 2.47 2.34 CHB107D 1.60 7.91 2.24 2.41 1.14 CHB114D 4.57 17.70 4.68 2.05 2.17 CHA049D 3.27 33.80 3.19 2.48 3.18 CHB185D 1.28 11.45 2.13 2.55 1.38 HZB05D* 2.92 10.80 2.14 2.39 1.39 HZB056D* 2.75 19.90 4.15 2.48 2.48 HZB065D* 4.58 25.60 3.83 2.21 2.61 HZB072D* 3.69 16.25 4.90 2.20 2.22 HZB093D* 1.05 10.80 1.85 2.29 1.12 CHB098D 花岗
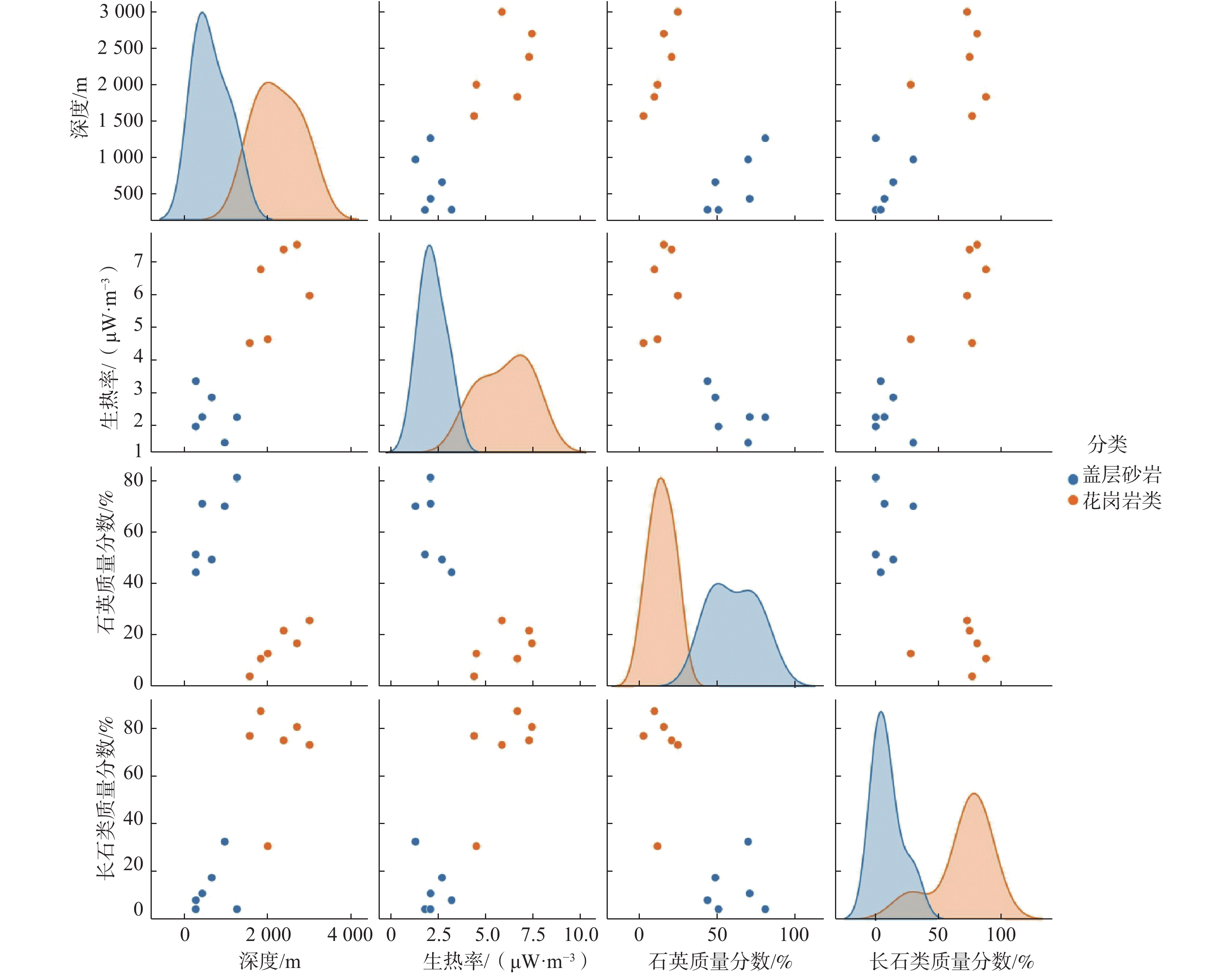
岩类3.00 10.15 3.56 2.53 1.78 CHB196D 4.74 29.60 5.71 2.67 3.92 CHA006D 5.43 31.80 6.60 2.66 4.34 CHB110D 4.23 68.30 22.70 2.62 10.63 CHB164D 4.60 55.60 24.10 2.59 10.04 CHB127D 5.42 35.60 7.33 2.45 4.40 CHB068D 4.13 16.05 3.22 2.58 2.22 CHB130D 6.75 39.70 11.35 2.58 6.02 CHB176D 5.35 46.30 9.09 2.58 5.77 CHA047D 3.87 19.45 5.79 2.37 2.81 CHB126D 5.91 33.30 5.53 2.54 4.02 CHB063D 4.72 46.50 21.40 2.57 8.72 CHB048D 4.81 41.20 11.55 2.54 5.90 CHB060D 5.70 14.70 2.89 2.68 2.28 CHB049D 4.37 25.00 29.30 2.61 9.35 CHB029D 5.43 37.70 14.90 2.62 6.74 CHB102D 5.19 67.50 15.30 2.47 8.31 CHB171D 4.90 55.40 11.90 2.66 7.24 CHB100D 4.41 81.70 20.90 2.60 11.01 CHA018D 4.60 31.30 11.35 2.54 5.19 CHB101D 4.70 61.20 17.05 2.62 8.79 CHB088D 5.11 41.90 7.20 2.46 4.76 CHB193D 5.28 49.60 8.42 2.68 6.04 CHA004D 3.89 20.10 4.29 2.67 2.83 CHB037D 6.06 25.30 4.59 2.59 3.36 HZB032D* 4.58 30.90 16.35 2.32 5.82 HZB036D* 3.30 31.40 7.81 2.24 3.72 HZB075D* 0.30 51.10 13.80 2.24 5.90 HZB086D* 4.62 37.00 14.25 2.34 5.77 HZB098D* 3.89 28.90 6.83 2.15 3.28 HZB017D* 页岩 5.15 20.00 3.78 2.36 2.48 HZB023D* 2.06 15.35 1.39 2.40 1.43 HZB043D-1* 2.80 16.25 3.32 1.93 1.60 HZB043D-2* 3.59 20.80 4.83 2.15 2.40 注:*样品数据来自闫晓雪[28]。 表 2 惠热1井钻孔岩心热物性参数统计特征值[28]
Table 2. Thermal properties of cores from HR1 in the Huangshadong geothermal field
编号 深度/m 岩性 测量热导率
/(W·m−1·K−1)校正热导率
/(W·m−1·K−1)生热率
/(μW∙m−3)HR-1 273 砂岩 3.53 3.45 1.79 HR-2 276 砂岩 6.157 5.99 3.21 HR-3 427 砂岩 7.294 6.97 2.09 HR-4 655 砂岩 2.778 2.69 2.71 HR-5 968 砂岩 2.778 2.64 1.29 HR-6 1262 砂岩 5.197 4.58 2.09 HR-7 1568 花岗岩类 1.697 1.64 4.39 HR-8 1832 花岗岩类 6.778 5.73 6.69 HR-9 2005 花岗岩类 4.361 3.72 4.52 HR-10 2383 花岗岩类 1.937 1.93 7.31 HR-11 2704 花岗岩类 5.311 5.30 7.46 HR-12 3005 花岗岩类 5.87 表 3 惠热1井及周边岩石中各矿物组成质量占比
Table 3. Mineral composition of different rock types in HR1 and the surrounding area
编号 质量分数/% 钾长石 钠长石 石英 方解石 云母 黏土矿物 HR-1* 2 47 51 HR-2* 2 2 5 1 51 39 HR-3* 7 62 22 9 HR-4* 14 19 37 30 HR-5* 26 44 HR-6* 49 19 32 HR-7* 64 13 2 20 1 HR-8* 54 34 8 4 HR-9* 8 5 46 HR-10* 34 41 20 5 HR-11* 39 42 15 4 HR-12* 38 35 24 3 CHA004D 13.5 32.6 47.4 6.5 CHA006D 17.8 22.9 45.7 13.6 CHB028D 100 CHB037D 21.7 27.3 51 CHB045D 100 CHB088D 16.2 18.9 64.9 CHB102D 24.7 26.7 48.5 CHB126D 20.3 18.8 52.1 8.8 CHB164D 16.3 33.1 50.6 CHB176D 16.5 31.6 38.9 13 CHB193D 19.6 26.5 44.5 9.4 注:*样品数据来自闫晓雪[28];表中空白表示无此项或未测,其余表中空白同此解释。 表 4 黄沙洞地热田岩石圈分层结构及热物性
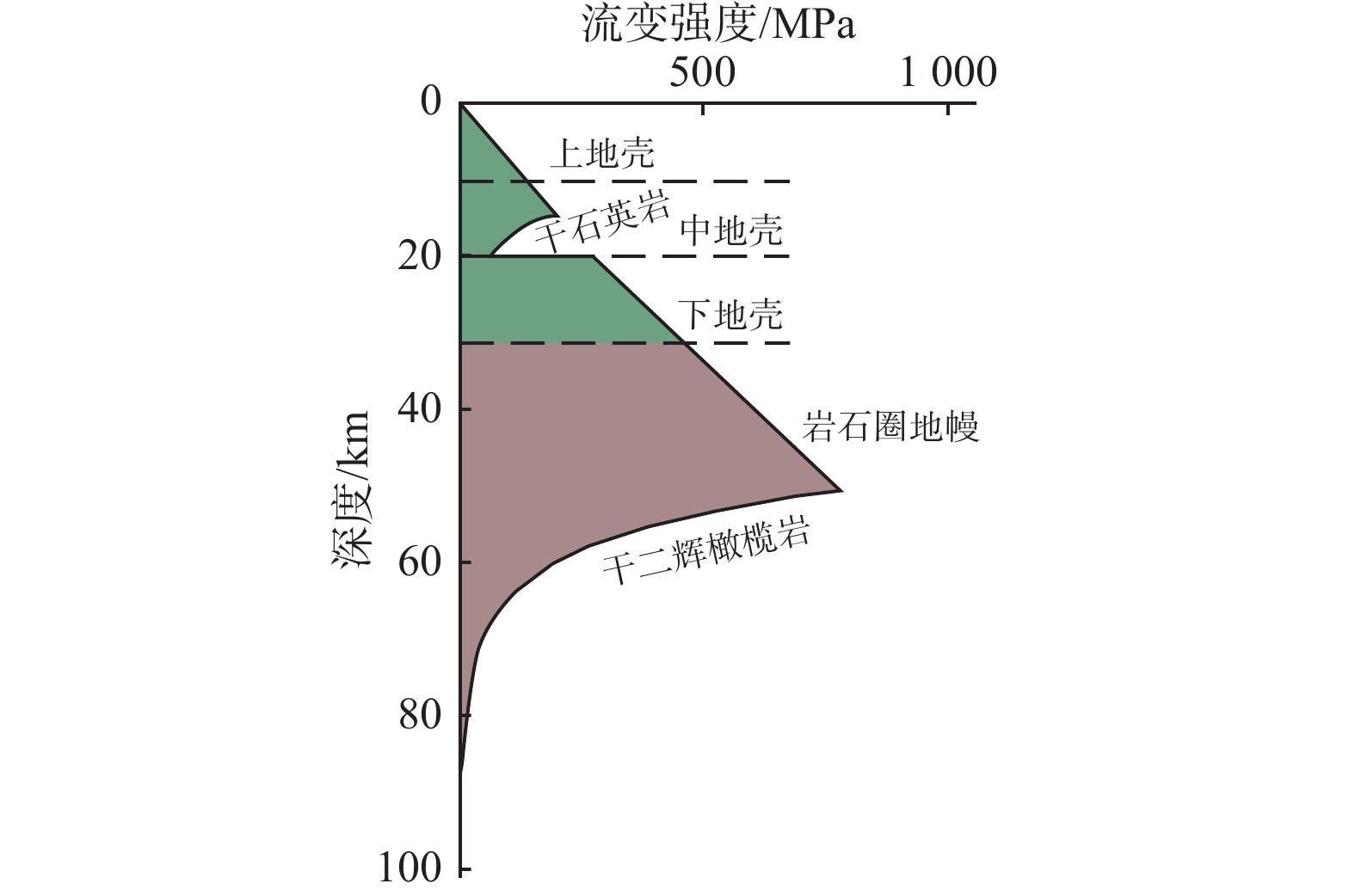
Table 4. Lithospheric layered structure and relative radiogenic heat production and thermal conductivity in Huangshadong geothermal field
地表热通量
/ (mW∙m−2)岩石圈分层/km 放射性生热率
/(μW∙m−3)热导率
/(W·m−1·K−1)130.3(水热活动区)/
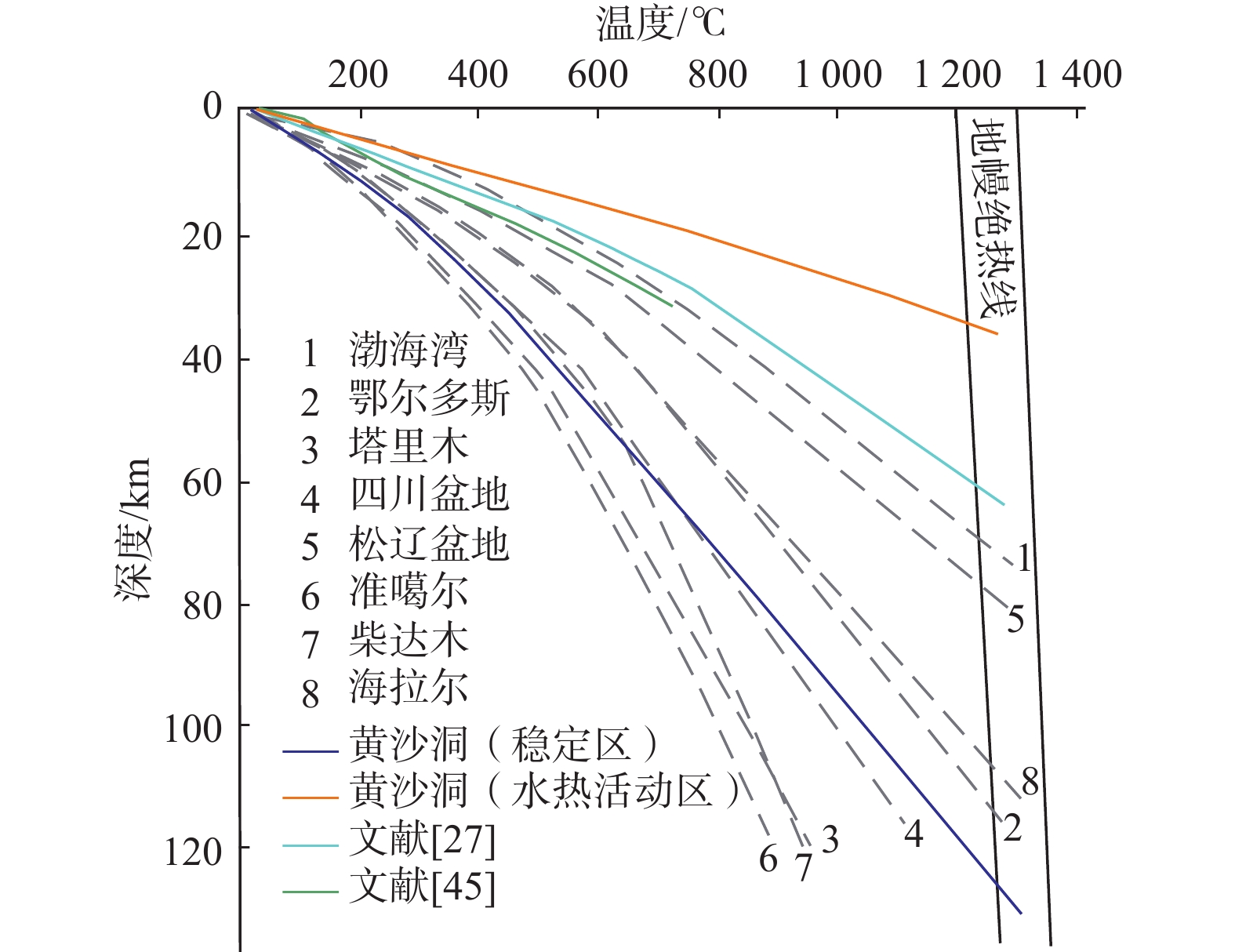
70(稳定区)上地壳 0~3 4.27 3.92 >3~10 4.27exp(−z/D) 3.06 中地壳 (>10~20) 0.80 2.70 下地壳 (>20~32) 0.03 3.00 岩石圈地幔 (>32) 0.03 3.40 表 5 黄沙洞地热田岩石圈热结构及深部温度
Table 5. Lithospheric thermal structure and deep temperature in Huangshadong geothermal field
热结构 水热活动区
热流值稳定区
热流值热流组成
/(mW∙m−2)地表热流 130.30 70.00 地壳热流 38.26 38.26 地幔热流 31.74 31.74 构造热流 60.30 地壳热流/地幔热流 1.2 1.2 地壳深部
温度/°C地壳底界温度 1091.4 442.7 10 km处温度 362.2 178.2 20 km处温度 722.3 314.9 30 km处温度 1030.0 421.6 -
[1] KIRBY S H,KRONENBERG A K. Rheology of the lithosphere:Selected topics[J]. Reviews of Geophysics,1987,25(6):1219. doi: 10.1029/RG025i006p01219
[2] CHEN Wangping,HUNG S H,TSENG T L,et al. Rheology of the continental lithosphere:Progress and new perspectives[J]. Gondwana Research,2012,21(1):4 − 18. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.07.013
[3] BUROV E B. Rheology and strength of the lithosphere[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2011,28(8):1402 − 1443. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.05.008
[4] LACHENBRUCH A H. Crustal temperature and heat production:Implications of the linear heat-flow relation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,1970,75(17):3291 − 3300. doi: 10.1029/JB075i017p03291
[5] FURLONG K P,CHAPMAN D S. Heat flow,heat generation,and the thermal state of the lithosphere[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,2013,41:385 − 410. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.031208.100051
[6] 邱楠生, 胡圣标, 何丽娟. 沉积盆地地热学[M]. 青岛: 中国石油大学出版社, 2019
QIU Nansheng, HU Shengbiao, HE Lijuan. Geothermics in sedimentary basins[M]. Qingdao: China University of Pertoleum Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[7] 王良书, 李成, 刘福田, 等. 中国东、西部两类盆地岩石圈热-流变学结构[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2000, 30(增刊1): 116-121
WANG Liangshu, LI Cheng, LIU Futian, et al. Thermorheological structure of lithosphere in eastern and western basins of China[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2000, 30(Sup 1): 116 – 121. (in Chinese)
[8] 王贵玲,蔺文静,刘峰,等. 地热系统深部热能聚敛理论及勘查实践[J]. 地质学报,2023,97(3):639 − 660. [WANG Guiling,LIN Wenjing,LIU Feng,et al. Theory and survey practice of deep heat accumulation in geothermal system and exploration practice[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2023,97(3):639 − 660. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.03.001
WANG Guiling, LIN Wenjing, LIU Feng, et al. Theory and survey practice of deep heat accumulation in geothermal system and exploration practice[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(3): 639-660. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.03.001
[9] 刘俊来. 大陆中部地壳应变局部化与应变弱化[J]. 岩石学报,2017,33(6):1653 − 1666. [LIU Junlai. Strain localization and strain weakening in the continental middle crust[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2017,33(6):1653 − 1666. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Junlai. Strain localization and strain weakening in the continental middle crust[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(6): 1653-1666. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王恺,熊熊,周宇明,等. 联合多种资料确定华北岩石圈三维热-流变结构:对裂陷形成的意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学),2020,50(7):946 − 961. [WANG Kai,XIONG Xiong,ZHOU Yuming,et al. Three-dimensional thermo-rheological structure of the lithosphere in the North China Craton determined by integrating multiple observations:Implications for the formation of rifts[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae),2020,50(7):946 − 961. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2019-0139
WANG Kai, XIONG Xiong, ZHOU Yuming, et al. Three-dimensional thermo-rheological structure of the lithosphere in the North China Craton determined by integrating multiple observations: Implications for the formation of rifts[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2020, 50(7): 946-961. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2019-0139
[11] 李忠海,崔起华,钟辛易,等. 大陆动力学数值模拟:问题、进展与展望[J]. 地质学报,2021,95(1):238 − 258. [LI Zhonghai,CUI Qihua,ZHONG Xinyi,et al. Numerical modeling of continental dynamics:Questions,progress and perspectives[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2021,95(1):238 − 258. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Zhonghai, CUI Qihua, ZHONG Xinyi, et al. Numerical modeling of continental dynamics: questions, progress and perspectives[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(1): 238-258. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 龙登红, 周小龙, 杨坤光, 等. 青藏高原东北缘深部地质构造与地热资源分布关系研究[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(3): 721 – 731.
LONG Denghong, ZHOU Xiaolong, YANG Kunguang, et al. Research on relationship between the deep structure and geothermal resource distribution in the Northeastern Xizang Plateau[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(3): 721 – 731. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] LI Zhengxiang,LI Xianhua. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:A flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology,2007,35(2):179 – 182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1
[14] LI Sanzhong,SUO Yanhui,LI Xiyao,et al. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian ocean continent connection zone to subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2019,192:91 − 137. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.03.003
[15] 袁玉松,马永生,胡圣标,等. 中国南方现今地热特征[J]. 地球物理学报,2006,49(4):1118 − 1126. [YUAN Yusong,MA Yongsheng,HU Shengbiao,et al. Present-day geothermal characteristics in South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2006,49(4):1118 − 1126. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.04.025
YUAN Yusong, MA Yongsheng, HU Shengbiao, et al. Present-day geothermal characteristics in South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2006, 49(4): 1118-1126. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.04.025
[16] 王贵玲,张薇,梁继运,等. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报,2017,38(4):449 − 450. [WANG Guiling,ZHANG Wei,LIANG Jiyun,et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2017,38(4):449 − 450. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02
WANG Guiling, ZHANG Wei, LIANG Jiyun, et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4): 449-450. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02
[17] 姚足金, 陈宗宇. 中国东南沿海地区地热资源的地质评价[C]//中国地质科学院水文地质工程地质研究所所刊(第6号). 1990, 47 – 80
YAO Zujin, CHEN Zhongyu. Geological assessment of geothermal potential for regional development in southeast coast of China[C]// Bull. Institute of Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology CAGS (No. 6). 1990, 47 – 80. (in Chinese)
[18] 李亭昕,蔺文静,甘浩男,等. 东南沿海干热岩资源成因模式探讨及勘查进展[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(2):187 − 200. [LI Tingxin,LIN Wenjing,GAN Haonan,et al. Research on the genetic model and exploration progress of hot dry rock resources on the southeast coast of China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(2):187 − 200. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.02.018
LI Tingxin, LIN Wenjing, GAN Haonan, et al. Research on the genetic model and exploration progress of hot dry rock resources on the southeast coast of China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(2): 187-200. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.02.018
[19] TIAN Jiao,STEFÁNSSON A,LI Yiman,et al. Geochemistry of thermal fluids and the genesis of granite-hosted Huangshadong geothermal system,Southeast China[J]. Geothermics,2023,109:102647. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2023.102647
[20] XIAO Zhicai,WANG Shuai,QI Shihua,et al. Petrogenesis,tectonic evolution and geothermal implications of Mesozoic granites in the Huangshadong geothermal field,South China[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2020,31(1):141 − 158. doi: 10.1007/s12583-019-1242-9
[21] 袁建飞. 广东沿海地热系统水文地球化学研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2013
YUAN Jianfei. Hydrogeochemistry of the geothermal systems in coastal areas of Guangdong Province, South China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 蔺文静,甘浩男,王贵玲,等. 我国东南沿海干热岩赋存前景及与靶区选址研究[J]. 地质学报,2016,90(8):2043 − 2058. [LIN Wenjing,GAN Haonan,WANG Guiling,et al. Occurrence prospect of HDR and target site selection study in southeastern of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2016,90(8):2043 − 2058. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.08.031
LIN Wenjing, GAN Haonan, WANG Guiling, et al. Occurrence prospect of HDR and target site selection study in southeastern of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(8): 2043-2058. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.08.031
[23] 蔺文静,王贵玲,邵景力,等. 我国干热岩资源分布及勘探:进展与启示[J]. 地质学报,2021,95(5):1366 − 1381. [LIN Wenjing,WANG Guiling,SHAO Jingli,et al. Distribution and exploration of hot dry rock resources in China:Progress and inspiration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2021,95(5):1366 − 1381. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.05.004
LIN Wenjing, WANG Guiling, SHAO Jingli, et al. Distribution and exploration of hot dry rock resources in China: Progress and inspiration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(5): 1366-1381. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.05.004
[24] GAN Haonan,WANG Guiling,WANG Bo,et al. Abnormally low heat flow in Southeast China resulted from remnant slab subducted beneath the East Asian lithosphere[J]. Terra Nova,2022,34(4):340 − 348. doi: 10.1111/ter.12598
[25] LIN Wenjing,YIN XiaoXiao. Temperature estimation of a deep geothermal reservoir based on multiple methods:A case study in Southeastern China[J]. Water,2022,14:3205. doi: 10.3390/w14203205
[26] 范艳霞,李海龙,张军龙,等. 东南沿海黄沙洞地热田地应力与控热构造研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2022,65(10):3944 − 3961. [FAN Yanxia,LI Hailong,ZHANG Junlong,et al. Research on the in situ stress state and the geothermal-controlling structure of the Huangshadong geothermal field in the southeast coast of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2022,65(10):3944 − 3961. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0892
FAN Yanxia, LI Hailong, ZHANG Junlong, et al. Research on the in situ stress state and the geothermal-controlling structure of the Huangshadong Geothermal Field in the Southeast Coast of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(10): 3944-3961. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0892
[27] XI Yufei,WANG Guiling,LIU Shuang,et al. The formation of a geothermal anomaly and extensional structures in Guangdong,China:Evidence from gravity analyses[J]. Geothermics,2018,72:225 − 231. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2017.11.009
[28] 闫晓雪. 广东惠州黄沙洞地热系统表征及成因机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2019
YAN Xiaoxue. The characteristic and genesis mechanism in Huangshadong geothermal field, Guangdong[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] KUANG Jian,WANG Shuai,QI Shihua,et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of South China:A brief review,and new insights from the Huangshadong-Shiba area,Southeast China[J]. Geological Journal,2020,55(12):7716 − 7737. doi: 10.1002/gj.3870
[30] 王帅. 地下水中稀有气体同位素及其火山型地热成因研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020
WANG Shuai. Isotope geochemistry of rare gases in groundwater and their volcanic geothermal gensis[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 祝小辉. 广东河源高埔岗地热资源热储特征及资源潜力评价[J]. 西部探矿工程,2021,33(6):126 − 128. [ZHU Xiaohui. Thermal storage characteristics and resource potential evaluation of Gaopugang geothermal resources in Heyuan,Guangdong Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering,2021,33(6):126 − 128. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2021.06.041
ZHU Xiaohui. Thermal storage characteristics and resource potential evaluation of Gaopugang geothermal resources in Heyuan, Guangdong Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2021, 33(6): 126-128. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2021.06.041
[32] 甘浩男,王贵玲,蔺文静,等. 中国干热岩资源主要赋存类型与成因模式[J]. 科技导报,2015,33(19):22 − 27. [GAN Haonan,WANG Guiling,LIN Wenjing,et al. Research on the occurrence types and genetic models of hot dry rock resources in China[J]. Science & Technology Review,2015,33(19):22 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GAN Haonan, WANG Guiling, LIN Wenjing, et al. Research on the occurrence types and genetic models of hot dry rock resources in China[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2015, 33(19): 22-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 旷健,祁士华,王帅,等. 广东惠州花岗岩体及其地热意义[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(4):1466 − 1480. [KUANG Jian,QI Shihua,WANG Shuai,et al. Granite intrusion in Huizhou,Guangdong Province and its geothermal implications[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(4):1466 − 1480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
KUANG Jian, QI Shihua, WANG Shuai, et al. Granite intrusion in Huizhou, Guangdong Province and its geothermal implications[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(4): 1466-1480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 舒良树. 华南构造演化的基本特征[J]. 地质通报,2012,31(7):1035 − 1053. [SHU Liangshu. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2012,31(7):1035 − 1053. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.07.003
SHU Liangshu. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(7): 1035-1053. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.07.003
[35] SHU Liangshu,WANG Bo,CAWOOD P A,et al. Early Paleozoic and early Mesozoic intraplate tectonic and magmatic events in the cathaysia block,South China[J]. Tectonics,2015,34(8):1600 − 1621. doi: 10.1002/2015TC003835
[36] 李三忠,索艳慧,李玺瑶,等. 西太平洋中生代板块俯冲过程与东亚洋陆过渡带构造-岩浆响应[J]. 科学通报,2018,63(16):1550 − 1593. [LI Sanzhong,SUO Yanhui,LI Xiyao,et al. Mesozoic plate subduction in West Pacific and tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian Ocean-continent connection zone[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2018,63(16):1550 − 1593. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/N972017-01113
LI Sanzhong, SUO Yanhui, LI Xiyao, et al. Mesozoic plate subduction in West Pacific and tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian Ocean-continent connection zone[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(16): 1550-1593. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/N972017-01113
[37] LI Jianhua,CAWOOD P A,RATSCHBACHER L,et al. Building Southeast China in the late Mesozoic:Insights from alternating episodes of shortening and extension along the Lianhuashan fault zone[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2020,201:103056. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103056
[38] TANNOCK L,HERWEGH M,BERGER A,et al. The effects of a tectonic stress regime change on crustal-scale fluid flow at the Heyuan geothermal fault system,South China[J]. Tectonophysics,2020,781:228399. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2020.228399
[39] FAURE M,CHEN Yan,FENG Zhuohai,et al. Tectonics and geodynamics of South China:An introductory note[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2017,141:1 − 6. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.11.031
[40] 邱楠生,许威,左银辉,等. 渤海湾盆地中—新生代岩石圈热结构与热-流变学演化[J]. 地学前缘,2017,24(3):13 − 26. [QIU Nansheng,XU Wei,ZUO Yinhui,et al. Evolution of Meso-Cenozoic thermal structure and thermal-rheological structure of the lithosphere in the Bohai Bay Basin,Eastern North China Craton[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2017,24(3):13 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
QIU Nansheng, XU Wei, ZUO Yinhui, et al. Evolution of Meso-Cenozoic thermal structure and thermal-rheological structure of the lithosphere in the Bohai Bay Basin, eastern North China Craton[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(3): 13-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] CORREIA A,RAMALHO E C. One-dimensional thermal models constrained by seismic velocities and surface radiogenic heat production for two main geotectonic units in southern Portugal[J]. Tectonophysics,1999,306(3/4):261 − 268.
[42] RANALLI G. Regional variations in lithosphere rheology from heat flow observations[M]//ČERMÁK V, RYBACH L, Eds. Exploration of the Deep Continental Crust. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1991: 1 − 22.
[43] WANG Yang. Heat flow pattern and lateral variations of lithosphere strength in China mainland:Constraints on active deformation[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,2001,126:121 − 146. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9201(01)00251-5
[44] MOTTAGHY D,VOSTEEN H D,SCHELLSCHMIDT R. Temperature dependence of the relationship of thermal diffusivity versus thermal conductivity for crystalline rocks[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences,2008,97(2):435 − 442. doi: 10.1007/s00531-007-0238-3
[45] LIN Wenjing, WANG Guiling, GAN Haonan, et al. Heat source model for Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) under different geological conditions in China[J/OL]. Gondwana Research, (2022-08-19)[2023-01-20]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2022.08.007
[46] XIAO Zhicai,WANG Shuai,QI Shihua,et al. Crustal thermo-structure and geothermal implication of the Huangshadong geothermal field in Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2023,34(1):194 − 204. doi: 10.1007/s12583-021-1486-z
[47] ZHENG Herong,LUO Jun,ZHANG Ying,et al. Geological characteristics and distribution of granite geothermal reservoir in southeast coastal areas in China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2021,9:683696. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.683696
[48] GARD M,HASTEROK D,HAND M,et al. Variations in continental heat production from 4 Ga to the present:Evidence from geochemical data[J]. Lithos,2019,342/343:391 − 406. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.05.034
[49] 邓阳凡,李守林,范蔚茗,等. 深地震测深揭示的华南地区地壳结构及其动力学意义[J]. 地球物理学报,2011,54(10):2560 − 2574. [DENG Yangfan,LI Shoulin,FAN Weiming,et al. Crustal structure beneath South China revealed by deep seismic soundings and its dynamics implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2011,54(10):2560 − 2574. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.10.013
DENG Yangfan, LI Shoulin, FAN Weiming, et al. Crustal structure beneath South China revealed by deep seismic soundings and its dynamics implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(10): 2560-2574. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.10.013
[50] 熊小松,高锐,李秋生,等. 深地震探测揭示的华南地区莫霍面深度[J]. 地球学报,2009,30(6):774 − 786. [XIONG Xiaosong,GAO Rui,LI Qiusheng,et al. The Moho depth of South China revealed by seismic probing[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2009,30(6):774 − 786. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2009.06.009
XIONG Xiaosong, GAO Rui, LI Qiusheng, et al. The Moho depth of South China revealed by seismic probing[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2009, 30(6): 774-786. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2009.06.009
[51] JIANG Guangzheng, HU Shengbiao, SHI Yizuo, et al. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China: Updated dataset and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics 2019, 753, 36 − 48.
[52] LUAN F C,PATERSON M S. Preparation and deformation of synthetic aggregates of quartz[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,1992,97(B1):301 − 320. doi: 10.1029/91JB01748
[53] BERCKHEMER H,AUER F,DRISLER J. High-temperature anelasticity and elasticity of mantle peridotite[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,1979,20(1):48 − 59. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(79)90107-9
[54] 安美建,石耀霖. 中国大陆岩石圈厚度分布研究[J]. 地学前缘,2006,13(3):23 − 30. [AN Meijian,SHI Yaolin. Review on lithospheric thickness research of the Chinese continent[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2006,13(3):23 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.03.005
AN Meijian, SHI Yaolin. Review on lithospheric thickness research of the Chinese continent[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(3): 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.03.005
[55] 汪集暘, 庞中和, 胡圣标, 等. 地热学及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015
WANG Jiyang, PANG Zhonghe, HU Shengbiao, et al. Geothermics and its applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[56] CLAUSER C,GIESE P,HUENGES E,et al. The thermal regime of the crystalline continental crust:Implications from the KTB[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1997,102(B8):18417 − 18441. doi: 10.1029/96JB03443
[57] GOUTORBE B,POORT J,LUCAZEAU F,et al. Global heat flow trends resolved from multiple geological and geophysical proxies[J]. Geophysical Journal International,2011,187(3):1405 − 1419. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05228.x
[58] GOES S,HASTEROK D,SCHUTT D L,et al. Continental lithospheric temperatures:A review[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,2020,306:106509. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2020.106509
[59] RUDNICK R L,MCDONOUGH W F,O’CONNELL R J. Thermal structure,thickness and composition of continental lithosphere[J]. Chemical Geology,1998,145(3/4):395 − 411.
[60] ARTEMIEVA I M,MOONEY W D. Thermal thickness and evolution of Precambrian lithosphere:A global study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2001,106(B8):16387 − 16414. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900439
[61] GLEASON G C,TULLIS J. A flow law for dislocation creep of quartz aggregates determined with the molten salt cell[J]. Tectonophysics,1995,247(1/2/3/4):1 − 23.
[62] 姜光政,高堋,饶松,等. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(8):2892 − 2910. [JIANG Guangzheng,GAO Peng,RAO Song,et al. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China(4th edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2016,59(8):2892 − 2910. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20160815
JIANG Guangzheng, GAO Peng, RAO Song, et al. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China(4th edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(8): 2892-2910. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20160815
[63] DAVIES J H. Global map of solid earth surface heat flow[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2013,14(10):4608 − 4622.
[64] 熊绍柏,金东敏,孙克忠,等. 福建漳州地热田及其邻近地区的地壳深部构造特征[J]. 地球物理学报,1991,34(1):55 − 63. [XIONG Shaobai,JIN Dongmin,SUN Kezhong,et al. Some characteristics of deep structure of the Zhangzhou geothermal field and it’s neighbourhood in the Fujian Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,1991,34(1):55 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1991.01.006
XIONG Shaobai, JIN Dongmin, SUN Kezhong, et al. Some characteristics of deep structure of the Zhangzhou geothermal field and it's neighbourhood in the Fujian Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1991, 34(1): 55-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1991.01.006
[65] 廖志杰. 福建无岩浆热源的深循环水热系统[J]. 现代地质,2012,26(1):85 − 98. [LIAO Zhijie. Deep-circulation hydrothermal systems without magmatic heat source in Fujian Province[J]. Geoscience,2012,26(1):85 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.01.009
LIAO Zhijie. Deep-circulation hydrothermal systems without magmatic heat source in Fujian Province[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(1): 85-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.01.009
[66] WANG Qiang,HAWKESWORTH C J,WYMAN D,et al. Pliocene-Quaternary crustal melting in central and northern Xizang and insights into crustal flow[J]. Nature Communications,2016,7:11888. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11888
[67] WANG Shuai,KUANG Jian,HUANG Xuelian,et al. Upwelling of mantle-derived material in southeast China:Evidence from noble gas isotopes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition),2022,96(1):100 − 110. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14686
[68] 魏正安,黄少鹏,王成善,等. 粤港澳大湾区地下热水地球化学特征及其热储含义[J]. 地球学报,2023,44(1):117 − 132. [WEI Zhengan,HUANG Shaopeng,WANG Chengshan,et al. Geochemistry and its geothermal reservoir implications of geothermal water in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay area,South China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2023,44(1):117 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2022.121701
WEI Zhengan, HUANG Shaopeng, WANG Chengshan, et al. Geochemistry and its geothermal reservoir implications of geothermal water in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay area, South China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2023, 44(1): 117-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2022.121701
-



 下载:
下载: