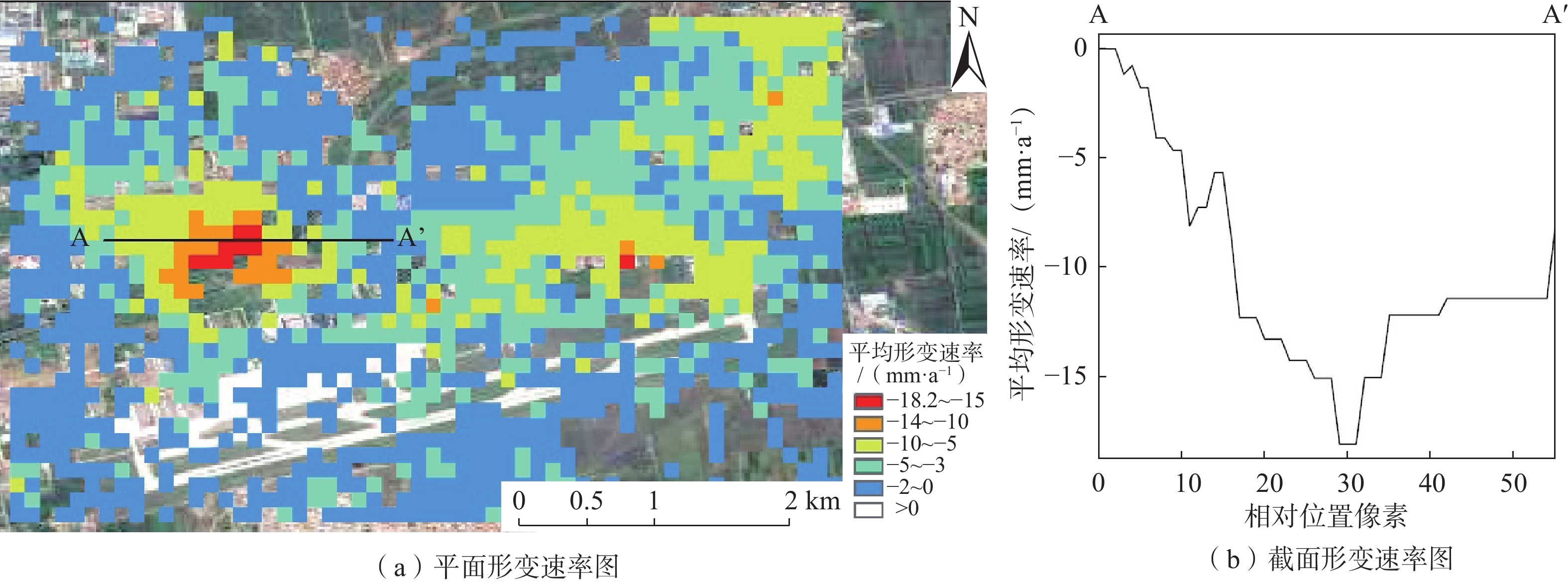
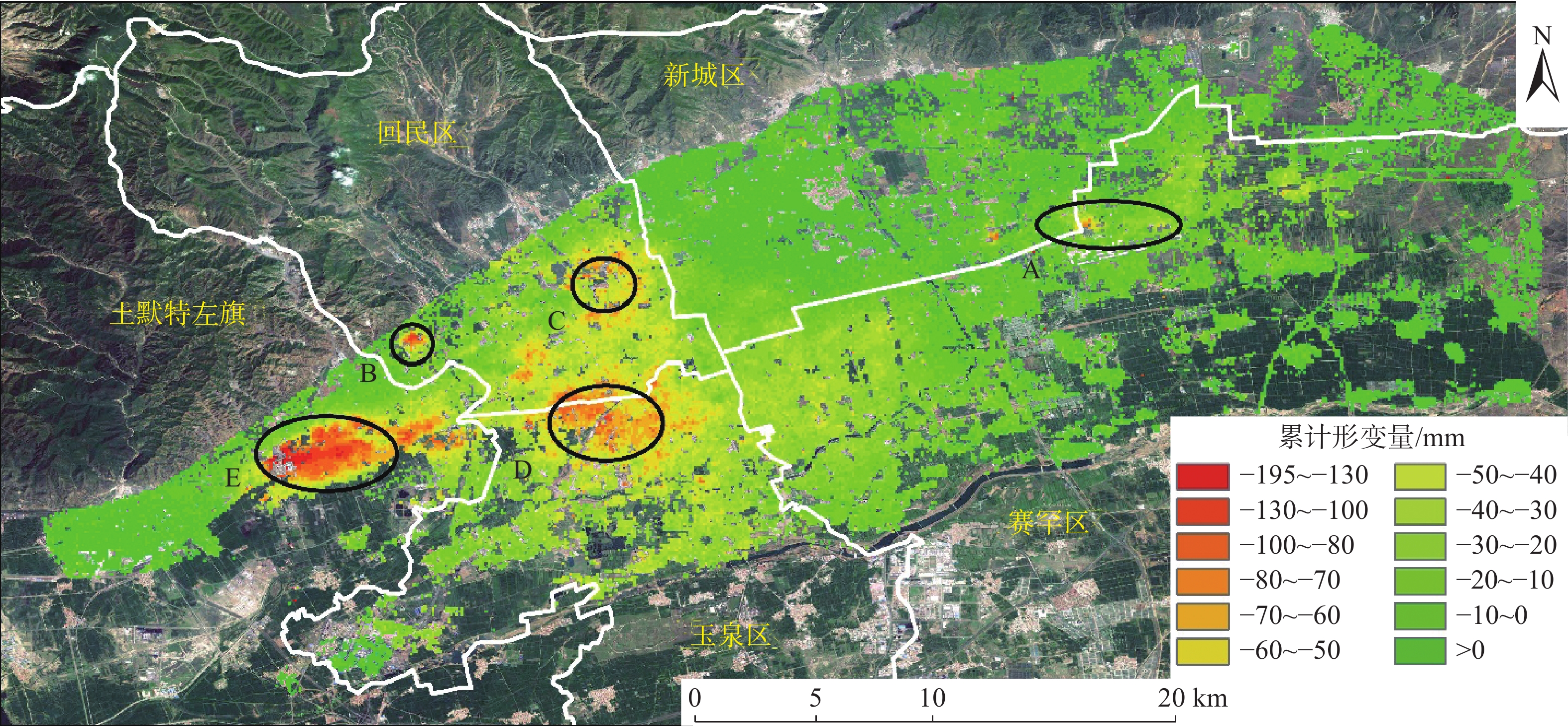
Surface deformation analysis of Hohhot urban area based on SAR data from Sentinel-1A
-
摘要:
为了实现对呼和浩特市城区形变监测,采用永久散射体合成孔径雷达干涉测量(PS-InSAR)技术,对2017年3月—2021年4月期间25景呼和浩特市城区Sentinel-1A数据进行时序干涉处理,提取了城区地表沉降信息,并分析了主要沉降中心沉降原因。结果表明:呼和浩特市城区地表存在5个明显的沉降中心,整体地表平均年沉降速率3.65 mm/a,平均累计沉降量为15.50 mm,其沉降主要原因是由于地下水过度开采。Sentinel-1A数据具有时间基线短、影像数量足、数据免费等优点,利于InSAR时序分析,可满足同类城区地表形变监测工作,服务城市安全。
-
关键词:
- 地表沉降 /
- Sentinel-1A /
- 时序分析 /
- 永久散射体干涉技术 /
- 呼和浩特
Abstract:In order to realize the monitoring of deformation in the urban area of Hohhot city, this paper uses the permanent scatterer synthetic aperture radar interferometry (PS-InSAR) technique to perform temporal interferometric processing on 25 scenes of Sentinel-1A data from March 2017 to April 2021 in the urban area of Hohhot city to extract the surface subsidence information in the urban area and analyze the causes of subsidence in the main subsidence centers. The results show that there are five obvious centres of subsidence in the urban area of Hohhot, and that the overall average annual surface subsidence rate is 3.65 mm/a, with an average cumulative subsidence of 15.50 mm. The subsidence is mainly due to over-exploitation of groundwater. Given that the free Sentinel-1A data has the advantages of short time baseline and sufficient number of images, it is conducive to InSAR time series analysis, which can meet similar urban surface deformation monitoring work and serve urban safety.
-
Key words:
- ground subsidence /
- Sentinel-1A /
- time series analysis /
- permanent scatterer interferometry /
- Hohhot
-

-
表 1 研究所采用的Sentinel-1A数据参数
Table 1. Summary of the Sentinel-1A data parameters used in the study
影像编号 成像日期 空间基线距/m 时间基线距/d 影像编号 成像日期 空间基线距/m 时间基线距/d 1 2017-03-19 −34.87 −564 14 2019-04-02 −28.33 180 2 2017-04-12 −37.39 −540 15 2019-06-01 −23.04 240 3 2017-06-11 26.72 −480 16 2019-08-12 −78.11 312 4 2017-07-29 −40.10 −432 17 2019-10-11 53.56 372 5 2017-10-09 −33.23 −360 18 2019-12-10 87.43 432 6 2017-12-08 45.08 −300 19 2020-02-08 62.98 492 7 2018-02-06 −31.88 −240 20 2020-04-08 63.07 552 8 2018-04-07 12.50 −180 21 2020-05-14 −30.41 588 9 2018-06-06 −22.68 −120 22 2020-08-06 29.23 672 10 2018-08-05 −18.48 −60 23 2020-10-05 −33.29 732 11 2018-10-04 0.00 0 24 2020-12-04 23.03 792 12 2018-12-03 48.10 60 25 2021-04-03 5.72 912 13 2019-02-01 45.28 120 -
[1] 侯保俭,翟家齐,侯红雨,等. 呼和浩特市平原区地下水数值模拟[J]. 水电能源科学,2019,37(2):27 − 30. [HOU Baojian,ZHAI Jiaqi,HOU Hongyu,et al. Numerical simulation of groundwater in plain area of Hohhot[J]. Water Resources and Power,2019,37(2):27 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 王超,董少刚,刘晓波,等. 城市化对呼和浩特市潜水补给影响研究[J]. 现代地质,2018,32(3):574 − 583. [WANG Chao,DONG Shaogang,LIU Xiaobo,et al. Influence of urbanization on unconfined groundwater recharge in Hohhot,Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience,2018,32(3):574 − 583. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.03.15
[3] 郭道强. 呼和浩特市地下水现状与发展浅析[J]. 内蒙古水利,2012(6):37 − 39. [GUO Daoqiang. Analysis on the present situation and development of groundwater in Hohhot[J]. Inner Mongolia Water Conservancy,2012(6):37 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘昱彤. PS-InSAR技术的地表沉降监测研究[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2020
LIU Yutong. Surface subsidence monitoring of PS-InSAR technique[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张剑. 基于Sentinel-1数据的兰州市中心城区地面沉降监测研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2020
ZHANG Jian. Research on land subsidence monitoring in Lanzhou City center based on Sentinel-1 data[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 廖明生,裴媛媛,王寒梅,等. 永久散射体雷达干涉技术监测上海地面沉降[J]. 上海国土资源,2012,33(3):5 − 10. [LIAO Mingsheng,PEI Yuanyuan,WANG Hanmei,et al. Subsidence monitoring in Shanghai using the PSInSAR technique[J]. Shanghai Land and Resources,2012,33(3):5 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 马秀露. 永久散射体雷达干涉测量技术研究及工程应用[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2019
MA Xiulu. Study and engineering application on permanent scatterers interferometric synthetic aperture radar[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 郑佳兵,郑佳荣,张丽丽,等. 道路交通对北京平原区沉降的影响[J]. 交通运输研究,2020,6(6):62 − 72. [ZHENG Jiabing,ZHENG Jiarong,ZHANG Lili,et al. Influence of road traffic on subsidence of Beijing plain area[J]. Transport & Research,2020,6(6):62 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16503/j.cnki.2095-9931.2020.06.008
[9] 张勤,黄观文,杨成生. 地质灾害监测预警中的精密空间对地观测技术[J]. 测绘学报,2017,46(10):1300 − 1307. [ZHANG Qin,HUANG Guanwen,YANG Chengsheng. Precision space observation technique for geological hazard monitoring and early warning[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographic Sinica,2017,46(10):1300 − 1307. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王平豪. PS-InSAR在沉降监测中的应用研究: 以深圳福田区为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.
WANG Pinghao. The application of PS-InSAR technology in Shenzhen Futian settlement monitoring[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张荐铭,甘淑,袁希平,等. PS-InSAR技术的昆明地表沉降特征提取与分析[J]. 测绘科学,2019,44(1):53 − 59. [ZHANG Jianming,GAN Shu,YUAN Xiping,et al. The extraction and analysis of Kunming ground deformation characteristics based on PS-InSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2019,44(1):53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2019.01.011
[12] 林凯. 卡尔曼滤波-BP神经网络组合模型在地铁变形监测中的应用[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2019
LIN Kai. Application of kalman filter-BP neural network combintion model in metro deformation monitoring[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 胡勇平. 基于CEEMDAN-PSO-LSSVM模型的基坑变形预测研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2018
HU Yongping. Study on deformation prediction of foundation pit based on CEEMDAN-PSO-LSSVM model[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张凯,相福斌. 呼和浩特轨道交通2号线某车站基坑开挖沉降监测分析[J]. 现代隧道技术,2020,57(增刊 1):884 − 889. [ZHANG Kai,XIANG Fubin. Monitoring and analysis of settlements induced by foundation pit excavation in metro station of Hohhot area[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2020,57(Sup 1):884 − 889. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13807/j.cnki.mtt.2020.S1.118
[15] 杨红樱,熊峰. 降雨对呼和浩特地震台形变观测的影响[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,2019,40(5):101 − 108. [YANG Hongying,XIONG Feng. Influence of rainfall in deformation at Hohhot seismic station[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,2019,40(5):101 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 石鸿蕾,郝奇琛,邵景力,等. 基于多源数据的弱透水层水文地质参数反演研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,42(2):1 − 7. [SHI Honglei,HAO Qichen,SHAO Jingli,et al. Research on hydrogeological parameter inversion of an aquitard based on multi-source data:A case study of a silt layer in the Hohhot Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,42(2):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 徐杰,龚萍,金良. 基于生态绿当量的呼和浩特市土地利用结构优化评价与分析[J]. 生态经济,2019,35(1):196 − 201. [XU Jie,GONG Ping,JIN Liang. Optimization evaluation and analysis on land use structure city based on ecological green equivalent in Hohhot[J]. Ecological Economy,2019,35(1):196 − 201. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 查娜. 呼和浩特市水资源利用管理研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2019
Zhana. Research on the management of water resources utilization in Hohhot City[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 畅利毛. 呼和浩特地区地下水动态变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地下水,2016,38(6):62 − 64. [CHANG Limao. Analysis on dynamic changes characteristics of groundwater level and influencing factors in Hohhot[J]. Ground Water,2016,38(6):62 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2016.06.021
[20] 张恒星. 呼和浩特盆地浅层地下水水化学特征及其富砷机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2018
ZHANG Hengxing. Study on the hydrochemical characteristics and arcsenic enrichment mechanism of shallow groundwater in Hohhot Basin[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 李潇瀚,张翼龙,王瑞,等. 呼和浩特盆地地下水化学特征及成因[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2018,16(4):136 − 145. [LI Xiaohan,ZHANG Yilong,WANG Rui,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Hohhot Basin[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2018,16(4):136 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2018.0107
[22] 张泽鹏,朱玉晨,郝奇琛,等. 呼和浩特盆地地下水流系统变异机制及其资源效应[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):63 − 68. [ZHANG Zepeng,ZHU Yuchen,HAO Qichen,et al. A study on variation mechanism of groundwater flow system in the Hohhot basin and its resources effect analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):63 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.02.10
[23] 赵瑞科,曹文庚,杨会峰,等. 呼和浩特盆地地下水演化特征研究[J]. 人民黄河,2018,40(5):78 − 82. [ZHAO Ruike,CAO Wengeng,YANG Huifeng,et al. Study on evolution characteristics of groundwater in Hohhot Basin[J]. Yellow River,2018,40(5):78 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2018.05.017
[24] 石鸿蕾,郝奇琛,邵景力,等. 基于多源数据的弱透水层水文地质参数反演研究—以呼和浩特盆地某淤泥层为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):1 − 7. [SHI Honglei,HAO Qichen,SHAO Jingli,et al. Research on hydrogeological parameter inversion of an aquitard based on multi-source data:A case study of a silt layer in the Hohhot Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202010013
[25] 张翼龙. 呼和浩特盆地开采胁迫下的地下水系统响应及适应性对策研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2012
ZHANG Yilong. Aquifer system response and its adaptability countermeasures to exploitation in the Hohhot Basin[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 吴龙飞,陈凌伟,彭卫平. PSInSAR技术在广州市南沙区地面沉降监测中的应用研究[J]. 城市勘测,2019(3):127 − 130. [WU Longfei,CHEN Lingwei,PENG Weiping. Research of PSInSAR technology in land subsidence monitoring in Nansha of Guangzhou[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2019(3):127 − 130. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8262.2019.03.029
[27] 姚佳明,姚鑫,陈剑,等. 基于InSAR技术的缓倾煤层开采诱发顺层岩体地表变形模式研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):135 − 146. [YAO Jiaming,YAO Xin,CHEN Jian,et al. A study of deformation mode and formation mechanism of a bedding landslide induced by mining of gently inclined coal seam based on InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):135 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201903072
[28] 姜珊珊. PSInSAR技术在公路沉降监测中的应用研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2018.
JIANG Shanshan. Application of PSInSAR technology in monitoring highway subsidence[D]. Nanchang: East China Jiaotong University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 洪江法. D-InSAR技术在地面沉降调查中的应用研究[D]. 马鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2019
HONG Jiangfa. Application of D-InSAR technology in land subsidence investigation: A case study of Yongjing County, Gansu Province[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 程霞,张永红,邓敏,等. Sentinel-1A卫星的黄河三角洲近期地表形变分析[J]. 测绘科学,2020,45(2):43 − 51. [CHENG Xia,ZHANG Yonghong,DENG Min,et al. Analysis of recent surface deformation in the Yellow River delta based on Sentinel-1A satellite[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2020,45(2):43 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2020.02.007
[31] 徐东卓,朱传宝,孟宪纲,等. 山西中北部地区地壳垂直形变时空演化特征及与强震的关系[J]. 地震研究,2018,41(3):446 − 450. [XU Dongzhuo,ZHU Chuanbao,MENG Xiangang,et al. Temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of crust vertical deformation and its relationship with strong earthquakes in central and northern Shanxi[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,2018,41(3):446 − 450. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2018.03.014
[32] 徐凯,赵鹏. 利用水准数据分析晋冀蒙地区垂直形变演化特征[J]. 山西地震,2020(4):29 − 32. [XU Kai,ZHAO Peng. An analysis of the evolution characteristics of vertical deformation in Jin-JI-Meng region based on leveling data[J]. Earthquake Research in Shanxi,2020(4):29 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6265.2020.04.006
[33] 任超,施显健,周吕,等. 基于哨兵-1A时间序列合成孔经雷达的地铁沿线地面沉降监测与分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2020,20(2):803 − 808. [REN Chao,SHI Xianjian,ZHOU Lyu,et al. Land subsidence detection and analysis along Subway based on Sentinel-1A time series synthetic aperture radar[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(2):803 − 808. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.02.055
[34] 王姝琼. 呼和浩特市承压地下水超采现状[J]. 科技视界,2020,20(2):1 − 3. [WANG Shuqiong. Overexploitation of confined groundwater in Hohhot[J]. Science & Technology Vision,2020,20(2):1 − 3. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19694/j.cnki.issn2095-2457.2020.02.001
[35] 内蒙古自治区人民政府.内政发[2015]-3 号内蒙古自治区人民政府关于公布自治区地下水超采及禁采区和限采范围的通知[A]. 内蒙古自治区人民政府公报 . (2015-01-12)[2021-12-20]
Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region People's Government . Internal affairs [2015]-3 notice of the people's government of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region on the announcement of the overexploitation of groundwater in the autonomous region, the forbidden areas and the limits on the exploitation scope [A]. Bulletin of the People's Government of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region . (2015-01-12)[2021-12-20].(in Chinese)
[36] 卢旺,王承安,常帅. 基于哨兵1号的呼和浩特市沉降及成因分析[J]. 内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版),2022,51(3):236 − 242. [LU Wang,WANG Chengan,CHANG Shuai. Analysis of surface deformation of Hohhot based on Sentinel-1[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Normal University(Natural Science Edition),2022,51(3):236 − 242. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8735.2022.03.003
[37] 卢旺. 呼和浩特市区地面沉降空间分布及趋势预测[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2022
LU Wang. Spatial distribution and trend prediction of land subsidence in Hohhot[D]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Normal University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 王天祥. 基于时序InSAR技术的地表形变监测研究——以兰州地区为例[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2015
WANG Tianxiang. Surface deformation monitoring research based on time-series InSAR technology: A case study of Lanzhou[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] 陈国浒,刘云华. 单新建. PS-InSAR技术在北京采空塌陷区地表形变测量中的应用探析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2010,21(2):59 − 63. [CHEN Guohu,LIU Yunhua,SHAN Xinjian. Application of PS-InSAR technique in the deformation monitoring in mining collapse areas in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2010,21(2):59 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.02.012
[40] 程蕊,朱琳,周佳慧,等. 北京潮白河冲洪积扇地面沉降时空异质性特征及驱动因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(4):1182 − 1192. [CHENG Rui,ZHU Lin,ZHOU Jiahui,et al. Spatio-temporal heterogeneity and driving factors of land subsidence in middle-lower part of chaobai river alluvial fan[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(4):1182 − 1192. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] 秦胜伍, 张延庆, 张领帅, 等. 基于Stacking模型融合的深基坑地面沉降预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(5):1316 − 1323. [QIN Shengwu, ZHANG Yanqing, ZHANG Lingshuai, et al. Prediction of ground settlement around deep foundation pit based on stacking model fusion[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(5):1316 − 1323. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: