Analysis on the evolution law of creep-fatigue failure energy of deep anchored jointed rock mass
-
摘要:
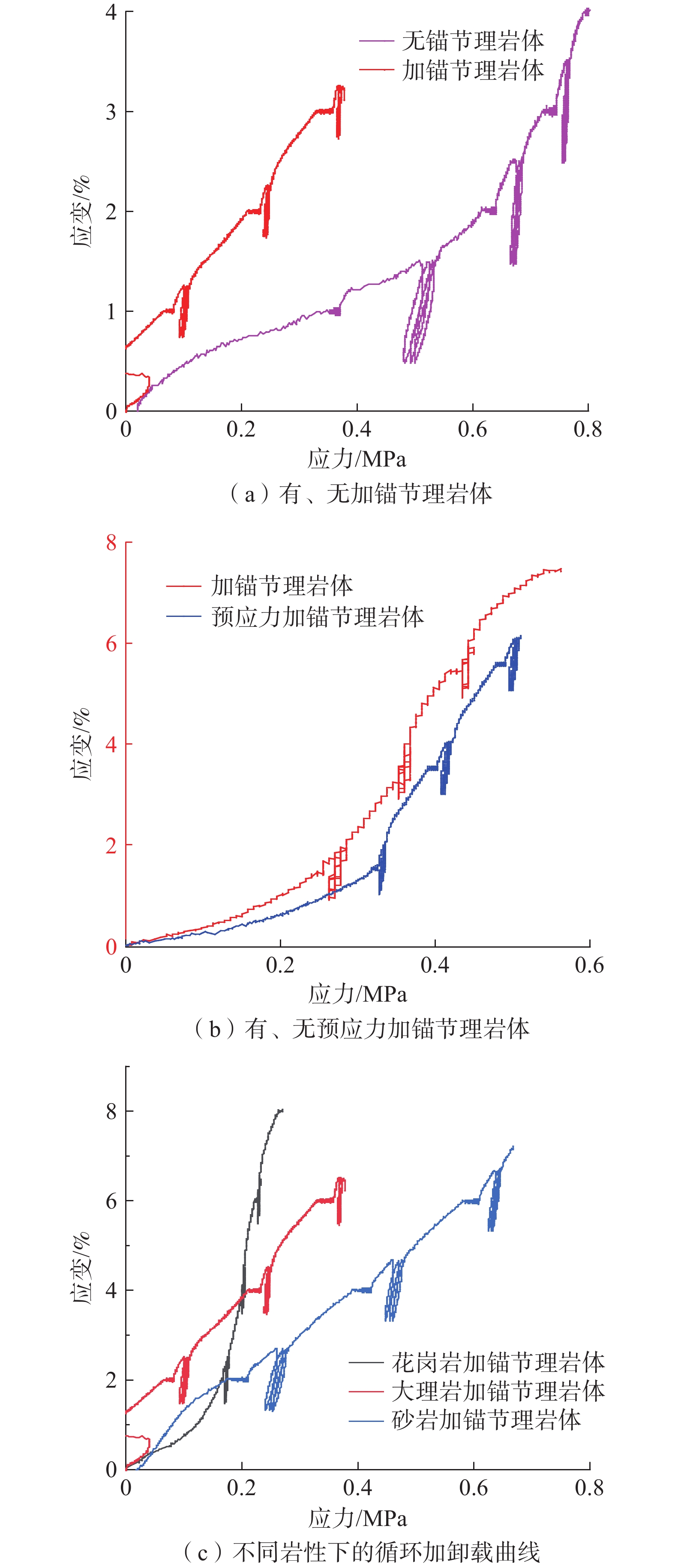
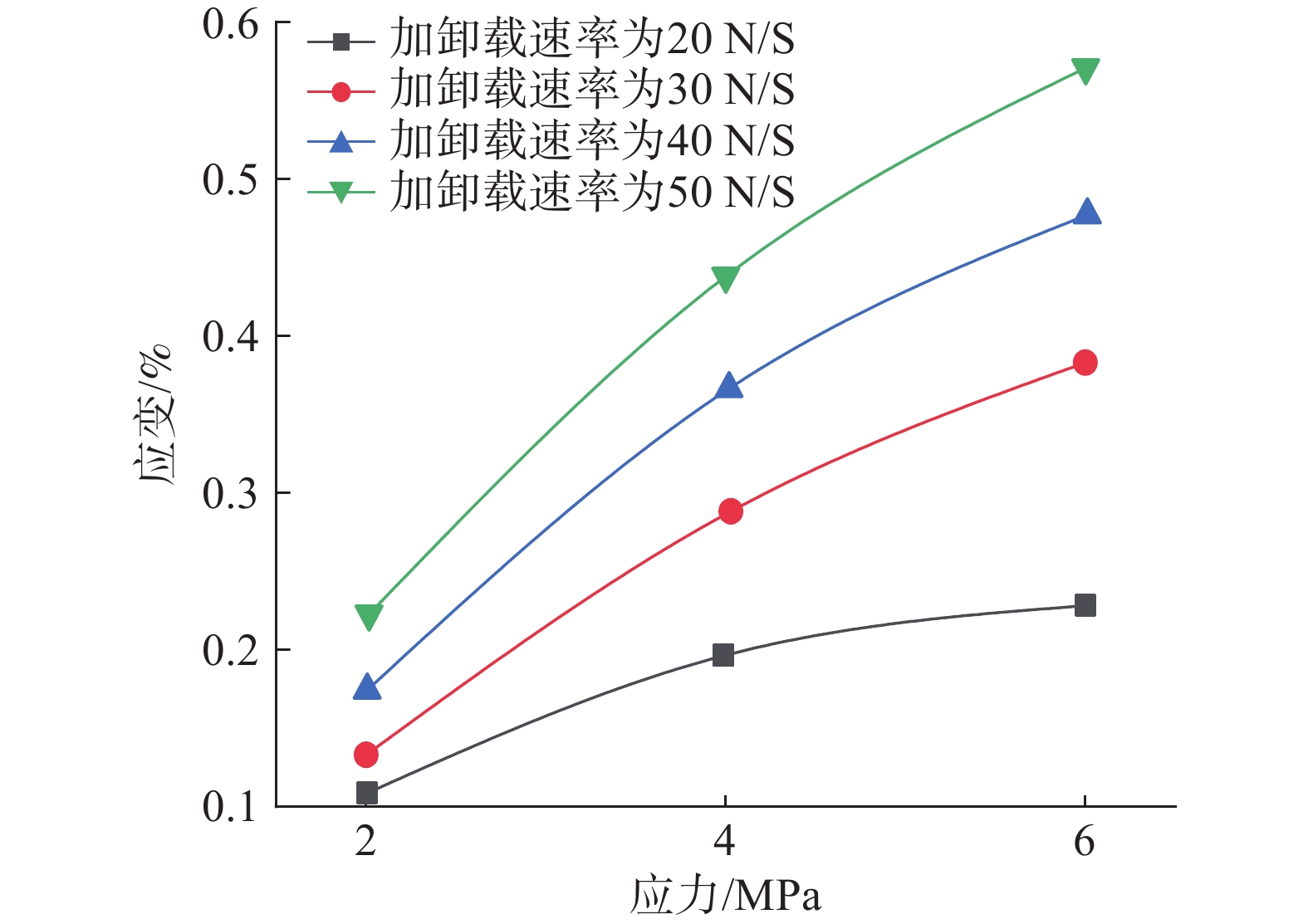
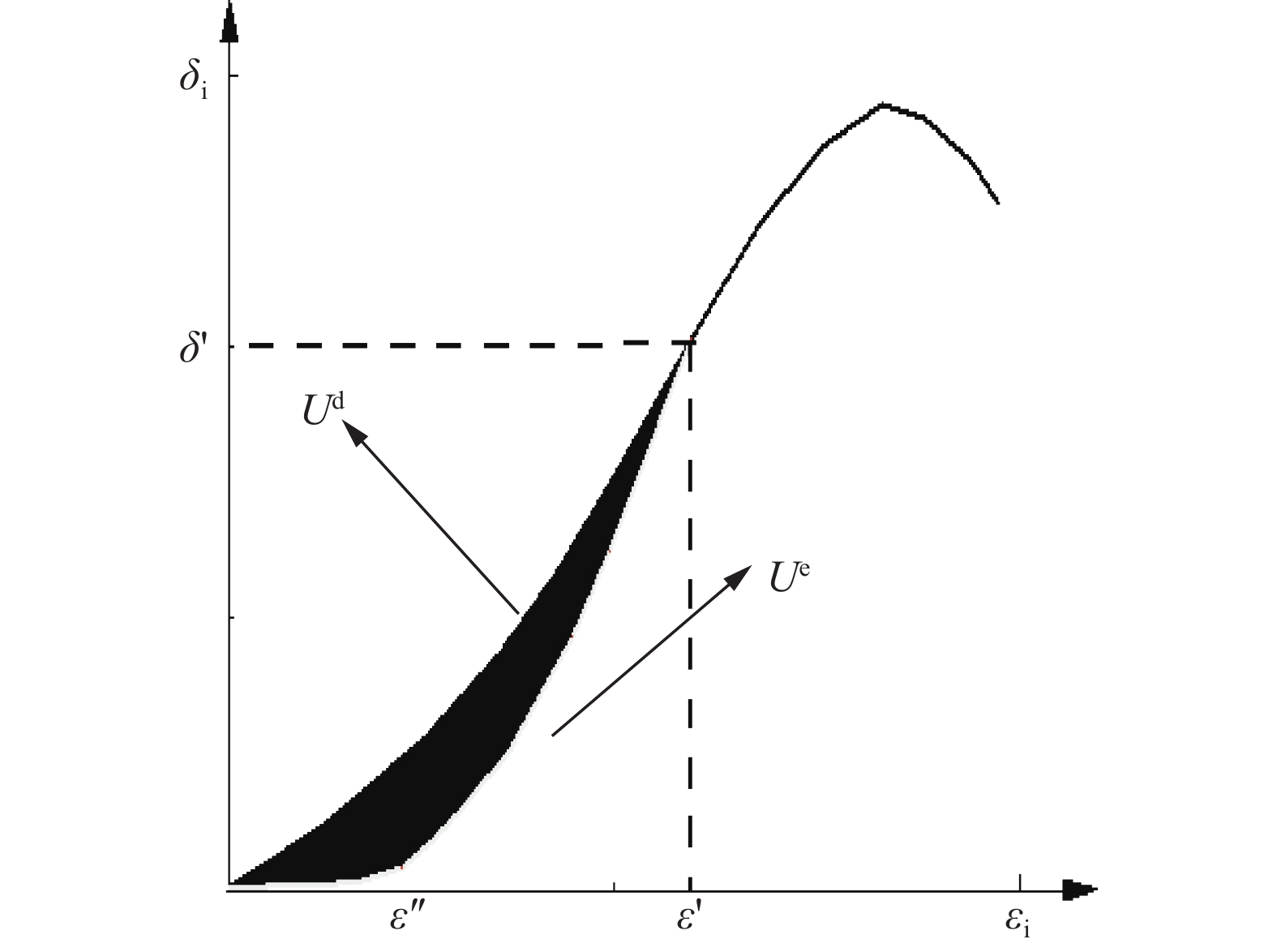
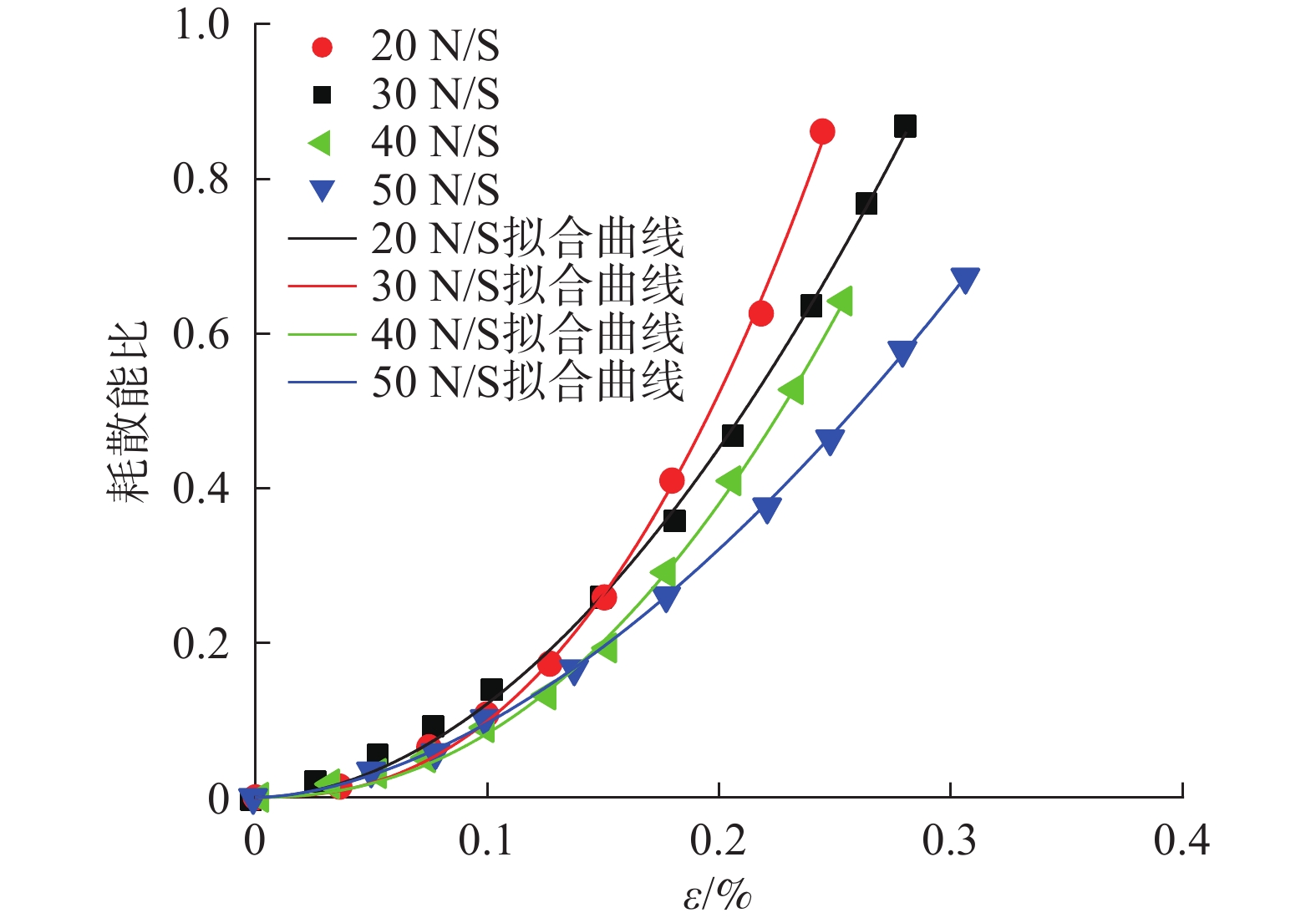
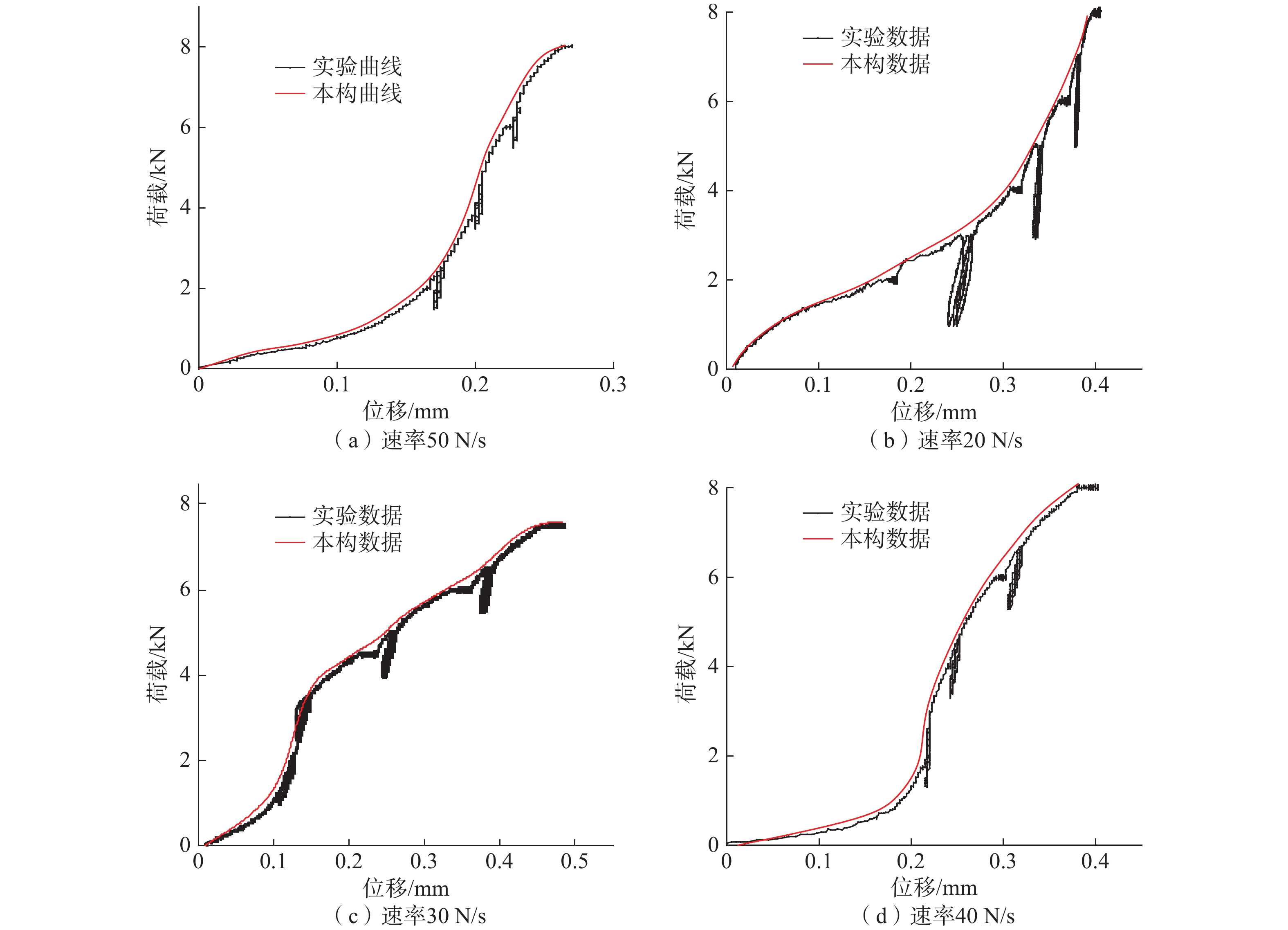
为探究深部岩体在爆破、开挖等扰动荷载下的力学特性,开展锚固岩体在蠕变-疲劳荷载下的室内试验,并进一步探究其能量演化规律。结果表明:(1)在疲劳荷载作用下,加锚节理岩体比无锚条件下的滞回环面积小,在施加预应力时,其滞回环面积又大幅度减少,说明加锚预应力能有效降低其能量损耗;(2)岩石强度越高,其滞回环面积越小,对应的能量耗散越小,反之能量耗散大;(3)对比不同加卸载速率可知:在每一级循环荷载过程中,加卸载速率越大其对应的应变值、切线斜率就越大。考虑加卸载速率对节理岩体劣化作用,依据应变等价原理,得出节理岩体峰值损伤本构方程,并通过试验验证模型的准确性,为深部岩体结构支护提供思路。
Abstract:In order to explore the mechanical properties of deep rock masses under disturbance loads such as blasting and excavation, laboratory tests of anchored rock masses under creep-fatigue loads were carried out, and the law of energy evolution was further explored. The results show that: (1) Under the action of fatigue load, the area of the anchored jointed rock mass is smaller than the of the unanchored condition. When prestress is applied, the hysteresis area of the jointed rock mass is greatly reduced, indicating that the anchored prestress can effectively reduce its energy loss. (2) The higher the rock strength, the smaller the hysteresis loop area, the smaller the corresponding energy dissipation. Conversely, the lower the rock strength, the larger the hysteresis loop area and the larger the corresponding energy dissipation. (3) Comparing different loading and unloading rates, experimental results show that during each level of cyclic loading, the greater the loading and unloading rate, the greater the corresponding strain value and tangent slope. Considering the effect of loading and unloading rate on the deterioration of jointed rock masses, based on the principle of strain equivalence, the peak damage constitutive equation of jointed rock masses is obtained, and the accuracy of the model is verified through experiments, which provides ideas for deep rock structure support.
-
Key words:
- shear creep /
- hysteresis area /
- loading unloading rate /
- energy loss /
- damage constitutive equation
-

-
表 1 不同岩性的能量值
Table 1. Energy values of different lithologies
岩性 工况 岩石吸收的能量 弹性应变能 消耗能 耗能比 花岗岩 无锚 0.0756 0.0205 0.0551 0.729 加锚 0.1152 0.0758 0.0394 0.342 预应力 0.1903 0.1208 0.0595 0.313 大理岩 无锚 0.0604 0.0198 0.0406 0.672 加锚 0.0955 0.0543 0.0412 0.431 预应力 0.1705 0.1028 0.0677 0.397 砂岩 无锚 0.0463 0.0138 0.0325 0.702 加锚 0.0963 0.0459 0.0504 0.523 预应力 0.1620 0.0866 0.0754 0.465 表 2 拟合曲线的相关参数
Table 2. Related parameters of fitting curve
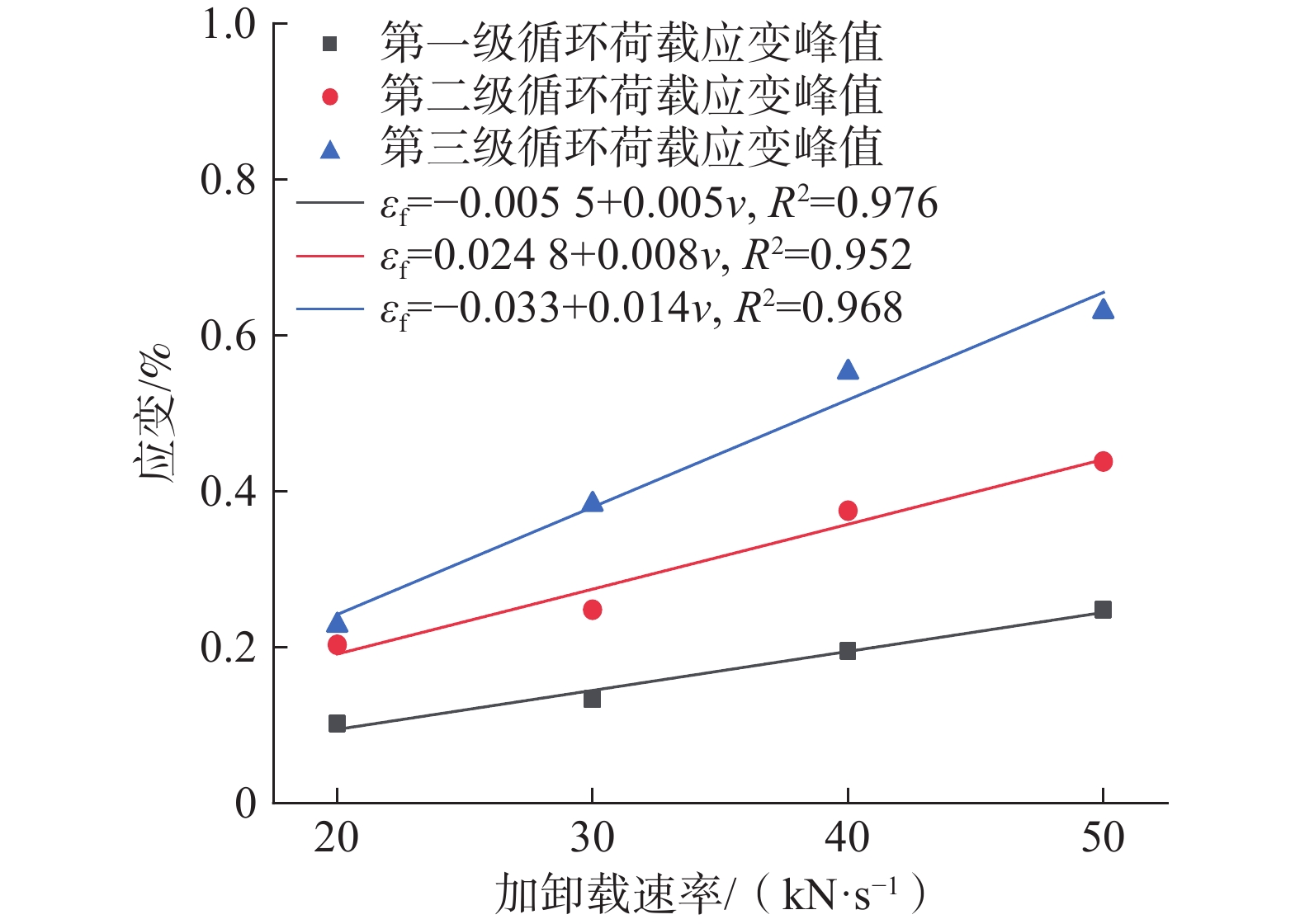
岩样 加卸载速率/(N·s−1) a b 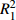
c d 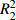
ɛf R2 砂岩 20 7.80 1.898 0.9983 −0.0055 0.005 0.976 0.385 0.946 30 21.59 2.404 0.9985 −0.033 0.008 0.952 0.320 0.956 40 14.41 2.199 0.9985 0.0248 0.012 0.968 0.295 0.967 50 4.46 1.737 0.9996 0.0364 0.014 0.972 0.285 0.973 大理岩 20 10.38 1.934 0.9982 −0.0035 0.006 0.965 0.410 0.972 30 23.92 2.274 0.9991 −0.028 0.009 0.958 0.359 0.981 40 15.79 2.107 0.9987 0.0293 0.012 0.967 0.297 0.964 花岗岩 50 6.35 1.825 0.9995 0.0415 0.015 0.957 0.283 0.953 20 11.95 1.746 0.9986 −0.0047 0.008 0.964 0.395 0.943 30 25.78 2.524 0.9987 −0.029 0.010 0.981 0.374 0.946 40 17.31 2.126 0.9985 0.0317 0.012 0.972 0.365 0.975 50 7.86 1.809 0.9998 0.0434 0.015 0.961 0.299 0.954 -
[1] 陈旭光, 张强勇. 岩石剪切破坏过程的能量耗散和释放研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2010,27(2):179 − 184. [CHEN Xuguang, ZHANG Qiangyong. Research on the energy dissipation and release in the process of rock shear failure[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2010,27(2):179 − 184. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2010.02.008
[2] 陈子全, 何川, 吴迪, 等. 深埋碳质千枚岩力学特性及其能量损伤演化机制[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(2):445 − 456. [CHEN Ziquan, HE Chuan, WU Di, et al. Mechanical properties and energy damage evolution mechanism of deep-buried carbonaceous phyllite[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(2):445 − 456. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 宋洋, 任萌, 张维东, 等. 非贯通非共面凝灰岩节理岩体各向异性及其能量特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):126 − 132. [SONG Yang, REN Meng, ZHANG Weidong, et al. Analysis of anisotropy and energy characteristics of tuffs with non-penetrating joints[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):126 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 李安润, 邓辉, 王红娟, 等. 水-岩作用下粉砂质泥岩含水损伤本构模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):106 − 113. [LI Anrun, DENG Hui, WANG Hongjuan, et al. Constitutive model of water-damaged silty mudstone under water-rock interactions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):106 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 辛亚军, 李梦远. 岩石分级加载蠕变的能量耗散与变形机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(增刊1): 2883 − 2897
XIN Yajun, LI Mengyuan. Study on deformation mechanism and energy dissipation of rock creep under step loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(Sup 1): 2883 − 2897. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 邓华锋, 胡玉, 李建林, 等. 循环加卸载过程中砂岩能量耗散演化规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(增刊1): 2869 − 2875
DENG Huafeng, HU Yu, LI Jianlin, et al. The evolution of sandstone energy dissipation under cyclic loading and unloading[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(Sup 1): 2869 − 2875. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 翟明磊, 郭保华, 李冰洋, 等. 岩石节理分级剪切加载-蠕变-卸载的能量与变形特征[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(8):2865 − 2872. [ZHAI Minglei, GUO Baohua, LI Bingyang, et al. Energy and deformation characteristics of rock joints under multi-stage shear loading-creep-unloading conditions[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(8):2865 − 2872. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] FENG J J, WANG E Y, CHEN X, et al. Energy dissipation rate: an indicator of coal deformation and failure under static and dynamic compressive loads[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2018,28(3):397 − 406. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2017.11.006
[9] CHEN Z Q, HE C, WU D, et al. Fracture evolution and energy mechanism of deep-buried carbonaceous slate[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2017,12(6):1243 − 1260. doi: 10.1007/s11440-017-0606-5
[10] CHEN Z Q, HE C, MA G Y, et al. Energy damage evolution mechanism of rock and its application to brittleness evaluation[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2019,52(4):1265 − 1274. doi: 10.1007/s00603-018-1681-0
[11] MENG Q B, ZHANG M W, ZHANG Z Z, et al. Experimental research on rock energy evolution under uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading compression[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal,2018,41(4):20170233. doi: 10.1520/GTJ20170233
[12] LI D Y, SUN Z, XIE T, et al. Energy evolution characteristics of hard rock during triaxial failure with different loading and unloading paths[J]. Engineering Geology,2017,228:270 − 281. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.08.006
[13] 谢和平, 彭瑞东, 鞠杨. 岩石变形破坏过程中的能量耗散分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(21):3565 − 3570. [XIE Heping, PENG Ruidong, JU Yang. Energy dissipation of rock deformation and fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(21):3565 − 3570. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.21.001
[14] KACHANOV M. On the time to failure under creep conditions[J]. Izv An sssr Otd Tekhn Nauk,1958,8(2):26 − 31.
[15] JEAN L. A continuous damage mechanics model for ductile fracture[J]. Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology,1985,107(1):83 − 89. doi: 10.1115/1.3225775
[16] WEN T, TANG H M, MA J W, et al. Energy analysis of the deformation and failure process of sandstone and damage constitutive model[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2019,23(2):513 − 524. doi: 10.1007/s12205-018-0789-9
-



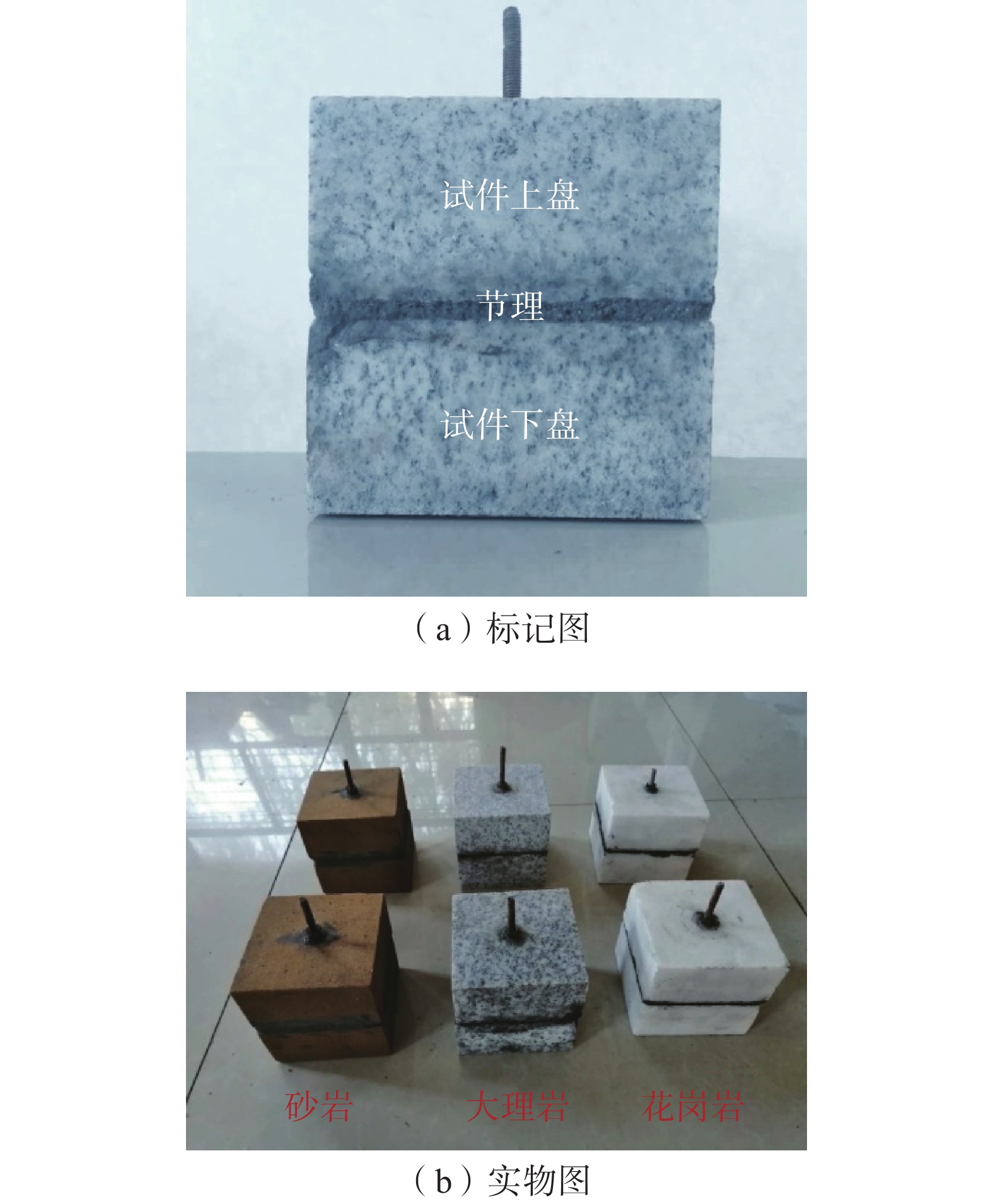
 下载:
下载: