Study on risk assessment of geological hazards in Huizhou District, Huangshan City, Anhui Province
-
摘要:
皖南山区是安徽省地质灾害高发区域。本文选取黄山市徽州区为研究区,根据区内地形地貌和地质构造特点,选取了高程、坡度、坡向、断裂构造、水系、土地覆盖类型、工程地质岩组、人类活动强度等8项致灾因子作为地质灾害危险性评价指标。结合地质灾害野外实地调查成果,采用信息量模型法对研究区进行地质灾害危险性评价,探索建立适合皖南山区的地质灾害危险性评价模型。
Abstract:The mountainous area in southern Anhui Province is a high incidence area of geological disasters. This paper chooses Huizhou District of Huangshan City as the research area. According to the characteristics of landform and geological structure, eight impact factors, including elevation, slope, slope direction, fault structure, water system, land cover type, engineering geological rock formation and human activity intensity, were selected as the risk assessment indexes of geological disaster. Combined with the field survey results of geological disasters, the risk assessment of geological hazard in the study area was carried out by the method of information quantity model. A geological hazard assessment model suitable for the southern Anhui mountains was established.
-

-
表 1 高程分级及信息量统计表
Table 1. Satistics of elevation classification and information
评价指标 高程分级/m Si/S Ni/N 信息量I 数据 0~200 0.0732 0.0526 −0.3303 200~300 0.1717 0.1383 −0.2164 300~400 0.1967 0.3027 0.4310 400~500 0.2024 0.2355 0.1514 500~700 0.2475 0.2051 −0.1882 700~1300 0.1085 0.0659 −0.4984 表 2 坡度分级及信息量统计表
Table 2. Satistics of slope classification and information
评价指标 坡度分级/(°) Si/S Ni/N 信息量I 数据 0~10 0.0951 0.0173 −1.7023 10~20 0.1798 0.1207 −0.3985 20~30 0.3081 0.3682 0.1780 30~40 0.3071 0.3955 0.2530 40~50 0.1075 0.0966 −0.1066 50~90 0.0025 0.0017 −0.3454 表 3 坡向分级及信息量统计表
Table 3. Satistics of slope classification and information
评价指标 坡向分级/(°) Si/S Ni/N 信息量I 数据 315~45 0.1761 0.1494 −0.1644 45~135 0.2890 0.3008 0.0399 135~225 0.2646 0.2808 0.0592 225~315 0.2703 0.2691 −0.0045 表 4 断裂分级及信息量统计表
Table 4. Satistics of fracture classification and information
评价指标 断裂分级/m Si/S Ni/N 信息量I 数据 0~300 0.3637 0.5310 0.3785 300~600 0.2541 0.2833 0.1087 600~1000 0.2042 0.1406 −0.3731 1000~1500 0.1146 0.0287 −1.3833 >1500 0.0636 0.0164 −1.3550 表 5 水系密度分级及信息量统计表
Table 5. Satistics of the river system density classification and information
评价指标 水系密度分级/(km−1) Si/S Ni/N 信息量I 数据 0~1.4052 0.7717 0.7523 −0.0255 1.4052~2.8695 0.1552 0.1689 0.0850 2.8695~6.2644 0.0731 0.0788 0.0745 表 6 各土地利用类型信息量统计表
Table 6. Statistical table of information quantity of land use types
评价指标 用地分级 Si/S Ni/N 信息量I 数据 道路 0.0105 0.0168 0.4742 耕地 0.1030 0.0956 −0.0753 城镇用地 0.0186 0.0231 0.2168 水域 0.0114 0.0119 0.0493 林地 0.7650 0.7154 −0.0671 茶园 0.0915 0.1372 0.4049 表 7 各工程地质岩组信息量统计表
Table 7. Statistical table of information of each engineering geological rock formation
评价指标 工程地质岩组分级 Si/S Ni/N 信息量I 数据 NH1x 0.1644 0.1429 −0.1404 PT2n 0.2790 0.2198 −0.2385 PT2d 0.4122 0.4889 0.1706 γδ 0.1105 0.0852 −0.2601 Q4 0.0065 0.0056 −0.1358 Qdl+el 0.0225 0.0523 0.8421 强风化层 0.0006 0.0011 0.6807 Qapl 0.0043 0.0036 −0.1669 表 8 人类活动强度分级及信息量统计表
Table 8. Satistics of human activity intensity classification and information
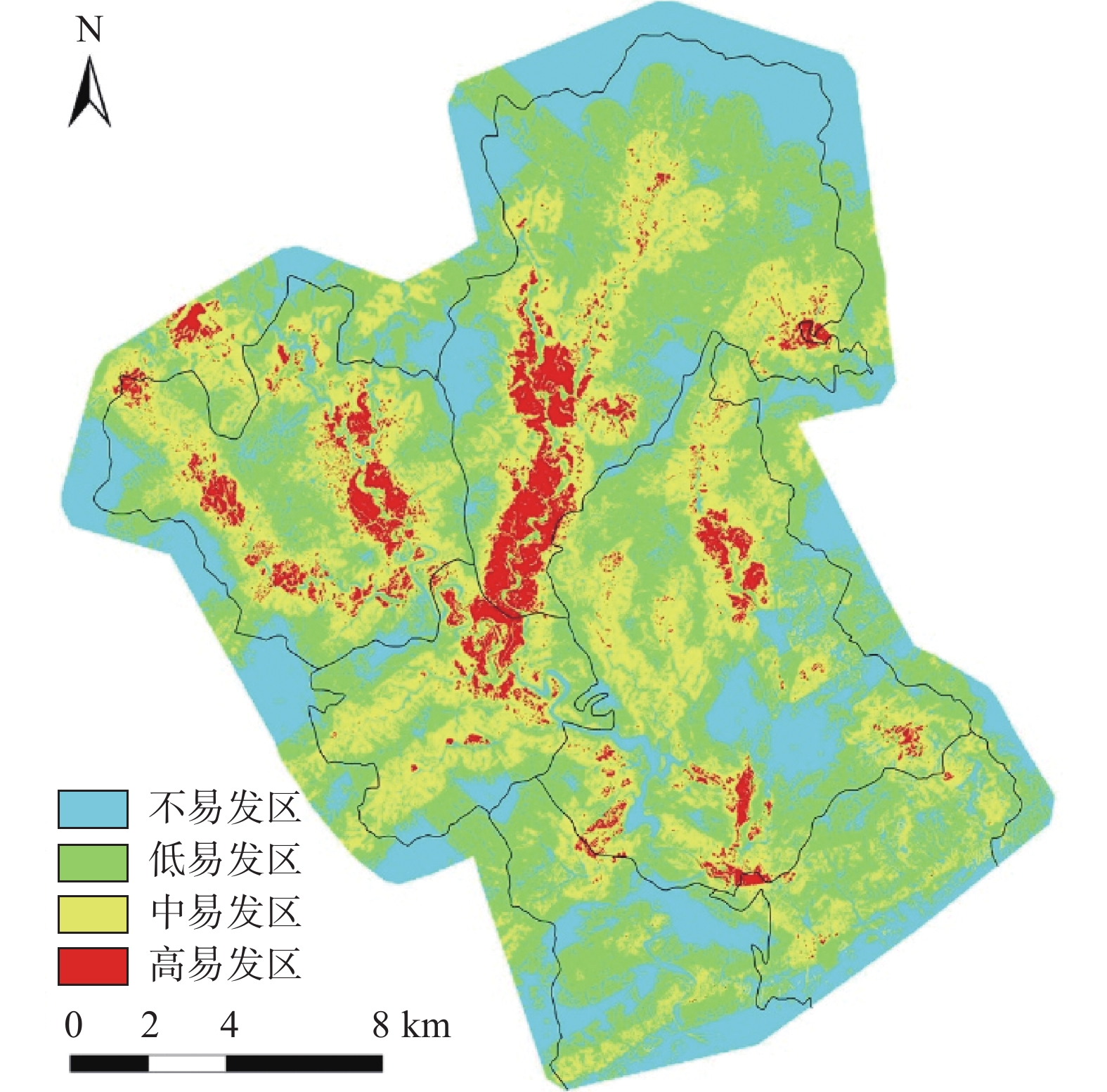
评价指标 人类活动分级 Si/S Ni/N 信息量I 数据 0~1.4185 0.4642 0.2406 −0.6569 1.4185~4.5309 0.3624 0.3496 −0.0362 4.5309~5.8821 0.0850 0.1530 0.5878 5.8821~12.2955 0.0884 0.2335 0.9712 表 9 地质灾害危险度分区面积统计表
Table 9. Statistical table of geological hazard area
危险度分区 信息量 分区面积/km2 不易发区 −4.732721~−1.18 104.49 低易发区 −1.18~−0.03 157.78 中易发区 −0.03~1.26 116.35 高易发区 1.26~3.449854 19.86 表 10 不同危险度分区内地质灾害点数量统计表
Table 10. Statistical table of the number of geological disaster points in different risk zones
易发区分类 分区面积/km2 地质灾害点数量/个 不易发区 104.49 0 低易发区 157.78 3 中易发区 116.35 80 高易发区 19.86 132 -
[1] 郑建中, 邹正明. 皖南山区环境地质特征与滑坡地质灾害防治[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2006,29(1):102 − 105. [ZHENG Jianzhong, ZOU Zhengming. Environmental geological characteristics of the mountain area of southern Anhui Province and treatment of geological disasters due to landslide[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science),2006,29(1):102 − 105. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 魏国灵, 金云龙, 邱锦安, 等. 粤东陆河县地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):51 − 56. [WEI Guoling, JIN Yunlong, QIU Jinan, et al. Susceptibility assessment of geological hazard in Luhe County of eastern Guangdong[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):51 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 罗大游, 温兴平, 张皓楠, 等. 基于GIS的元谋县地质灾害地貌特征研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2019,30(2):97 − 100. [LUO Dayou, WEN Xingping, ZHANG Haonan, et al. Study on geomorphological characteristics of geological hazards in Yuanmou County based on GIS[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2019,30(2):97 − 100. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2019.02.017
[4] 孙健, 陶慧, 杨世伟, 等. 皖南山区地质灾害发育规律与防治对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2011,38(5):98 − 101. [SUN Jian, TAO Hui, YANG Shiwei, et al. Development characteristics and prevention measures of geological hazards in mountain area of southern Anhui Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2011,38(5):98 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张波, 石长柏, 肖志勇, 等. 基于GIS和加权信息量的湖北鄂州地质灾害易发性区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(3):101 − 107. [ZHANG Bo, SHI Changbai, XIAO Zhiyong, et al. Geologic hazards susceptibility assessment in E'zhou City of Hubei Province based on GIS and weighted information value[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(3):101 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 周静静, 张晓敏, 赵法锁, 等. 陕南秦巴山区地质灾害危险性评价研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2019,25(4):544 − 553. [ZHOU Jingjing, ZHANG Xiaomin, ZHAO Fasuo, et al. Research on risk assessment of geological hazards in Qinling-Daba mountain area, south Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2019,25(4):544 − 553. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.04.053
[7] 张超, 田运涛, 张宇飞. 甘肃陇南石鸡坝乡幅地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2019,38(7):83 − 89. [ZHANG Chao, TIAN Yuntao, ZHANG Yufei. Geo-hazard risk assessment in Shijiba Town at Longnan area in Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Sciences),2019,38(7):83 − 89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 孙健, 吴超纲, 刘钦, 等. 黄山市徽州区坡面泥石流形成机理研究[J]. 中文科技期刊数据库(文摘版)自然科学,2016(3):148 − 149. [SUN Jian, WU Chaogang, LIU Qin, et al. Study on the formation mechanism of debris flow on the slope in Huizhou District, Huangshan City[J]. Chinese Journal of Science and Technology Database (Abstract Edition) Natural Science,2016(3):148 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 施成艳, 鹿献章, 刘中刚. 基于GIS的安徽黄山市徽州区地质灾害易发性区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(1):136 − 140. [SHI Chengyan, LU Xianzhang, LIU Zhonggang. GIS-based zoning of geological hazard's susceptibility in Huizhou District of Huangshan City of Anhui Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2016,27(1):136 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 邱海军, 崔鹏, 王彦民, 等. 基于关联维数的黄土滑坡空间分布结构及其成因分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(3):546 − 555. [QIU Haijun, CUI Peng, WANG Yanmin, et al. Spatial distribution structure of loess landslides and cause analysis based on correlated fractal dimension[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(3):546 − 555. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 樊芷吟, 苟晓峰, 秦明月, 等. 基于信息量模型与Logistic回归模型耦合的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(2):340 − 347. [FAN Zhiyin, GOU Xiaofeng, QIN Mingyue, et al. Information and logistic regression models based coupling analysis for susceptibility of geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(2):340 − 347. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 许英姿, 卢玉南, 李东阳, 等. 基于GIS和信息量模型的广西花岗岩分布区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(4):693 − 703. [XU Yingzi, LU Yunan, LI Dongyang, et al. GIS and information model based landslide susceptibility assessment in granite area of Guangxi Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(4):693 − 703. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王雷, 吴君平, 赵冰雪, 等. 基于GIS和信息量模型的安徽池州地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):96 − 103. [WANG Lei, WU Junping, ZHAO Bingxue, et al. Susceptibility assessment of geohazards in Chizhou City of Anhui Province based on GIS and informative model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王齐鑫, 王龙平, 王泽宇. 安徽阜阳中心城区地面沉降灾害风险评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(4):32 − 39. [WANG Qixin, WANG Longping, WANG Zeyu. Risk assessment of land subsidence in central area of Fuyang City, Anhui Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(4):32 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 方然可, 刘艳辉, 苏永超, 等. 基于逻辑回归的四川青川县区域滑坡灾害预警模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):181 − 187. [FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, SU Yongchao, et al. A early warning model of regional landslide in Qingchuan County,Sichuan Province based on logistic regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):181 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 郭伟, 王晨辉, 李鹏, 等. 基于LoRa的地质灾害分布式实时监测系统设计[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):107 − 113. [GUO Wei, WANG Chenhui, LI Peng, et al. Design of the distributed real-time monitoring system for geological hazards based on LoRa[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):107 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张茂省. 发挥新型举国体制优势提高地质灾害防治能力[J]. 西北地质,2019,52(2):Ⅰ − Ⅱ. [ZHANG Maosheng. Maximising the advantages of the new national system for improving the ability to prevent and mitigate geological disasters[J]. Northwestern Geology,2019,52(2):Ⅰ − Ⅱ. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张茂省, 薛强, 贾俊, 等. 山区城镇地质灾害调查与风险评价方法及实践[J]. 西北地质,2019,52(2):125 − 135. [ZHANG Maosheng, XUE Qiang, JIA Jun, et al. Ethods and practices for the investigation and risk assessment of geo-hazards in mountainous towns[J]. Northwestern Geology,2019,52(2):125 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 刘畅, 张平松, 杨为民, 等. 税湾地震黄土滑坡的岩土动力特性及其稳定性评价[J]. 西北地质,2020,53(4):176 − 185. [LIU Chang, ZHANG Pingsong, YANG Weimin, et al. Geotechnical dynamic characteristics and stability evaluation of loess landslides in Shuiwan Earthquake, Tianshui, Gansu[J]. Northwestern Geology,2020,53(4):176 − 185. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: