Study on the disaster effect and prevention countermeasures of landslide in Zhouqu fault zone
-
摘要:
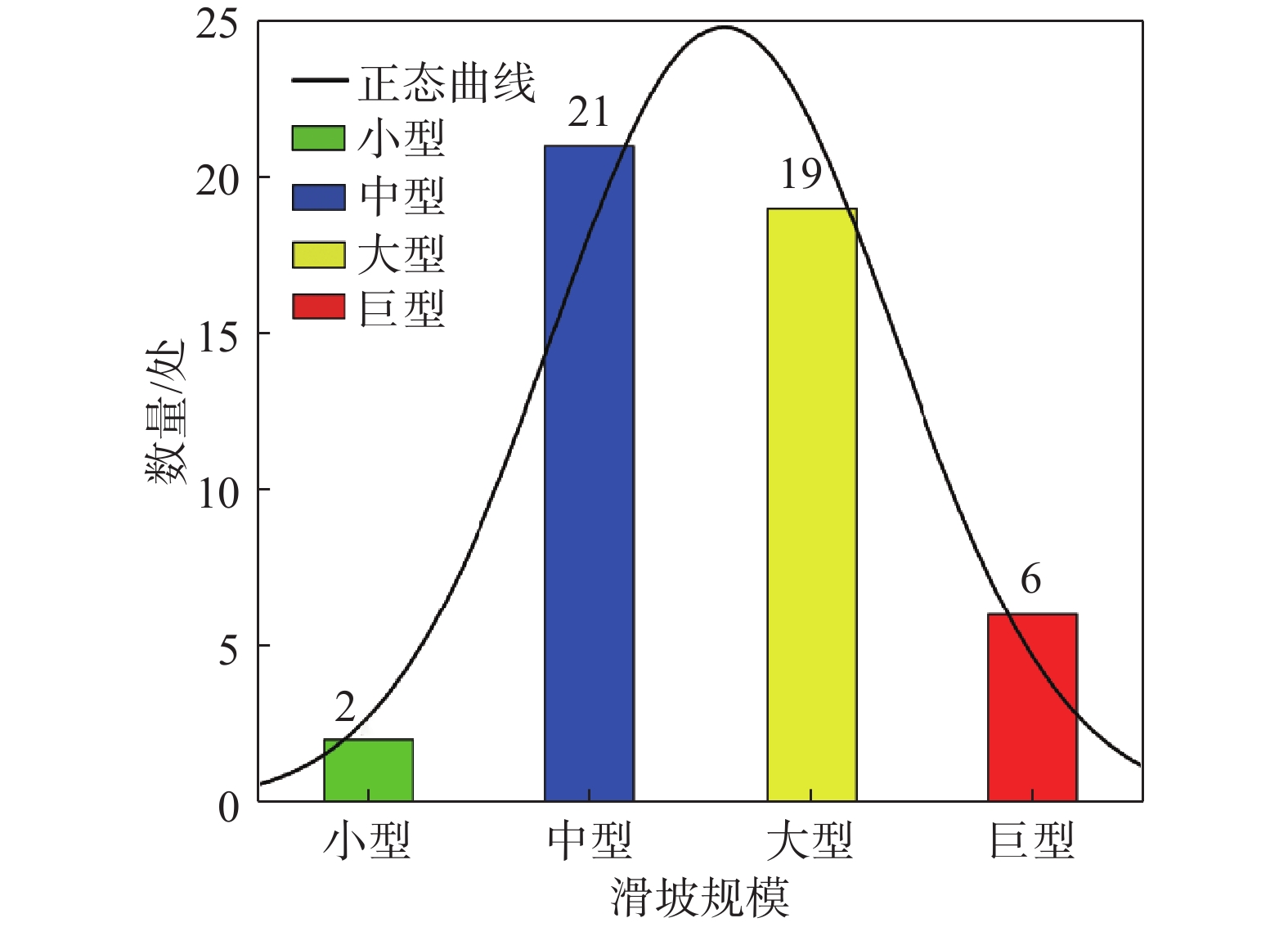
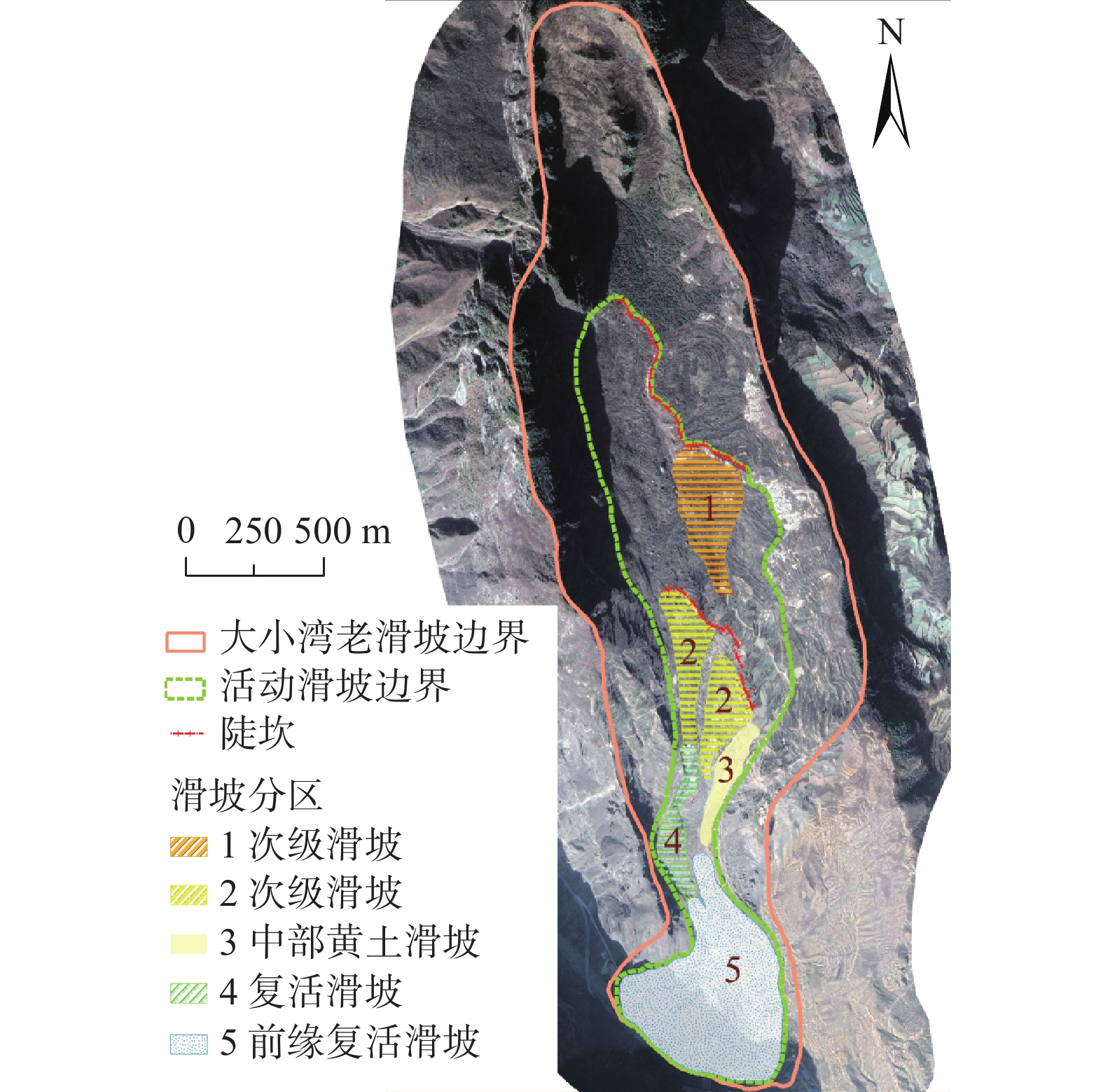
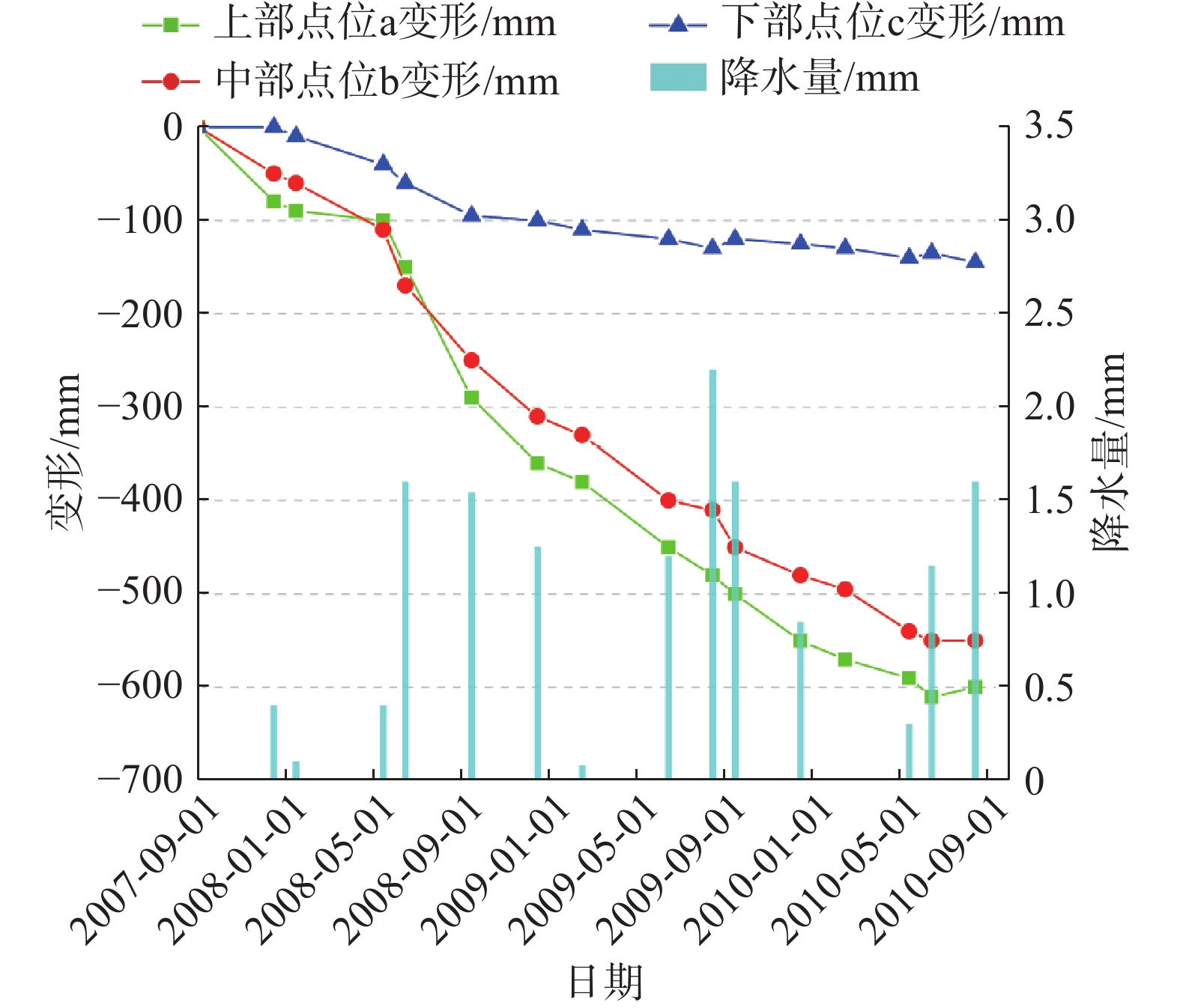
舟曲是我国滑坡灾害最严重的地区之一,其中断裂带滑坡活动频繁,危害巨大。文章在综合遥感、变形监测和现场调查的基础上,研究了断裂带滑坡特征及其灾害效应,提出了风险防控对策。研究表明:(1)断裂带滑坡形态上主要为长条形和簸箕形;滑体、滑床一般为板岩、千枚岩碎块石组成,滑带土为含砾黏土;滑坡具有多级、分块活动特征且块体差异性滑动特征显著;滑坡一般为慢速滑动,具有蠕滑特征;滑坡具有降雨敏感性特征,深层滑坡对降雨响应有明显的滞后性。(2)断裂带滑坡的成灾模式主要为慢速滑动过程中的蠕滑拉裂效应和冲击推挤效应,滑动后的堵江淹没效应、挤压侵蚀效应,以及社会影响效应等。(3)断裂带滑坡规模较大,地层破碎,治理条件差,工程治理措施难以奏效。但其突发性不强,应以管防为主,宜采取用地管控、监测预警、避险搬迁等防治措施,慎用工程治理措施。
Abstract:Zhouqu is one of the areas with the most serious landslide disasters in China, in which the fault zone landslide are frequent and the harm is huge. Based on the comprehensive remote sensing, deformation monitoring and field investigation, this paper studies the reactivation characteristics and disaster-causing mode of fault zone landslide, and puts forward the prevention and control countermeasures. The results show that: (1) the landslide in the fault zone is mainly in a strip shape and dustpan shape; The sliding body and sliding bed are generally composed of slate, phyllite and rubble, and the sliding zone soil is pebbly clay; The landslide has the characteristics of multi-level and block activity, and the differential sliding characteristics of different blocks are significant; Landslide is generally slow sliding and has fluidity characteristics; Landslide has the characteristics of rainfall sensitivity, and the response of deep landslide to rainfall has obvious lag. (2) the disaster modes of landslides in fault zone are mainly creep, tension crack effect and impact push effect in the process of slow sliding, river blocking and flooding effect, extrusion erosion effect and social impact effect after sliding. (3) the landslide conditions are large and the treatment measures are difficult to get together. However, its sudden nature is not strong, so it should focus on management and prevention. The recommended prevention measures are land use control, monitoring and early warning, risk avoidance and relocation, and engineering treatment measures are not recommended.
-
Key words:
- fault zone /
- landslide /
- features /
- disaster effect /
- countermeasures
-

-
[1] 苏琦,梁明剑,袁道阳,等. 白龙江流域构造地貌特征及其对滑坡泥石流灾害的控制作用[J]. 地球科学,2016,41(10):1758 − 1770. [SU Qi,LIANG Mingjian,YUAN Daoyang,et al. Geomorphic features of the Bailongjiang River drainage basin and its relationship with geological disaster[J]. Earth Science,2016,41(10):1758 − 1770. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 陈冠,孟兴民,郭鹏,等. 白龙江流域基于GIS与信息量模型的滑坡危险性等级区划[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2011,47(6):1 − 6. [CHEN Guan,MENG Xingmin,GUO Peng,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on GIS and information value model in Bailong River basin[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2011,47(6):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 李淑贞,戴霜,王华伟,等. 白龙江地区断裂构造与滑坡分布及发生关系[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2015,51(2):145 − 152. [LI Shuzhen,DAI Shuang,WANG Huawei,et al. Fault features and their implications on distribution and formation of landslides in Bailongjiang Region[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2015,51(2):145 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 杨为民,黄晓,张春山,等. 白龙江流域坪定—化马断裂带滑坡特征及其形成演化[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2014,44(2):574 − 583. [YANG Weimin,HUANG Xiao,ZHANG Chunshan,et al. Deformation behavior of landslides and their formation mechanism along Pingding-Huama active fault in Bailongjiang River region[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2014,44(2):574 − 583. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 余志山. 泄流坡滑坡灾害损失预测及成灾方式研究[J]. 甘肃科技,2007,23(12):72 − 76. [YU Zhishan. Study on disaster loss prediction and disaster mode of xieliupo landslide[J]. Gansu Science and Technology,2007,23(12):72 − 76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0952.2007.12.027
[6] 蒋树,文宝萍,赵成,等. 甘肃舟曲泄流坡滑坡活动机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(3):1 − 7. [JIANG Shu,WEN Baoping,ZHAO Cheng,et al. Creep mechanism analysis of Xieliupo landslide in Zhouqu County of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(3):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张卫雄,翟向华,丁保艳,等. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖滑坡成因分析与综合治理措施[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):7 − 14. [ZHANG Weixiong,ZHAI Xianghua,DING Baoyan,et al. Causative analysis and comprehensive treatment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):7 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.05.02
[8] 窦晓东,张泽林. 甘肃舟曲垭豁口滑坡复活机理及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):9 − 18. [DOU Xiaodong,ZHANG Zelin. Mechanism and causal analysis on the Yahuokou landslide reactivation and causes(Zhouqu County,Gansu,China)[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):9 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.02.02
[9] 蒋树,文宝萍,黎志恒,等. 甘肃舟曲锁儿头滑坡活动特征分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(2):69 − 74. [JIANG Shu,WEN Baoping,LI Zhiheng,et al. An analysis of the activity features of the Suoertou landslide in Zhouqu County of Gansu[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(2):69 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2016.02.10
[10] 宿星,吴玮江,叶伟林,等. 甘肃舟曲县龙江新村滑坡特征及稳定性[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2014,50(1):7 − 14. [SU Xing,WU Weijiang,YE Weilin,et al. Characteristics and stability assessment of Longjiangxincun landslide in Zhouqu County,Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2014,50(1):7 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 焦赟,姚正学,董耀刚. 舟曲南桥滑坡稳定性分析及治理对策研究[J]. 甘肃地质,2012,21(1):59 − 63. [JIAO Yun,YAO Zhengxue,DONG Yaogang. Nanqiao landslide stability and countermeasures in Zhouqu[J]. Gansu Geology,2012,21(1):59 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 蒋秀姿,文宝萍,蒋树,等. 甘肃舟曲锁儿头滑坡活动的主控因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2015,45(6):1798 − 1807. [JIANG Xiuzi,WEN Baoping,JIANG Shu,et al. Main factors analysis for controlling kinematic behavior of Suoertou landslide[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2015,45(6):1798 − 1807. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 黄晓,杨为民,张春山,等. 舟曲泄流坡滑坡变形特征及其形成机理[J]. 地质力学学报,2013,19(2):178 − 187. [HUANG Xiao,YANG Weimin,ZHANG Chunshan,et al. Deformation characteristics and formation mechanism of xieliupo landslide in Zhouqu[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2013,19(2):178 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 郭长宝,任三绍,李雪,等. 甘肃舟曲南峪江顶崖古滑坡发育特征与复活机理[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(1):206 − 217. [GUO Changbao,REN Sanshao,LI Xue,et al. Development characteristics and reactivation mechanism of the jiangdingya ancient landslide in the Nanyu town,Zhouqu County,Gansu Province[J]. Geoscience,2019,33(1):206 − 217. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.01.20
[15] 刘秋强,杜岩,郭富赟,等. 青藏高原东端甘肃舟曲牙豁口滑坡复活机理研究[J]. 灾害学,2021,36(2):113 − 117. [LIU Qiuqiang,DU Yan,GUO Fuyun,et al. The reactivation mechanism of yahuokou landslide at the eastern end of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau,Zhouqu County,Gansu Province,China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021,36(2):113 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.02.019
[16] 韩旭东,付杰,李严严,等. 舟曲江顶崖滑坡的早期判识及风险评估研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):180 − 186. [HAN Xudong,FU Jie,LI Yanyan,et al. A study of the early identification and risk assessment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):180 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202104028
[17] 刘东飞,王雄师,杨欢,等. 基于可靠度分析的甘肃舟曲泄流坡滑坡风险评价[J]. 山地学报,2017,35(3):323 − 331. [LIU Dongfei,WANG Xiongshi,YANG Huan,et al. Risk assessment of Zhouqu xieliupo landslide based on reliability analysis in Zhouqu County of Gansu Province[J]. Mountain Research,2017,35(3):323 − 331. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 贾虎军,王立娟,范冬丽. 无人机载LiDAR和倾斜摄影技术在地质灾害隐患早期识别中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):60 − 65. [JIA Hujun,WANG Lijuan,FAN Dongli. The application of UAV LiDAR and tilt photography in the early identification of geo-hazards[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):60 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.02.08
[19] 刘文,王猛,朱赛楠,等. 基于光学遥感技术的高山极高山区高位地质灾害链式特征分析—以金沙江上游典型堵江滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):29 − 39. [LIU Wen,WANG Meng,ZHU Sainan,et al. An analysis on chain characteristics of highstand geological disasters in high mountains and extremely high mountains based on optical remote sensing technology:A case study of representative large landslides in upper reach of Jinsha River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):29 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.05-04
[20] 潘建平,邓福江,徐正宣,等. 基于轨道精炼控制点精选的极艰险区域时序InSAR地表形变监测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):98 − 104. [PAN Jianping,DENG Fujiang,XU Zhengxuan,et al. Time series InSAR surface deformation monitoring in extremely difficult area based on track refining control points selection[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):98 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.05-12
[21] 褚宏亮,邢顾莲,李昆仲,等. 基于地面三维激光扫描的三峡库区危岩体监测[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):124 − 132. [CHU Hongliang,XING Gulian,LI Kunzhong,et al. Monitoring of dangerous rock mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir area based on the terrestrial laser scanning methodFull text replacement[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):124 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008015
[22] 侯燕军,周小龙,石鹏卿,等. “空-天-地”一体化技术在滑坡隐患早期识别中的应用—以兰州普兰太公司滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):12 − 20. [HOU Yanjun,ZHOU Xiaolong,SHI Pengqing,et al. Application of “Air-Space-Ground” integrated technology in early identification of landslide hidden danger:Taking Lanzhou Pulantai Company Landslide as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):12 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 俞晶星,郑文俊,袁道阳,等. 西秦岭西段光盖山-迭山断裂带坪定-化马断裂的新活动性与滑动速率[J]. 第四纪研究,2012,32(5):957 − 967. [YU Jingxing,ZHENG Wenjun,YUAN Daoyang,et al. Late quaternary active characteristics and slip-rate of pingdinghuama fault,the eastern segment of Guanggaishan-Dieshan fault zone(west Qinling Mountain)[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2012,32(5):957 − 967. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.05.13
[24] 陈宗良,叶振南,王志宏,等. 白龙江流域中上游第四纪沉积物的发育特征及其灾害效应[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(2):29 − 36. [CHEN Zongliang,YE Zhennan,WANG Zhihong,et al. Development characteristics and disaster effect of the Quaternary sediments in the middle and upper reaches of the Bailongiang River basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(2):29 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.02.05
[25] 陈明,王运生,梁瑞锋,等. 白龙江流域大型滑坡发育分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(2):325 − 333. [CHEN Ming,WANG Yunsheng,LIANG Ruifeng,et al. Research on development and distribution rules of largescale landslides in Bailongjiang River basin[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(2):325 − 333. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-037
-




 下载:
下载: