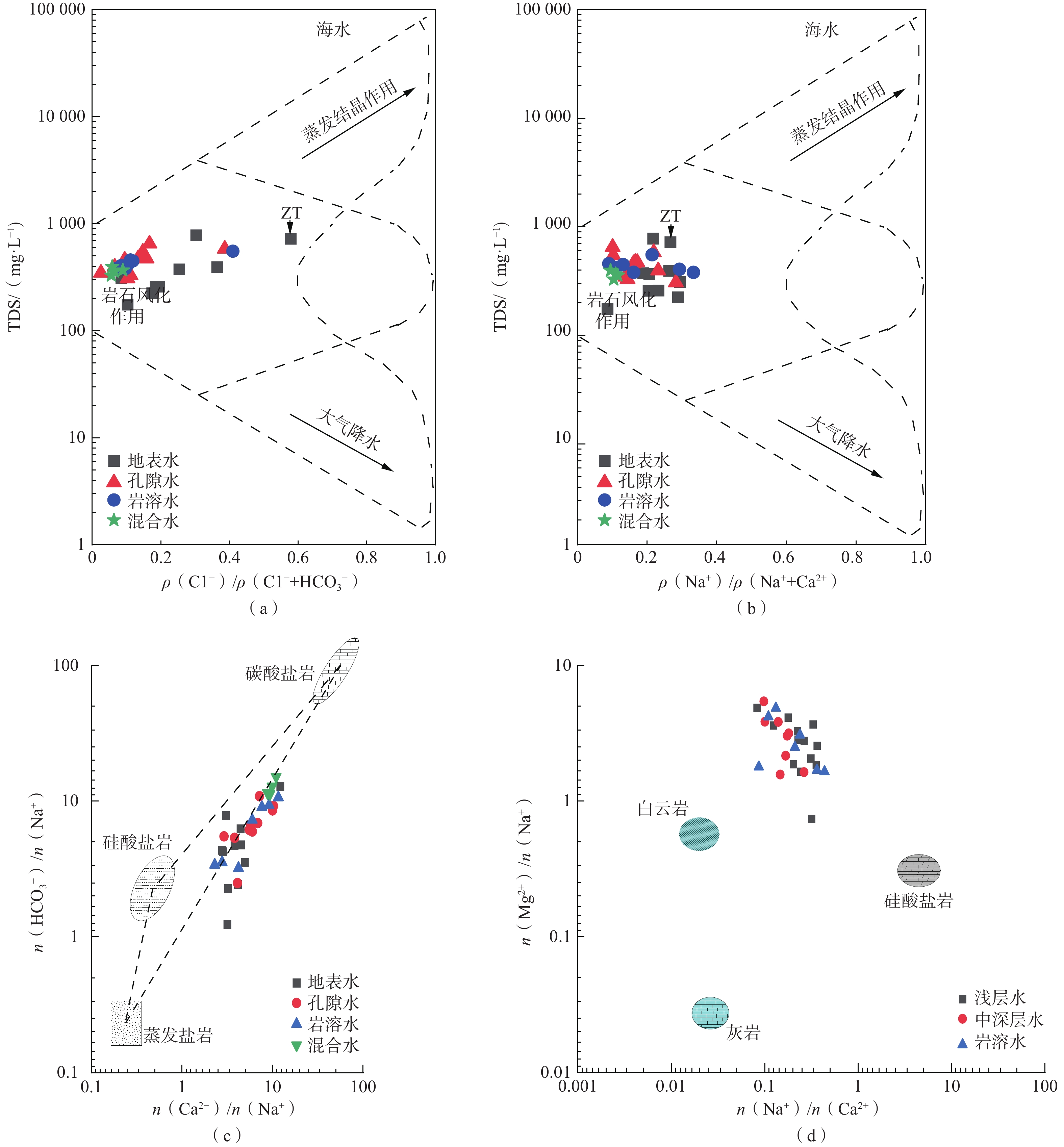
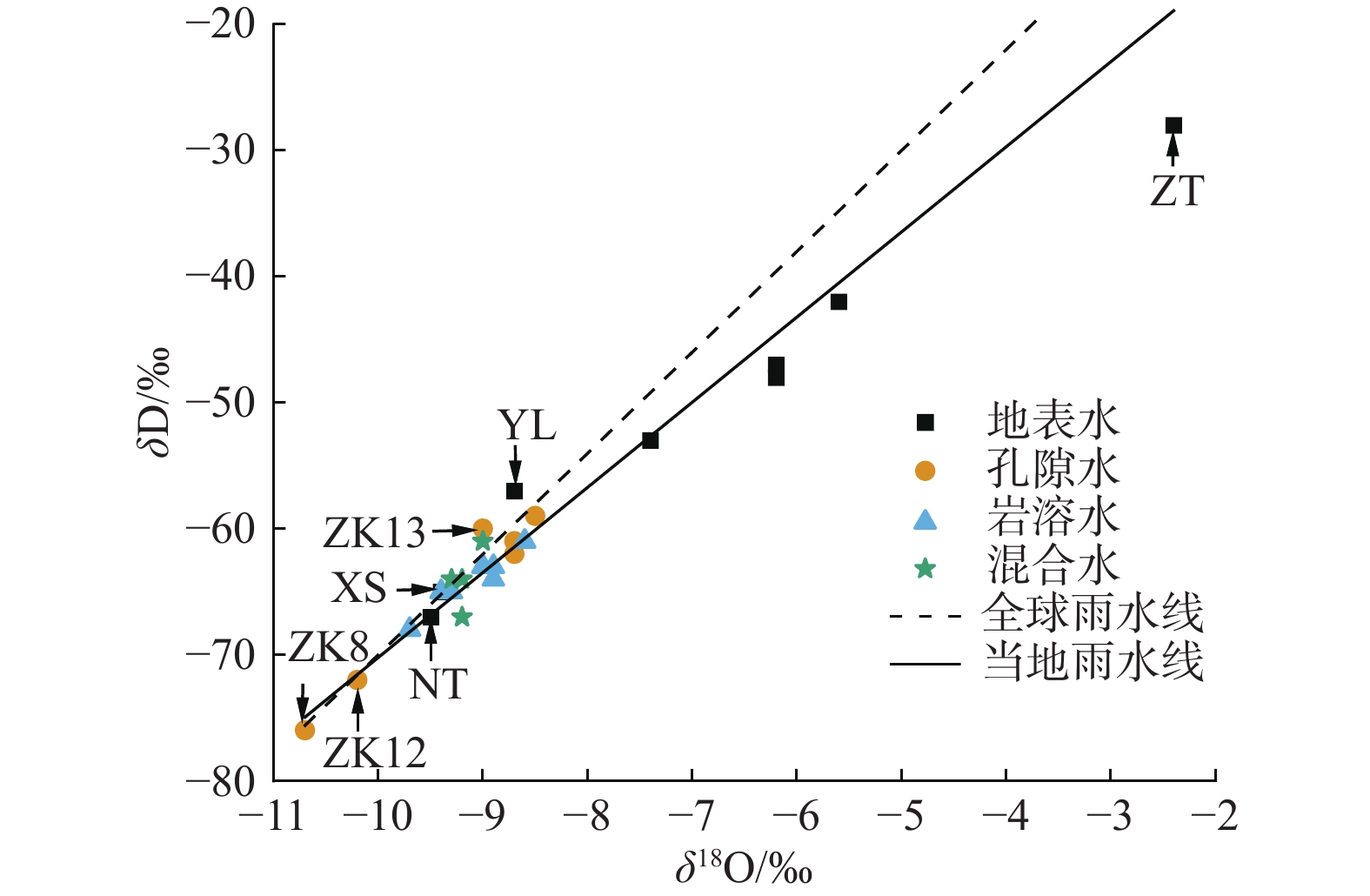
An analysis of groundwater circulation in the Pingyu mining area based on hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater
-
摘要:
矿区地下水对周边居民生活及煤炭工业建设起到重要的支撑作用,但煤矿开采过程中的矿井排水会改变原有的矿区地下水循环过程,进而改变地下水环境,因此,明晰“地下水、地表水、大气水”间的相互转化关系,是科学利用矿区水资源的关键。本研究通过分析平禹矿区地下水常规水化学及氢氧同位素,识别矿区地下水中主要组分来源及控制性因素,以明晰矿区在大规模矿井排水后的地下水循环特征。结果显示:研究区地下水水化学类型主要为HCO3—Ca·Mg,水化学组分受硅酸盐岩的风化溶解作用控制,地下水中离子主要来源于水-岩相互作用和人类活动所产生的废弃物,存在${\rm{NO}}_3^- $超标现象。氢氧同位素分析表明,矿区地下水以大气降水补给为主,孔隙水和岩溶水存在紧密的水力联系;矿井排水后,矿区地下水循环过程发生改变,岩溶水由原先顶托补给上层孔隙水转变为接受上层孔隙水的越流补给,再由矿井排水排放至地表水体当中,矿井排水成为矿区主要地下水排泄方式。研究结果可为矿区地下水开发与管理和地面沉降防治工作提供科学有效的依据。
Abstract:Groundwater in mining areas play an important supporting role in the surrounding residents' living and the construction of coal industries. Mine drainage during coal mining will change the original groundwater circulation process in mining areas, leading to changes in the groundwater environment. Therefore, clarifying the mutual transformation relationship between the “three waters” is the key to the scientific utilization of water resources in mining areas. Chemical components and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of the groundwater in the Pingyu mining area are combined to determine the characteristics of groundwater circulation after large-scale drainage of the mine, identify the origin and controlling factors of the major components in the groundwater. Hydrohemical analyses show that most of the groundwater are of HCO3—Ca·Mg type, The hydrochemical components are controlled by the weathering and dissolution of silicate, and the ions in the groundwater mainly come from water-rock interactions and the waste generated by human activities, with concentration of ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ exceeding the standard. The hydrogen and oxygen isotopic data demonstrates that the groundwater in the study area receives recharge from modern precipitation, and there is a close hydraulic relationship between the groundwater in the unconsolidated aquifers and the groundwater in the karst aquifer. After the mine drainage, the groundwater circulation process in the mining area changes, the karst groundwater changes from supporting the upper pore groundwater to accepting the leakage recharge of the upper pore groundwater, and then discharges to the surface water by the mine drainage. The mine drainage becomes the main groundwater drainage way in the mine area. The research results can provide scientific and effective basis for groundwater development management and land subsidence prevention in mining areas.
-

-
表 1 研究区主要水化学指标及统计值
Table 1. Main hydrochemical indicators and statistics in the study area
层位 样品编号 pH 质量浓度(ρ)/ (mg·L−1) TDS/ (mg·L−1) EC/(μS·cm−1) K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ H2SiO3 地表水 XF 7.15 5.45 19.35 46.53 26.13 20.74 73.20 223.62 6.86 20.12 310.64 485 YL 7.19 3.70 4.07 43.09 10.45 15.95 23.65 139.00 4.86 7.44 175.55 259 NT 7.22 12.00 17.44 67.21 26.13 25.52 61.28 290.10 12.70 24.49 368.10 505 XS 7.25 9.12 15.10 86.17 29.26 35.10 83.16 314.27 16.55 5.36 432.17 586 HS 7.28 9.38 16.10 39.64 15.68 38.29 13.50 181.31 1.30 5.89 225.28 342 YH 7.33 6.56 42.06 151.66 36.58 118.05 237.70 271.96 53.42 16.48 782.56 1139 HTL 7.35 4.36 11.46 44.81 19.86 35.10 68.60 145.05 1.29 6.41 258.43 374 LFS 7.40 8.74 13.55 44.81 19.86 38.29 48.26 169.22 1.09 1.24 259.60 368 LW 7.47 4.32 18.02 77.55 17.77 57.43 101.60 169.22 13.60 0.20 375.37 480 YW 7.49 4.89 24.01 67.21 26.13 82.95 116.20 145.05 <0.88 0.20 394.33 517 ZT 7.52 13.42 58.90 162.00 22.99 264.81 98.12 193.40 5.38 10.93 723.37 963 平均值 7.33 7.45 21.82 75.52 22.80 66.57 84.12 203.84 11.71 8.98 391.40 547.09 标准差 0.13 3.31 15.49 43.13 7.15 72.27 59.94 62.29 15.66 8.19 195.31 268.88 变异系数/% 0.02 0.44 0.71 0.57 0.31 1.09 0.71 0.31 1.34 0.91 0.50 0.49 孔隙水 ZK3 7.23 3.84 20.71 99.96 34.49 63.81 48.84 338.45 31.15 19.14 472.64 678 ZK2 7.35 4.97 14.92 133.07 42.78 72.99 82.75 364.34 94.25 30.71 651.66 828 ZK4 7.32 3.03 35.92 128.26 35.00 149.39 48.20 237.61 64.34 18.17 583.22 1404 ZK7 7.22 1.89 11.54 72.14 23.33 8.69 23.68 332.66 22.30 22.48 347.62 597 ZK9 7.36 0.13 15.44 134.43 31.35 60.62 52.66 350.53 76.20 23.24 546.47 808 ZK8 7.26 4.88 19.02 48.26 30.31 31.91 30.45 278.01 3.38 10.78 307.72 489 ZK11 7.22 1.10 20.18 105.13 22.99 33.50 86.68 320.31 31.15 18.19 461.31 707 ZK13 7.26 4.08 19.57 98.24 31.35 54.24 55.82 350.53 37.00 17.45 475.93 805 ZK12 7.29 3.48 25.48 84.45 21.95 25.52 50.60 362.62 3.51 21.16 396.74 664 ZK16 7.32 7.77 13.87 82.73 11.50 31.91 28.83 253.83 26.68 14.59 330.69 580 平均值 7.28 3.52 19.67 98.66 28.50 53.26 50.85 318.89 39.00 19.59 457.40 756.00 标准差 0.05 2.18 6.99 28.05 8.76 39.23 21.03 46.02 30.12 5.37 113.67 252.69 变异系数/% 0.01 0.62 0.36 0.28 0.31 0.74 0.41 0.14 0.77 0.27 0.25 0.33 岩溶水 SMH 7.30 3.94 26.90 98.56 43.56 159.53 63.60 229.66 43.50 21.98 554.76 852 MZ−1 7.32 0.99 11.93 95.22 26.34 35.10 75.55 296.14 28.71 16.12 422.23 712 ZK14 7.32 4.46 16.91 87.90 26.13 35.10 22.94 326.36 23.80 18.25 380.86 596 PYX 7.35 5.81 32.84 79.28 29.26 28.71 61.30 308.23 14.96 25.81 406.79 582 PYD 7.38 7.77 33.58 67.21 29.26 22.33 61.32 302.18 7.98 27.63 381.23 544 ZK19 7.30 3.38 12.90 130.30 12.16 45.62 39.76 364.34 31.12 19.45 458.02 466 DC−3 7.28 2.73 13.84 91.88 35.46 44.67 76.20 332.40 17.96 21.61 449.33 724 平均值 7.32 4.15 21.27 92.91 28.88 53.01 57.24 308.47 24.00 21.55 436.18 639.43 标准差 0.03 2.18 9.56 19.61 9.60 47.68 19.37 41.67 11.75 4.08 60.35 130.37 变异系数/% 0.00 0.53 0.45 0.21 0.33 0.90 0.34 0.14 0.49 0.19 0.14 0.20 混合水 DC−1 7.25 1.01 10.73 82.02 27.35 22.33 28.83 327.57 21.70 19.15 358.14 539 DC−2 7.26 0.94 10.89 88.54 23.30 31.91 23.73 326.36 24.45 15.93 367.31 567 XLZ−1 7.33 0.96 9.52 81.86 20.26 19.14 19.52 325.15 14.86 16.32 329.13 515 CZ 7.42 0.07 9.04 86.17 31.35 22.33 50.94 362.62 15.25 12.36 396.81 532 平均值 7.32 0.74 10.04 84.65 25.57 23.93 30.76 335.42 19.07 15.94 362.85 485.78 标准差 0.08 0.45 0.91 3.27 4.83 5.53 13.98 18.16 4.77 2.78 27.88 106.66 变异系数/% 0.01 0.60 0.09 0.04 0.19 0.23 0.45 0.05 0.25 0.17 0.08 0.22 表 2 孔隙水和岩溶水地下水化学成分分类
Table 2. Classification of chemical components of pore water and karst water in groundwater
水样类型 水化学类型 样品数/个 占比/% 孔隙水 HCO3—Ca·Mg 7 70.00 HCO3—Ca 2 20.00 Cl·HCO3—Ca·Mg 1 10.00 岩溶水 HCO3—Ca·Mg 5 75.00 HCO3—Ca 1 12.50 Cl·HCO3—Ca·Mg 1 12.50 混合水 HCO3—Ca·Mg 4 100.00 表 3 研究区主要化学组分相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis of the main chemical components in the study area
K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ H2SiO3 TDS 地表水 K+ 1 Na+ 0.509 1 Ca2+ 0.427 0.915** 1 Mg2+ 0.225 0.507 0.587 1 Cl− 0.491 0.946** 0.858** 0.263 1 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ −0.092 0.614* 0.744** 0.798** 0.440 1 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ 0.490 0.207 0.386 0.723* −0.009 0.354 1 ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ −0.073 0.415 0.635* 0.765** 0.203 0.920** 0.572 1 H2SiO3 0.351 0.239 0.222 0.436 0.024 0.184 0.599 0.334 1 TDS 0.392 0.912** 0.979** 0.723* 0.801** 0.833** 0.449 0.715* 0.281 1 孔隙水 K+ 1 Na+ −0.102 1 Ca2+ −0.353 0.243 1 Mg2+ −0.212 0.236 0.527 1 Cl− −0.049 0.720* 0.673* 0.594 1 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ −0.292 0.131 0.643* 0.439 0.241 1 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ −0.375 −0.382 0.208 0.299 −0.372 0.433 1 ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ −0.195 0.002 0.902** 0.638* 0.623 0.517 0.150 1 H2SiO3 −0.300 −0.213 0.655* 0.479 0.134 0.508 0.653* 0.691* 1 TDS −0.286 0.298 0.940** 0.761* 0.727* 0.700* 0.266 0.906** 0.691* 1 岩溶水 K+ 1 Na+ 0.860* 1 Ca2+ −0.596 −0.664 1 Mg2+ 0.077 0.397 −0.493 1 Cl− −0.169 0.113 0.268 0.621 1 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ −0.243 0.105 −0.256 0.503 0.128 1 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ −0.072 −0.474 0.340 −0.814* −0.747 −0.390 1 ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ −0.578 −0.371 0.672 0.157 0.805* −0.091 −0.423 1 H2SiO3 0.872* 0.891** −0.596 0.292 −0.062 0.203 −0.178 −0.582 1 TDS −0.356 −0.074 0.497 0.465 0.927** 0.274 −0.549 0.818* −0.132 1 混合水 K+ 1 Na+ 0.742 1 Ca2+ −0.353 0.161 1 Mg2+ −0.768 −0.282 0.214 1 Cl− 0.159 0.650 0.850 −0.060 1 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ −0.947 −0.567 0.290 0.932 −0.135 1 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ −0.994** −0.707 0.311 0.830 −0.179 0.976* 1 ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ 0.531 0.956* 0.426 −0.105 0.822 −0.363 −0.501 1 H2SiO3 0.888 0.737 −0.548 −0.420 −0.029 −0.707 −0.833 0.514 1 TDS −0.809 −0.208 0.641 0.884 0.325 0.891 0.834 0.060 −0.641 1 注: *和**分别表示在0.005和0.01水平上相关性显著。 表 4 研究区不同水体水化学参数的旋转因子载荷矩阵
Table 4. Rotation factor loading matrix of hydrochemical parameters of different water bodies in the study area
参数 地表水主成分 孔隙水主成分 S1 S2 S3 P1 P2 P3 K+ 0.646 −0.416 0.569 −0.128 −0.060 −0.887 Na+ 0.933 0.271 0.149 0.111 0.910 0.182 Ca2+ 0.839 0.495 0.160 0.903 0.147 0.203 Mg2+ 0.246 0.645 0.660 0.740 0.141 0.164 Cl− 0.987 0.096 −0.069 0.652 0.739 −0.112 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 0.366 0.910 0.156 0.630 −0.065 0.429 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ 0.062 0.331 0.876 0.264 −0.672 0.568 ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ 0.152 0.910 0.291 0.957 −0.013 −0.047 H2SiO3 0.048 0.128 0.783 0.749 −0.458 0.259 TDS 0.775 0.576 0.257 0.967 0.162 0.191 特征值 3.790 3.030 2.366 4.694 2.112 1.514 方差百分比 /% 37.904 30.299 23.660 46.944 21.117 15.144 累积方差 /% 37.904 68.203 91.863 46.944 68.061 83.205 参数 岩溶水主成分 混合水主成分 C1 C2 C3 M1 M2 M3 K+ 0.960 −0.162 −0.200 −0.763 0.638 −0.104 Na+ 0.957 0.113 0.138 −0.257 0.909 0.328 Ca2+ −0.689 0.335 −0.529 0.247 −0.101 0.964 Mg2+ 0.320 0.528 0.697 0.999 −0.014 −0.036 Cl− 0.007 0.990 0.103 −0.021 0.375 0.927 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ −0.076 0.049 0.899 0.929 −0.370 0.024 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ −0.315 −0.716 −0.508 0.825 −0.563 0.052 ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ −0.485 0.844 −0.164 −0.073 0.833 0.548 H2SiO3 0.907 −0.088 0.148 −0.422 0.826 −0.374 TDS −0.207 0.920 0.115 0.898 −0.127 0.422 特征值 3.620 3.492 1.962 4.240 3.231 2.529 方差百分比 /% 36.195 34.915 19.624 42.401 32.307 25.293 累积方差 /% 36.195 71.111 90.734 42.401 74.707 100.000 -
[1] 刘久潭,李颖智,高宗军,等. 拉萨河流域中下游地区水化学及地表水-地下水转化关系研究[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版),2020,39(5):10 − 20. [LIU Jiutan,LI Yingzhi,GAO Zongjun,et al. Hydrochemistry and relationship between groundwater and surface water in the middle and lower reaches of Lhasa River Basin[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science),2020,39(5):10 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Jiutan, LI Yingzhi, GAO Zongjun, et al . Hydrochemistry and relationship between groundwater and surface water in the middle and lower reaches of Lhasa River Basin[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science),2020 ,39 (5 ):10 −20 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 王现国,狄艳松,李扬,等. 洛阳断陷盆地浅层孔隙地下水环境演化特征[J]. 人民黄河,2020,42(7):77 − 79. [WANG Xianguo,DI Yansong,LI Yang,et al. Evolutionary characteristics of shallow pore ground water in fault basins[J]. Yellow River,2020,42(7):77 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Xianguo, DI Yansong, LI Yang, et al . Evolutionary characteristics of shallow pore ground water in fault basins[J]. Yellow River,2020 ,42 (7 ):77 −79 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 张清华,赵玉峰,唐家良,等. 京津冀西北典型流域地下水化学特征及补给源分析[J]. 自然资源学报,2020,35(6):1314 − 1325. [ZHANG Qinghua,ZHAO Yufeng,TANG Jialiang,et al. Hydrochemistry characteristics and the recharge source of groundwater in typical watersheds of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region,China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2020,35(6):1314 − 1325. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20200605
ZHANG Qinghua, ZHAO Yufeng, TANG Jialiang, et al . Hydrochemistry characteristics and the recharge source of groundwater in typical watersheds of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2020 ,35 (6 ):1314 −1325 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] 梁杏,张婧玮,蓝坤,等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(1):21 − 33. [LIANG Xing,ZHANG Jingwei,LAN Kun,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(1):21 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIANG Xing, ZHANG Jingwei, LAN Kun, et al . Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020 ,39 (1 ):21 −33 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] YANG Qingchun,LI Zijun,MA Hongyun,et al. Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes and assessment of groundwater quality using classic integrated geochemical methods in the Southeastern part of Ordos Basin,China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2016,218:879 − 888. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.017
[6] WANG Ping,YU Jingjie,ZHANG Yichi,et al. Groundwater recharge and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Ejina Basin,northwest China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2013,476:72 − 86. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.10.049
[7] ZHANG Han, CHEN Zongyu, TANG Changyuan. Tracing runoff components in the headwater area of Heihe River by isotopes and hydrochemistry[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2022,10(4):405 − 412.
[8] 赵春红,梁永平,卢海平,等. 娘子关泉域岩溶水氢氧同位素特征及影响因素浅析[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(5):200 − 205. [ZHAO Chunhong,LIANG Yongping,LU Haiping,et al. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic characteristics and influencing factors of Karst water in the niangziguan spring area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(5):200 − 205. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Chunhong, LIANG Yongping, LU Haiping, et al . Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic characteristics and influencing factors of Karst water in the niangziguan spring area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018 ,37 (5 ):200 −205 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] SPRENGER M,HERBSTRITT B,WEILER M. Established methods and new opportunities for pore water stable isotope analysis[J]. Hydrological Processes,2015,29(25):5174 − 5192. doi: 10.1002/hyp.10643
[10] ZHANG Zhuo,GUO Huaming,WANG Zhen. Differences in major ions as well as hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of sediment pore water and lake water[J]. Water Science and Engineering,2018,11(2):147 − 156. doi: 10.1016/j.wse.2018.07.005
[11] 易冰,刘景涛,吕晓立,等. 高寒干旱区地表水与地下水水化学特征及转换关系:以大通河流域为例[J]. 环境科学,2023,44(2):752 − 760. [YI Bing,LIU Jingtao,LYU Xiaoli,et al. Hydrochemical and isotopic evidence for groundwater conversion of surface water in alpine arid areas:A case study of the Datong River Basin[J]. Environmental Science,2023,44(2):752 − 760. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YI Bing, LIU Jingtao, LYU Xiaoli, et al . Hydrochemical and isotopic evidence for groundwater conversion of surface water in alpine arid areas: A case study of the Datong River Basin[J]. Environmental Science,2023 ,44 (2 ):752 −760 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 王诗语,孙从建,陈伟,等. 典型西北山地-绿洲系统不同水体水化学特征及其水力关系分析[J]. 环境科学,2023,44(3):1416 − 1428. [WANG Shiyu,SUN Congjian,CHEN Wei,et al. Analysis of water chemistry characteristics and hydraulic relationships of different water bodies in typical mountain-oasis systems in the northwest inland area[J]. Environmental Science,2023,44(3):1416 − 1428. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Shiyu, SUN Congjian, CHEN Wei, et al . Analysis of water chemistry characteristics and hydraulic relationships of different water bodies in typical mountain-oasis systems in the northwest inland area[J]. Environmental Science,2023 ,44 (3 ):1416 −1428 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 刘景明,丁建丽,包青岭,等. 基于同位素揭示艾比湖流域地下水特征[J]. 干旱区地理,2023,46(2):201 − 210. [LIU Jingming,DING Jianli,BAO Qingling,et al. Study on characteristics of groundwater in Ebinur Lake Basin using isotopes method[J]. Arid Land Geography,2023,46(2):201 − 210. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Jingming, DING Jianli, BAO Qingling, et al. Study on characteristics of groundwater in Ebinur Lake Basin using isotopes method[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(2): 201 − 210. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 孙龙,刘廷玺,段利民,等. 矿区流域不同水体同位素时空特征及水循环指示意义[J]. 水科学进展,2022,33(5):805 − 815. [SUN Long,LIU Tingxi,DUAN Limin,et al. Spatial and temporal characteristics of isotopes of different water sources and implications for water circulation in mining areas[J]. Advances in Water Science,2022,33(5):805 − 815. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Long, LIU Tingxi, DUAN Limin, et al . Spatial and temporal characteristics of isotopes of different water sources and implications for water circulation in mining areas[J]. Advances in Water Science,2022 ,33 (5):805 −815 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[15] YANG Zhongyuan,HUANG Pinghua,DING Fengfan. Groundwater hydrogeochemical mechanisms and the connectivity of multilayer aquifers in a coal mining region[J]. Mine Water and the Environment,2020,39(4):808 − 822.
[16] 张坤. 同位素在河南煤矿水文地质条件研究中的应用[D]. 焦作:河南理工大学,2012. [ZHANG Kun. The application of isotope at the study of hydrogeological conditions of coal mine in Henan Province[D]. Jiaozuo:Henan Polytechnic University,2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Kun. The application of isotope at the study of hydrogeological conditions of coal mine in Henan Province[D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 李倩,马龙,刘廷玺,等. 采煤对海流兔流域大气降水-地表水-地下水-矿井水转化关系的影响[J]. 中国沙漠,2022,42(5):146 − 157. [LI Qian,MA Long,LIU Tingxi,et al. Conversion of precipitation,surface water,groundwater and mine water affected by coal mining in the Hailiutu River Basin,Inner Mongolia,China[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2022,42(5):146 − 157. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Qian, MA Long, LIU Tingxi, et al . Conversion of precipitation, surface water, groundwater and mine water affected by coal mining in the Hailiutu River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2022 ,42 (5 ):146 −157 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 唐辉. 河南平禹一矿岩溶水疏降流场数值模拟与预测[D]. 焦作:河南理工大学,2011. [TANG Hui. Numerical simulation and prediction of Karst water dewatering flow in Pingyu 1st coal mine,Henan Province[D]. Jiaozuo:Henan Polytechnic University,2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TANG Hui. Numerical simulation and prediction of Karst water dewatering flow in Pingyu 1st coal mine, Henan Province[D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 潘国营,张坤,王佩璐,等. 利用稳定同位素判断矿井水补给来源——以平禹一矿为例[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2011,22(6):119 − 122. [PAN Guoying,ZHANG Kun,WANG Peilu,et al. Judgement of mine water recharge source using stable isotope:A case study of 1st mine of Pingyu[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2011,22(6):119 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PAN Guoying, ZHANG Kun, WANG Peilu, et al . Judgement of mine water recharge source using stable isotope: A case study of 1st mine of Pingyu[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2011 ,22 (6 ):119 −122 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[20] 张富有. 许昌市地下水含水层组划分和同位素对比研究[J]. 地下水,2017,39(4):40 − 41. [ZHANG Fuyou. Division and isotope correlation study of groundwater aquifer group in Xuchang[J]. Ground Water,2017,39(4):40 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Fuyou . Division and isotope correlation study of groundwater aquifer group in Xuchang[J]. Ground Water,2017 ,39 (4 ):40 −41 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] 於昊天,马腾,邓娅敏,等. 江汉平原东部地区浅层地下水水化学特征[J]. 地球科学,2017,42(5):685 − 692. [YU Haotian,MA Teng,DENG Yamin,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in eastern Jianghan plain[J]. Earth Science,2017,42(5):685 − 692. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YU Haotian, MA Teng, DENG Yamin, et al . Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in eastern Jianghan plain[J]. Earth Science,2017 ,42 (5 ):685 −692 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[22] 殷俊. 邯郸市地下水污染修复和防治[D]. 西安:长安大学,2017. [YIN Jun. Remediation and prevention of groundwater pollution in Handan city[D]. Xi’an:Chang’an University,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YIN Jun. Remediation and prevention of groundwater pollution in Handan city[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 孔令健,王振龙,王兵. 阜阳市集中式深层地下水饮用水源地水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2020(3):78 − 82. [KONG Lingjian,WANG Zhenlong,WANG Bing. An analysis of the hydro-chemical characteristics and causes of drinking water source of concentrated deep groundwater in Fuyang city[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2020(3):78 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
KONG Lingjian, WANG Zhenlong, WANG Bing . An analysis of the hydro-chemical characteristics and causes of drinking water source of concentrated deep groundwater in Fuyang city[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2020 (3 ):78 −82 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[24] 袁宏颖,杨树青,丁雪华,等. 乌拉特灌域地下水水化学离子特征评价及来源分析[J]. 节水灌溉,2020(2):67 − 72. [YUAN Hongying,YANG Shuqing,DING Xuehua,et al. Evaluation and source analysis of chemical ion characteristics of groundwater in wulate irrigation area[J]. Water Saving Irrigation,2020(2):67 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YUAN Hongying, YANG Shuqing, DING Xuehua, et al . Evaluation and source analysis of chemical ion characteristics of groundwater in wulate irrigation area[J]. Water Saving Irrigation,2020 (2 ):67 −72 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[25] 赵江涛,周金龙,梁川,等. 新疆焉耆盆地平原区地下水演化的主要水文地球化学过程分析[J]. 环境化学,2017,36(6):1397 − 1406. [ZHAO Jiangtao,ZHOU Jinlong,LIANG Chuan,et al. Hydrogeochemical process of evolution of groundwater in plain area of Yanqi,Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2017,36(6):1397 − 1406. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Jiangtao, ZHOU Jinlong, LIANG Chuan, et al . Hydrogeochemical process of evolution of groundwater in plain area of Yanqi, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2017 ,36 (6 ):1397 −1406 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[26] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science,1970,170(3962):1088 − 1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
[27] 何锦,张幼宽,赵雨晴,等. 鲜水河断裂带虾拉沱盆地断面地下水化学特征及控制因素[J]. 环境科学,2019,40(3):1236 − 1244. [HE Jin,ZHANG Youkuan,ZHAO Yuqing,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of groundwater in the xialatuo basin section of the Xianshui River[J]. Environmental Science,2019,40(3):1236 − 1244. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HE Jin, ZHANG Youkuan, ZHAO Yuqing, et al . Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of groundwater in the xialatuo basin section of the Xianshui River[J]. Environmental Science,2019 ,40 (3 ):1236 −1244 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[28] 张涛,王明国,张智印,等. 然乌湖流域地表水水化学特征及控制因素[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(9):4003 − 4010. [ZHANG Tao,WANG Mingguo,ZHANG Zhiyin,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of the surface water in ranwu lake basin[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(9):4003 − 4010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Tao, WANG Mingguo, ZHANG Zhiyin, et al . Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of the surface water in ranwu lake basin[J]. Environmental Science,2020 ,41 (9 ):4003 −4010 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[29] 金阳,姜月华,董贤哲,等. 浙江宁波平原地下水水化学特征及其生态环境效应[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(5):1527 − 1542. [JIN Yang,JIANG Yuehua,DONG Xianzhe,et al. Chemical characteristics and eco-environmental effect of groundwater in Ningbo Plain,Zhejiang Province[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(5):1527 − 1542. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIN Yang, JIANG Yuehua, DONG Xianzhe, et al . Chemical characteristics and eco-environmental effect of groundwater in Ningbo Plain, Zhejiang Province[J]. Geology in China,2022 ,49 (5 ):1527 −1542 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[30] RAVIKUMAR P,SOMASHEKAR R K. Principal component analysis and hydrochemical facies characterization to evaluate groundwater quality in Varahi River Basin,Karnataka state,India[J]. Applied Water Science,2017,7(2):745 − 755. doi: 10.1007/s13201-015-0287-x
[31] SHEKHA Y A. Evaluation of water quality for Greater Zab River by principal component analysis/ factor analysis[J]. Iraqi Journal of Science,2016,57(4b):2650 − 2663.
[32] YANG Wenjie,ZHAO Yue,WANG Dong,et al. Using principal components analysis and IDW interpolation to determine spatial and temporal changes of surface water quality of xin'anjiang river in Huangshan,China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2020,17(8):2942. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082942
[33] OMOIRABOR O O,OLOBANIYI S B,ODUYEMI K,et al. Surface and groundwater water quality assessment using multivariate analytical methods:A case study of the Western Niger Delta,Nigeria[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,Parts A/B/C,2008,33(8/9/10/11/12/13):666-673.
[34] MGBENU C N,EGBUERI J C. The hydrogeochemical signatures,quality indices and health risk assessment of water resources in Umunya district,southeast Nigeria[J]. Applied Water Science,2019,9(1):1 − 19. doi: 10.1007/s13201-018-0879-3
[35] ARORA S,KESHARI A K. Pattern recognition of water quality variance in Yamuna River (India) using hierarchical agglomerative cluster and principal component analyses[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2021,193(8):1 − 18.
[36] 马燕华,苏春利,刘伟江,等. 水化学和环境同位素在示踪枣庄市南部地下水硫酸盐污染源中的应用[J]. 环境科学,2016,37(12):4690 − 4699. [MA Yanhua,SU Chunli,LIU Weijiang,et al. Identification of sulfate sources in the groundwater system of Zaozhuang:Evidences from isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics[J]. Environmental Science,2016,37(12):4690 − 4699. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MA Yanhua, SU Chunli, LIU Weijiang, et al . Identification of sulfate sources in the groundwater system of Zaozhuang: Evidences from isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics[J]. Environmental Science,2016 ,37 (12 ):4690 −4699 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[37] 崔亚莉,刘峰,郝奇琛,等. 诺木洪冲洪积扇地下水氢氧同位素特征及更新能力研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(6):1 − 7. [CUI Yali,LIU Feng,HAO Qichen,et al. Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes and renewability of groundwater in the Nuomuhong alluvial fan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(6):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CUI Yali, LIU Feng, HAO Qichen, et al . Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes and renewability of groundwater in the Nuomuhong alluvial fan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015 ,42 (6 ):1 −7 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[38] 于静洁,宋献方,刘相超,等. 基于 δD和 δ18O及水化学的永定河流域地下水循环特征解析[J]. 自然资源学报,2007,22(3):415 − 423. [YU Jingjie,SONG Xianfang,LIU Xiangchao,et al. A study of groundwater cycle in Yongding River Basin by using δD, δ18O and hydrochemical data[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2007,22(3):415 − 423. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YU Jingjie, SONG Xianfang, LIU Xiangchao, et al . A study of groundwater cycle in Yongding River Basin by using δD, δ18O and hydrochemical data[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2007 ,22 (3 ):415 −423 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[39] 江欣悦,李静,郭林,等. 豫北平原浅层地下水化学特征与成因机制[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(5):290 − 300. [JIANG Xinyue,LI Jing,GUO Lin,et al. Chemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in the northern Henan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(5):290 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIANG Xinyue, LI Jing, GUO Lin, et al . Chemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in the northern Henan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021 ,40 (5 ):290 −300 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[40] 崔玉环,王杰,刘友存,等. 升金湖河湖交汇区地表-地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 环境科学,2021,42(7):3223 − 3231. [CUI Yuhuan,WANG Jie,LIU Youcun,et al. Hydro-chemical characteristics and ion origin analysis of surface groundwater at the Shengjin Lake and Yangtze River interface[J]. Environmental Science,2021,42(7):3223 − 3231. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CUI Yuhuan, WANG Jie, LIU Youcun, et al . Hydro-chemical characteristics and ion origin analysis of surface groundwater at the Shengjin Lake and Yangtze River interface[J]. Environmental Science,2021 ,42 (7 ):3223 −3231 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[41] 武茜茜,陈粉丽,周鑫,等. 郑州与福州降水同位素特征及水汽来源对比分析[J]. 环境化学,2022,41(1):125 − 134. [WU Xixi,CHEN Fenli,ZHOU Xin,et al. Comparative analysis of precipitation isotopes and water vapor sources in Zhengzhou and Fuzhou[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2022,41(1):125 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Xixi, CHEN Fenli, ZHOU Xin, et al . Comparative analysis of precipitation isotopes and water vapor sources in Zhengzhou and Fuzhou[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2022 ,41 (1 ):125 −134 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[42] 谷洪彪,迟宝明,王贺,等. 柳江盆地地表水与地下水转化关系的氢氧稳定同位素和水化学证据[J]. 地球科学进展,2017,32(8):789 − 799. [GU Hongbiao,CHI Baoming,WANG He,et al. Relationship between surface water and groundwater in the Liujiang Basin hydrochemical constrains[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2017,32(8):789 − 799. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.08.0789
GU Hongbiao, CHI Baoming, WANG He, et al . Relationship between surface water and groundwater in the Liujiang Basin hydrochemical constrains[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2017 ,32 (8 ):789 −799 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -




 下载:
下载: