Surface deformation monitoring and analysis of Southwest University of Science and Technology based on time series InSAR
-
摘要:
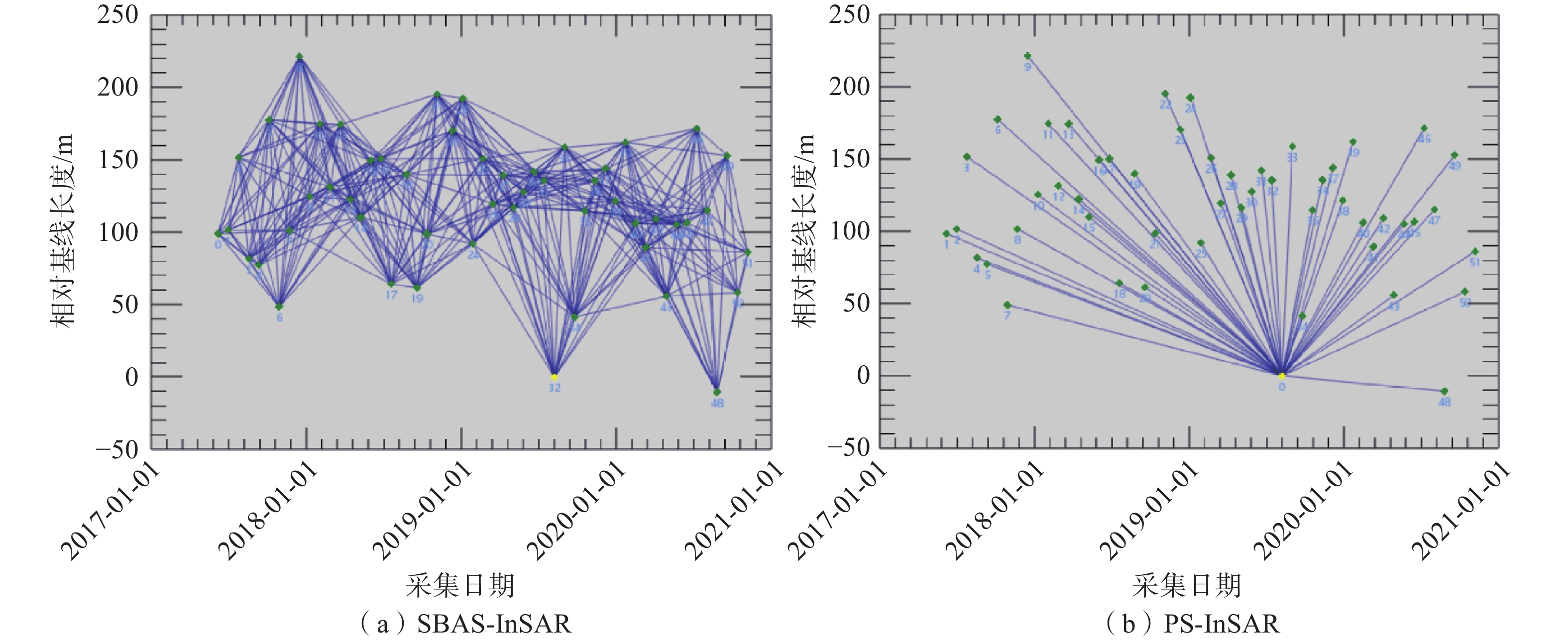
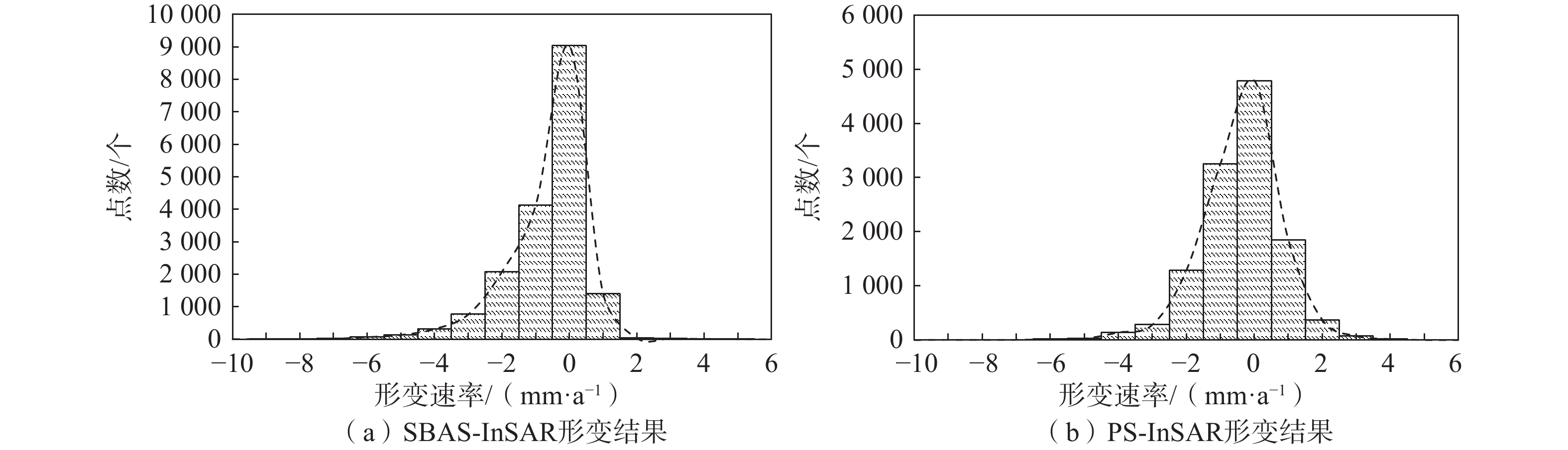
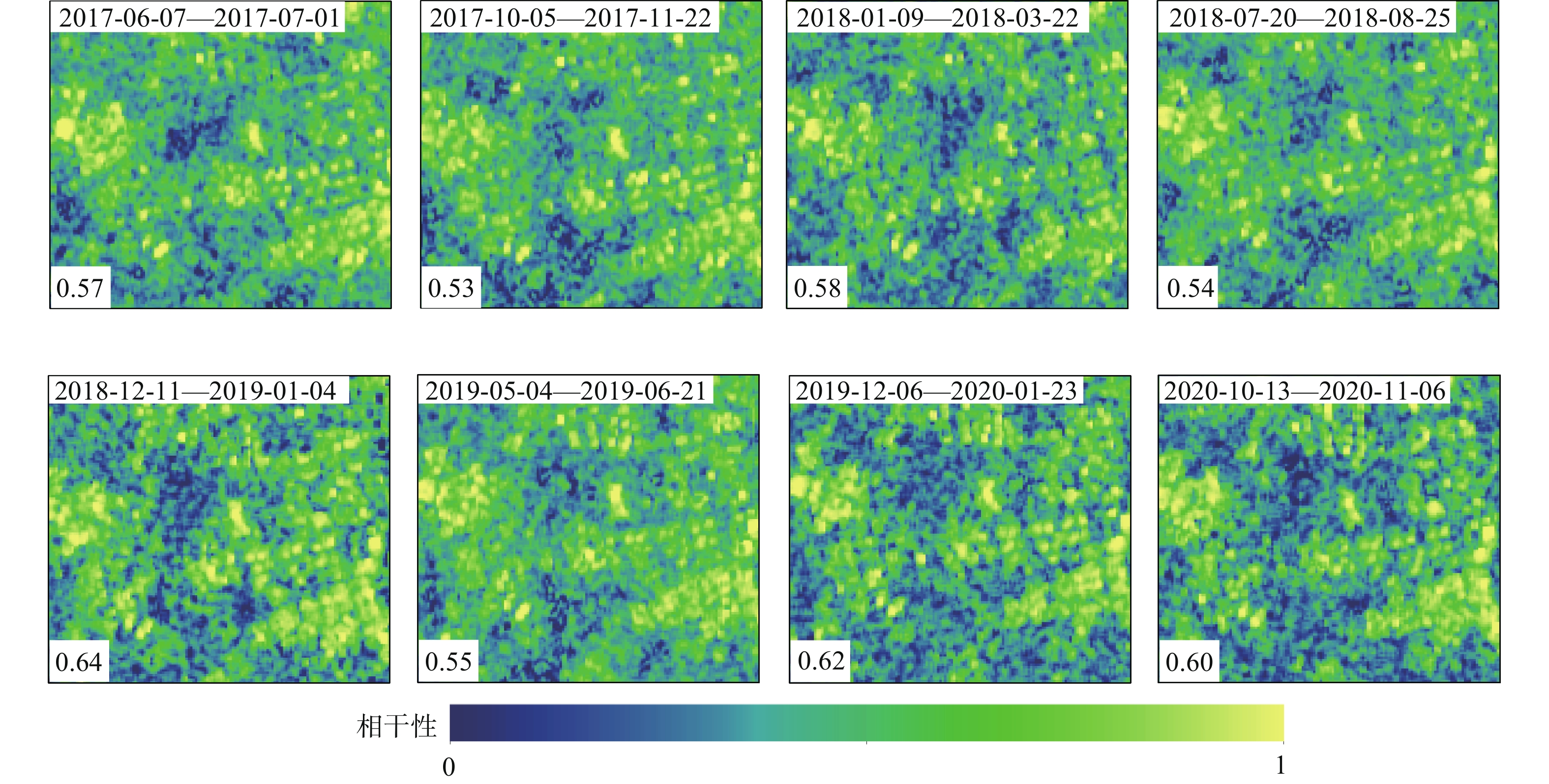
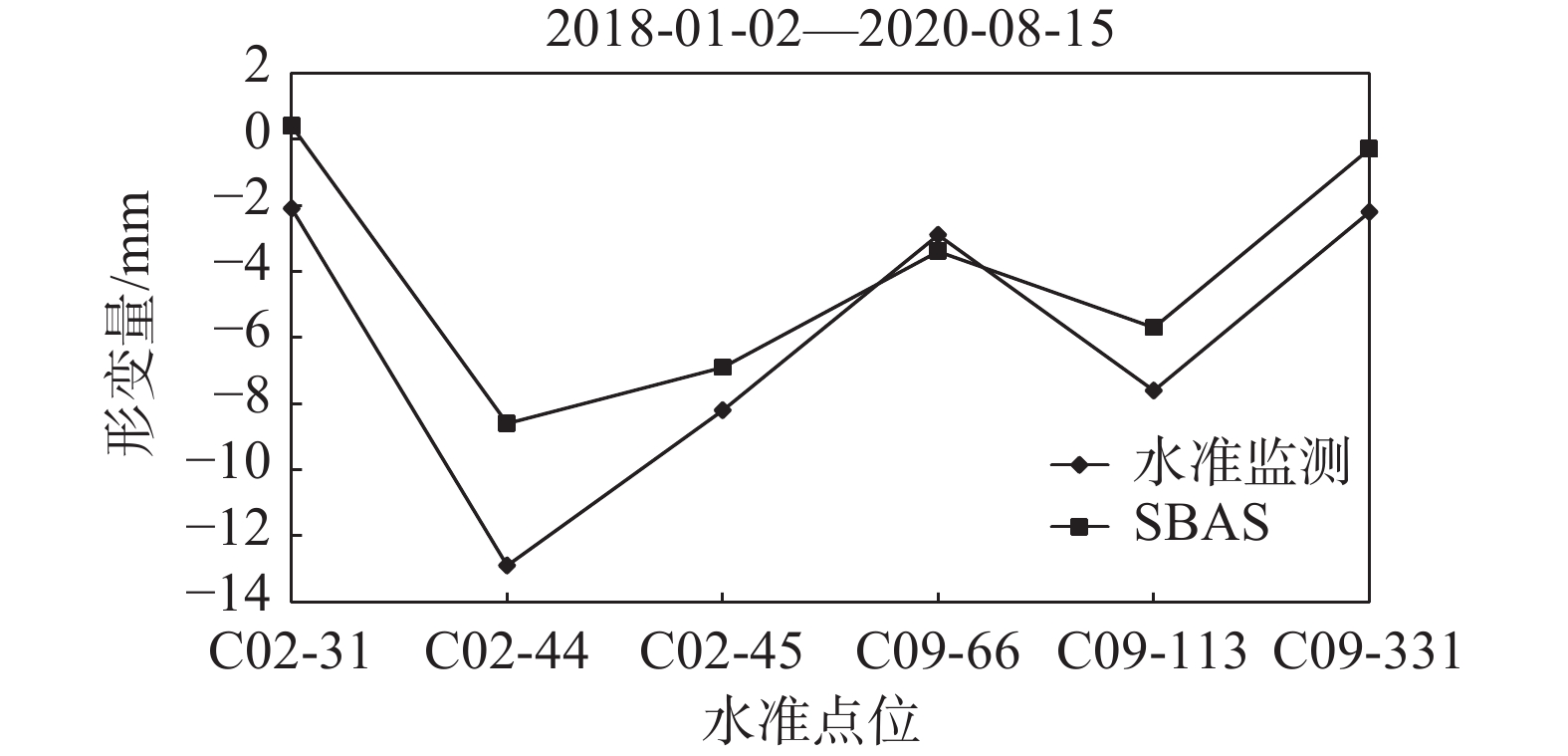
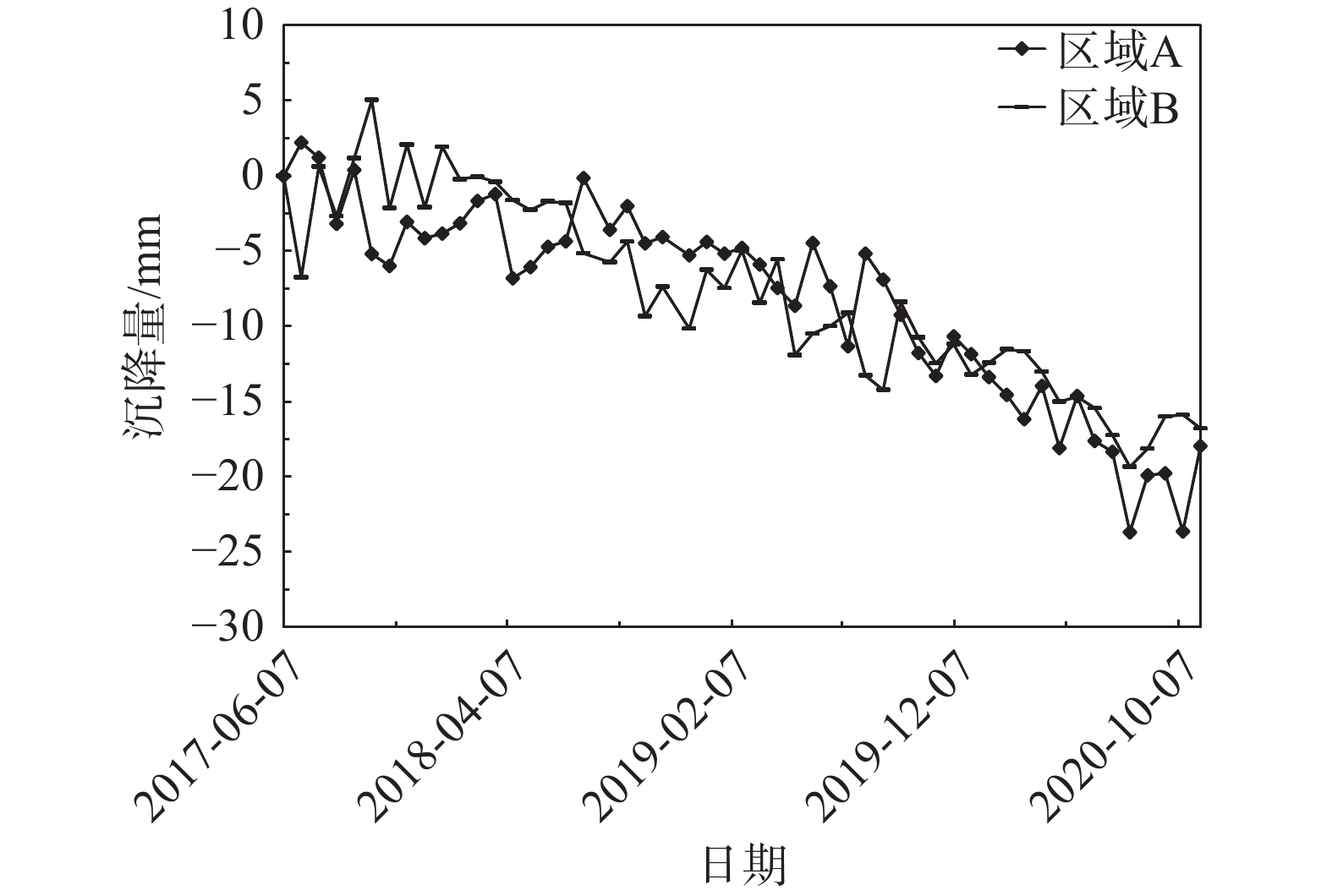
以西南科技大学青义校区为研究区,利用SBAS-InSAR和PS-InSAR对52景升轨Sentinel-1A雷达影像,分别获取了研究区2017年6月至2020年11月的地表形变速率及时序形变量。结合相干性系数、形变速率、方差及标准差对两种时序InSAR结果进行检验对比,从自然、人为因素两方面探讨了研究区地表形变机理与演化过程。结果表明:研究区存在多处显著沉降,最大垂直沉降速率可达15 mm/a,地表形变与学生公寓楼、道路扩建等人为因素有关,地表沉降区与强降雨、岩性及地势地貌关联紧密,地层界线与地表形变不显著相关。相较而言,两种监测结果总体一致性较好,SBAS-InSAR相比PS-InSAR的监测结果稳健性更好。
Abstract:Taking Qingyi campus of Southwest University of Science and Technology as the study area, the surface deformation rate and time sequence variables of the study area from June 2017 to November 2020 were obtained by using SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR on 52 scene ascending Sentinel-1A radar images. Combined with coherence coefficient, deformation rate, variance and standard deviation, the results of two Time Series InSAR are tested and compared, and the mechanism and evolution process of surface deformation in the study area are discussed from two aspects of natural and human factors. The results show that there are many significant settlements in the study area, and the maximum vertical settlement rate can reaches 15 mm/a. The surface deformation is related to the factors such as student apartment buildings and road expansion. The surface settlement area is closely related to heavy rainfall, lithology and topography, and the stratigraphic boundary is not significantly related to the surface deformation. In general, the two monitoring results are generally consistent, and the monitoring results of SBAS-InSAR are more robust than PS-InSAR.
-
Key words:
- time series InSAR /
- campus expansion /
- surface deformation /
- rainfall /
- lithology
-

-
表 1 实验数据参数
Table 1. Parameters of the experimental data
数据名称 参数 值 Sentinel-1A 极化方式 VV 轨道方向 升轨 分辨率/m2 5  20
20入射角/(°) 39 重访周期/d 12 雷达波长/cm 5.63 幅宽/km 250 时间间隔 2017-06-07—2020-11-06 SRTM 空间分辨率/m 30 中国气象数据网 气象站 56196 表 2 形变矢量结果统计
Table 2. Statistics of deformation vector results
时序InSAR 矢量
点数/个平均速率
/(mm·a−1)相干性
系数均值方差 标准差 SBAS-InSAR 18011 0.721 0.608 1.358 1.165 PS-InSAR 12144 0.441 0.583 1.395 1.181 -
[1] 侯安业,张景发,刘斌,等. PS-InSAR与SBAS-InSAR监测地表沉降的比较研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2012,32(4):125 − 128. [HOU Anye,ZHANG Jingfa,LIU Bin,et al. Comparative study on monitoring surface subsidence with PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2012,32(4):125 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2012.04.029
[2] 史绪国,张路,许强,等. 黄土台塬滑坡变形的时序InSAR监测分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):1027 − 1034. [SHI Xuguo,ZHANG Lu,XU Qiang,et al. Monitoring slope displacements of loess terrace using time series InSAR analysis technique[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):1027 − 1034. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] DONG Jie,ZHANG Lu,TANG Minggao,et al. Mapping landslide surface displacements with time series SAR interferometry by combining persistent and distributed scatterers:A case study of Jiaju landslide in Danba,China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2018,205:180 − 198. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.11.022
[4] 张凯翔. 基于“3S”技术的地质灾害监测预警系统在我国应用现状[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):1 − 11. [ZHANG Kaixiang. Review on geological disaster monitoring and early warning system based on “3S” technology in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 潘光永,陶秋香,陈洋,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR的山东济阳矿区沉降监测与分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):100 − 106. [PAN Guangyong,TAO Qiuxiang,CHEN Yang,et al. Monitoring and analysis of sedimentation in Jiyang mining area of Shandong Province based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):100 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.04.13
[6] 李丹,杨斌,陈财. 基于Sentinel-1A数据反演九寨沟地震地表形变场[J]. 遥感技术与应用,2018,33(6):1141 − 1148. [LI Dan,YANG Bin,CHEN Cai. Obtaining coseismic deformation field of Jiuzhai earthquake with sentinel-1A[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application,2018,33(6):1141 − 1148. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李军,褚宏亮,李滨,等. 基于高分影像与InSAR解译的西藏林芝则隆弄高位链式地质灾害发育特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):42 − 50. [LI Jun,CHU Hongliang,LI Bin,et al. Analysis of development characteristics of high-elevationchain geological hazard in Zelongnong,Nyingchi,Xizang based on high resolution image and InSAR interpretation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):42 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 朱建军,李志伟,胡俊. InSAR变形监测方法与研究进展[J]. 测绘学报,2017,46(10):1717 − 1733. [ZHU Jianjun,LI Zhiwei,HU Jun. Research progress and methods of InSAR for deformation monitoring[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2017,46(10):1717 − 1733. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170350
[9] BERARDINO P,FORNARO G,LANARI R,et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375 − 2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
[10] FERRETTI A,PRATI C,ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2001,39(1):8 − 20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661
[11] 赵富萌,张毅,孟兴民,等. 基于小基线集雷达干涉测量的中巴公路盖孜河谷地质灾害早期识别[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):142 − 152. [ZHAO Fumeng,ZHANG Yi,MENG Xingmin,et al. Early identification of geological hazards in the Gaizi Valley near the Karakoran Highway based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):142 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201902020
[12] 潘建平,邓福江,徐正宣,等. 基于轨道精炼控制点精选的极艰险区域时序InSAR地表形变监测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):98 − 104. [PAN Jianping,DENG Fujiang,XU Zhengxuan,et al. Time series InSAR surface deformation monitoring in extremely difficult area based on track refining control points selection[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):98 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.05-12
[13] 张红峰,刘瀛. 基于改进PSInSAR技术的非城区地表形变监测[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2021,41(6):568 − 571. [ZHANG Hongfeng,LIU Ying. Non-urban surface deformation monitoring based on improved PSInSAR[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2021,41(6):568 − 571. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张本浩,魏云杰,杨成生,等. 西藏然乌地区地质灾害隐患点InSAR识别与监测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):18 − 26. [ZHANG Benhao,WEI Yunjie,YANG Chengsheng,et al. InSAR identification and monitoring of geological hazards in Ranwu region of Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):18 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.01-03
[15] 许强,蒲川豪,赵宽耀,等. 延安新区地面沉降时空演化特征时序InSAR监测与分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(7):957 − 969. [XU Qiang,PU Chuanhao,ZHAO Kuanyao,et al. Time series InSAR monitoring and analysis of spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence in Yan’an new district[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(7):957 − 969. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 董廷旭,可华明. 绵阳市涪城区耕地景观格局时空演变特征分析[J]. 西南科技大学学报,2013,28(3):16 − 23. [DONG Tingxu,KE Huaming. The temporal evolution of landscape pattern for cultivated land in hilly area of northwest Sichuan[J]. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology,2013,28(3):16 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8755.2013.03.004
[17] 张路,廖明生,董杰,等. 基于时间序列InSAR分析的西部山区滑坡灾害隐患早期识别—以四川丹巴为例[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2018,43(12):2039 − 2049. [ZHANG Lu,LIAO Mingsheng,DONG Jie,et al. Early detection of landslide hazards in mountainous areas of west China using time series SAR interferometry:A case study of Danba,Sichuan[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2018,43(12):2039 − 2049. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 蒲川豪,许强,赵宽耀,等. 利用小基线集InSAR技术的延安新区地面抬升监测与分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(7):983 − 993. [PU Chuanhao,XU Qiang,ZHAO Kuanyao,et al. Land uplift monitoring and analysis in Yan’an new district based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(7):983 − 993. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 胡波,汪汉胜. 用PSInSAR技术监测地面沉降研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2010,30(2):34 − 39. [HU Bo,WANG Hansheng. Monitoring ground subsidence with permanent scatterers interferometry[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2010,30(2):34 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2010.02.008
[20] 冯文凯,顿佳伟,易小宇,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的金沙江流域沃达村巨型老滑坡形变分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):384 − 393. [FENG Wenkai,DUN Jiawei,YI Xiaoyu,et al. Deformation analysis of Woda Village old landslide in Jinsha River Basin using SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):384 − 393. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-411
[21] 马德云,南锟,宋佳,等. 某超期深基坑对周边建筑物沉降影响的研究[J]. 建筑科学,2014,30(11):112 − 116. [MA Deyun,NAN Kun,SONG Jia,et al. Study on influence of deep foundation pit excavation to adjacent building[J]. Building Science,2014,30(11):112 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13614/j.cnki.11-1962/tu.2014.11.021
[22] 于军,武健强,王晓梅,等. 基于“区域分解”思想的苏锡常地区地面沉降相关预测模型研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2004,31(4):92 − 95. [YU Jun,WU Jianqiang,WANG Xiaomei,et al. Research on the correlative prediction model with a regional decompo-sition base of the land subsidence in the Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou area[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2004,31(4):92 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2004.04.018
-




 下载:
下载: