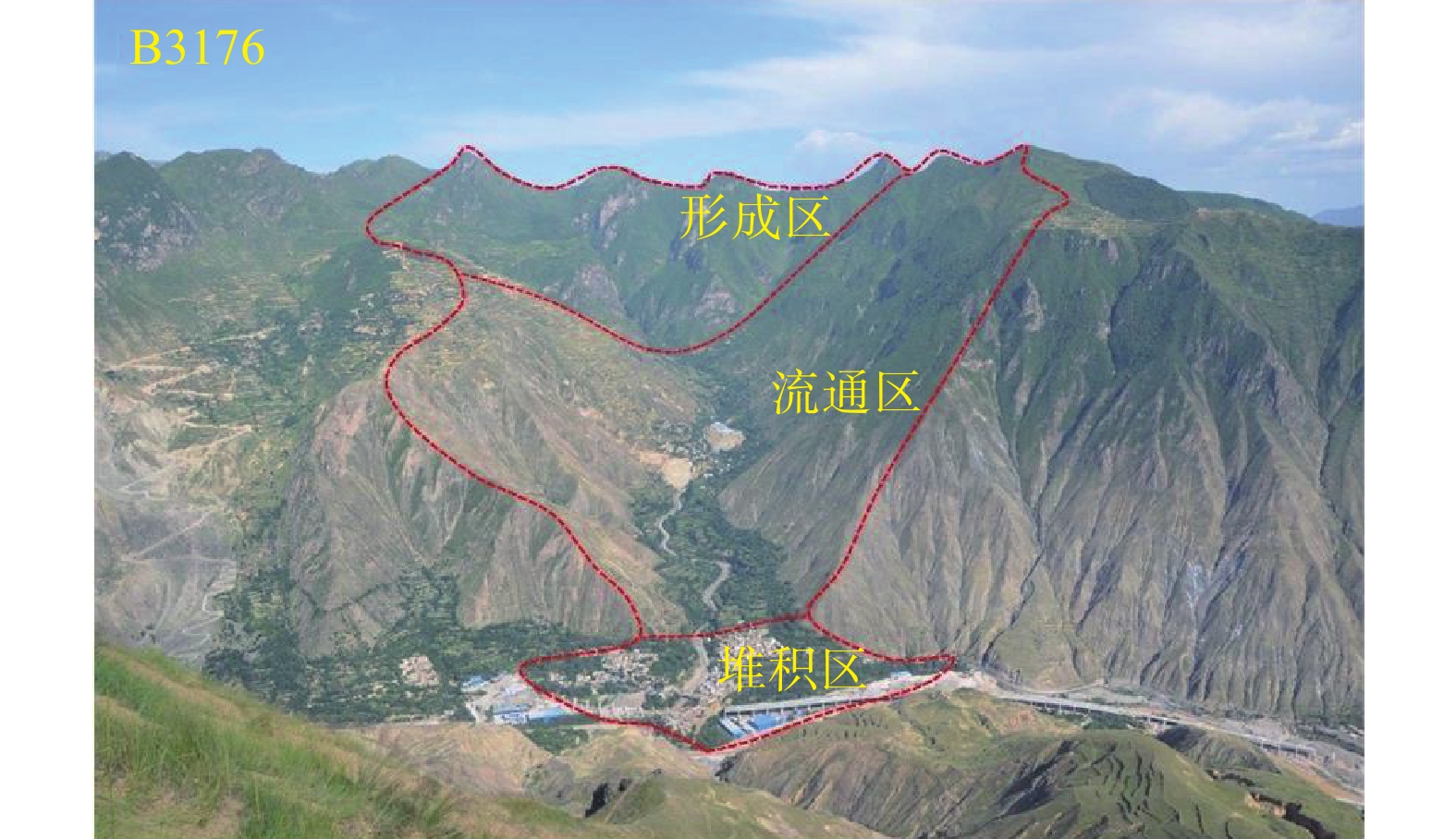
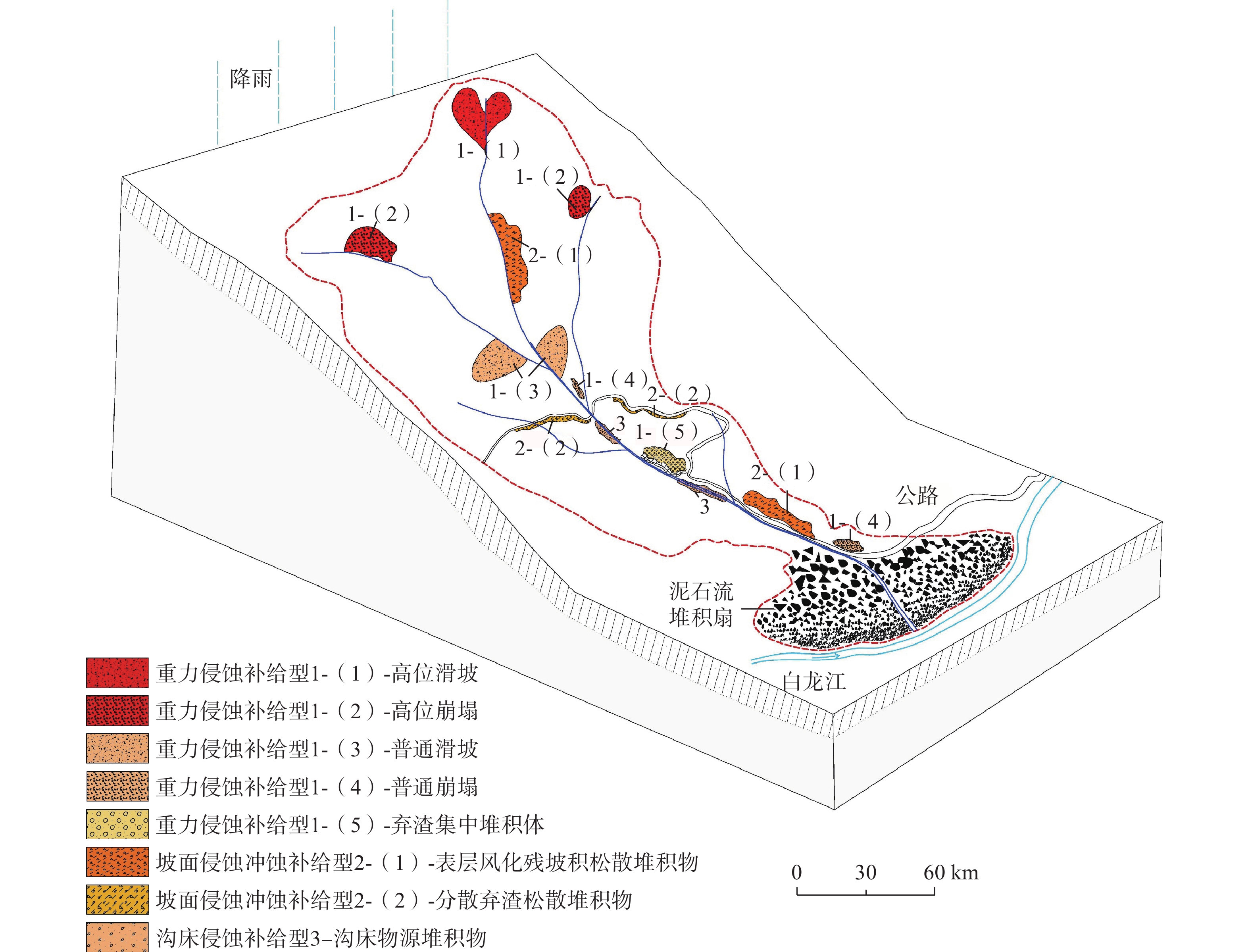
Formation conditions and the disaster modes of debris flows along middle and upper reaches of the Bailongjiang River Basin
-
摘要:
白龙江中上游泥石流发育极为严重,危害、威胁巨大,研究该区泥石流的成灾模式和致灾模式对泥石流灾害防治、国土空间规划、生态文明建设具有重要的科学意义和实践指导价值。文中在分析白龙江流域中上游241条泥石流形成条件的基础上,对泥石流的成灾模式、致灾模式及泥石流防治进行了分析。
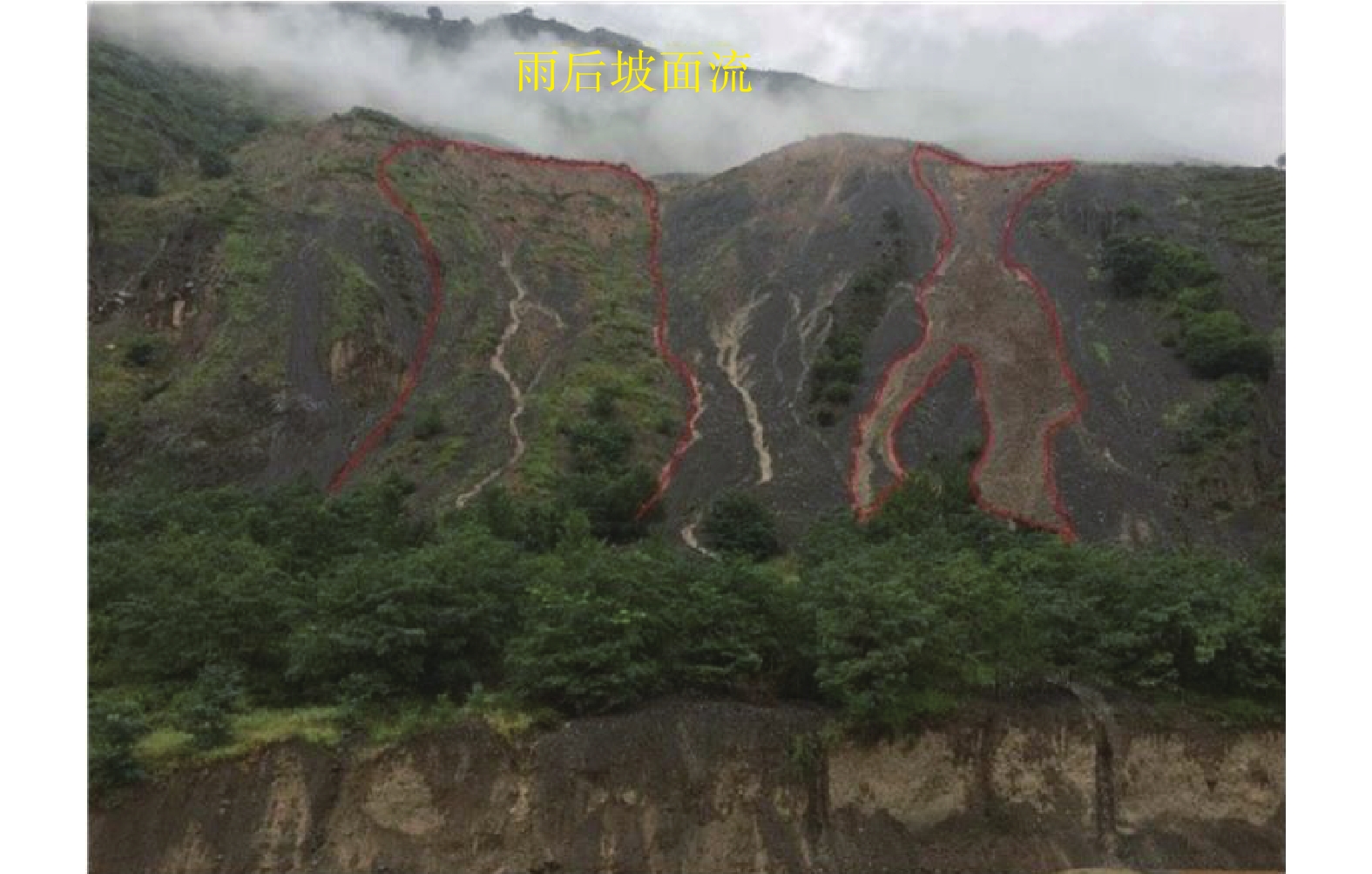
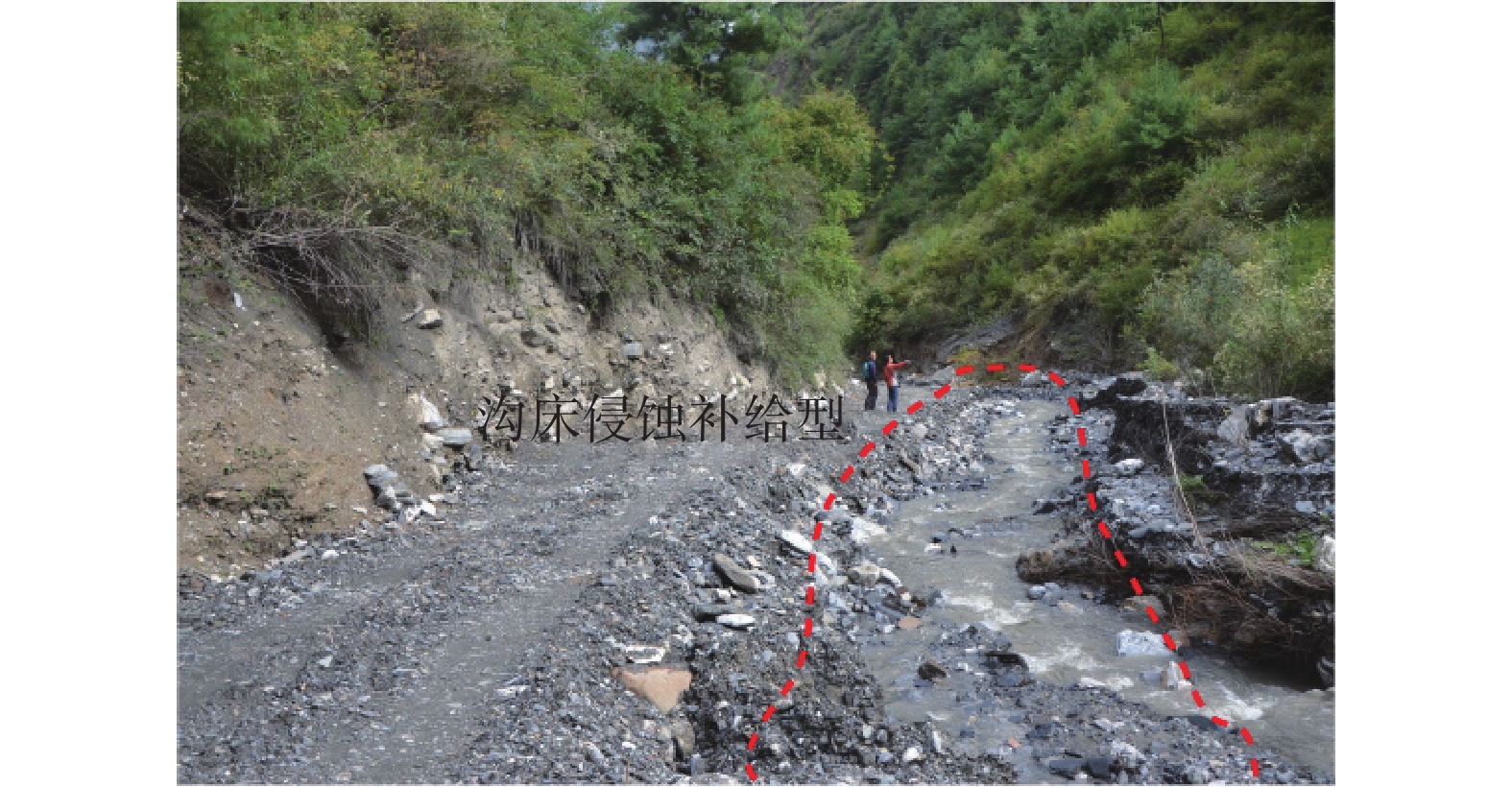
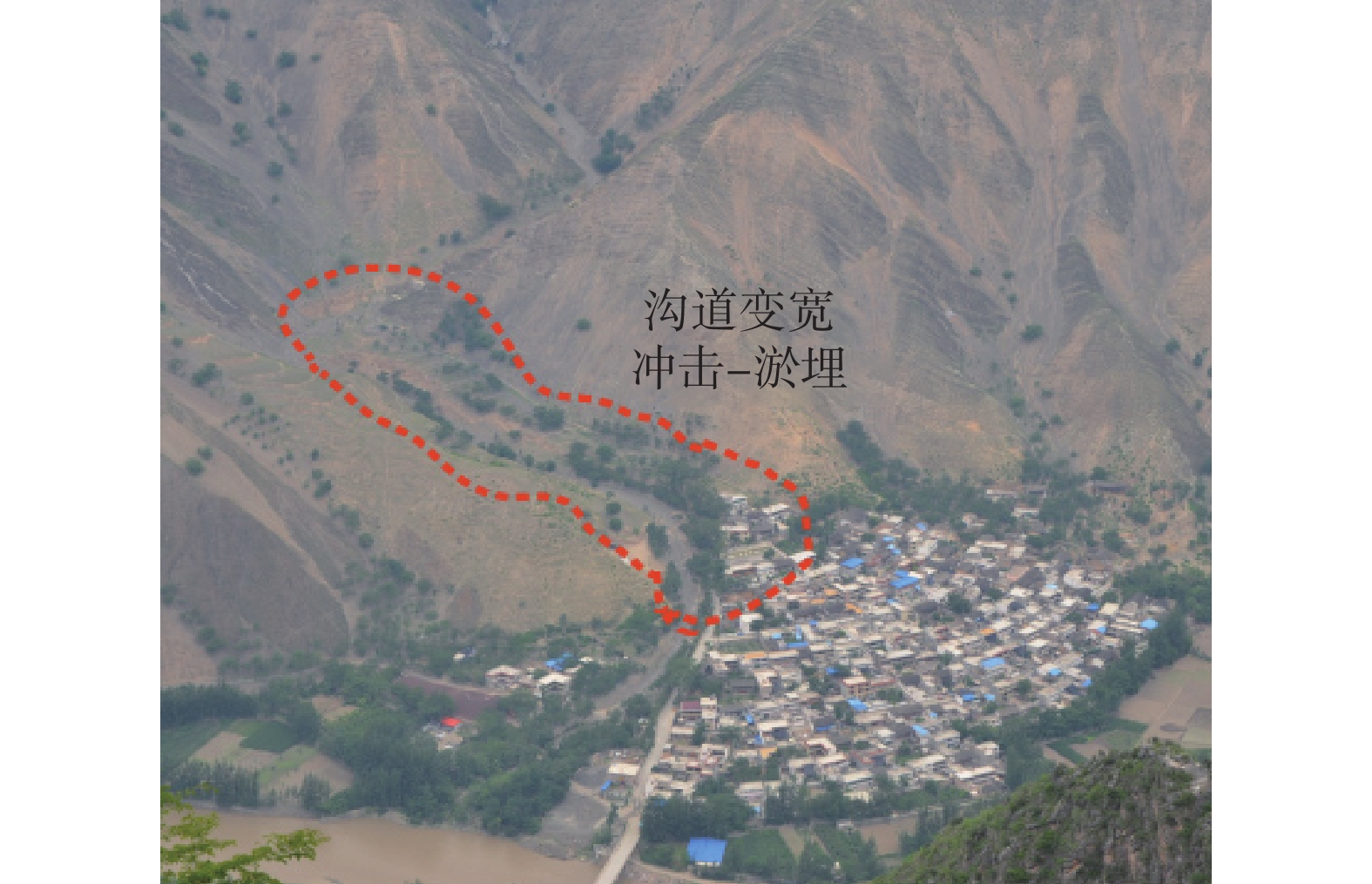
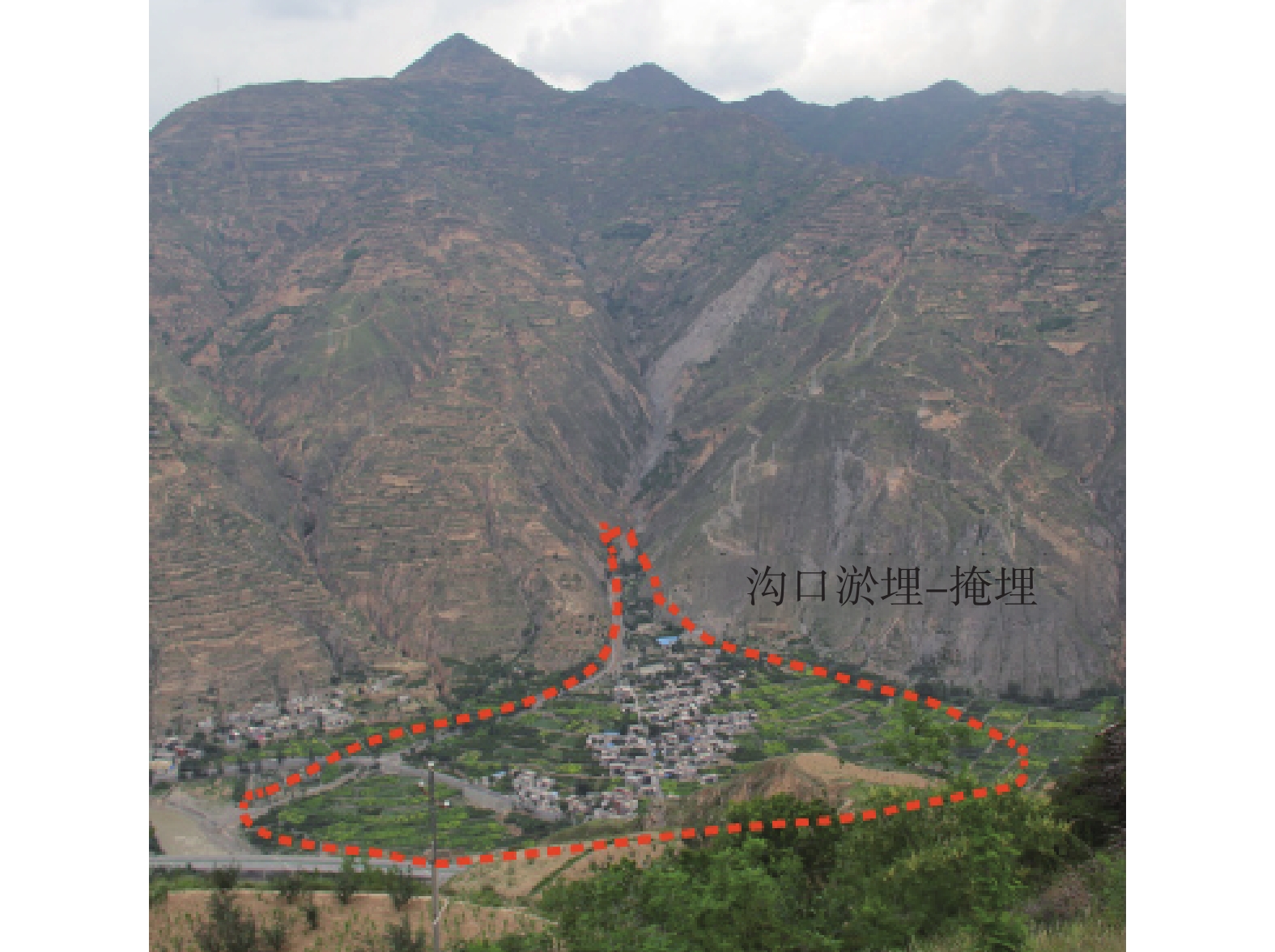
研究结果表明:(1)泥石流受地形地貌影响显著,高差大于1000 m占总数74.3%,主沟沟床纵比降>200‰占总数93.4%;(2)众多滑坡体物源沿着坪定-化马断裂带呈条带状分布,泥石流物源主要来源于千枚岩、变质砂岩、残坡积层、黄土等软弱地层的崩塌、滑坡体,物源分布与下伏基岩坡向关系不大;(3)该区泥石流按地貌特征分主要有沟谷型泥石流(占总数69.7%)、坡面型泥石流(占总数30.3%),基于固体物质补给方式划分泥石流成灾模式主要有重力侵蚀补给型(占总数71%)、坡面侵蚀冲蚀补给型(占总数10%)、沟床侵蚀补给型(占总数19%);(4)泥石流主要的致灾模式为溃决-冲毁、冲积-淤埋、爬高-堆积、侵蚀-坍塌、淤埋-掩埋、堰塞-次生灾害;(5)重力侵蚀补给型泥石流重点防治沟内重大灾害体,坡面侵蚀冲蚀补给型泥石流防治以拦挡、排导工程为主,沟道侵蚀补给型泥石流防治以清淤、排导为主。
Abstract:Debris flows are extremely serious along middle and upper reaches of Bailongjiang River Basin. It is of great scientific significance and practical value to study the disaster mode and hazard mode of debris flows in this area for disaster prevention, land space planning and ecological civilization construction. Based on the analysis of formation conditions of 241 debris flows in the middle and upper reaches of Bailongjiang River Basin, the disaster-forming, hazard modes and prevention of debris flows are analyzed. The results show that: (1) Debris flows are greatly affected by topography and landform, with height differences greater than 1000 m accounting for 74.3% of the total, and the longitudinal ratio of the main ditch bed being >200‰ accounting for 93.4% of the total. (2) Most of landslide sources are mainly distributed along the Pingding-Huama Fault Zone in a strip shape. Debris flows material source mainly comes from the collapse and landslide of the soft strata such as phyllite, metamorphic sandstone, residual slope deposit and Loess. The distribution of sediment source has little relationship with the slope aspect direction of underlying bedrock. (3) According to the landform characteristics, the debris flows in this area mainly include gully debris flows (69.7%) and slope debris flows (30.3%). According to the mode of solid material supply, the main debris flows disaster mode is gravity erosion supply type (71%), slope erosion supply type (10%) and gully erosion supply type (19%). (4) The main hazard modes of debris flows are burst-erosion, alluvial-silting, climbing-stacking, erosion-collapse, silting-burying, and barrier-secondary hazard. (5) The gravity erosion-recharge type debris flow is mainly to prevent and control the major disaster bodies in the gully. Slope erosion-recharge type debris flows are mainly based on blocking and drainage works. Gully erosion-recharge type debris flows are mainly based on desilting and drainage works.
-
Key words:
- the Bailongjiang River basin /
- debris flow /
- sediment source /
- disaster mode /
- hazard mode
-

-
表 1 典型物源斜坡结构组成
Table 1. Structural composition of typical source slopes
斜坡结构 致灾地层 致灾地层物源占各结构总物源的体积比/% 顺向坡 产出于千枚岩、板岩上覆坡积层、黄土、全风化岩层或几种软弱岩层组合中的物源 87.5 逆向坡 产出于千枚岩、板岩上覆残坡积层、黄土、全风化岩层或几种软弱岩层组合中的物源 86.5 横向坡 产出于千枚岩、板岩上覆残坡积层、黄土、全风化岩层或几种软弱岩层组合中的物源 87.7 -
[1] 王建力,王勇,师玉娥. 白龙江流域全新世泥石流与环境演变的初步研究[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2000,25(4):452 − 456. [WANG Jianli,WANG Yong,SHI Yue. A preliminary study on debris flow and environmental evolution in Holocene at the Bailongjiang River Valley[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science),2000,25(4):452 − 456. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5471.2000.04.017
[2] 孟兴民,陈冠,郭鹏,等. 白龙江流域滑坡泥石流灾害研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2013,33(4):1 − 15. [MENG Xingmin,CHEN Guan,GUO Peng,et al. Research of landslides and debris flows in Bailong River basin:Progrss and prospect[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2013,33(4):1 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 黄江成,杨顺,潘华利,等. 白龙江流域泥石流特征分析[J]. 水土保持通报,2014,34(1):311 − 315. [HUANG Jiangcheng,YANG Shun,PAN Huali,et al. Debris flow characteristics in Bailong River basin[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2014,34(1):311 − 315. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2014.01.019
[4] 熊木齐,孟兴民,庆丰,等. 甘肃省陇南市白龙江流域泥石流灾害事件与降水特征的关系[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2016,52(3):295 − 300. [XIONG Muqi,MENG Xingmin,QING Feng,et al. Relationship between debris flow activities and precipitation characteristics in Bailong River Basin of Longnan Region,Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2016,52(3):295 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张茂省,黎志恒,王根龙,等. 白龙江流域地质灾害特征及勘查思路[J]. 西北地质,2011,44(3):1 − 9. [ZHANG Maosheng,LI Zhiheng,WANG Genlong,et al. The geological hazard characteristics and exploration ideas of the Bailong River basin[J]. Northwestern Geology,2011,44(3):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2011.03.001
[6] 梁学战. 白龙江流域第四纪泥石流活动分期研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2016,30(2):153 − 157. [LIANG Xuezhan. Quaternary debris flow stages activity in Bailongjiang River basin[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2016,30(2):153 − 157. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2016.062
[7] 李晓婷,刘文龙. 模糊综合评判法在甘肃陇南武都区石门乡泥石流危险性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):71 − 76. [LI Xiaoting,LIU Wenlong. Application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method to debris flow risk evaluation in Shimen Township in Wudu District of Longnan City,Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):71 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.04.09
[8] 刘德玉,贾贵义,李松,等. 地形因素对白龙江流域甘肃段泥石流灾害的影响及权重分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(3):33 − 39. [LIU Deyu,JIA Guiyi,LI Song,et al. Impacts of topographical factors on debris flows and weight analysis at the Gansu segment of the Bailongjiang River basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):33 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.03.05
[9] 杨月巧,胡俊锋,郗蒙浩. 基于灰色关联法的舟曲泥石流灾害影响因素分析[J]. 自然灾害学报,2011,20(3):139 − 144. [YANG Yueqiao,HU Junfeng,XI Menghao. Analysis of influence factors of debris flow disaster in Zhouqu based on grey relevance method[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2011,20(3):139 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2011.0322
[10] 刘传正. 中国崩塌滑坡泥石流灾害成因类型[J]. 地质论评,2014,60(4):858 − 868. [LIU Chuanzheng. Genetic types of landslide and debris flow disasters in China[J]. Geological Review,2014,60(4):858 − 868. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2014.04.017
[11] 郝红兵,赵松江,李胜伟,等. 汶川地震区特大泥石流物源集中启动模式和特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(6):159 − 165. [HAO Hongbing,ZHAO Songjiang,LI Shengwei,et al. The star-up mode on large debris flow material source in Wenchuan earthquake region[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(6):159 − 165. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2015.06.25
[12] 曾庆利,杨志法,张西娟,等. 帕隆藏布江特大型泥石流的成灾模式及防治对策—以扎木镇-古乡段为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2007,18(2):27 − 33. [ZENG Qingli,YANG Zhifa,ZHANG Xijuan,et al. Hazard model and countermeasure to super-large debris-flow in Parlung River:Case study of the section from Zamu Town to Guxiang Gully[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2007,18(2):27 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2007.02.006
[13] 张永双,成余粮,姚鑫,等. 四川汶川地震-滑坡-泥石流灾害链形成演化过程[J]. 地质通报,2013,32(12):1900 − 1910. [ZHANG Yongshuang,CHENG Yuliang,YAO Xin,et al. The evolution process of Wenchuan earthquake-landslide-debris flow geohazard chain[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2013,32(12):1900 − 1910. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杨成林,陈宁生,李战鲁. 汶川地震次生泥石流形成模式与机理[J]. 自然灾害学报,2011,20(3):31 − 37. [YANG Chenglin,CHEN Ningsheng,LI Zhanlu. Formation mode and mechanism fordebris flow induced by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2011,20(3):31 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2011.0306
[15] 黄玉华,冯卫,李政国. 陕北延安地区2013年“7.3”暴雨特征及地质灾害成灾模式浅析[J]. 灾害学,2014,29(2):54 − 59. [HUANG Yuhua,FENG Wei,LI Zhengguo. Characteristics and geological disaster mode of the rainstorm happened on July 3.2013 in Yanan area of Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2014,29(2):54 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李永红,刘海南,杨渊,等. 秦巴山区泥石流动力学特征及致灾模式[J]. 灾害学,2018,33(1):71 − 75. [LI Yonghong,LIU Hainan,YANG Yuan,et al. Dynamical characteristic and hazard mode of a certain debris flow in Qinling-Bashan mountains[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2018,33(1):71 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 杨强,王高峰,丁伟翠,等. 多种组合模型的区域滑坡易发性及精度评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(2):36 − 51. [YANG Qiang,WANG Gaofeng,DING Weicui,et al. Susceptibility and accuracy evaluation of regional landsldie based on multiple hybrid models[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(2):36 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2021.0204
[18] 周健,杜强,李翠娜. 降雨强度对泥石流起动影响的模型试验研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2016,25(3):104 − 113. [ZHOU Jian,DU Qiang,LI Cuina. Model test of rainfall intensity influence on debris flow starting[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2016,25(3):104 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2016.0312
[19] 李鸿琏, 曾思伟. 甘肃泥石流[M]. 甘肃: 人民交通出版社, 1982
LI Honglian, ZENG Siwei. Gansu debris flow[M]. Gansu: China Communications Press, 1982. (in Chinese)
[20] 唐邦兴. 中国泥石流[M]. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2000
TANG Bangxing. Debris Flows in China[M]. Beijing: The Commercial Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: