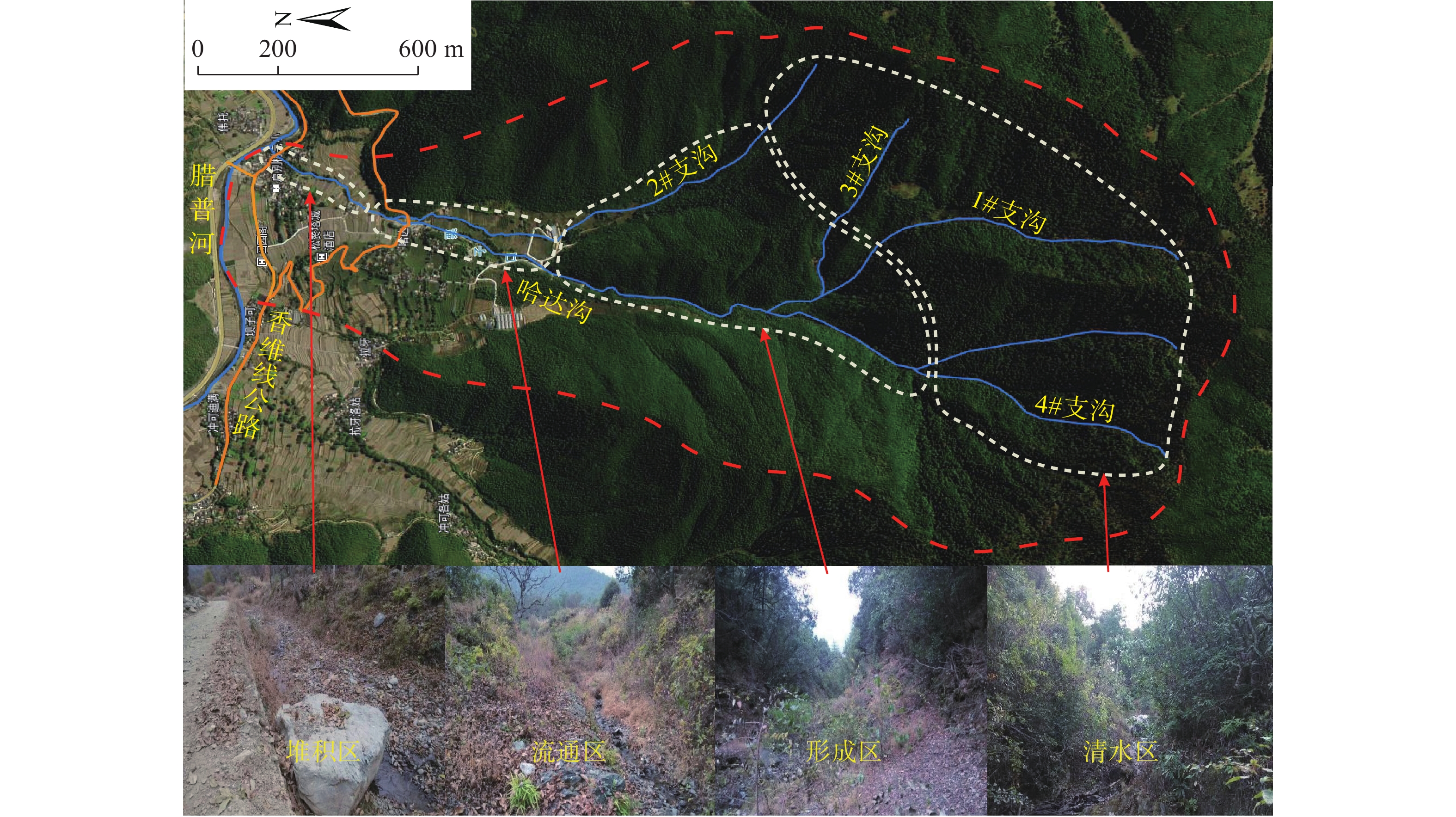
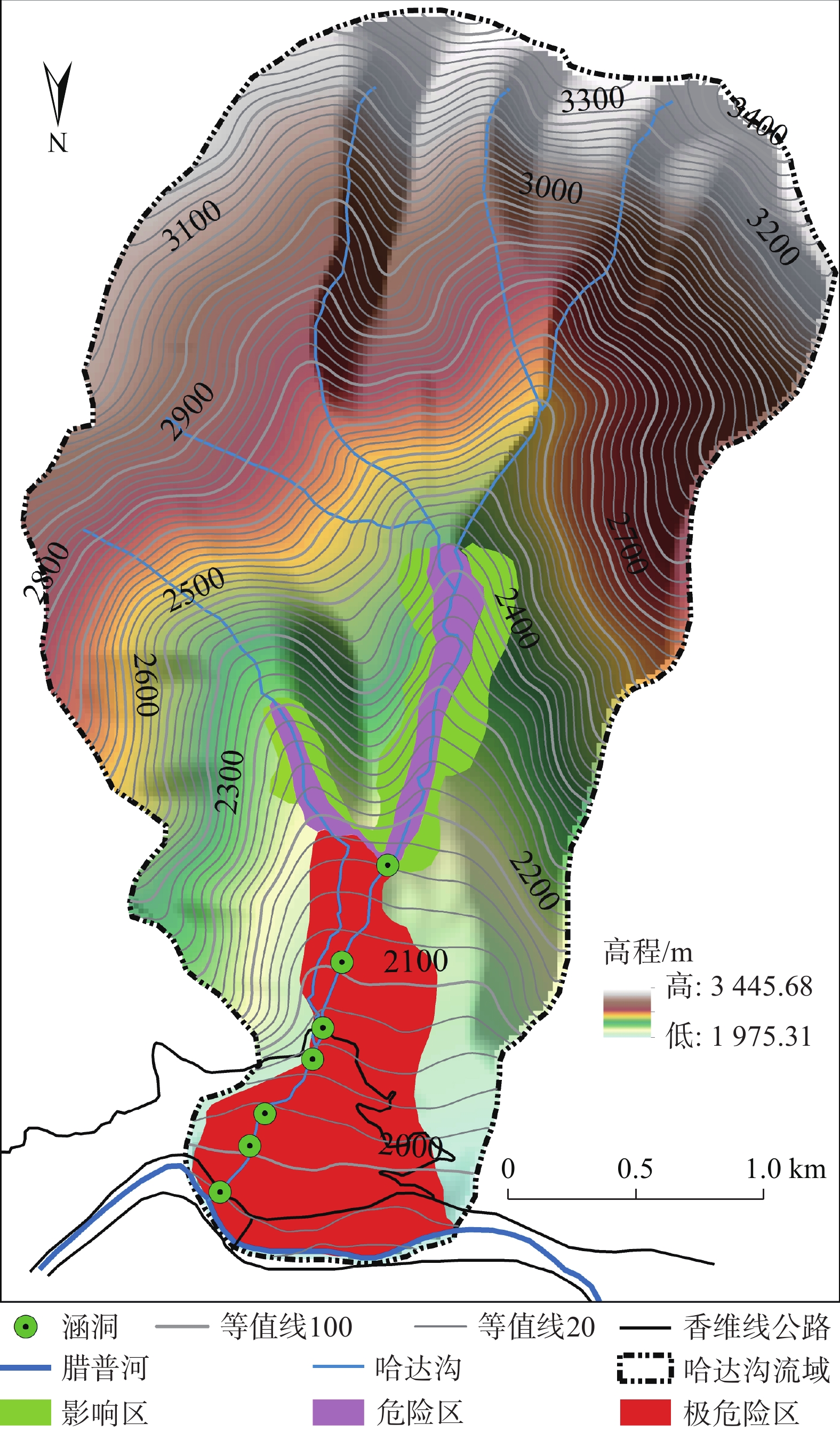
Characteristics of intermediate frequency debris flow and analysis of the hazard of blockage in Hada gully, Weixi County of Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
中频泥石流具有较大危险性和暴发周期较长的特点,人类活动会诱发其发生并加剧其成灾严重程度,当沟道不能满足泄流输水能力时将发生堵溃,危及两岸甚至是主河河道安全。由于目前中频泥石流危险性分析的缺乏,因此以云南省哈达沟中频泥石流为例,探讨其特征和再次发生泥石流及导致沟道堵溃的危险性,并提出防治建议。结果显示:泥石流重度1.62 t/m3,泥石流沟口流速4.794 m/s,基于暴发频率10%情况下的沟口峰值流量为54.43 m3/s以及一次冲出总量为11072.03 m3;在下游沟道处修建有涵洞,其过流量为16.5 m3/s,小于20 a一遇泥石流流量,一旦发生大型泥石流,则有堵溃危险。研究发现哈达沟中频泥石流危险度为高度危险,堵溃历史判断其再次发生沟道堵溃并有泥石流堵塞腊普河的可能性。
Abstract:Intermediate-frequency debris flows has the characteristics of high danger and long outbreak period. Human activities can trigger its occurrence and aggravate its disaster severity. When the channel cannot meet the capacity for drainage and water transport, it will cause blockage and endanger the safety of both sides of the strait and even the main river channel. Due to the lack of analysis on the danger of intermediate-frequency debris flows, this paper takes the intermediate-frequency debris flow in Hada Gully, Yunnan Province as an example to explore its characteristics and the danger of its recurrence and channel blockage caused by debris flows and proposes prevention and control suggestions. The results show that the debris flow has a density of 1.62 t/m3, a flow velocity of 4.794 m/s at the outlet of the channel, a peak flow rate of 54.43 m3/s at the channel outlet and a total discharge of 11072.03 m3 for a single occurrence based on the 10% burst frequency. A culvert was constructed in the downstream channel, with a flow capacity of 16.5 m3/s, which is less than the flow rate of a debris flow once in 20 years. Once a large debris flow occurs, there is a risk of blockage. The study found that the hazard level of intermediate-frequency debris flows in Hada gully is highly dangerous, and the history of blockage indicates the possibility of its recurrence and the risk of debris flow blocking the Lapu River.
-
Key words:
- Hada gully /
- intermediate frequency debris flow /
- hazard analysis /
- blocking
-

-
表 1 哈达沟泥石流物源汇总统计表
Table 1. Summary of source of debris flow in Hada gully
物源类型 坡面侵蚀物源/104 m3 崩塌堆积物源/104 m3 沟床堆积物源/104 m3 合计/104 m3 总量 动储量 总量 动储量 总量 动储量 总量 动储量 数值 306.7 4.73 9.65 3.05 12.5 3.68 328.85 11.46 表 2 不同频率H24值表
Table 2. List of parameters and results of 24-hour rainstorm intensity of different precipitation frequencies in Hada gully
设计暴雨的频率P 倍比
系数KpH24p
/mm备注 100年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=1%) 2.11 116.05 云南省水文
手册查定50年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=2%) 1.92 105.6 30年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=3.33%) 1.79 98.45 20年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=5%) 1.67 91.85 10年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=10%) 1.47 80.85 表 3 哈达沟泥石流流体重度查表法结果统计表
Table 3. List of parameters and results of basic characteristics of the Hada gully debris flow
易发程度
数量化评分易发程度
评价重度
/(t·m−3)平均重度
/(t·m−3)1+φ
(γh=2.65)97 易发 1.669 1.611 1.701 表 4 不同频率下清水洪峰流量计算成果表
Table 4. List of parameters and results of peak flow discharge calculation at different precipitation frequencies in Hada gully
设计暴雨
频率/%流域汇流
时间/h平均1 h降雨强度
/(mm·h−1)最大清水流量
/(m3·s−1)1 2.74 42.97 35.95 2 2.42 39.15 31.75 3.33 2.21 36.34 28.81 5 1.99 34.13 26.36 10 1.66 30.11 22.22 表 5 哈达沟泥石流流速计算表
Table 5. List of flow velocity results at different site location of the Hada gully debris flow
序号 平均泥深
/m泥位纵坡降
/‰流速系数 泥石流流速
/(m·s−1)1(形成区上部) 2.000 461 10 7.857 2(形成区中部) 2.000 416 10 6.633 3(形成区下部) 2.000 387 10 6.538 4(堵塞隐患点7) 2.000 361 10 6.447 5(堵塞隐患点6) 1.800 339 10 6.404 6(堵塞隐患点5) 1.800 332 10 6.340 7(堵塞隐患点4) 1.600 313 10 5.371 8(堵塞隐患点3) 1.600 311 10 5.364 9(堵塞隐患点2) 1.500 306 10 4.901 10(堵塞隐患点1
公路涵洞)1.500 296 10 4.869 11 1.500 285 10 4.832 12(全流域沟口处) 1.200 274 10 4.794 表 6 哈达沟泥石流其他动态参数模型
Table 6. List of dynamic parameter model of the Hada gully debris flow
估算模型 计算的主要参数 设计暴雨频率/% 参数特征值 全沟域不同
频率下泥石流
流量/(m3·s−1)Qc= QB(1+φ)Dc
雨洪修正法[15]QB由表4所得,
φ=(γc−1)/(γh−γc)=0.633;
Dc取1.5,γc取1.62;γh取2.6。1.00 88.06 2.00 77.77 3.33 70.57 5.00 64.57 10.00 54.43 全沟域不同
频率下一次
泥石流总量/m3Q=0.264TQC《泥石流灾害防治工程勘查规范》
(DT/T0220-2006)附录I提供的计算公式[11]T=1800 s 1.00 17906.06 2.00 15818.86 3.33 14478.68 5.00 13132.24 10.00 11072.03 注:表中Qc是泥石流流量。 表 7 泥石流基本特征汇总表
Table 7. Summary of basic characteristics of debris flow
特征项目 基本特征 分类 泥石流发生的地形条件 泥石流的发生、运动和堆积过程,在发育完整的沟谷内进行,可划分为形成水源区、流通区及堆积区 沟谷型泥石流 物质组成 主要为碎石土 泥石型 泥石流流体性质 堆积物松散,断面无明显的分选性;流体呈稀浆状,ρc=1.62 t/m3,固体物质ρH=2.6 t/m3。 黏性泥石流 固体物质提供方式 上部形成水源区主要为沟道堆积物源,中部流通区主要为崩滑堆积物源及沟道堆积物源 滑坡、崩塌 水体供给 雨量充沛,暴雨激发 暴雨泥石流 暴发频率 现场调查,资料统计,历年不同危害程度发生 中频泥石流 灾害严重程度 哈达村50户222人及启别村64户310人的生命财产安全,以及居民耕地多余0.52km2。并且威胁省道S303线香维公路的安全,总计威胁资产约5000万元,直接经济损失可达1000万元,潜在经济损失巨大。 大型 发展阶段 根据物源、坡度、不良地质现象、主河变形情况判定 发展期 成因 自然因素为主,人类活动影响较小 自然泥石流 规模 根据泥石流一次堆积总量 中型 综合分类 暴雨激发、沟谷泥石型、中型、中频发展期黏性泥石流 表 8 下游涵洞泥石流流量计算成果
Table 8. List of parameters and results of sediment flush-out calculation of the Hada gully debris flow in downstream culverts
位置 设计暴雨频率
/%最大清水流量
/(m3·s−1)泥石流流量
/(m3·s−1)沟口涵洞 1 36.71 89.91 2 32.43 79.43 3.33 29.42 72.07 5 26.92 65.94 10 22.70 55.59 表 9 泥石流危险度分级标准
Table 9. Classification standards of hazard level of debris flow
危险等级 轻度危险 中度危险 高度危险 极度危险 判别标准 0~0.35 0.35~0.6 0.6~0.85 0.85~1 表 10 泥石流危险因子等级划分
Table 10. Classification of hazard factors of debris flow
评价因子 数值 等级 危险系数 0 0.4 0.7 1 泥石流规模y1/104 m3 2.48 ≤1 (1,10) [10,100) ≥100 0.4 松散物源量y2/104 m3 328.85 ≤10 (10,100) [100,200) ≥200 1 24 h最大降雨量y3/mm 80.85 ≤25 (25,50) [50,100) ≥100 0.7 泥石流发生频率y4/% 10 10 5 2 1 0 沟谷流域面积y5/km2 8.79 ≤0.5 (0.5,10) [10,35) ≥35 0.4 主沟长度y6/km 5.02 ≤1 (1,5) [5,10) ≥10 0.7 流域相对高差y7/km 1.46 ≤1 (1,1.5) [1.5,2) ≥2 0.4 不稳定沟床比降y8 0.461 ≤0.1 (0.1,0.3) [0.3,0.6) ≥0.6 0.7 表 11 矩阵权重计算结果
Table 11. Summary of matrix weight calculation results of the Hada Gully debris flow
y1 y2 y3 y4 y5 y6 y7 y8 权重 y1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 0.3698 y2 1/2 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 0.1849 y3 1/3 1/2 1 2 3 4 5 7 0.1233 y4 1/4 1/3 1/2 1 2 3 4 6 0.0925 y5 1/5 1/4 1/3 1/2 1 2 3 5 0.0740 y6 1/6 1/5 1/4 1/3 1/2 1 2 4 0.0616 y7 1/7 1/6 1/5 1/4 1/3 1/4 1 3 0.0528 y8 1/9 1/8 1/7 1/6 1/5 1/2 1/3 1 0.0411 表 12 哈达沟泥石流危险分区评述
Table 12. Description of hazard zones for Hada gully debris flow
危险等级 区域范围 极危险区 哈达沟中下游段至沟口腊普河河边区域,主要为历史最高泥位线以下地区,面积约0.85 km2 危险区 河沟两岸崩塌、滑坡后缘裂隙以上50~100 m的范围,面积约0.19 km2 影响区 高于危险区与危险区相邻的地区,它不会直接与泥石流遭遇,但却有可能间接受到泥石流危害的
牵连而发生某些级别的灾害的地区,面积约0.27 km2 -
[1] 韩全芳,骆华松,韩吉全. 基于人地关系的地质灾害探讨—以三江并流带兰坪县为例[J]. 云南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2005,25(1):55 − 59. [HAN Quanfang,LUO Huasong,HAN Jiquan. On study of the geological hazards based on human-land relationship:Lanpin County in three rivers as an example[J]. Journal of Yunnan Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition),2005,25(1):55 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9793.2005.01.015
[2] 王欢,丁明涛,陈廷方. 基于GIS的三江并流区泥石流危险性评价[J]. 水土保持通报,2011,31(5):167 − 170. [WANG Huan,DING Mingtao,CHEN Tingfang. GIS-based risk assessment of debris flows in three-parallel-river area[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2011,31(5):167 − 170. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2011.05.016
[3] 高云建,陈宁生,田树峰,等. 基于堆积物石块磨圆度的泥石流暴发频率判识[J]. 水土保持研究,2018,25(4):370 − 374. [GAO Yunjian,CHEN Ningsheng,TIAN Shufeng,et al. Frequency identification of debris flow outbreak based on roundness of debris flow cumulative stones[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,25(4):370 − 374. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2018.04.054
[4] 钟政,胡桂胜,杨溢,等. 九龙县踏卡河流域乌拉溪沟低频泥石流特征与危险性[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,48(1):111 − 120. [ZHONG Zheng,HU Guisheng,YANG Yi,et al. Characteristics of low frequency debris flow and its risk analysis in Wulaxi Gully of Taka River Basin,Jiulong County,Sichuan,China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2021,48(1):111 − 120. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2021.01.12
[5] 曲瑞,李仲先,何政伟,等. 甘肃天水大沟短时强降水诱发低频泥石流特征及成因[J]. 山地学报,2018,36(3):488 − 495. [QU Rui,LI Zhongxian,HE Zhengwei,et al. Characteristics and causes of low frequency debris flow induced by heavy rainfall in Dagou Village,Tianshui city,Gansu Province,China[J]. Mountain Research,2018,36(3):488 − 495. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 韩林. 泥石流暴发频率与其形成区颗粒粒径的关系研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2010
HAN Lin. Study the relationship between frequency of debris flows and the particles size in channels of debris flows[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 刘忠敏. 云南省维西县哈达沟泥石流形成条件及动力学参数取值研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018
LIU Zhongmin. Study on formation conditions and dynamic parameters of hadagou debris flow in Weixi County, Yunnan Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 艾绍周,艾琦森. 小流域典型暴雨实测洪水对榆林水文手册中计算方法的验证[J]. 山西水土保持科技,2014(2):16 − 18. [AI Shaozhou,AI Qisen. Verification of calculation method in Yulin Hydrological Manual by measured flood of typical rainstorm in small watershed[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi,2014(2):16 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0120.2014.02.006
[9] 陈志,杨志全,刘传秋. 云南省麻栗坡县猛硐河“9·02”泥石流调查[J]. 山地学报,2019,37(4):631 − 638. [CHEN Zhi,YANG Zhiquan,LIU Chuanqiu. Investigation of the “9·02” debris flows in Mengdong River,Malipo County,Yunnan,China[J]. Mountain Research,2019,37(4):631 − 638. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000454
[10] 刘丹. 泥石流运动特征参数计算[J]. 四川建材,2017,43(5):82 − 84. [LIU Dan. Calculation of characteristic parameters of debris flow movement[J]. Sichuan Building Materials,2017,43(5):82 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4011.2017.05.0041
[11] 四川省国土资源厅. 泥石流灾害防治工程勘查规范: DZT 0220-2006[S]. 2006 [Sichuan Provincial Department of Land and Resources. Engineering exploration specification for debris flow disaster prevention and control: DZT 0220-2006
S]. 2006. [Sichuan Provincial Department of Land and Resources. Engineering exploration specification for debris flow disaster prevention and control: DZT 0220-2006 [S]. 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 胡林,肖进,罗绍强,等. 西藏拉萨市城关区格布沟泥石流特征及成灾机理研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2021,32(2):27 − 32. [HU Lin,XIAO Jin,LUO Shaoqiang,et al. Characteristics and study on disaster mechanism of gebugou debris flow in Chengguan district,Xizangautonomous region[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2021,32(2):27 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2021.02.005
[13] 高士麟. 四川省小流域设计洪水分析及应用[J]. 四川建筑,2021,41(5):230 − 233. [GAO Shilin. Analysis and application of design flood in small watershed of Sichuan Province[J]. Sichuan Architecture,2021,41(5):230 − 233. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8983.2021.05.075
[14] 田树峰,陈宁生,高云建,等. 九绵高速平武段泥石流运动参数特征与工程危害[J]. 人民长江,2018,49(11):64 − 70. [TIAN Shufeng,CHEN Ningsheng,GAO Yunjian,et al. Characteristics of dynamic parameters and engineering hazard of debris flows in Ping-Wu section of Jiu-Mian highway[J]. Yangtze River,2018,49(11):64 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2018.11.013
[15] 冯磊,冯婷洁,薛会师. 黄河茨哈峡桑吉沟泥石流灾害特征及防治措施研究[J]. 资源环境与工程,2021,35(1):76 − 80. [FENG Lei,FENG Tingjie,XUE Huishi. Study on the disaster characteristics and prevention measures of Sangjigou debris flow in Tshaxia of Yellow River[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2021,35(1):76 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16536/j.cnki.issn.1671-1211.2021.01.015
[16] 侯兰功,崔鹏. 单沟泥石流灾害危险性评价研究[J]. 水土保持研究,2004,11(2):125 − 128. [HOU Langong,CUI Peng. The study on assessment of debris flow hazards in the solo channel[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2004,11(2):125 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2004.02.040
[17] 刘希林. 区域泥石流风险评价研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2000,9(1):54 − 61. [LIU Xilin. Regional risk assessment on debris flow[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2000,9(1):54 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2000.01.009
[18] 杨志全,张焜,杨溢,等. 汶川县麻柳沟泥石流动力学特征及危险性评价[J]. 地质科技情报,2016,35(5):214 − 220. [YANG Zhiquan,ZHANG Kun,YANG Yi,et al. Dynamic characteristics and hazard assessment of debris flows in Maliu gully,Wenchuan County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2016,35(5):214 − 220. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 崔志超,王俊豪,崔传峰,等. 基于层次分析法和模糊数学相结合的甘肃东乡八丹沟泥石流易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):44 − 50. [CUI Zhichao,WANG Junhao,CUI Chuanfeng,et al. Evaluation of the susceptibility of debris flow in Badan Gully of Dongxiang County of Gansu based on AHP and Fuzzy mathematics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):44 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.01.07
[20] 李彩侠,马煜,何元勋. 泥石流致灾因子敏感性分析—以四川都江堰龙溪河流域为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):32 − 39. [LI Caixia,MA Yu,HE Yuanxun. Sensitivity analysis of debris flow to environmental factors:A case of Longxi River Basin in Dujiangyan,Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):32 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王长宝,郭凤双. 层次分析法模型下的王家沟泥石流危险性评价[J]. 四川建材,2020,46(8):57 − 59. [WANG Changbao,GUO Fengshuang. Evaluation of Wangjiagou debris flow risk and catastrophe theory model under AHP[J]. Sichuan Building Materials,2020,46(8):57 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 侯圣山,曹鹏,陈亮,等. 基于数值模拟的耳阳河流域泥石流灾害危险性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):143 − 151. [HOU Shengshan,CAO Peng,CHEN Liang,et al. Debris flow hazard assessment of the Eryang River watershed based on numerical simulation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):143 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: