Analysis on the distributive characteristics and causes of the geological disasters induced by the “8·8” heavy rainstorm in Qu County, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
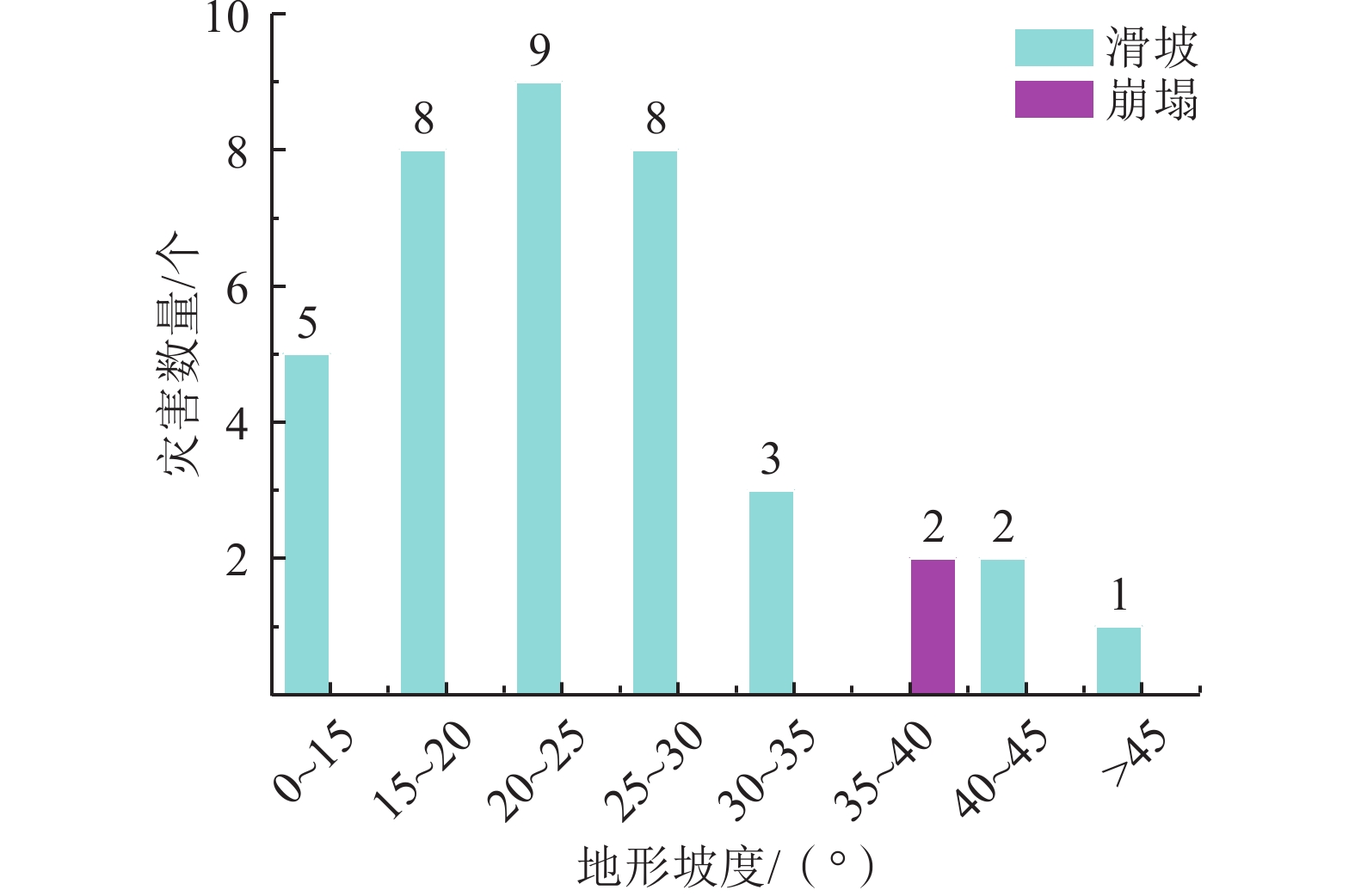
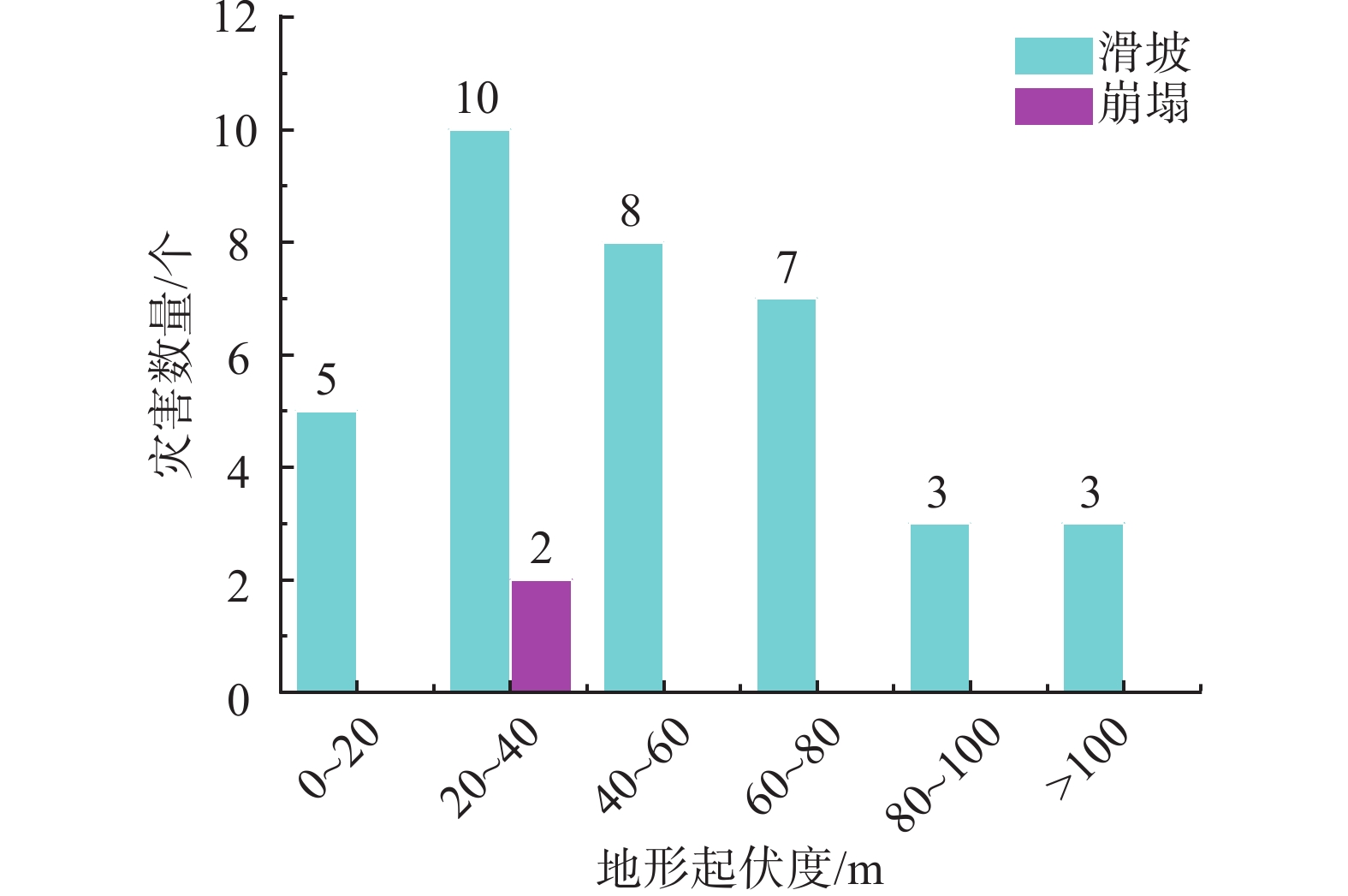
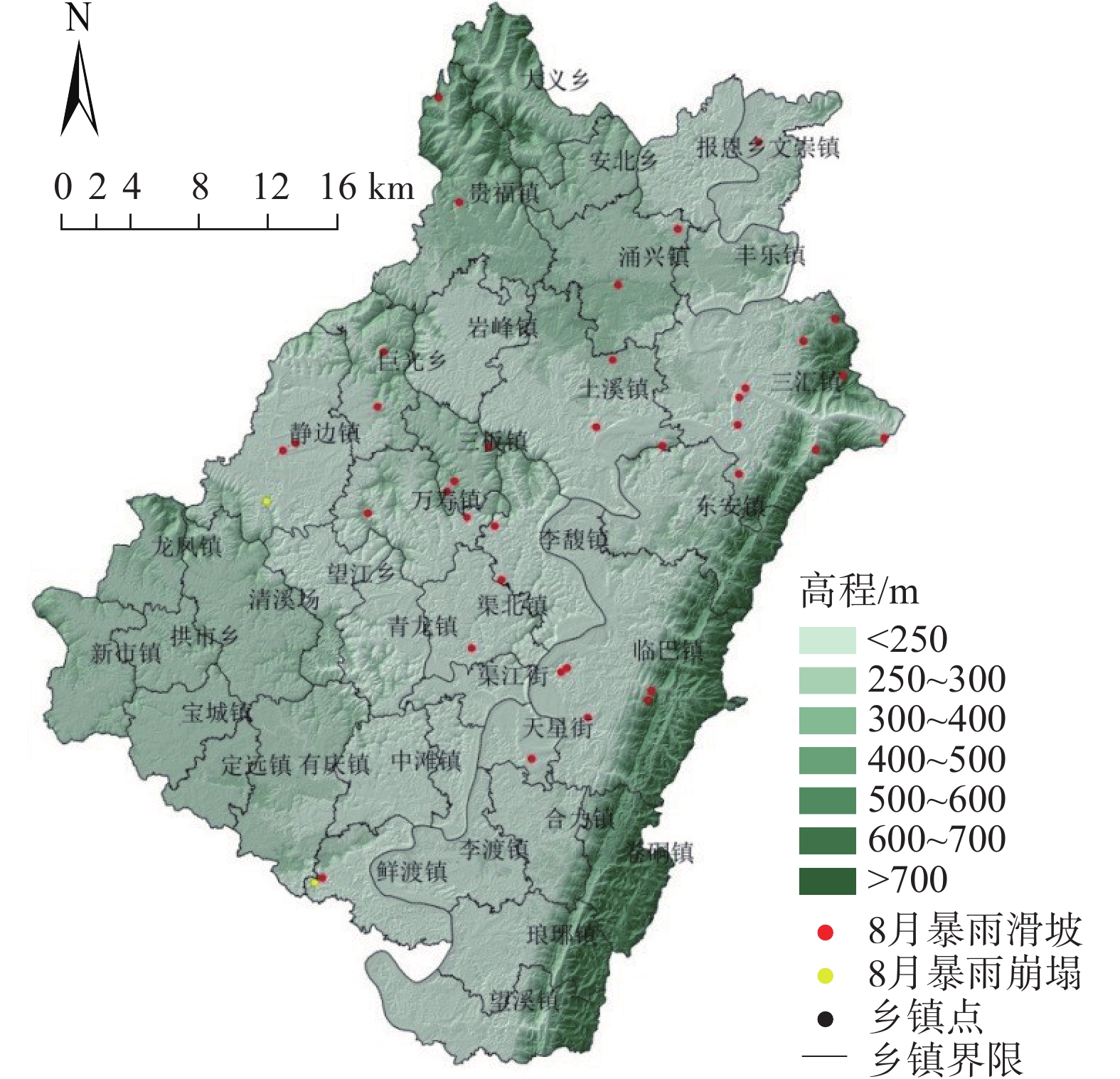
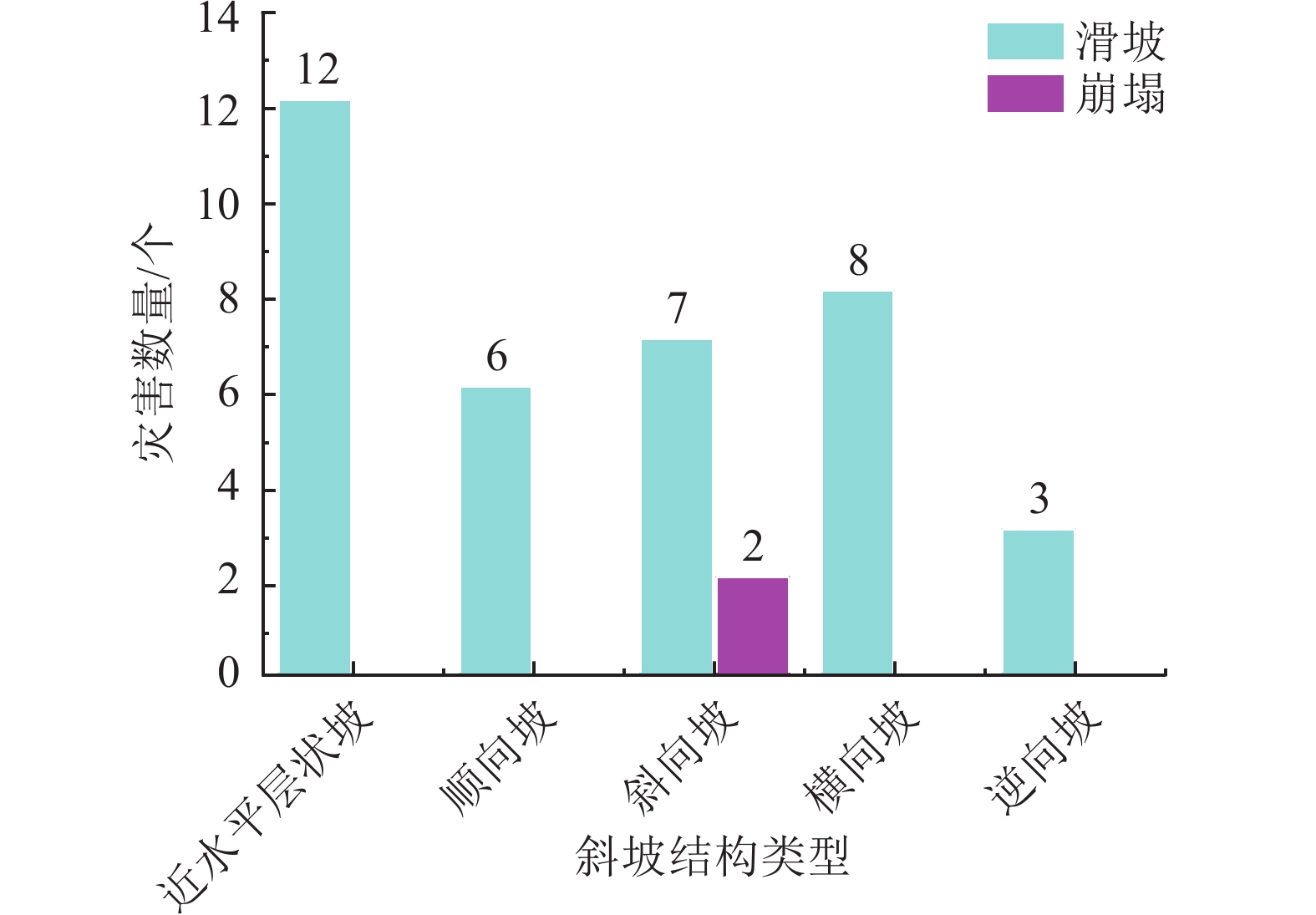
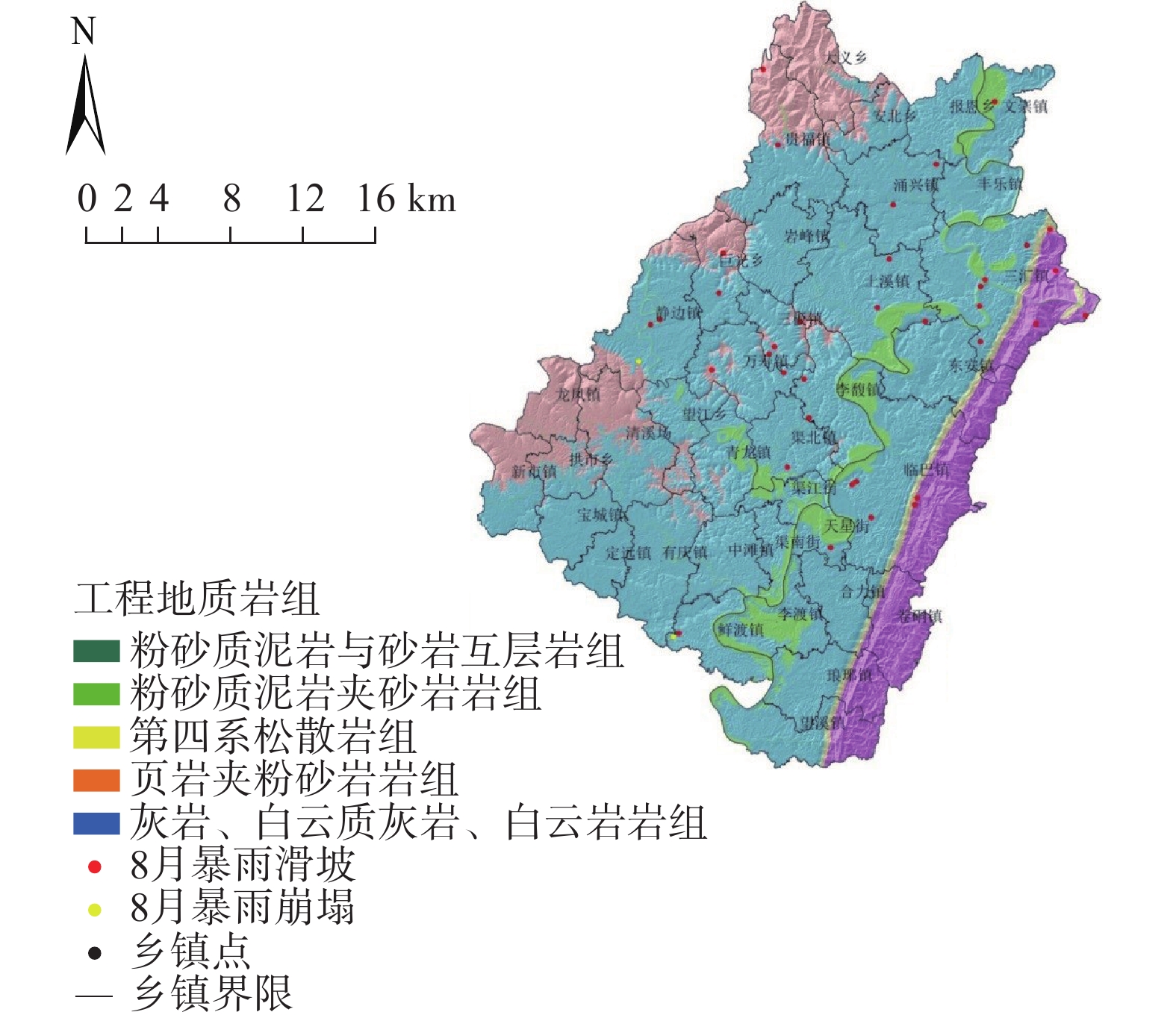
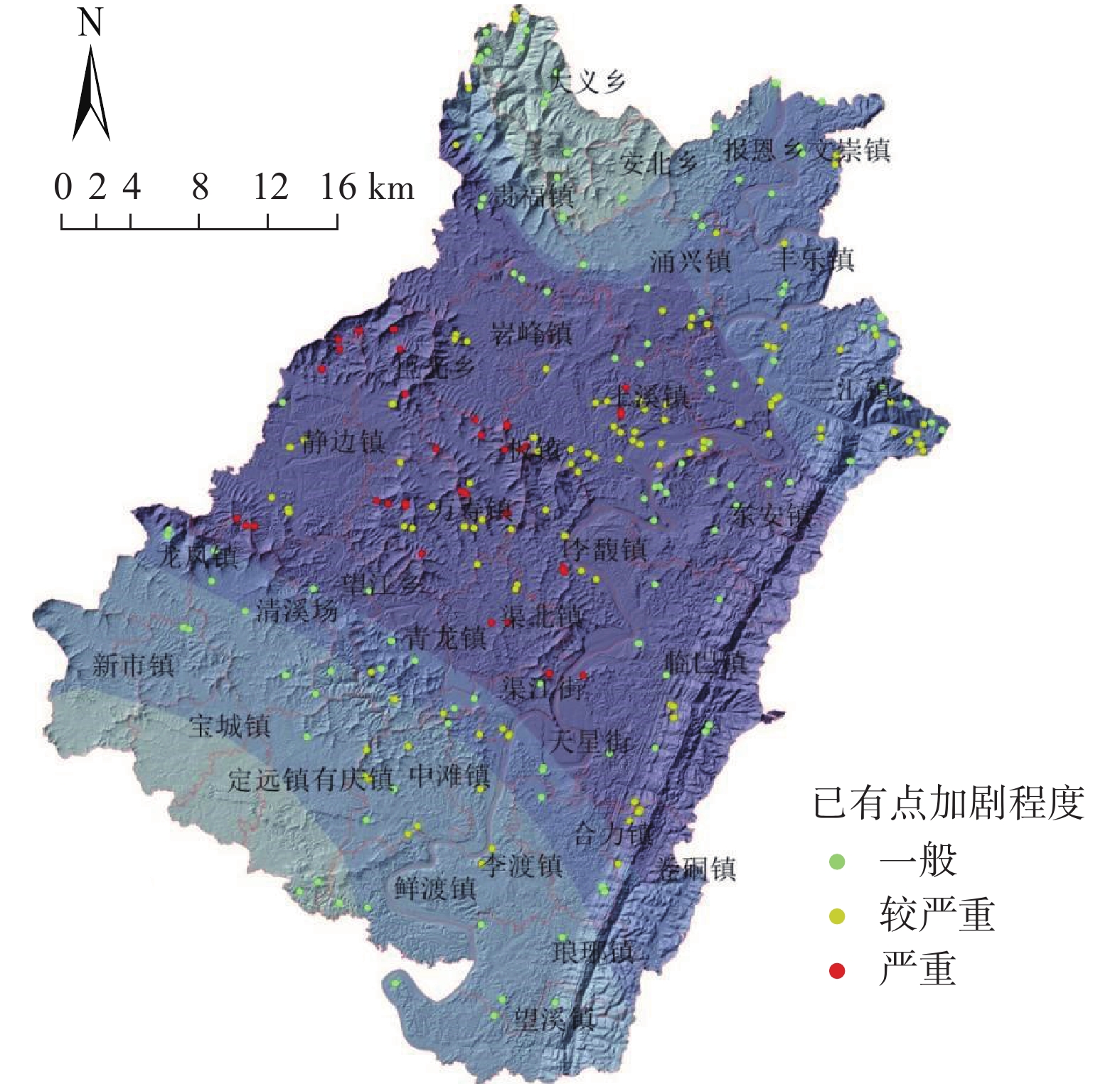
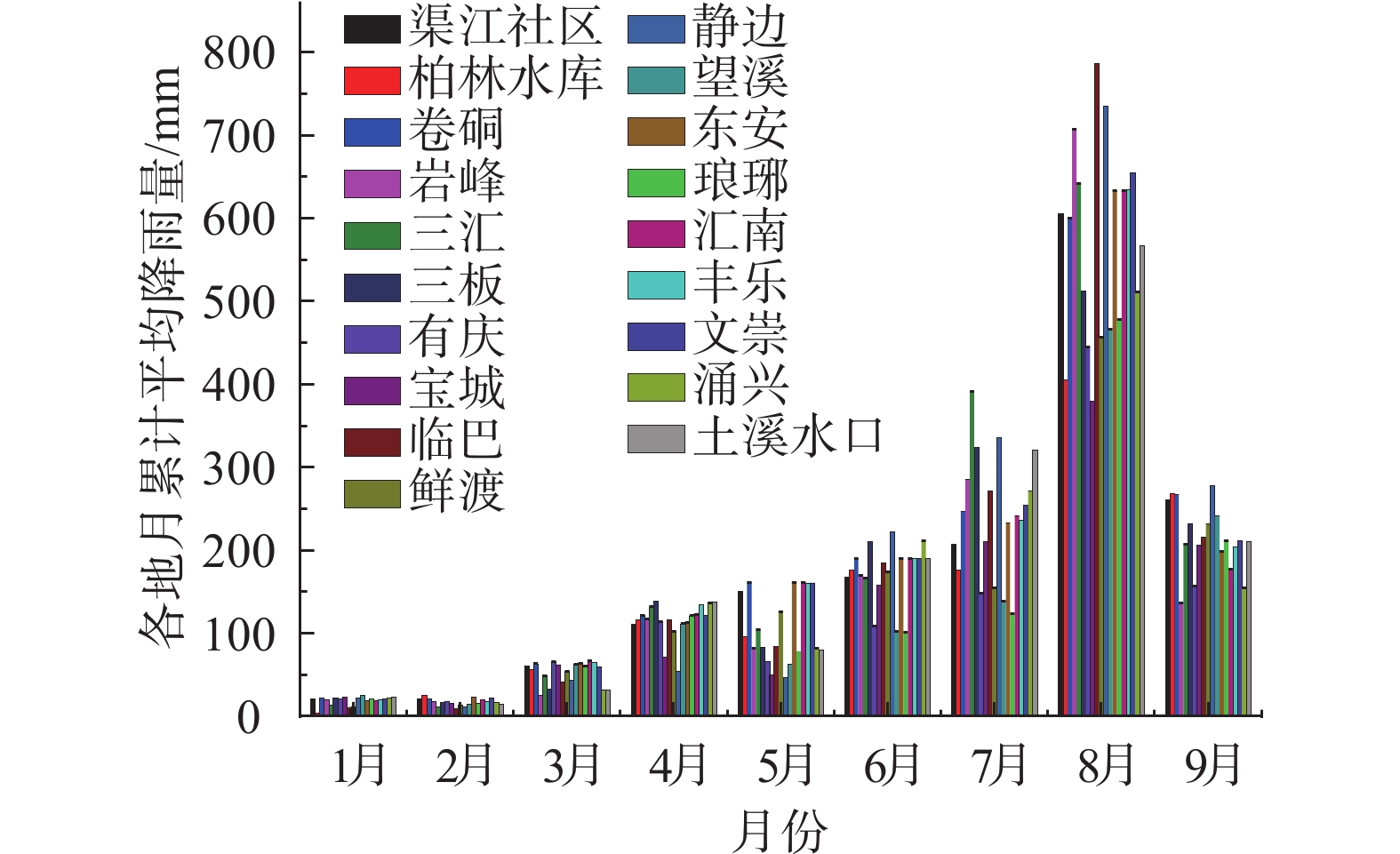
2021年8月8日渠县遭遇特大暴雨袭击,引发新增灾害38处,不同程度加剧已有灾害点109处。文中基于实地调查资料,对特大暴雨引发灾害的特征和孕灾地质条件与灾害分布关系开展研究,对比研究了累计降雨量与新增灾害数量和已有灾害加剧程度之间的关系。结果表明:此次渠县特大暴雨引发新增灾害点主要为土质滑坡,占比94.7%;区域斜坡结构对灾害发生的影响程度最高;土质滑坡集中发生在300~325 mm累计雨量区间,高达27处,变形迹象加剧程度严重的灾害点23处,分布在累计雨量为337~348 mm区间内;为该县地质灾害防治区划与汛期地质灾害防御提供科学依据,为类似地区特大暴雨地质灾害防灾减灾提供参考。
Abstract:On August 8, 2021, Quxian County was hit by a heavy rainstorm, causing 38 new disasters and aggravating 109 existing disasters to varying degrees. Based on field survey , this paper studies the characteristics of disasters caused by heavy rainstorms and the relationship between the hazard including and geological conditions and disaster distribution. The results show that: the new disaster points caused by the heavy rain in Quxian County are mainly soil landslides, accounting for 94.7%; the regional slope structure has the highest impact on the disaster occurrence; Soil landslides occurred in 300~325 mm accumulative rainfall range, up to 27 places; There are 23 disaster points with serious signs of aggravation of deformation, which are distributed in the range of accumulative rainfall of 337~348 mm; It can provide a scientific basis for the county’s geological disaster prevention and control zoning and flood season geological disaster prevention, and can provide a reference for disaster prevention and mitigation of geological disasters in similar areas with heavy rainstorms.
-

-
[1] 铁永波,阮崇飞,杨顺,等. 云南省贡山县“5·25”暴雨诱发地质灾害的特征与形成机制[J]. 水土保持通报,2021,41(2):10 − 15. [TIE Yongbo,RUAN Chongfei,YANG Shun,et al. Characteristics and mechanism of geological disasters induced by “5.25”rainstorm in Gongshan County of Yuanan Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,41(2):10 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 黄玉华,冯卫,李政国. 陕北延安地区2013年“7.3”暴雨特征及地质灾害成灾模式浅析[J]. 灾害学,2014,29(2):54 − 59. [HUANG Yuhua,FENG Wei,LI Zhengguo. Characteristics and geological disaster mode of the rainstorm happened on July 3.2013 in Yanan area of Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2014,29(2):54 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 曾维刚,吴福. 广西北部湾经济区台风暴雨引发的地质灾害风险评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(1):121 − 127. [ZENG Weigang,WU Fu. Risk assessment on geological disaster caused by typhoon and rainstorm in Beibu gulf economic zone of Guangxi zhuang autonomous region[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(1):121 − 127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 纪晓玲,杨婧,朱海斌,等. 宁夏西吉两次诱发地质灾害的极值暴雨对比分析[J]. 灾害学,2016,31(4):54 − 60. [JI Xiaoling,YANG Jing,ZHU Haibin,et al. Comparative analysis of extreme rainstorms inducing geologic hazards in Xiji[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2016,31(4):54 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2016.04.010
[5] 刘艳辉,温铭生,苏永超,等. 台风暴雨型地质灾害时空特征及预警效果分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(5):119 − 126. [LIU Yanhui,WEN Mingsheng,SU Yongchao. et al. Characteristics of geo-hazards induced by typhoon rainstorm and evaluation of geo-hazards early warning[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(5):119 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 黄玉华,武文英,冯卫,等. 陕北延安“7·3暴雨”诱发地质灾害主要类型与特征[J]. 西北地质,2014,47(3):140 − 146. [HUANG Yuhua,WU Wenying,FENG Wei,et al. Main types and characteristics of the geo-hazards triggered by heavy rain on July 3 in Yan’an,Shananxi[J]. Northwestern Geology,2014,47(3):140 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.03.019
[7] 李政国,薛强,张茂省,等. 陕西省延安市地质灾害气象预警信息系统研究—以“7·3”暴雨为例[J]. 灾害学,2016,31(2):69 − 73. [LI Zhengguo,XU Qiang,ZHANG Maosheng,et al. Study on the meteorological early-warning information system of geological disasters in Yanan city of Shaanxi province: Taking the rainstorm of “7·3” as an example[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2016,31(2):69 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2016.02.014
[8] 陈骏峰,杨宜军,王乐新,等. 神农架林区“8·22”暴雨型地质灾害案例分析[J]. 资源环境与工程,2013,27(5):665 − 667. [CHEN Junfeng,YANG Yijun,WANG Lexin,et al. Case study of geological hazards of “8·22”heavy rainfall in Shennongjia forest region[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2013,27(5):665 − 667. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2013.05.012
[9] 唐名富,全洪波,梁文寿,等. 广西龙胜镇浸沟暴雨型泥石流灾变机理及治理效果评价[J]. 现代矿业,2021,37(1):204 − 207. [TANG Mingfu,QUAN Hongbo,LIANG Wenshou,et al. Catastrophic mechanism and evaluation of drought storm debris flow in Longsheng Town,Guangxi Province[J]. Modern Mining,2021,37(1):204 − 207. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 黄楚惠,李国平,张芳丽,等. 近10a气候变化影响下四川山地暴雨事件的演变特征[J]. 暴雨灾害,2020,39(4):335 − 343. [HUANG Chuhui,LI Guoping,ZHANG Fanglil,et al. Evolution characteristics of mountain rainstorms over Sichuan Province in the past ten years under the influence of climate change[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters,2020,39(4):335 − 343. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 唐尧,王立娟,唐梓洋,等. 基于“高分+应急监测”的“8·20”汶川暴雨灾害链灾情分析[J]. 国土资源信息化,2020(3):22 − 27. [TANG Yao,WANG Lijuan,TANG Zhiyang,et al. Disaster analysis of "8·20" Wenchuan rainstorm disaster chain based on "Gaofen + emergency monitoring"[J]. Land and Resources Informatization,2020(3):22 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 顾婷婷,邓闯,潘娅英,等. 基于模糊综合评价法的浙江省高速公路暴雨灾害风险评估[J]. 干旱气象,2018,36(5):873 − 878. [GU Tingting,DENG Chuang,PAN Yaying,et al. Risk division of rainstorm disasters on expressway in Zhejiang Province based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology,2018,36(5):873 − 878. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李守定,乔华,马世伟,等. 基于温度-降雨双参数的新疆地质灾害预警模型[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文),2021,52(11):207 − 218. [LI Shouding,QIAO Hua,MA Shiwei,et al. Temperature-rainfall dual parameter-based early warning model for geological disasters in Xinjiang[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2021,52(11):207 − 218. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李滨,冯振,赵瑞欣,等. 三峡地区“14·9”极端暴雨型滑坡泥石流成灾机理分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):118 − 127. [LI Bing,FENG Zhen,ZHAO Ruixin,et al. Mechanism of “14·9”rainstorm triggered landslides and debris-flows in the Three Gorges area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):118 − 127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 何秉顺. 河南郑州山区4市2021年“7·20”特大暴雨灾害调查的思考与建议[J]. 中国防汛抗旱, 2022
HE Bingshun. Reflections and suggestions on the investigation of the "July 20" severe rainstorm disaster in 4 cities in the mountainous area of Zhengzhou, Henan in 2021[J]. China Flood & Drought Management, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 刘志中,宋英旭,叶润青. 渝东北2014年“8·31”暴雨诱发滑坡遥感解译与分析[J]. 自然资源遥感,2021,33(4):192 − 199. [LIU Zhizhong,SONG Yingxu,YE Runqing. An analysis of rainstorm - induced landslides in northeast Chongqing on August 31,2014 based on interpretation of remote sensing images[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources,2021,33(4):192 − 199. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 陈宫燕,普布桑姆,次仁,等. 西藏林芝降水引发的山洪地质灾害分布特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(2):100 − 103. [CHEN Gongyan,PU Busangmu,CI Ren,et al. Distribution characteristics of mountain flood and geological disaster caused by precipitation of Nyingchi in Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(2):100 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 林虹宇,丁明涛,佘涛,等. 岷江上游典型泥石流活动特征及其易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(4):6 − 15. [LIN Hongyu,DING Mingtao,SHE Tao,et al. Characteristic analysis and susceptibility assessment of the typical debris flow in the upper reaches of Min river[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(4):6 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 杨建林,王来贵,李喜林,等. 粉砂质泥岩遇水损伤规律及化学改性研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2016,35(6):1883 − 1890. [YANG Jianlin,WANG Laigui,LI Xilin,et al. Damage-law of silty-mudstone in water and chemical modification[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2016,35(6):1883 − 1890. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: