Analysis on development characteristics and formation mechanism of karst collapse in Shakou Town, Yingde City of Guandong Province
-
摘要:
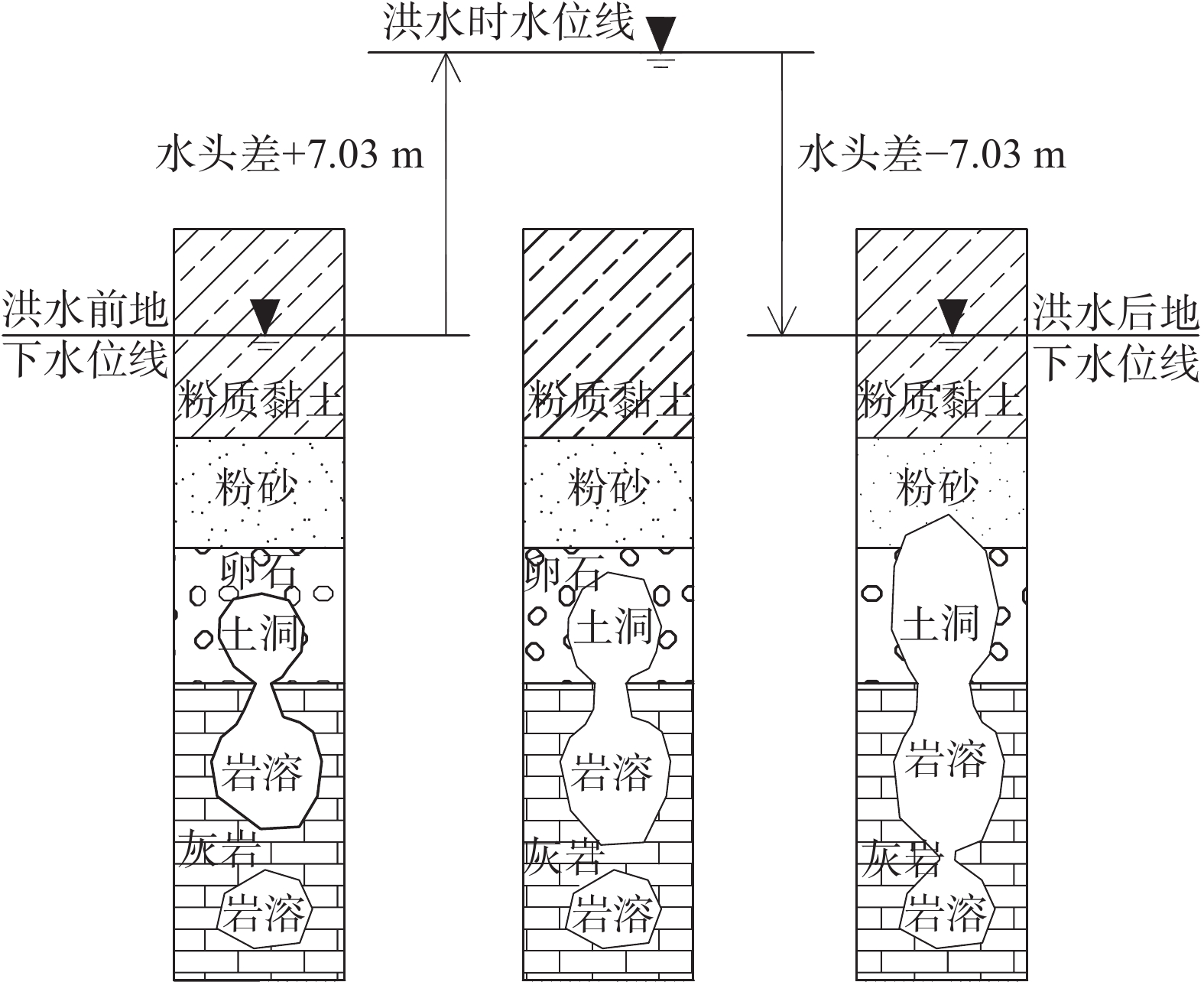
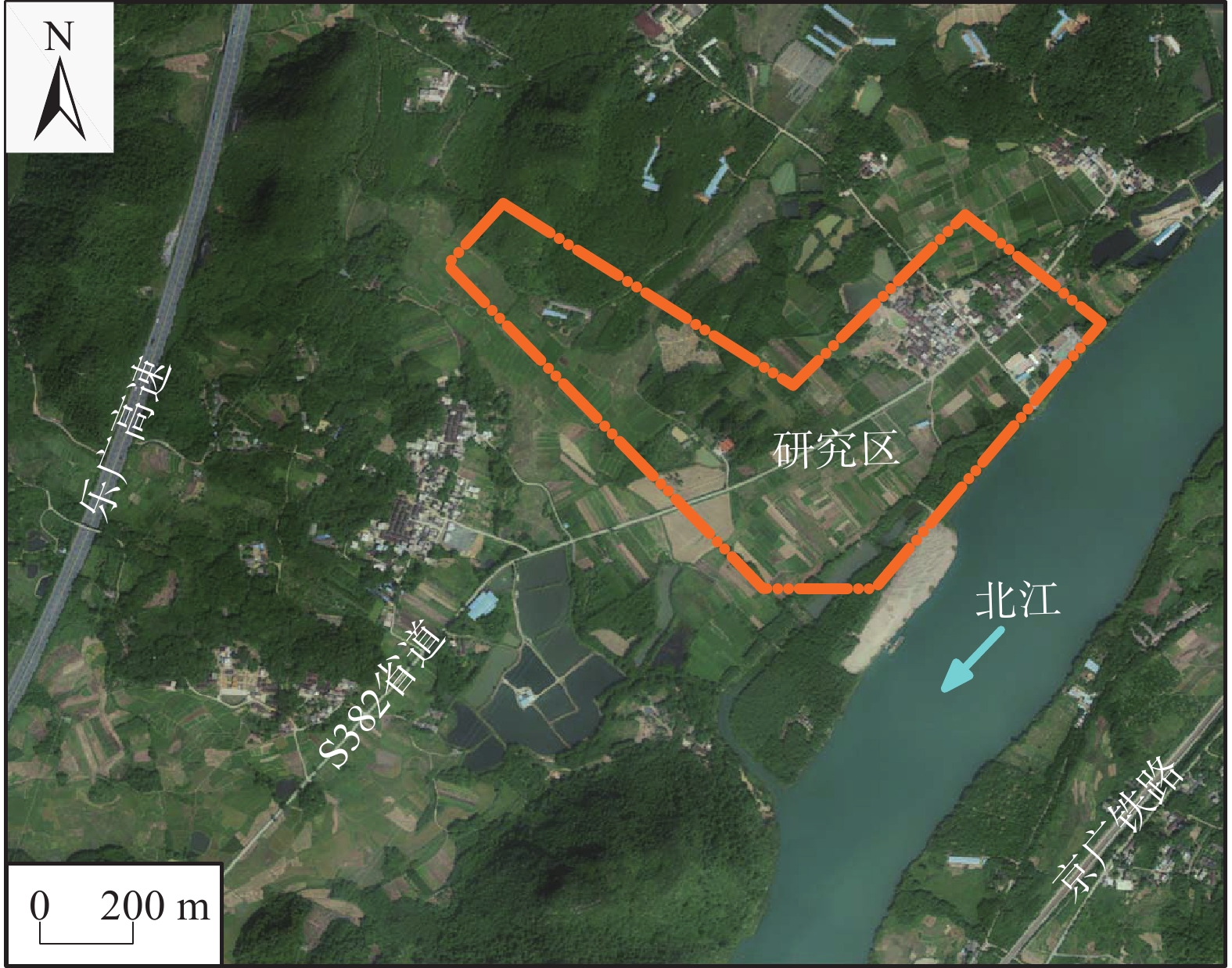
近年,广东省粤北山区隐伏区岩溶地面塌陷日益增加,直接影响人民生产生活。英德市沙口镇某村地质环境复杂,第四系覆盖层厚度薄,底部卵石层与下覆天子岭组灰岩直接接触,溶洞与断层破碎带发育,溶洞与溶洞间连通性较好,岩溶地面塌陷地质灾害严重。在综合分析沙口镇某村地质环境条件基础上,从内、外两方面因素,对岩溶地面塌陷发育特征及形成机理进行分析,认为在长期地下水位波动、潜蚀及淘蚀等作用松散盖层土体颗粒流失形成土洞,地表水与地下水强烈交替形成正负压力等作用下,土洞上部盖层发生塌陷。研究结论为科学制定岩溶地面塌陷防治方案提供依据。
Abstract:In recent years, the collapse of hidden karst ground in the mountainous area of north Guangdong Province is increasing, which directly affects people's production and life. In a village of Shakou Town, Yingde City, where the geological environment conditions are complex and the quaternary overburden is thin, serious geological disaster of karst ground collapse has occurred due to the development of the karst cave and fault fracture zone and the connectivity between karst cave and karst cave. The direct contact between the bottom pebble layer and the overlying limestone of Tianziling Formation also accounts for the disastrous consequence. Based on the comprehensive analysis of the geological environment conditions of the village in Shakou Town, the development characteristics and formation mechanism of karst ground collapse from internal and external factors were analyzed. It is concluded that the loose cavern is formed by the loss of soil particles in the loose cavern under the interaction of long-term fluctuation of groundwater level, erosion and scouring; the strong alternation of surface water and groundwater forms the positive and negative pressure action; the ground collapse is caused by the loss of bearing capacity of the upper cavern. The conclusion of the research provides sufficient basis for making projects of preventing karst ground collapse scientifically.
-

-
表 1 研究区岩溶地面塌陷统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of karst ground collapse in the study area
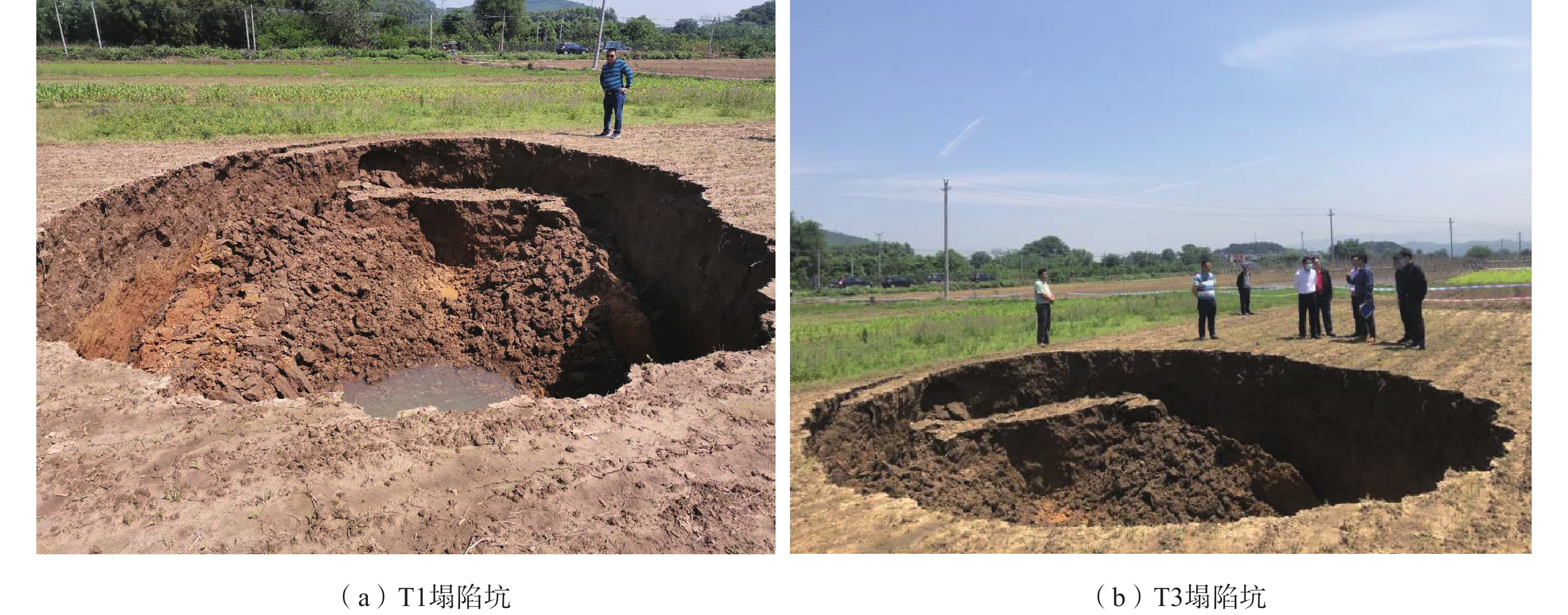
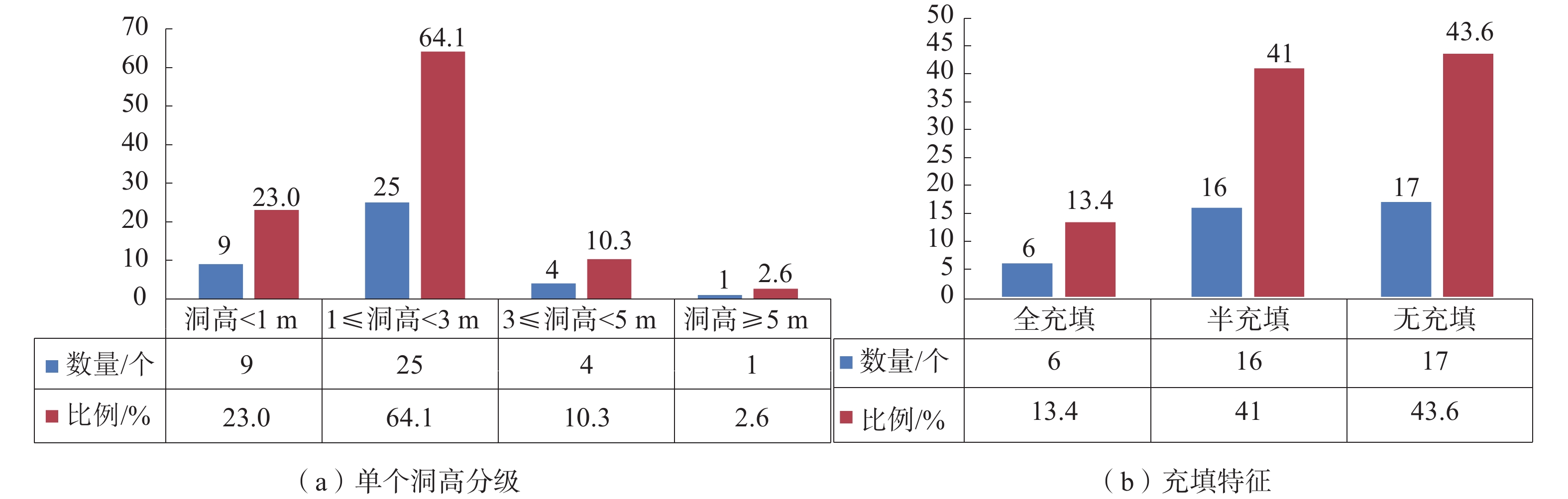
编号 发生时间 平面形态 地貌及第四系岩性 造成损失 T1 2020-04-26 呈16.45×14.03 m的椭圆形,深4.9m 河流阶地,粉质黏土、粉砂及卵石 毁田 T2 2020-04-26 呈直径9.5 m的近圆形,深3.8 m 河流阶地,粉质黏土、粉砂及卵石 毁田 T3 2020-04-26 呈12.1×10.03 m的椭圆形,深3.8 m 河流阶地,粉质黏土、粉砂及卵石 毁田 T4 2020-02-04 呈7.95×6.80 m的椭圆形,深6.5 m 河流阶地,粉质黏土、粉砂及卵石 毁田 T5 2020-02-05 呈7.7×4.4 m的椭圆形,深6.5 m 河流阶地,粉质黏土、粉砂及卵石 毁田 T6 2020-02-05 呈10.1×7.24 m的椭圆形,深5.2 m 丘陵坡地,粉质黏土 毁竹林 T7 2020-07-19 呈6.68 m的近圆形,深4.3 m 河流阶地,粉质黏土、粉砂及卵石 毁田 T8 1978年 呈5.0 m的近圆形,深5.0 m 河流阶地,粉质黏土、粉砂及卵石 毁田 表 2 钻孔揭露土洞、溶洞特征表
Table 2. Characteristics of cave and karst cave exposed by boreholes
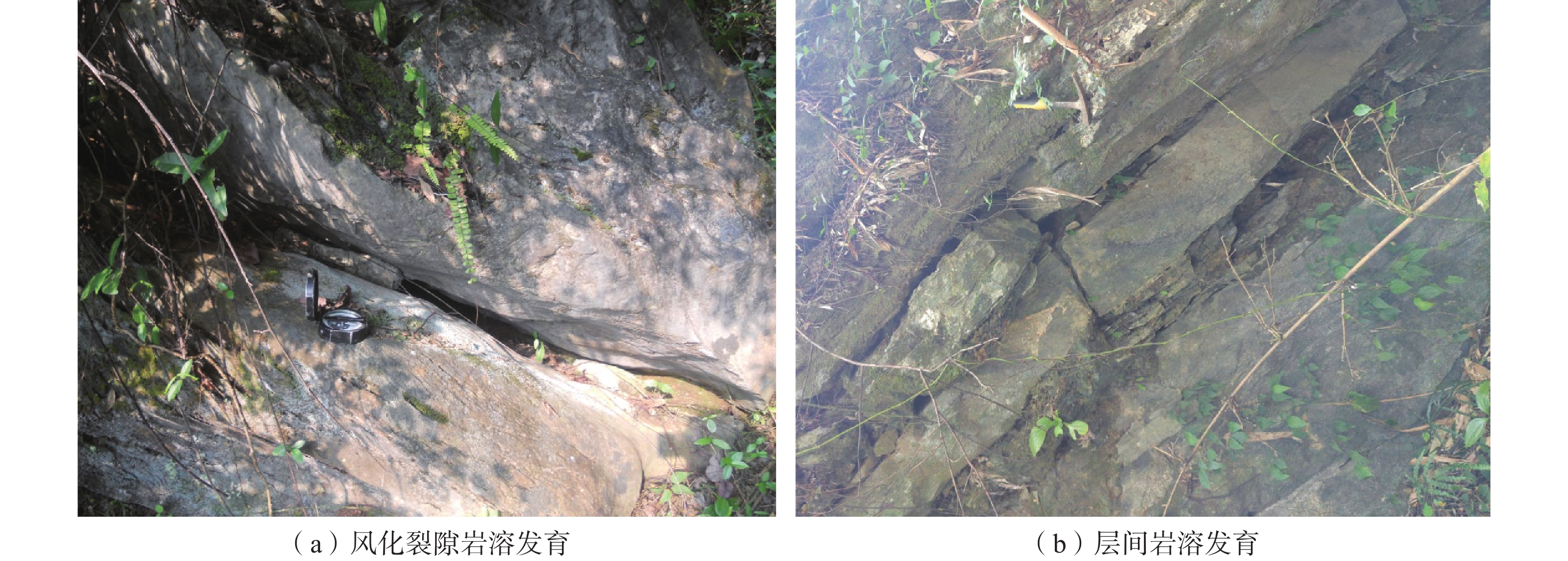
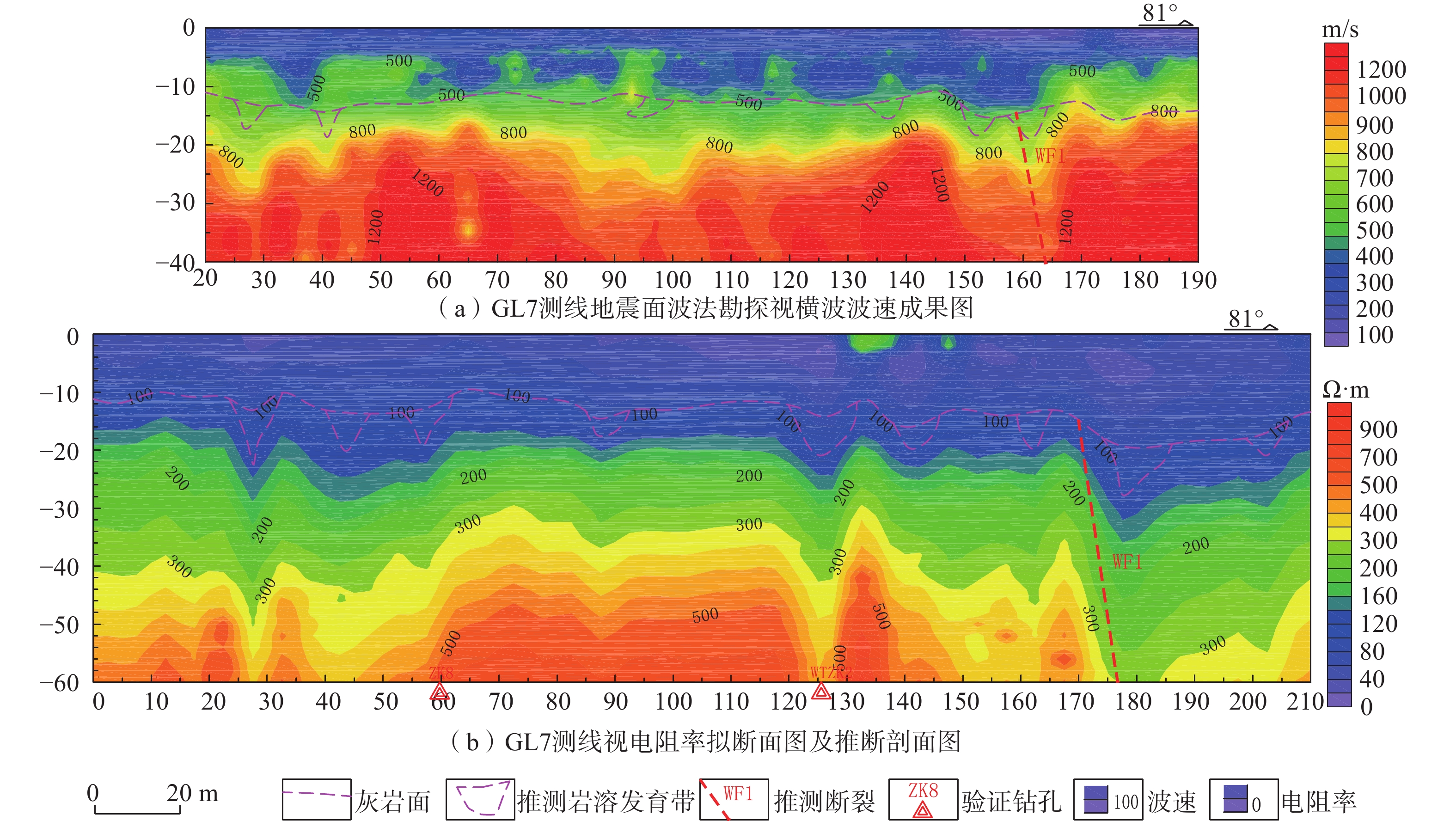
孔号 岩面埋深/m 溶洞顶板埋深/m 洞高/m 充填情况 溶洞层数 WTK1 19.2 19.2 1.1 全充填 1 WTK2 13.4 13.8 2.8 半充填 2 17.1 1.8 半充填 WTK3 33.1 30.8(土洞) 1.1 无充填 4 33.4 1.05 半充填 34.7 3.8 半充填 38.8 1.4 半充填 WTK6 11.6 12.2 0.2 无充填 1 WTK7 17.6 18.3 0.6 半充填 1 WTK8 12.8 14.4 1.2 半充填 1 WTK10 30.3 31.6 0.7 半充填 1 WTK11 19.7 22.1 0.5 半充填 1 ZK1 12.2 13.4 1.5 全充填 1 ZK2 19.7 18.2 1.3 半充填 1 ZK3 18.6 16.4(土洞) 2.2 无 2 18.7 1.6 全充填 ZK4 12.3 12.4 0.5 全充填 2 13.2 1.5 ZK5 16.1 16.3 1.6 半充填 1 ZK6 20.2 20.7 2.4 半充填 2 23.6 1.3 半充填 ZK7 12.3 13.1 1.1 全充填 2 15.1 1.8 ZK8 12.1 12.5 2.3 全充填 1 ZK10 11.6 12.4 0.4 全充填 1 ZK12 20.9 21.0 4.2 全充填 2 26.1 6.7 ZK14 13.6 17.3 1.8 全充填 1 ZK15 21.4 18.1(土洞) 3.3 半充填 1 ZK16 19.1 19.6 2.3 全充填 2 22.2 0.5 ZK18 11.2 11.8 0.4 全充填 4 13.7 2.6 16.4 2.0 18.8 3.6 ZK19 10.8 12.9 1.9 无充填 2 16.1 1.1 无充填 ZK21 20.4 21.6 0.7 半充填 1 ZK26 15.6 15.9 1.3 半充填 1 -
[1] 刘传正. 地质灾害勘查指南[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000
LIU Chuanzheng. Geological hazard exploration Guide[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000. (in Chinese)
[2] 韩庆定,罗锡宜. 广东佛山市高明区李家村岩溶塌陷群成因机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):56 − 64. [HAN Qingding,LUO Xiyi. Analysis on the formation mechanism and development process of karst collapses in Lijia Village,Gaoming District of Foshan City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):56 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 郑晓明,金小刚,陈标典,等. 湖北武汉岩溶塌陷成因机理与致塌模式[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):75 − 82. [ZHENG Xiaoming,JIN Xiaogang,CHEN Biaodian,et al. Mechanism and modes of karst collapse in Wuhan City,Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):75 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 周长松,邹胜章,朱丹尼,等. 广昆铁路复线秀宁隧道大皮坡—中村段岩溶塌陷成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(3):146 − 152. [ZHOU Changsong,ZOU Shengzhang,ZHU Danni,et al. An analysis of the cause of Karst collapses near the Dapipo-Zhongcun section of the Xiuning tunnel of the Guangzhou-Kunming railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):146 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 刘勇健,刘雅恒,刘湘秋,等. 广花盆地岩溶地面塌陷特征及形成机理研究[J]. 广东工业大学学报,2013,30(1):25 − 30. [LIU Yongjian,LIU Yaheng,LIU Xiangqiu,et al. Study of collapse characteristics of karst ground in the Guanghua basin and its formation mechanism[J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Technology,2013,30(1):25 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7162.2013.01.005
[6] 郑小战. 广花盆地岩溶地面塌陷灾害形成机理及风险评估研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010
ZHENG Xiaozhan. Research on genetic mechanism and risk evaluation of the karst collapse in Guanghua basin[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 黄健民,邓雄文,胡让全. 广州金沙洲岩溶区地下水位变化与地面塌陷及地面沉降关系探讨[J]. 中国地质,2015,42(1):300 − 307. [HUANG Jianmin,DENG Xiongwen,HU Rangquan. The relationship between groundwater and ground collapse and land subsidence in Jinshazhou,Guangzhou City[J]. Geology in China,2015,42(1):300 − 307. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.024
[8] 郑智杰,敖文龙,曾洁,等. 综合物探法在柳州泗角村岩溶塌陷区调查中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(5):143 − 149. [ZHENG Zhijie,AO Wenlong,ZENG Jie,et al. Application of integrated geophysical methods to karst collapse investigation in the Sijiao Village near Liuzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(5):143 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 缪世贤,黄敬军,武鑫,等. 徐州岩溶地质调查及其发育特征分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):172 − 177. [MIAO Shixian,HUANG Jingjun,WU Xin,et al. Karst geological survey and analysis of its development characteristics in Xuzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):172 − 177. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 史箫笛, 黄勋, 康小兵, 等. 高密度电法在覆盖型岩溶地区探测中的应用[J]. 人民长江, 2018(增刊2): 117 − 120.
SHI Xiaodi, HUANG Xun, KANG Xiaobing, et al. Application of high density electrical method in detecting covered Karst areas[J]. Yangtze River, 2018, 49(Sup 2): 117 − 120. (in Chinese)
[11] 易顺民. 广东省地面塌陷特征及防治对策[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2007,18(2):127 − 131. [YI Shunmin. Distribution characteristics of ground collapse and its countermeasures in Guangdong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2007,18(2):127 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2007.02.025
[12] 罗小杰. 武汉地区浅层岩溶发育特征与岩溶塌陷灾害防治[J]. 中国岩溶,2013,32(4):419 − 432. [LUO Xiaojie. Features of the shallow karst development and control of karst collapse in Wuhan[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2013,32(4):419 − 432. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 韩庆定,罗锡宜,易守勇,等. 广东佛山市高明区三洲盆地岩溶塌陷发育特征与时空分布规律[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):131 − 139. [HAN Qingding,LUO Xiyi,YI Shouyong,et al. Characteristics and spatial-temporal distribution law of karst collapse in Sanzhou basin in Gaoming District of Foshan City,Guangdong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):131 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 高宗军,马海会,王敏,等. 岩溶地面塌陷预测模型初探[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2009,20(4):66 − 71. [GAO Zongjun,MA Haihui,WANG Min,et al. Preliminary analysis on forecasting model of karst collapse[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2009,20(4):66 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2009.04.014
[15] 余政兴,金福喜,段选亮. 河床透-阻型岩溶塌陷形成机理[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):57 − 66. [YU Zhengxing,JIN Fuxi,DUAN Xuanliang. Formation mechanism of karst collapse with unconfined aquifer-aquitaed system in riverbed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):57 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.02.08
[16] 罗小杰. 覆盖型岩溶地面塌陷防治与应急处置[J]. 人民长江,2016,47(5):38 − 44. [LUO Xiaojie. Prevention,control and emergency disposal of covered karst ground collapse[J]. Yangtze River,2016,47(5):38 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: