The impacts of deep faults on fluid migration, heat accumulation with implication to genesis of Yingshan geothermal system
-
摘要:
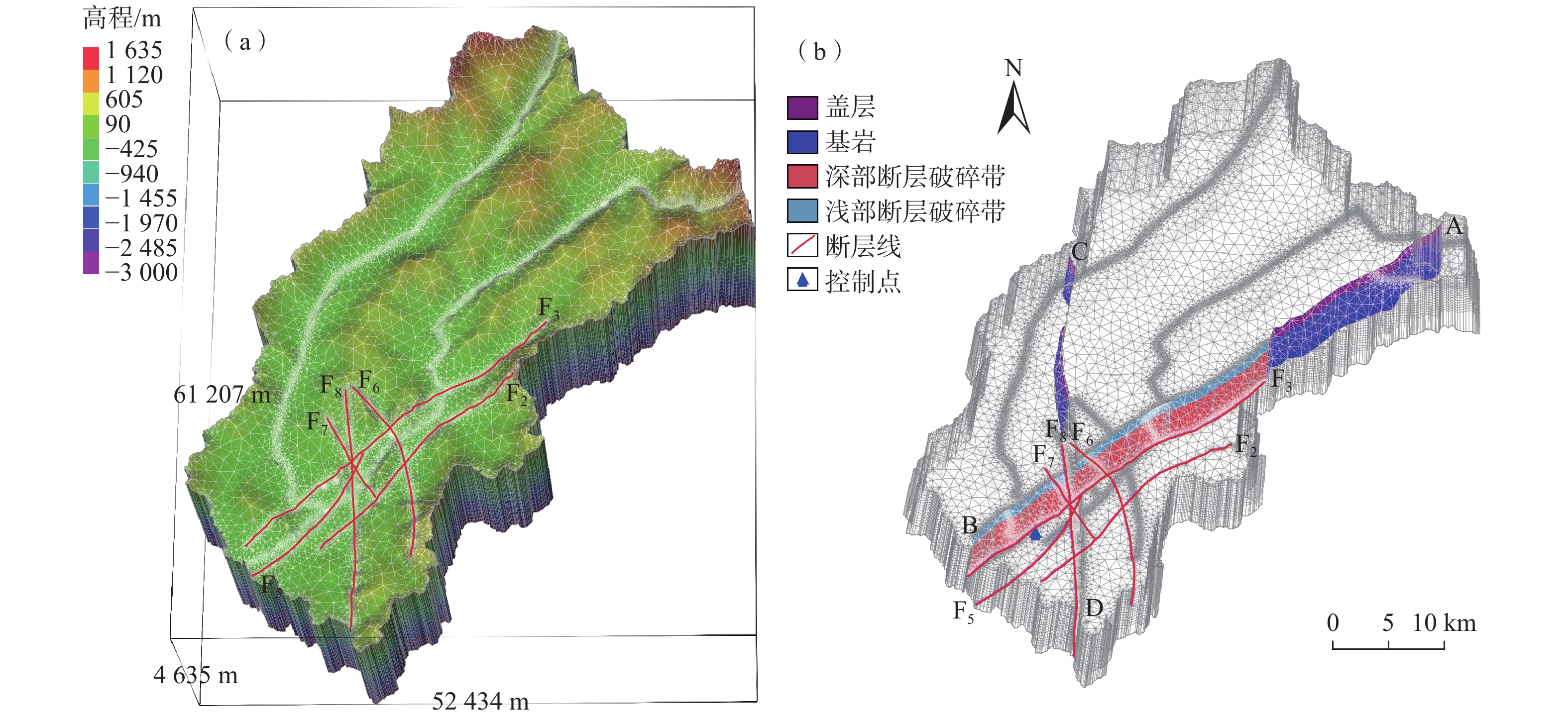
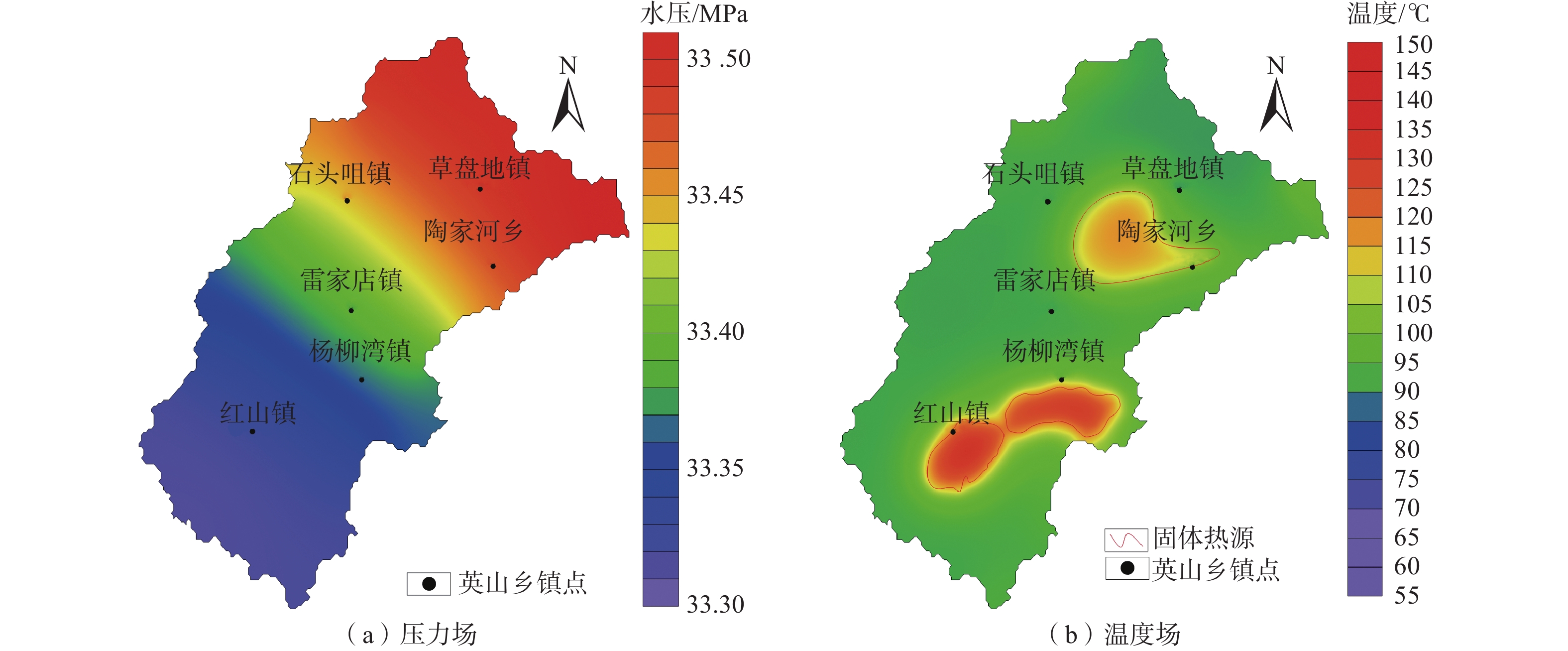
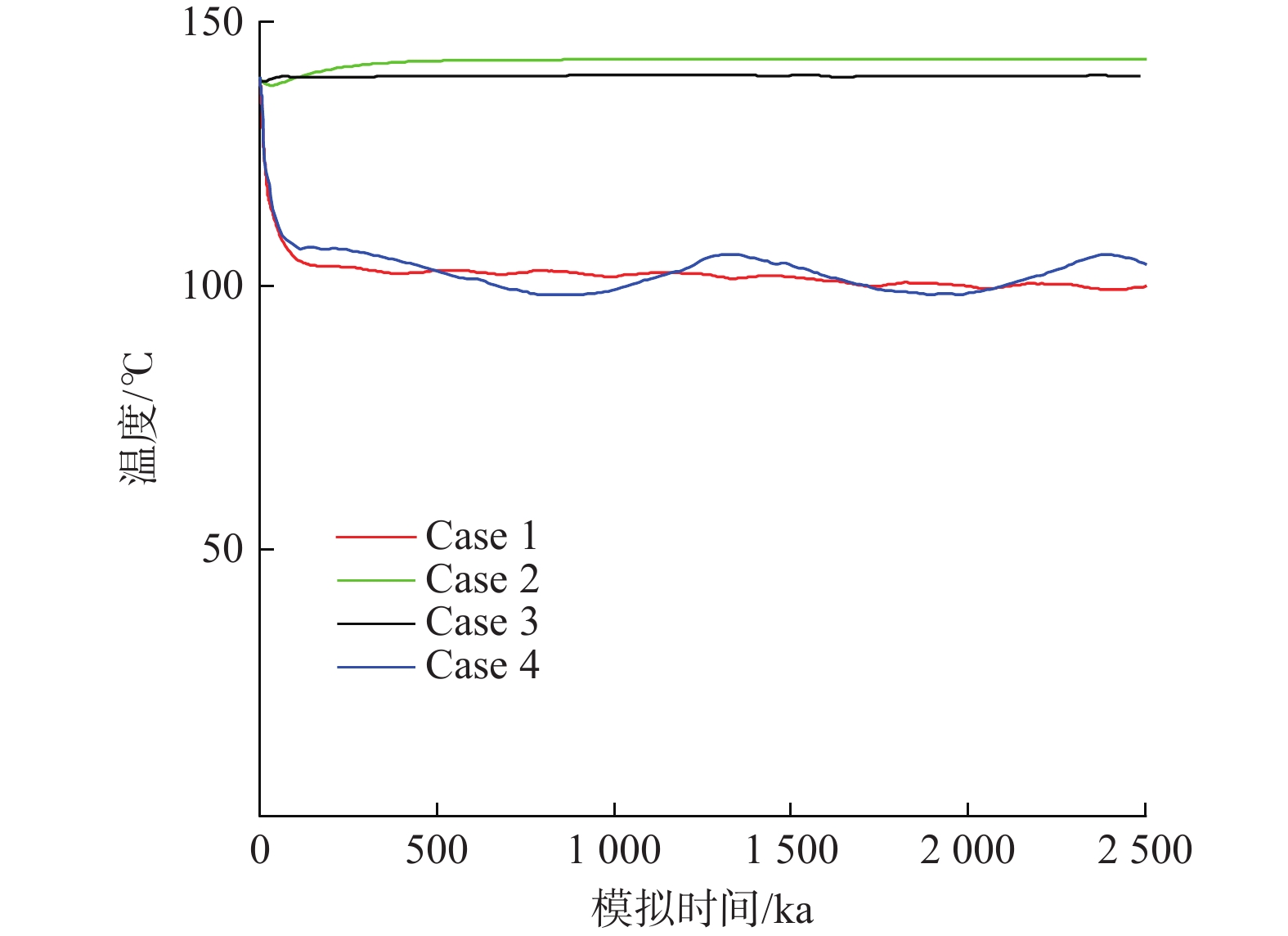
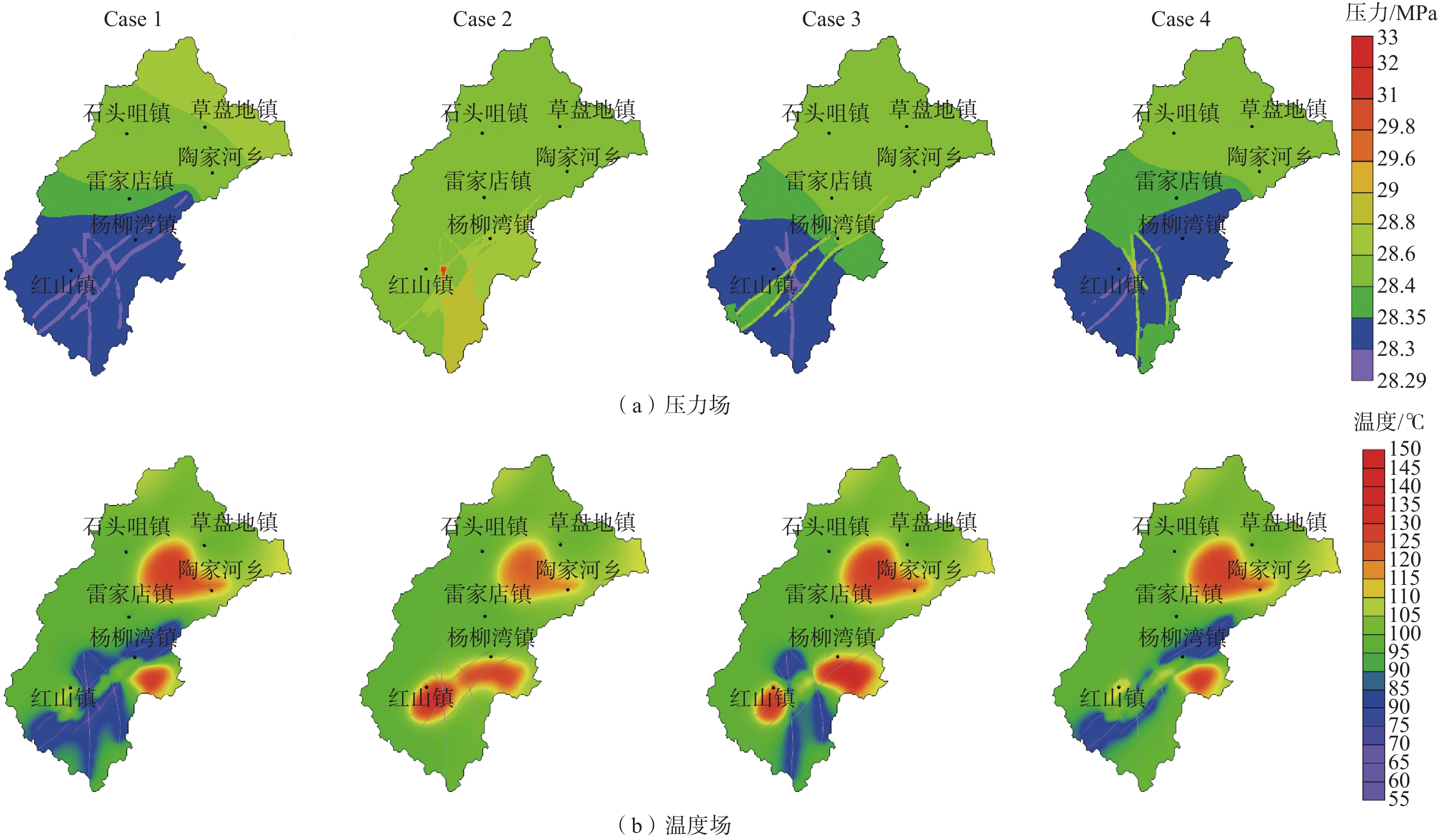
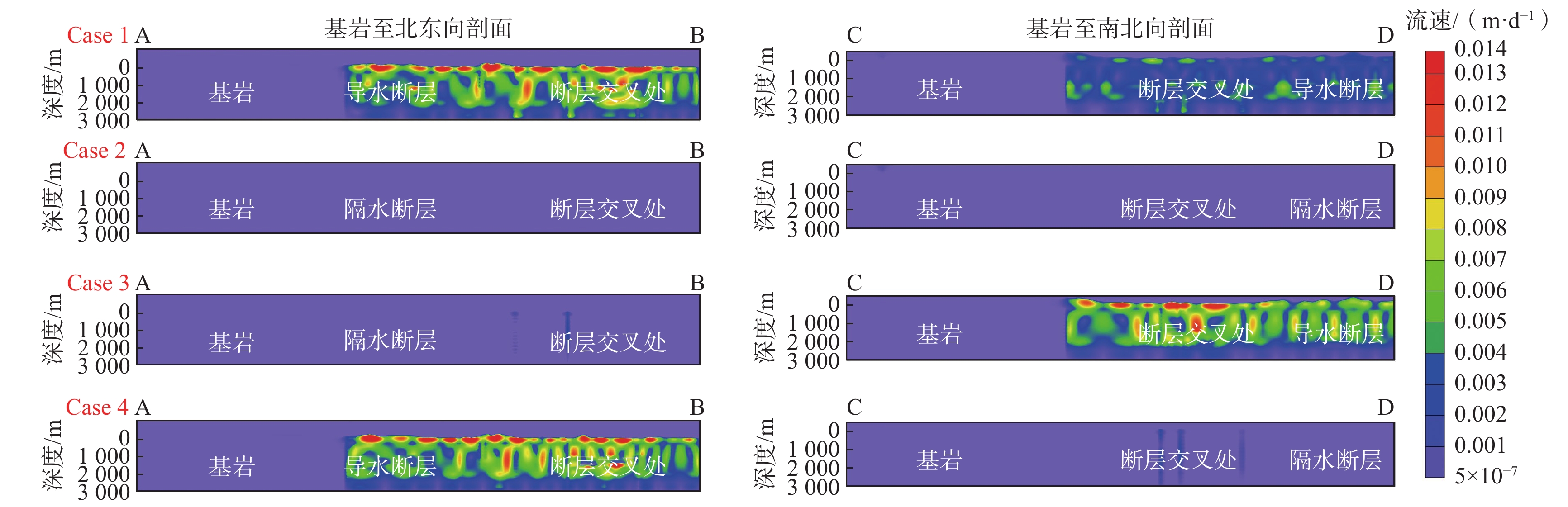
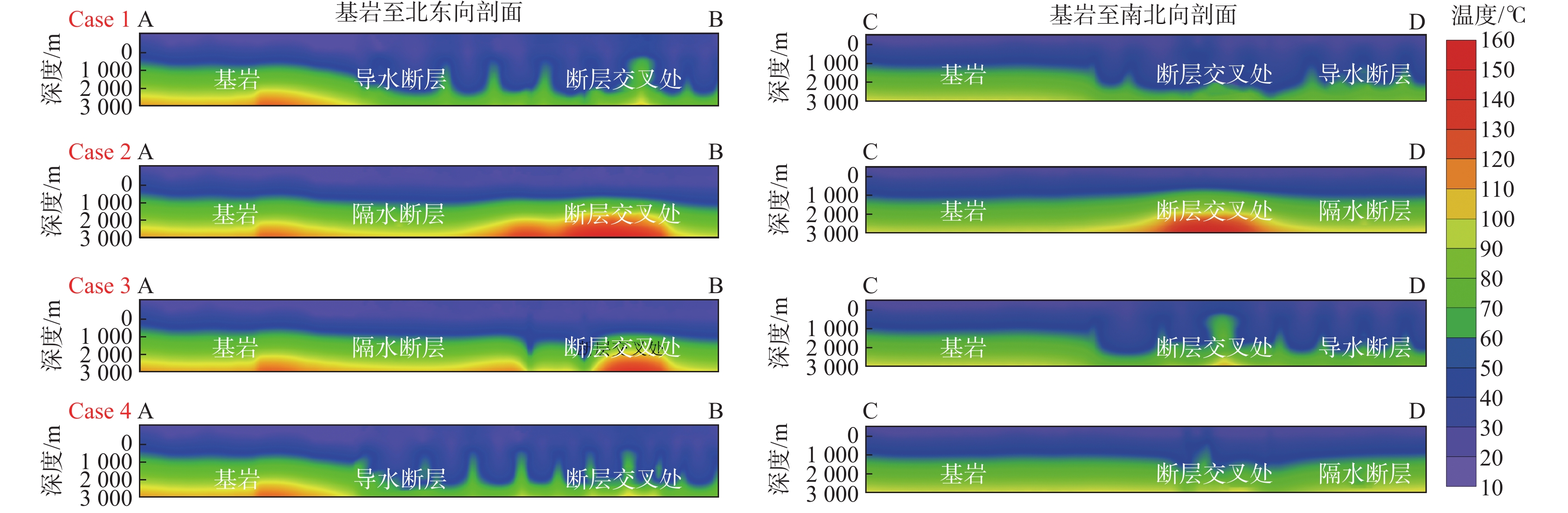
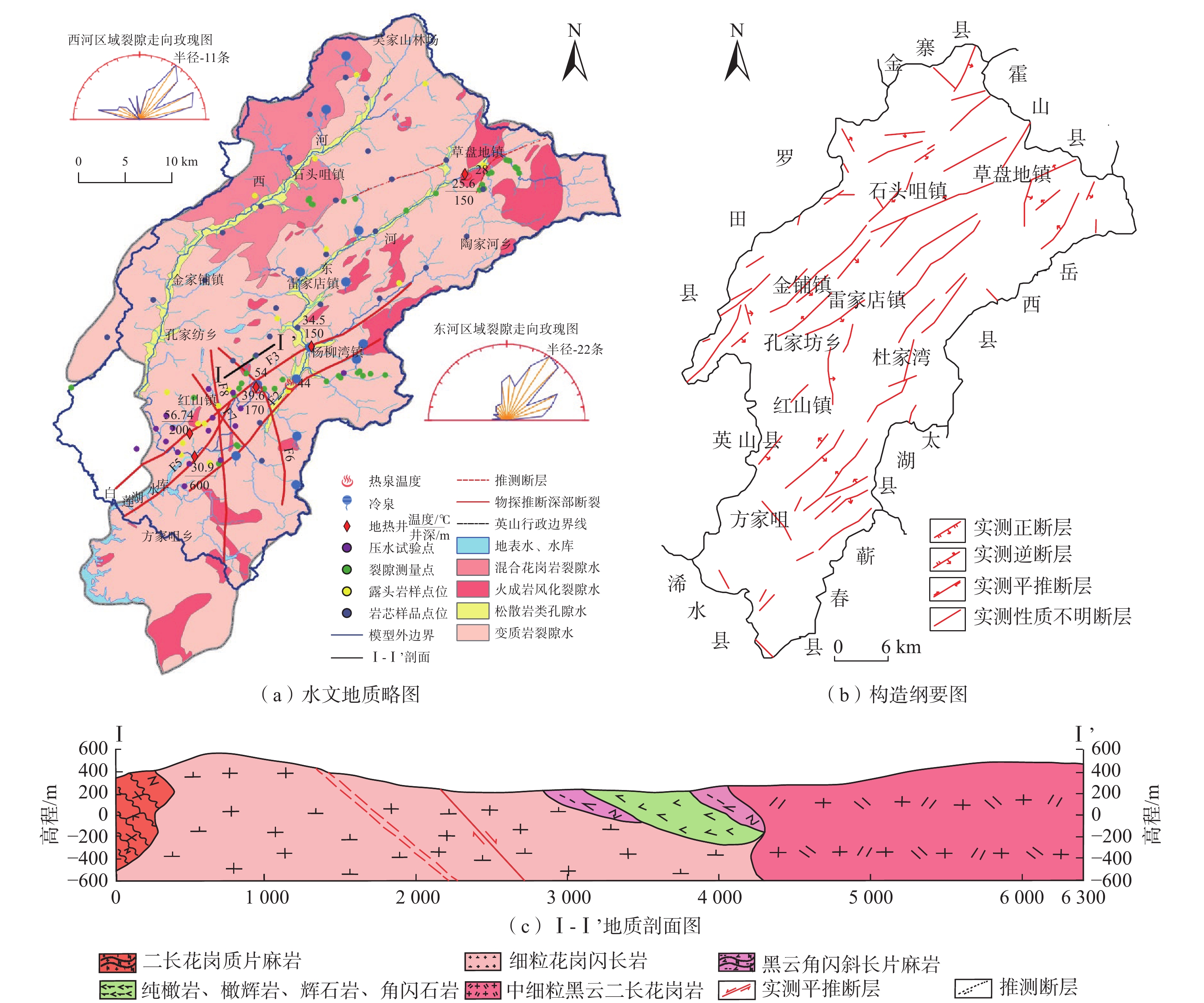
目前对英山地区深部地温场的分布情况以及构造控热模式尚无系统研究,不利于地热资源科学的开发利用。基于野外裂隙测量、浅层连续测温、钻孔压水试验等成果,建立了英山裂隙岩体地下水渗流-传热三维模型,对深部储层在不同构造组合模式下的压力场、温度场和达西流速场进行分析。研究结果表明:研究区深部温度场和压力场受断裂系统影响较大,在致密基岩及隔水断层处,流体运动微弱,热量运移以热传导为主,导水断层处以热对流为主;在深部导水断层区域温度和水压偏低,与导水断层处相比,隔水断层处水压偏高;在2000 m深度以深,高温区和水力交换强烈区与导水断层带处完全对应,表明断层是储层中最主要的流体和热量运移通道;区内断层组合模式为复合模式,北东向断层为英山地区主要导水导热构造,热水在沿北东向断层向上运移的过程中,受南北向断层的阻隔,最终在两组断层的交叉复合位置处形成温泉。该研究可为研究区内的地热资源科学勘查和合理开发利用提供参考。
Abstract:The distribution of the deep geothermal field and the tectonic thermal control mode in the Yingshan area were not understood systematically, which would bring in constraints to the sustainable exploration of local geothermal resources. Based on the field survey on continuous temperature, fracture measurements in the outcrops of granite rock, slug-test, and pumping test in the boreholes, a three-dimensional model coupling fluid flow and heat transfer process in fractured rock reservoir was established. Then the distribution of fluid pressure temperature and the Darcy velocity in the whole geothermal reservoir were calculated considering different treatment combinations of main faults. The results show that the deep temperature field and fluid pressure distribution are greatly affected by the faults system. At the location of bedrock and impermeable fault, the fluid movement is very weak, and the heat transfer is mainly controlled by heat conduction, while in the high permeable fault, it is mainly controlled by heat convection. Low temperature and fluid pressure occurred in the deep, high-permeable fault zone whereas high fluid pressure occurred in the impermeable fault zone. At a depth larger than 2000 m, the zones with high temperatures and intense hydraulic exchange coincide with the conductive fault zones, which indicates that the high-permeable faults are the most important channel for seepage and heat transfer in the reservoir. Therefore, the northeast faults are the dominant channel for fluid migration and heat conduction in the Yinshan area. Hot water migrates upward along the northeast faults and is blocked by the north-south fault. The hot spring is formed at the intersecting position of two groups of faults. This study is helpful for scientific, sustainable exploration of geothermal resources in the Yingshan area.
-

-
表 1 模型各类岩石及断层破碎带的水文地质参数赋值范围
Table 1. Hydrogeological parameters assigned to the different rock mass and fault zones in the model
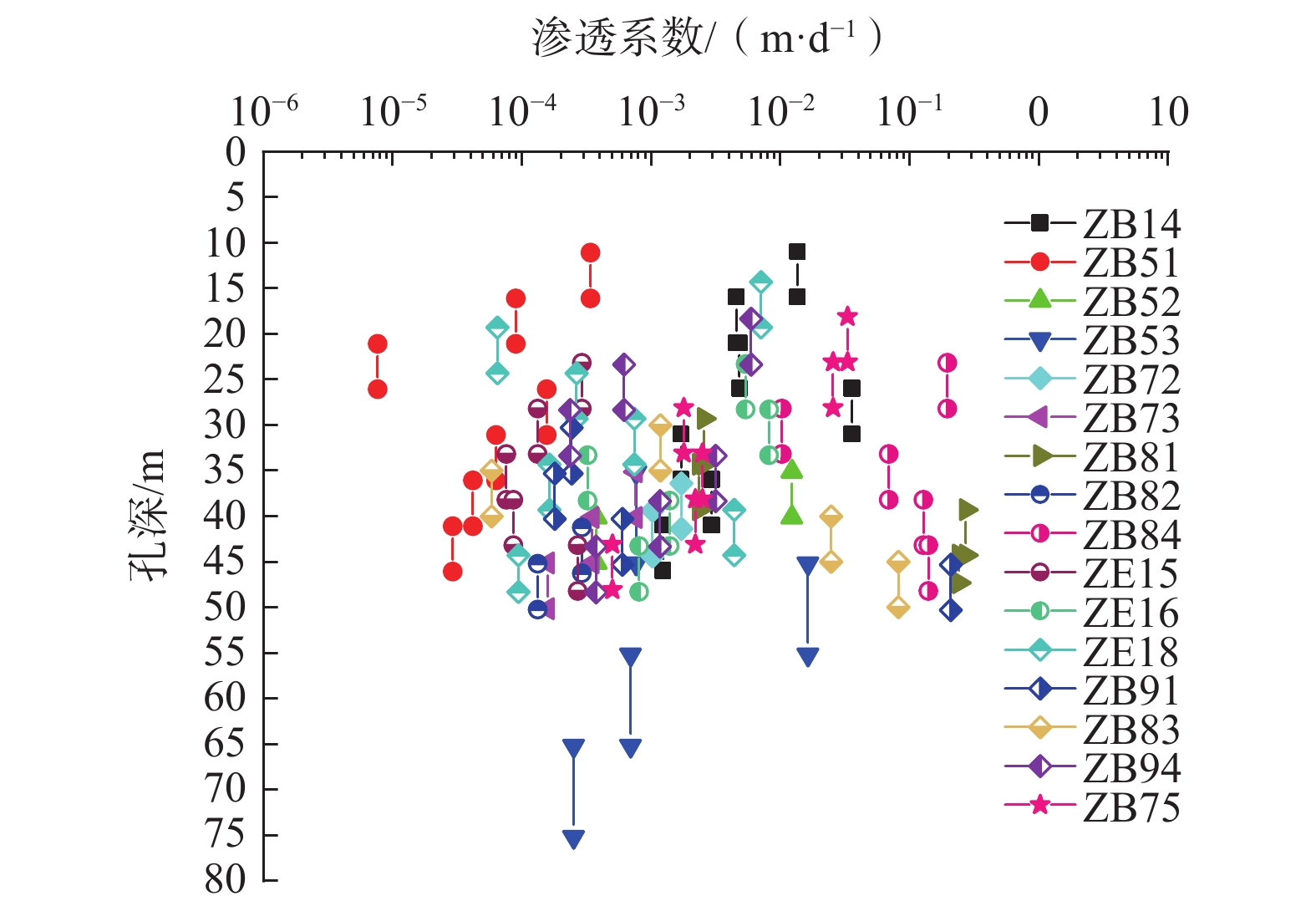
热储分类 渗透系数/(m·d−1) 孔隙度 有效传热孔隙率 Kxx Kyy Kzz 松散沉积物 5.19×10−2 5.19×10−2 5.19×10−3 0.19 0.14 花岗岩基岩 7.64×10−7~7.64×10−3 7.64×10−7~7.64×10−3 7.64×10−9~7.64×10−5 0.02~0.04 0.10~0.14 导水断层破碎带 0.010~0.273 0.010~0.273 0.01~27.30 0.05~0.29 0.2~0.4 隔水断层破碎带 7.64×10−10~7.64×10−6 7.64×10−10~7.64×10−6 7.64×10−12~7.64×10−8 0.05~0.29 0.2~0.4 表 2 4种断裂带分组组合情况下Fracture离散单元参数设置
Table 2. Parameters of the discrete fracture unit under 4 Cases of fault group
模型 断裂带分组/属性设置 渗透系数/(m·d−1) 有效传热孔隙率 导热系数/(W·m−1·K−1) 比热容/(106 J·m−3·K−1) Case1 全部断层/导水导热 86.4~432.0 1 5 2 Case2 全部断层/隔水阻热 7.64×10−12~7.64×10−8 0.0001 0.278 0.02 Case3 北东向(F2、F3、F5)/隔水阻热 7.64×10−12~7.64×10−8 0.0001 0.278 0.02 南北向(F6、F7、F8)/导水导热 86.4~432 1 5 2 Case4 北东向(F2、F3、F5)/导水导热 86.4~432 1 5 2 南北向(F6、F7、F8)/隔水阻热 7.64×10−12~7.64×10−8 0.0001 0.278 0.02 -
[1] 拓明明,周训,郭娟,等. 重庆温泉及地下热水的分布及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(1):165 − 172. [TA Mingming,ZHOU Xun,GUO Juan,et al. Occurrence and formation of the hot springs and thermal groundwater in Chongqing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(1):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TA Mingming, ZHOU Xun, GUO Juan, et al. Occurrence and formation of the hot springs and thermal groundwater in Chongqing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(1): 165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 刘琼颖,何丽娟. 挽近重大构造-热事件及其对深层地热能的潜在影响[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(3):835 − 856. [LIU Qiongying,HE Lijuan. Neoid major tectono-thermal events and their potential impacts on deep geothermal energy[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(3):835 − 856. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Qiongying, HE Lijuan. Neoid major tectono-thermal events and their potential impacts on deep geothermal energy[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(3): 835 − 856. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 闫佰忠, 李瑶, 秦光雄, 等. 基于遥感技术的贵德盆地多元信息干热岩靶区预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2023,53(4):1288 − 1300. [YAN Baizhong, LI Yao, QIN Guangxiong, et al. Prediction of dry-hot rock targets with multivariate information in Guide Basin based on remote sensing technology[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2023,53(4):1288 − 1300. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YAN Baizhong, LI Yao, QIN Guangxiong, et al. Prediction of dry-hot rock targets with multivariate information in Guide Basin based on remote sensing technology[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1288 − 1300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 尹政,柳永刚,张旭儒,等. 张掖盆地地热资源赋存特征及成因分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(1):168 − 178. [YIN Zheng,LIU Yonggang,ZHANG Xuru,et al. An analysis of the endowment characteristics and geneses of geothermal resources in the Zhangye Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(1):168 − 178. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YIN Zheng, LIU Yonggang, ZHANG Xuru, et al. An analysis of the endowment characteristics and geneses of geothermal resources in the Zhangye Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(1): 168 − 178. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 王贵玲,蔺文静. 我国主要水热型地热系统形成机制与成因模式[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(7):1923 − 1937. [WANG Guiling,LIN Wenjing. Main hydro-geothermal systems and their genetic models in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(7):1923 − 1937. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Guiling, LIN Wenjing. Main hydro-geothermal systems and their genetic models in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7): 1923 − 1937. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 康凤新,赵季初,黄迅,等. 华北盆地梁村古潜山岩溶热储聚热机制及资源潜力[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(3):1080 − 1092. [KANG Fengxin,ZHAO Jichu,HUANG Xun,et al. Heat accumulation mechanism and resources potential of the Karst geothermal reservoir in Liangcun buried uplift of Linqing depression[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(3):1080 − 1092. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
KANG Fengxin, ZHAO Jichu, HUANG Xun, et al. Heat accumulation mechanism and resources potential of the Karst geothermal reservoir in Liangcun buried uplift of Linqing depression[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(3): 1080 − 1092. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 陆金波,王丹丹,丁郑军. 广东省花岗岩地区水热型地热成藏要素及探测实例分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2023,35(3):67 − 71. [LU Jinbo,WANG Dandan,DING Zhengjun. Analysis of hydrothermal geothermal reservoir forming and survey Case for granite areas in Guangdong[J]. Coal Geology of China,2023,35(3):67 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LU Jinbo, WANG Dandan, DING Zhengjun. Analysis of hydrothermal geothermal reservoir forming and survey Case for granite areas in Guangdong[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2023, 35(3): 67 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 汪集旸,胡圣标,庞忠和,等. 中国大陆干热岩地热资源潜力评估[J]. 科技导报,2012,30(32):25 − 31. [WANG Jiyang,HU Shengbiao,PANG Zhonghe,et al. Estimate of geothermal resources potential for hot dry rock in the continental area of China[J]. Science & Technology Review,2012,30(32):25 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Jiyang, HU Shengbiao, PANG Zhonghe, et al. Estimate of geothermal resources potential for hot dry rock in the continental area of China[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2012, 30(32): 25 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 张英,冯建赟,何治亮,等. 地热系统类型划分与主控因素分析[J]. 地学前缘,2017,24(3):190 − 198. [ZHANG Ying,FENG Jianyun,HE Zhiliang,et al. Classification of geothermal systems and their formation key factors[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2017,24(3):190 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Ying, FENG Jianyun, HE Zhiliang, et al. Classification of geothermal systems and their formation key factors[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(3): 190 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 何治亮,张英,冯建赟,等. 基于工程开发原则的干热岩目标区分类与优选[J]. 地学前缘,2020,27(1):81 − 93. [HE Zhiliang,ZHANG Ying,FENG Jianyun,et al. Classification of geothermal resources based on engineering considerations and HDR EGS site screening in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2020,27(1):81 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HE Zhiliang, ZHANG Ying, FENG Jianyun, et al. Classification of geothermal resources based on engineering considerations and HDR EGS site screening in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(1): 81 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 韩江涛, 牛璞, 刘立家, 等. 地热资源与地震活动共生深部驱动机制研究现状与展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2023,53(6):1950 − 1968. [HAN Jiangtao, NIU Pu, LIU Lijia, et al. Research status and prospect of deep driving mechanism of co-occurrence of geothermal resources and seismic activity[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2023,53(6):1950 − 1968. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HAN Jiangtao, NIU Pu, LIU Lijia, et al. Research status and prospect of deep driving mechanism of co-occurrence of geothermal resources and seismic activity[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1950 − 1968. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 邱楠生,唐博宁,朱传庆. 中国大陆地区温泉分布的深部热背景[J]. 地质学报,2022,96(1):195 − 207. [QIU Nansheng,TANG Boning,ZHU Chuanqing. Deep thermal background of hot spring distribution in the Chinese continent[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2022,96(1):195 − 207. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
QIU Nansheng, TANG Boning, ZHU Chuanqing. Deep thermal background of hot spring distribution in the Chinese continent[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(1): 195 − 207. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王凯, 张杰, 白大为, 等. 雄安新区地热地质模型探究:来自地球物理的证据[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(5):1453 − 1468. [WANG Kai, ZHANG Jie, BAI Dawei, et al. Geothermal-geological model of Xiong‘an New Area: Evidence from geophysics[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(5):1453 − 1468. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Kai, ZHANG Jie, BAI Dawei, et al. Geothermal-geological model of Xiong‘an New Area: Evidence from geophysics[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(5): 1453 − 1468. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 袁建飞,刘慧中,邓国仕,等. 广安市铜锣山背斜三叠纪岩溶热储结构特征及热水成因研究[J]. 中国岩溶,2022,41(4):623 − 635. [YUAN Jianfei,LIU Huizhong,DENG Guoshi,et al. Structural characteristics of Triassic carbonate geothermal reservoir and genesis of thermal water in the Tongluo Mountain anticline of Guang’an City,China[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2022,41(4):623 − 635. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YUAN Jianfei, LIU Huizhong, DENG Guoshi, et al. Structural characteristics of Triassic carbonate geothermal reservoir and genesis of thermal water in the Tongluo Mountain anticline of Guang’an City, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(4): 623 − 635. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 孙东,李金玺,曹楠,等. 四川盆地地热地质条件及勘探潜力评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):193 − 206. [SUN Dong,LI Jinxi,CAO Nan,et al. A preliminary study of the geothermal geological characteristics and exploration potential of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):193 − 206. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Dong, LI Jinxi, CAO Nan, et al. A preliminary study of the geothermal geological characteristics and exploration potential of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(3): 193 − 206. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 徐梓矿,徐世光,张世涛. 安宁地热田浅部热储水化学特征及补给通道位置[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(11):4175 − 4187. [XU Zikuang,XU Shiguang,ZHANG Shitao. Hydro-geochemistry of Anning geothermal field and flow channels inferring of upper geothermal reservoir[J]. Earth Science,2021,46(11):4175 − 4187. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Zikuang, XU Shiguang, ZHANG Shitao. Hydro-geochemistry of Anning geothermal field and flow channels inferring of upper geothermal reservoir[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(11): 4175 − 4187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 刘春雷,李亚松,洪炳义,等. 福建盐田海水补给型地热系统地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(1):158 − 167. [LIU Chunlei,LI Yasong,HONG Bingyi,et al. Geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the seawater-recharged geothermal systems in Yantian of Fujian,China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(1):158 − 167. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Chunlei, LI Yasong, HONG Bingyi, et al. Geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the seawater-recharged geothermal systems in Yantian of Fujian, China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(1): 158 − 167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张梦昭,郭清海,刘明亮,等. 山西忻州盆地地热水地球化学特征及其成因机制[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(3):973 − 987. [ZHANG Mengzhao,GUO Qinghai,LIU Mingliang,et al. Geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the geothermal waters in the Xinzhou Basin,Shanxi Province[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(3):973 − 987. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Mengzhao, GUO Qinghai, LIU Mingliang, et al. Geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the geothermal waters in the Xinzhou Basin, Shanxi Province[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(3): 973 − 987. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 张云辉,李晓,徐正宣,等. 川藏铁路康定隧址区地热水成因及其工程影响分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):46 − 53. [ZHANG Yunhui,LI Xiao,XU Zhengxuan,et al. An analysis of the genesis and engineering influence of geothermal water in the Kangding tunnel site of the Sichuan-Tibet Railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):46 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Yunhui, LI Xiao, XU Zhengxuan, et al. An analysis of the genesis and engineering influence of geothermal water in the Kangding tunnel site of the Sichuan-Tibet Railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 46 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 李馨馨,李典庆,徐轶. 地热对井系统裂隙岩体三维渗流传热耦合的等效模拟方法[J]. 工程力学,2019,36(7):238 − 247. [LI Xinxin,LI Dianqing,XU Yi. Equivalent simulation method of three-dimensional seepage and heat transfer coupling in fractured rock mass of geothermal-borehole system[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2019,36(7):238 − 247. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Xinxin, LI Dianqing, XU Yi. Equivalent simulation method of three-dimensional seepage and heat transfer coupling in fractured rock mass of geothermal-borehole system[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2019, 36(7): 238 − 247. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 陈金龙,罗文行,窦斌,等. 涿鹿盆地三维多裂隙地质模型地温场数值模拟[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(3):22 − 33. [CHEN Jinlong,LUO Wenxing,DOU Bin,et al. Numerical simulation of geothermal field in a three-dimensional multi-fractured geological model of Zhuolu Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(3):22 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Jinlong, LUO Wenxing, DOU Bin, et al. Numerical simulation of geothermal field in a three-dimensional multi-fractured geological model of Zhuolu Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 22 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] PRZYBYCIN A M,SCHECK-WENDEROTH M,SCHNEIDER M. The origin of deep geothermal anomalies in the German Molasse Basin:Results from 3D numerical models of coupled fluid flow and heat transport[J]. Geothermal Energy,2017,5(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40517-016-0059-3
[23] POLA M,CACACE M,FABBRI P,et al. Fault control on a thermal anomaly:Conceptual and numerical modeling of a low-temperature geothermal system in the southern Alps foreland basin (NE Italy)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),2020,125(5):e2019JB017394. doi: 10.1029/2019JB017394
[24] 刘波,陈金国. 英罗地区地热资源形成条件及找矿前景[J]. 资源环境与工程,2014,28(3):313 − 317. [LIU Bo,CHEN Jinguo. Forming conditions of geothermal resources and its prospecting potential in Yingshan-Luotian Area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2014,28(3):313 − 317. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Bo, CHEN Jinguo. Forming conditions of geothermal resources and its prospecting potential in Yingshan-Luotian Area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2014, 28(3): 313 − 317. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 王鹏,陈晓宏,沈立成,等. 西藏地热异常区热储温度及其地质环境效应[J]. 中国地质,2016,43(4):1429 − 1438. [WANG Peng,CHEN Xiaohong,SHEN Licheng,et al. Reservoir temperature of geothermal anomaly area and its environmental effect in Tibet[J]. Geology in China,2016,43(4):1429 − 1438. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Peng, CHEN Xiaohong, SHEN Licheng, et al. Reservoir temperature of geothermal anomaly area and its environmental effect in Tibet[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(4): 1429 − 1438. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 高洪雷,胡志华,万汉平,等. 西藏谷露地热田地热地质特征[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(3):1014 − 1029. [GAO Honglei,HU Zhihua,WAN Hanping,et al. Characteristics of geothermal geology of the gulu geothermal field in Tibet[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(3):1014 − 1029. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GAO Honglei, HU Zhihua, WAN Hanping, et al. Characteristics of geothermal geology of the gulu geothermal field in Tibet[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(3): 1014 − 1029. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] EGGER A E,GLEN J M G,MCPHEE D K. Structural controls on geothermal circulation in Surprise Valley,California:A re-evaluation of the Lake City fault zone[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,2014,126(3/4):523 − 531.
[28] UZELLI T,BABA A,GÜL MUNGAN G,et al. Conceptual model of the Gülbahçe geothermal system,Western Anatolia,Turkey:Based on structural and hydrogeochemical data[J]. Geothermics,2017,68:67 − 85. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2017.03.003
[29] 陶春辉,郭志馗,梁锦,等. 超慢速扩张西南印度洋中脊硫化物成矿模型[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2023,53(6):1216 − 1234. [TAO Chunhui,GUO Zhidao,LIANG Jin,et al. Sulfide metallogenic model on the ultraslow-spreading Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae),2023,53(6):1216 − 1234. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2023-0013
TAO Chunhui, GUO Zhidao, LIANG Jin, et al. Sulfide metallogenic model on the ultraslow-spreading Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2023, 53(6): 1216 − 1234. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2023-0013
[30] LÓPEZ D L,SMITH L. Fluid flow in fault zones:Influence of hydraulic anisotropy and heterogeneity on the fluid flow and heat transfer regime[J]. Water Resources Research,1996,32(10):3227 − 3235. doi: 10.1029/96WR02101
[31] MCNAMARA D D,MASSIOT C,LEWIS B,et al. Heterogeneity of structure and stress in the Rotokawa Geothermal Field,New Zealand[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),2015,120(2):1243 − 1262. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011480
[32] 戴竹,詹文,陈金国. 东大别黄冈地区干热岩赋存条件及远景分析[J]. 资源环境与工程,2021,35(6):807 − 812. [DAI Zhu,ZHAN Wen,CHEN Jinguo. Occurrence conditions and prospect analysis of hot-dry-rocks in Huanggang Area,east dabie[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2021,35(6):807 − 812. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DAI Zhu, ZHAN Wen, CHEN Jinguo. Occurrence conditions and prospect analysis of hot-dry-rocks in Huanggang Area, east dabie[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2021, 35(6): 807 − 812. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 潘桂棠,肖庆辉,陆松年,等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质,2009,36(1):1 − 16. [PAN Guitang,XIAO Qinghui,LU Songnian,et al. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China,2009,36(1):1 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
PAN Guitang, XIAO Qinghui, LU Songnian, et al. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(1): 1 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 王焰新,胡祥云,谢先军. 英山县深部高温地热资源预可行性勘查水文地质专项调查报告[R]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2023. [WANG Yanxin,HU Xiangyun,XIE Xianjun,et al. Special hydrogeological investigation report on the preliminary feasibility survey of deep high-temperature geothermal resources in Yingshan County[R]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences,Wuhan,2023. (in Chinese)]
WANG Yanxin, HU Xiangyun, XIE Xianjun, et al. Special hydrogeological investigation report on the preliminary feasibility survey of deep high-temperature geothermal resources in Yingshan County[R]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 2023. (in Chinese)
[35] 张攀,陈金国,傅清心. 英罗地区地热资源成因分析及勘查靶区预测[J]. 资源环境与工程,2018,32(增刊1):44 − 47. [ZHANG Pan,CHEN Jinguo,FU Qingxin. Genetic analysis of geothermal resources and prediction of exploration targets in yingluo area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2018,32(Sup 1):44 − 47. (in Chinese)]
ZHANG Pan, CHEN Jinguo, FU Qingxin. Genetic analysis of geothermal resources and prediction of exploration targets in yingluo area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(Sup 1): 44 − 47. (in Chinese)
[36] 毛官辉,张立勇,陈俊兵,等. 浙江省大地热流及其地热资源意义[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(3):1030 − 1039. [MAO Guanhui,ZHANG Liyong,CHEN Junbing,et al. Terrestrial heat flow in Zhejiang Province and its significance of geothermal resources[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(3):1030 − 1039. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MAO Guanhui, ZHANG Liyong, CHEN Junbing, et al. Terrestrial heat flow in Zhejiang Province and its significance of geothermal resources[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(3): 1030 − 1039. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: