Interpretation method for regional co-seismic collapses based on multi-feature fusion of optical remote sensing
-
摘要:
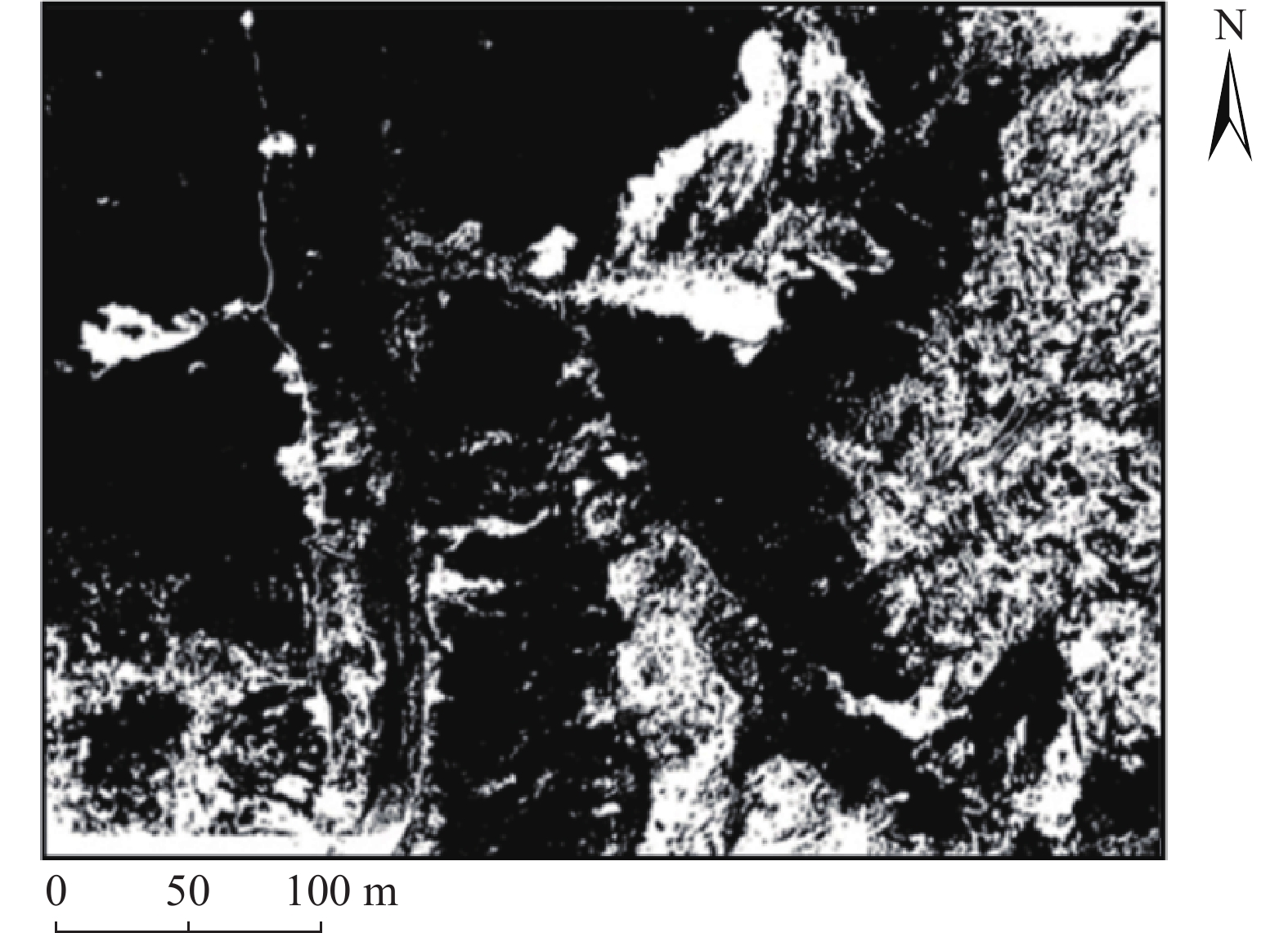
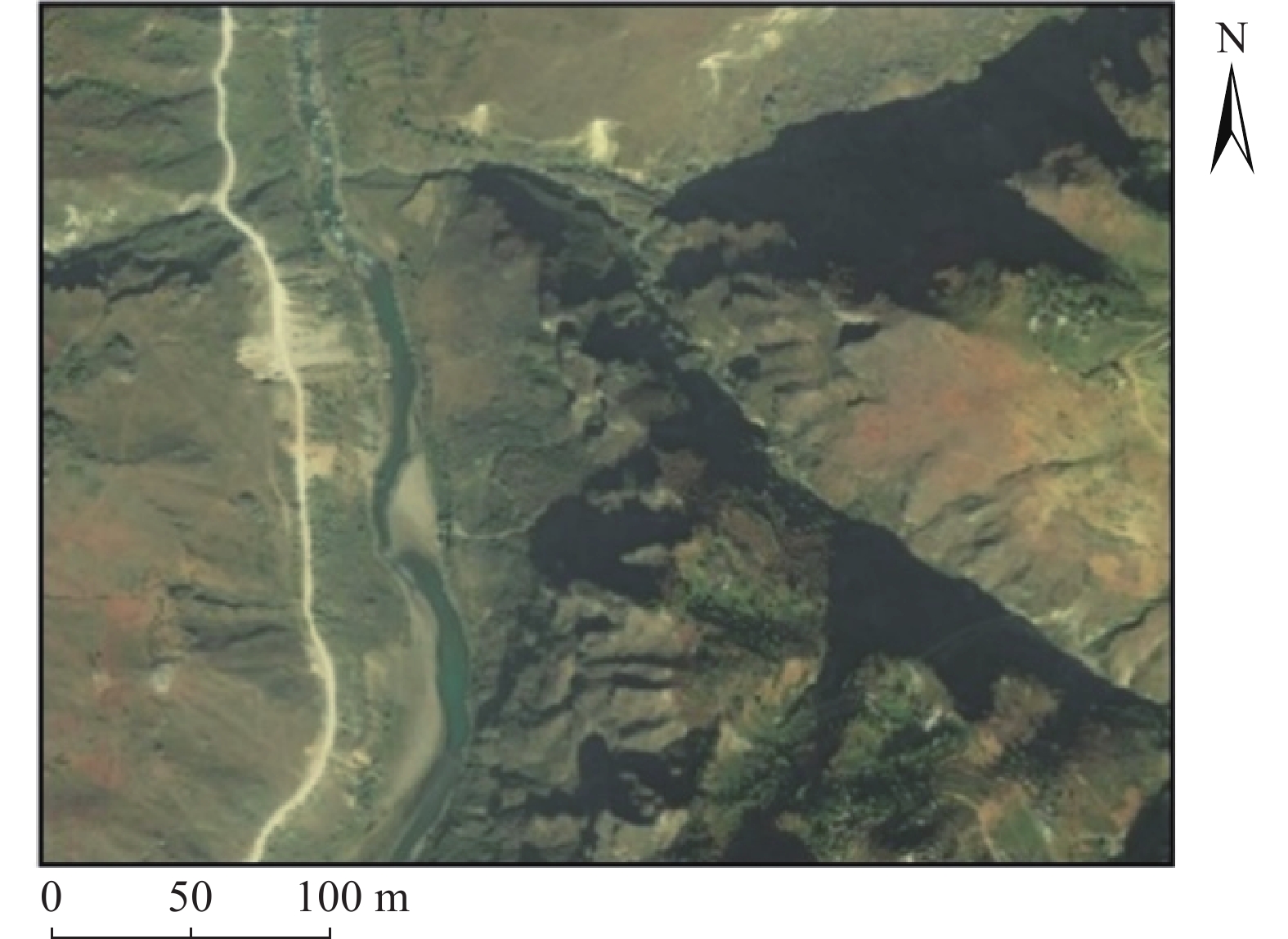
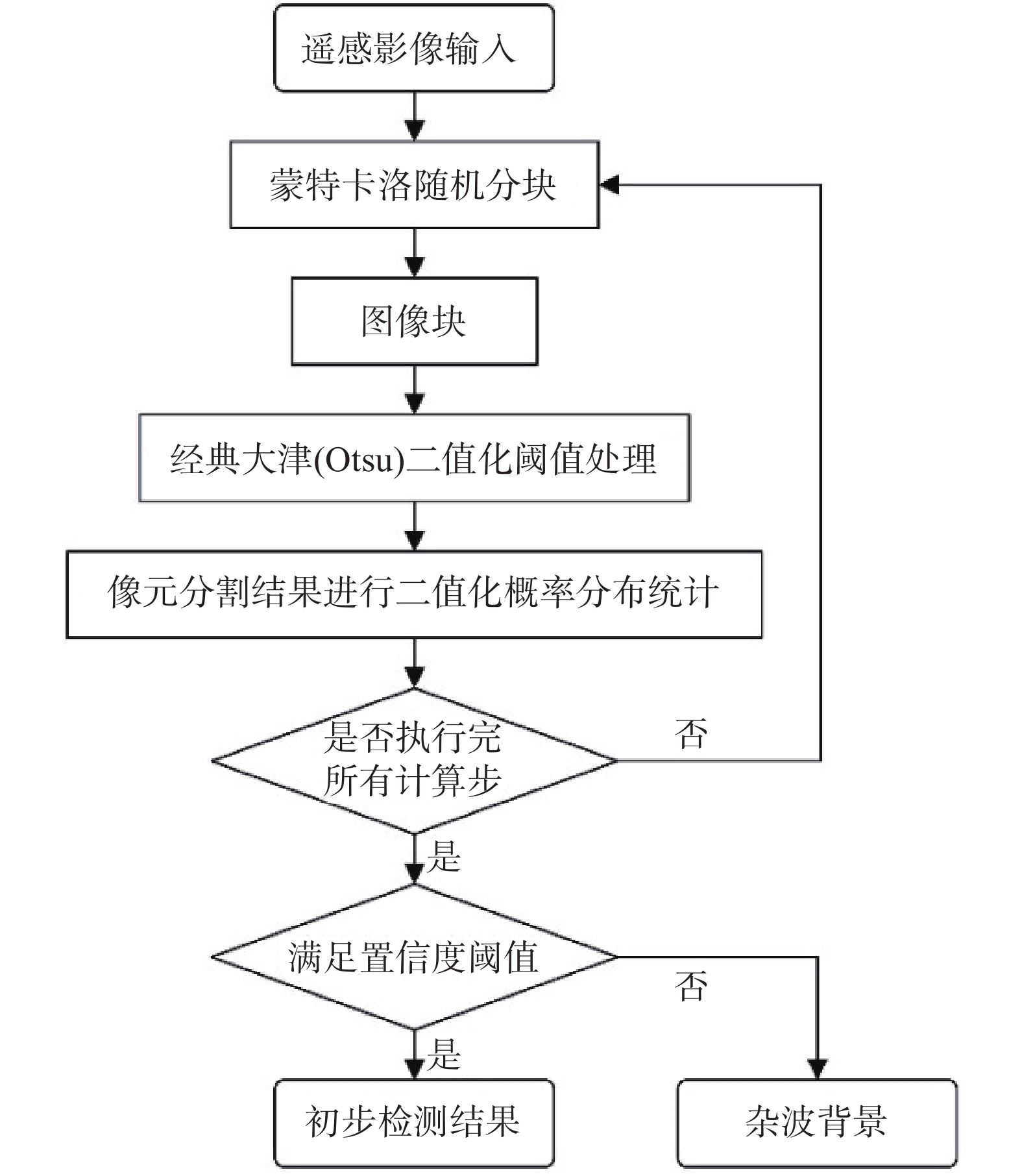
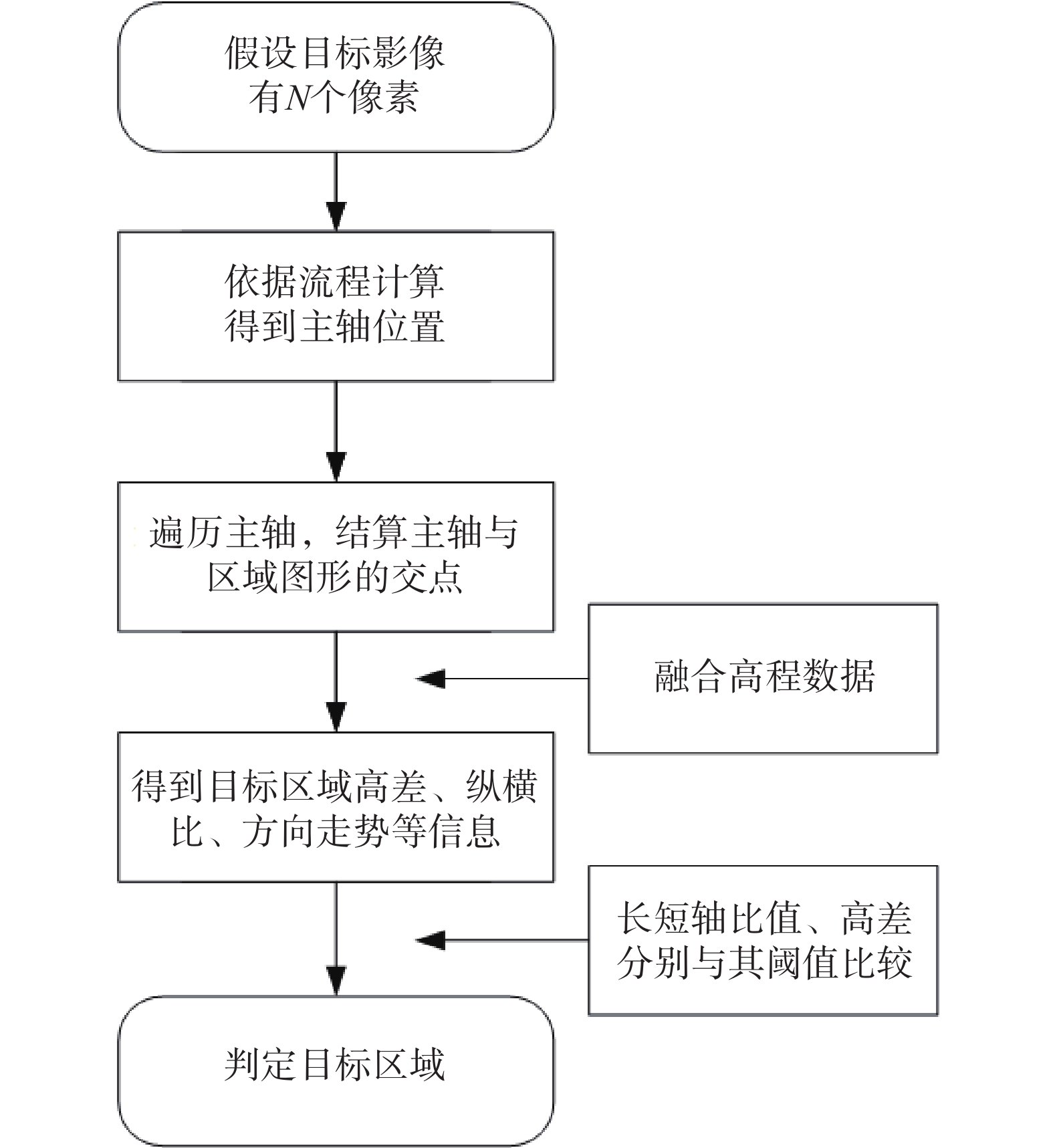
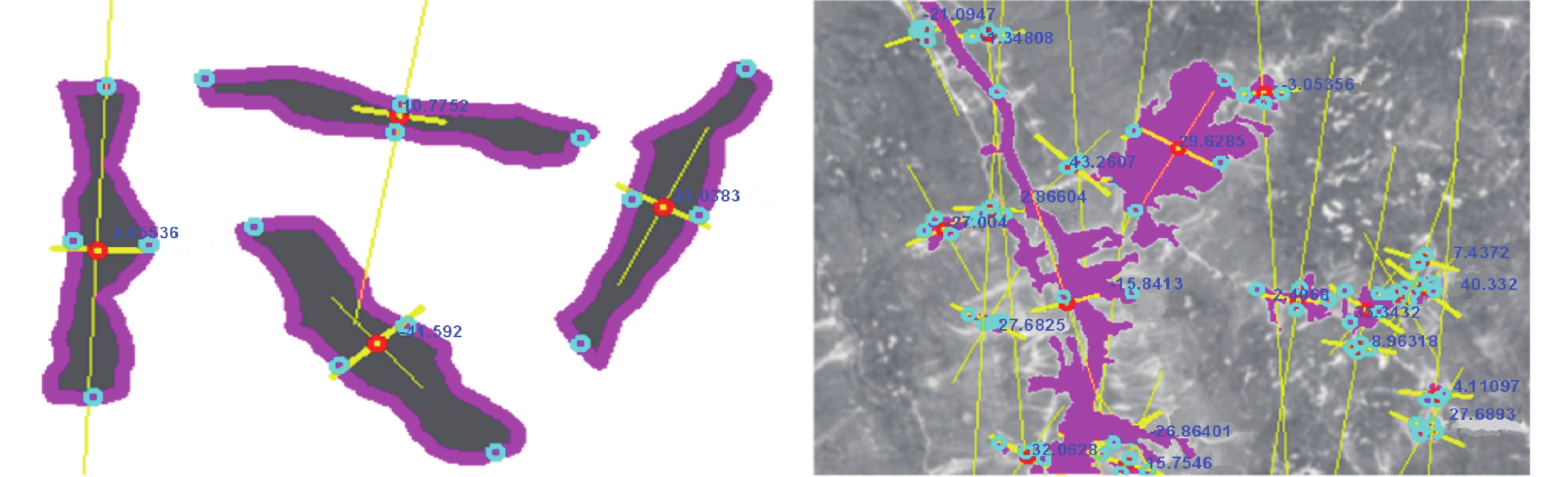
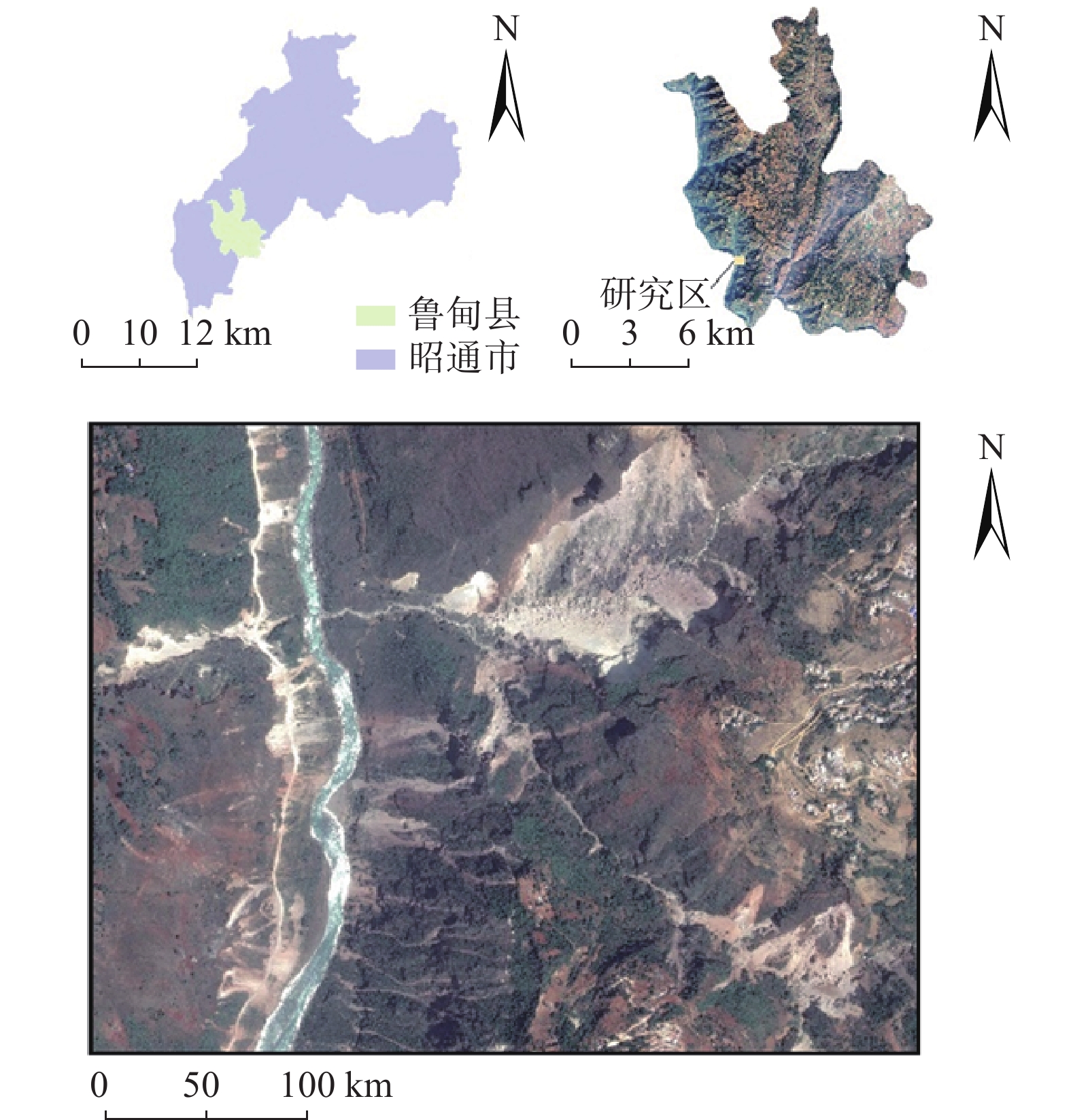
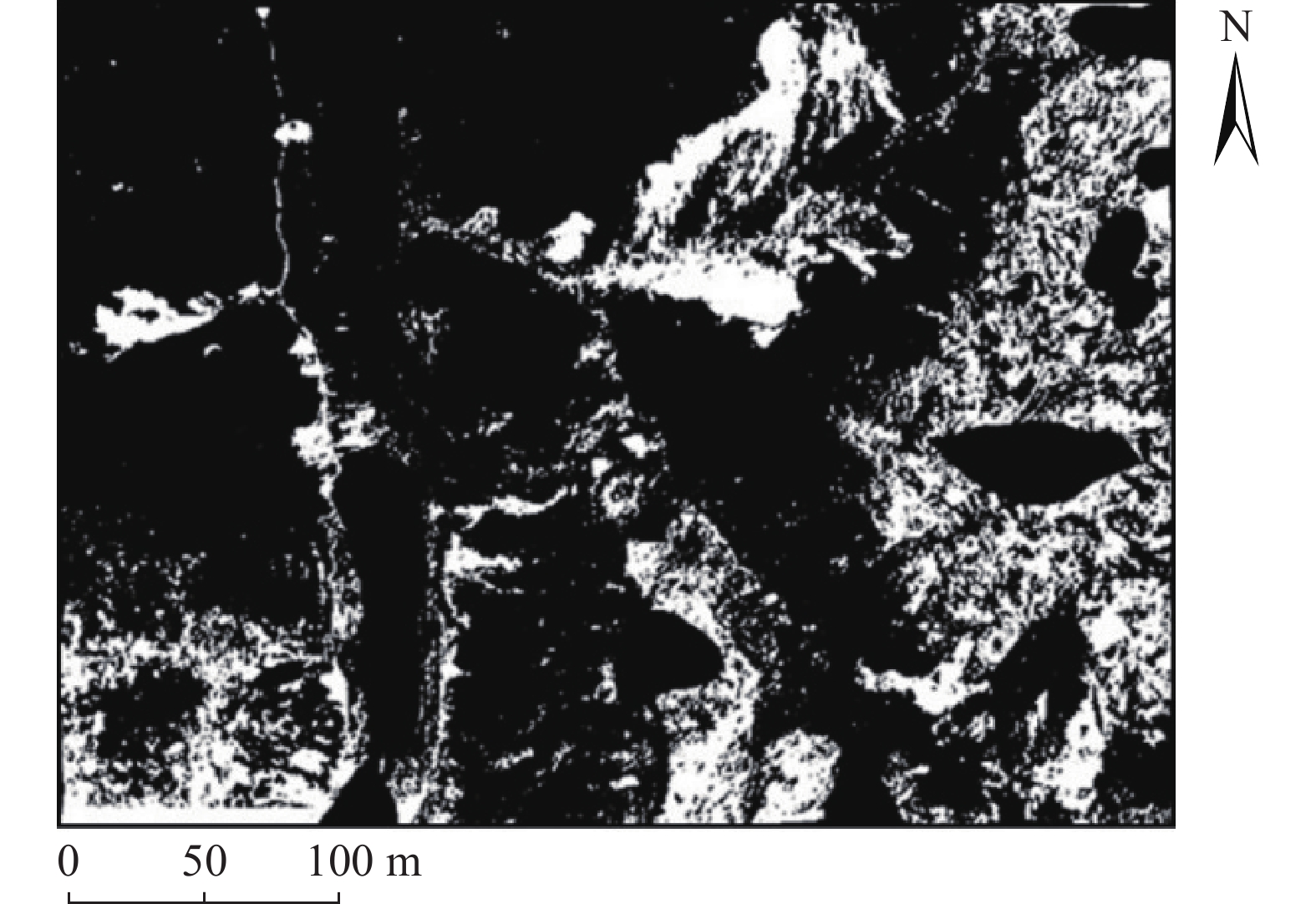
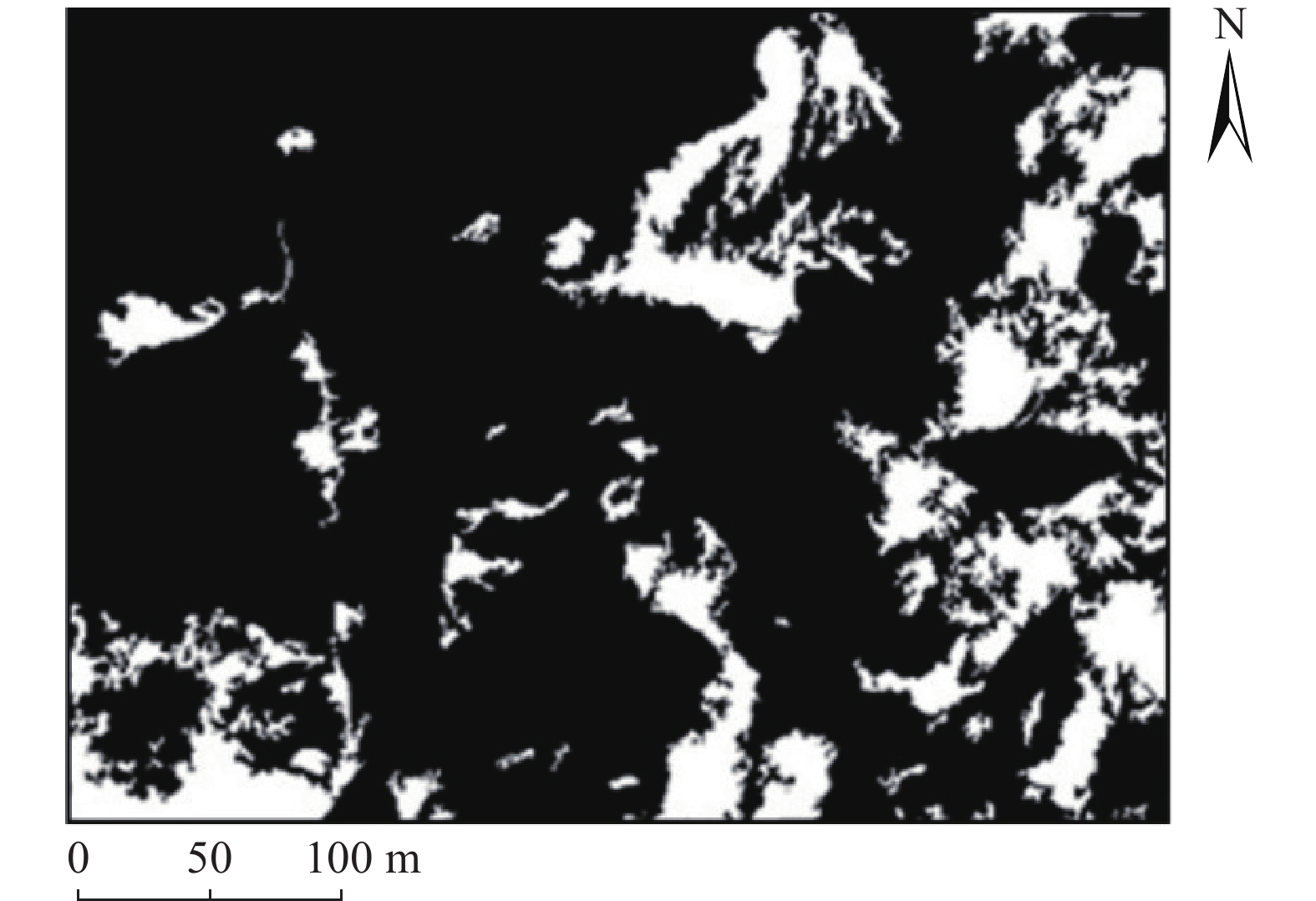
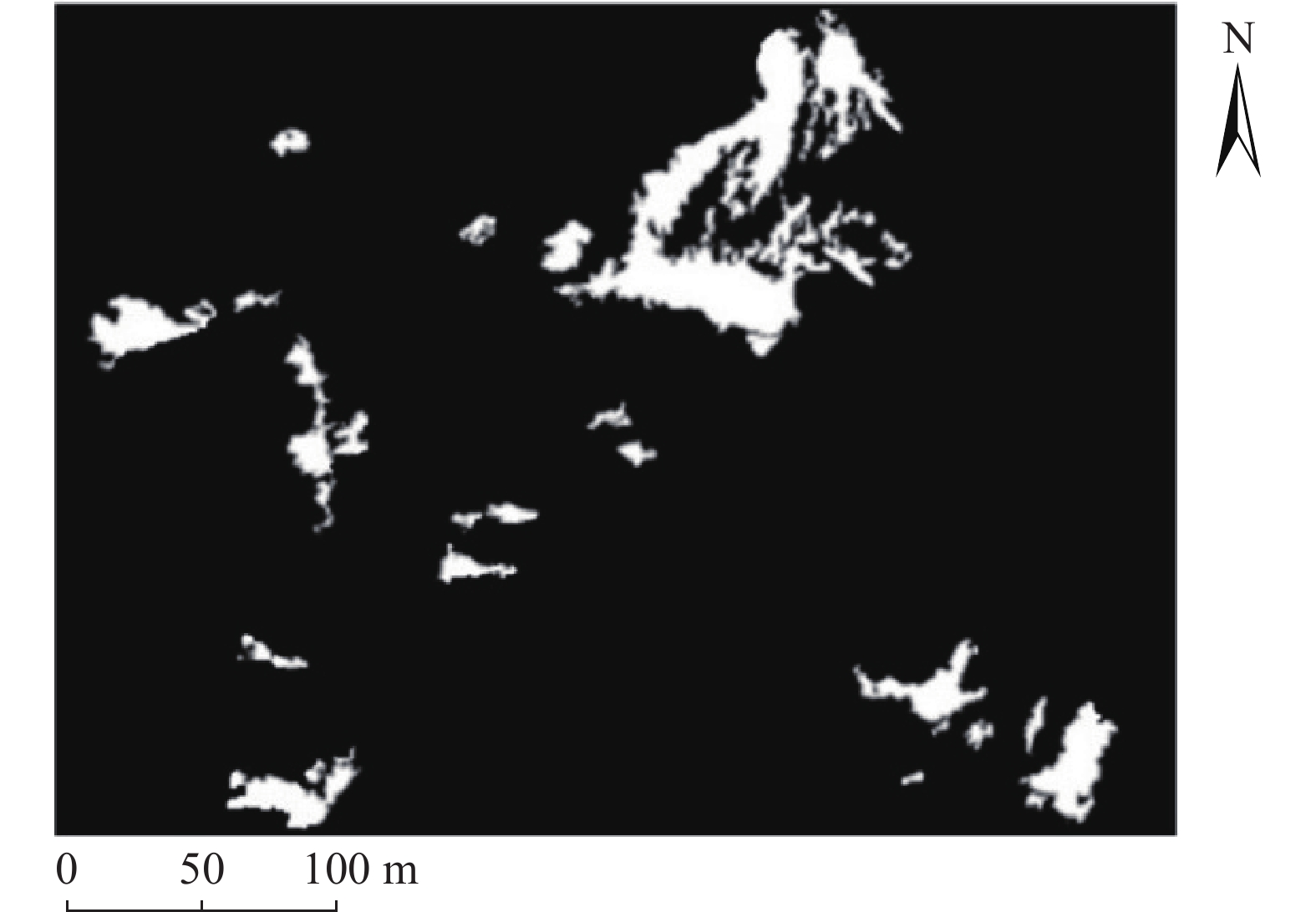
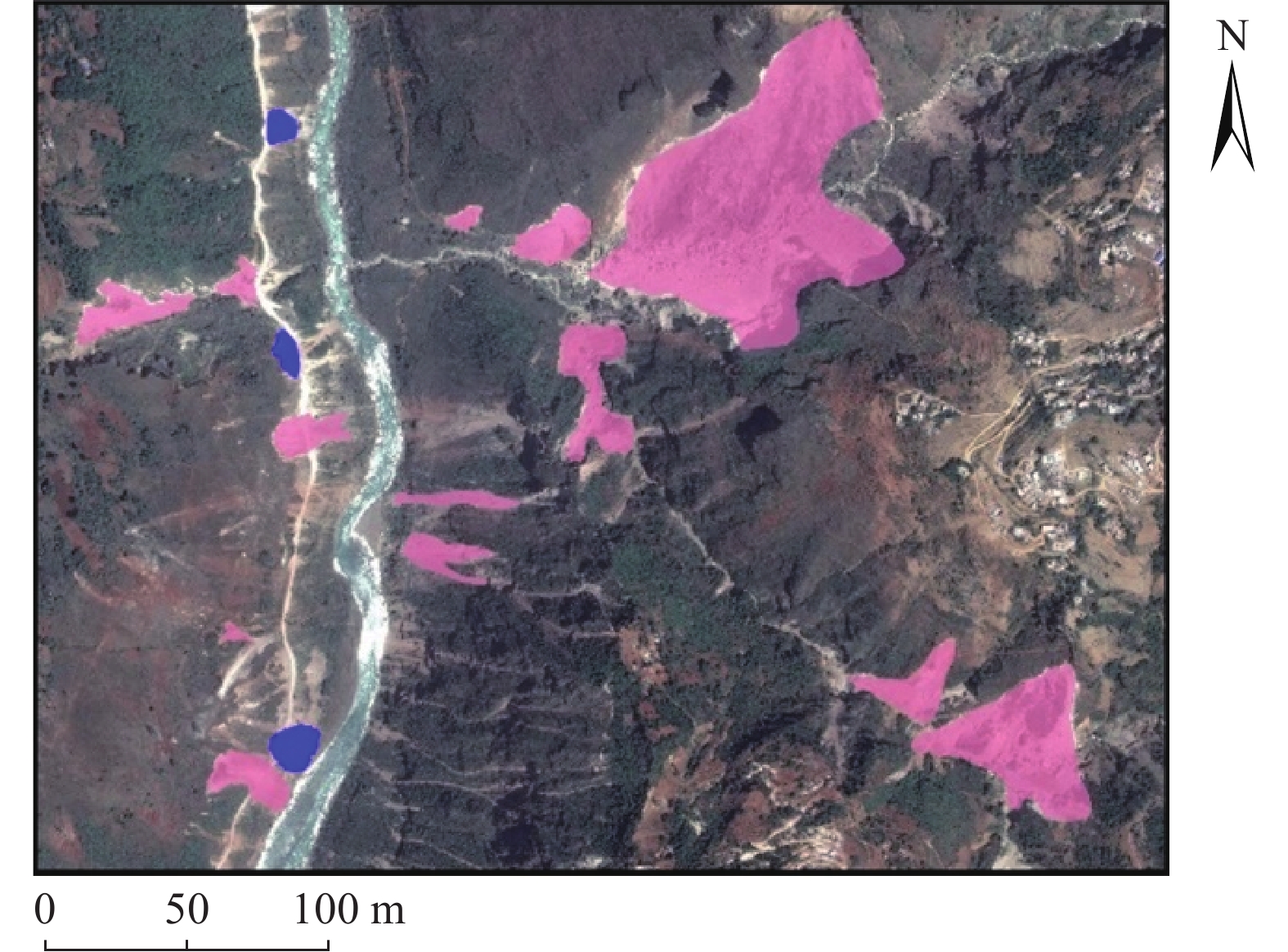
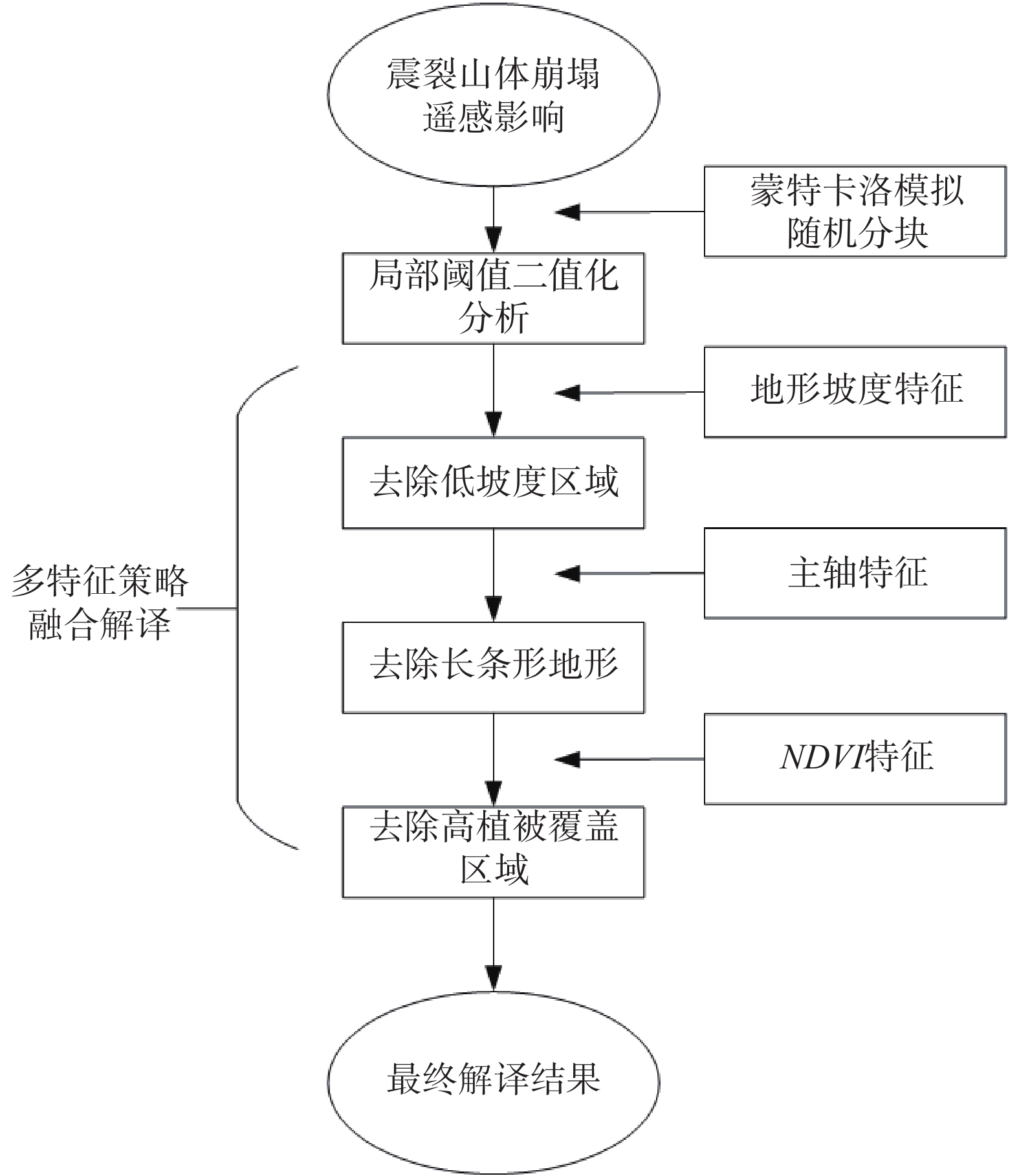
同震崩塌滑坡的解译及定位是震区灾后恢复工作中需要重点解决的问题,如何在灾害快速、自动解译的基础上,不断提高解译精度,是目前同震崩塌滑坡解译的研究热点之一,也是促使地质灾害早期识别向智能化、科学化发展的必要前提。文章在团队前期所提出的遥感影像局部阈值二值化方法的基础上,针对同震崩塌滑坡解译结果假阳率偏高的问题,分析了假阳性地物的光学和几何特点,提出了融合目标区域光学影像灰度特征、区域坡度信息、NDVI指数特征及解译地物主轴特征的同震崩塌滑坡多特征融合解译方法。为验证所提出模型的准确性,以2014年云南鲁甸地震龙头山镇为研究区,利用震后获取的高分一号(GF-1)卫星影像数据及数字高程模型对该同震崩塌滑坡进行了解译识别,结果表明,文中提出的方法准确解译出了同震崩塌滑坡区域,并有效去除了假阳性地物干扰,提高了解译精度。
Abstract:Interpretation of co-seismic collapse landslides is a key problem that needs to be solved in the post-disaster recovery work in earthquake areas. The issue regarding continuously improvement of interpretation accuracy for rapid and automatic interpretation of disasters is currently a hot topic, which is also a prerequisite to promote the development of early recognition of geological disasters towards intelligence and scientific. Based on the local threshold binarization method of remote sensing image proposed by the team in the early stage, this paper analyzes the optical and geometric characteristics of false positive features and proposes a fusion for the high false positive rate of the interpreted results of co-seismic mountain collapse. The multi-feature fusion interpretation method of the co-seismic mountain collapse with the gray feature of the optical image of the target area, the regional slope information, the NDVI feature and the interpretation of the main axis feature of the ground feature. In order to verify the accuracy of the proposed model, based on the 2014 Ludian earthquake in Yunnan, a case study was carried out in the Longtoushan town area. The Gaofen-1 (GF-1) satellite image data obtained after the earthquake and the digital elevation model were used for the earthquake in this area. The interpretation and recognition of the collapse of the cracked mountain shows that the method proposed in this paper accurately interprets the collapsed area of the cracked mountain body, effectively removes the false positive ground object interference, and improves the accuracy of interpretation.
-

-
表 1 原始数据参数信息表
Table 1. Information of the input data
原始数据 谱段范围/μm 空间分辨率/m 高分一号(GF-1)
卫星影像数据0.45~0.90 2.00 0.45~0.52 8.00 0.52~0.59 0.63~0.69 0.77~0.89 数字高程模型DEM − 30.00 -
[1] 范一大,吴玮,王薇,等. 中国灾害遥感研究进展[J]. 遥感学报,2016,20(5):1170 − 1184. [FAN Yida,WU Wei,WANG Wei,et al. Research progress of disaster remote sensing in China[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing,2016,20(5):1170 − 1184. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 常昊,张吕. 云南鲁甸Ms6.5级地震震区滑坡易发性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(2):38 − 48. [CHANG Hao,ZHANG Lyu. Analysis of Susceptibility causes of landslides triggered by earthquake in Ludian Ms6.5 earthquake region[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(2):38 − 48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 曹颖,黄江培,钱佳威,等. 利用时移层析成像方法揭示与2014年云南鲁甸MS6.5地震有关的P波速度变化[J]. 地球物理学报,2021,64(5):1569 − 1584. [CAO Ying,HUANG Jiangpei,QIAN Jiawei,et al. Application of time-lapse seismic tomography based on double-difference tomography to reveal P wave velocity changes related to the 2014 Ludian MS6.5 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2021,64(5):1569 − 1584. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 韩继冲,张朝,曹娟. 基于逻辑回归的地震滑坡易发性评价—以汶川地震、鲁甸地震为例[J]. 灾害学,2021,36(2):193 − 199. [HAN Jichong,ZHANG Zhao,CAO Juan. Assessing earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility based on logistic regression in 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and 2014 Ludian earthquake[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021,36(2):193 − 199. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.02.034
[5] 胡华,吴轩,张越. 基于模拟试验的强降雨条件下花岗岩残积土斜坡滑塌破坏机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):92 − 97. [HU Hua,WU Xuan,ZHANG Yue. Experimental study on slope collapse characteristics of granite residual soil slope under heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):92 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 魏正发,张俊才,曹小岩,等. 青海西宁南北山滑坡、崩塌成因及影响分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):47 − 55. [WEI Zhengfa,ZHANG Juncai,CAO Xiaoyan,et al. Causes and influential factor analysis of landslides and rockfalls in north & south mountain areas of Xining City,Qinghai Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):47 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 龙玉洁,李为乐,黄润秋,等. 汶川地震震后10 a绵远河流域滑坡遥感自动提取与演化趋势分析[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版,2020,45(11):1792 − 1800. [LONG Yujie,LI Weile,HUANG Runqiu,et al. Automatic extraction and evolution trend analysis of landslides in Mianyuan River basin in the 10 years after Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(11):1792 − 1800. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 孙国庆,陈方,于博,等. 2001—2017年尼泊尔中部地区滑坡变化及其影响因素[J]. 中国科学院大学学报,2020,37(3):308 − 316. [SUN Guoqing,CHEN Fang,YU Bo,et al. Landslide change and its influence factors in central Nepal from 2001 to 2017[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2020,37(3):308 − 316. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2020.03.003
[9] 许冲,戴福初,陈剑,等. 汶川Ms8.0地震重灾区次生地质灾害遥感精细解译[J]. 遥感学报,2009,13(4):754 − 762. [XU Chong,DAI Fuchu,CHEN Jian,et al. Remote sensing fine interpretation of secondary geological disasters in the hardest hit areas of Wenchuan Ms8.0 earthquake[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing,2009,13(4):754 − 762. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11834/jrs.20090416
[10] LU P,QIN Y Y,LI Z B,et al. Landslide mapping from multi-sensor data through improved change detection-based Markov random field[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2019,231:111235. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111235
[11] LI Z B,SHI W Z,LU P,et al. Landslide mapping from aerial photographs using change detection-based Markov random field[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2016,187:76 − 90. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.10.008
[12] STUMPF A,KERLE N. Object-oriented mapping of landslides using Random Forests[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2011,115(10):2564 − 2577. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.05.013
[13] VAN DEN EECKHAUT M,KERLE N,POESEN J,et al. Object-oriented identification of forested landslides with derivatives of single pulse LiDAR data[J]. Geomorphology,2012,173/174:30 − 42. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.05.024
[14] MARTHA T R,KERLE N,JETTEN V,et al. Characterising spectral,spatial and morphometric properties of landslides for semi-automatic detection using object-oriented methods[J]. Geomorphology,2010,116(1/2):24 − 36.
[15] SUN W Y,TIAN Y S,MU X M,et al. Loess landslide inventory map based on GF-1 satellite imagery[J]. Remote Sensing,2017,9(4):314. doi: 10.3390/rs9040314
[16] LESHCHINSKY B A,OLSEN M J,TANYU B F. Contour Connection Method for automated identification and classification of landslide deposits[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2015,74:27 − 38.
[17] LI Y G,CHEN G Q,HAN Z,et al. A hybrid automatic thresholding approach using panchromatic imagery for rapid mapping of landslides[J]. GIScience & Remote Sensing,2014,51(6):710 − 730.
[18] HAN Z,SU B,LI Y G,et al. An enhanced image binarization method incorporating with Monte-Carlo simulation[J]. Journal of Central South University,2019,26(6):1661 − 1671. doi: 10.1007/s11771-019-4120-9
[19] HAN Z,LI Y G,DU Y F,et al. Noncontact detection of earthquake-induced landslides by an enhanced image binarization method incorporating with Monte-Carlo simulation[J]. Geomatics,Natural Hazards and Risk,2019,10(1):219 − 241. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2018.1520745
[20] CASTELLANOS F J,GALLEGO A J,CALVO-ZARAGOZA J. Unsupervised neural domain adaptation for document image binarization[J]. Pattern Recognition,2021,119:108099. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108099
[21] XIONG W,ZHOU L,YUE L,et al. An enhanced binarization framework for degraded historical document images[J]. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing,2021,2021(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13640-021-00556-4
[22] 皮新宇,曾永年,贺城墙. 融合多源遥感数据的高分辨率城市植被覆盖度估算[J]. 遥感学报,2021,25(6):1216 − 1226. [PI Xinyu,ZENG Yongnian,HE Chengqiang. High-resolution urban vegetation coverage estimation based on multi-source remote sensing data fusion[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin,2021,25(6):1216 − 1226. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] ASHOK A,RANI H P,JAYAKUMAR K V. Monitoring of dynamic wetland changes using NDVI and NDWI based landsat imagery[J]. Remote Sensing Applications:Society and Environment,2021,23:100547. doi: 10.1016/j.rsase.2021.100547
[24] 陈安,李景吉,黎文婷,等. 2001—2018年雅砻江流域植被NDVI时空动态及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 水土保持研究,2022,29(1):169 − 175. [CHEN An,LI Jingji,LI Wenting,et al. Spatiotemporal of NDVI in the Yalong River basin from 2001 to 2018 and its response to climate change[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2022,29(1):169 − 175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] SHEN J X,EVANS F. The potential of landsat NDVI sequences to explain wheat yield variation in fields in western Australia[J]. Remote Sensing,2021,13(11):2202. doi: 10.3390/rs13112202
[26] 岳思聪,赵荣椿,王庆. 基于象素主轴方向灰度变化特征的特征点检测算法[J]. 西北工业大学学报,2008,26(2):162 − 167. [YUE Sicong,ZHAO Rongchun,WANG Qing. Feature point detection using intensity variations along pixel principal orientation axes[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University,2008,26(2):162 − 167. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2008.02.006
[27] 杨雨奇,高晓光,冯晓毅,等. 基于主轴分析和团块特征提取的ISAR目标检测方法[J]. 西北工业大学学报,2010,28(5):689 − 694. [YANG Yuqi,GAO Xiaoguang,FENG Xiaoyi,et al. A new method for ISAR target detection based on chief axis analysis and block feature extraction[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University,2010,28(5):689 − 694. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2010.05.010
[28] 郝军保,邵磊. 惯性主轴方向的最佳判别[J]. 连云港职业大学学报,1993,6(1):92 − 95. [HAO Junbao,SHAO Lei. The best discrimination of the direction of inertia spindle[J]. Journal of Lianyungang Technical College,1993,6(1):92 − 95. (in Chinese)
[29] 蔡建乐. 用特征矩阵的伴随矩阵求解惯量主轴方向[J]. 大学物理,1995,14(9):21 − 22. [CAI Jianle. A calculation for the principal axes of inertia by adjoint matrix of eigen matrix[J]. College Physics,1995,14(9):21 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 罗斌. 灰度图象的惯性主轴方向特征[J]. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版),1998,22(4):40 − 42. [LUO Bin. Least inertia moment axis of grey scale image[J]. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Sciences),1998,22(4):40 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 周智勇. 基于Landsat遥感影像的围场县植被覆盖时空格局变化[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):81 − 90. [ZHOU Zhiyong. Change in temporal-spatial pattern of vegetation coverage in Weichang County based on Landsat remote sensing image[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):81 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 贺军亮,韦锐,李丽,等. 基于时间序列植被指数资料的承德市植被覆盖时空演变分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):91 − 98. [HE Junliang,WEI Rui,LI Li,et al. Temporal and spatial evolution of vegetation cover in Chengde based ontime series NDVI data[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):91 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 杜春雨,范文义. 叶面积指数与植被指数关系研究[J]. 林业勘查设计,2013(2):77 − 80. [DU Chunyu,FAN Wenyi. Research and analysis of the correlation between leaf area index and vegetation index[J]. Forest Investigation Design,2013(2):77 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4505.2013.02.035
[34] 潘霞,高永,汪季,等. 植被指数遥感演化研究进展[J]. 北方园艺,2018(20):162 − 169. [PAN Xia,GAO Yong,WANG Ji,et al. Review on vegetation index using remote sensing evolution[J]. Northern Horticulture,2018(20):162 − 169. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 张慧,李平衡,周国模,等. 植被指数的地形效应研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报,2018,29(2):669 − 677. [ZHANG Hui,LI Pingheng,ZHOU Guomo,et al. Advances in the studies on topographic effects of vegetation indices[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2018,29(2):669 − 677. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 张华,李明,宋金岳,等. 基于地理探测器的祁连山国家公园植被NDVI变化驱动因素分析[J]. 生态学杂志,2021,40(8):2530 − 2540. [ZHANG Hua,LI Ming,SONG Jinyue,et al. Analysis of driving factors of vegetation NDVI change in Qilian Mountain National Park based on geographic detector[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2021,40(8):2530 − 2540. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 武正丽. 2000~2012年祁连山植被覆盖变化及其对气候的响应研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2014
WU Zhengli. The research of the vegetation change and the sensitivity between NDVI and climatic factors in Qilian Mountains from2000to2012[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 周庆,吴果. 鲁甸6.5级地震崩滑地质灾害分布与成因探讨[J]. 地震地质,2015,37(1):269 − 278. [ZHOU Qing,WU Guo. Seismic landslides and seismogenic structure of the 2014 Ludian ms6.5 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology,2015,37(1):269 − 278. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.021
[39] 田颖颖,许冲,徐锡伟,等. 2014年鲁甸MS6.5地震震前与同震滑坡空间分布规律对比分析[J]. 地震地质,2015,37(1):291 − 306. [TIAN Yingying,XU Chong,XU Xiwei,et al. Spatial distribution analysis of coseismic and pre-earthquake landslides triggered by the 2014 Ludian ms6.5 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology,2015,37(1):291 − 306. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.023
[40] 许强, 李为乐. 汶川地震诱发滑坡方向效应研究[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2010, 42(增刊1): 7 − 14
XU Qiang, LI Weile. Study on the direction effects of landslides triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2010, 42(Sup 1): 7 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] 许强,李为乐. 汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(6):818 − 826. [XU Qiang,LI Weile. Distribution of large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(6):818 − 826. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.06.002
-



 下载:
下载: