Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment based on multiple hybrid models at county level: A case study for Puge County, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
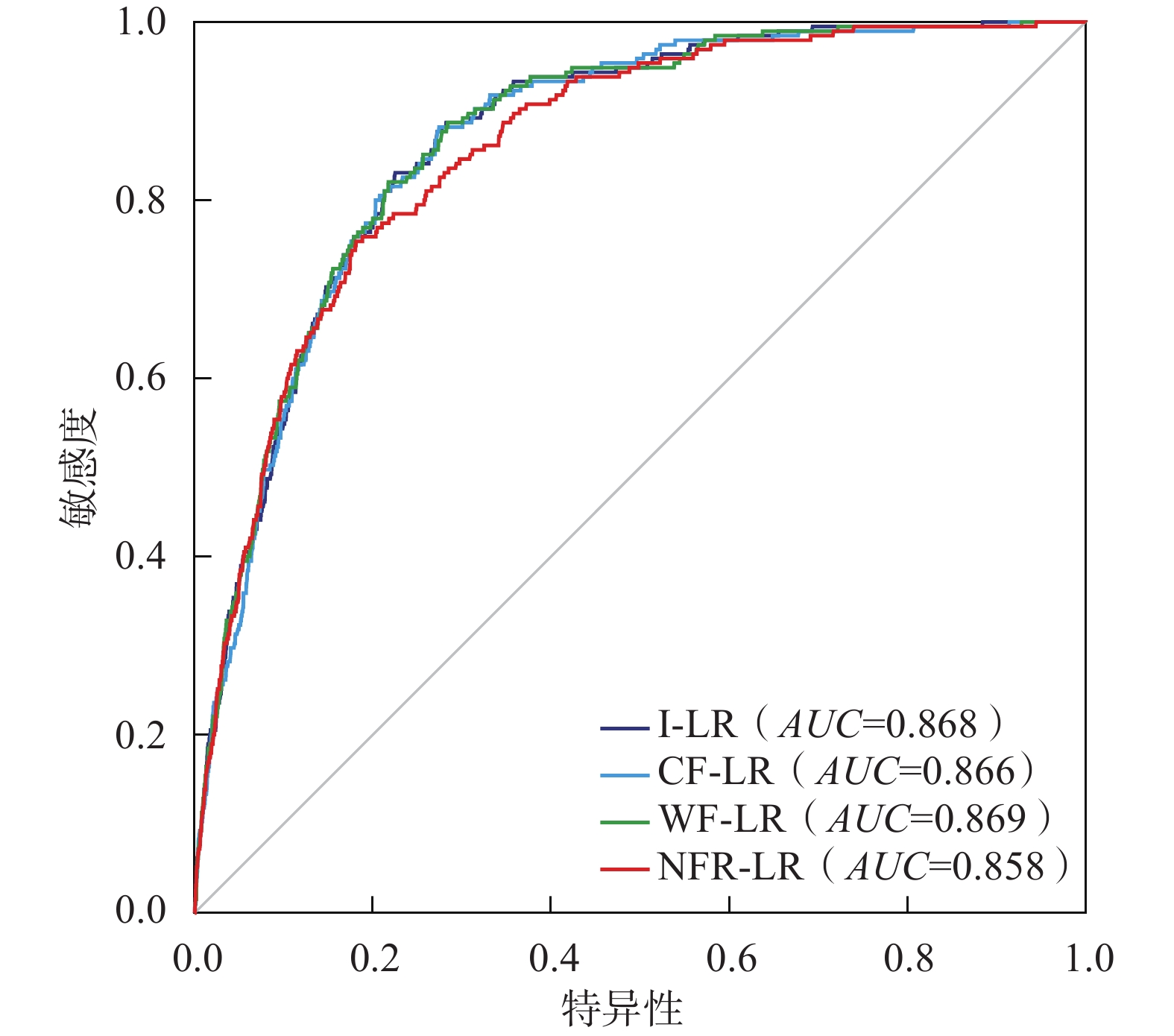
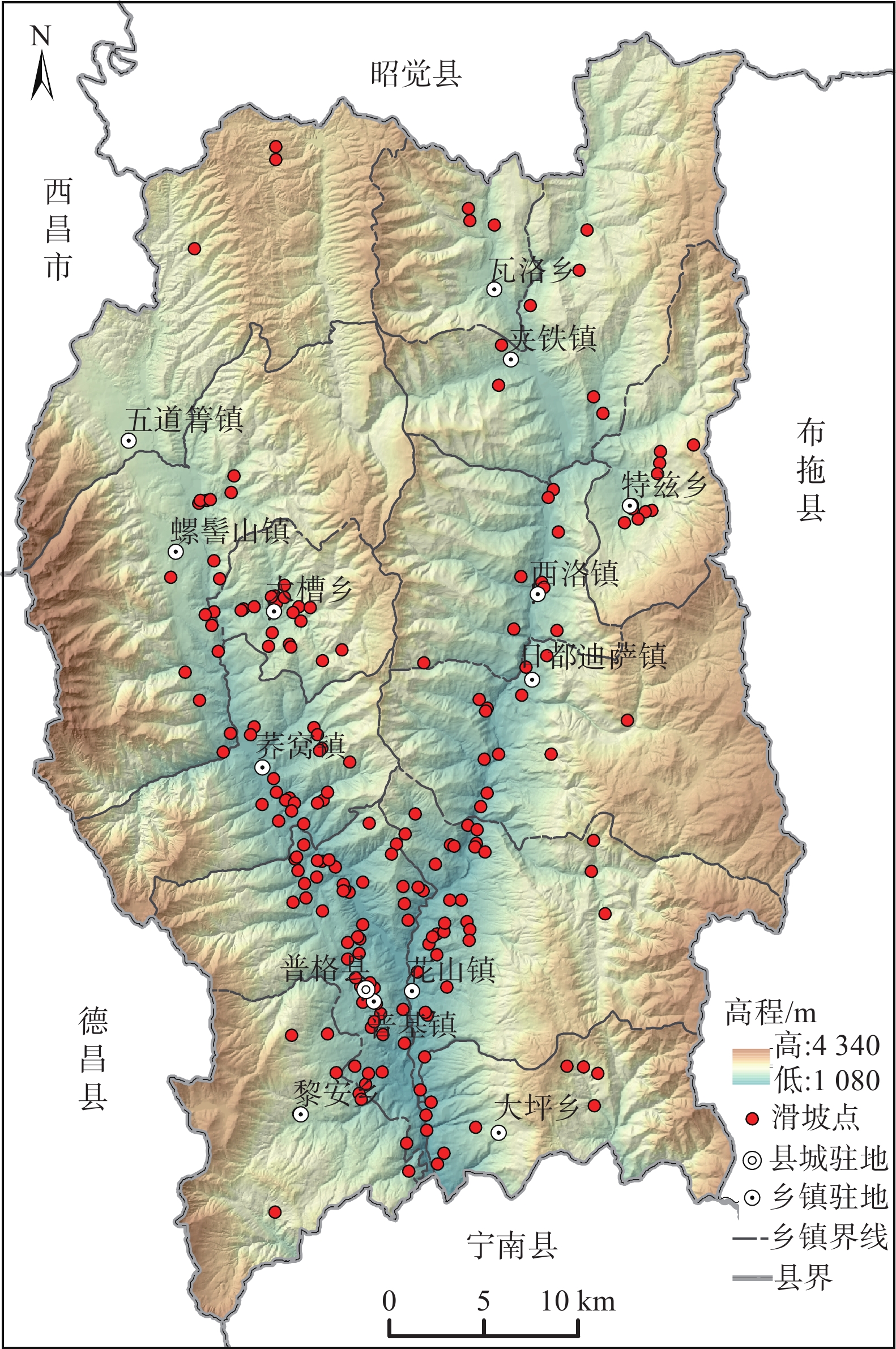
为有效预测县域滑坡发生的空间概率,探索不同统计学耦合模型滑坡易发性定量评价结果的合理性和精度,以四川省普格县为研究对象。选取坡度、坡向、高程、工程地质岩组、断层和斜坡结构等6项孕灾因子作为评价指标体系,基于信息量模型(I)、确定性系数模型(CF)、证据权模型(WF)、频率比模型(FR)分别与逻辑回归模型(LR)耦合开展滑坡易发性评价。结果表明:各耦合模型评价结果和易发程度区划均是合理的,极高易发区主要分布于则木河、黑水河河谷两侧斜坡带,面积介于129.04~183.43 km2(占比6.77%~9.62%),各模型评价精度依次为WF-LR模型(AUC=0.869)>I-LR模型(AUC=0.868)>CF-LR模型(AUC=0.866)>NFR-LR模型(AUC=0.858)。研究成果可为川西南山区县域滑坡易发性定量评估提供重要参考。
Abstract:In order to effectively predict the spatial probability of landslide occurrence at county scale, the quantitative evaluation and comparative study of landslide susceptibility were carried out based on different statistical coupling models in Puge County, Southwest Sichuan. Six evaluation factors including slope, slope direction, elevation, engineering geological rock group, distance from fault and slope structure are selected to construct the evaluation index system. Information model (I), certainty factor model (CF), weight of evidence model (WF) and frequency ratio model (FR) are coupled with logistic regression model (LR) respectively to conduct landslide susceptibility evaluation. The results show that the evaluation results of each coupled model and the zoning of susceptibility are reasonable. The extremely high susceptibility areas with 129.04 −183.43 km2 (accounting for 6.77% −9.62%) are mainly distributed in the slope zones on both sides of Zemu River and Heishui River Valley. The evaluation accuracy decreases from WF-LR model (AUC=0.869), I-LR model (AUC=0.868), CF-LR model (AUC=0.866), to NFR-LR model (AUC=0.858). The research results can provide an important reference for the quantitative evaluation of county landslide susceptibility in mountainous areas of Southwest Sichuan.
-

-
表 1 评价因子分级及I值、CF值、WF值和NFR值
Table 1. Calculation results of I, CF, WF and NFR values for classification level of each evaluation factor
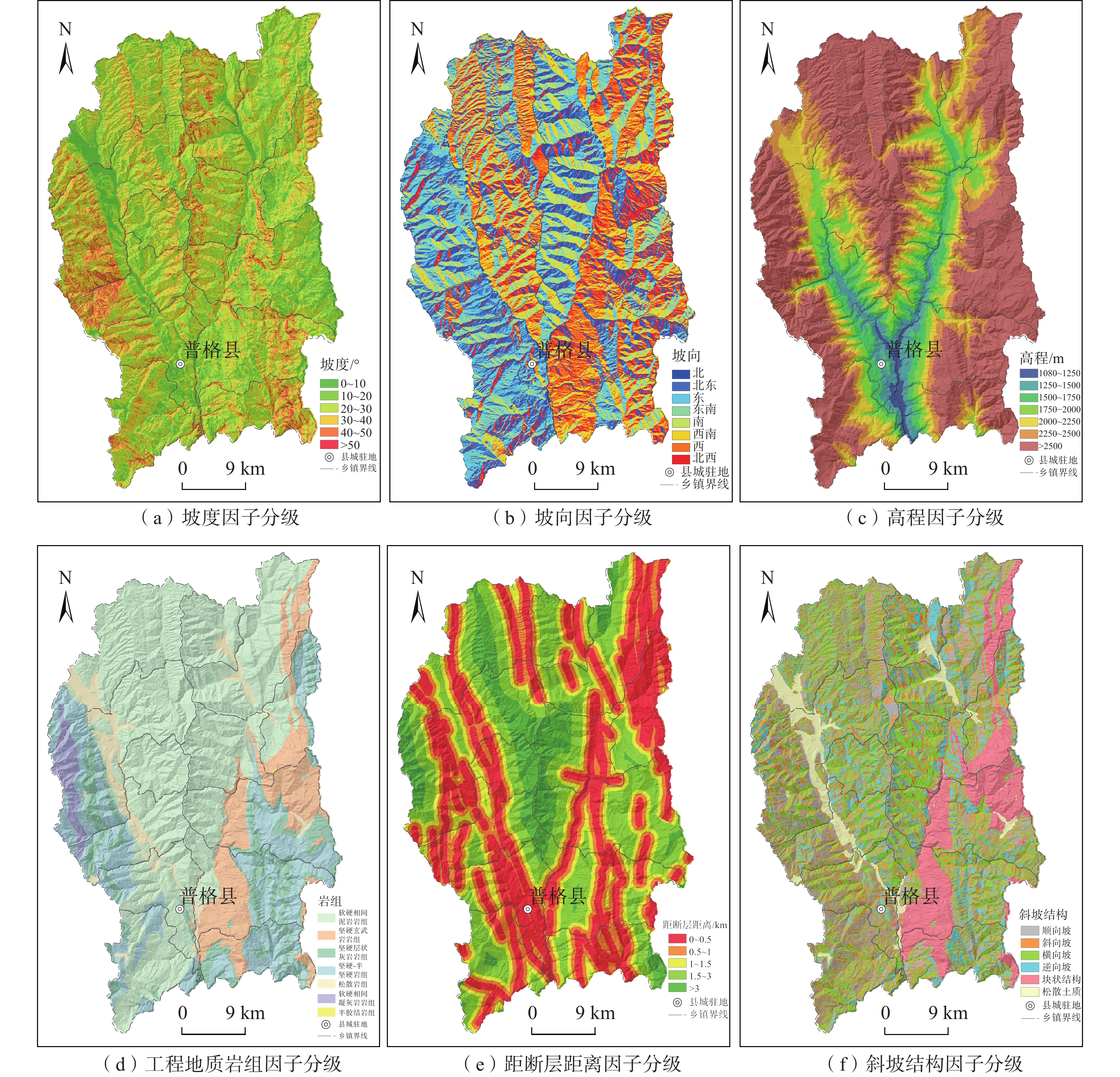
评价因子 分级 分级面积/km2 滑坡点/个 信息量值(I) 确定性系数值(CF) 证据权值(WF) 归一化评率比值(NFR) 坡度/(°) 0~10 190.90 17 −0.2634 −0.2316 −0.2888 0.1837 10~20 497.15 78 0.3889 0.3222 0.5724 0.3527 20~30 620.30 77 0.2321 0.2071 0.3667 0.3015 30~40 438.61 20 −0.6898 −0.4983 −0.8286 0.1199 40~50 138.49 3 −1.7342 −0.8235 −1.7967 0.0422 >50 21.54 0 −1.7342 −1.0000 −1.6118 0.0000 坡向 北 237.61 17 −0.7700 −0.5370 −0.8436 0.0582 北东 229.75 17 −0.2255 −0.2019 −0.2528 0.1003 东 264.22 29 −0.0776 −0.0747 −0.0895 0.1163 东南 223.00 23 0.0920 0.0879 0.1048 0.1378 南 213.81 23 0.0828 0.0795 0.0938 0.1365 西南 228.02 22 0.1185 0.1118 0.1358 0.1415 西 269.04 42 0.4051 0.3331 0.4907 0.1885 北西 241.54 22 −0.0392 −0.0384 −0.0447 0.1209 高程/m 1080~1250 18.04 8 1.5566 0.7892 1.5932 0.2481 1250~1500 73.97 60 2.0284 0.8685 2.3385 0.3977 1500~1750 127.88 39 1.0536 0.6513 1.1978 0.1500 1750~2000 181.76 38 0.7973 0.5495 0.9348 0.1161 2 000~2250 260.21 31 0.2378 0.2116 0.2812 0.0664 2250~2500 277.74 10 −1.0438 −0.6479 −1.1486 0.0184 >2500 967.41 9 −2.7618 −0.9368 −3.4370 0.0033 工程地质岩组 软硬相间砂泥岩岩组 1012.50 137 0.2928 0.2538 0.7790 0.2852 坚硬玄武岩岩组 244.86 20 −0.2247 −0.2012 −0.2538 0.1700 坚硬层状灰岩岩组岩、白云质灰岩岩组 195.97 8 −0.6951 −0.5010 −0.7509 0.1062 坚硬−半坚硬砂岩组 324.87 14 −1.2006 −0.6990 −1.3347 0.0641 松软岩组 90.32 16 0.5650 0.4316 0.6035 0.3745 软硬相间凝灰岩 38.21 0 −1.2006 −1.0000 −0.9848 0.0000 半胶结岩组 0.27 0 −1.2006 −1.0000 −0.9848 0.0000 距断层距离/km 0~0.5 577.04 108 0.5763 0.4381 0.9892 0.4092 0.5~1 372.13 44 0.1105 0.1047 0.1393 0.2568 1~1.5 272.36 20 −0.2133 −0.1921 −0.2448 0.1858 1.5~3 476.60 19 −0.8907 −0.5896 −1.0700 0.0944 >3 208.88 4 −1.4520 −0.7659 −1.5421 0.0538 斜坡结构 顺向坡 284.78 49 0.4893 0.3870 0.6068 0.2398 斜向坡 513.76 46 −0.1274 −0.1196 −0.1706 0.1294 横向坡 521.17 43 −0.1973 −0.1791 −0.2624 0.1207 逆向坡 252.00 22 −0.1356 −0.1268 −0.1547 0.1284 块状结构斜坡 240.57 16 −0.4146 −0.3394 −0.4625 0.0971 松散土质斜坡 94.72 19 0.6605 0.4834 0.7107 0.2846 表 2 普格县滑坡易发性不同模型评价结果对比(训练集)
Table 2. Comparison of landslide susceptibility evaluation results of different models
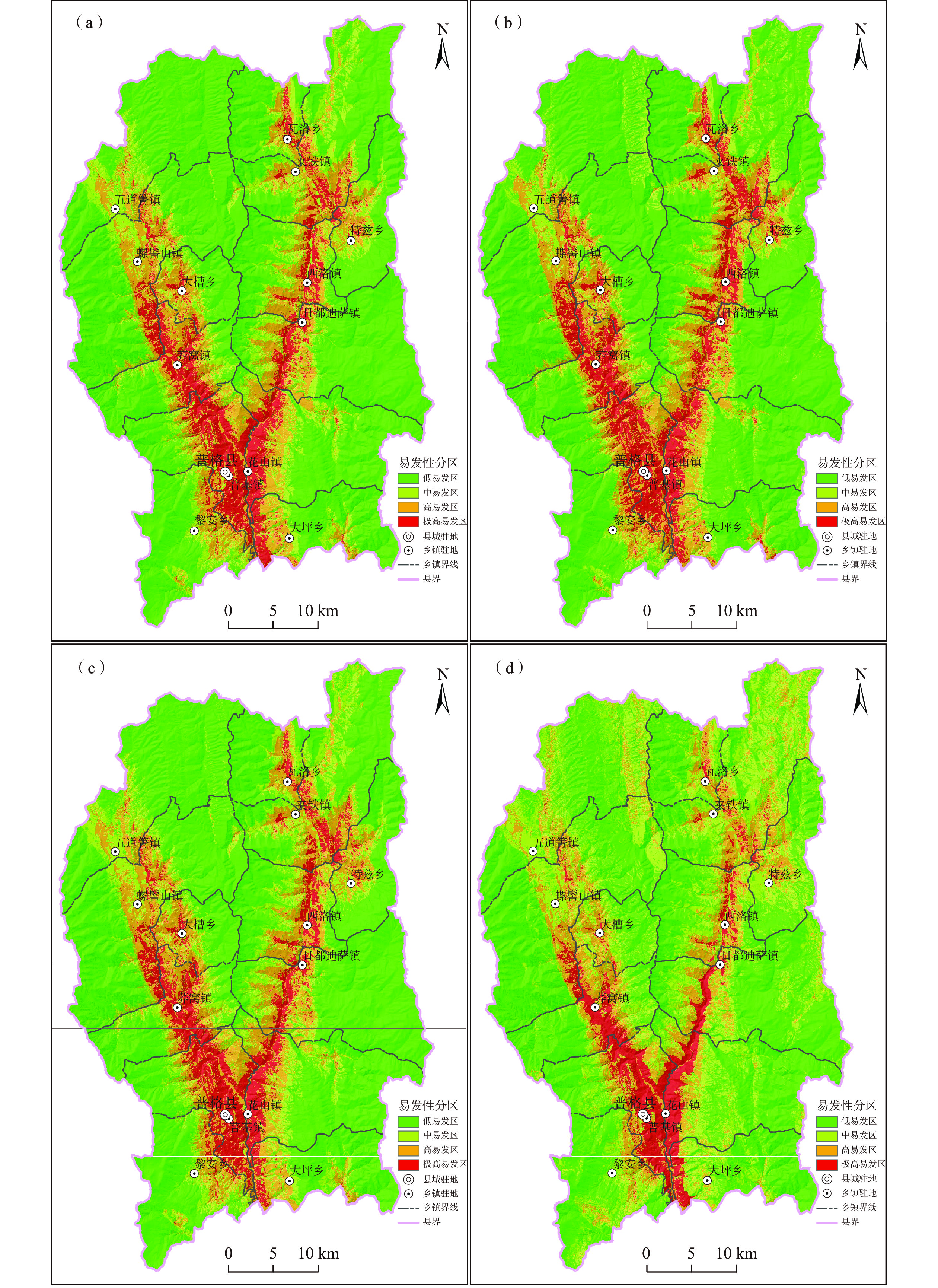
评价模型 易发性等级 面积/km2 面积占比/% 训练集滑坡点(156个) 滑坡数量/个 占比/% 点密度/个/km2 I-LR 极高易发 169.89 8.91 80 51.28 0.47 高易发 303.28 15.90 50 32.05 0.16 中易发 269.10 14.11 20 12.82 0.07 低易发 1164.73 61.08 6 3.85 0.01 CF-LR 极高易发 183.43 9.62 80 51.28 0.44 高易发 284.62 14.92 47 30.13 0.17 中易发 233.42 12.24 21 13.46 0.09 低易发 1205.53 63.22 8 5.13 0.01 WF-LR 极高易发 168.77 8.85 78 50.00 0.46 高易发 302.78 15.88 51 32.69 0.17 中易发 278.71 14.62 21 13.46 0.08 低易发 1156.74 60.66 6 3.85 0.01 NFR-LR 极高易发 129.04 6.77 68 43.59 0.53 高易发 248.98 13.06 50 32.05 0.20 中易发 519.76 27.26 31 19.87 0.06 低易发 1009.23 52.92 7 4.49 0.01 表 3 普格县滑坡易发性评价模型结果对比(测试样本)
Table 3. Comparison of landslide susceptibility evaluation results of different models
评价模型 易发性等级 面积/km 面积占比Sai/% 测试样本滑坡点(39个) Rei=Gei/Sai 滑坡数量/个 占比Gei/% I-LR 极高易发 169.89 8.91 19 48.72 5.47 高易发 303.28 15.90 12 30.77 1.93 中易发 269.10 14.11 3 7.69 0.55 低易发 1164.73 61.08 5 12.82 0.21 CF-LR 极高易发 183.43 9.62 19 48.72 5.06 高易发 284.62 14.92 13 33.33 2.23 中易发 233.42 12.24 2 5.13 0.42 低易发 1205.53 63.22 5 12.82 0.20 WF-LR 极高易发 168.77 8.85 20 51.28 5.79 高易发 302.78 15.88 12 30.77 1.94 中易发 278.71 14.62 2 5.13 0.35 低易发 1156.74 60.66 5 12.82 0.21 NFR-LR 极高易发 129.04 6.77 19 48.72 7.20 高易发 248.98 13.06 10 25.64 1.96 中易发 519.76 27.26 5 12.82 0.47 低易发 1009.23 52.92 5 12.82 0.24 -
[1] BRABB E, PAMPEYAN E, BONILLA M. Landslide susceptibility in San Mateo County[R]. fornia. 1972. https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/mf360
[2] COROMINAS J,VAN WESTEN C,FRATTINI P,et al. Recommendations for the quantitative analysis of landslide risk[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2014,73(2):209 − 263. doi: 10.1007/s10064-013-0538-8
[3] FELL R,COROMINAS J,BONNARD C,et al. Guidelines for landslide susceptibility,hazard and risk zoning for land use planning[J]. Engineering Geology,2008,102(3/4):85 − 98. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.03.022
[4] YIN K L, YAN T Z. Statistical prediction models for slope instability of metamorphosed rocks[J]. Landslides Proc 5th Symposium, Lausanne, 1988 (2): 1269 − 1272. https://www.mendeley.com/research/statistical-prediction-models-slope-instability-metamorphosed-rocks/
[5] 周天伦,曾超,范晨,等. 基于快速聚类-信息量模型的汶川及周边两县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):137 − 150. [ZHOU Tianlun,ZENG Chao,FAN Chen,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on K-means cluster information model in Wenchuan and two neighboring counties,China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):137 − 150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 王雷,吴君平,赵冰雪,等. 基于GIS和信息量模型的安徽池州地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):96 − 103. [WANG Lei,WU Junping,ZHAO Bingxue,et al. Susceptibility assessment of geohazards in Chizhou City of Anhui Province based on GIS and informative model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] DEVKOTA K C,REGMI A D,POURGHASEMI H R,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping using certainty factor,index of entropy and logistic regression models in GIS and their comparison at Mugling-Narayanghat Road section in Nepal Himalaya[J]. Natural Hazards,2013,65(1):135 − 165. doi: 10.1007/s11069-012-0347-6
[8] 杨光,徐佩华,曹琛,等. 基于确定性系数组合模型的区域滑坡敏感性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(5):1153 − 1163. [YANG Guang,XU Peihua,CAO Chen,et al. Assessment of regional landslide susceptibility based on combined model of certainty factor method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(5):1153 − 1163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] LEE S,CHOI J. Landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS and the weight-of-evidence model[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science,2004,18(8):789 − 814. doi: 10.1080/13658810410001702003
[10] 张艳玲,南征兵,周平根. 利用证据权法实现滑坡易发性区划[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2012,39(2):121 − 125. [ZHANG Yanling,NAN Zhengbing,ZHOU Pinggen. Division of landslide susceptibility based on weights of evidence model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2012,39(2):121 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 范强,巨能攀,向喜琼,等. 证据权法在区域滑坡危险性评价中的应用—以贵州省为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(3):474 − 481. [FAN Qiang,JU Nengpan,XIANG Xiqiong,et al. Landslides hazards assessment with weights of evidence: A case study in Guizhou,China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(3):474 − 481. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 吴常润,角媛梅,王金亮,等. 基于频率比-逻辑回归耦合模型的双柏县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(4):213 − 224. [WU Changrun,JIAO Yuanmei,WANG Jinliang,et al. Frequency ratio and logistic regression models based coupling analysis for susceptibility of landslide in Shuangbai County[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(4):213 − 224. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] GUZZETTI F,CARRARA A,CARDINALI M,et al. Landslide hazard evaluation:A review of current techniques and their application in a multi-scale study,Central Italy[J]. Geomorphology,1999,31(1 − 4):181 − 216. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(99)00078-1
[14] 王进,郭靖,王卫东,等. 权重线性组合与逻辑回归模型在滑坡易发性区划中的应用与比较[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2012,43(5):1932 − 1939. [WANG Jin,GUO Jing,WANG Weidong,et al. Application and comparison of weighted linear combination model and logistic regression model in landslide susceptibility mapping[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2012,43(5):1932 − 1939. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 许冲,戴福初,徐素宁,等. 基于逻辑回归模型的汶川地震滑坡危险性评价与检验[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(3):98 − 104. [XU Chong,DAI Fuchu,XU Suning,et al. Application of logistic regression model on the Wenchuan earthquake triggered landslide hazard mapping and its validation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(3):98 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] VORPAHL P,ELSENBEER H,MÄRKER M,et al. How can statistical models help to determine driving factors of landslides?[J]. Ecological Modelling,2012,239:27 − 39. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2011.12.007
[17] 何书,鲜木斯艳·阿布迪克依木,胡萌,等. 基于自组织特征映射网络-随机森林模型的滑坡易发性评价—以江西大余县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):132 − 140. [HE Shu,ABUDIKEYIMU XMSY,HU Meng,et al. Evaluation on landslide susceptibility based on self-organizing feature map network and random forest model:a case study of Dayu County of Jiangxi ProvinceFull text replacement[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.01-16
[18] GUZZETTI F,GALLI M,REICHENBACH P,et al. Landslide hazard assessment in the Collazzone area,Umbria,Central Italy[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2006,6(1):115 − 131. doi: 10.5194/nhess-6-115-2006
[19] LEE C T,HUANG C C,LEE J F,et al. Statistical approach to earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility[J]. Engineering Geology,2008,100(1/2):43 − 58. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.03.004
[20] 樊芷吟,苟晓峰,秦明月,等. 基于信息量模型与Logistic回归模型耦合的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(2):340 − 347. [FAN Zhiyin,GOU Xiaofeng,QIN Mingyue,et al. Information and logistic regression models based coupling analysis for susceptibility of geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(2):340 − 347. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 栗泽桐,王涛,周杨,等. 基于信息量、逻辑回归及其耦合模型的滑坡易发性评估研究:以青海沙塘川流域为例[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(1):235 − 245. [LI Zetong,WANG Tao,ZHOU Yang,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on information value model,logistic regression model and their integrated model:A case in Shatang River Basin,Qinghai Province[J]. Geoscience,2019,33(1):235 − 245. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 罗路广,裴向军,黄润秋,等. GIS支持下CF与Logistic回归模型耦合的九寨沟景区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(2):526 − 535. [LUO Luguang,PEI Xiangjun,HUANG Runqiu,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Jiuzhaigou scenic area with GIS based on certainty factor and logistic regression model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(2):526 − 535. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-202
[23] 张钟远,邓明国,徐世光,等. 镇康县滑坡易发性评价模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(1):157 − 171. [ZHANG Zhongyuan,DENG Mingguo,XU Shiguang,et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang County,Yunnan Province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,41(1):157 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0360
[24] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归-信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang,YANG Zhihua,YUAN Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 沈迪,郭进京,陈俊合. 甘肃定西地区地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):134 − 142. [SHEN Di,GUO Jinjing,CHEN Junhe. Risk assessment of geological hazards in Dingxi region of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):134 − 142. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] SÜZEN M L,DOYURAN V. A comparison of the GIS based landslide susceptibility assessment methods:multivariate versus bivariate[J]. Environmental Geology,2004,45(5):665 − 679. doi: 10.1007/s00254-003-0917-8
[27] FELICÍSIMO Á M,CUARTERO A,REMONDO J,et al. Mapping landslide susceptibility with logistic regression,multiple adaptive regression splines,classification and regression trees,and maximum entropy methods:a comparative study[J]. Landslides,2013,10(2):175 − 189. doi: 10.1007/s10346-012-0320-1
[28] GOETZ J N,BRENNING A,PETSCHKO H,et al. Evaluating machine learning and statistical prediction techniques for landslide susceptibility modeling[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2015,81:1 − 11. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2015.04.007
[29] 凌飞, 杨东, 王双, 等. 四川省普格县地质灾害风险调查评价(1∶50000)成果报告[R]. 四川: 四川志德岩土工程有限责任公司, 2021
LING Fei, YANG Dong, WANG Shuang, et al. Report on the results of geological disaster risk investigation and evaluation (1∶50000) in Puge County, Sichuan Province [R]. Sichuan: Sichuan Zhide Geotechnical Engineering Co. Ltd., 2021. (in Chinese)
[30] FAWCETT T. An introduction to ROC analysis[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters,2006,27(8):861 − 874. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
[31] SRIDEVI JADI,S. SARKAR,杨健. 斜坡不稳定性分类的统计模型[J]. 世界地质,1997,16(1):83 − 88. [SRIDEVI JADI,SARKAR S,YANG J. Statistical model of slope instability classification[J]. World Geology,1997,16(1):83 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: