Mechanism and causal analysis on the Yahuokou landslide reactivation and causes (Zhouqu County, Gansu, China)
-
摘要:
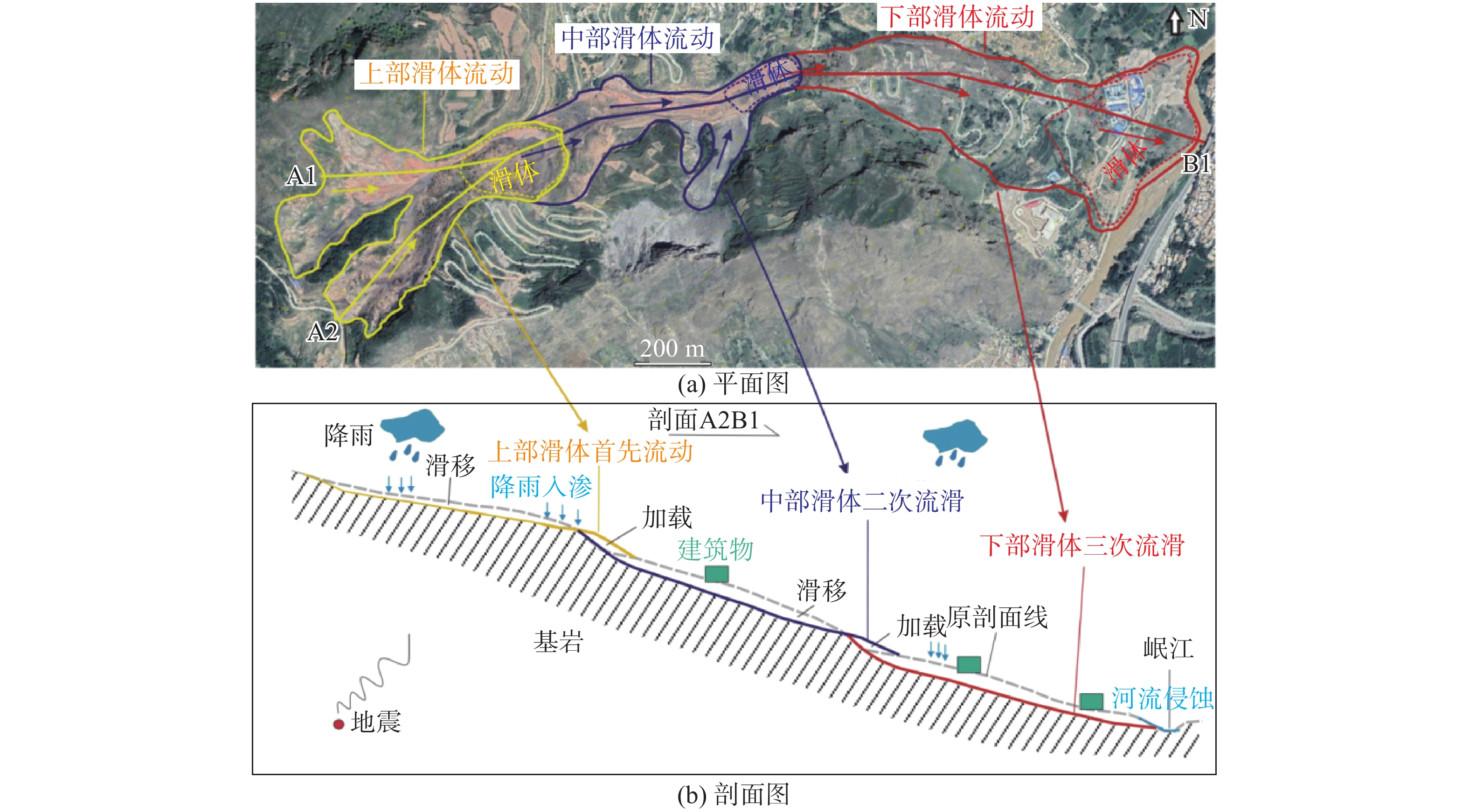
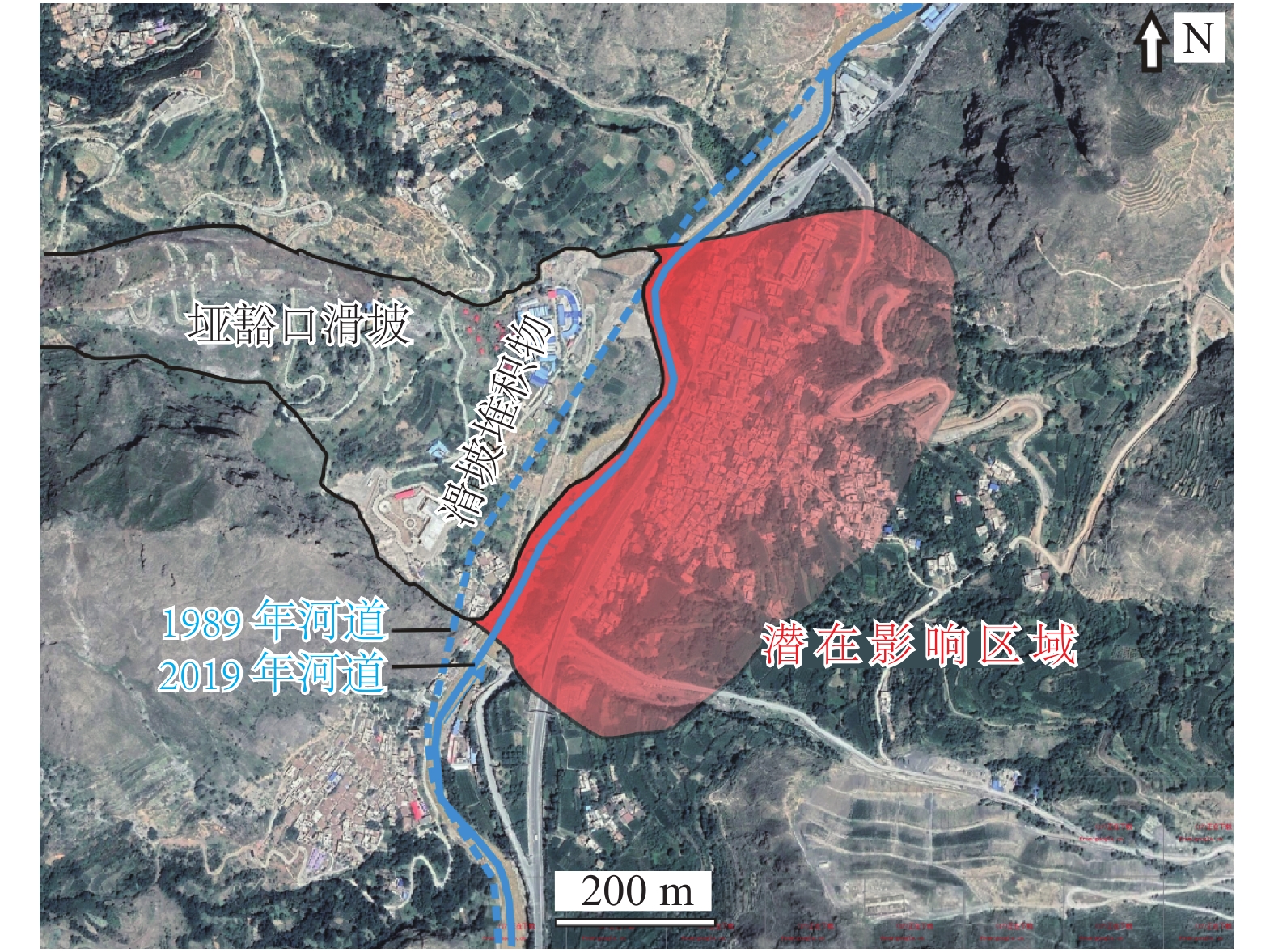
2019年7月19日18时许,甘肃舟曲县垭豁口滑坡复活,约3.92×106 m3的滑体顺坡而下,迅速流入岷江,堵塞河道,造成河道水位上升,江边公路中断,滑坡变形持续至8月中旬。基于野外勘察、遥感解译、钻孔勘探等方法获取了滑坡变形的基本特征,并开展了滑坡监测工作,并结合气象资料,探讨了该滑坡复活原因及启动机制。初步研究认为,该滑坡为降雨诱发。通过对滑坡变形历史进行梳理,结合滑带证据,滑坡复活机理可概括为:首先上部块体缓慢蠕变,降雨后发生塑性流滑;其次,因上部滑体堆积在滑坡中部,造成中部平台堆载,引发中部滑体变形;最终一滑而下,刮产连带下部滑体坠入河道。滑坡的上中下三部分滑体逐步被激活,最初缓慢变形,随后加速启动。滑坡变形模式为蠕滑—拉裂—流滑。对滑坡变形过程和机理的初步判断为滑坡灾害应急处置提供了科学依据。
Abstract:The report described a recent landslide happened in Zhouqu Country, China. At 18: 00 pm Beijing time, on July 19, 2019, the Yahuokou landslide was reactivated, about 3.92 × 106 m3 of debris slumped from the slope caused Minjiang River channel blockage, water level rise, and road interruption. Fortunately, nobody was injured. In order to seek the geomorphologic and stratigraphic characteristics, the reactivated causes and the dynamics mechanism of the landslide, field survey, remote sensing image, drilling prospecting, landslide monitoring and rainfall data analysis were conducted. The outlook of the landslide event was given. Evidences of the sliding zone indicated the landslide is a flow-slide deformation pattern. The landslide mechanism is summarized as: firstly, slow plastic flow-slide occurred in the upper sliding body. Then the platform in the middle gentle slope was preloaded by the post upper part failure deposits, resulting in the “cutting and filling” effect. The failure form is creep-tension cracks-debris flow-slide. At last, the block on the lower part slumped. Specifically, the upper, middle and lower parts of the landslide all transferred stress in this mode, being activated step by step, and slowly slumped into the river.
-
Key words:
- Yahuokou landslide /
- Zhouqu County /
- slumped /
- flow slid
-

-
表 1 垭豁口滑坡变形破坏事件统计
Table 1. Approximate timeline of slope deformation and failure at the Yahuokou landslide
时间轴 垭豁口滑坡活动特征 1989年 滑坡首次滑动,堵塞河道形成堰塞湖 2019-07-16 斜坡中部可见20 cm裂缝,并且该部位30 m的下部土方松动。 2019-07-17 在斜坡下部的路面上可见22 cm的裂缝 2019-07-18 道路塌陷,滑体向前移动约20 m,堆积宽度约30 m。 2019-07-19 滑坡再次发生。在中间部分,滑体向前推动45 m,宽度为50 m。一条300 m长的公路在滑坡的前缘被毁。滑坡体积约
3.92×106 m3,主体距岷江100 m。2019-07-20 滑体又向下推动了10 m,道路周围的农田都发生变形。 2019-07-21 安装了滑坡监测仪器(图3) 2019-08-09—12 滑坡仍在变形。滑坡体处于连续滑动状态,前缘变形区向岷江扩展。 2019-08-14—16 滑坡前缘和中部裂隙增大、变宽,隆起高度增大,偶有碎块落入河中。山体滑坡的松散堆积物坠入河中堵塞宽度约4~8.5 m,部分河道窄至4.8 m。河道上下游水位差约0.4 m,河床略有抬升。 -
[1] 郭长宝, 任三绍, 李雪, 等. 甘肃舟曲南峪江顶崖古滑坡发育特征与复活机理[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(1):206 − 217. [GUO Changbao, REN Sanshao, LI Xue, et al. Development characteristics and reactivation mechanism of the Jiangdingya ancient landslide in the Nanyu town, Zhouqu County, Gansu Province[J]. Geoscience,2019,33(1):206 − 217. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张永双, 吴瑞安, 郭长宝, 等. 古滑坡复活问题研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2018,33(7):728 − 740. [ZHANG Yongshuang, WU Ruian, GUO Changbao, et al. Research progress and prospect on reactivation of ancient landslides[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2018,33(7):728 − 740. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.07.0728
[3] 吴玮江, 王念秦. 甘肃滑坡灾害[M]. 兰州: 兰州大学出版社, 2006.
WU Weijiang, WANG Nianqin. Landslide hazards in Gansu[M]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University Press, 2006. (in Chinese).
[4] 王立朝, 温铭生, 冯振, 等. 中国西藏金沙江白格滑坡灾害研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):1 − 9. [WANG Lichao, WEN Mingsheng, FENG Zhen, et al. Researches on the baige landslide at Jinshajiang river, Xizang, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张卫雄, 翟向华, 丁保艳, 等. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖滑坡成因分析与综合治理措施[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):7 − 14. [ZHANG Weixiong, ZHAI Xianghua, DING Baoyan, et al. Causative analysis and comprehensive treatment of the Jiangdingya Landslide in Zhouqu County of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):7 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] WANG L M, WU Z J, WANG P, et al. Characteristics, causation, and rehabilitation of Zhouqu extraordinarily serious debris flows in 2010, China[J]. Journal of Central South University,2013,20(8):2342 − 2348. doi: 10.1007/s11771-013-1742-1
[7] WANG G L. Lessons learned from protective measures associated with the 2010 Zhouqu debris flow disaster in China[J]. Nat Hazards,2013,69:1835 − 1847. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0772-1
[8] XIAO H J, LUO Z D, NIU Q G, et al. The 2010 Zhouqu mudflow disaster: possible causes, human contributions, and lessons learned[J]. Natural Hazards,2013,67(2):611 − 625. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0592-3
[9] 赵俊华. 舟曲县滑坡泥石流遥感影像判读与灾害防治[J]. 人民长江,2004,35(12):1 − 2. [ZHAO Junhua. Remote sensing image interpretation of landslide and mud-rock flow in Zhouqu County and disaster prevention[J]. Yangtze River,2004,35(12):1 − 2. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2004.12.001
[10] 姜鑫, 滕鸿伟, 冯娟. 舟曲县峰迭乡水泉沟西南滑坡成因机制及稳定性分析[J]. 长春工程学院学报(自然科学版),2015(3):84 − 88. [JIANG Xin, TENG Hongwei, FENG Juan. The genesis mechanism and stability analysis of the southwest landslide in Shuiquangou Fengdie of Zhouqu[J]. Journal of Changchun Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2015(3):84 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 焦赟, 王国亚. 地震荷载对滑坡稳定性的影响评估—以甘肃舟曲南桥滑坡为例[J]. 冰川冻土,2013,35(3):692 − 700. [JIAO Yun, WANG Guoya. The impact assessment of earthquake on landslide stability: A case study of landslides in Nanqiao village, Zhouqu, Gansu[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2013,35(3):692 − 700. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 李文彦, 张媛, 韩鑫, 等. 舟曲锁儿头滑坡裂缝变形特征研究[J]. 人民长江,2013,44(3):33 − 35. [LI Wenyan, ZHANG Yuan, HAN Xin, et al. Research on deformation characteristics of cracks in Suo'ertou landslide in Zhouqu[J]. Yangtze River,2013,44(3):33 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2013.03.009
[13] 宋丙辉, 谌文武, 吴玮江, 等. 甘肃舟曲泄流坡滑坡滑带土的抗剪强度特性[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2011,47(6):7 − 12. [SONG Binghui, CHEN Wenwu, WU Weijiang, et al. Shear strength characteristics of soil in the slide zone of Xieliupo landslide in Zhouqu, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2011,47(6):7 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 侯圣山, 李昂, 陈亮, 等. 基于普适型仪器的滑坡监测预警初探—以甘肃兰州岷县三处滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):47 − 53. [HOU Shengshan, LI Ang, CHEN Liang, et al. Application of universal geo-hazard monitoring instruments in landslides and early warning of three landslides in Gansu Province: a case study in Minxian County and Lanzhou City of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):47 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 卫童瑶, 殷跃平, 高杨, 等. 三峡库区巫山县塔坪H1滑坡变形机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):73 − 81. [WEI Tongyao, YIN Yueping, GAO Yang, et al. Deformation mechanism of the Taping H1 landslide in Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):73 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 刘兴旺, 袁道阳, 邵延秀, 等. 甘肃迭部—白龙江南支断裂中东段晚第四纪构造活动特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2015,37(6):111 − 119. [LIU Xingwang, YUAN Daoyang, SHAO Yanxiu, et al. Characteristics of late quaternary tectonic activity in the middle-eastern segment of the southern branch of Diebu-Bailongjiang fault, Gansu[J]. Journal of Earch Sciences and Environment,2015,37(6):111 − 119. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2015.06.010
[17] 任进舟. 南峪滑坡与小震活动[J]. 西北地震学报,1993(2):94 − 96. [REN Jinzhou. The Nanyu landslip and small earthquake activity[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,1993(2):94 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 黄晓, 杨为民, 张春山, 等. 舟曲泄流坡滑坡变形特征及其形成机理[J]. 地质力学学报,2013,19(2):178 − 187. [HUANG Xiao, YANG Weimin, ZHANG Chunshan, et al. Deformation characteristics and formation mechanism of xieliupo landslide in Zhouqu[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2013,19(2):178 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2013.02.007
[19] 杜国梁, 张永双, 高金川, 等. 基于GIS的白龙江流域甘肃段滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质力学学报,2016,22(1):1 − 11. [DU Guoliang, ZHANG Yongshuang, GAO Jinchuan, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on gis in Bailongjiang watershed, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2016,22(1):1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.01.001
[20] 李绍红, 朱建东, 王少阳, 等. 考虑降雨类型的基岩型浅层边坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):131 − 135. [LI Shaohong, ZHU Jiandong, WANG Shaoyang, et al. Stability analysis methods for the bedrock shallow slope considering rainfall types[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(2):131 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: