Debris flow risk assessment considering different rainfall sensitivity: A case study in southeast Xizang
-
摘要:
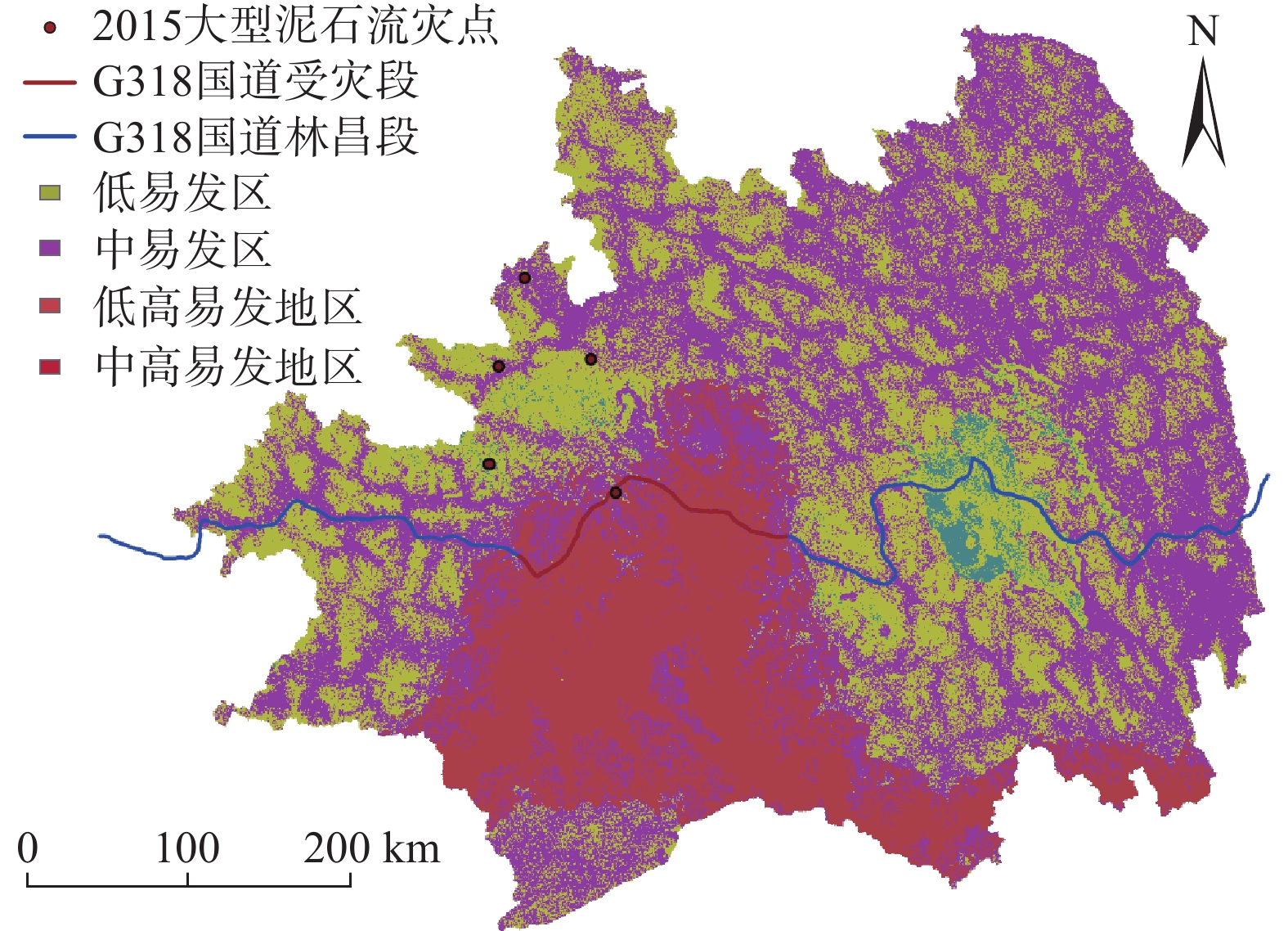
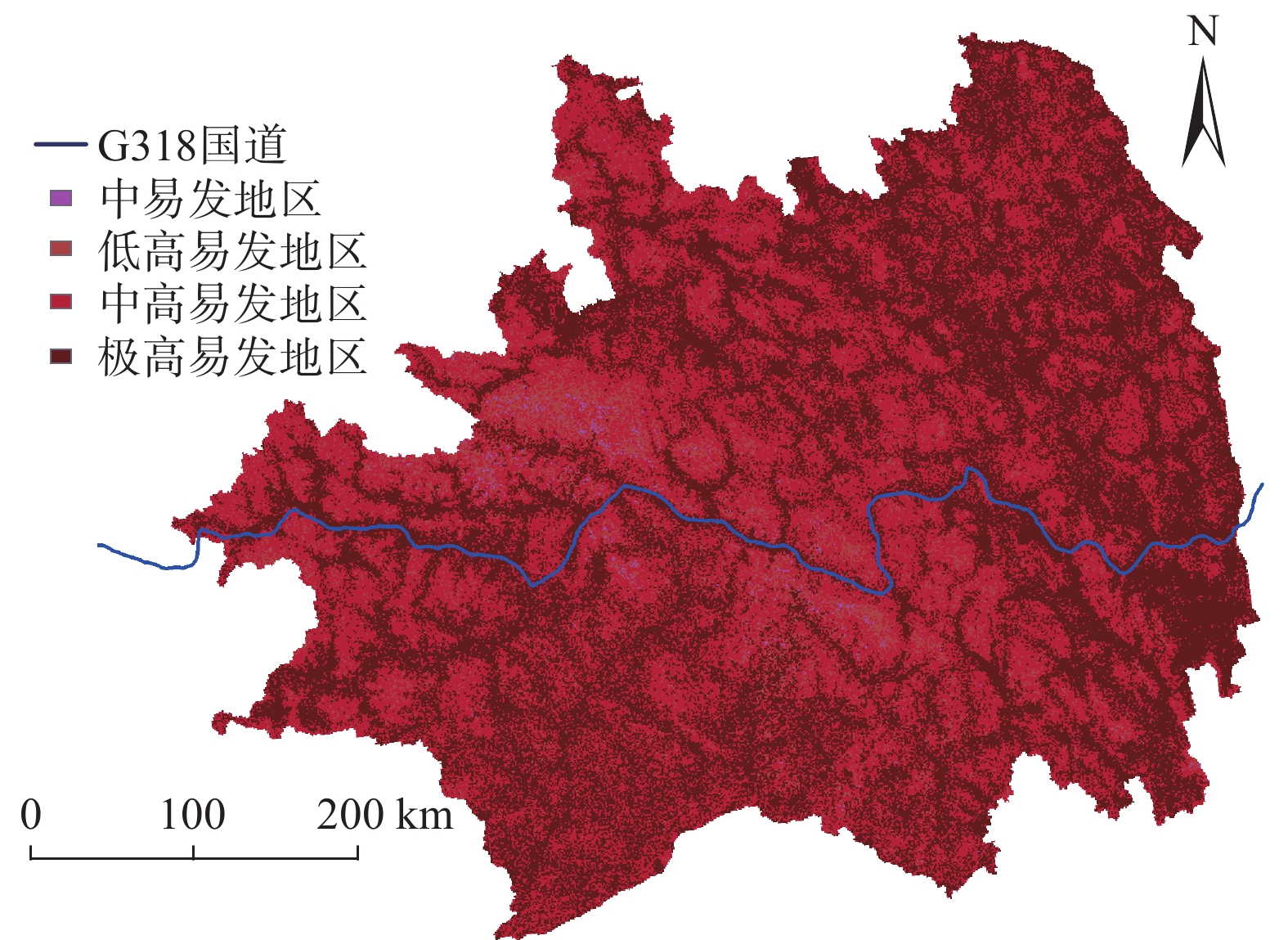
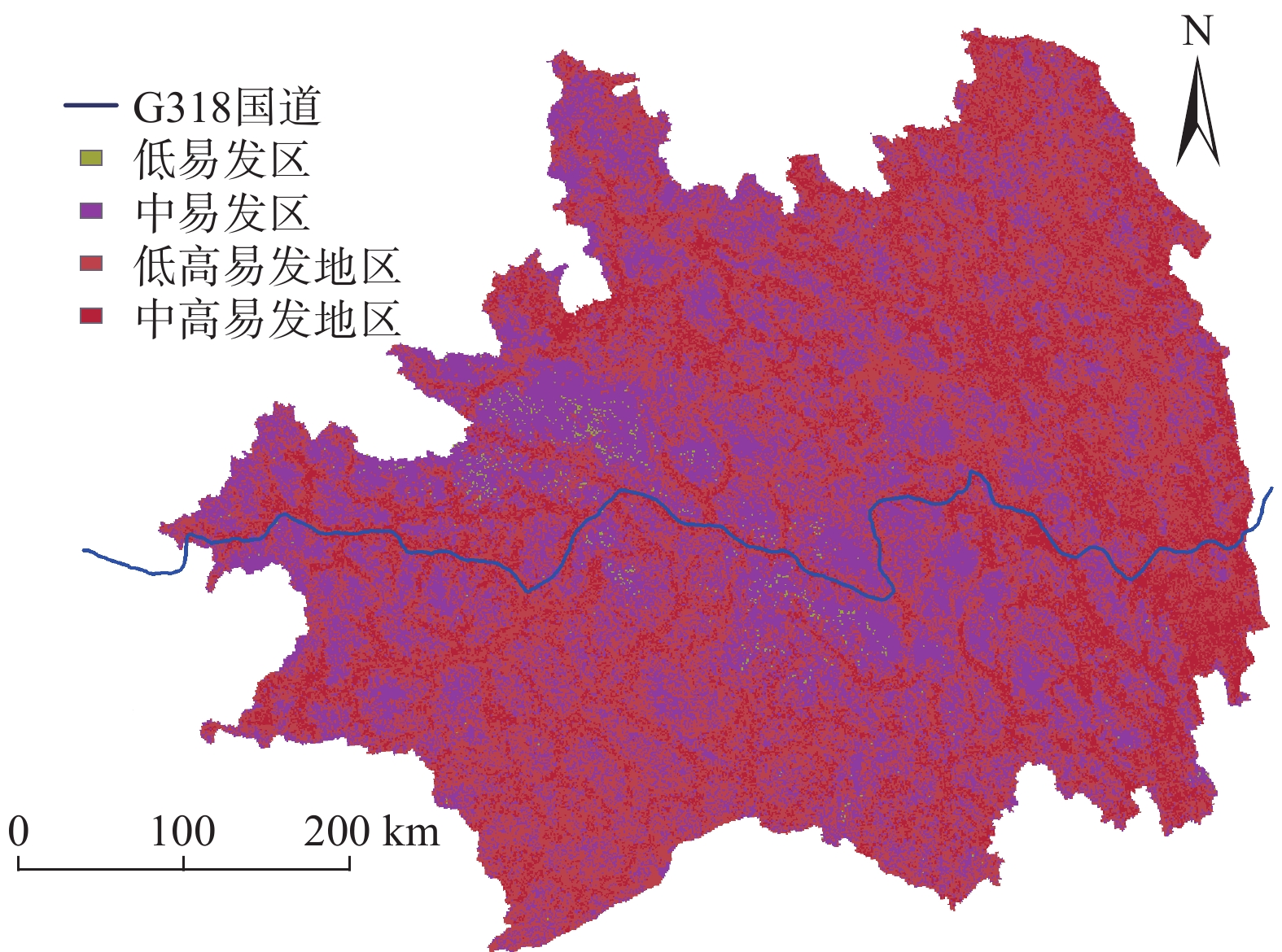
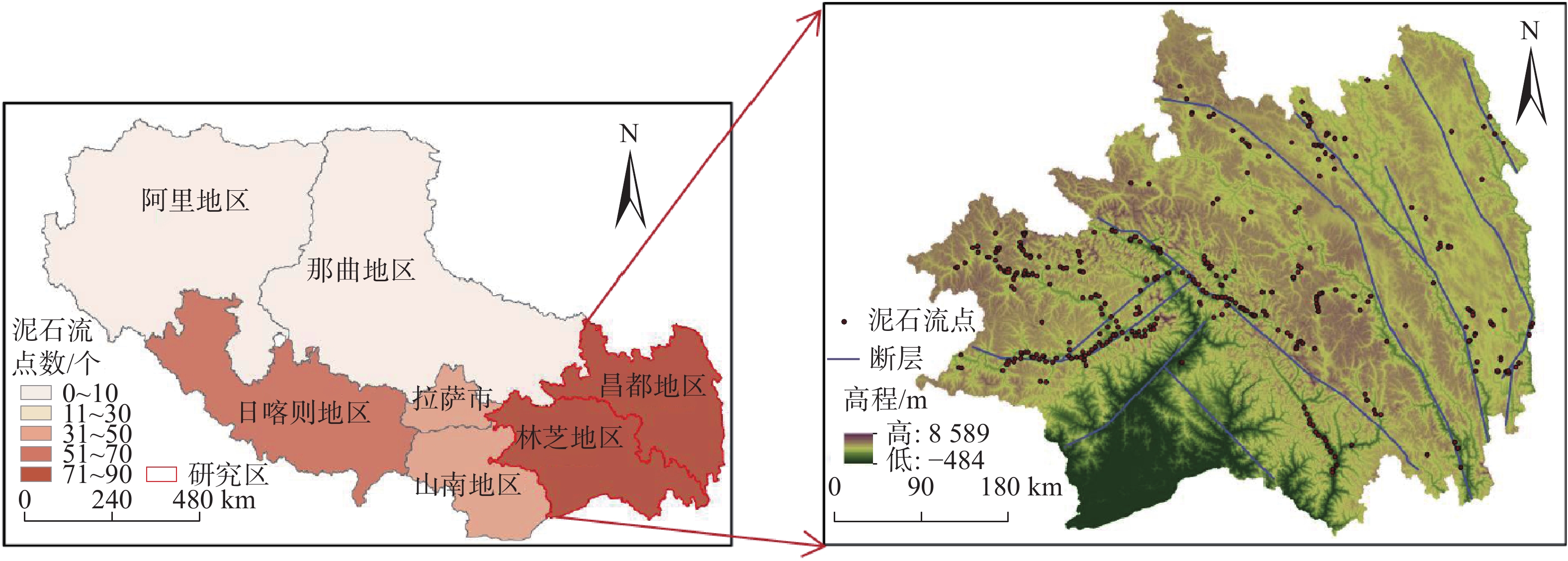
藏东南是泥石流发生的高频地区,也是G318国道铁路的途径之地,泥石流对当地社会发展和重大工程建设构成严重的威胁。文中针对藏东南区域的条件选取了距公路距离、距河流距离、距断层距离、高程、坡度、降雨、NDVI等11个致灾因子来研究该地区的泥石流发生规律。在ArcGIS中导出并分析泥石流点各因子数据,进行相关性检验和建立因子敏感度等级。利用层次分析法计算权重后,结合因子敏感图层制作2015年藏东南地区泥石流危险分布图来检验模型的正确性。针对不同降雨敏感度制作不同的危险分布图来预测未来的泥石流易发区。当全区降雨敏感度为3时,藏东南近一半地区都是泥石流的极高易发区,G318国道沿线都处于高危险地区中。降雨敏感度为2时,藏东南没有极高易发区,全区危险指数大大降低,G318国道沿线高危险部分占84.56%。结果表明降雨量对研究地区泥石流的危险性分布影响较大,该研究成果可为藏东南的社会发展及重大工程基础建设提供理论支撑。
Abstract:Southeast Xizang is an area with high frequency of debris flow, and also the place G318 pass through. Debris flow poses a serious threat to local social development and major engineering construction. In this paper, according to the conditions of southeast Xizang, 11 disaster-causing factors such as highway distance, watershed distance, fault distance, elevation, slope, rainfall and NDVI etc. are selected to study the occurrence regularity of debris flow in this area. Each factor data of debris flow point is derived and analyzed in ArcGIS, correlation test is carried out and factor sensitivity grade is established. After calculating the weights by AHP, the risk distribution map of debris flow in southeast Xizang in 2015 was made by combining factor sensitive layers to verify the correctness of the model. Different risk distribution maps are made according to different rainfall sensitivities to predict the future debris flow prone areas. When the rainfall sensitivity of the whole region is 3, nearly half of the southeast Xizang is highly prone to debris flow, and all along G318 are in high risk areas. When the rainfall sensitivity is 2, there is no extremely high risk area in southeast Xizang, the risk index of the whole region is greatly reduced, and the high risk part along G318 accounts for 84.56%. The results show that rainfall has a great influence on the risk distribution of debris flow in the study area. The research results can provide theoretical support for the social development and major project construction in southeast Xizang.
-
Key words:
- southeast Xizang /
- debris flow /
- rainfall sensitivity /
- ArcGIS /
- analytic hierarchy process /
- risk level
-

-
表 1 近8年地质灾害调查报告
Table 1. Geological disaster investigation report in recent 8 years
年份 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2013 2012 2011 发生地质灾害数量/次 56 67 59 185 82 138 59 139 泥石流数量/次 30 39 23 118 62 75 35 77 泥石流灾害占比/% 54 58 39 64 76 54 59 55 注:西藏历史年鉴中没有公开2014年数据。 表 2 泥石流致灾因子及数据来源
Table 2. Debris flow disaster factors and data sources
一级因子 二级因子 数据来源 固体物源 距公路距离 1∶100万全国基础地理信息数据 距河道距离 距断层距离 中国地震和火山 地形 高程 ASTGTM2 DEM30m 坡度 坡向 水源 降雨 中国科学院资源环境
科学与技术中心水文 诱发因子 植被覆盖率 土地利用率 地貌 地理空间数据云 表 3 泥石流7个致灾因子的相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis of 7 disaster-causing factors of debris flow
指标 距公路距离 距河道距离 距断层距离 高程 坡度 植被覆盖率 土地利用率 距公路距离 1 距河道距离 0.520** 1 距断层距离 −0.076 −0.054 1 高程 0.259** 0.416** 0.263** 1 坡度 0.171** 0.175** −0.021 0.245** 1 植被覆盖率 0.185** 0.220** −0.160** −0.199** 0.174** 1 土地利用率 0.094 0.084 0.188** 0.298** 0.105 −0.341** 1 表 4 量化表
Table 4. Quantitative table
因素i比因素j 量化值 同等 1 稍微 3 较强 5 强烈 7 极端 9 两相邻判断中间值 2,4,6,8 倒数 aij=1/aij 表 5 第一准则层判断矩阵
Table 5. The judgment matrix of first criterion layer
固体因子B1 水源因子B2 地形因子B3 诱发因子B4 固体因子B1 1 1/6 1/4 3 水源因子B2 6 1 4 8 地形因子B3 4 1/4 1 5 诱发因子B4 1/3 1/8 1/5 1 表 6 第二准则层判断矩阵
Table 6. The judgment matrix of second criterion layer
距公路距离C1 距河道距离C2 距断层距离C3 固体物源
因子判断
矩阵距公路距离C1 1 4 7 距河道距离C2 1/4 1 4 距断层距离C3 1/7 1/4 1 高程C4 坡度C5 坡向C6 地形判断
因子矩阵高程C4 1 1/7 1/3 坡度C5 7 1 4 坡向C6 3 1/4 1 降雨C7 水文C8 水源判断
因子矩阵降雨C7 1 7 水文C8 1/7 1 植被覆盖率C9 土地利用率C10 地貌C11 诱发因子
判断矩阵植被覆盖率C9 1 2 4 土地利用率C10 1/2 1 3 地貌C11 1/4 1/3 1 表 7 致灾因子敏感度及权重
Table 7. Sensitivity and weight of disaster-inducing factors
第一准则层 第二准则层 分类 泥石流数量 总占比/% 敏感度 权重 固体
物源
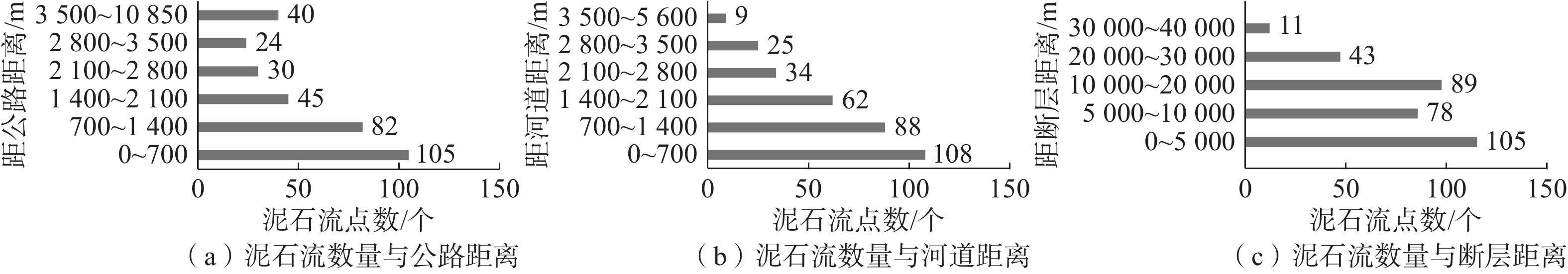
因子距公路距离C1 [0, 700),[700, 1 400) 105,82 57.4 3 0.0688 [1 400, 2100),[2 100, 2 800), [2 800,3 500) 45,30,24 30.4 2 [3 500, 10 850) 40 12.3 1 距河道距离C2 [0, 1 400) 197 60.4 3 0.0234 [1 400, 2 800) 96 29.4 2 [2 800, 5 600) 34 10.4 1 距断层距离C3 [0, 5 000) 105 32.2 3 0.0078 [5 000, 10 000),[10 000, 20 000) 78,89 51.2 2 [20 000, 30 000),[30 000, 40 000) 43,11 16.6 1 地形
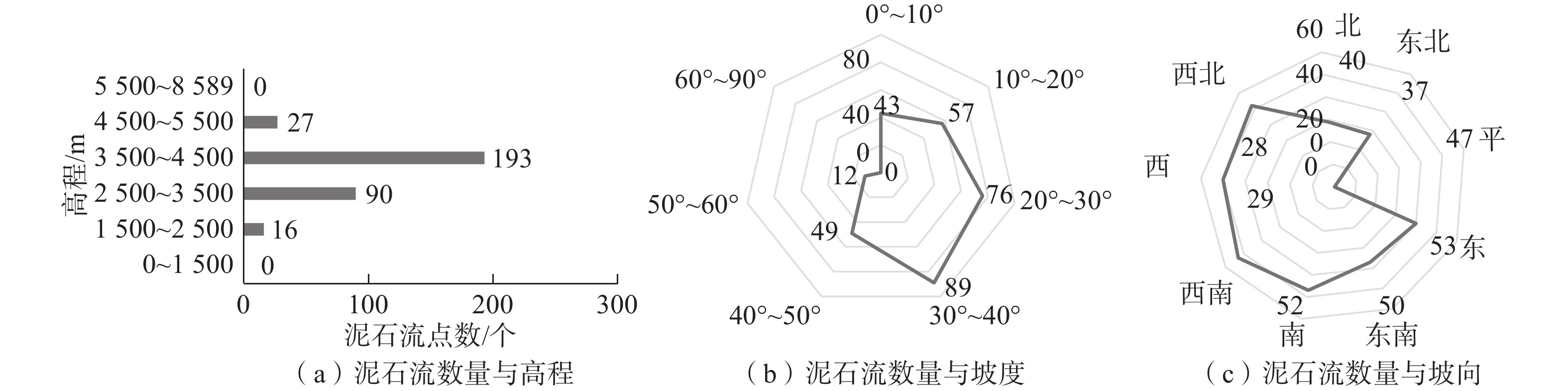
因子高程C4 [3 500, 4 500) 193 59.2 3 0.02125 [2 500, 3 500) 90 27.6 2 [1 500, 2 500),[4 500, 5 500) 16,27 13.2 1 坡度C5 [20, 30),[30, 40) 76,89 50.6 3 0.17525 [0, 10),[10, 20),[40, 50) 43,57,49 45.7 2 [50, 60) 12 03.7 1 坡向C6 西北,西南,西 52,53,50 47.5 3 0.05325 南,东,东南 47,40,37 38.0 2 北,东北 29,28 17.5 1 水源
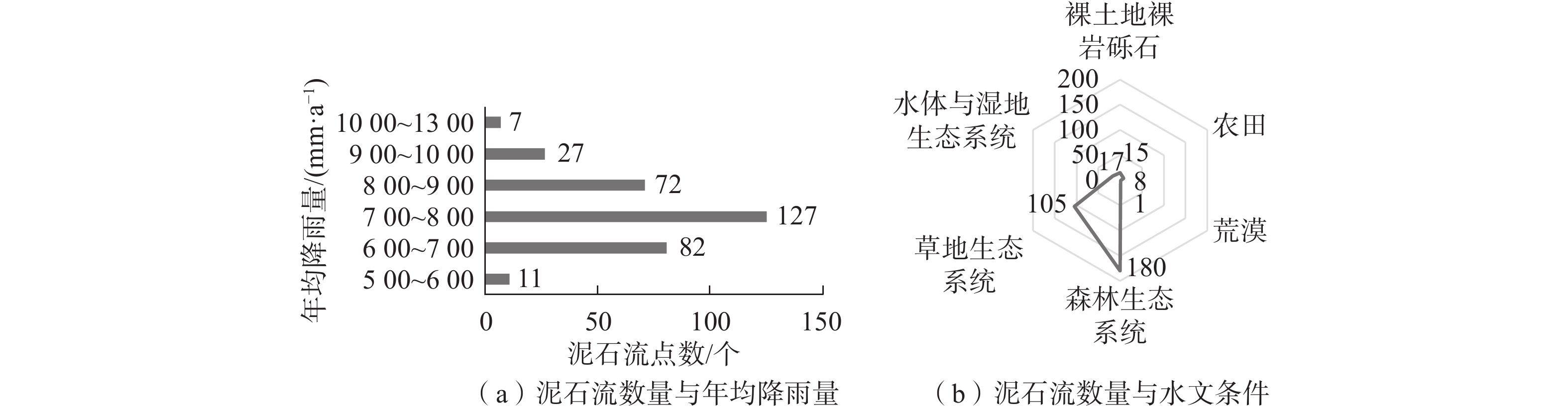
因子年均降雨量
(2001—2009年)
C7[700, 800) 127 39.0 3 0.528 [600, 700),[800, 900) 82,72 47.2 2 [500, 600),[900, 1 300) 11/34 13.8 1 水文C8 森林生态系统 180 55.2 3 0.072 草地生态系统 105 32.2 2 湿地,农田,裸土地系统 17,8,15 12.3 1 诱发
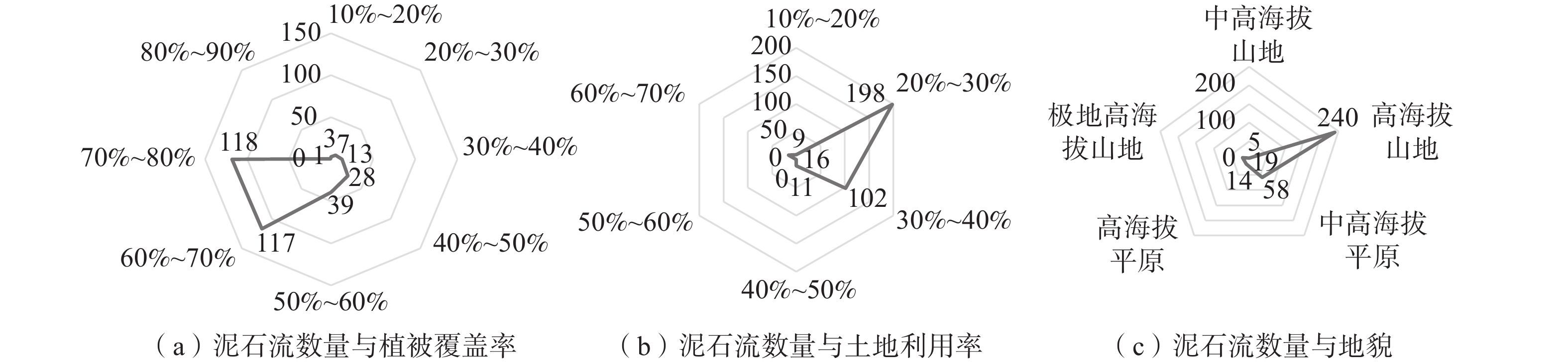
因子植被
覆盖率
C9[0.6, 0.7),[0.7, 0.8) 117,118 72.1 3 0.02785 [0.4, 0.5),[0.5, 0.6) 28,39 20.6 2 [0.1, 0.4) 23 7.1 1 土地
利用率
C10[20, 30) 198 60.7 3 0.016 [30, 40) 102 31.3 2 [10, 20),[40, 50),[60, 70) 9,11,16 11.0 1 地貌
C11高海拔山地 240 73.6 3 0.00615 中高海拔平原 58 17.8 2 其余地貌 38 11.7 1 表 8 图层数值与易发性对应表
Table 8. Corresponding table of layer values and debris flow susceptibility
图层数值 易发性 [0, 1) 非易发区(几乎不会发生泥石流) [1, 1.5) 低易发区(极少发生泥石流) [1.5, 2) 中易发区(受体条件影响容易发生泥石流) [2, 3) 高易发区 [2, 2.3) 低高易发区 [2.3, 2.6) 中高易发区 [2.6, 3) 极高易发区 表 9 2015重大泥石流事件信息
Table 9. Information on major debris flow events in 2015
县市 位置 发生日期 来源 预测易发性 昌都边坝无名冰湖 G318国道附近 2015年7月3日 《西藏冰湖溃决灾害事件极端气候特征》 中易发区 昌都边坝金岭乡结玉村江卡自然村 边坝县讲卡村 2015年7月3日 中国天气网西藏站 中易发区 林芝扎木弄沟泥石流 波密县易贡藏布河域附近 2015年8月16日 《西藏林芝扎木弄沟泥石流规模变化趋势研究》 中易发区 林芝巴宜区 排龙乡河谷路段 2015年8月17日 中国新闻网 高易发区 昌都边坝 边坝镇普玉二村荣达自然村 2015年9月12日 人民网 中易发区 林芝 G318国道林芝境内 2015年8月—2015年9月 拉萨新华社 高易发区 -
[1] 马海荣,程新文,陈联君,等. 基于GIS与层次分析法的公路泥石流危险性评价[J]. 公路工程,2016,41(1):33 − 37. [MA Hairong,CHENG Xinwen,CHEN Lianjun,et al. Hazard evaluation of debris flow along highway based on GIS and AHP[J]. Highway Engineering,2016,41(1):33 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0610.2016.01.008
[2] 王毅,唐川,李为乐,等. 基于GIS的模糊数学模型在泥石流敏感性评价中的应用[J]. 自然灾害学报,2017,26(1):19 − 26. [WANG Yi,TANG Chuan,LI Weile,et al. Application of GIS-based fuzzy mathematics model to sensitivity evaluation of debris flow[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2017,26(1):19 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 王骏,丁明涛,庙成,等. 基于GIS和AHP的芦山地震灾区泥石流危险性评价[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2014,23(11):1580 − 1587. [WANG Jun,DING Mingtao,MIAO Cheng,et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow based on GIS and AHP in Lushan earthquake disaster area[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2014,23(11):1580 − 1587. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 武辰爽,郭永刚,苏立彬. 基于地理信息系统的色季拉山土地利用时空动态变化[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(7):2602 − 2608. [WU Chenshuang,GUO Yonggang,SU Libin. Dynamics of land use in Sedgila Mountain based on geographic information system[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(7):2602 − 2608. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.07.006
[5] 张明,王章琼,白俊龙,等. 基于ArcGIS的“三高”地区高速公路泥石流危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):24 − 32. [ZHANG Ming,WANG Zhangqiong,BAI Junlong,et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow along highway of high altitude cold and intensity regions with aid of ArcGIS[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):24 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 刘佳,赵海军,马凤山,等. 基于改进变异系数法的G109拉萨—那曲段泥石流危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):63 − 70. [LIU Jia,ZHAO Haijun,MA Fengshan,et al. Risk assessment of G109 Lhasa-Naqu Debris flow based on improved coefficient of variation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):63 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 胡桂胜,陈宁生,邓虎. 基于GIS的西藏林芝地区泥石流易发与危险区分析[J]. 水土保持研究,2012,19(3):195 − 199. [HU Guisheng,CHEN Ningsheng,DENG Hu. Analysis of debris flow-prone and dangerous area in Nyingchi of Xizang based on GIS[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2012,19(3):195 − 199. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 何坤,胡卸文,刘波,等. 川藏铁路某车站泥石流群发育特征及对线路的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):137 − 149. [HE Kun,HU Xiewen,LIU Bo,et al. Characteristics and potential engineering perniciousness of the debris flow group in one station of the Sichuan-Xizang railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):137 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 史洪滨,胡卸文,文强,等. 拟建川藏铁路夏里2#沟泥石流发育特征及动力学过程数值模拟[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2021,32(3):39 − 46. [SHI Hongbin,HU Xiewen,WEN Qiang,et al. Debris flow development characteristics and dynamic process numerical simulation of Xiali 2# gully on the proposed Sichuan-Xizang railway[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2021,32(3):39 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2021.03.006
[10] 黄勇. 川藏铁路昌都至林芝段交通廊道安全稳定性分区研究[J]. 铁道标准设计,2021,65(9):1 − 8. [HUANG Yong. Research on safety and stability zoning of Changdu-Linzhi railway corridor of Sichuan-Xizang railway[J]. Railway Standard Design,2021,65(9):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13238/j.issn.1004-2954.202011010001
[11] 王高峰,高幼龙,姚亚辉,等. 甘肃省白龙江流域降雨型潜在泥石流危险性预报模型[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(3):732 − 748. [WANG Gaofeng,GAO Youlong,YAO Yahui,et al. Prediction model of potential debris flow hazard of rainfall type in Bailong River basin,Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(3):732 − 748. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 马艳鲜,余忠水. 西藏泥石流、滑坡时空分布特征及其与降水条件的分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究,2009,29(1):55 − 58. [MA Yanxian,YU Zhongshui. Analysis on temparal and spatial distribution characteristic of mud-rock flow and landslide with the rainfall condition[J]. Plateau and Mountain Meteorology Research,2009,29(1):55 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2184.2009.01.010
[13] 武辰爽. 基于GIS的川藏铁路林芝段地质灾害危险性评价[D]. 拉萨: 西藏大学, 2021
WU Chenshuang. Evaluation of geological hazard risk based on geological information system in Nyingchi section of Sichuan-Xizang railway[D]. Lasa: Xizang University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李廷. 基于遥感技术的昌都地区土地覆被和地质灾害分析研究[D]. 拉萨: 西藏大学, 2021
LI Ting. Based on remote sensing technology analysis of land cover and geological disasters in Qamdo area based on remote sensing technology[D]. Lasa: Xizang University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 郭长宝,王磊,李任杰,等. 西藏贡觉粉砂质泥岩工程地质特性与蠕变强度研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):54 − 64. [GUO Changbao,WANG Lei,LI Renjie,et al. Engineering geology properties and creeping strength characteristics of the silty mudstone in Gongjue County in Xizang of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):54 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202107012
[16] 刘鑫,邓广辉. 川藏公路邦达至林芝段泥石流环境背景及激发因子分析[J]. 公路,2020,65(5):70 − 74. [LIU Xin,DENG Guanghui. Analysis of environmental background and triggering factors of debris flow on Bangda to Nyingchi section of Sichuan-Xizang highway[J]. Highway,2020,65(5):70 − 74. (in Chinese)
[17] 潘华利,安笑,邓其娟,等. 泥石流松散固体物源研究进展与展望[J]. 科学技术与工程,2020,20(24):9733 − 9741. [PAN Huali,AN Xiao,DENG Qijuan,et al. Progress and prospects of research on debris flow solid source[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(24):9733 − 9741. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.24.007
[18] 倪化勇,陈绪钰,周维,等. 高寒高海拔山原区沟谷型泥石流成因与特征—以四川省雅江县祝桑景区为例[J]. 水土保持通报,2013,33(1):211 − 215. [NI Huayong,CHEN Xuyu,ZHOU Wei,et al. Formation and characteristics of gully-type debris flow on hilly plateau planes with cold climate and high altitude of Sichuan province:A case study of the Zhusang scenic spot in Yajiang County of Sichuan Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2013,33(1):211 − 215. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 屈永平, 唐川, 刘洋, 等. 西藏林芝地区冰川降雨型泥石流调查分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(增刊2): 4013 − 4022
QU Yongping, TANG Chuan, LIU Yang, et al. Investigation and analysis of glacier debris flow in Nyingchi area, Xizang[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(Sup 2): 4013 − 4022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 邓国卫,孙俊,郭海燕,等. 四川泥石流灾害分区及其与诱发降水关系[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版),2020,42(1):95 − 102. [DENG Guowei,SUN Jun,GUO Haiyan,et al. Zoning of debris flow hazards in Sichuan Province and their relationship with inducing precipitation[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition),2020,42(1):95 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 陈飞,郭顺,熊如宗,等. 基于层次分析法的地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 有色金属科学与工程,2018,9(5):54 − 60. [CHEN Fei,GUO Shun,XIONG Ruzong,et al. Risk assessment of geological hazards based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering,2018,9(5):54 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李元松,余再富,朱冬林,等. 基于ArcGIS的公路工程地质选线模型[J]. 公路,2021,66(9):105 − 111. [LI Yuansong,YU Zaifu,ZHU Donglin,et al. Model for highway engineering geological line selection based on ArcGIS[J]. Highway,2021,66(9):105 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: