Characteristics, distribution and source of dissolved organic matter and its implications for antimony contamination in Zijiang River basin
-
摘要:
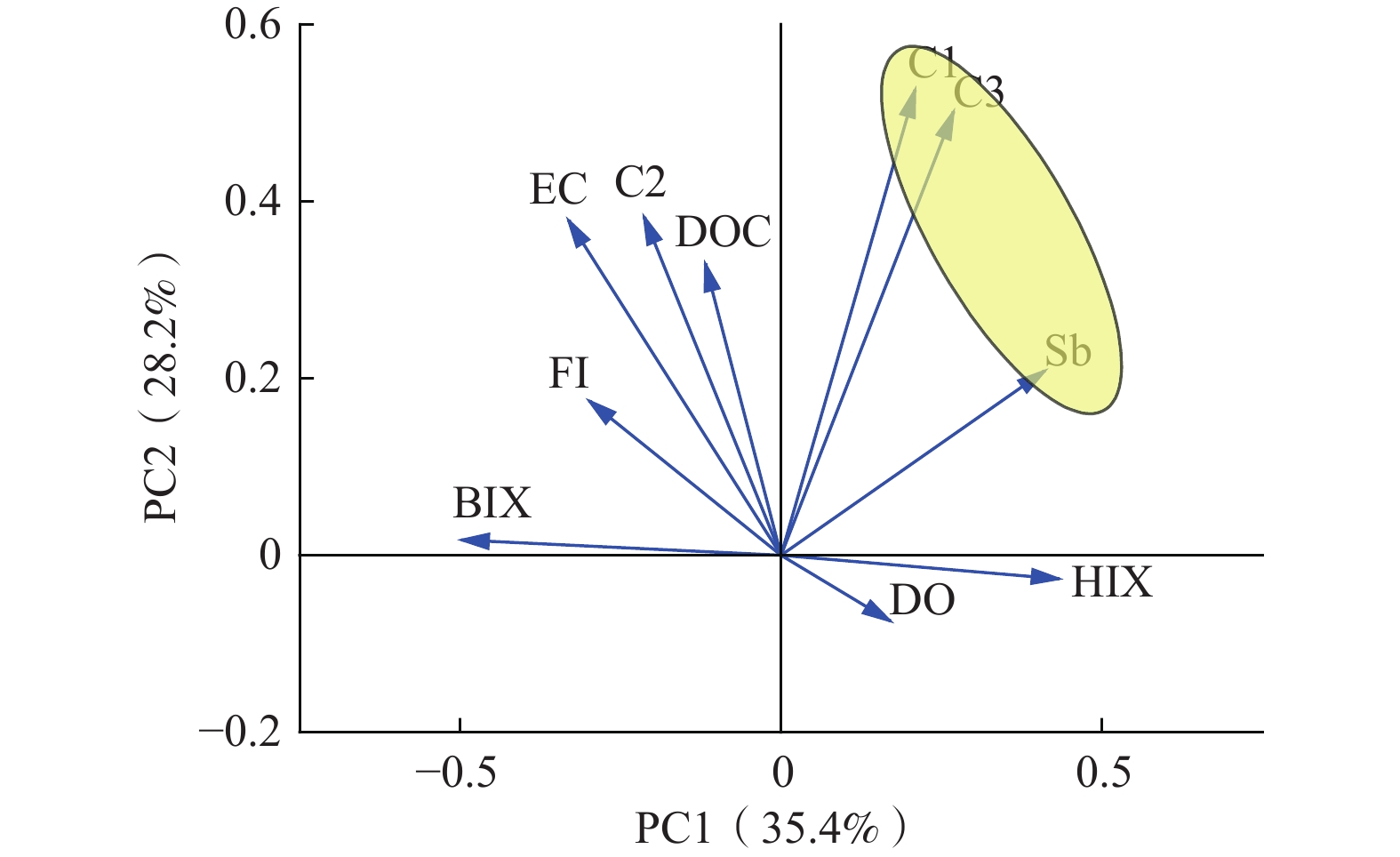
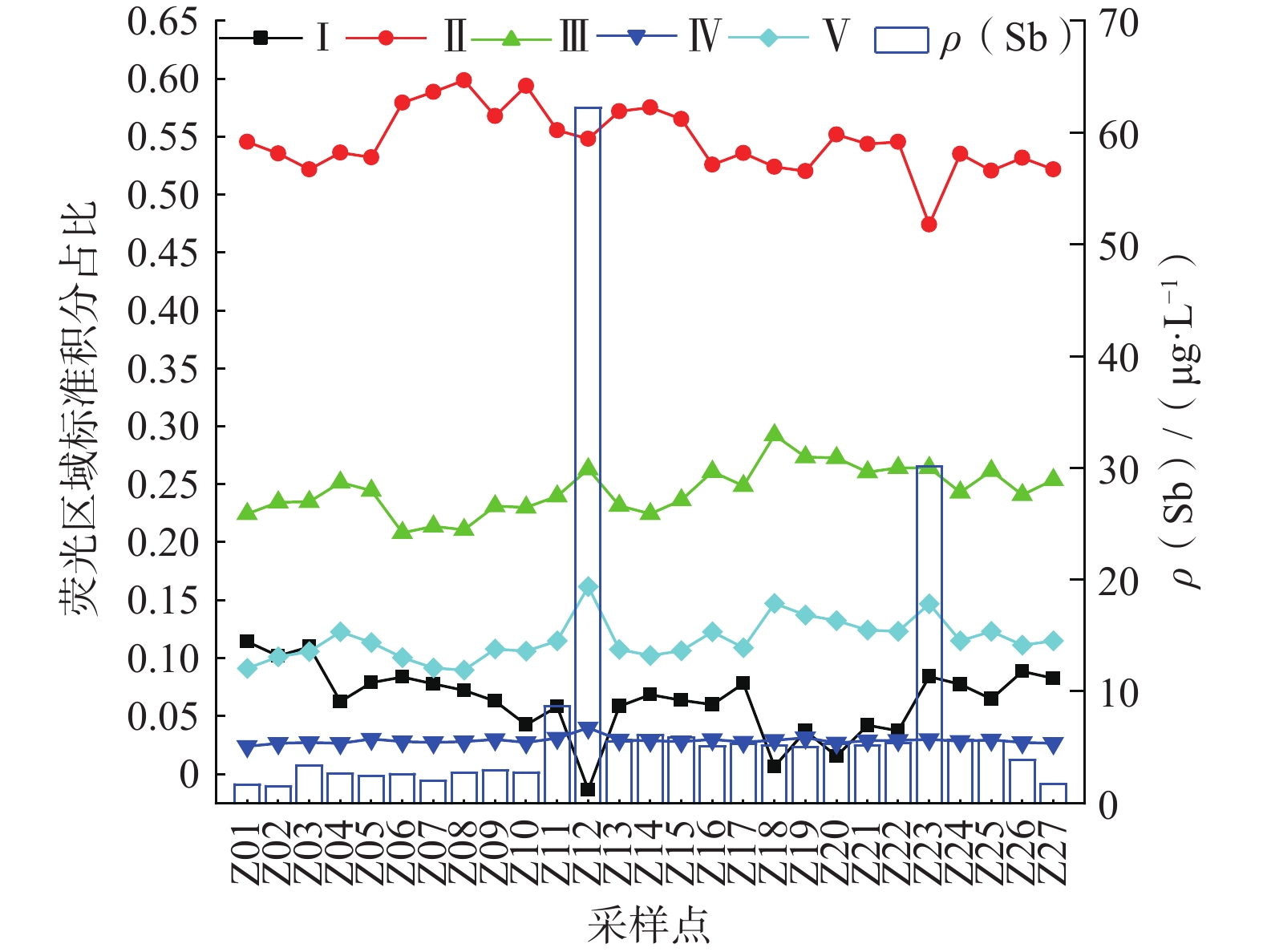
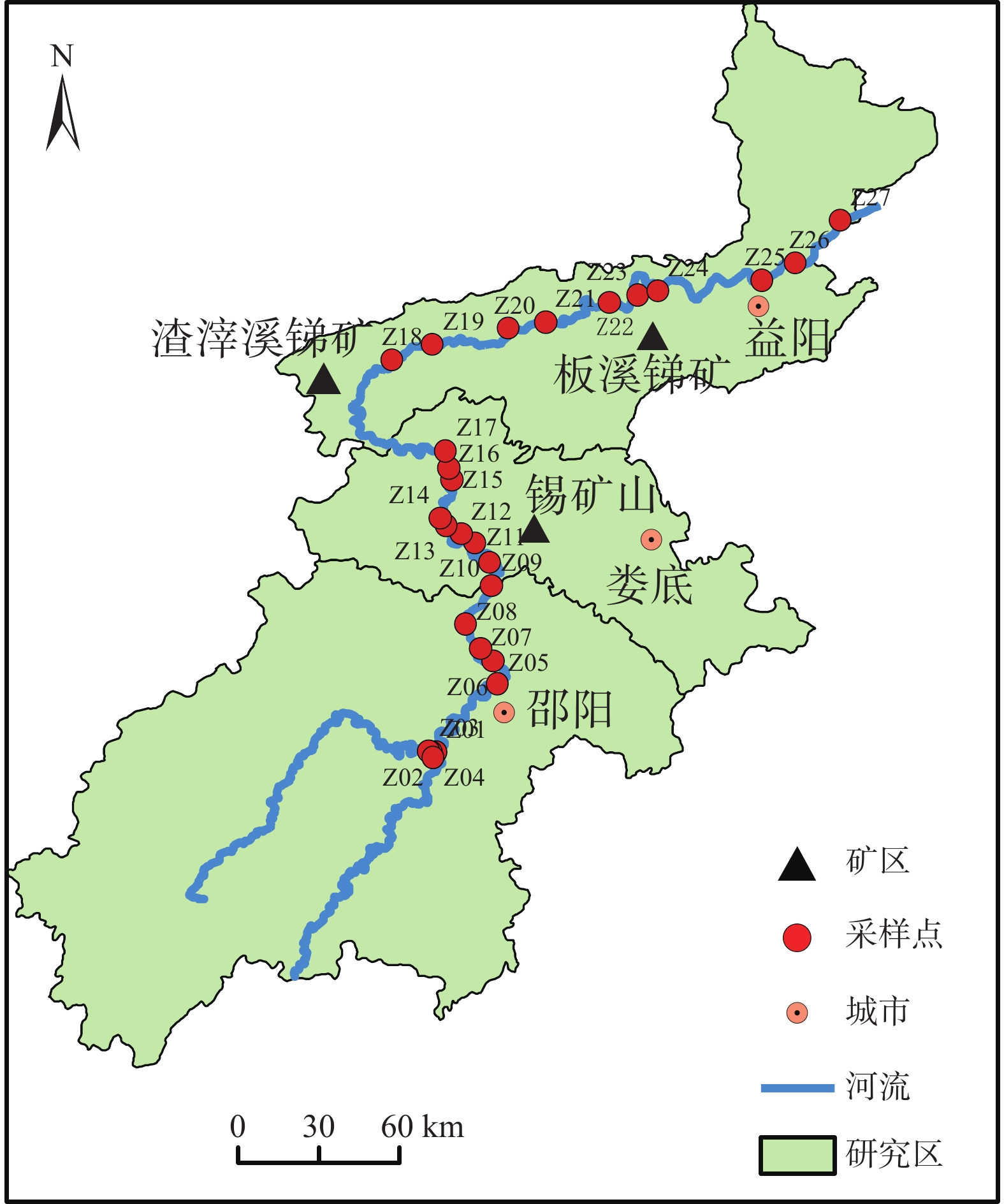
溶解性有机质(dissolved organic matter, DOM)是影响重金属元素在水体中迁移转化的关键因素之一。资江是洞庭湖第三大支流,流域内锑矿开发导致资江江水中锑(Sb)的质量浓度处于较高水平。为了解析资江流域江水中DOM的特征及来源,探索DOM对Sb迁移的指示意义,研究对资江流域江水进行了三维荧光光谱分析,利用平行因子法分析了水体中DOM的组分和荧光特征以及各组分与Sb质量浓度的关联。结果表明:(1)资江流域江水中Sb质量浓度为1.50~62.20 μg/L,平均值为7.26 μg/L,其中有55.56%的采样点Sb质量浓度超过最低限制5 μg/L;(2)资江流域江水DOM有C1、C2和C3共3个组分,依次为陆源的类富里酸组分、类腐殖质组分以及可作为电子运输工具的醌类腐殖质组分,以C1和C2组分为主;(3) DOM主要通过2种方式影响Sb的迁移,一是水体中DOM的醌类基团作为电子传递体并参与有机质的氧化及铁氧化物的还原,二是富里酸基团与Sb进行络合形成DOM-Sb型复合物,2种方式协同促进了资江流域江水中Sb的富集,提高了Sb的迁移能力。研究结果将为资江流域江水Sb污染溯源和防治提供新的方向和理论依据。
Abstract:Dissolved organic matter (DOM) is critical to affecting heavy metal migration and transformation in water. Zijiang River, the third largest tributary of Dongting Lake in Hunan Province, has a high level of antimony (Sb) mass concentration due to the rapid development of the antimony mining and smelting. Excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy (EEMs) and parallel factor analysis (PARAFA)were used to analyze the source and characteristics of DOM in Zijiang River and its indicative significance on antimony migration. The results show that the mass concentration of antimony in the river water in Zijiang River ranges from 1.50 to 62.20 μg/L, with an average of 7.26 μg/L, of which 55.56% exceed the antimony minimum limit of 5 μg/L. DOM of Zijiang River consists of three different components (C1, C2, and C3), which are terrestrial sources, humic-like substance, and the quinone-like humic substance used as electron transport tool, respectively. DOM is mainly composed of C1 and C2. Antimony migration and transformation are influenced by DOM in two ways: The quinone-like humic component, as an electron transfer tools, participates in the reduction of DOM and iron oxide; the complexation of fulvic acid with antimony results in the formation of DOM-Sb complex. The two approaches synergistically enhance the enrichment and transport capabilities of antimony in the Zijiang River. This study will provide a new direction and theoretical basis for the source and prevention of river water antimony pollution in the Zijiang River.
-

-
表 1 荧光光谱参数描述
Table 1. Description of fluorescence spectral parameter
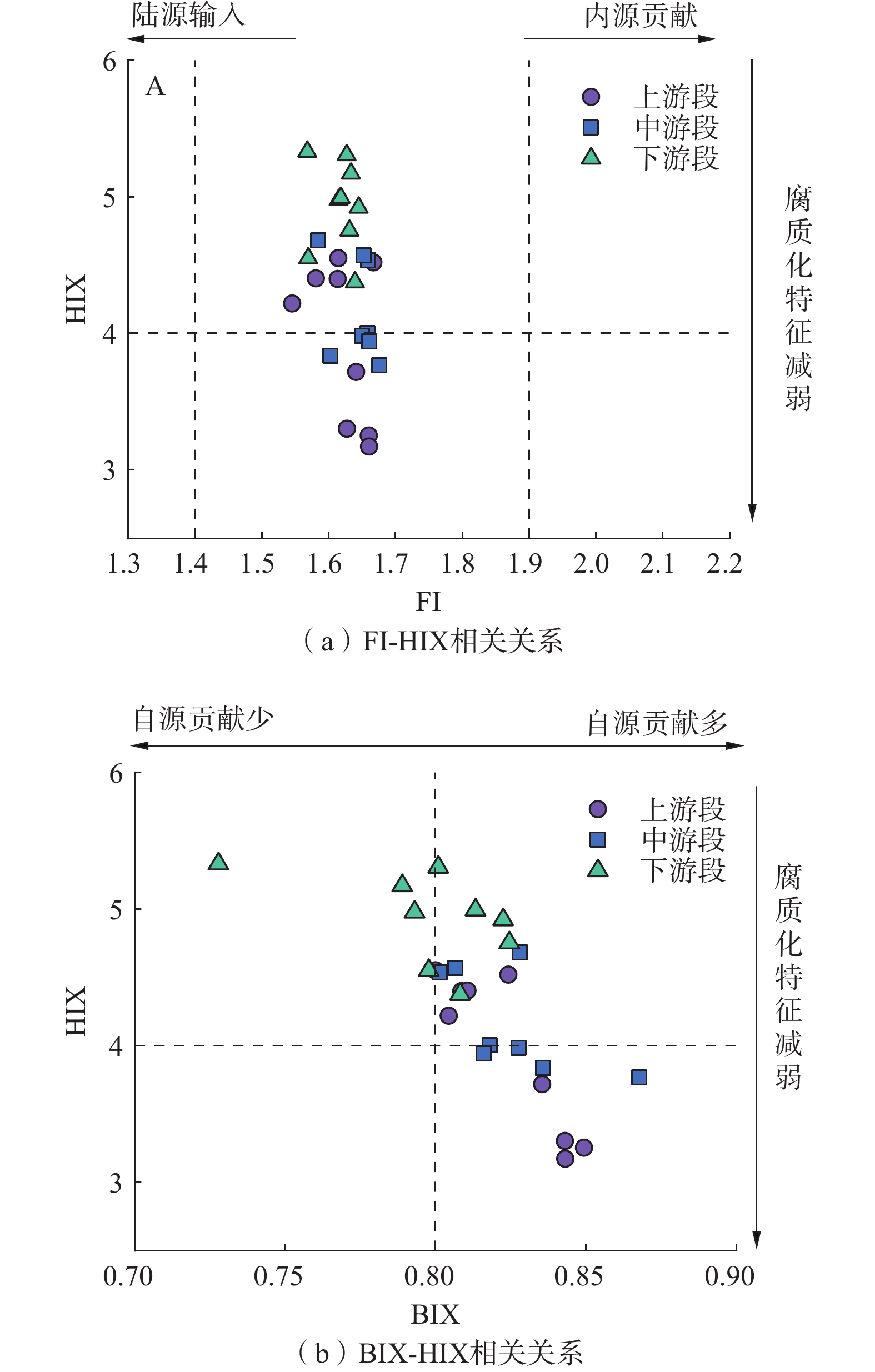
荧光光谱参数 计算方法 意义 特征描述 荧光指数[28]
(fluorescence index,FI)k为370 nm时,j为470 nm与
520 nm的荧光强度之比微生物来源有机质占
总有机质的比例<1.4,陆源有机物; >1.9,微生物来源;
1.4~1.9,陆源内源混合来源;自生源指数[29]
(autochthonous index,BIX)k为310 nm时,j为380 nm与
430 nm的荧光强度之比微生物来源有机质和
外源有机质的比值,衡量自生来源
有机质的贡献率<0.6,自生来源贡献少;0.6~0.8,中度新近自
生来源特征;>0.8 较强的自生来源特征;腐殖化指数[30]
( humification index,HIX)k为255 nm时,j为435~480 nm与
300~345 nm之间荧光强度之和的比值表征DOM腐殖化程度 1.5~4,具有弱腐质化特征;
4~6,具有较强腐质化特征;表 2 资江流域江水水质指标特征
Table 2. Characteristics of water quality index of the Zijiang River
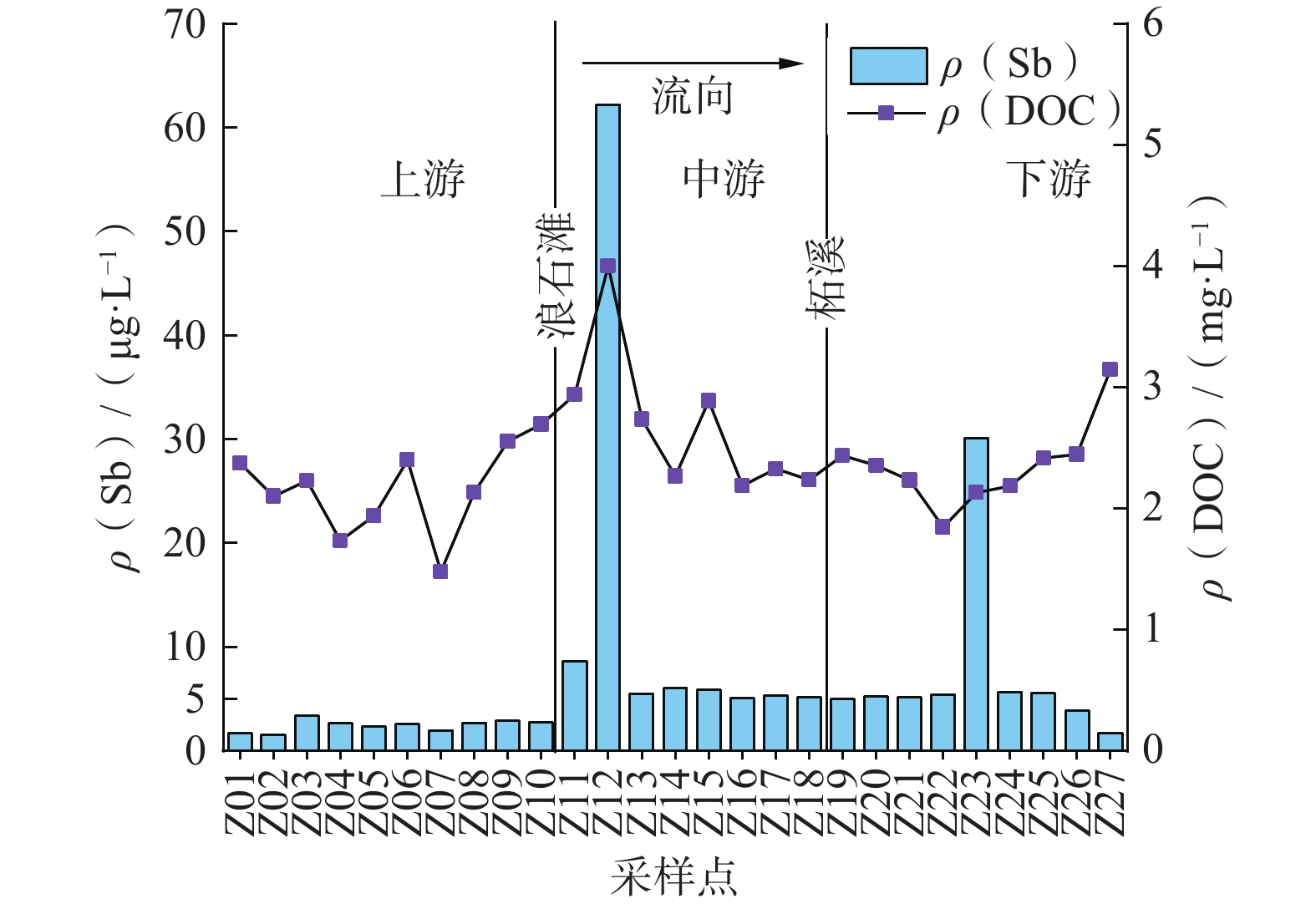
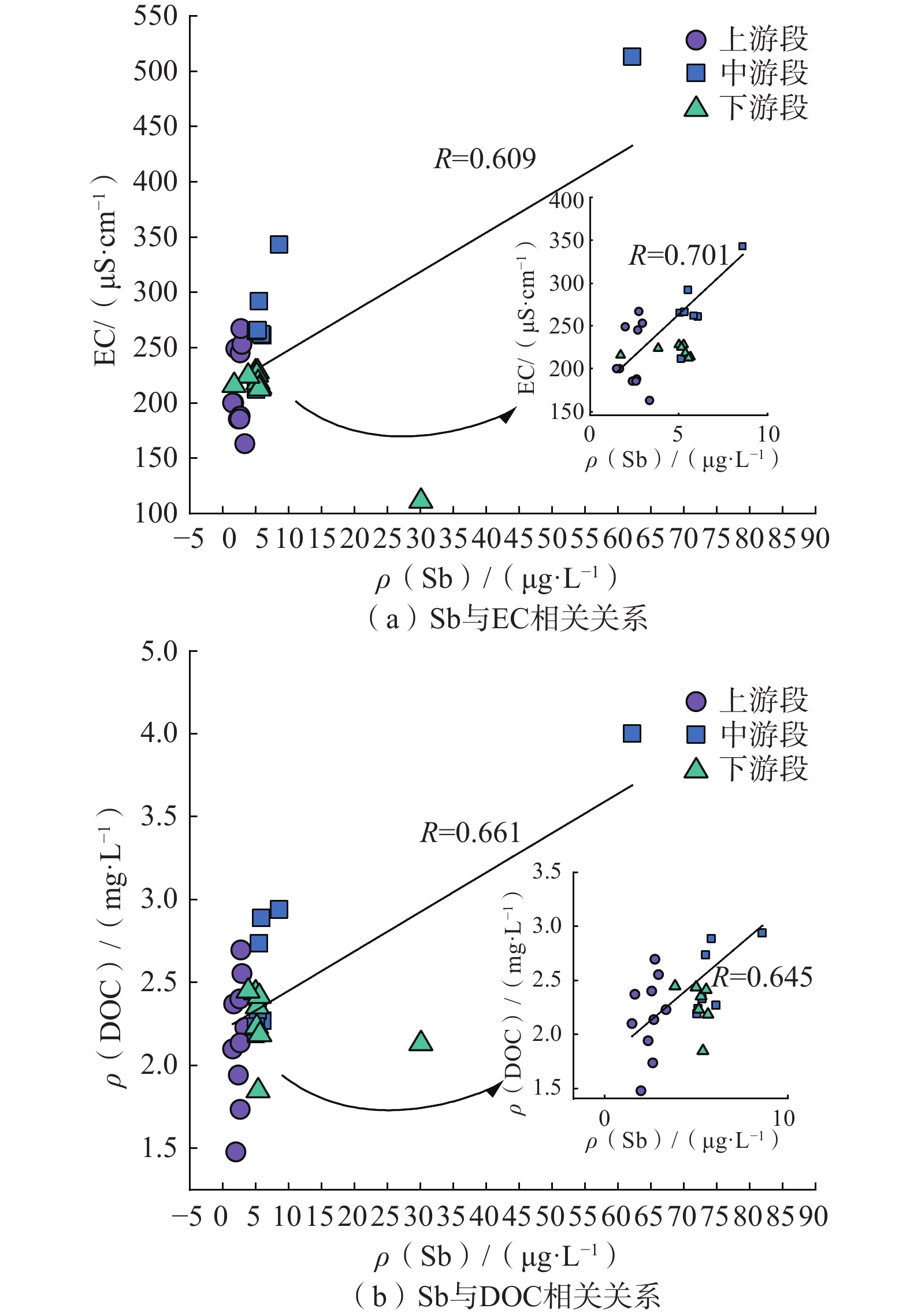
水体 统计值 pH EC DO DOC 元素质量浓度 Sb As Cd Cr 上游段 范围 7.99~9.12 163.00~267.00 8.13~10.96 1.48~2.70 1.50~3.36 0.83~1.62 0.02~0.06 0.16~1.24 平均值 8.63 213.56 9.53 2.16 2.45 1.19 0.03 0.53 标准差 0.40 34.39 0.87 0.35 0.55 0.21 0.02 0.34 变异系数 0.05 0.16 0.09 0.16 0.22 0.17 0.52 0.64 中游段 范围 8.00~8.32 211.90~513.00 7.63~9.81 2.19~4.00 5.00~62.20 2.05~3.21 0.02~0.07 0.35~1.64 平均值 8.16 293.54 8.63 2.67 12.09 2.42 0.04 0.78 标准差 0.10 85.11 0.81 0.54 17.75 0.36 0.02 0.50 变异系数 0.01 0.29 0.09 0.20 1.47 0.15 0.38 0.64 下游段 范围 8.10~8.41 111.10~228.00 8.78~11.01 1.85~3.15 1.71~30.10 0.64~5.43 0.02~0.12 0.37~1.76 平均值 8.24 206.10 10.07 2.34 7.83 2.80 0.07 0.74 标准差 0.10 36.28 0.66 0.35 8.50 1.25 0.03 0.44 变异系数 0.01 0.18 0.07 0.15 1.09 0.45 0.41 0.59 总体 范围 7.99~9.12 111.10~513.00 7.63~11.01 1.48~4.00 1.50~62.20 0.64~5.43 0.02~0.12 0.16~1.76 平均值 8.33 238.49 9.35 2.39 7.26 2.08 0.05 0.67 标准差 0.33 69.24 0.98 0.48 11.96 1.00 0.03 0.44 变异系数 0.04 0.29 0.10 0.20 1.65 0.48 0.57 0.65 注:表中pH和变异系数为无量纲;EC单位为μS/cm;DO、DOC单位为mg/L;其他指标单位为μg/L。 表 3 水体中3个荧光组分特征及其与确定组分的对比
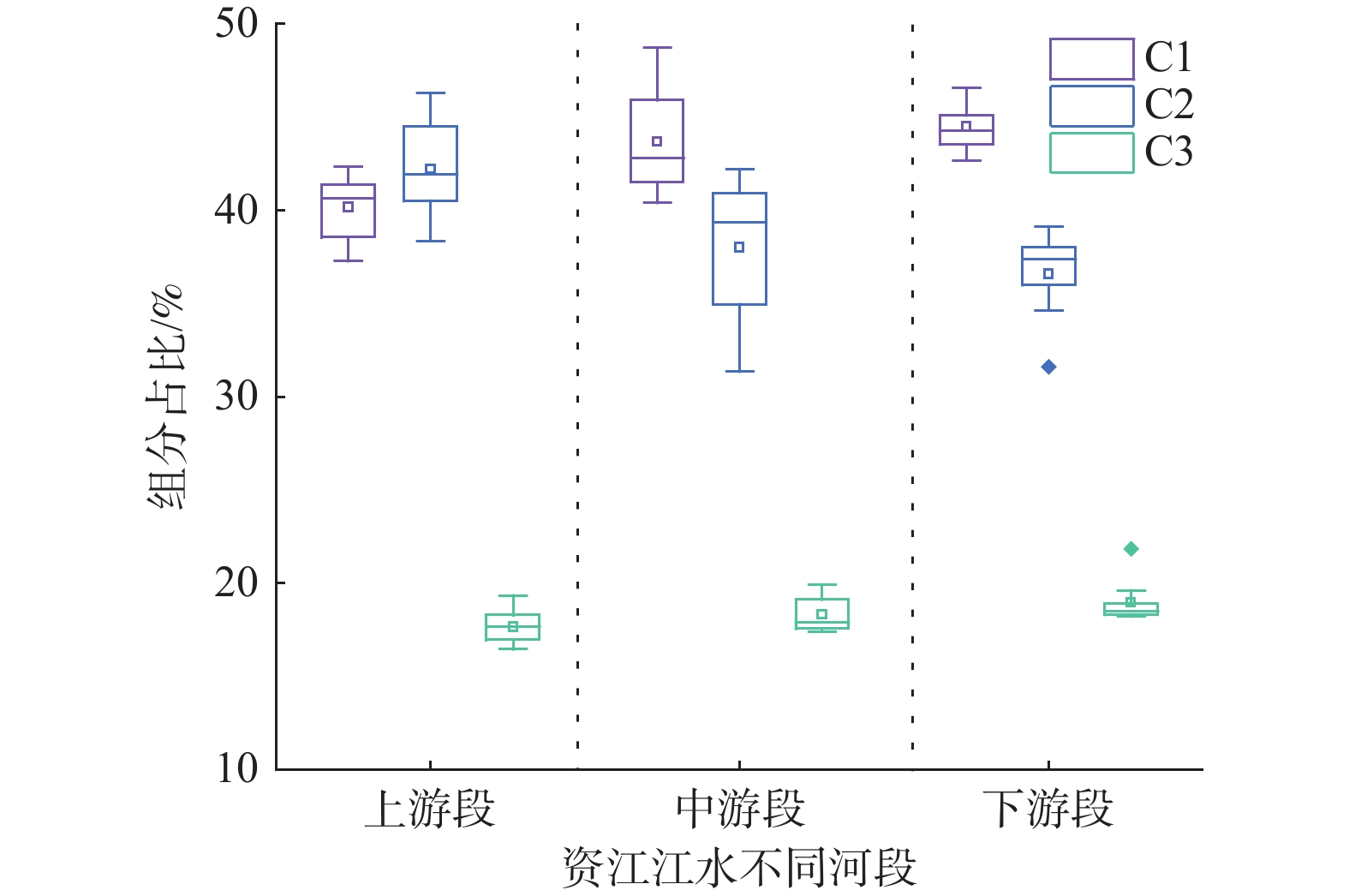
Table 3. Characteristics of the three fluorescence components and their comparison with previous identified components
表 4 三维荧光光谱指数分布情况
Table 4. Distribution of spectra indices based on EEMs
指标 最大值 最小值 平均值 变异系数/% 总体 FI 1.68 1.55 1.63 2.08 BIX 0.87 0.73 0.82 3.19 HIX 5.33 3.17 4.33 14.08 上游段 FI 1.67 1.55 1.62 2.35 BIX 0.85 0.80 0.83 2.27 HIX 4.55 3.17 3.93 14.14 中游段 FI 1.68 1.58 1.64 1.94 BIX 0.87 0.80 0.83 2.50 HIX 4.68 3.77 4.16 8.82 下游段 FI 1.65 1.57 1.62 1.77 BIX 0.82 0.73 0.80 3.62 HIX 5.33 4.38 4.93 6.60 -
[1] 何伟,白泽琳,李一龙,等. 溶解性有机质特性分析与来源解析的研究进展[J]. 环境科学学报,2016,36(2):359 − 372. [HE Wei,BAI Zelin,LI Yilong,et al. Advances in the characteristics analysis and source identification of the dissolved organic matter[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2016,36(2):359 − 372. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HE Wei, BAI Zelin, LI Yilong, et al. Advances in the characteristics analysis and source identification of the dissolved organic matter[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(2): 359 − 372. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] WANG Liying,WU Fengchang,ZHANG Runyu,et al. Characterization of dissolved organic matter fractions from Lake Hongfeng,Southwestern China Plateau[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2009,21(5):581 − 588. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62311-6
[3] 陈昭宇,李思悦. 三峡库区城镇化背景下河流DOM的吸收及荧光光谱特征[J]. 环境科学,2019,40(12):5309 − 5317. [CHEN Zhaoyu,LI Siyue. Absorption and fluorescence spectra of dissolved organic matter in rivers of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area under the background of urbanization[J]. Environmental Science,2019,40(12):5309 − 5317. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Zhaoyu, LI Siyue. Absorption and fluorescence spectra of dissolved organic matter in rivers of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area under the background of urbanization[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(12): 5309 − 5317. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] HE Mengchang,WANG Xiangqin,WU Fengchang,et al. Antimony pollution in China[J]. Sci Total Environ,2012,421/422:41 − 50. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.009
[5] CAI Yongbing,MI Yuting,ZHANG Hua. Kinetic modeling of antimony(III) oxidation and sorption in soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2016,316:102 − 109. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.027
[6] GUO Wenjing,Fu Zhiyou,WANG Hao,et al. Environmental geochemical and spatial/temporal behavior of total and speciation of antimony in typical contaminated aquatic environment from Xikuangshan,China[J]. Microchemical Journal,2018,137:181 − 189. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2017.10.010
[7] 张菊梅,刘灵飞,龙健,等. 土壤锑污染及其修复技术研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术,2019,42(4):61 − 70. [ZHANG Jumei,LIU Lingfei,LONG Jian,et al. Research progress on soil antimony pollution and its remediation technology[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,42(4):61 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Jumei, LIU Lingfei, LONG Jian, et al. Research progress on soil antimony pollution and its remediation technology[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(4): 61 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] LI Gang,KHAN S,IBRAHIM M,et al. Biochars induced modification of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in soil and its impact on mobility and bioaccumulation of arsenic and cadmium[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,348:100 − 108. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.031
[9] DONG Lu,ZHANG Jian,GUO Zizhang,et al. Distributions and interactions of dissolved organic matter and heavy metals in shallow groundwater in Guanzhong Basin of China[J]. Environmental Research,2022,207:112099. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112099
[10] WANG Yuqing,LIU Jiang,LIEM-NGUYEN V,et al. Binding strength of mercury (II) to different dissolved organic matter:The roles of DOM properties and sources[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,807:150979. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150979
[11] KARIMIAN N,BURTON E D,JOHNSTON S G. Antimony speciation and mobility during Fe(II)-induced transformation of humic acid-antimony(V)-iron(III) coprecipitates[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,254:113112. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113112
[12] HEIER L S,MELAND S,LJONES M,et al. Short-term temporal variations in speciation of Pb,Cu,Zn and Sb in a shooting range runoff stream[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2010,408(11):2409 − 2417. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.02.019
[13] FAN Yurui,ZHENG Chunli,HUO Aidi,et al. Investigating the binding properties between antimony(V) and dissolved organic matter (DOM) under different pH conditions during the soil sorption process using fluorescence and FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2019,181:34 − 42. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.076
[14] 陈诗雨,李燕,李爱民. 溶解性有机物研究中三维荧光光谱分析的应用[J]. 环境科学与技术,2015,38(5):64 − 68. [CHEN Shiyu,LI Yan,LI Aimin. Application of three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy in the study of dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,38(5):64 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Shiyu, LI Yan, LI Aimin. Application of three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy in the study of dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 38(5): 64 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 黄爽兵,王焰新,曹菱,等. 包气带土壤DOM三维荧光表征及对砷污染的指示意义[J]. 地球科学,2012,37(3):605 − 611. [HUANG Shuangbing,WANG Yanxin,CAO Ling,et al. Characterization of DOM from soil in unsaturated zone and its implications on arsenic mobilization into groundwater[J]. Earth Science,2012,37(3):605 − 611. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Shuangbing, WANG Yanxin, CAO Ling, et al. Characterization of DOM from soil in unsaturated zone and its implications on arsenic mobilization into groundwater[J]. Earth Science, 2012, 37(3): 605 − 611. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王翔,罗艳丽,邓雯文,等. 新疆奎屯地区高砷地下水DOM三维荧光特征[J]. 中国环境科学,2020,40(11):4974 − 4981. [WANG Xiang,LUO Yanli,DENG Wenwen,et al. The 3D-EEM characteristics of DOM in high arsenic groundwater of Kuitun,Xinjiang[J]. China Environmental Science,2020,40(11):4974 − 4981. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.039
WANG Xiang, LUO Yanli, DENG Wenwen, et al. The 3D-EEM characteristics of DOM in high arsenic groundwater of Kuitun, Xinjiang[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(11): 4974 − 4981. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.039
[17] 李琬钰,周建伟,贾晓岑,等. 湖南锡矿山锑矿区水环境中DOM三维荧光特征及其对锑污染的指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(4):215 − 224. [LI Wanyu,ZHOU Jianwei,JIA Xiaocen,et al. EEMs characteristics of dissolved organic matter in water environment and its implications for antimony contamination in antimony mine of Xikuangshan,Hunan Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(4):215 − 224. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Wanyu, ZHOU Jianwei, JIA Xiaocen, et al. EEMs characteristics of dissolved organic matter in water environment and its implications for antimony contamination in antimony mine of Xikuangshan, Hunan Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 215 − 224. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 付胜云,邓蕾,唐分配,等. 湖南安化—桃江地区锑矿地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 金属矿山,2016(11):113 − 118. [FU Shengyun,DENG Lei,TANG Fenpei,et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting indicator of Sb deposit in Anhua-Taojiang Area,Hunan Province[J]. Metal Mine,2016(11):113 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2016.11.024
FU Shengyun, DENG Lei, TANG Fenpei, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting indicator of Sb deposit in Anhua-Taojiang Area, Hunan Province[J]. Metal Mine, 2016(11): 113 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2016.11.024
[19] FU Shanling,LAN Qing,YAN Jun. Trace element chemistry of hydrothermal quartz and its genetic significance:A case study from the Xikuangshan and Woxi giant Sb deposits in Southern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2020,126:103732. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103732
[20] ZHANG Zhaoxue,LU Yi,LI Haipu,et al. Assessment of heavy metal contamination,distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River,China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,645:235 − 243. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.026
[21] 刘文辉,马腾,李俊琦,等. 资江河口区农田土壤重金属污染评价及来源分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(2):138 − 146. [LIU Wenhui,MA Teng,LI Junqi,et al. Pollution assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in agricultural soil around Zijiang River Estuary[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(2):138 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Wenhui, MA Teng, LI Junqi, et al. Pollution assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in agricultural soil around Zijiang River Estuary[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 138 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] TAO Yanru,SU Hailei,LI Huixian,et al. Ecological and human health risk assessment of antimony (Sb) in surface and drinking water in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,318:128514. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128514
[23] Liu Huiji,Zeng Wei,He Mengchang,et al. Occurrence,distribution,and migration of antimony in the Zijiang River around a superlarge antimony deposit zone[J]. Environmental Pollution,2023,316:120520. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120520
[24] ZHOU Jianwei,NYIRENDA T M,XIE Lina,et al. Mine waste acidic potential and distribution of antimony and arsenic in waters of the Xikuangshan Mine,China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2017,77:52 − 61. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.04.010
[25] 唐雅宁,王兴华,王英男,等. 缺氧酸性条件下三价铁对锑释放的作用机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(6):175 − 183. [TANG Yaning,WANG Xinghua,WANG Yingnan,et al. Mechanism of action of Fe(Ⅲ) on antimony release under anoxic acidic conditions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(6):175 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TANG Yaning, WANG Xinghua, WANG Yingnan, et al. Mechanism of action of Fe(Ⅲ) on antimony release under anoxic acidic conditions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(6): 175 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 兰建梅,江涛,梅金华,等. 典型锑矿区地下水中锑污染年际变化特征和成因分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(5):192 − 202. [LAN Jianmei,JIANG Tao,MEI Jinhua,et al. Characterization and causes of interannual variation of antimony contamination in groundwater of a typical antimony mining area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(5):192 − 202. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LAN Jianmei, JIANG Tao, MEI Jinhua, et al. Characterization and causes of interannual variation of antimony contamination in groundwater of a typical antimony mining area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(5): 192 − 202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 仇存璞, 唐晓雪, 文喜贤, 等. 钙盐对秸秆腐解过程及产物可溶性有机质三维荧光光谱特征的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2023,43(7):2301 − 2307. [QIU. Cunpu, TANG Xiaoxue, WEN Xixian, et al. Effects of calcium salts on the decomposition process of straw and the characteristics of three-dimensional excitation-emission matrices of the dissolved organic matter in decomposition products[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2023,43(7):2301 − 2307. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
QIU. Cunpu, TANG Xiaoxue, WEN Xixian, et al. Effects of calcium salts on the decomposition process of straw and the characteristics of three-dimensional excitation-emission matrices of the dissolved organic matter in decomposition products[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2023, 43(7): 2301 − 2307. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] MAIE N,PARISH K J,WATANABE A,et al. Chemical characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen in an oligotrophic subtropical coastal ecosystem[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2006,70(17):4491 − 4506. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.06.1554
[29] HUGUET A,VACHER L,RELEXANS S,et al. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2009,40(6):706 − 719. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.03.002
[30] NEBBIOSO A,PICCOLO A. Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM):A critical review[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2013,405(1):109 − 124. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-6363-2
[31] 李秋华,林秋奇,韩博平. 广东大中型水库电导率分布特征及其受N、P营养盐的影响[J]. 生态环境,2005,14(1):16 − 20. [LI Qiuhua,LIN Qiuqi,HAN Boping. Conductivity distribution of water supply reservoirs in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2005,14(1):16 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Qiuhua, LIN Qiuqi, HAN Boping. Conductivity distribution of water supply reservoirs in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2005, 14(1): 16 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 国家环境保护总局,国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 地表水环境质量标准:GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京:中国环境科学出版社,2002. [State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China,General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental quality standards for surface water:GB 3838—2002[S]. Beijing:China Environmental Science Press,2002. (in Chinese)]
State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental quality standards for surface water: GB 3838—2002[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002. (in Chinese)
[33] 许青阳,戴亮亮,彭志刚,等. 湖南省龙山县土壤重金属特征与健康风险评价[J/OL]. 中国地质,(2023-08-15)[2023-10-06]. [XU Qingyang,DAI Liangliang,PENG Zhigang,et al. Characteristics and health risk evaluation of soil heavy metals in Longshan County,Hunan Province[J/OL]. Geology in China,(2023-08-15)[2023-10-06]. Https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20230815.1025.002.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Qingyang, DAI Liangliang, PENG Zhigang, et al. Characteristics and health risk evaluation of soil heavy metals in Longshan County, Hunan Province[J/OL]. Geology in China, (2023-08-15)[2023-10-06]. Https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20230815.1025.002.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] STEDMON C A,MARKAGER S. Resolving the variability in dissolved organic matter fluorescence in a temperate estuary and its catchment using PARAFAC analysis[J]. Limnology and Oceanography,2005,50(2):686 − 697. doi: 10.4319/lo.2005.50.2.0686
[35] OSBURN C L,HANDSEL L T,MIKAN M P,et al. Fluorescence tracking of dissolved and particulate organic matter quality in a river-dominated estuary[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2012,46(16):8628 − 8636.
[36] CORY R M,MCKNIGHT D M. Fluorescence spectroscopy reveals ubiquitous presence of oxidized and reduced quinones in dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2005,39(21):8142 − 8149.
[37] HUDSON N,BAKER A,REYNOLDS D. Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural,waste and polluted waters:A review[J]. River Research and Applications,2007,23(6):631 − 649. doi: 10.1002/rra.1005
[38] 马志强,胥思勤,彭刚毅,等. 富里酸对金属Sb(Ⅲ)的吸附作用研究[J]. 应用化工,2020,49(9):2190 − 2194. [MA Zhiqiang,XU Siqin,PENG Gangyi,et al. Study on the adsorption of fulvic acid to metal Sb(Ⅲ)[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2020,49(9):2190 − 2194. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.09.011
MA Zhiqiang, XU Siqin, PENG Gangyi, et al. Study on the adsorption of fulvic acid to metal Sb(Ⅲ)[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(9): 2190 − 2194. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.09.011
[39] 梁梦钰,郭华明,李晓萌,等. 贵德盆地三河流域高砷地下水中溶解性有机物三维荧光特性及其指示意义[J]. 地学前缘,2019,26(3):243 − 254. [LIANG Mengyu,GUO Huaming,LI Xiaomeng,et al. Excitation-emission matrix spectroscopic characteristics of dissolved organic matters and the significance in high arsenic groundwater research in the Guide Basin,China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2019,26(3):243 − 254. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIANG Mengyu, GUO Huaming, LI Xiaomeng, et al. Excitation-emission matrix spectroscopic characteristics of dissolved organic matters and the significance in high arsenic groundwater research in the Guide Basin, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(3): 243 − 254. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: