Hazard assessment of shallow loess landslides induced by rainfall:A case study of Liulin County of Shanxi Province
-
摘要:
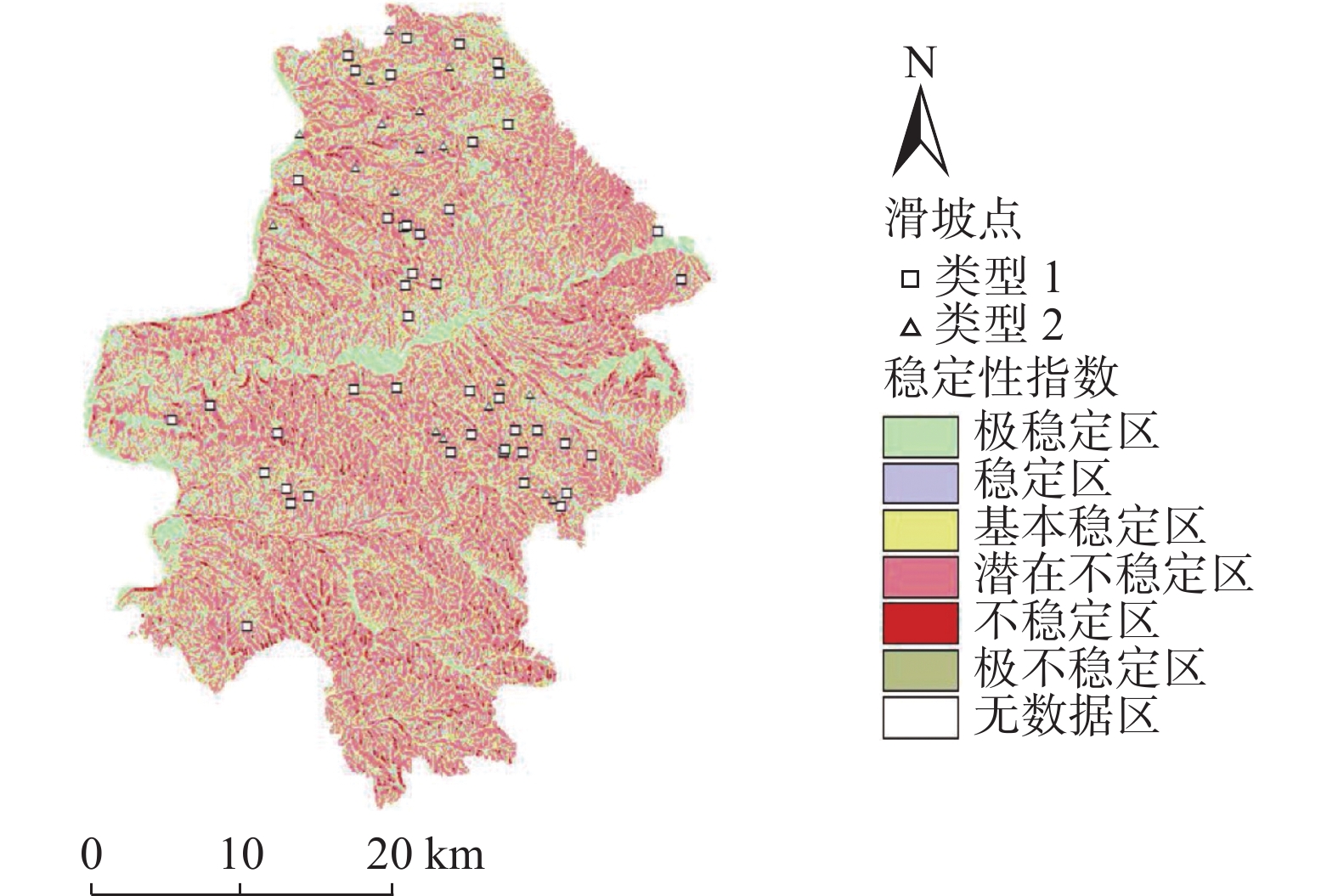
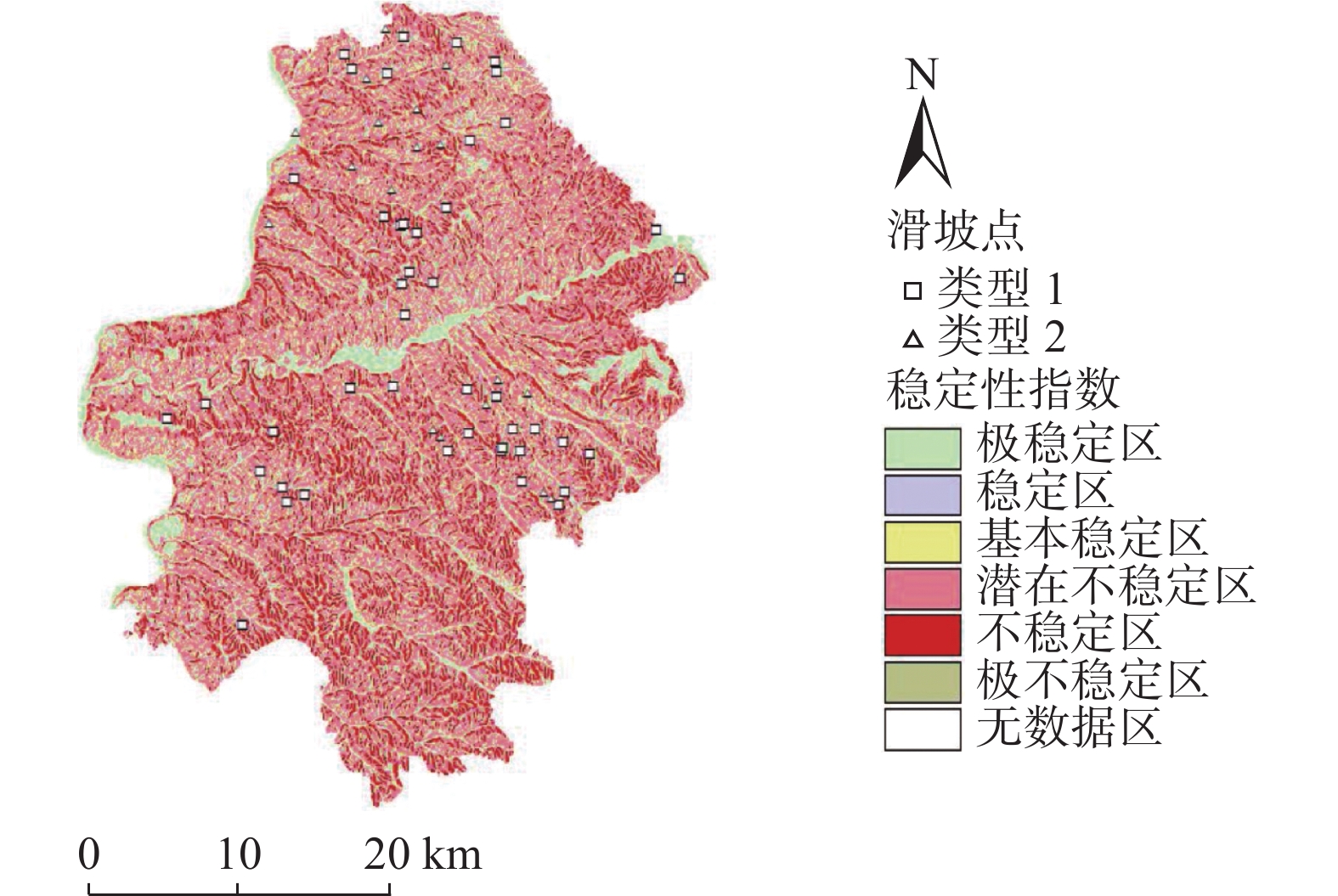
黄土高原是我国地质灾害最为发育的地区之一,其中降雨诱发的浅层黄土滑坡又最为典型。以典型黄土地貌区-柳林县为例,应用SINMAP模型,探讨模型在黄土地区的适用性,分析了随着研究区内降雨量的增加,滑坡变形失稳区域的面积变化、分布位置和扩展趋势。研究表明,随着降雨量的增加,滑坡所处位置逐渐由稳定状态向失稳状态发展,位于失稳分区的滑坡数量逐渐增加,说明降雨对该研究区的斜坡稳定性影响较为明显。通过将模拟结果与实际发生的由降雨触发的滑坡灾害进行对比分析,可以得出SINMAP模型在黄土地区,对区域性降雨诱发浅层黄土滑坡稳定性的模拟预测有效,可以用于黄土地区浅层滑坡的稳定性评价研究。
Abstract:Loess Plateau is one of the most developed areas of geological disasters in China, and the shallow loess landslide induced by rainfall is the most typical. Taking Liulin County, a typical loess landform area, as an example. With the increase of rainfall in the study area, the area change, distribution location and expansion trend of the landslide deformation instability area are analyzed. The research shows that with the increase of rainfall, the location of landslides gradually develops from a stable state to an unstable state, and the number of landslides in the unstable zone gradually increases, indicating that rainfall has a significant impact on the slope stability of the study area. By comparing the simulation results with the actual rainfall-triggered landslide disasters. It can be concluded that the SINMAP model is effective in simulating and predicting the regional stability of shallow loess landslide induced by rainfall in the loess region, as well as can be used in the stability assessment of shallow landslide in the loess region.
-
Key words:
- rainfall /
- shallow loess landslides /
- stability /
- SINMAP model
-

-
图 1 山西省柳林县地貌分区图[34]
Figure 1.
表 1 模型选取的参数值
Table 1. Parameter values selected by the model
重力加速度/(m·s−2) 湿度/% 内聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 土体密度/(kg·m−3) 土体的导水系数/(m2·d−1) 下限 上限 下限 上限 9.81 10 3 15 15 24 1540 135 表 2 稳定性分类定义
Table 2. Stability classification definition
序号 条件 类 预测状态 未建模因素的可能影响 1 SI>1.5 1 极稳定 不稳定需要巨大的不稳定因素 2 1.5≥SI>1.25 2 稳定 不稳定需要适度的不稳定因素 3 1.25≥SI>1.0 3 基本稳定 较小的不稳定因素可能导致不稳定 4 1.0≥SI>0.5 4 潜在不稳定 不稳定不需要不稳定因素 5 0.5≥ SI>0 5 不稳定 稳定因素可能是稳定的原因 6 SI=0 6 极不稳定 稳定需要稳定因素 -
[1] 梁四宝. 明清晋陕黄土高原的水土流失与水土保持[J]. 中国水土保持,1990(6):50 − 52. [LIANG Sibao. Soil erosion and water and soil conservation in the loess plateau of Shanxi and Shaanxi in the Ming and Qing Dynasties[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China,1990(6):50 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 彭建兵, 林鸿州, 王启耀, 等. 黄土地质灾害研究中的关键问题与创新思路[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(4):684 − 691. [PENG Jianbing, LIN Hongzhou, WANG Qiyao, et al. The critical issues and creative concepts in mitigation research of loess geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(4):684 − 691. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] TANG Y M, XUE Q, LI Z G, et al. Three modes of rainfall infiltration inducing loess landslide[J]. Natural Hazards,2015,79(1):137 − 150. doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-1833-4
[4] 巨玉文, 齐琼, 董震, 等. 山西西部地区黄土地质灾害与降雨的关联性分析[J]. 自然灾害学报,2016,25(1):81 − 87. [JU Yuwen, QI Qiong, DONG Zhen, et al. Analysis of relevance between loess geological disasters and rainfalls in the western area of Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2016,25(1):81 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] LI Z, ZHENG F L, LIU W Z, et al. Spatially downscaling GCMs outputs to project changes in extreme precipitation and temperature events on the loess plateau of China during the 21st Century[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2012,82/83:65 − 73. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2011.11.008
[6] WANG G L, LI T L, XING X L, et al. Research on loess flow-slides induced by rainfall in July 2013 in Yan’an, NW China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2015,73(12):7933 − 7944. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3951-9
[7] 唐亚明, 薛强, 李政国, 等. 基于单体和区域尺度的黄土滑坡监测预警方法与实例[J]. 灾害学,2015,30(4):91 − 95. [TANG Yaming, XUE Qiang, LI Zhengguo, et al. Loess landslide monitoring and early-warning methods and practices on scale of single slope and regional scope[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2015,30(4):91 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2015.04.018
[8] 吴赛男, 田毅. 我国单体滑坡模拟和区域滑坡易发性评价研究进展[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(3):113 − 119. [WU Sainan, TIAN Yi. Review on progress of individual landslide simulation and assessment of reginal landslide susceptibility in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(3):113 − 119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 姜彤, 马莎, 李永新. 抗剪强度c, φ值概率分布对边坡可靠性分析的影响[J]. 华北水利水电学院学报,2004,25(3):46 − 49. [JIANG Tong, MA Sha, LI Yongxin. The study of effect on the reliability of rock slope by different probability distribution of shear strength c, φ[J]. Journal of North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power,2004,25(3):46 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 曾亚武, 田伟明. 边坡稳定性分析的有限元法与极限平衡法的结合[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(增刊 2):5355 − 5359. [ZENG Yawu, TIAN Weiming. Slope stability analysis by combining fem with limit equilibrium method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(Sup 2):5355 − 5359. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 郭子仪, 范振华, 朱云升, 等. 边坡稳定性分析中的有限元极限平衡法[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版),2014,38(1):79 − 84. [GUO Ziyi, FAN Zhenhua, ZHU Yunsheng, et al. Finite element and limit equilibrium method applied on the stability analysis of road slope[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Engineering),2014,38(1):79 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 崔志杰. 灌溉条件下黄土阶地斜坡区域稳定性评价: 以黑台为例[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017
CUI Zhijie. Slope stability assessment of irrigated loess terraces—A case study at heitai, Gansu Province, China[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 张永波. 斜坡稳定性分析的模糊综合评判方法[J]. 太原工业大学学报,1996,27(1):59 − 63. [ZHANG Yongbo. Fuzzy mathematics method of the analysis of slope stability[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology,1996,27(1):59 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王亚强, 王兰民, 张小曳. GIS支持下的黄土高原地震滑坡区划研究[J]. 地理科学,2004,24(2):170 − 176. [WANG Yaqiang, WANG Lanmin, ZHANG Xiaoye. GIS based seismic landslide zonation of the loess plateau[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2004,24(2):170 − 176. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2004.02.007
[15] 唐亚明, 程秀娟, 薛强, 等. 基于层次分析法的黄土滑塌风险评价指标权重分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2012,23(4):40 − 46. [TANG Yaming, CHENG Xiujuan, XUE Qiang, et al. Weights analysis of loess collapse risk assessing factors based on analytical hierarchy process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2012,23(4):40 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 戴悦. 基于信息量模型的三峡库区滑坡区域危险性评价方法研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2013
DAI Yue. Study on the method of regional early warning of landslide in Three Gorges area based on information model[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 殷坤龙, 朱良峰. 滑坡灾害空间区划及GIS应用研究[J]. 地学前缘,2001,8(2):279 − 284. [YIN Kunlong, ZHU Liangfeng. Landslide hazard zonation and application of gis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2001,8(2):279 − 284. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.02.010
[18] 戴福初, 姚鑫, 谭国焕. 滑坡灾害空间预测支持向量机模型及其应用[J]. 地学前缘,2007,14(6):153 − 159. [DAI Fuchu, YAO Xin, TAN Guohuan. Landslide susceptibility mapping using support vector machines[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2007,14(6):153 − 159. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.06.019
[19] 许冲, 徐锡伟. 基于不同核函数的2010年玉树地震滑坡空间预测模型研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2012,55(9):2994 − 3005. [XU Chong, XU Xiwei. The 2010 Yushu earthquake triggered landslides spatial prediction models based on several kernel function types[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2012,55(9):2994 − 3005. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.09.018
[20] DAI F C, LEE C F. Landslide characteristics and slope instability modeling using GIS, Lantau Island, Hong Kong[J]. Geomorphology,2002,42(3/4):213 − 228.
[21] 方然可, 刘艳辉, 苏永超, 等. 基于逻辑回归的四川青川县区域滑坡灾害预警模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):181 − 187. [FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, SU Yongchao, et al. A early warning model of regional landslide in Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province based on logistic regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):181 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] BISWAJEET P, SARO L. Utilization of optical remote sensing data and GIS tools for regional landslide hazard analysis using an artificial neural network model[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2007,14(6):143 − 151. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60008-1
[23] 杨华阳, 许向宁, 杨鸿发. 基于证据权法的九寨沟地震滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):20 − 29. [YANG Huayang, XU Xiangning, YANG Hongfa. The Jiuzhaigou co-seismic landslide hazard assessment based on weight of evidence method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):20 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] SIFA S F, MAHMUD T, TARIN M A, et al. Event-based landslide susceptibility mapping using weights of evidence (WoE) and modified frequency ratio (MFR) model: A case study of Rangamati district in Bangladesh[J]. Geology, Ecology, and Landscapes,2020,4(3):222 − 235. doi: 10.1080/24749508.2019.1619222
[25] TANG Y M, FENG F, GUO Z Z, et al. Integrating principal component analysis with statistically-based models for analysis of causal factors and landslide susceptibility mapping: a comparative study from the loess plateau area in Shanxi (China)[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,277:124159. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124159
[26] 康超. 确定性模型在黄土沟壑区斜坡稳定性预测中的应用[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2010
KANG Chao. Application of deterministic model in analysis and prediction of stability in loess gully area[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] MICHEL G P, KOBIYAMA M, GOERL R F. Comparative analysis of SHALSTAB and SINMAP for landslide susceptibility mapping in the Cunha River Basin, southern Brazil[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2014,14(7):1266 − 1277. doi: 10.1007/s11368-014-0886-4
[28] 武利. 基于SINMAP模型的区域滑坡危险性定量评估及模型验证[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2012,28(2):35 − 39. [WU Li. A SINMAP-based quantitative assessment and model verification of regional landslide hazard[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science,2012,28(2):35 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 庄建琦, 彭建兵, 张利勇. 不同降雨条件下黄土高原浅层滑坡危险性预测评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2013,43(3):867 − 876. [ZHUANG Jianqi, PENG Jianbing, ZHANG Liyong. Risk assessment and prediction of the shallow landslide at different precipitation in loess plateau[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2013,43(3):867 − 876. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] KIM D, IM S, LEE S H, et al. Predicting the rainfall-triggered landslides in a forested mountain region using TRIGRS model[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2010,7(1):83 − 91. doi: 10.1007/s11629-010-1072-9
[31] 夏蒙, 王家鼎, 谷天峰, 等. 基于TRIGRS模型的浅层黄土滑坡破坏概率评价[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2013,49(4):453 − 458. [XIA Meng, WANG Jiading, GU Tianfeng, et al. Evaluation of shallow loess landslide destruction probability based on TRIGRS model[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2013,49(4):453 − 458. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 刘磊, 殷坤龙, 徐勇, 等. 考虑降雨及库水位变动的区域滑坡灾害稳定性评价研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(2):403 − 414. [LIU Lei, YIN Kunlong, XU Yong, et al. Evaluation of regional landslide stability considering rainfall and variation of water level of reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(2):403 − 414. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 文杰. 基于SCOOPS3D和TRIGRS模型的区域性降雨滑坡危险性评价: 以陇南武都区典型地段为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019
WEN Jie. Regional rainfall landslide hazard assessment based on SCOOPS3D and TRIGRS models—A case study in typical areas in wudu district of south Gansu Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 李鹏强. 火电厂地下水污染溶质运移数值模拟研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2012
LI Pengqiang. Numerical simulation study of solute transportion during groundwater polluted in thermal power plant[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] PACK R T, TARBOTON D G, GOODWIN C N. The SINMAP approach to terrain stability mapping. In: MOORE D, HUNGER O, eds. Proceedings of 8th congress of the International Association of Engineering Geology. Netherlands: A Balkema Publisher, 1998. 1157-1165.
[36] 兰恒星, 周成虎, 伍法权, 等. GIS支持下的降雨型滑坡危险性空间分析预测[J]. 科学通报,2003(5):507 − 512. [LAN Hengxin, ZHOU Chenghu, WU Faquan, et al. Spatial analysis and prediction of the risk of rainfall-type landslides supported by GIS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2003(5):507 − 512. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.05.021
[37] 赵敦江, 任六平, 卫中平. 吕梁地区暴雨规律分析[J]. 山西水土保持科技,2001,3:6 − 8. [ZHAO Dunjiang,REN Liuping,WEI Zhongping. Analysis on the law of rainstorm in Luliang area[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi,2001,3:6 − 8. (in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: