Monitoring and analyzing the development trend of land subsidence in Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province
-
摘要:
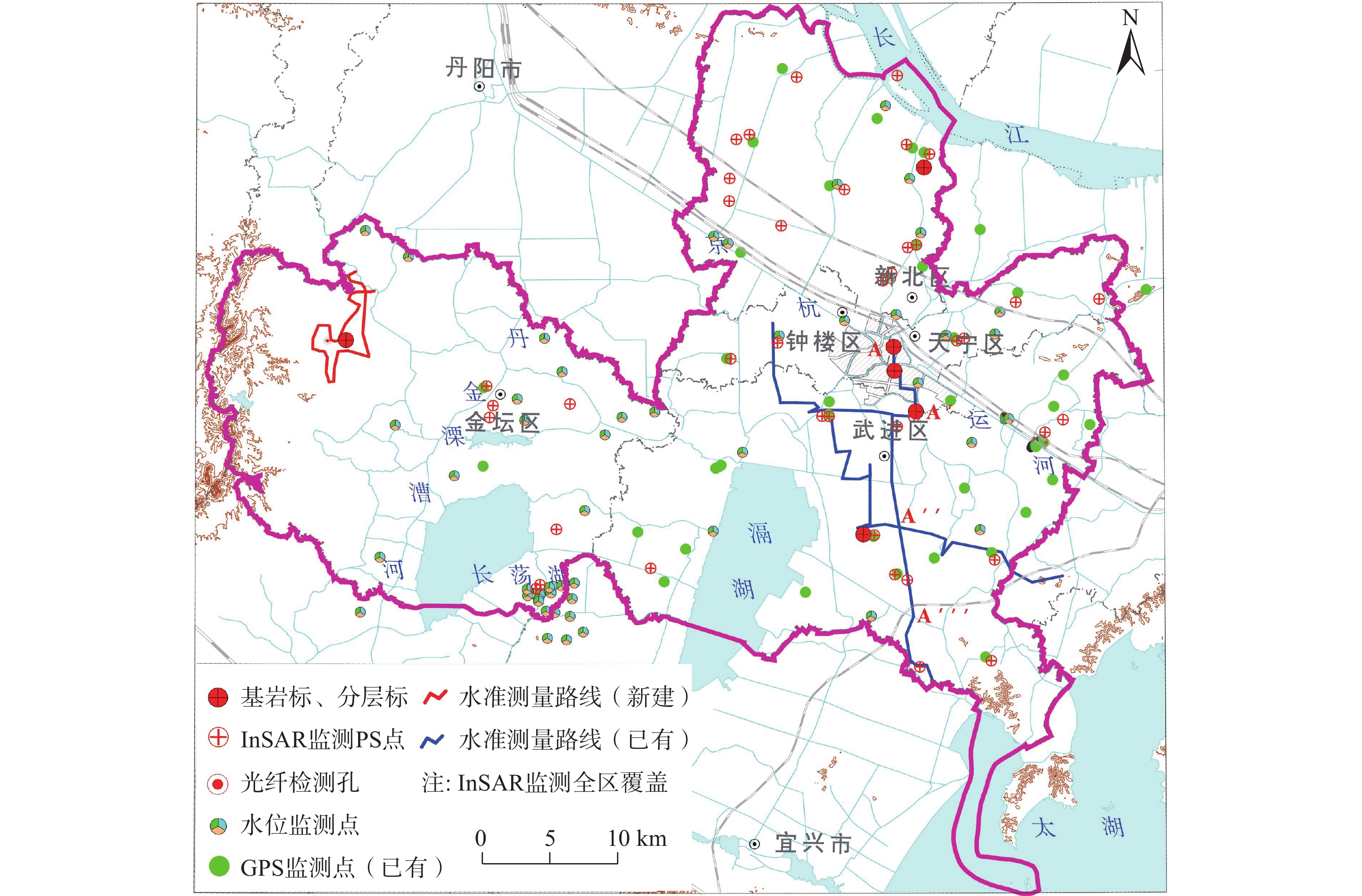
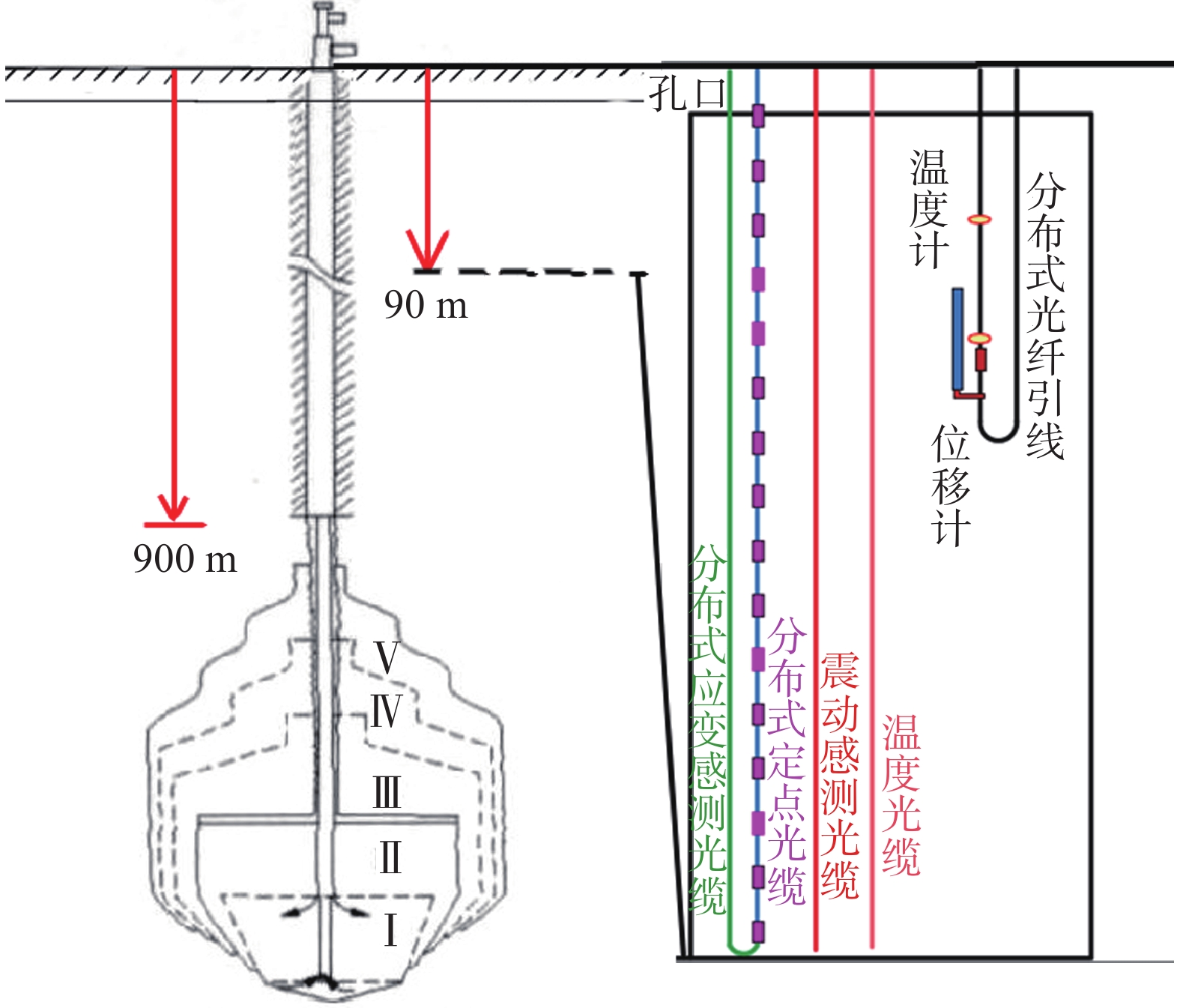
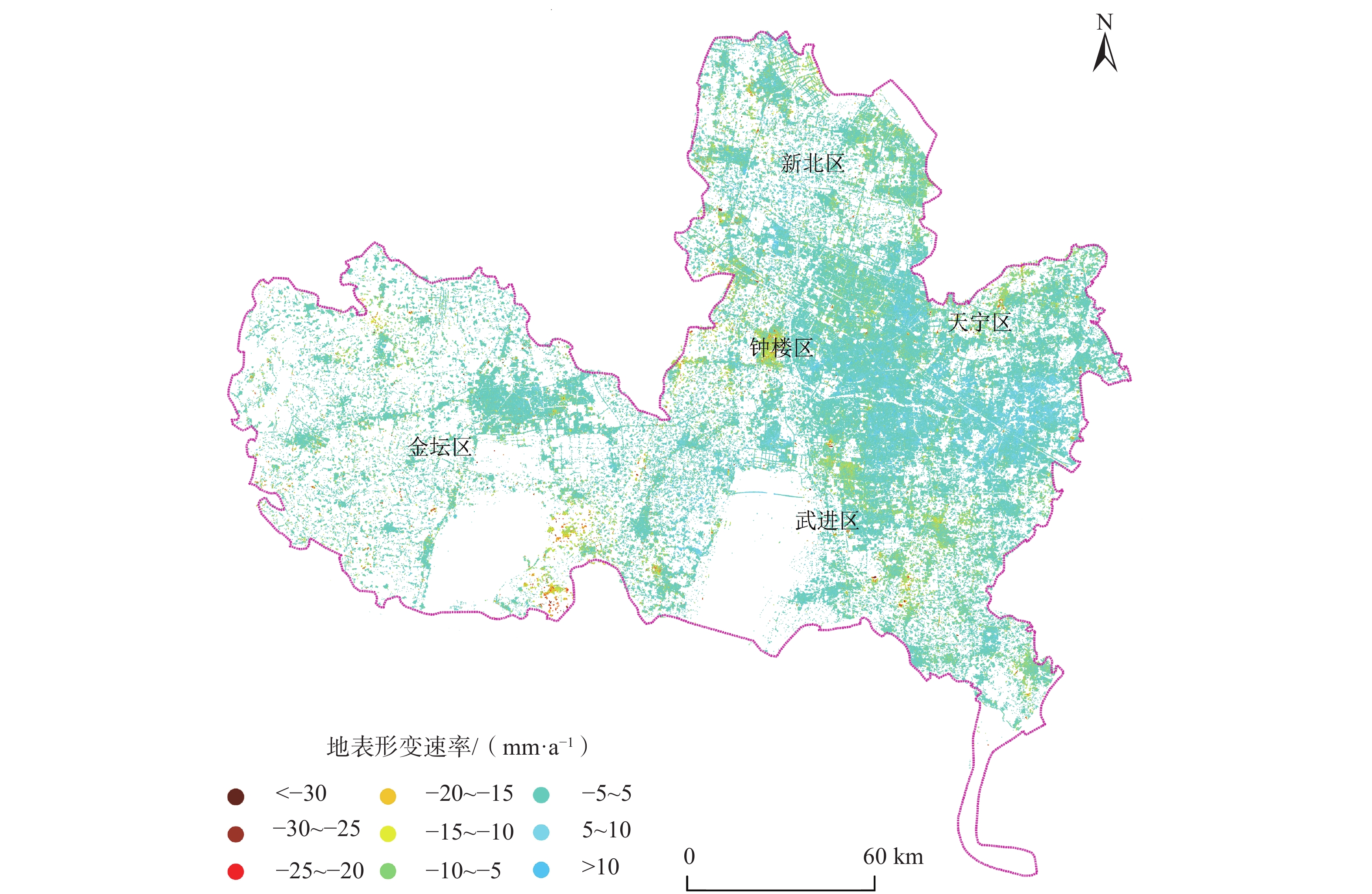
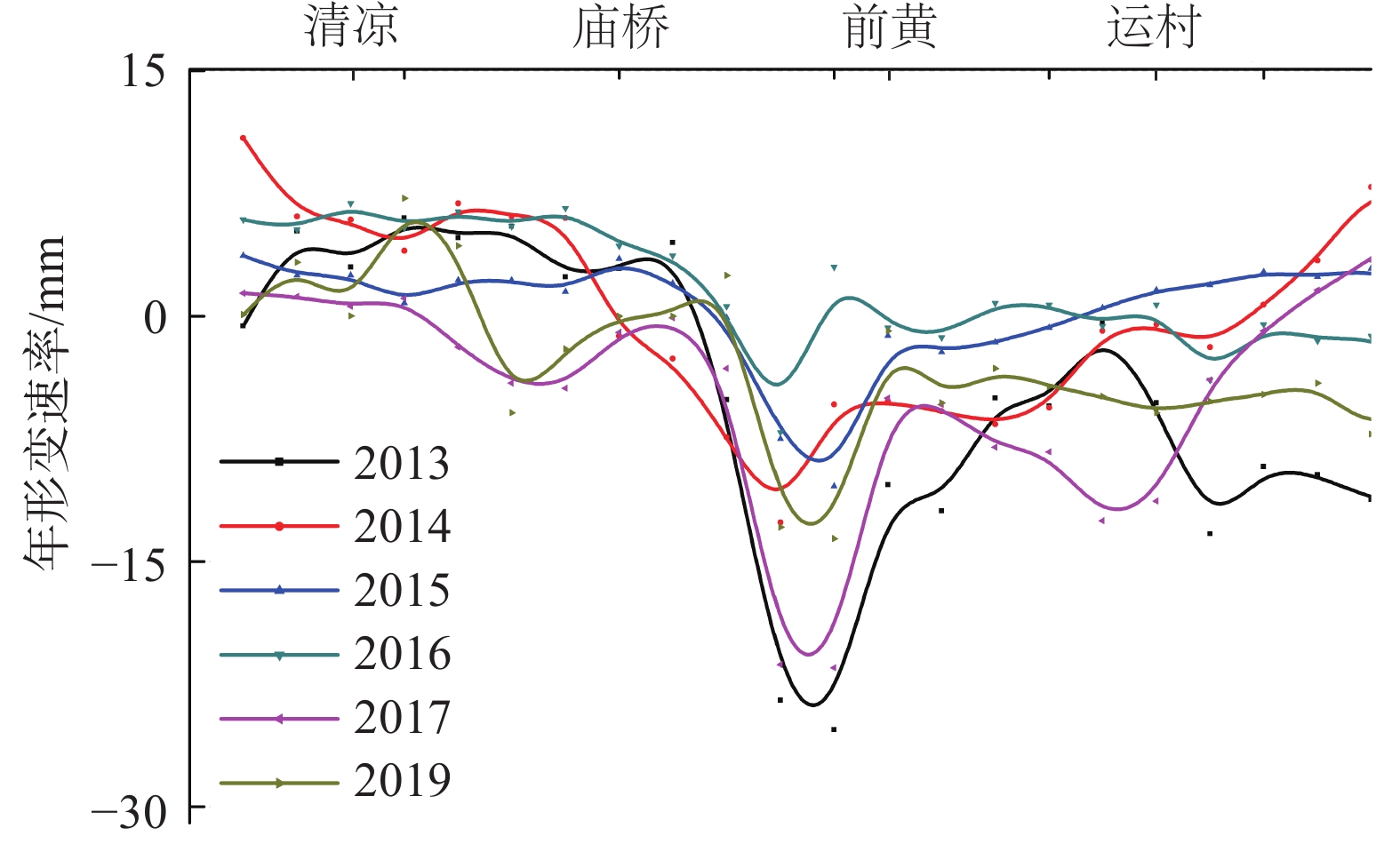
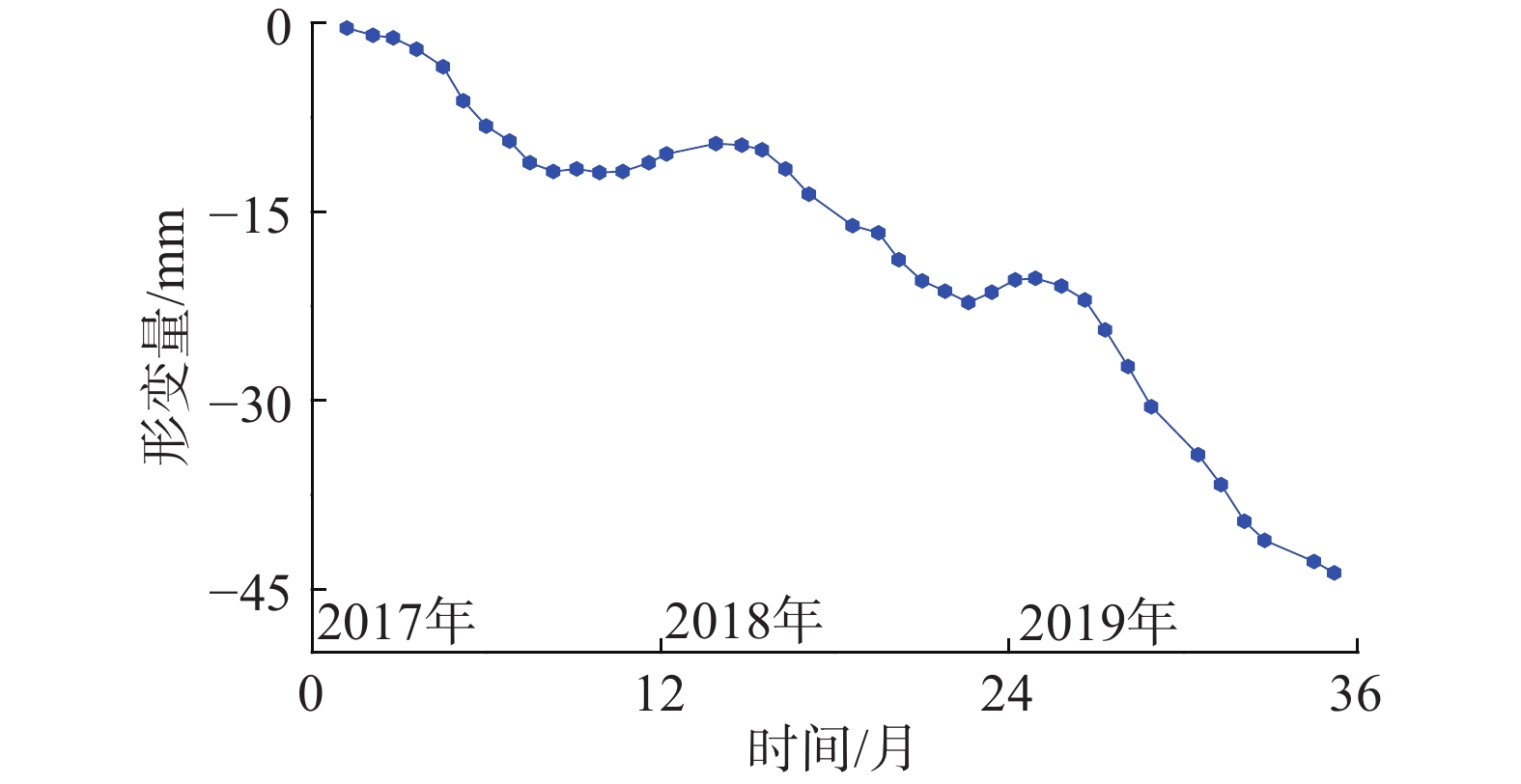
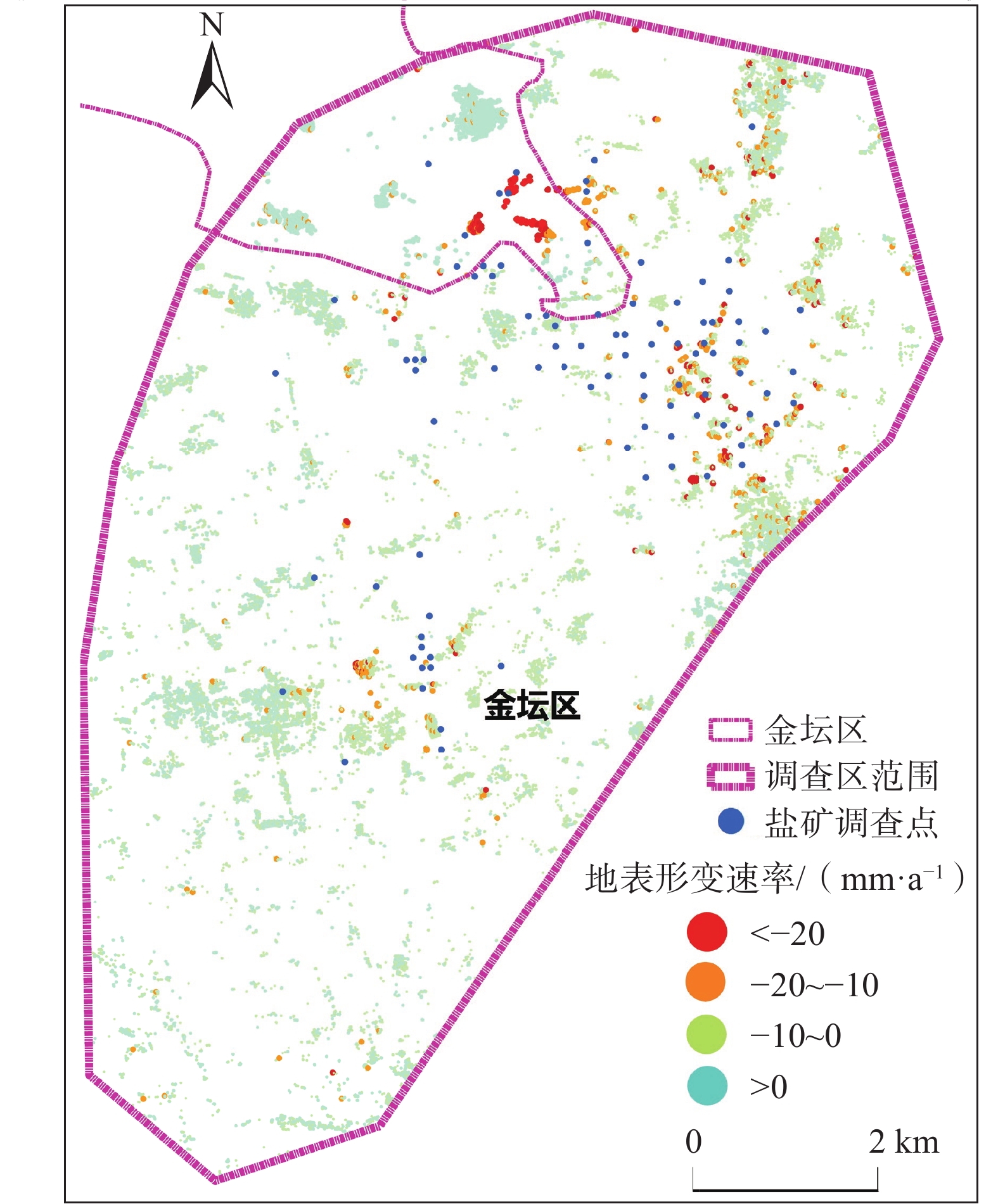
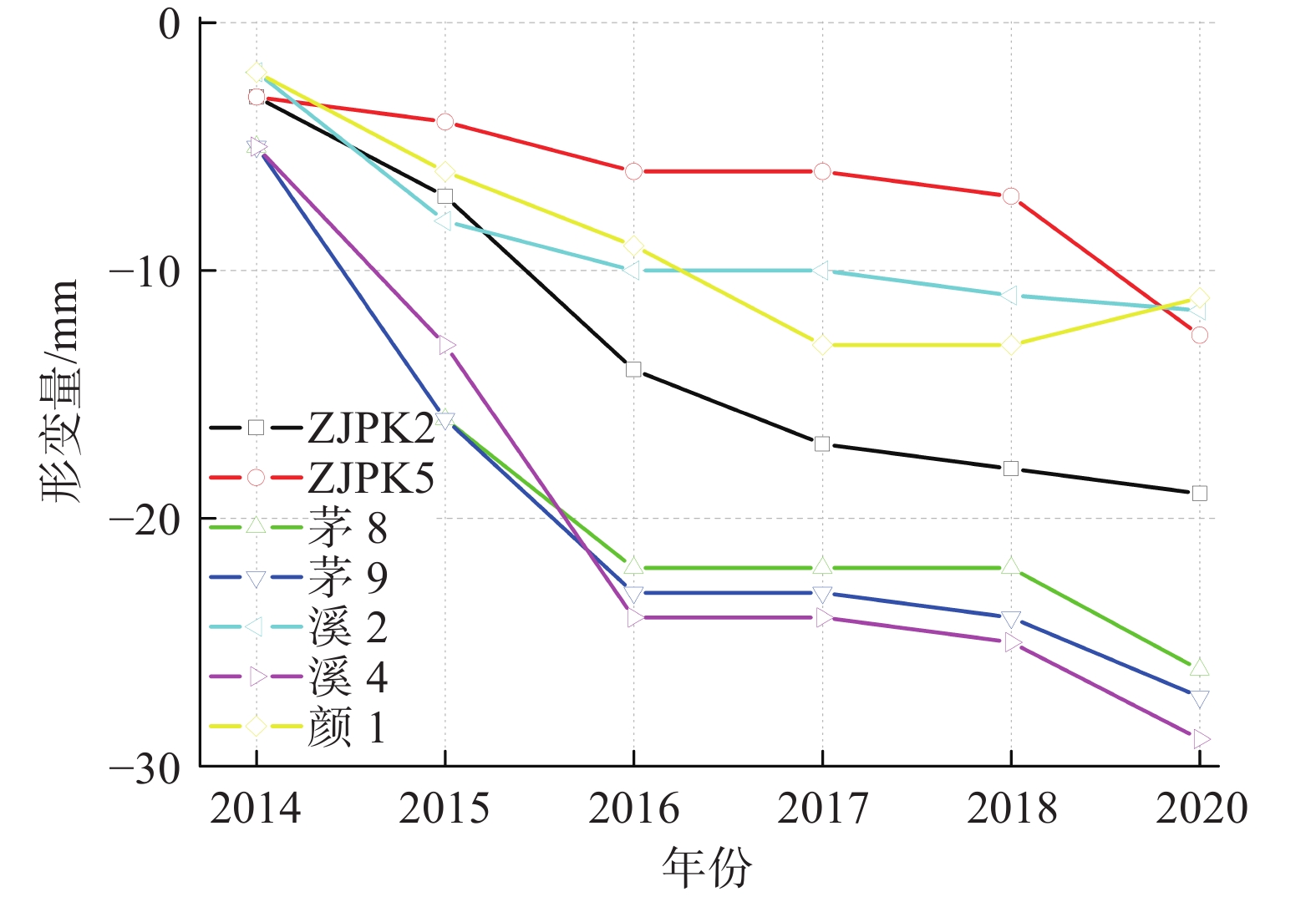
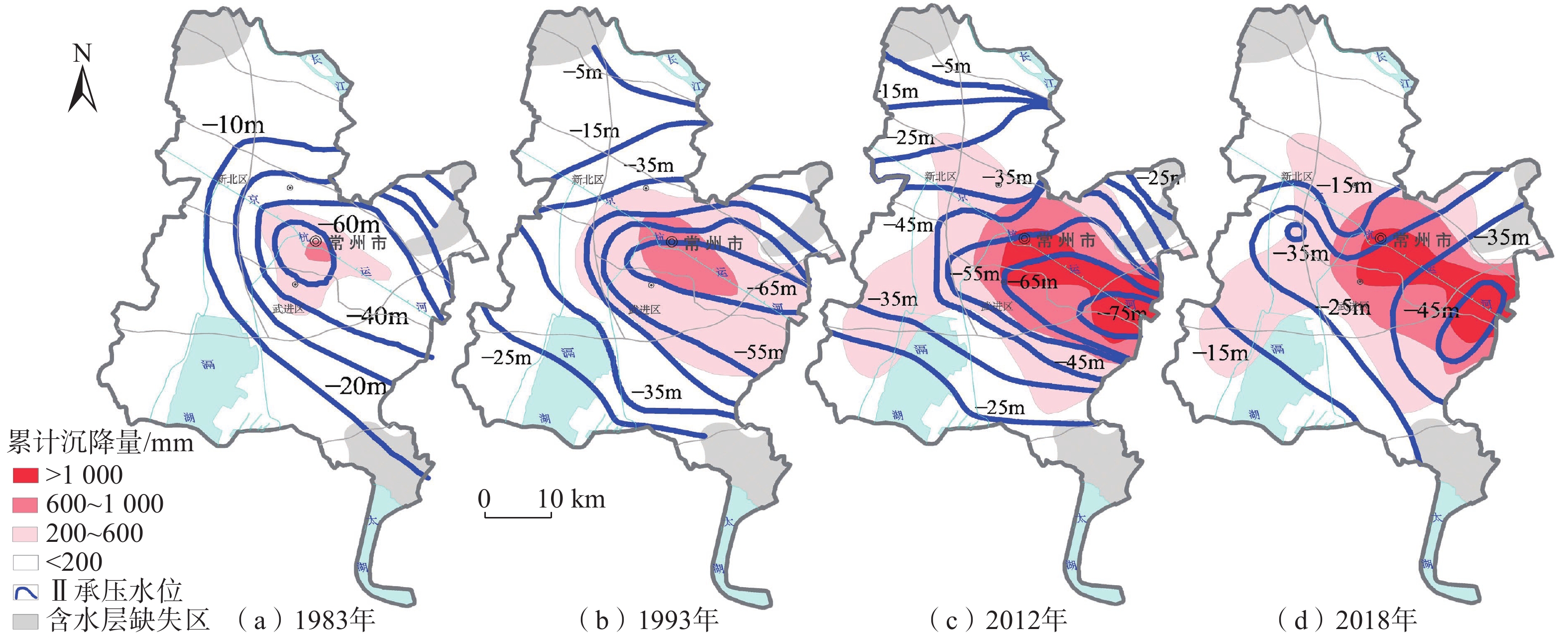
地面沉降是常州市区主要地质灾害之一,也是制约常州城市经济发展的重要环境地质问题。为了厘清常州市区地面沉降态势,提升灾害防治能力,文章优化形成了集一等水准测量、GPS-InSAR监测、基岩标和分层标、光纤监测孔等多种监测技术方法,点-线-面相结合的常州市地面沉降立体监测网络,有效提升了常州市区地面沉降监测的精度及可靠性。基于常州城市地质调查成果,系统归纳了近几十年常州市区地面沉降发展历程。利用建成的多方法地面沉降监测网络获取的沉降变形数据,得出常州市区地面沉降总体现状及发展趋势、重点沉降区分布、主要沉降层位及成因机理等,最终提出常州市区地面沉降防治建议,为以后城市地质调查工作中地面沉降监测与防控工作提供参考。
Abstract:Land subsidence is one of the main geological hazards in the urban area of Changzhou City, and it is also an important environmental geological issue that restricts the economic development of Changzhou City. To improve disaster prevention and mitigation, a three-dimensional monitoring network of land subsidence, which combines point-line-surface methods, has been established. This network utilizes various monitoring technologies such as In-SAR monitoring, GPS monitoring, primary level measurement, bedrock standard and layered standard, optical fiber monitoring hole, etc. The monitoring network has significantly enhanced the accuracy and reliability of land subsidence monitoring in Changzhou. Based on the results of the urban geological survey in Changzhou, the development process of land subsidence in recent decades has been systematically summarized. Using the subsidence deformation data obtained by the established multi-method monitoring network, the development trend of land subsidence in the urban area of Changzhou, the distribution of key subsidence areas, and the main subsidence layers and causation mechanism have been determined. Finally, suggestions for land subsidence prevention and control in Changzhou City have been proposed, providing a reference for future land subsidence monitoring and prevention and control work in urban geological surveying.
-
Key words:
- land subsidence /
- monitoring method system /
- prevention suggestions /
- urban geology
-

-
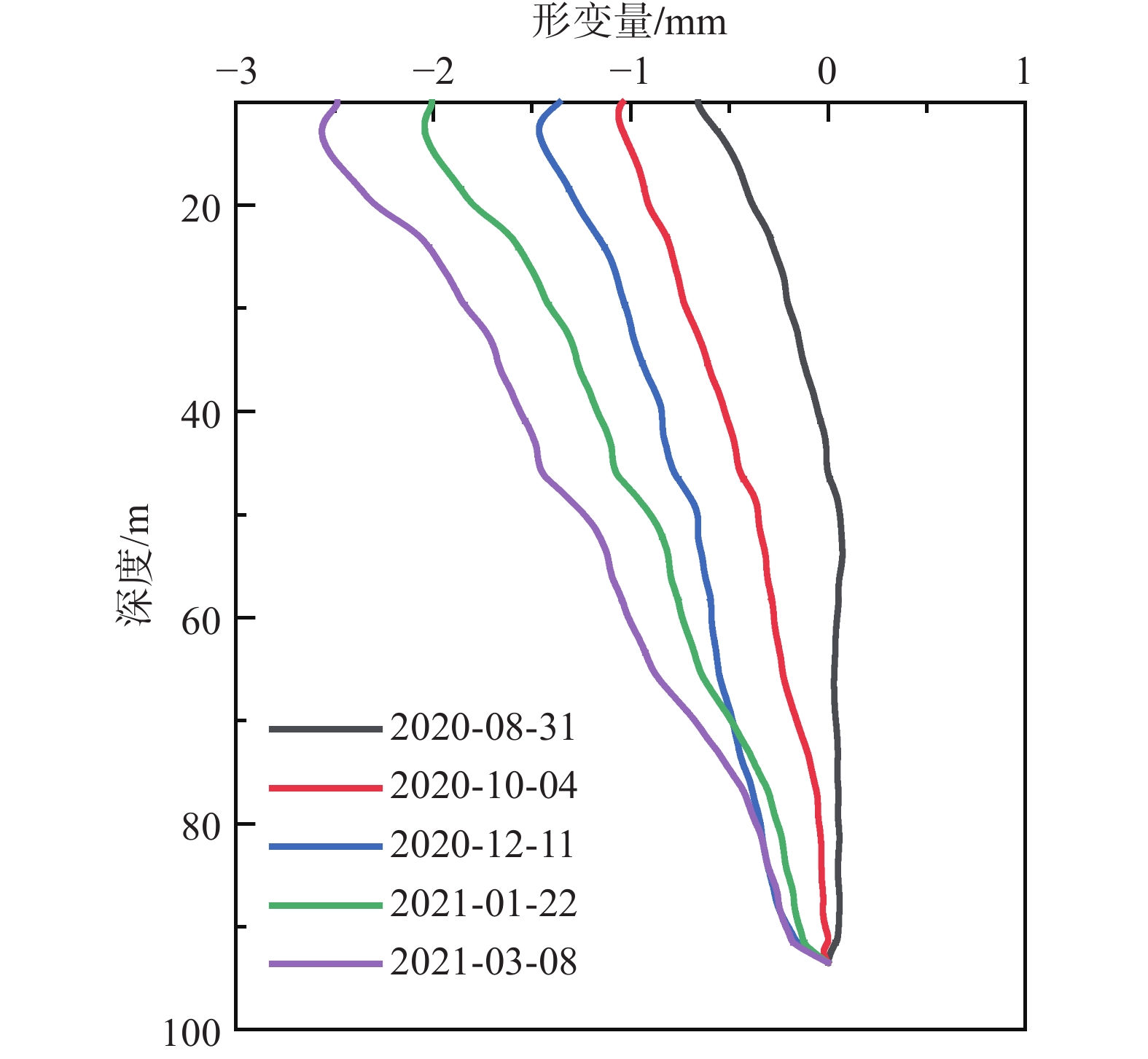
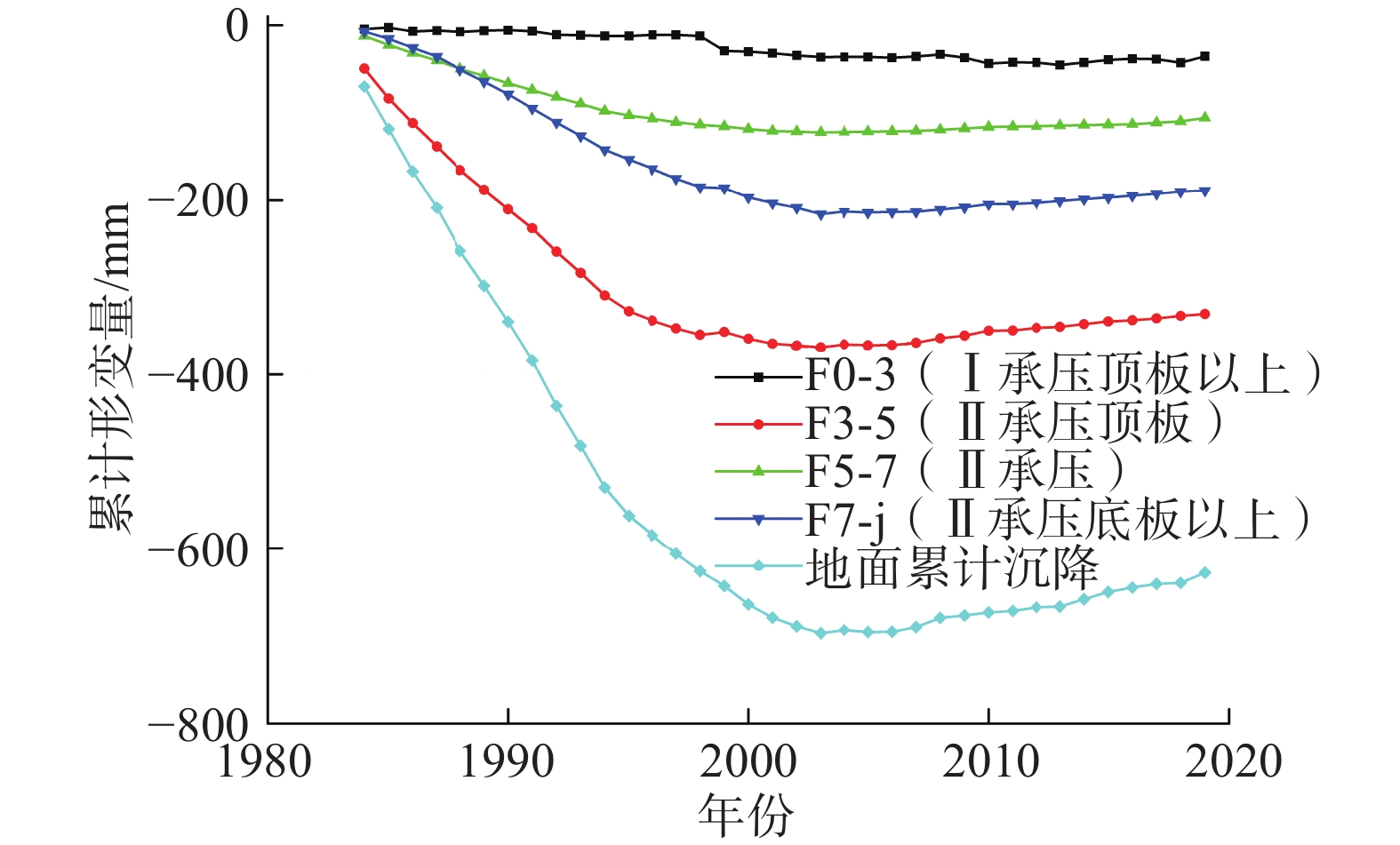
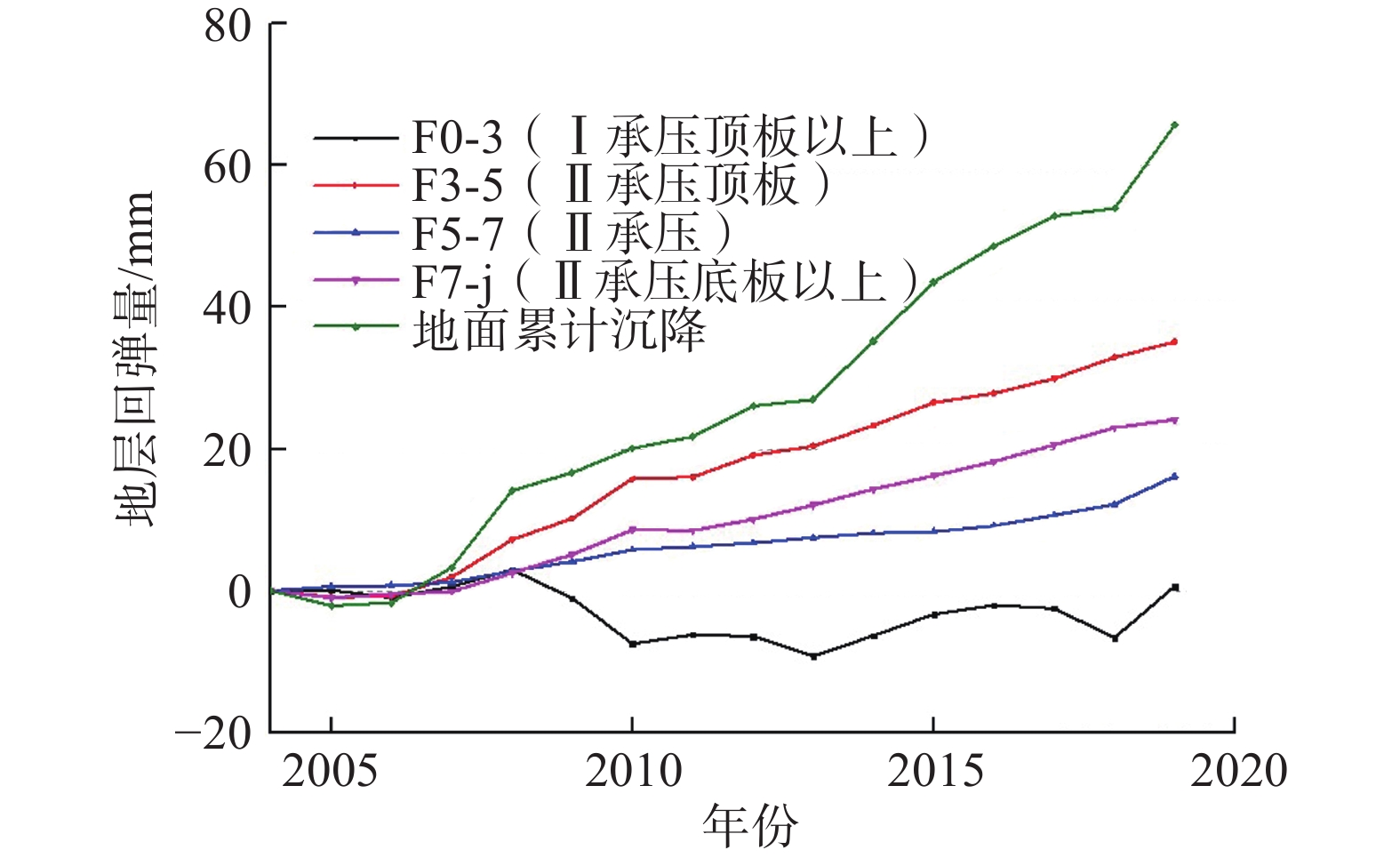
表 1 1984—2020年土层累计压缩/回弹量统计表
Table 1. Summary table of cumulative soil compression/ rebound measurements from 1984 to 2020
地层层段 1984—2004年累计
压缩量/mm分层沉降
占比/%2004—2020年累计
回弹量/mm分层回弹
占比/%0~39 m 16.57 2.48 0 0 39~92 m 365.58 54.77 35 46.7 92~109 m 79.11 11.84 22 29.3 109 m 206.90 30.91 18 24.0 累计沉降 668.00 100.00 75 100.0 -
[1] Emery T Cleaves, Issues of scale, geology and urban development[C]. Geological Society of America, Northeastern Section, 38th Annual Meeting, March 2004, 36( 2) : 41.
[2] N.Subba Rao. R.Prathap Reddy. Geoenvironmental appraisal in a developing urban area[J]. Environmental Geology, 2004, 47(1): 20-29.
[3] 李伟,武健强. 苏锡常地区地面沉降监测方法体系建设[J]. 世界地质,2015,34(3):862 − 869. [LI Wei,WU Jianqiang. Research on monitoring method system of land subsidence in Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou area[J]. Global Geology,2015,34(3):862 − 869. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.03.035
[4] 缪晓图,朱兴贤,陆美兰,等. 苏锡常地区Ⅱ承压水开采与地面沉降控制研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2007,18(2):132 − 139. [MIAO Xiaotu,ZHU Xingxian,LU Meilan,et al. Groundwater exploration from the confined aquiferous Ⅱ and land subsidence control of Suxichang area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2007,18(2):132 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2007.02.026
[5] 于军. 苏锡常地区地面沉降监测网络体系建设初探[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2000,11(3):82 − 85. [YU Jun. Preliminary design of establishment of land subsidence monitoring network system in Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou(Su-Xi-Chang) area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2000,11(3):82 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2000.03.020
[6] 郭海朋,李文鹏,王丽亚,等. 华北平原地下水位驱动下的地面沉降现状与研究展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):162 − 171. [GUO Haipeng,LI Wenpeng,WANG Liya,et al. Present situation and research prospects of the land subsidence driven by groundwater levels in the North China Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):162 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202012037
[7] 王双,严学新,揭江,等. 珠江三角洲平原区地面沉降影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):98 − 104. [WANG Shuang,YAN Xuexin,JIE Jiang,et al. Analysis on factors affecting ground settlement in plain area of Pearl River Delta[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):98 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.05.13
[8] 顾春生, 杨磊, 武健强, 等. 常州城市地质调查地质灾害调查与评价专题报告[R]. 南京: 江苏省地质调查研究院. 2020.
GU Chunsheng, YANG Lei, WU Jianqiang, et al. Report on geological hazard investigation and evaluation of Changzhou urban geological survey [R]. Nanjing: Geological Survey of Jiangsu Province. 2020. (in Chinese)
[9] 杨磊, 崔龙玉, 唐鑫, 等. 常州城市地质调查报告[R]. 南京: 江苏省地质调查研究院. 2021.
YANG Lei, CUI Longyu, TANG Xin, et al. Report of Changzhou urban geological survey[R]. Nanjing: Geological Survey of Jiangsu Province. 2021.(in Chinese)
[10] 顾春生. 苏锡常地区采水型地裂缝发育演化规律试验研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017
GU Chunsheng. Experimental study on the development and evolution of ground fissures caused by extraction of groundwater in Suzhou-wuxichangzhou region[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 顾晟彦,姚维军,徐明钻,等. 江苏盐城地面沉降风险评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):36 − 43. [GU Shengyan,YAO Weijun,XU Mingzuan,et al. Risk evaluation of land subsidence in Yancheng of Jiangsu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):36 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.01.06
[12] 蔡田露,龚绪龙,卢毅,等. 江苏沿海地区InSAR精度评定与多源数据验证[J]. 遥感技术与应用,2020,35(6):1426 − 1435. [CAI Tianlu,GONG Xulong,LU Yi,et al. Accuracy assessment and multi-source data validation of InSAR in Jiangsu coastal area[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application,2020,35(6):1426 − 1435. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 孔祥如,罗勇,刘贺,等. PS-InSAR技术在北京通州区地面沉降监测中的应用[J]. 城市地质,2021,16(1):25 − 31. [KONG Xiangru,LUO Yong,LIU He,et al. Application of PS-InSAR technology in the land subsidence survey in Tongzhou District,Beijing[J]. Urban Geology,2021,16(1):25 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2021.01.004
[14] 王商富. PS-InSAR技术在福州市建筑物沉降监测中的应用研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,2022,45(1):67 − 70. [WANG Shangfu. Application research of PS-InSAR technology on building subsidence monitoring in Fuzhou[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology,2022,45(1):67 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2022.01.017
[15] 何健辉,张进才,陈勇,等. 基于弱光栅技术的地面沉降自动化监测系统[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):146 − 153. [HE Jianhui,ZHANG Jincai,CHEN Yong,et al. Automatic land subsidence monitoring system based on weak-reflection fiber gratings[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):146 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201912053
[16] 江苏省人民代表大会常务委员会. 江苏省人民代表大会常务委员会关于在苏锡常地区限期禁止开采地下水的决定[J]. 江苏水利,2000(10):9. [The Standing Committee of Jiangsu Provincial People's Congress. Decision of the Standing Committee of Jiangsu Provincial People’s Congress on banning the exploitation of groundwater within a time limit in Suzhou,Wuxi and Changzhou areas[J]. Jiangsu Water Resources,2000(10):9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 许才军, 王华, 黄劲松. GPS与INSAR数据融合研究展望[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2003, 28(增刊1): 58 − 61
XU Caijun, WANG Hua, HUANG Jinsong. Prospect on the integration of GPS and INSAR data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2003, 28(Sup 1): 58 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] GABRIEL A K,GOLDSTEIN R M,ZEBKER H A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas:differential radar interferometry[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,1989,94(B7):9183. doi: 10.1029/JB094iB07p09183
[19] HU Jun,LI Zhiwei,DING Xiaoli,et al. Two-dimensional Co-seismic surface displacements field of the Chi-Chi earthquake inferred from SAR image matching[J]. Sensors (Basel,Switzerland),2008,8(10):6484 − 6495. doi: 10.3390/s8106484
[20] 张艺. 金坛盐矿老腔改建储气库可行性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2011
ZHANG Yi. Research on feasibility of old cavity rebuild to gas storage in Jintan salt mines[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 杨春和,梁卫国,魏东吼,等. 中国盐岩能源地下储存可行性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(24):4409 − 4417. [YANG Chunhe,LIANG Weiguo,WEI Donghou,et al. Investigation on possibility of energy storage in salt rock in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(24):4409 − 4417. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.24.002
[22] 完颜祺琪,冉莉娜,韩冰洁,等. 盐穴地下储气库库址地质评价与建库区优选[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2015,37(1):57 − 64. [WANYAN Qiqi,RAN Lina,HAN Bingjie,et al. Study on site selection and evaluation of underground gas storage in salt cavern[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition),2015,37(1):57 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 丁国生. 金坛盐穴地下储气库建库关键技术综述[J]. 天然气工业,2007,27(3):111 − 113. [DING Guosheng. General introduction on key technologies of the construction of Jintan underground salt cavern gas storage[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2007,27(3):111 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.03.037
[24] 卢毅,施斌,席均,等. 基于BOTDR的地裂缝分布式光纤监测技术研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(1):8 − 13. [LU Yi,SHI Bin,XI Jun,et al. Field study of botdr-based distributed monitoring technology for ground fissures[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(1):8 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.01.002
[25] 余成,葛伟亚,贾军元,等. 苏南地区地质灾害区划评价[J]. 中国地质调查,2019,6(5):131 − 136. [YU Cheng,GE Weiya,JIA Junyuan,et al. Regionalization and assessment of the geological hazard areas in south Jiangsu[J]. Geological Survey of China,2019,6(5):131 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2019.05.15
[26] 龚绪龙,杨蕴,朱锦旗,等. 苏南平原区地裂缝现状及其需要解决的几个问题[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(2):103 − 109. [GONG Xulong,YANG Yun,ZHU Jinqi,et al. Ground fissures in south plain of Jiangsu Province and related issues[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(2):103 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2015.02.18
-



 下载:
下载: