Monitoring and analysis of ground and building settlement of deep trough in Houhai based on PS-InSAR technology
-
摘要:
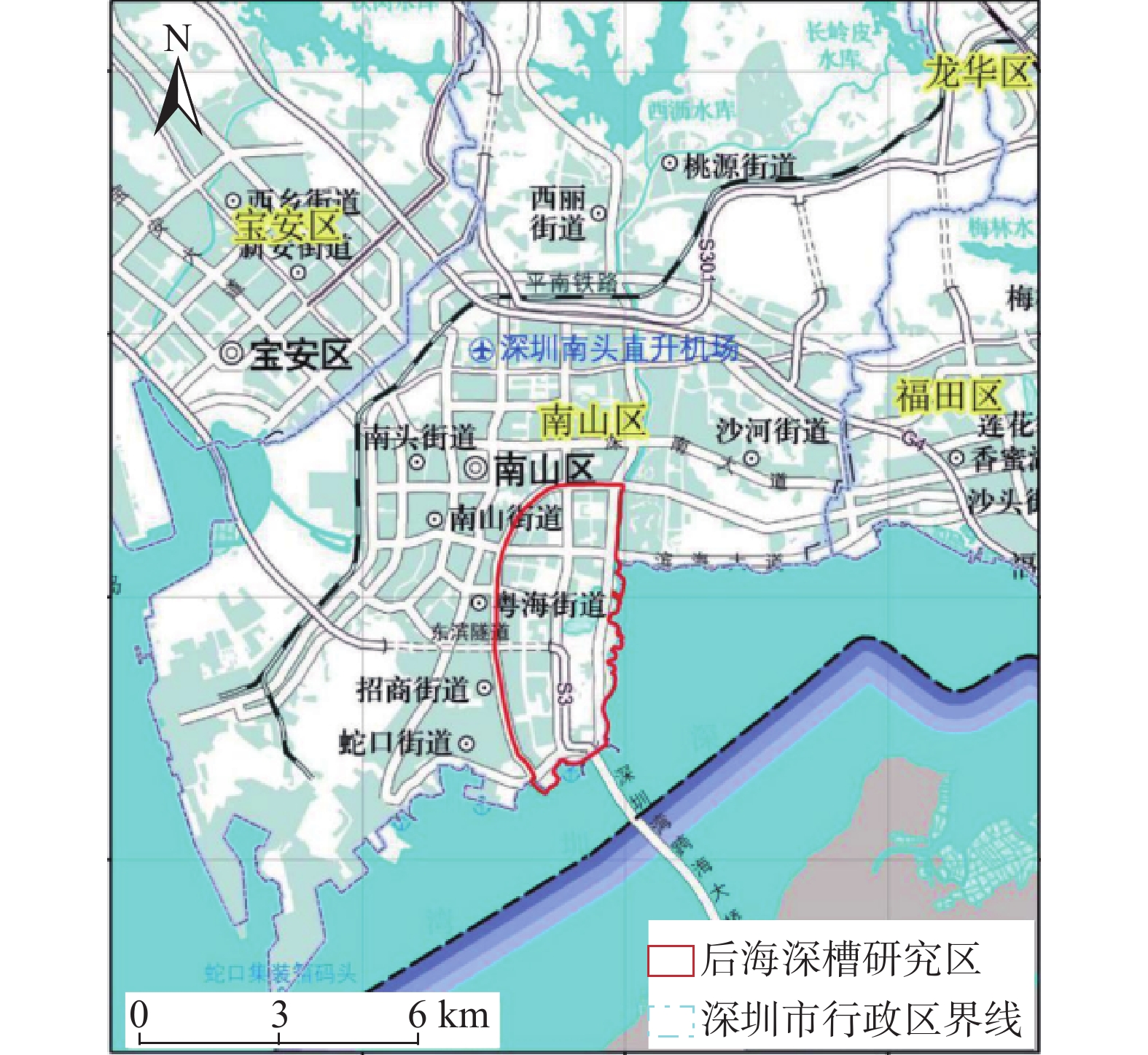
深圳市南山区后海片区为总部大厦基地,莲花山断裂带和珠江口大断裂带在此交汇,区域内基岩埋藏较深,断层较发育,存在巨厚的风化深槽,地面高层建筑多采用超长桩基础。文中研究采用永久散射体合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术对深圳市南山区后海片区南部东侧沿海部分的地面和建(构)筑物进行大范围、长时间形变监测。监测结果表明,深槽上建筑物以及其他构筑物沉降相对稳定,目前在后海巨厚深槽上的建筑桩基施工工艺安全有效。沉降量较大的区域为深圳湾公园草地及其周边区域,主要由于填海造陆软土引起形变。经过与传统监测技术的对比,InSAR技术监测精度满足规范要求。在大范围、低成本、高精度、高效率的形变监测需求方面,InSAR技术具有优势。
-
关键词:
- 南山后海 /
- 深槽 /
- 永久散射体合成孔径雷达干涉测量 /
- PS-InSAR /
- 沉降监测
Abstract:The Houhai area in Nanshan District of Shenzhen is the base of the headquarters building, where the Shenzhen fault zone and the Pearl River Mouth fault zone meet here. In this region, the bedrock is buried deeply, the faults are well developed, and there is huge thick weathered deep trough. Thus, overlength pile foundation is used in high-rise buildings. In this study, the permanent scatterers interferometric synthetic aperture radar technique was used to monitor the settlement of ground and structures in houhai Deep trough research area, Nanshan District, Shenzhen. The monitoring results show that the settlement of buildings and other structures on deep trough is relatively stable, and the pile foundation construction technology in Houhai research area is safe and effective at present. The grassland of Shenzhen Bay Park and its surrounding areas have a large amount of settlement, which is mainly caused by the settlement of soft land reclaimed from the sea. Compared with the traditional monitoring technology, the monitoring accuracy of InSAR technology meets the requirements. The InSAR technology has advantages for large-scale, low-cost, high-precision and high-efficiency deformation monitoring.
-

-
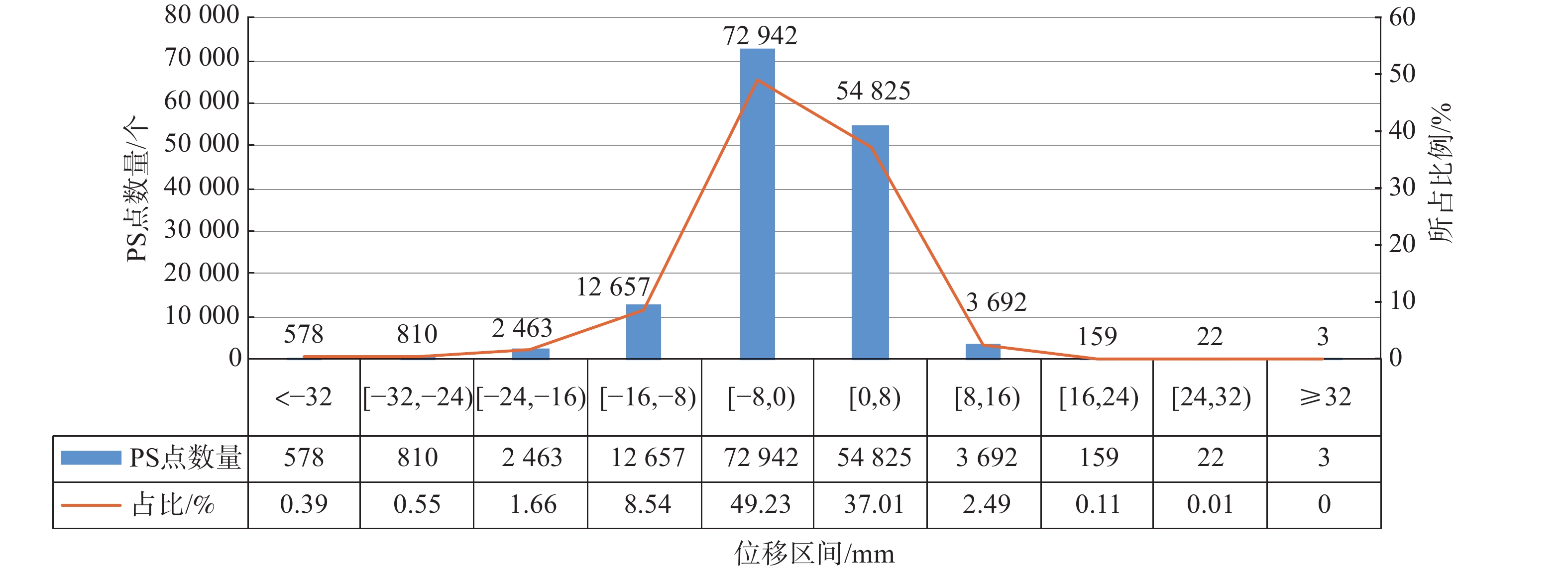
表 1 In-SAR数据基本参数
Table 1. Basic Parameters of In-SAR Data
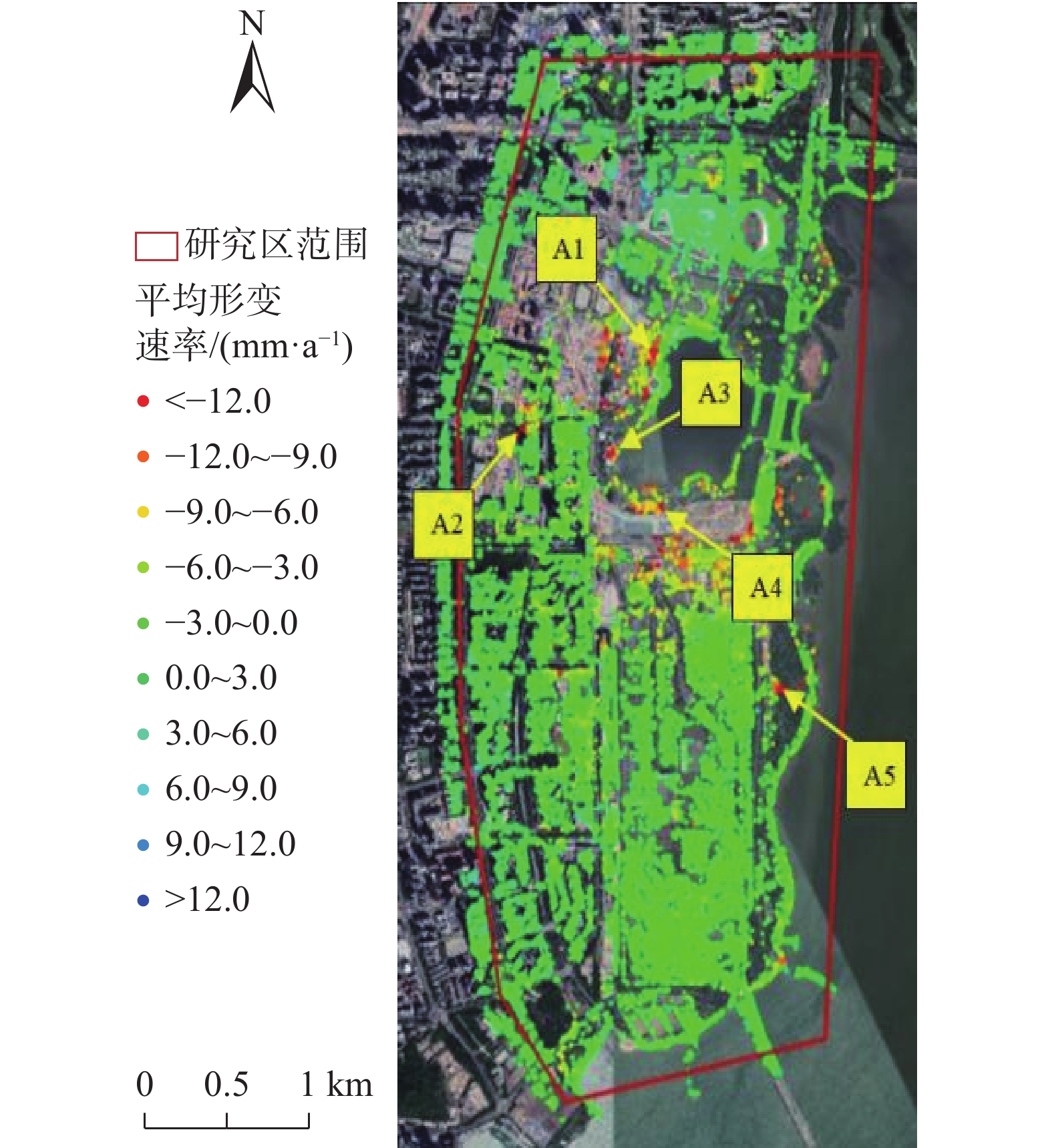
参数 数值 监测日期 卫星类型 COSMO-SkyMed 2018-02-04 、2018-03-08 、2018-03-24 、2018-04-09 、2018-05-11 成像模式 StripMap (条带成像)模式 2018-06-12 、2018-07-11 、2018-09-13 、2018-10-02 、2018-10-18 数据波段 X波段(3.1cm) 2018-11-03 、2018-11-19 、2018-12-01 、2019-01-06 、2019-01-22 空间分辨率/m 3 2019-02-07 、2019-02-19 、2019-03-11 、2019-03-27 、2019-04-12 升/降轨模式 降轨 2019-04-28 、2019-05-10 、2019-06-10 、2019-06-26 、2019-07-12 极化方式 HH极化 2019-07-28 、2019-08-14 、2019-08-29 、2019-10-09 、2019-10-25 中心入射角/(°) 32.55 2019-11-01 、2019-12-03 、2020-01-13 、2020-02-05 、2020-02-21 影像数量 52景 2020-03-24 、2020-04-09 、2020-04-25 、2020-05-11 、2020-05-27 数据级别 SLC数据(单视复) 2020-06-12 、2020-06-28 、2020-07-14 、2020-07-30 、2020-08-15 监测日期 2018-02-04—2020-12-21 2020-09-16 、2020-10-11 、2020-10-18 、2020-11-03 、2020-11-19 处理方法 PS-InSAR 2020-12-05 、2020-12-21 表 2 监测特征点形变特点及曲线
Table 2. Deformation characteristics and curves of feature points
监测特征点
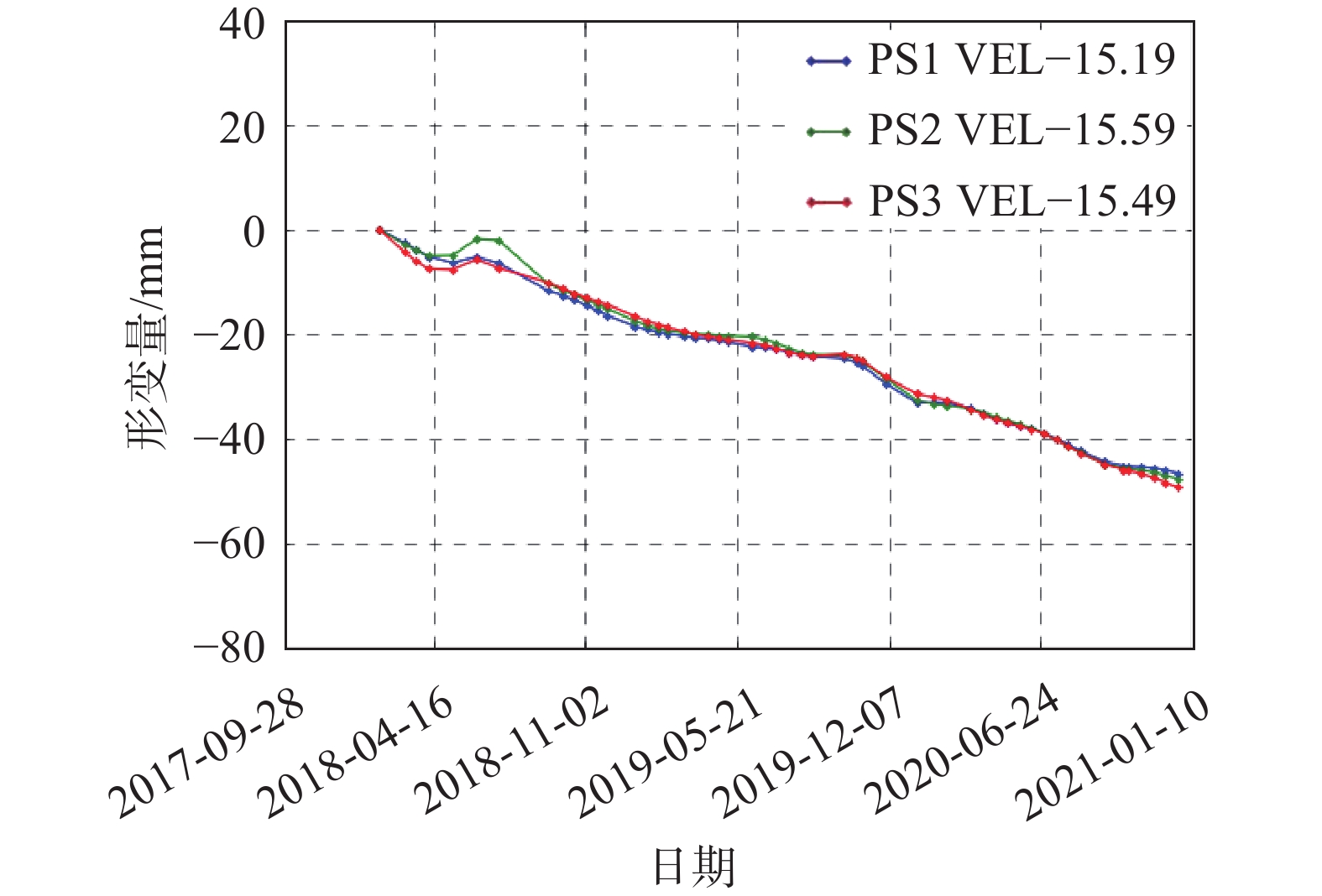
分类监测特征点位置 沉降形变特点 典型形变—日期序列曲线 已有高层建筑 点2舜远金融大厦
点3大成基金总部大厦
点5海信南方大厦
点6深圳湾一号
点7卓越维港名苑形变曲线总体均呈略有
起伏的变化趋势,
整体形变稳定
见右侧点7卓越维港名苑形变—日期曲线图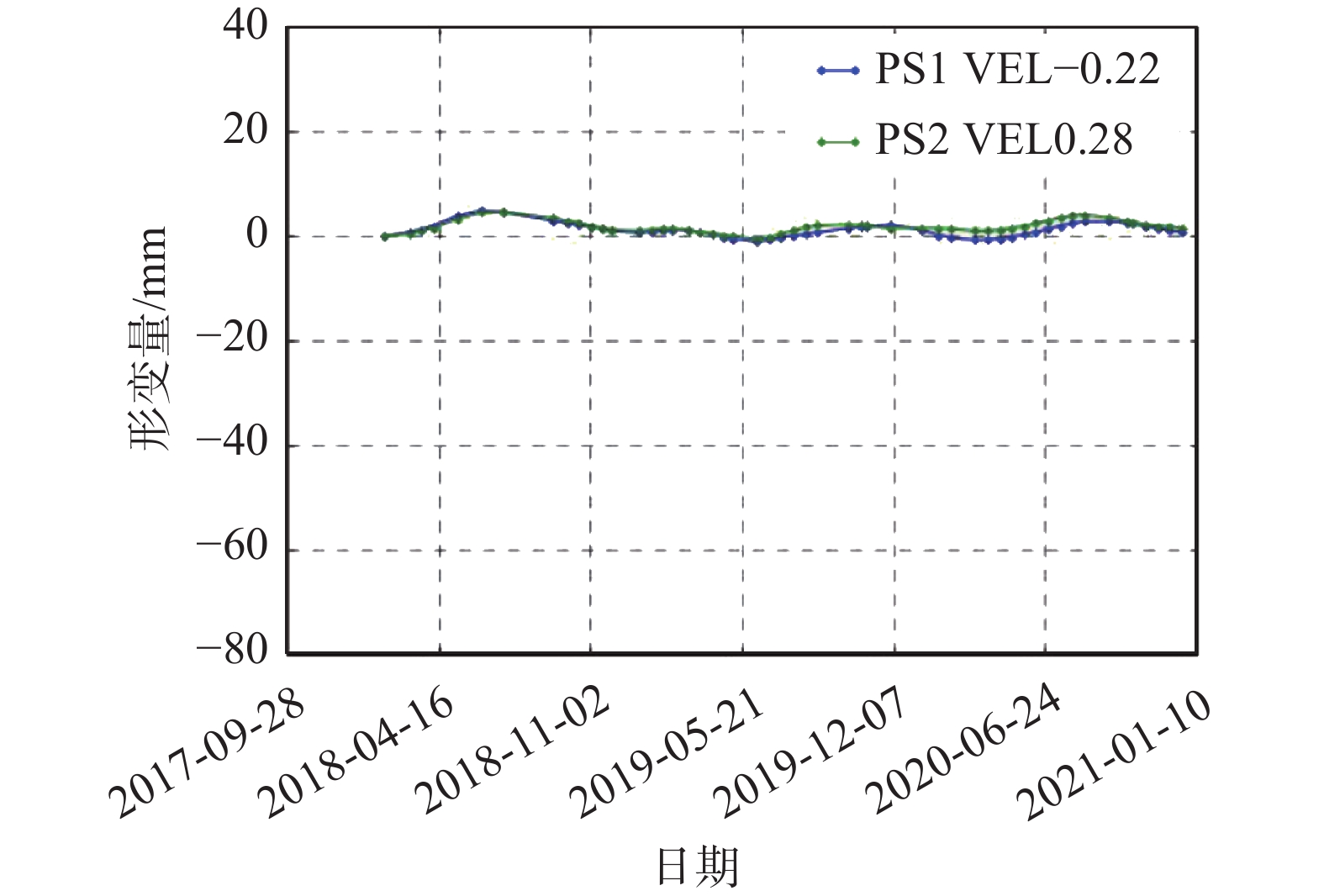
在建项目 点1红土创新广场
点4恒裕深圳湾监测期间受施工影响,形变曲线不规律,或呈略有起伏上升趋势,或呈略有起伏下降趋势
见右侧点1红土创新广场形变—日期曲线图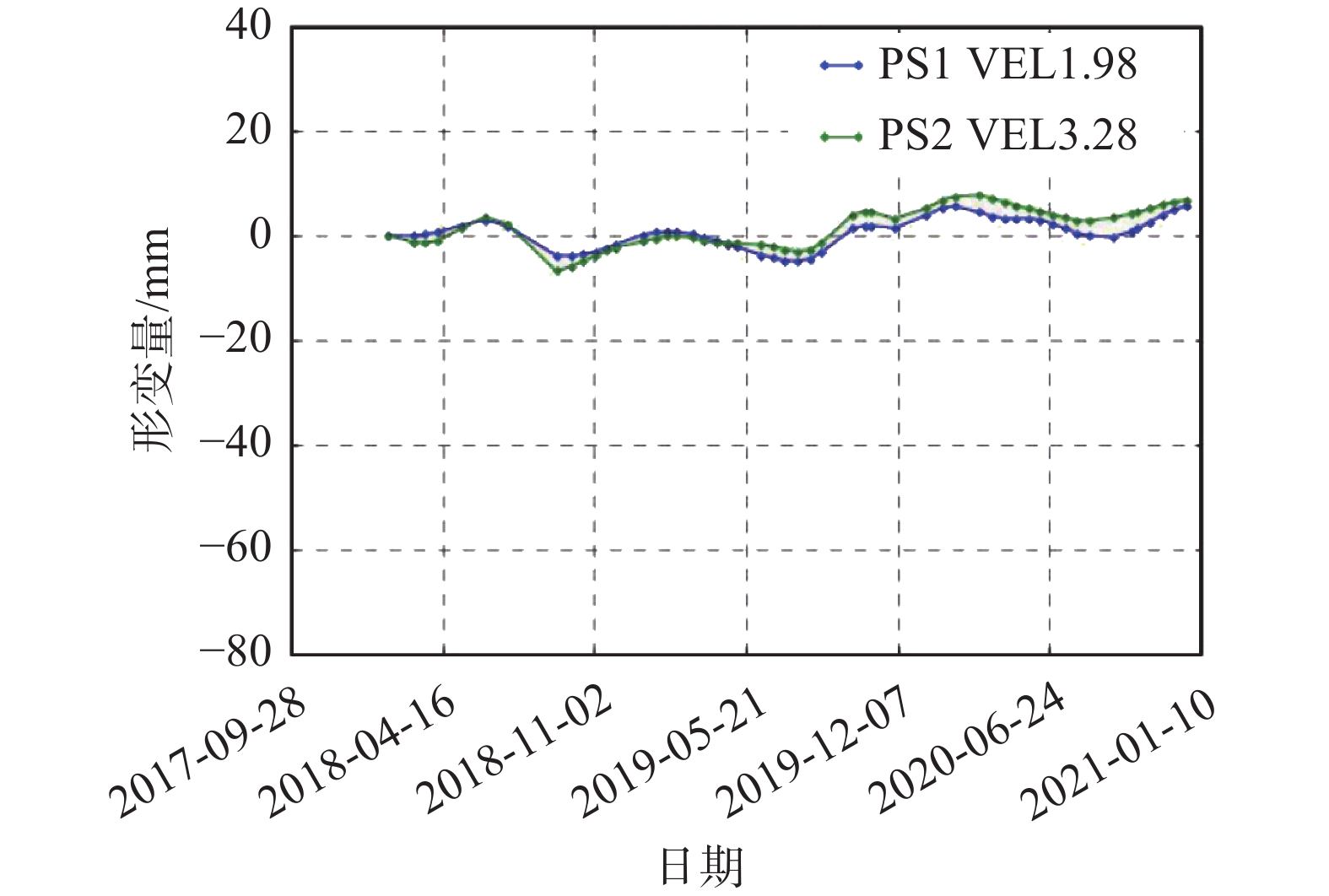
桥梁 点8滨海海滨立交桥
点17桥梁
点21桥梁形变曲线总体呈略有起伏的变化趋势,整体形变稳定
见右侧点17桥梁形
变—日期曲线图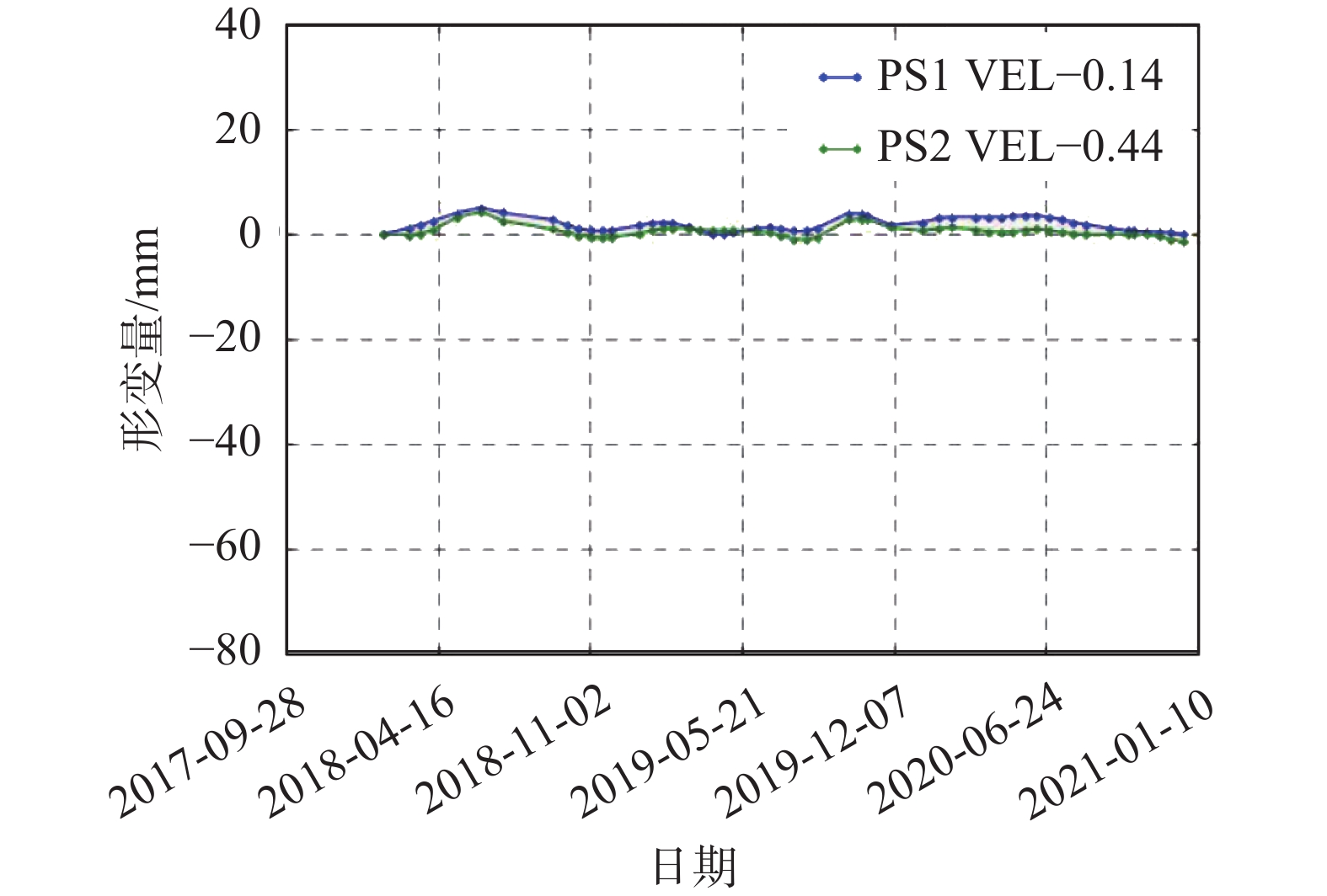
道路 点9海德三道
点10创业路
点11望海路
点12望海路
点20东滨路形变曲线总体呈略有起伏的变化趋势,整体形变稳定
见右侧点12望海路形
变—日期曲线图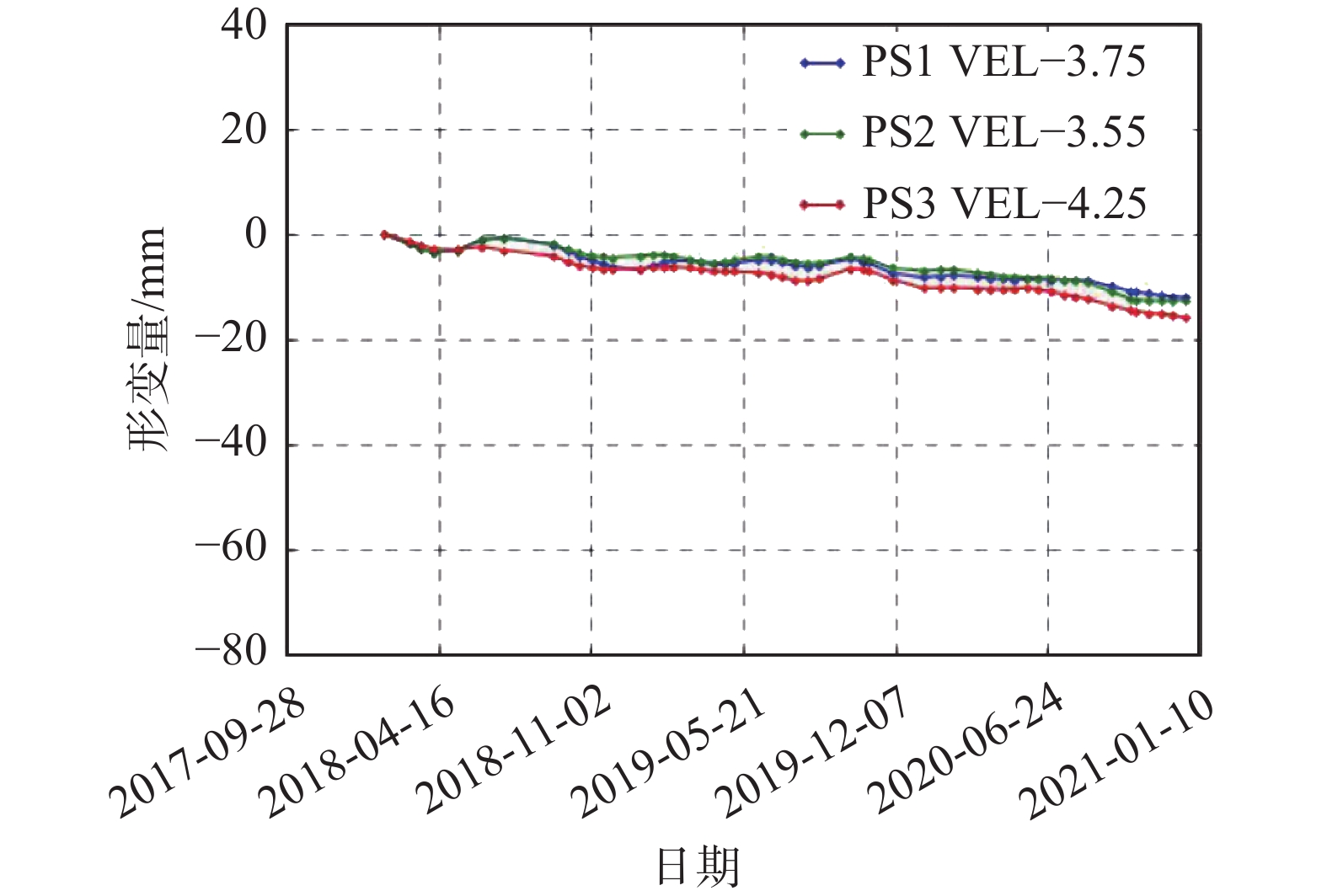
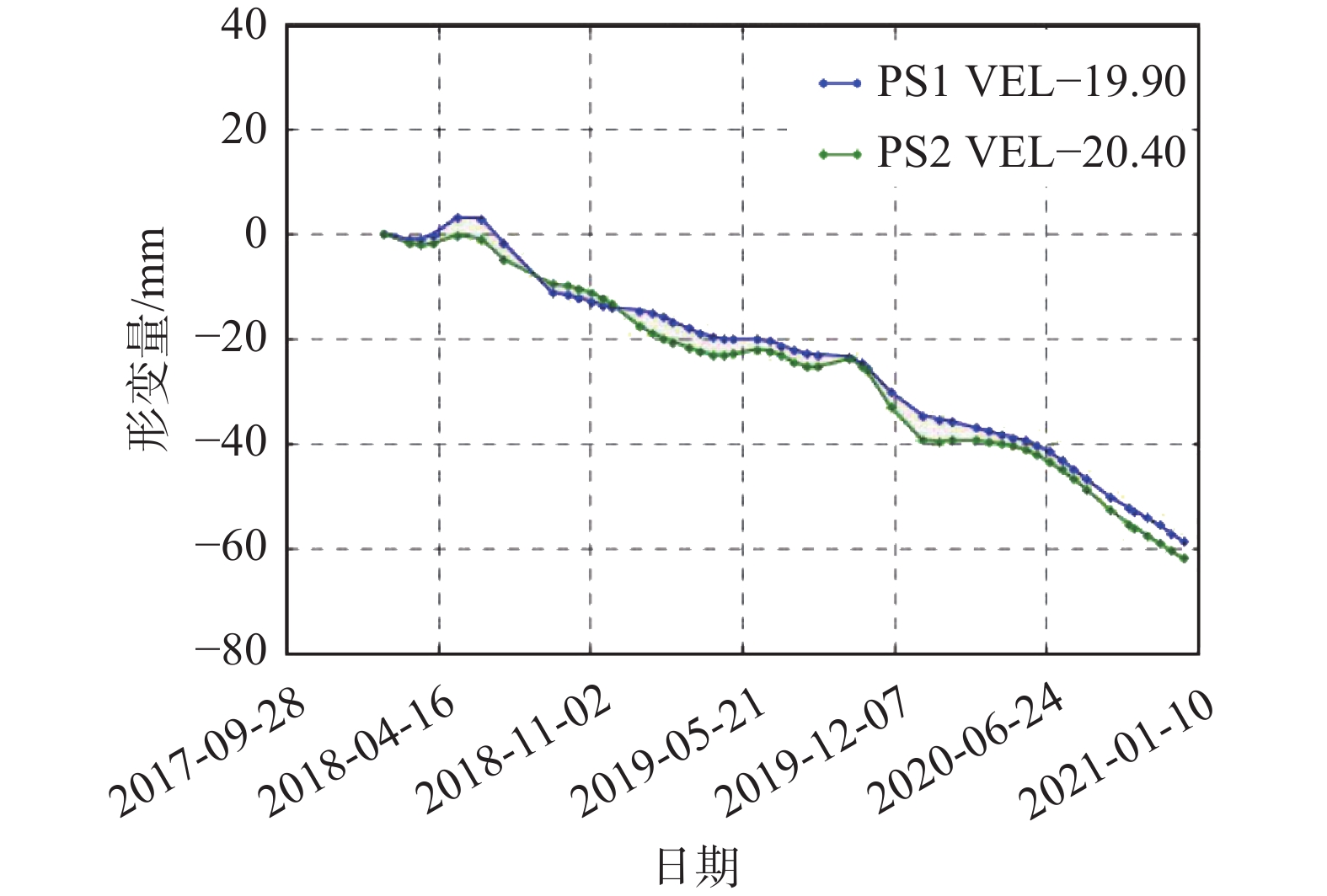
公园草地 点14绿化草地
点13、点16、点18、点19深圳湾公园草地
点15大运会纪念碑广场除了点18深圳湾公园草地形变曲线为均匀缓慢沉降趋势(见右侧点18形变—日期曲线图)外,其余形变曲线均为总体呈略有起伏的下降趋势,整体形变稳定 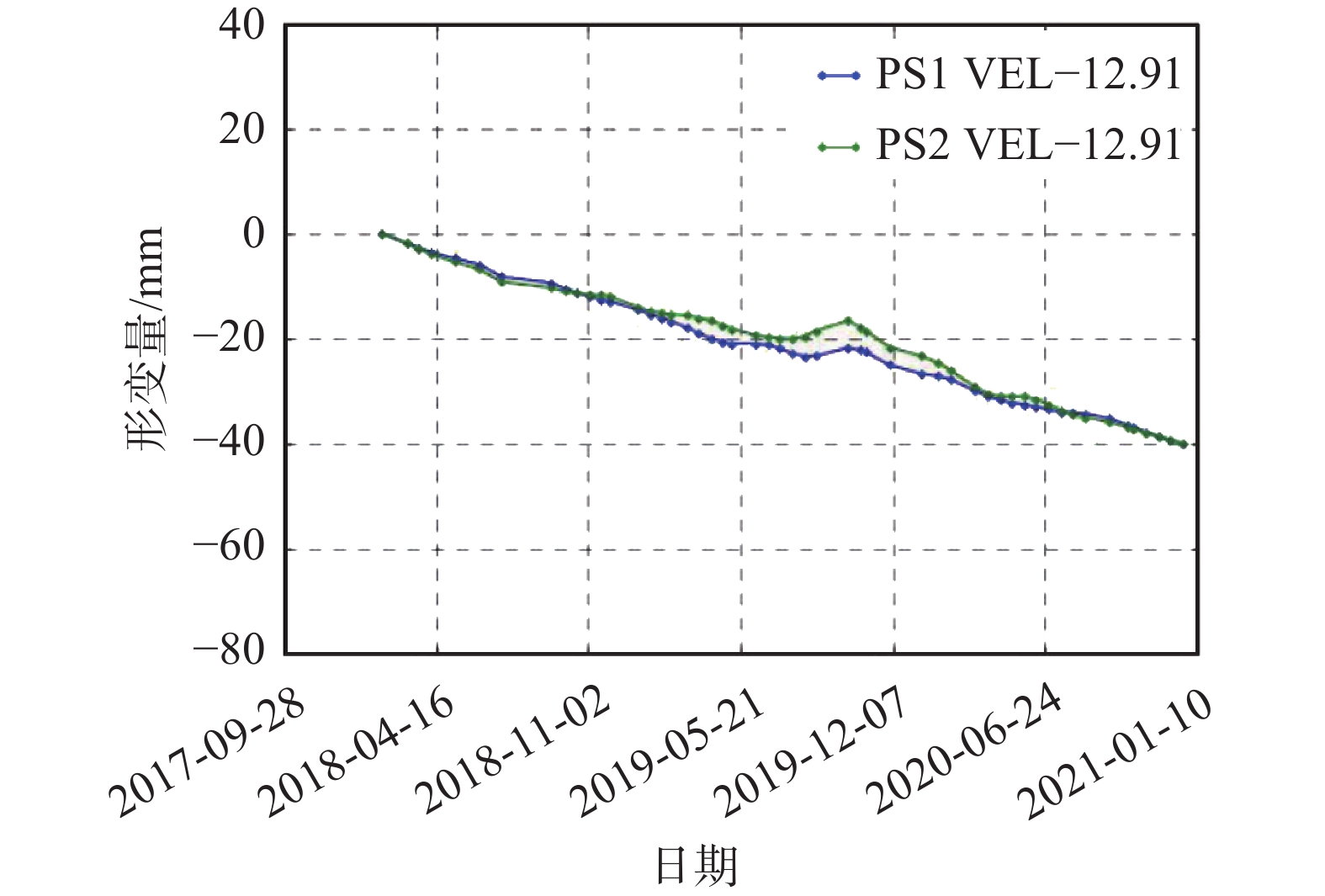
注:PS为监测特征点的控制点,VEL为高程。 表 3 相同位置不同技术手段成果对比
Table 3. Comparison of results of different technical means in the same position
项目 蛇口文体中心基坑
支护形变监测项目后海断裂带项目 技术手段 S05级水准仪(134次) InSAR(52期) 对应位置 点7附近
(深圳市育才舒曼艺术学校体育场)点7
(卓越维港名苑)监测时间 2019年2月—2020年4月 累计形变/mm −1.9 −1.6 表 4 地层岩性特征
Table 4. Formation lithologic characteristics
地层岩性 地层岩性特征 第四系人工
填土层液性指数 压缩指数
/MPa−1压缩模量
/MPa0.45 0.5 4.0 主要为素填土,层厚1.2~26.9 m,呈松散~稍密状,物理力学性质不均匀,工程性质较差,承载力较低,在上部较大荷载长期作用下易产生沉降及不均匀沉降 第四系海积
冲积层液性指数 压缩指数
/MPa−1压缩模量
/MPa1.36 1.28 2.0 主要为淤泥软土层,层厚0.3~17.0 m,呈流塑状,含较多腐殖质、贝壳碎屑,承载力极低,灵敏度高 第四系残积层及燕山四期侵入花岗岩 残积的砾质黏性土和全风化花岗岩、强风化花岗岩,粉粒含量高,受水浸湿或浸泡后,易软化变形,强度、承载力骤减 -
[1] 代志宏,卢鹏,张志芳,等. 基于PS-InSAR技术的南宁地表沉降监测与分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2021,41(5):491 − 496. [DAI Zhihong,LU Peng,ZHANG Zhifang,et al. Surface subsidence monitoring and analysis of Nanning based on PS-InSAR technology[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2021,41(5):491 − 496. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 叶凯,金典琦,张勇,等. 基于PS-InSAR技术的深圳北站表面位移监测研究[J]. 测绘地理信息,2021,46(3):29 − 32. [YE Kai,JIN Dianqi,ZHANG Yong,et al. Surface deformation monitoring of Shenzhen north station using PS-InSAR technology[J]. Journal of Geomatics,2021,46(3):29 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 李晓恩,周亮,苏奋振,等. InSAR技术在滑坡灾害中的应用研究进展[J]. 遥感学报,2021,25(2):614 − 629. [LI Xiaoen,ZHOU Liang,SU Fenzhen,et al. Application of InSAR technology in landslide hazard:Progress and prospects[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin,2021,25(2):614 − 629. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 潘光永,陶秋香,陈洋,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR的山东济阳矿区沉降监测与分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):100 − 106. [PAN Guangyong,TAO Qiuxiang,CHEN Yang,et al. Monitoring and analysis of sedimentation in Jiyang mining area of Shandong Province based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):100 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 魏纪成,张红霞,白泽朝,等. 融合D-InSAR与PS-InSAR的神东矿区开采沉陷监测方法[J]. 金属矿山,2019(10):55 − 60. [WEI Jicheng,ZHANG Hongxia,BAI Zechao,et al. Integrated monitoring method of the mining subsidence of Shendong mining area based on D-InSAR and PS-InSAR technology[J]. Metal Mine,2019(10):55 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李军,褚宏亮,李滨,等. 基于高分影像与InSAR解译的西藏林芝则隆弄高位链式地质灾害发育特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):42 − 50. [LI Jun,CHU Hongliang,LI Bin,et al. Analysis of development characteristics of high-elevationchain geological hazard in Zelongnong, Nyingchi, Xizang based on high resolution image and InSAR interpretation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):42 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 潘建平,邓福江,徐正宣,等. 基于轨道精炼控制点精选的极艰险区域时序InSAR地表形变监测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):98 − 104. [PAN Jianping,DENG Fujiang,XU Zhengxuan,et al. Time series InSAR surface deformation monitoring in extremely difficult area based on track refining control points selection[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):98 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 洪兆阳,金双根. 利用时序PS-InSAR监测青藏高原冻土区地表形变[J]. 测绘通报,2021(1):35 − 40. [HONG Zhaoyang,JIN Shuanggen. Permafrost deformation in Qinghai-Xizang plateau time-series PS-InSAR[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2021(1):35 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 许军强,马涛,卢意恺,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的豫北平原地面沉降监测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2019,49(4):1182 − 1191. [XU Junqiang,MA Tao, LU Yikai,et al. Land subsidence monitoring in north Henan plain based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2019,49(4):1182 − 1191. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] FERRETTI A,PRATI C,ROCCA F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2000,38(5):2202 − 2212. doi: 10.1109/36.868878
[11] FERRETTI A,PRATI C,ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2001,39(1):8 − 20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661
[12] 范军,左小清,李涛,等. PS-InSAR和SBAS-InSAR技术对昆明主城区地面沉降监测的对比分析[J]. 测绘工程,2018,27(6):50 − 58. [FAN Jun,ZUO Xiaoqing,LI Tao,et al. Analysis and comparison of PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR for ground subsidence monitoring in the main city of Kunming[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping,2018,27(6):50 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 《深圳地质》编写组. 深圳地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009
Editorial group of Shenzhen Geology. Shenzhen Geological[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009. (in Chinese)
[14] 雷斌,李超,童心,等. 灌注桩钢筋笼箍筋自动弯箍施工技术[J]. 建筑施工,2020,49(增刊 1):786 − 789. [LEI Bin,LI Chao,TONG Xin,et al. Construction technology of automatic bending hoop for reinforcing cage stirrup of cast-in-place piles[J]. Construction Technology,2020,49(Sup 1):786 − 789. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 夏小裕,王哲奇. PS-InSAR 与 DS-InSAR 监测城市地面沉降的精度检验与分析[J]. 海洋测绘,2020,40(4):65 − 71. [XIA Xiaoyu,WANG Zheqi. Accuracy test and analysis of PS-InSAR and DS-InSAR monitoring urban land subsidence[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting,2020,40(4):65 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 工程测量标准: GB 50026—2020[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2021.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for engineering surveying: GB 50026—2020[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2021. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: