Model test of debris flow source initiation mechanism in Suyu valley of Helan Mountain
-
摘要:
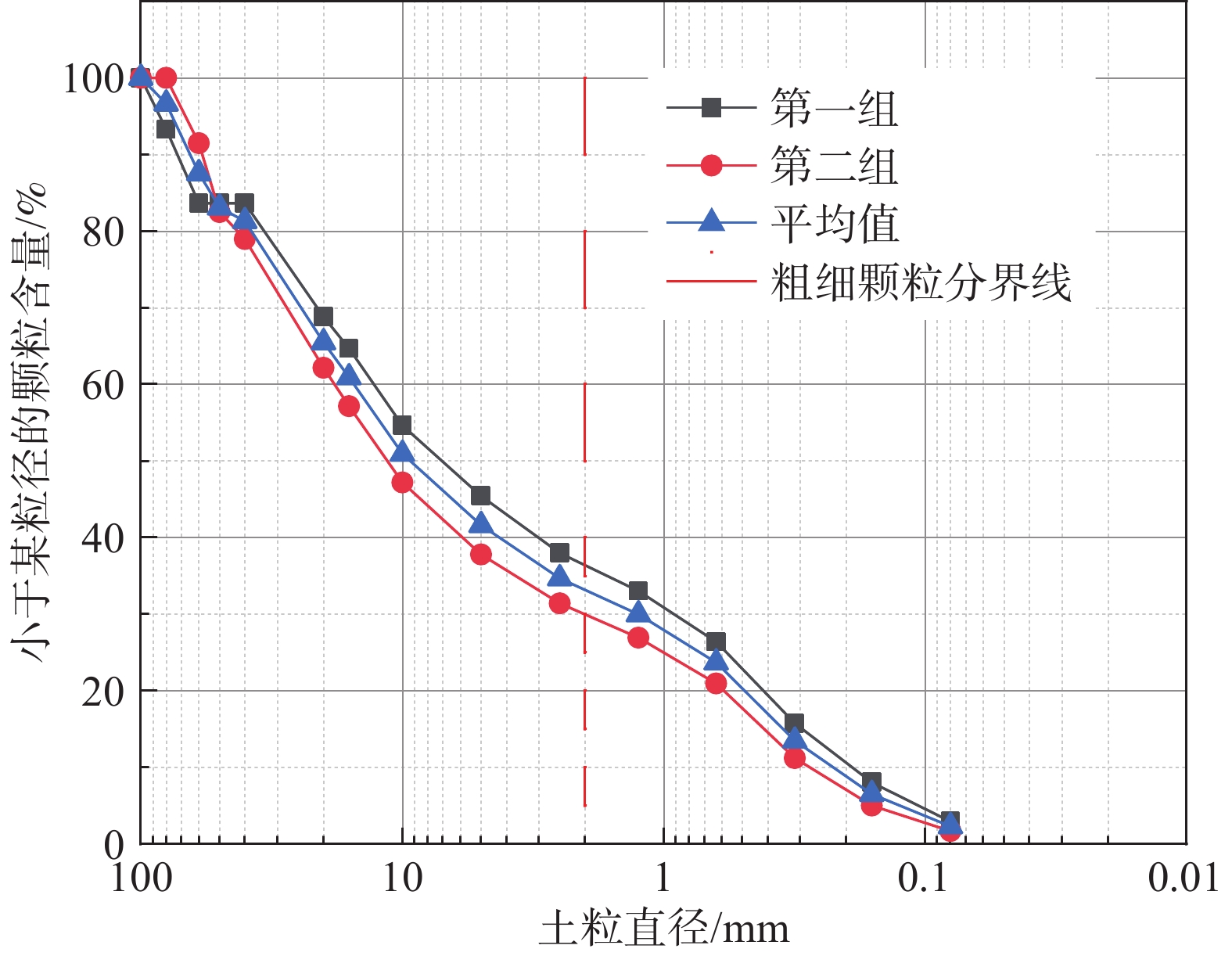
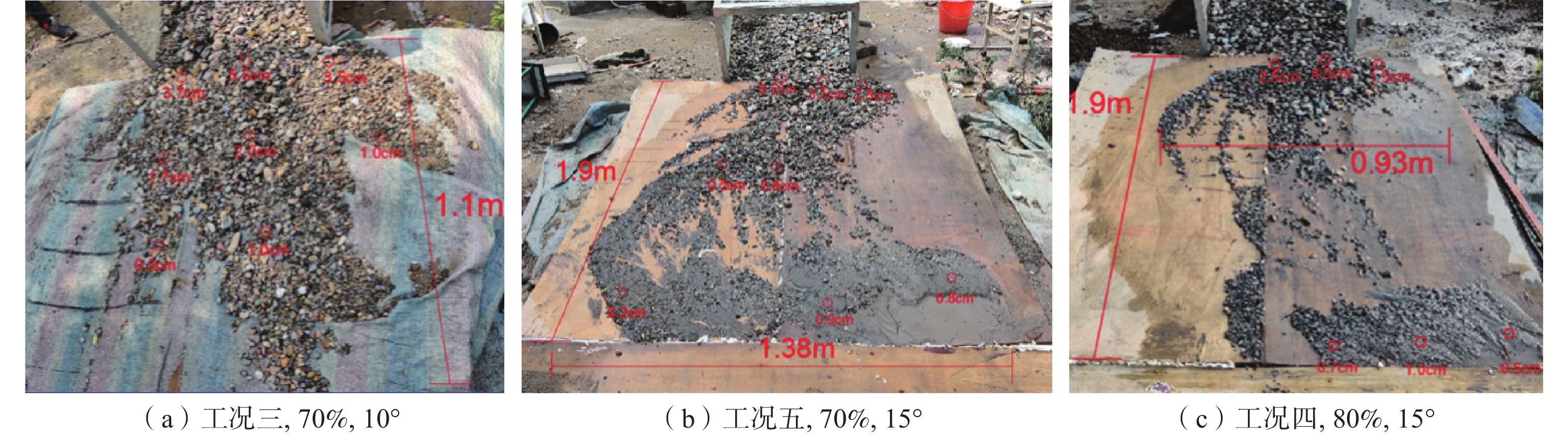
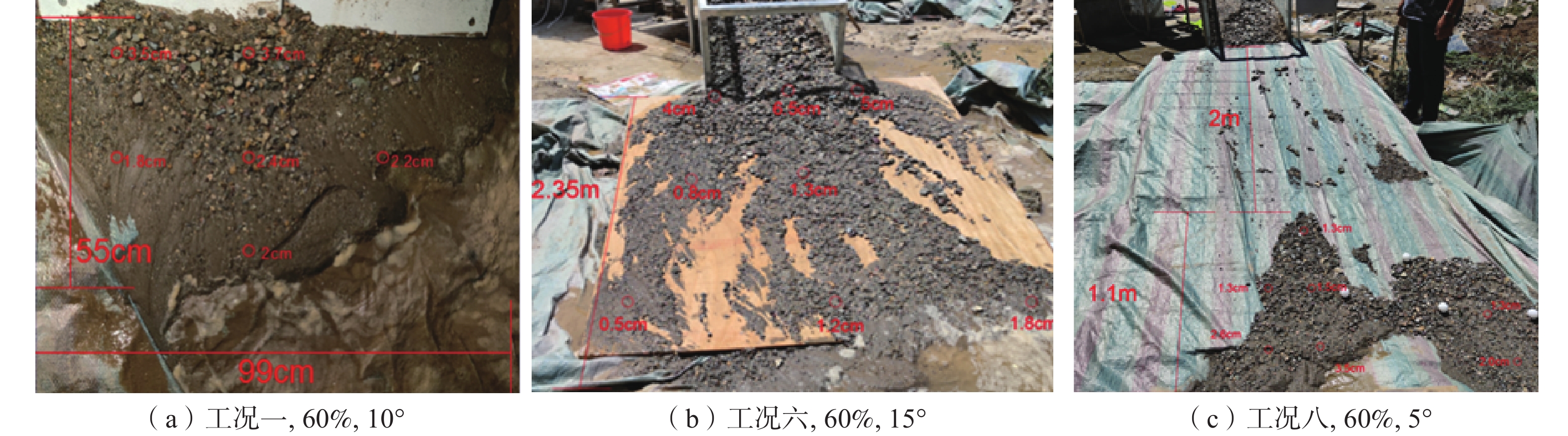
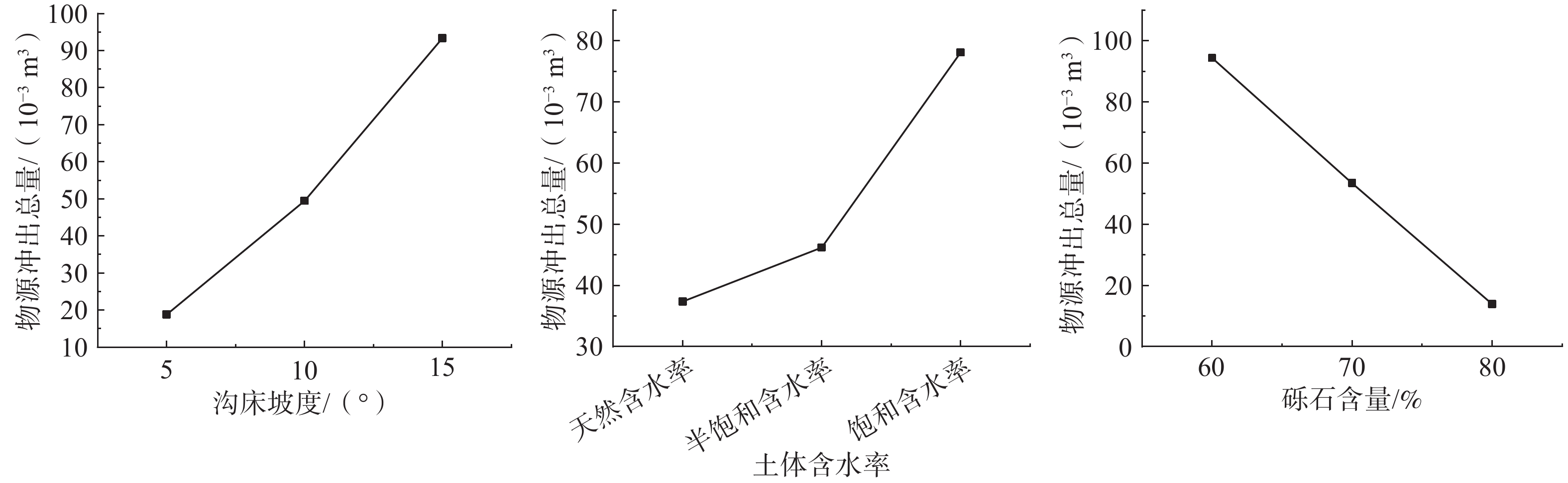
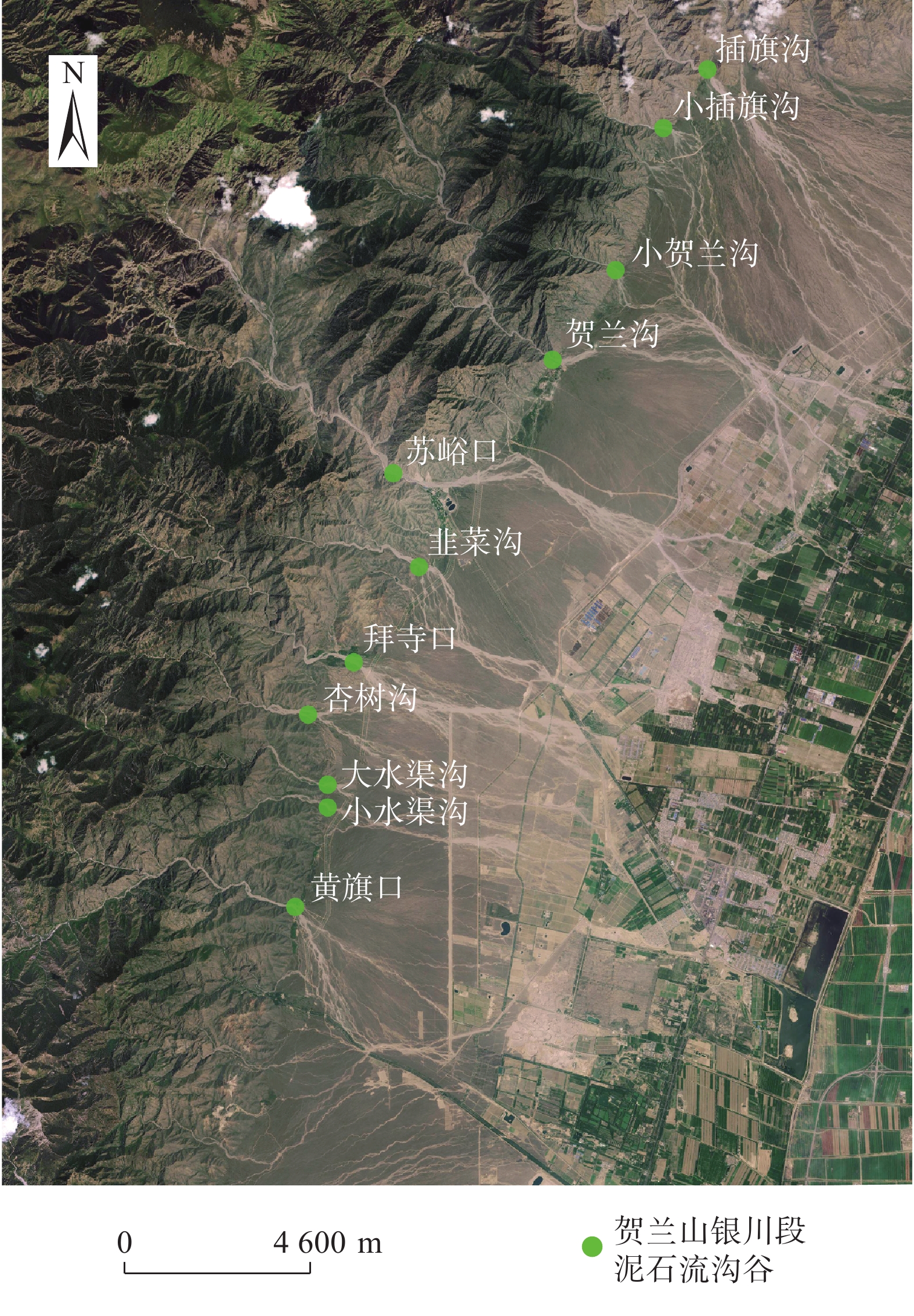
文中通过模型试验,对试验现象中泥石流启动模式和堆积特征进行观测,研究了贺兰山苏峪口泥石流的形成受沟床坡度、土体含水率、粗颗粒含量三个因素影响的状况,初步探讨了贺兰山东麓泥石流在三个因素影响下的变化情况,试验结果表明:三个因素对泥石流影响由大到小分别是粗颗粒含量,沟床坡度、土体含水率;且粗颗粒含量越低、沟床坡度越大、含水率越高越容易发育泥石流。细颗粒含量较高时,泥石流的类型为沟道侵蚀型,粗颗粒含量较高时,泥石流类型为堵溃型。
Abstract:In this paper, through model test, the test of the debris flow phenomenon incipient and run-out mode and accumulation characteristics were observed and studied the helan mountain Suyu valley debris flow affected by the gully bed slope, soil water content, and coarse particle content, preliminary discussed the helan mountain debris flow changes under the influence of the three factors, the experimental results showed that: coarse particle content is the strongest, gully slope is the second, and soil water content is the weakest. The lower the coarse particle content, the higher the gully slope and the higher the water content, the easier the debris flow development. The development mode of debris flow is affected by the content of coarse and fine particles. When the content of fine particles is higher, the type of debris flow is channel erosion, while when the content of coarse particles is higher, the type of debris flow is blocking.
-
Key words:
- debris flow /
- Suyu valley /
- prophase rainfall /
- gully slope /
- coarse particle content /
- hose test
-

-
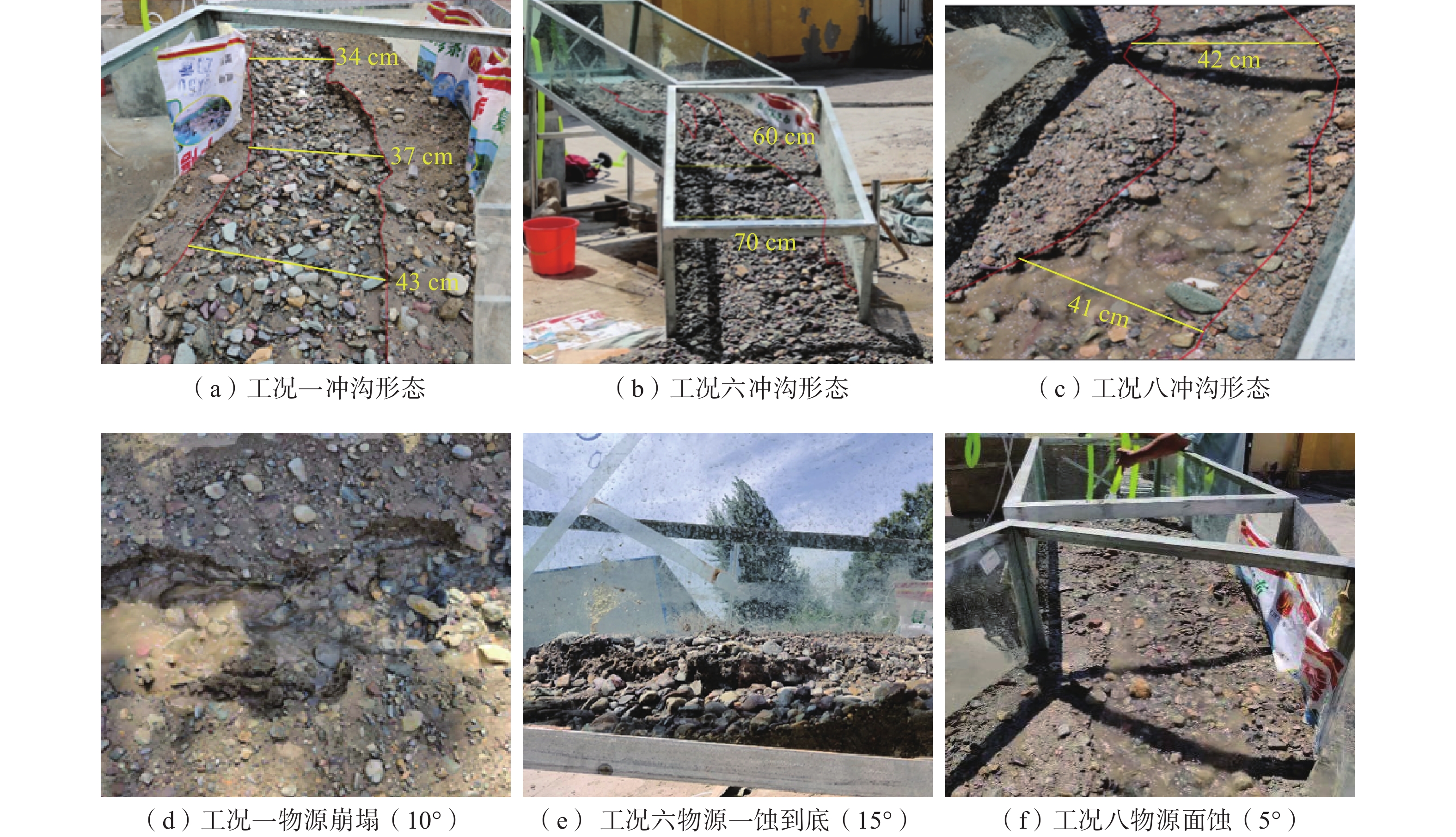
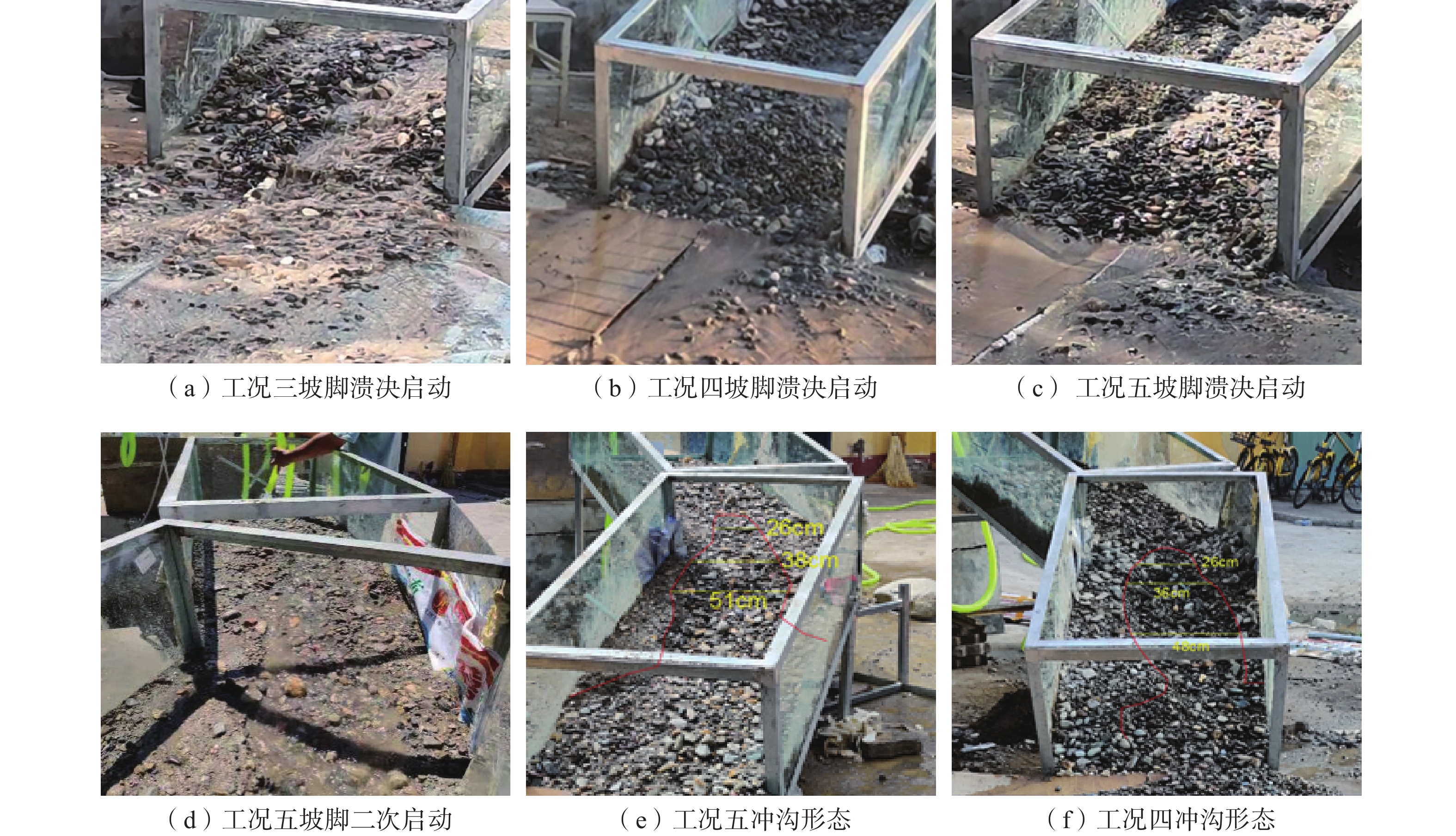
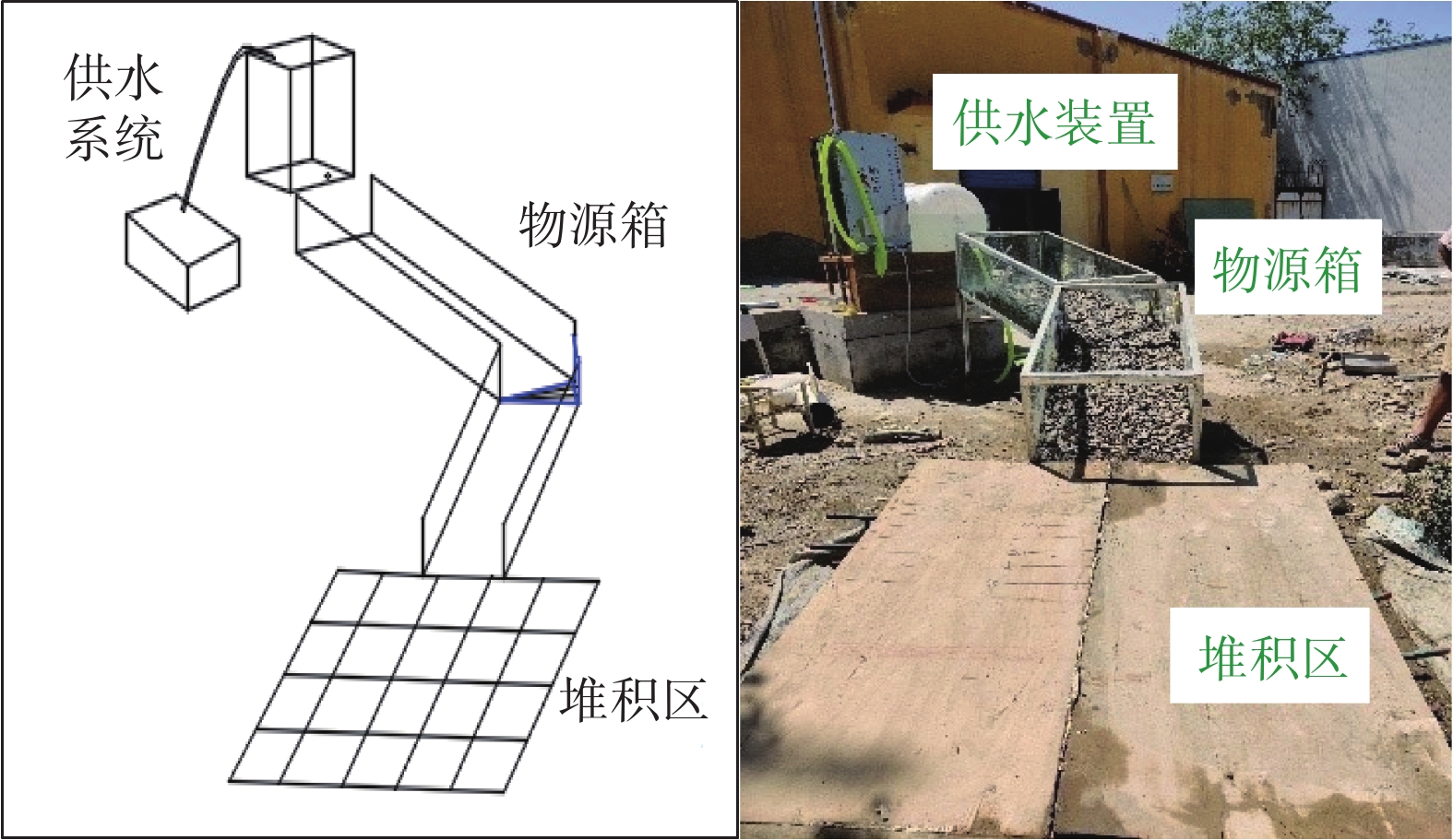
表 1 模型试验工况设计
Table 1. Model test condition design
工况 沟床坡度/(°) 土体含水率/% 粗颗粒含量/% 一 10 天然含水率 60 二 10 半饱和含水率 80 三 10 饱和含水率 70 四 15 天然含水率 80 五 15 半饱和含水率 70 六 15 饱和含水率 60 七 5 天然含水率 70 八 5 半饱和含水率 60 九 5 饱和含水率 80 表 2 试验数据正交分析表
Table 2. The test data orthogonal analysis table
数据 沟床坡度
/(°)土体含水率
/%粗颗粒含量
/%误差项 物源冲出总量/
(10−3 m3)Ⅰi 18.80 37.38 94.37 50.88 161.67 Ⅱi 49.48 46.20 53.40 52.09 Ⅲi 93.39 78.09 13.90 58.70 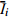
6.27 12.46 31.46 16.96 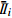
16.49 15.40 17.80 17.36 
31.13 26.03 4.63 19.57 Ri 24.86 13.57 26.82 2.61 注:Ⅰi、Ⅱi、Ⅲi表示某因素三个水平下的物源冲出量; 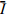 、
、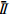 、
、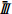 表示Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ的平均值,Ri表示极差。
表示Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ的平均值,Ri表示极差。表 3 泥石流影响因素方差分析表
Table 3. The anovary table of the factors affected by mudslides
来源 自由度 Adj SS Adj MS F 值 P 值 沟床坡度 2 0.000888 0.000444 110.00 0.009 土体含水率 2 0.000306 0.000153 37.88 0.026 粗颗粒含量 2 0.001026 0.000513 127.15 0.008 误差 2 0.000008 0.000004 合计 8 0.002228 -
[1] IVERSON R M,GEORGE D L. A depth-averaged debris-flow model that includes the effects of evolving dilatancy. I. Physical basis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A:Mathematical,Physical and Engineering Sciences,2014,470(2170):20130819.
[2] IVERSON R M,MAJOR J J. Groundwater seepage vectors and the potential for hillslope failure and debris flow mobilization[J]. Water Resources Research,1986,22(11):1543 − 1548. doi: 10.1029/WR022i011p01543
[3] GEORGE D L,IVERSON R M. A depth-averaged debris-flow model that includes the effects of evolving dilatancy. II. Numerical predictions and experimental tests[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A:Mathematical,Physical and Engineering Sciences,2014,470(2170):20130820.
[4] TAKAHASHI T. Debris flow[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,1981,13:57 − 77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fl.13.010181.000421
[5] 胡明鉴,汪稔. 蒋家沟流域暴雨滑坡泥石流共生关系试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2003,22(5):824 − 828. [HU Mingjian,WANG Ren. Testing study on the correlation among landslide,debris flow and rainfall in Jiangjia valley[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2003,22(5):824 − 828. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.05.025
[6] 陈中学,汪稔,胡明鉴,等. 云南东川蒋家沟泥石流形成内因初探[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(10):3053 − 3056. [CHEN Zhongxue,WANG Ren,HU Mingjian,et al. Study of internal factors for debris flow occurrence in Jiangjia ravine,Dongchun of Yunnan[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2009,30(10):3053 − 3056. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.10.029
[7] 陈中学,汪稔,胡明鉴,等. 黏土颗粒含量对蒋家沟泥石流启动影响分析[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(7):2197 − 2201. [CHEN Zhongxue,WANG Ren,HU Mingjian,et al. Study of content of clay particles for debris flow occurrence in Jiangjia Ravine[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(7):2197 − 2201. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.07.029
[8] 胡明鉴, 汪稔, 陈中学, 等. 泥石流启动过程PFC数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(增刊 1): 394 − 397
HU Mingjian, WANG Ren, CHEN Zhongxue, et al. Initiation process simulation of debris deposit based on particle flow code[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(Sup 1): 394 − 397. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王志兵,李凯,汪稔,等. 细粒含量对泥石流斜坡失稳模式与规模的影响[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2016,36(2):35 − 41. [WANG Zhibing,LI Kai,WANG Ren,et al. Impact of fine particle content on mode and scale of slope instability of debris flow[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources,2016,36(2):35 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 程尊兰,党超,刘晶晶,等. 藏东南部泥石流堵河试验研究[J]. 地学前缘,2007,14(6):181 − 187. [CHENG Zunlan,DANG Chao,LIU Jingjing,et al. Experiments of debris flow damming in Southeast Xizang[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2007,14(6):181 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.06.023
[11] 程尊兰,朱平一,宫怡文. 典型冰湖溃决型泥石流形成机制分析[J]. 山地学报,2003,21(6):716 − 720. [CHENG Zunlan,ZHU Pingyi,GONG Yiwen. Typical debris flow triggered by ice-lake break[J]. Journal of Mountain Research,2003,21(6):716 − 720. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2003.06.013
[12] 胡凯衡,崔鹏,李浦. 泥石流动力学模型与数值模拟[J]. 自然杂志,2014,36(5):313 − 318. [HU Kaiheng,CUI Peng,LI Pu. Debris flow dynamic models and numerical computation[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature,2014,36(5):313 − 318. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李明威,唐川,陈明,等. 汶川震区北川县泥石流流域崩滑体时空演变特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):182 − 190. [LI Mingwei,TANG Chuan,CHEN Ming,et al. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of landslides in debris flow catchment in Beichuan County in the Wenchuan earthquake zone[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):182 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 樊圆圆,宋玲,魏学利. 基于水槽试验的冰碛土泥石流启动机理分析:以中巴公路艾尔库然沟为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(1):1 − 9. [FAN Yuanyuan,SONG Ling,WEI Xueli. Analysis of the start-up mechanism of moraine debris flow based on flume test:A case study of the Aierkuran Gully along the Sino-Pakistan highway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(1):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王硕楠. 沟道泥石流堆积体复活启动机制研究—以栾川县柿树沟为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2015
WANG Shuonan. Study on the revival start mechanism of debris flow fan: Take Luanchuan Shishu gully as an example[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 周小军, 崔鹏, 贾世涛, 等. 基于正交设计的土体细颗粒迁移积聚水槽实验研究[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2012, 44(增刊 1): 83 − 88
ZHOU Xiaojun, CUI Peng, JIA Shitao, et al. Flume test study on the movement of fine grains based on orthogonal design[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2012, 44(Sup 1): 83 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 王飞. 泥石流物源降雨启动试验及三维颗粒流模拟研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018
WANG Fei. Study on rainfall initiation experiment for debris flow materials and initiation process simulation with PFC3D[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 马秋娟,尹红霞,刘亚峰,等. 太行山地区水石流起动及发展的模型研究[J]. 人民黄河,2016,38(11):5 − 8. [MA Qiujuan,YIN Hongxia,LIU Yafeng,et al. Model study on catastrophe characteristics for initiation debris-flows in Taihang mountain area[J]. Yellow River,2016,38(11):5 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2016.11.002
-



 下载:
下载: