Feature acquisition and stability evaluation of high dangerous rock mass based on oblique photography: A case study at Guanyinshan in Wanzhou , Chongqing Province
-
摘要:
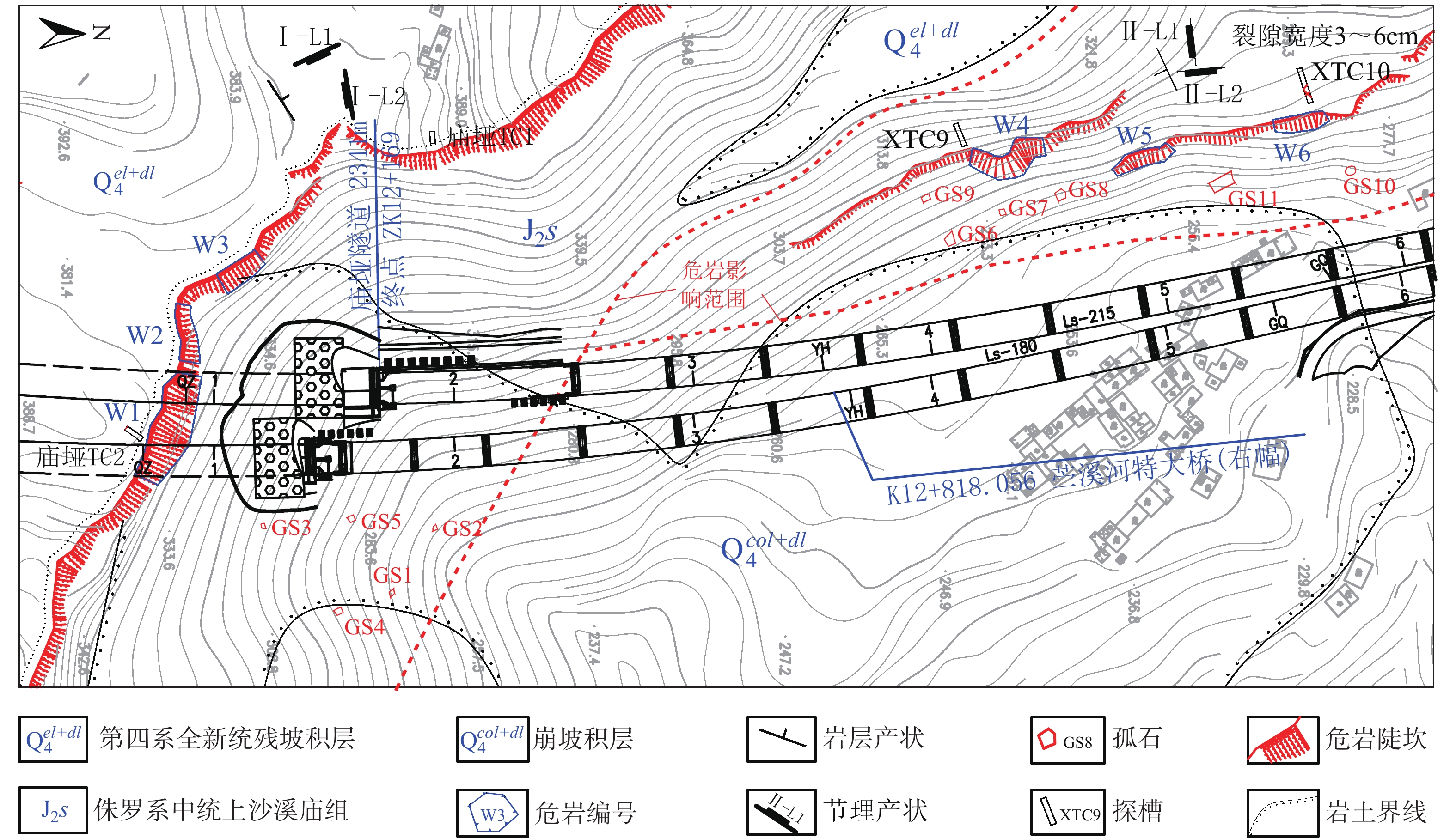
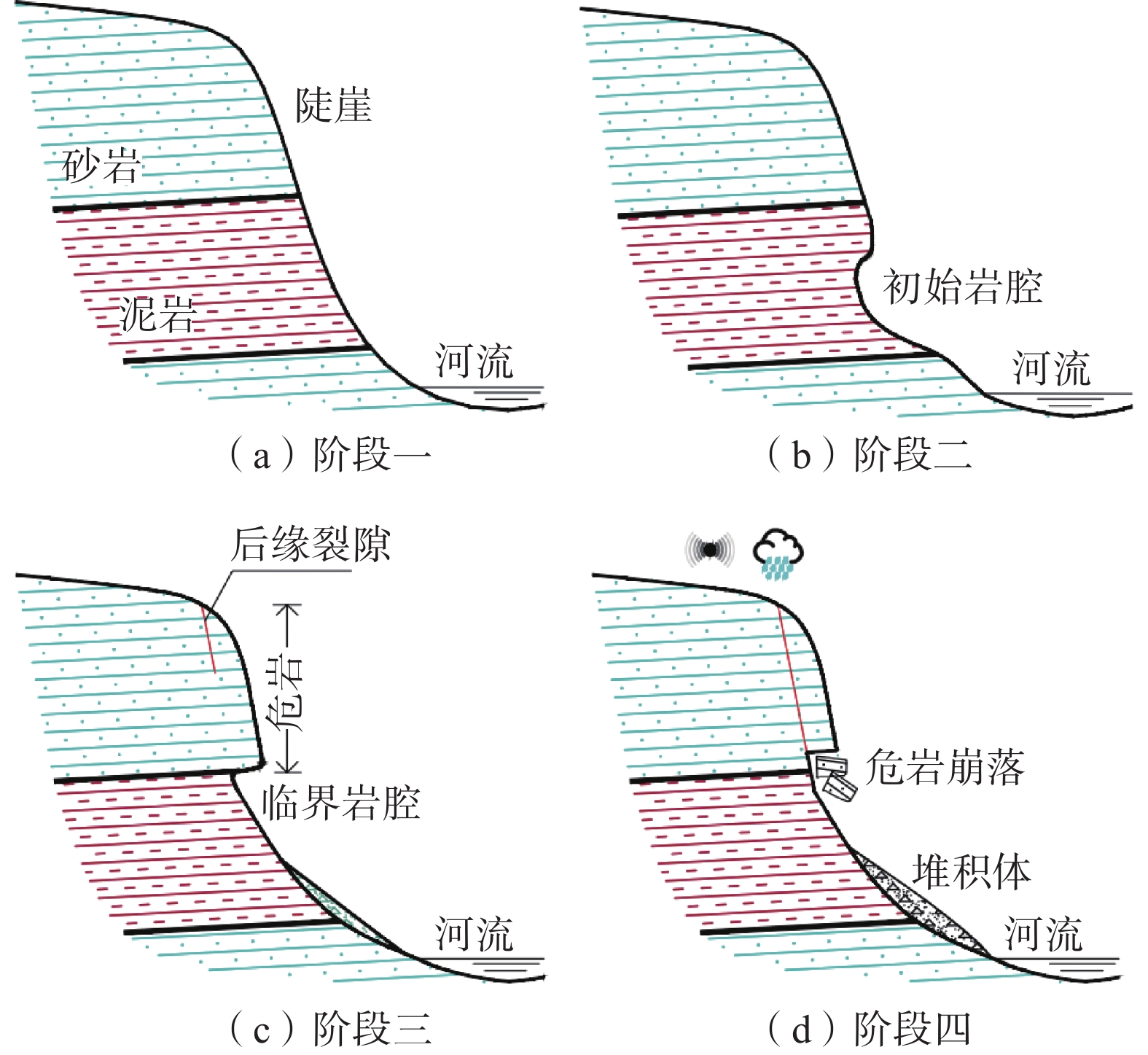
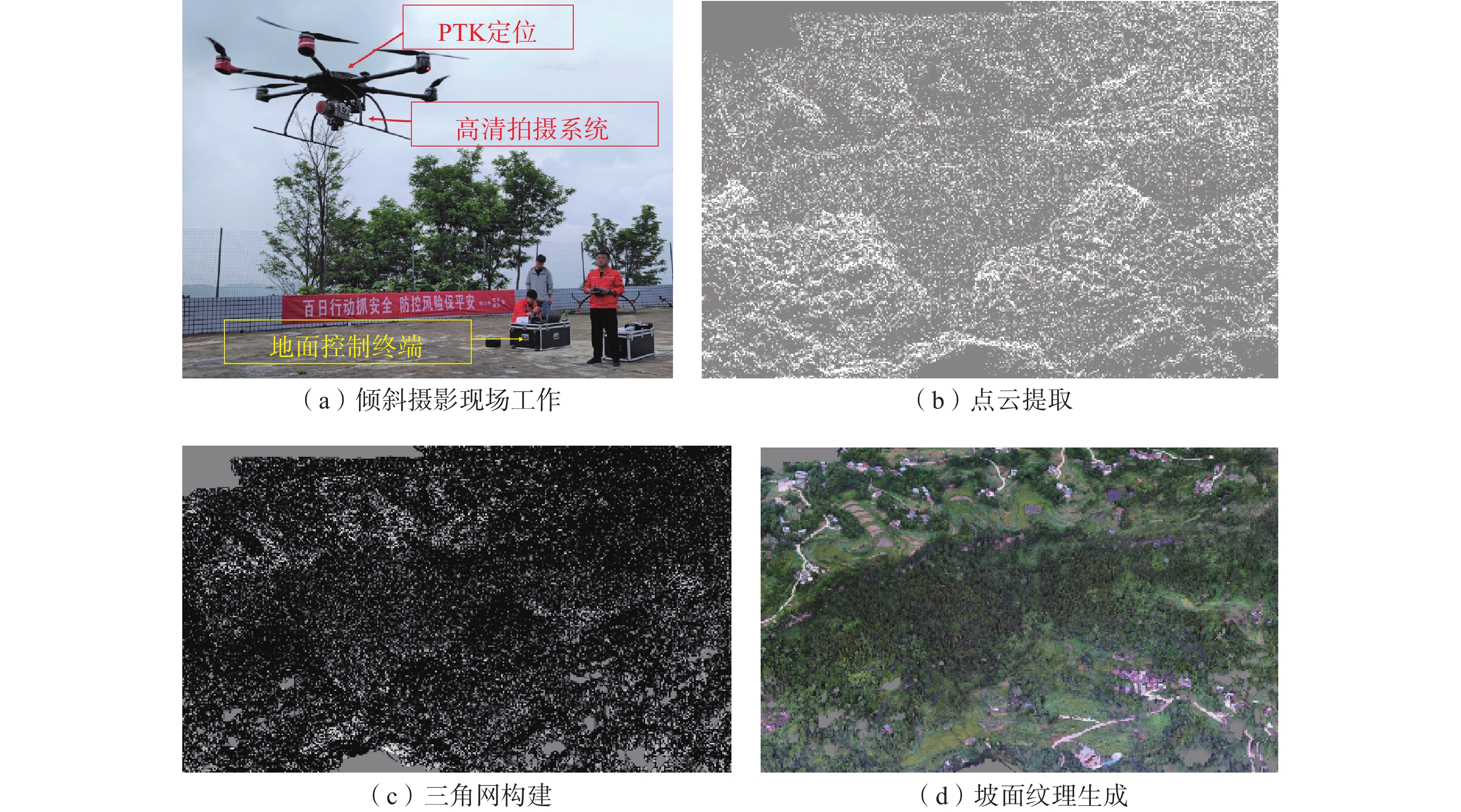
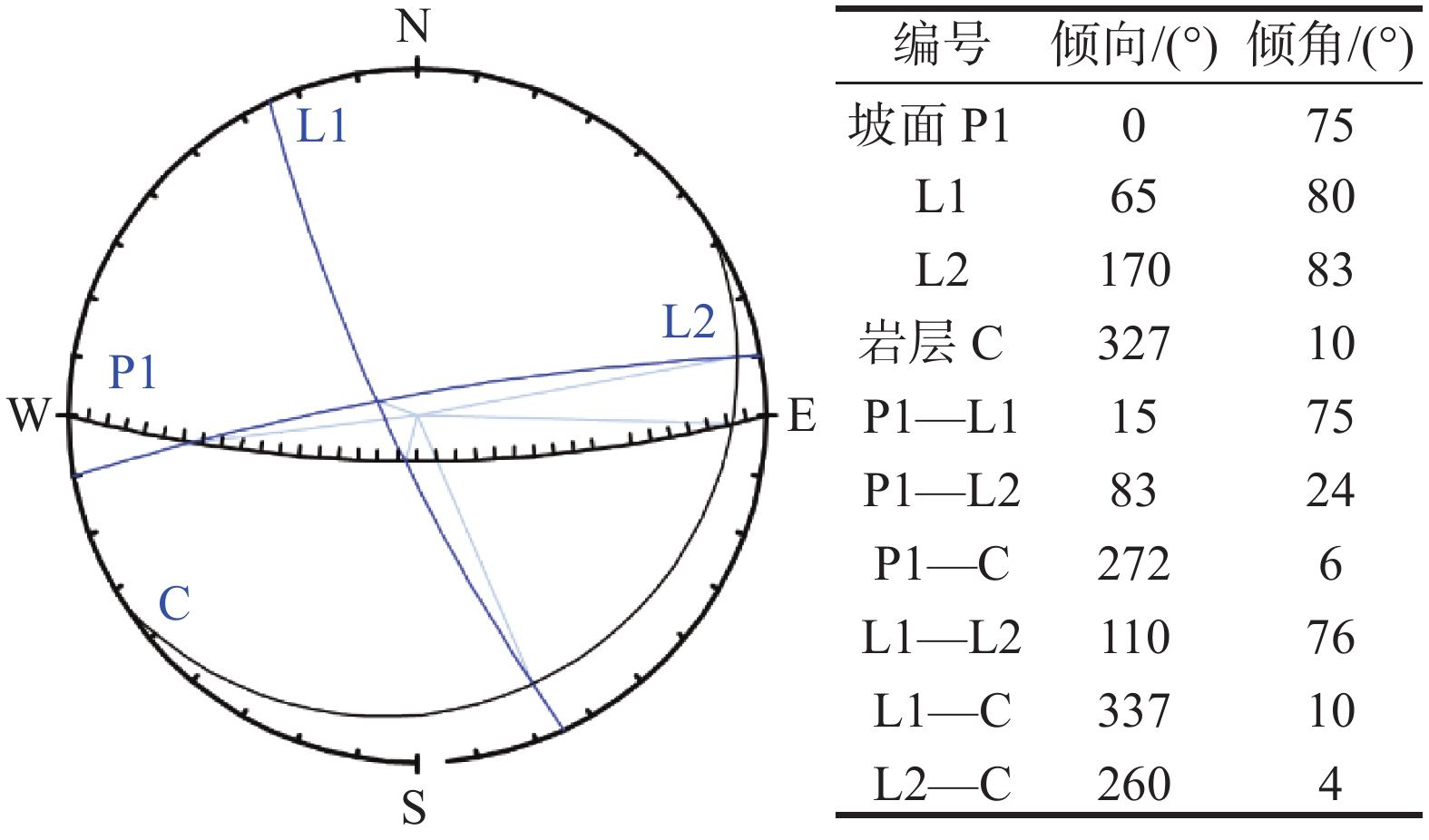
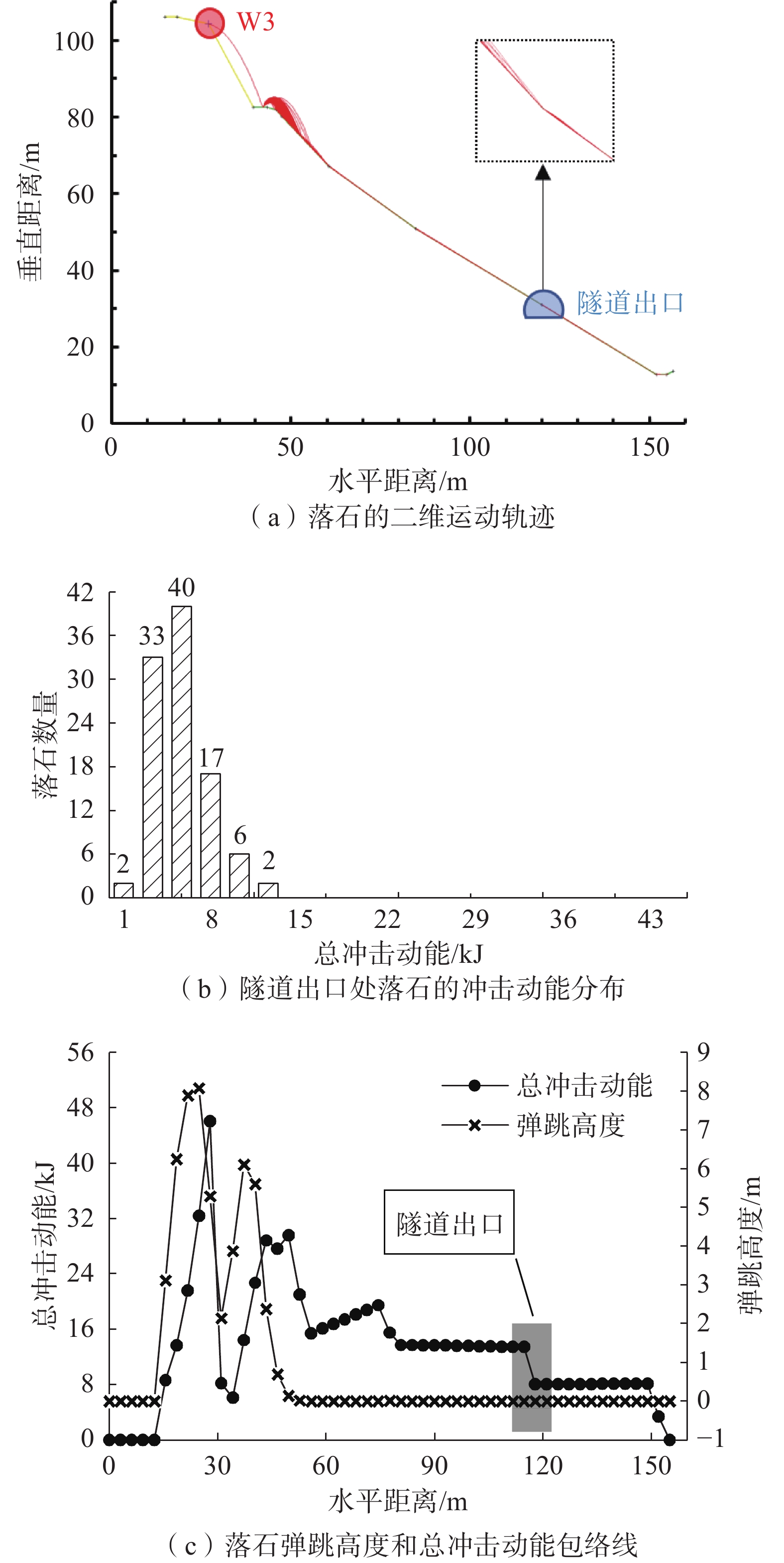
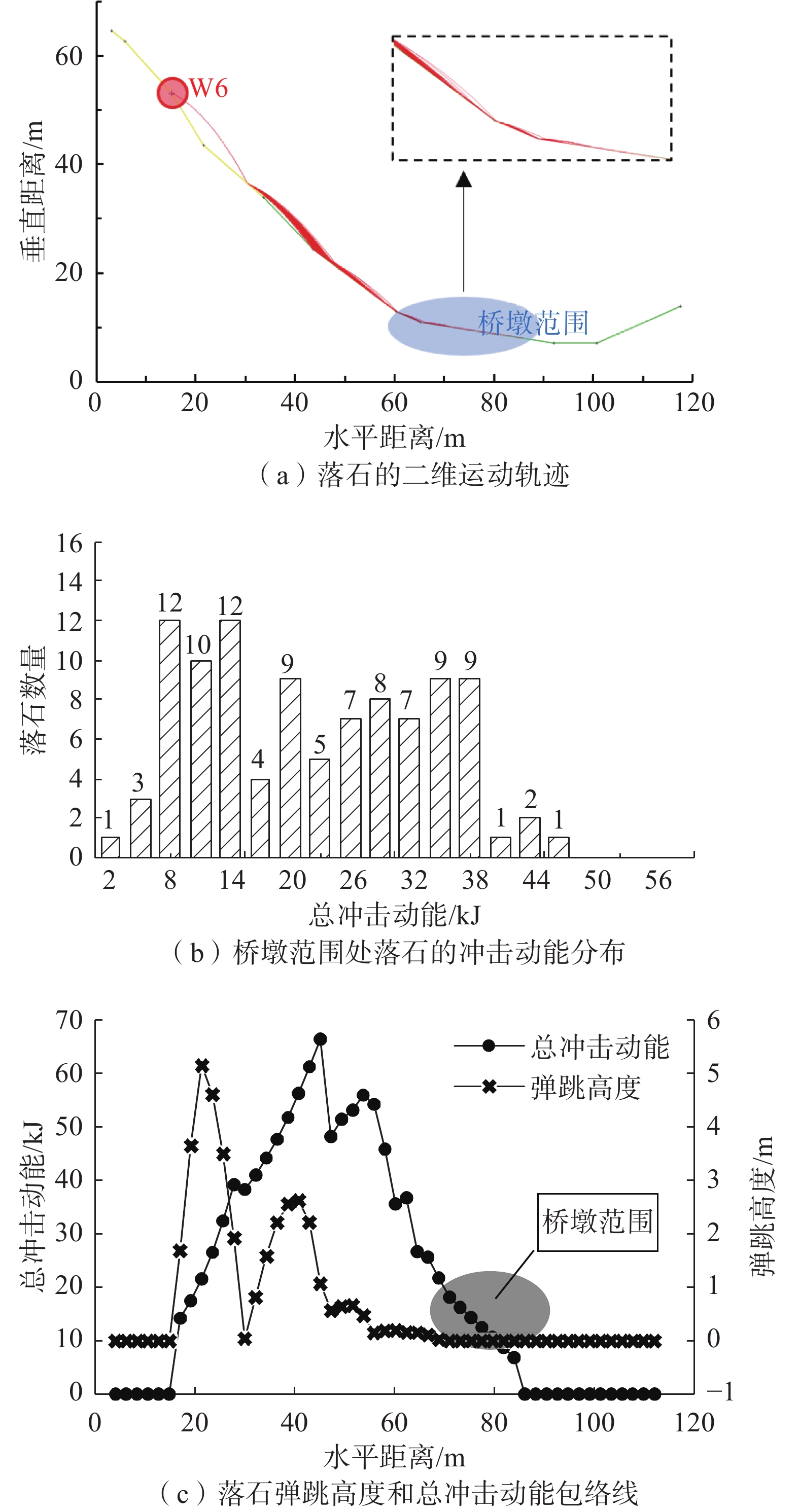
观音山危岩带对拟建恩广高速万开段庙垭隧道、苎溪河特大桥和临近居民构成安全威胁,急需调查治理,但因危岩地处高位,传统调查、评价手段难以实施。通过地质调查、钻孔取样和室内试验获取基础地质信息;利用倾斜摄影对危岩进行识别、几何特征获取和边界条件分析;以赤平投影法和刚体极限平衡法分别进行危岩带、危岩体的稳定性分析;对不稳定危岩单体利用Rocfall软件进行运动学模拟。结果表明:陡崖发育6处主要危岩单体,体积400~5000 m3不等;岩体受2组节理面切割和结构面组合控制,整体稳定性较差,易发生坠落式和倾倒式破坏;其中W3、W6危岩体在暴雨工况下处于不稳定状态,对拟建工程形成滚动冲击,动能为5~12 kJ不等。研究结果可以为观音山危岩治理措施的选型、规模提供设计参数,为高位危岩的调查防治提供参考,对利用航测手段提高传统地质调查效率和精度做出了新思考。
Abstract:The Guanyin mountain dangerous rock belt poses a security threat to the Miaoya tunnel of the proposed Wankai section of the Enguang Expressway, as well as Zhuxihe Bridge and the neighboring residents. It is urgent to be investigated and controled. Traditional investigation and evaluation methods are difficult to implement on the high dabgerous rock mass. Basic geological information is obtained through geological survey, drilling sampling and experiments, identification, geometric feature acquisition and boundary condition analysis of the dangerous rock mass are carried out by oblique photography, stability analysis of the dangerous rock belts and the dangerous rock masses are carried out by stereographic projection method and rigid body limit balance method, respectively. Simulation is carried out by Rocfall software for unstable dangerous rock. The results show that the cliffs develop six main dangerous rock zones with a volume of 400−5000 m3, and the rock mass is controlled by two groups of joint surfaces and structural surfaces combination, the overall stability is poor, prone to fall and tipping; among them, the W3 and W6 dangerous rock masses are in an unstable state under heavy rain conditions, forming a rolling impact on the proposed project, and the kinetic energy is 5−12 kJ. The research results can provide design parameters for the selection of the control measures of the dangerous rocks in Guanyin Mountain, and provide reference for the investigation and prevention of high dangerous rock mass, it puts forward new idea on the use of aerial survey methods to improve the efficiency and accuracy of traditional geological surveys.
-
Key words:
- perilous rock /
- oblique photography /
- stability /
- rockfall simulation /
- disaster prevention measures
-

-
图 1 万州地区构造纲要图[8]
Figure 1.
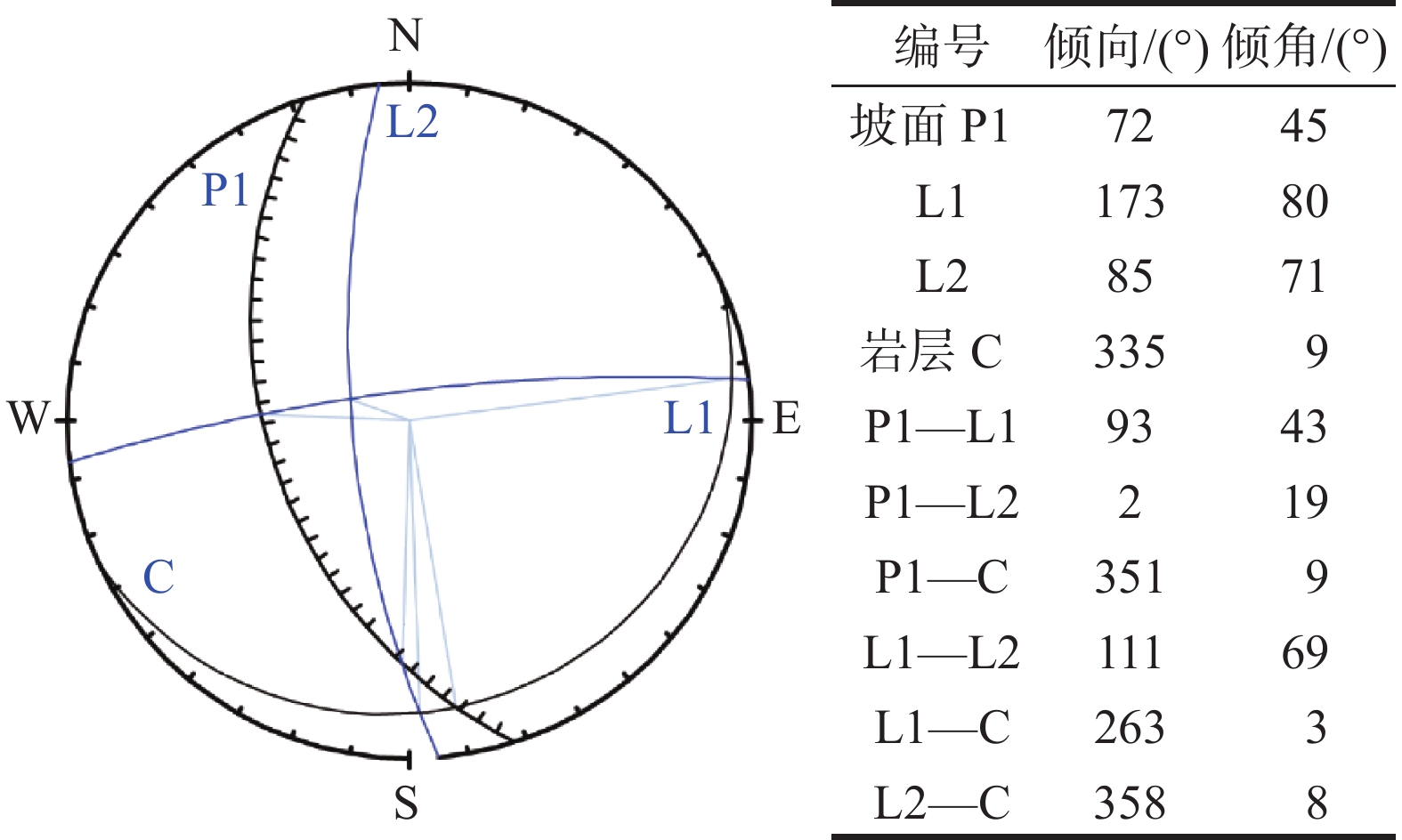
表 1 危岩体发育特征
Table 1. Development characteristics of dangerous rocks
编号 分布高程/m 形态 危岩体尺寸(长×厚×高)/m 体积/m3 凹腔尺寸(高×深)/m 失稳
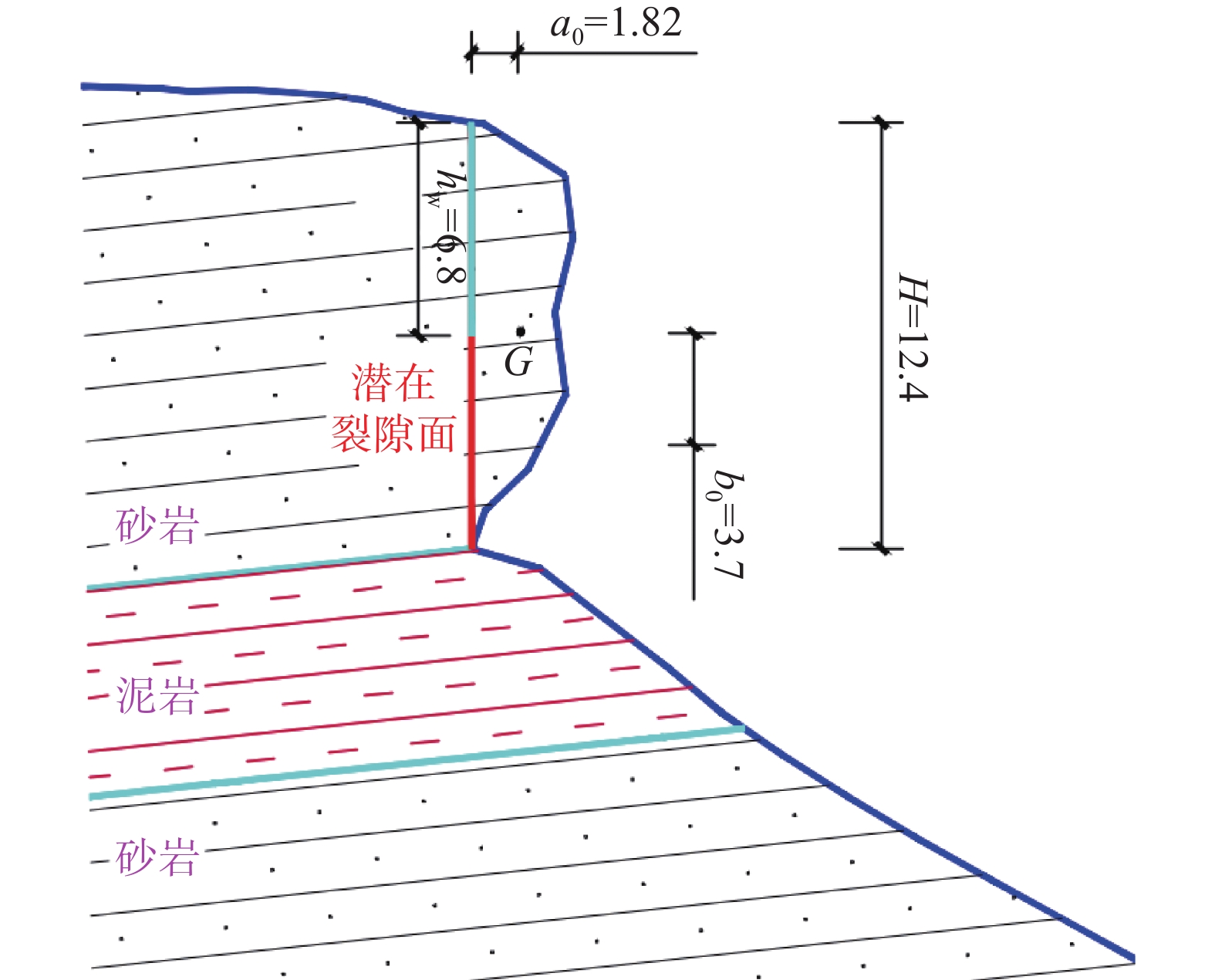
模式类别 W1 340~386 不规则 46.0×9.7×12.4 5532.88 14.0×4.7 坠落式 高位/特大型 W2 345~381 长方形 24.3×6.2×7.0 1054.62 8.5×3.8 坠落式 高位/特大型 W3 350~380 长方形 19.4×8.5×9.8 1616.02 11.0×4.0 坠落式 高位/特大型 W4 280~300 不规则 13.4×7.2×5.0 482.40 2.0×1.5 倾倒式 低位/特大型 W5 270~280 长方形 25.0×6.8×4.5 765.00 1.5×1.2 倾倒式 低位/大型 W6 280~285 长方形 22.0×7.0×3.7 569.80 1.0×0.8 倾倒式 低位/大型 注:类别划分依据《重庆地质灾害防治工程勘查规范》(DB 50/ T 143—2018)。 表 2 岩体物理力学参数
Table 2. Physical and mechanical parameters of rock mass
岩性 工况 γ
/(kN·m−3)c/kPa φ/(°) flk/kPa J2s
砂岩天然 24.6~25.2 737~1034 32.9~35.1 280~580 暴雨 24.9~25.8 643~976 31.6~34.8 220~495 表 3 岩体稳定性计算结果
Table 3. Rock mass stability calculation results
编号 工况 断面面积/m2 危岩高度/m Fs 评价 W1 天然 120.3 12.40 1.385 基本稳定 暴雨 1.162 欠稳定 W2 天然 43.40 7.00 1.741 稳定 暴雨 1.368 基本稳定 W3 天然 83.30 9.80 1.169 欠稳定 暴雨 0.895 不稳定 W4 天然 36.00 5.00 1.389 基本稳定 暴雨 1.102 欠稳定 W5 天然 30.60 4.50 1.483 稳定 暴雨 1.169 欠稳定 W6 天然 25.90 3.70 1.083 欠稳定 暴雨 0.925 不稳定 表 4 恢复系数
Table 4. Coefficient of restitution
碰撞系数 地面岩性 坚硬岩、较硬岩 较软岩、软岩、极软岩 硬土 普通土 松土 法向回弹系数Rn 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.26 0.22 切向回弹系数Rt 0.86 0.84 0.8 0.75 0.65 表 5 滚动摩擦系数
Table 5. Coefficient of rolling friction
坡面特征 滚动摩擦系数 摩擦角/(°) 光滑岩面、混凝土表面 0.30~0.60 21.8~31.0 块石堆积坡面 0.55~0.70 28.8~35.0 密实碎石堆积坡面、硬土坡面、
植被(灌木丛为主)发育0.55~0.85 28.8~40.4 软土坡面、植被不发育或少量杂草 0.50~0.85 26.6~40.4 表 6 模拟参数选取
Table 6. Selection of simulation parameters
边坡部位 Rn/St Rt/St φ/St 粗糙度 上部基岩裸露区 0.4/0.03 0.86/0.04 25.1/0.03 2.42 下部堆积区 0.3/0.03 0.84/0.02 31/0.02 3.00 -
[1] 冉涛, 宋志, 蒋正, 等. 三峡库区万州区四层岩危岩带发育特征、稳定性评价及防治对策[J/OL]. 沉积与特提斯地质: 1 − 13 [2022-03-03]
RAN Tao, SONG Zhi, JIANG Zheng, et al. Development characteristics, stability evaluation and control measures of the four-layer rock-hazardous rock belt in Wanzhou District of the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J/OL]. Sedimentation and Tethys Geology: 1 − 13 [2022-03-03]. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 叶四桥,唐红梅,祝辉. 万州地区危岩发育的典型成因[J]. 水力发电,2007,33(2):31 − 33. [YE Siqiao,TANG Hongmei,ZHU Hui. Typical formation causes of dangerous rock development in Wanzhou area[J]. Water Power,2007,33(2):31 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 陈洪凯,鲜学福,唐红梅,等. 三峡库区危岩群发性机理与防治—以万州太白岩为例[J]. 重庆大学学报(自然科学版),2008,31(10):1178 − 1184. [CHEN Hongkai,XIAN Xuefu,TANG Hongmei,et al. A massive development mechanism and countermeasures for perilous rocks in the Three Gorges Reservoir area of P. R. China:The example of the Taibaiyan cliff at Wanzhou[J]. Journal of Chongqing University (Natural Science Edition),2008,31(10):1178 − 1184. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘广宁, 陈州丰, 黄波林. 三峡库区万州段沿江危岩失稳模式及影响因素分析[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2012, 24(12): 14 − 17
LIU Guangning, CHEN Zhoufeng, HUANG Bolin. Analysis of the instability pattern and influencing factors of dangerous rocks along the Wanzhou section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Western Prospecting Engineering, 2012, 24(12): 14 − 17. (in Chinese)
[5] 邵其东. 三峡库区万州区天生城危岩滑坡治理技术[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2011, 23(2): 51 − 53
SHAO Qidong. Control technology for landslide of Tianshengcheng perilous rock in Wanzhou District of Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2011, 23(2): 51 − 53. (in Chinese)
[6] 刘长春, 殷坤龙. 重庆市万州区戴家岩危岩灾害风险分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(6): 128 − 133
LIU Changchun, YIN Kunlong. Risk analysis for the Daijiayan perilous rock in Wanzhou District of Chongqing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(6): 128 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract))
[7] 孙敬辉,石豫川. 重庆甑子岩崩塌落石动力学特征及危险性分区[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(3):6 − 11. [SUN Jinghui,SHI Yuchuan. Dynamics and hazard zoning of collapse and rockfall in Zhengziyan, Chongqing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(3):6 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.03.02
[8] 林松, 王薇, 邓小虎, 等. 三峡库区典型滑坡地球物理实测及其意义:以万州区四方碑滑坡为例[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(9):3135 − 3146. [LIN Song, WANG Wei, DENG Xiaohu, et al. Geophysical observation of typical landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir area and its significance:A case study of Sifangbei landslide in Wanzhou District[J]. Earth Science,2019,44(9):3135 − 3146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 陈洪凯, 唐红梅, 王林峰, 等. 危岩崩塌演化理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.
CHEN Hongkai, TANG Hongmei, WANG Linfeng, et al. Evolution theory and application ofperilous rock collapse[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[10] 张治平, 夏志雄, 金昶睿, 等. 基于摄影测量的落石路径获取及被动防护网服役性能评估[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(增刊2): 3274 − 3283
ZHANG Zhiping, XIA Zhixiong, JIN Changrui, et al. Acquisition of rockfall path and service performance analysis of passive protective net based on photogrammetry[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(Sup 2): 3274 − 3283. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 重庆市质量技术监督局.地质灾害防治工程勘查规范: DB 50/T 143—2018 [S]. 2018.
Chongqing Municipal Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Code for investigation of geological hazard control engineering: DB 50/T 143—2018[S]. 2018. (in Chinese)
[12] 王 翔,牌立芳,吴红刚. 拉林铁路变坡面倾角崩塌落石对桥梁结构破坏作用的模拟分析与试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1622 − 1633. [WANG Xiang,PAI Lifang,WU Honggang. Simulation analysis and experimental study on the damage of bridge structure caused by tilt collapse and rockfall on the slope of Lalin railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1622 − 1633. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0097
-




 下载:
下载: