Remote sensing detection of adverse geological bodies along Xichang-Shangri-La expressway
-
摘要:
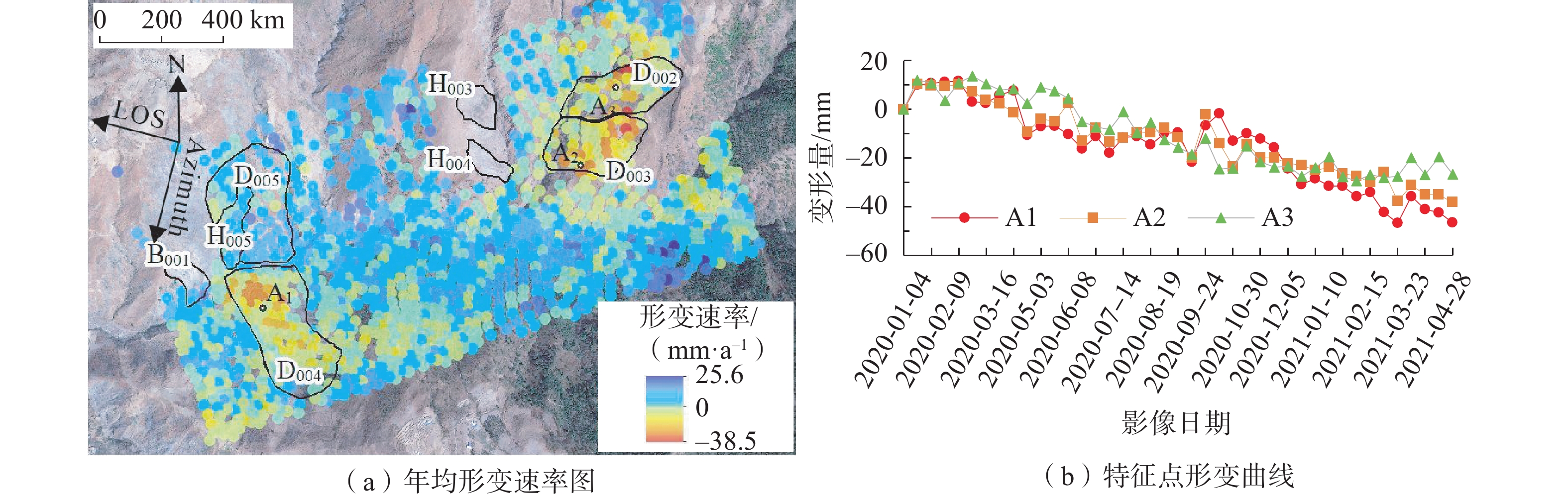
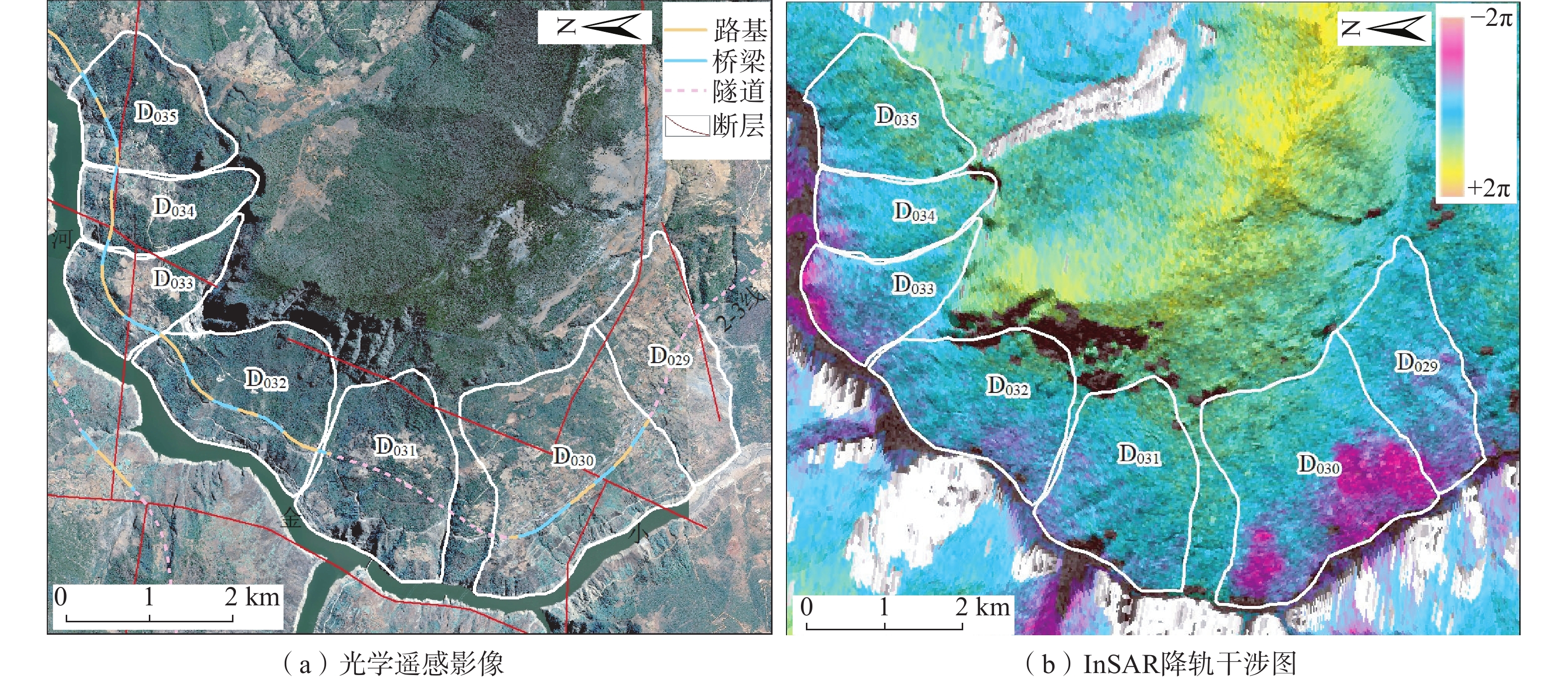
随着我国高速公路建设不断向西部山区发展,面临的崩塌、滑坡、泥石流等不良地质问题日益突出,迫切需要在选线阶段利用新的技术手段对拟建高速公路沿线不良地质体进行早期识别。以西昌—香格里拉拟建高速公路廊道为研究区,利用“天-空-地”一体化综合遥感手段,识别出不良地质体174处,其中滑坡74处、崩塌40处、泥石流16处、堆积体44处,利用小基线集合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术探测到26处不良地质体具有形变信号。针对磨盘山隧道—雅砻江桥段、牦牛山隧道出口段和下麦地隧道出口段不良地质体发育密集、规模大、稳定性差、对拟建线路威胁极大的区段,项目组开展了详细调查和分析评价。研究结果为西香高速线路比选和后期详细勘查提供了支撑,也为线路工程的不良地质体调查评价提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 西昌—香格里拉高速公路 /
- 不良地质体 /
- “天-空-地”综合遥感
Abstract:With the development of expressway construction towards the western mountainous areas in China, the adverse geological problems such as collapse, landslide and debris flow are becoming increasingly serious. It is urgent to use new technical means to identify the adverse geological bodies along the proposed expressway in the early stage of route selection. the article applied the integrated remote sensing method of " Space-Air-Ground " to identified 174 adverse geological bodies, including 74 landslides, 40 collapses, 16 debris flows and 44 deposits along the proposed Xichang-shangri-La expressway. Applied small baseline subsets interferometric synthetic aperture radar technique to detected 26 adverse geological bodies with deformation information. This article have carried out a detailed investigation and comprehensive evaluation on the section of Mopanshan tunnel - Yalong River bridge, the exit of Maoniushan tunnel, the exit of Xiamaidi tunnel where adverse geological bodies are densely developed, large in scale and poor in stability, posing great threat to the proposed line . The results provide support for routes comparison and later investigation of Xichang-Shangri-La expressway. It also provides reference for the investigation and estimate of adverse geological bodies along line engineering.
-

-
表 1 西香高速廊道不良地质体分段统计表
Table 1. Statistical list of adverse geological bodies in the corridor
区段 起止点 长度/km 崩塌/处 滑坡/处 泥石流/处 堆积体/处 总数量/处 密度/(处·km−1) 主线A段 K0+0.00—K73+100 73.10 3 18 3 13 37 0.51 主线B段 K73+100—K108+400 35.30 0 0 0 0 0 0 主线C段 K108+400—K165+400 57.00 18 13 5 10 46 0.81 木里支线 MK0+0.00—MK40+10 40.01 18 41 6 21 86 2.15 泸沽湖支线 LK0+0.00—LK12+920 12.92 1 2 2 0 5 0.42 合计 218.33 40 74 16 44 174 0.80 -
[1] 殷跃平. 贵州省三穗—凯里高速公路“5·11”滑坡灾害调查[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2003,14(3):138. [YIN Yueping. Investigation on "5·11" landslide disaster of Sansui-Kaili expressway in Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2003,14(3):138. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2003.03.029
[2] 央视网. 陕西延安黄延高速工地山体滑坡[OL]. (2014-10-12). http://tv.cctv.com/2014/10/12/VIDE1413047758298495.shtml
CCTV. Landslide at construction site of Huangling-Yan’an expressway in Yan’an, Shaanxi Province[OL]. (2014-10-12) . http://tv.cctv.com/2014/10/12/VIDE1413047758298495.shtml. (in Chinese)
[3] 詹越. 公路危岩崩塌安全监控及预警技术[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2016
ZHAN Yue. Highway dangerous-rock collapse safety monitoring and early warning technology[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张蕴灵,傅宇浩,李为乐,等. 2020年9月20日雅西高速姚河坝崩塌调查[J]. 山地学报,2021,39(3):450 − 460. [ZHANG Yunling,FU Yuhao,LI Weile,et al. Preliminary investigation on the Yaoheba rockfall along the Ya’an-Xichang highway on September 20,2020,Sichuan,China[J]. Mountain Research,2021,39(3):450 − 460. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000610
[5] 许也平,王萍. 遥感地质像片用于公路选线[J]. 公路,1988,33(6):20 − 22. [XU Yeping,WANG Ping. Remote sensing geological images are used for highway route selection[J]. Highway,1988,33(6):20 − 22. (in Chinese)
[6] 赵永国. 宝天公路选线工程地质环境遥感解译法的应用[J]. 中国公路学报,1992,5(4):44 − 49. [ZHAO Yongguo. The application of methods of remote sensing interpretation on engineering geological environments along preselected routes of Baoji-Tianshui highway[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,1992,5(4):44 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 陈楚江,薛重生,余绍淮. 西藏墨脱公路的灾害地质遥感识别[J]. 工程地质学报,2004,12(1):57 − 62. [CHEN Chujiang,XUE Chongsheng,YU Shaohuai. Identification of geological hazards with remote sensing in the Motuo,Xizang[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2004,12(1):57 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.01.011
[8] 张明华. 公路工程地质灾害遥感图像识别及解译方法[J]. 遥感技术与应用,2005,20(2):233 − 237. [ZHANG Minghua. The way of image recognizing and interpreting with remote sensing for geological disasters of highway engineering[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application,2005,20(2):233 − 237. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2005.02.004
[9] 李宁. 西藏林芝市派墨公路地质灾害风险评价[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016
LI Ning. Geological disaster risk assessment of the PAIMO highway engineering in the Xizang's Nyingchi City[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 安鑫,牛军强,匡经水,等. 遥感技术在国家高速公路G85麻柳湾―昭通段中的应用研究[J]. 公路交通技术,2012,28(5):31 − 36. [AN Xin,NIU Junqiang,KUANG Jingshui,et al. Research on application of remote sensing technology in Maliuwan—Zhaotong section of national expressway G85[J]. Technology of Highway and Transport,2012,28(5):31 − 36. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6477.2012.05.008
[11] 卢斌莹,陈正江,白延平,等. 高速公路地质灾害遥感调查方法:以陕西省为例[J]. 干旱区地理,2008,31(6):946 − 950. [LU Binying,CHEN Zhengjiang,BAI Yanping,et al. Remote sensing method for freeway geological disaster:A case study of Shaanxi Province[J]. Arid Land Geography,2008,31(6):946 − 950. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 梁京涛,王军,王猛,等. 四川省绵竹至茂县公路工程地质遥感调查与评价[J]. 灾害学,2012,27(1):83 − 86. [LIANG Jingtao,WANG Jun,WANG Meng,et al. Remote sensing survey and evaluation of engineering geology along Mianzhu-Maoxian highway in Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2012,27(1):83 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2012.01.017
[13] 许强,董秀军,李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957 − 966. [XU Qiang,DONG Xiujun,LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190088
[14] 中国地质调查局. 地灾隐患识别: 寻找大地上的“潜伏者”[OL]. (2021-05-10). https://www.cgs.gov.cn/xwl/cgkx/202105/t20210510_669916.html.
China Geological Survey. Identification of hazards: Looking for "lurkers" on the earth[OL]. (2021-05-10). https://www.cgs.gov.cn/xwl/cgkx/202105/t20210510_669916.html. (in Chinese)
[15] 许强. 对地质灾害隐患早期识别相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2020,45(11):1651 − 1659. [XU Qiang. Understanding and consideration of related issues in early identification of potential geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(11):1651 − 1659. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 陆会燕,李为乐,许强,等. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(9):1342 − 1354. [LU Huiyan,LI Weile,XU Qiang,et al. Early detection of landslides in the upstream and downstream areas of the Baige landslide,the Jinsha River based on optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(9):1342 − 1354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] DONG J,LIAO M S,XU Q,et al. Detection and displacement characterization of landslides using multi-temporal satellite SAR interferometry:A case study of Danba County in the Dadu River basin[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,240:95 − 109. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.04.015
[18] 王振林,廖明生,张路,等. 基于时序Sentinel-1数据的锦屏水电站左岸边坡形变探测与特征分析[J]. 国土资源遥感,2019,31(2):204 − 209. [WANG Zhenlin,LIAO Mingsheng,ZHANG Lu,et al. Detecting and characterizing deformations of the left bank slope near the Jinping hydropower station with time series Sentinel-1 data[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2019,31(2):204 − 209. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 张路,廖明生,董杰,等. 基于时间序列InSAR分析的西部山区滑坡灾害隐患早期识别—以四川丹巴为例[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2018,43(12):2039 − 2049. [ZHANG Lu,LIAO Mingsheng,DONG Jie,et al. Early detection of landslide hazards in mountainous areas of West China using time series SAR interferometry:A case study of Danba,Sichuan[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2018,43(12):2039 − 2049. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王天河. 基于多源遥感的康定—炉霍拟建高速公路地质灾害危险性评价及线路优化分析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019
WANG Tianhe. Risk assessment of geological hazards and route optimization analysis of Kangding-Luhuo proposed expressway based on multi-source remote sensing[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 李长顺. 攀西地区(西昌市)地质灾害详细调查报告[R].成都: 四川省地质调查院, 2013
LI Changshun. Detailed survey report of geological hazard in Panxi region (Xichang City)[R]. Chengdu: Sichuan Institute of Geological Survey, 2013.(in Chinese)
[22] 姚巍,赵其华,李坛,等. 四川省盐源县地质灾害分布特征与形成条件研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2008,19(1):48 − 51. [YAO Wei,ZHAO Qihua,LI Tan,et al. Characteristics of geology hazards distribution and formation conditions in Yanyuan Country,Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2008,19(1):48 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2008.01.011
[23] 田万生. 四川省2015年凉山州木里县地质灾害详细调查报告[R]. 兰州: 甘肃水文地质工程地质勘察院, 2016
TIAN Wansheng. Detailed investigation report on geological hazards in Muli County, Sichuan Province in 2015[R]. Lanzhou: Gansu Hydrogeology Engineering Geology Survey Institute, 2016. (in Chinese)
[24] 凉山彝族自治州交通运输局. G7611线西昌至香格里拉(四川境)高速公路项目社会资本方招标资格预审公告[EB/OL]. (2021-04-30). http://jtj.lsz.gov.cn/xxgk/fdzdgknr/tzgg_32060/202104/t20210430_1892777.html.
Transportation bureau of Liangshan Yi autonomous prefecture. G7611 line Xichang to Shangri-La (Sichuan border) highway project social capital bidding pre-qualification announcement[EB/OL]. (2021-04-30). http://jtj.lsz.gov.cn/xxgk/fdzdgknr/tzgg_32060/202104/t20210430_1892777.html. (in Chinese)
[25] ZHU L,DENG Y,HE S M. Characteristics and failure mechanism of the 2018 Yanyuan landslide in Sichuan,China[J]. Landslides,2019,16(12):2433 − 2444. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01262-z
[26] HU G S,LIU M,CHEN N S,et al. Real-time evacuation and failure mechanism of a giant soil landslide on 19 July 2018 in Yanyuan County,Sichuan Province,China[J]. Landslides,2019,16(6):1177 − 1187. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01175-x
[27] 伍康林,陈宁生,胡桂胜,等. 四川省盐源县玻璃村“7·19”特大滑坡灾害应急科学调查[J]. 山地学报,2018,36(5):806 − 812. [WU Kanglin,CHEN Ningsheng,HU Guisheng,et al. Emergency investigation to 7·19 landslide disaster in Boli Village,Yanyuan County,Sichuan,China[J]. Mountain Research,2018,36(5):806 − 812. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000376
[28] 翁其能,唐红梅,陈洪凯,等. 滑坡治理过程中岩土体变形场的演绎趋势分析:以西(昌)木(里)路新烧房滑坡为例[J]. 重庆交通学院学报,2001,20(1):69 − 73. [WENG Qineng,TANG Hongmei,CHEN Hongkai,et al. Developing tendency analysis of slope deformation composed of loose rock in the course of harnessing of landslide—Taking the XinShaofang landslide in the Highway from Xichang to Muli as Example[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong Institute,2001,20(1):69 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 陈敏,刘良春,叶胜华. 弯曲-拉裂型滑坡形成机制和稳定性分析:以木里河卡基娃滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2012,39(1):58 − 64. [CHEN Min,LIU Liangchun,YE Shenghua. The formation mechanism and stability analysis of bend-crack landslide:Taking the Kajiwa landslide of Muli River as an example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2012,39(1):58 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 董建辉,魏良帅,唐然,等. 木里县水洛乡东拉滑坡安全监测及变形破坏分析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2015,13(3):543 − 547. [DONG Jianhui,WEI Liangshuai,TANG Ran,et al. Safety monitoring and deformation damage of Dongla landslide in Shuiluo of Muli County[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2015,13(3):543 − 547. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2015.03.032
[31] 吴莉娟,肖天贵,顾林康,等. 四川凉山平川镇“7.14”泥石流灾害的气象成因[J]. 成都信息工程学院学报,2011,26(6):675 − 686. [WU Lijuan,XIAO Tiangui,GU Linkang,et al. Analysis onthe meteorological causes of the July 14 extreme debris flow hazards in Pingchuan town of Liangshan prefecture in Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Information Technology,2011,26(6):675 − 686. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 张楠,魏云杰. 四川省盐源县小河沟泥石流灾害调查研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(6):148 − 153. [ZHANG Nan,WEI Yunjie. Investigation of Xiaohegou debris flow in Yanyuan County,Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(6):148 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 罗宇. 四川省盐源县格地罗沟泥石流灾害性分析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2012
LUO Yu. Disaster analysis of debris flow in Gediluo gully, Yanyuan County, Sichuan Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 田淑芳, 詹骞. 遥感地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013
TIAN Shufang, ZHAN Qian. Remote sensing geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2013. (in Chinese)
[35] 卓宝熙. 工程地质遥感判释与应用[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2011
ZHUO Baoxi. Remote sensing interpretation & application of geology engineering[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 2011. (in Chinese)
[36] GAO J,MARO J. Topographic controls on evolution of shallow landslides in pastoral Wairarapa,New Zealand,1979-2003[J]. Geomorphology,2010,114(3):373 − 381. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.08.002
[37] MARCELINO E V,FORMAGGIO A R,MAEDA E E. Landslide inventory using image fusion techniques in Brazil[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2009,11(3):181 − 191. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2009.01.003
[38] FIORUCCI F,CARDINALI M,CARLÀ R,et al. Seasonal landslide mapping and estimation of landslide mobilization rates using aerial and satellite images[J]. Geomorphology,2011,129(1/2):59 − 70.
[39] BERARDINO P,FORNARO G,LANARI R,et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375 − 2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
[40] 李振洪,宋闯,余琛,等. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用:挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):967 − 979. [LI Zhenhong,SONG Chuang,YU Chen,et al. Application of satellite radar remote sensing to landslide detection and monitoring:Challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):967 − 979. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190098
[41] 李元松,高晖,陈峰,等. 乌尉高速公路边坡稳定性综合评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(4):150 − 156. [LI Yuansong,GAO Hui,CHEN Feng,et al. Comprehensive assessment of slope stability in Wu—Yu highway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(4):150 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] 邱明明,杨果林,张沛然,等. 浅埋洞口段黄土公路隧道施工变形性状现场测试研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):135 − 143. [QIU Mingming,YANG Guolin,ZHANG Peiran,et al. Field test on the construction deformation characteristics for a loess highway tunnel at the shallow portal section[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):135 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[43] 陈云生,刘光彬,张一铭,等. 阳鹿高速公路K52新滑坡变形特征与成因机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):83 − 91. [CHEN Yunsheng,LIU Guangbin,ZHANG Yiming,et al. Deformation characteristics and genetic mechanism of a new landslide at K52 of Luyang freeway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):83 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[44] 陈锐,范小光,吴益平. 基于数据挖掘技术的白水河滑坡多场信息关联准则分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):1 − 8. [CHEN Rui,FAN Xiaoguang,WU Yiping. Analysis on association rules of multi-field information of Baishuihe landslide based on the data mining[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[45] 廖小平,徐风光,蔡旭东,等. 香丽高速公路边坡地质灾害发育特征与易发性区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):121 − 129. [LIAO Xiaoping,XU Fengguang,CAI Xudong,et al. Development characteristics and susceptibality zoning of slope geological hazards in Xiangli expressway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):121 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: