Active landslide identification with a combined method of D-InSAR and random forest model
-
摘要:
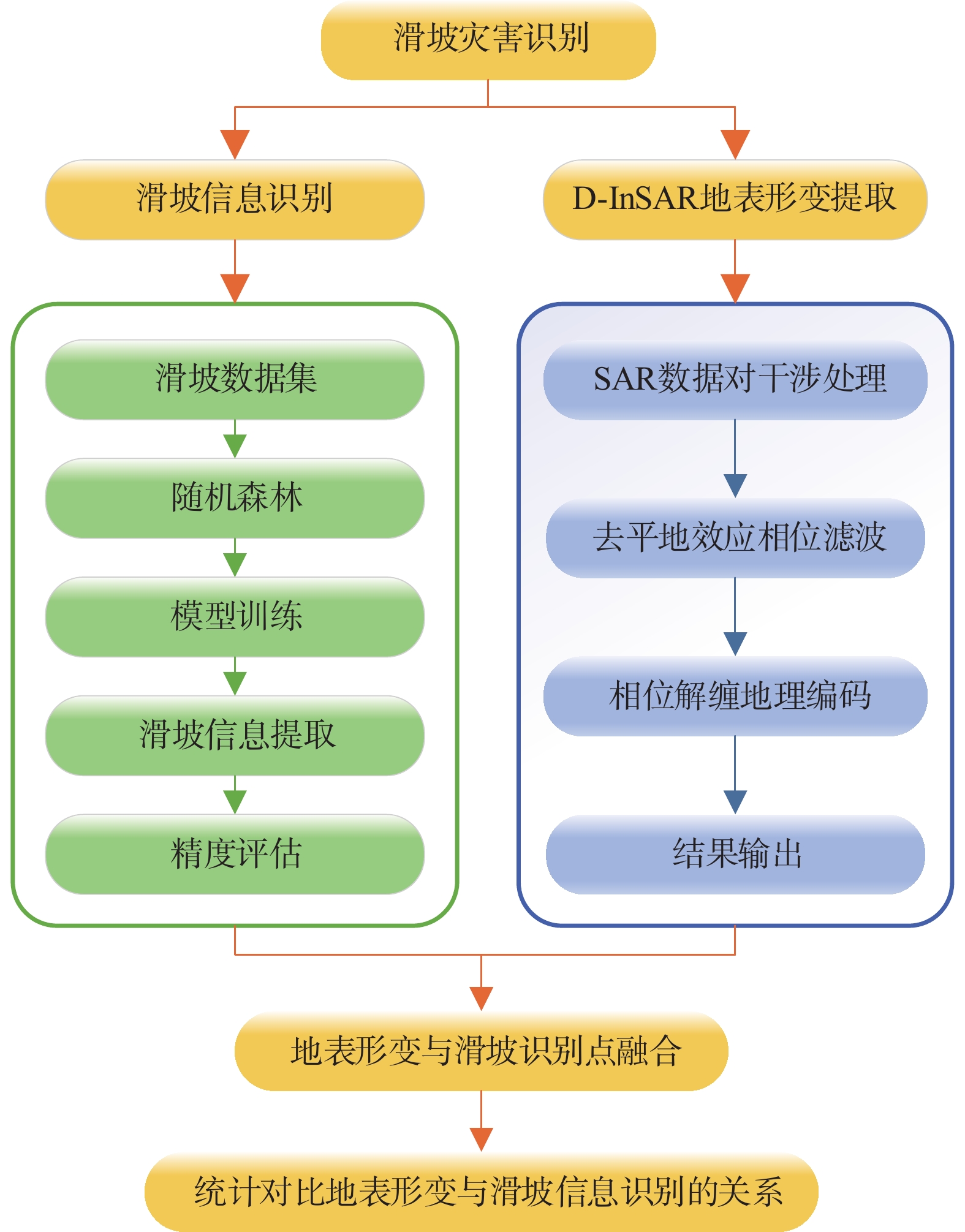
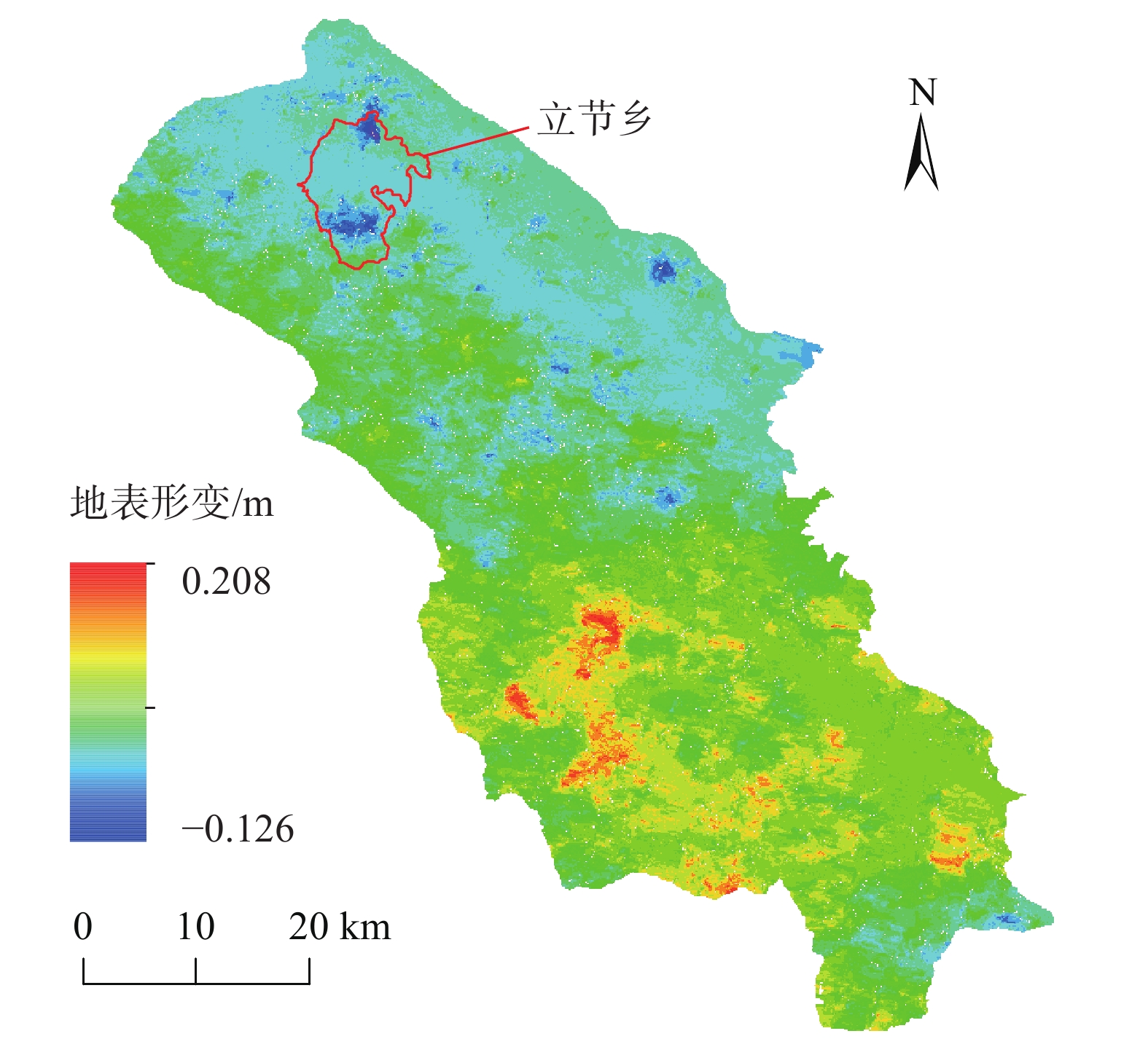
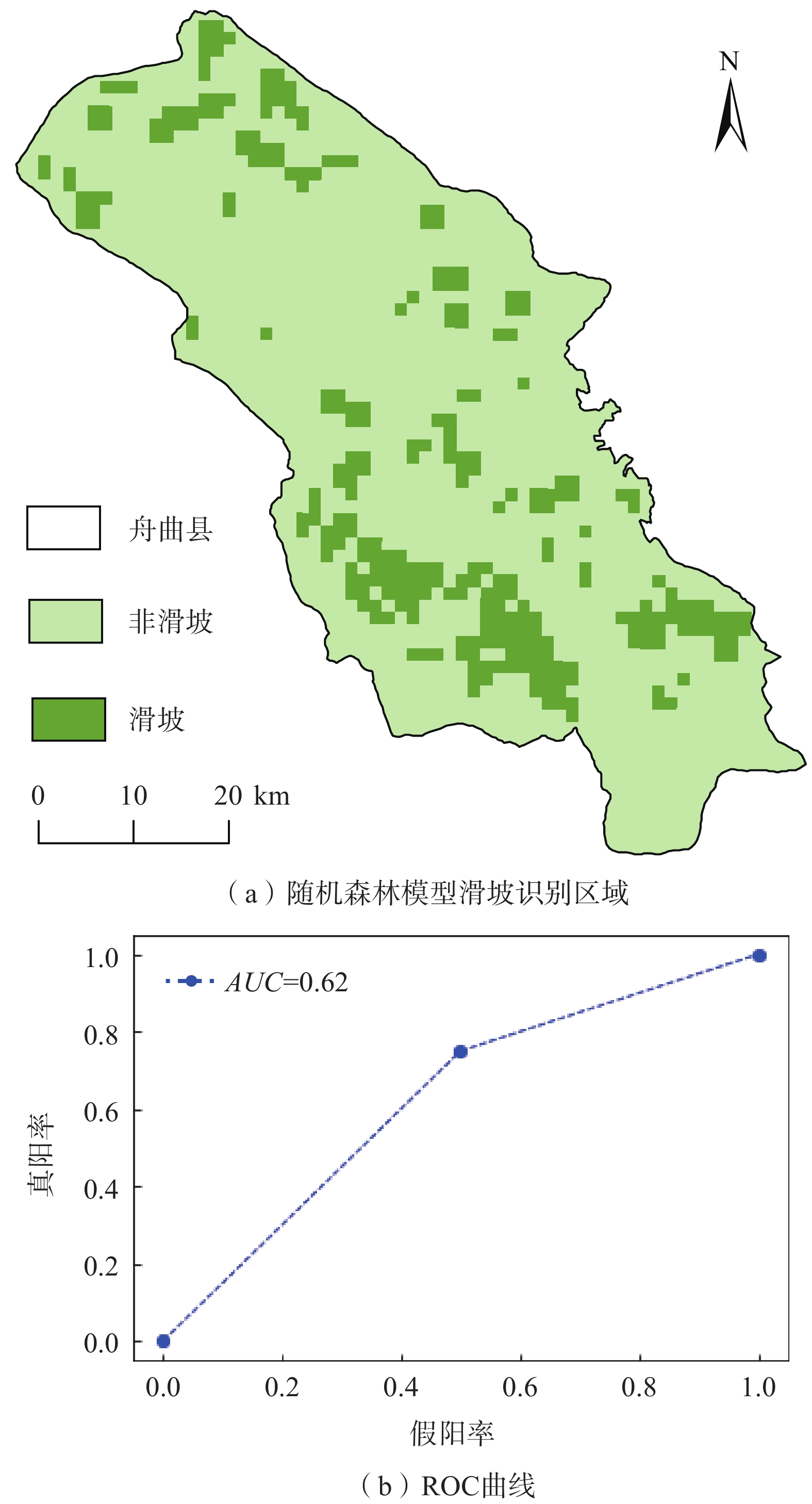
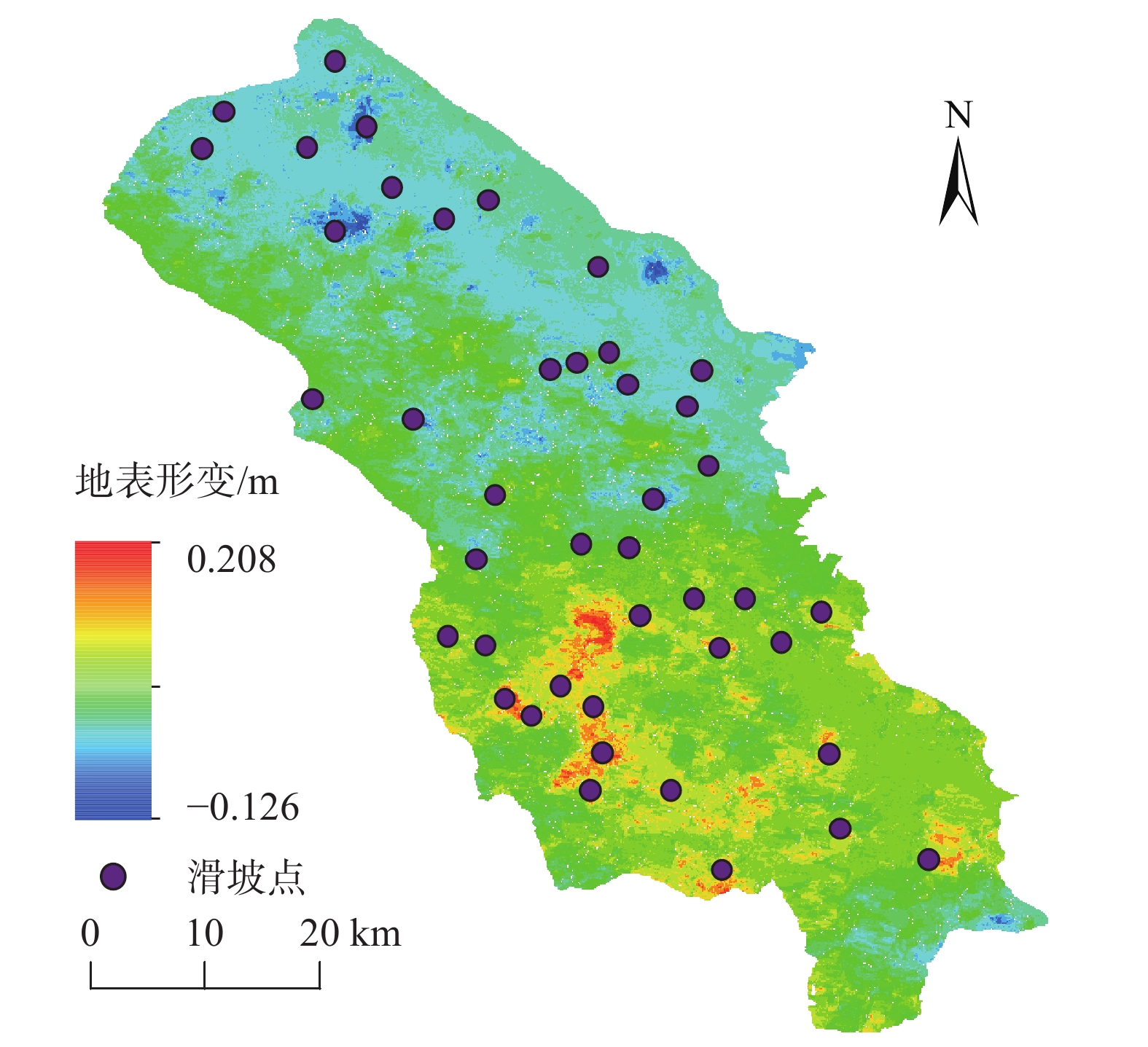
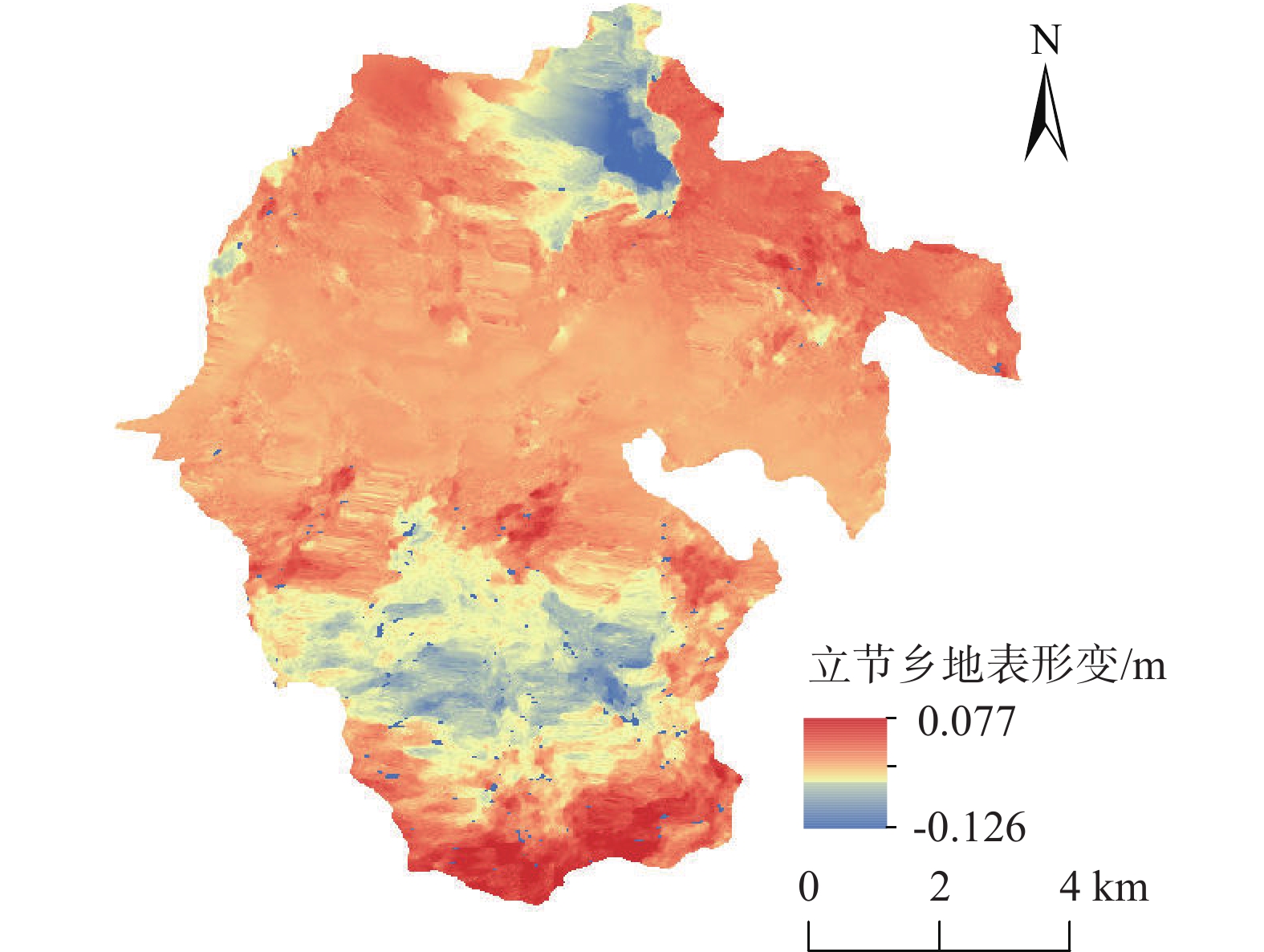
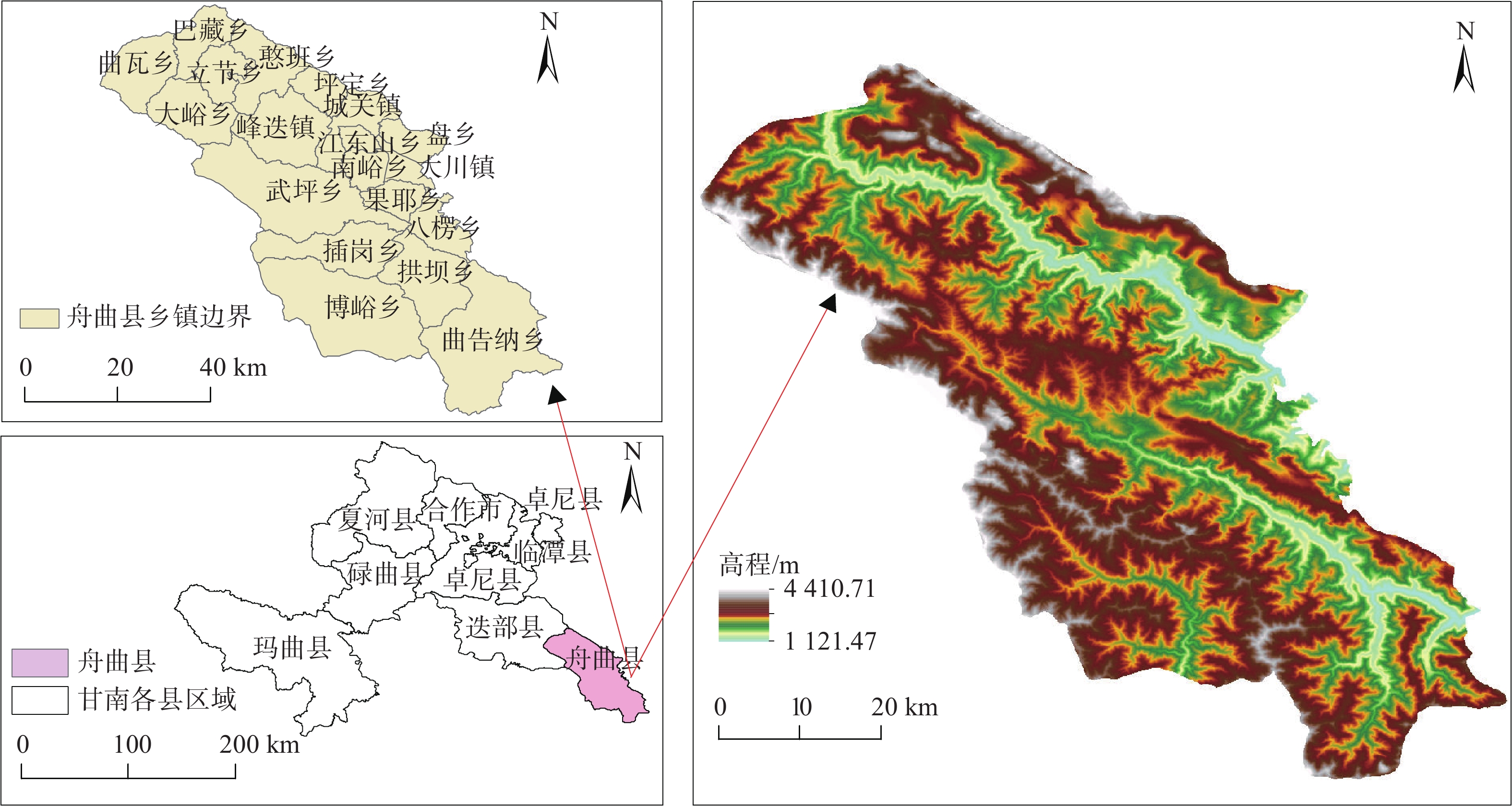
灾害的早期识别是防灾减灾领域的关键技术。文中以甘肃省舟曲县为例,利用2018年1月-2019年1月Sentinel-1A雷达卫星降轨数据和2021年5月Sentinel-2光学遥感影像数据,通过D-InSAR技术获取研究区地表形变信息,利用随机森林模型识别潜在的滑坡体。结果表明:使用已有的滑坡数据集,采用随机森林模型能够较好地识别出潜在滑坡体。潜在滑坡点分布位置均位于地表形变量大的区域。舟曲县整体形变沿东西向发生,主要分布于舟曲县东北和西南方向,与潜在滑坡点高度重合。识别出的潜在滑坡点(立节乡北山滑坡),年形变量达到0.12 m,于2021年1月18日发生滑坡,该滑坡典型案例也印证了文中方法的有效性。
Abstract:Early identification of disaster is a key technical problem in disaster prevention and mitigation. In this study, Zhouqu County, Gansu Province was taken as an example. Based on Sentinel-1A radar satellite orbit landing data from January 2018 to January 2019 and Sentinel-2 optical remote sensing image data from May 2021, D-InSAR technology was used to obtain surface deformation information in the study area, and Random Forest model was used to identify potential landslides. The results show that using the existing landslide data set, the random forest model can identify the potential landslide well. The distribution locations of potential landslide are all located in areas with large surface shape variables. The overall deformation occurred along the east-west direction, mainly distributed in the northeast and southwest directions of Zhouqu County, and overlapped with the potential landslide. The identified potential landslide point (Beishan landslide in Lijie Township) has an annual variable of 0.12 m, and the landslide occurred on January 18, 2021. This typical landslide case also confirms the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- disaster identification /
- InSAR /
- random forest /
- Zhouqu
-

-
表 1 卫星数据参数
Table 1. Satellite data parameters
卫星数据源 轨道方向 波段 中心入射角/(°) 分辨率/m 日期 Sentinel-1A 降轨 C 29~36 5×20 2018-01-21 Sentinel-1A 降轨 C 29~36 5×20 2019-01-04 Sentinel-2 红、绿、蓝 10 2021-05-09 -
[1] 李为乐,许强,陆会燕,等. 大型岩质滑坡形变历史回溯及其启示[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):1043 − 1053. [LI Weile,XU Qiang,LU Huiyan,et al. Tracking the deformation history of large-scale rocky landslides and its enlightenment[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):1043 − 1053. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 代聪,李为乐,陆会燕,等. 甘肃省舟曲县城周边活动滑坡InSAR探测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(7):994 − 1002. [DAI Cong,LI Weile,LU Huiyan,et al. Active landslides detection in Zhouqu County,Gansu Province using InSAR technology[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(7):994 − 1002. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 林荣福,刘纪平,徐胜华,等. 随机森林赋权信息量的滑坡易发性评价方法[J]. 测绘科学,2020,45(12):131 − 138. [LIN Rongfu,LIU Jiping,XU Shenghua,et al. Evaluation method of landslide susceptibility based on random forest weighted information[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2020,45(12):131 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 赵延岭. 基于InSAR技术的树坪滑坡识别与研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2017
ZHAO Yanling. Identification and research of Shuping landslide based on InSAR technology[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 赵超英,刘晓杰,张勤,等. 甘肃黑方台黄土滑坡 InSAR 识别、监测与失稳模式研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):996 − 1007. [ZHAO Chaoying,LIU Xiaojie,ZHANG Qin,et al. Research on loess landslide identification,monitoring and failure mode with InSAR technique in Heifangtai,Gansu[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):996 − 1007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] DONG J,LIAO M S,XU Q,et al. Detection and displacement characterization of landslides using multi-temporal satellite SAR interferometry:A case study of Danba County in the Dadu River Basin[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,240:95 − 109.
[7] 张拴宏,纪占胜. 合成孔径雷达干涉测量(InSAR)在地面形变监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2004,15(1):112 − 117. [ZHANG Shuanhong,JI Zhansheng. A review on the application of interferometric synthetic aperture radar on surface deformation monitoring[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2004,15(1):112 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.01.024
[8] SHIRVANI Z,ABDI O,BUCHROITHNER M. A synergetic analysis of Sentinel-1 and -2 for mapping historical landslides using object-oriented random forest in the Hyrcanian forests[J]. Remote Sens,2019,11(19):2300. doi: 10.3390/rs11192300
[9] PIRALILOU S T,SHAHABI H,JARIHANI B,et al. Landslide detection using multi-scale image segmentation and different machine learning models in the Higher Himalayas[J]. Remote Sensing,2019,11(21):2575. doi: 10.3390/rs11212575
[10] 涂宽,王文龙,谌华,等. 联合升降轨InSAR与高分辨率光学遥感的滑坡隐患早期识别—以宁夏隆德为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):72 − 81. [TU Kuan,WANG Wenlong,CHEN Hua,et al. Early identification of hidden dangers of lanslides based on the combination of ascending and descending orbits InSAR and high spatial resolution optical remote sensing:A case study of landslides in Longde County,southern Ningxia[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):72 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 王高峰,叶振南,李刚,等. 白龙江流域舟曲县城区地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 灾害学,2019,34(3):128 − 133. [WANG Gaofeng,YE Zhennan,LI Gang,et al. Geological hazard risk assessment of Zhouqu County in Bailong River basin[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2019,34(3):128 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2019.03.024
[12] SUN Q,ZHANG L,DING X L,et al. Slope deformation prior to Zhouqu,China landslide from InSAR time series analysis[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2015,156:45 − 57. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.09.029
[13] 张之贤,张强,陶际春,等. 2010年“8·8”舟曲特大山洪泥石流灾害形成的气候特征及地质地理环境分析[J]. 冰川冻土,2012,34(4):898 − 905. [ZHANG Zhixian,ZHANG Qiang,TAO Jichun,et al. Climatic and geological environmental characteristics of the exceptional debris flow outburst in Zhouqu,Gansu Province,on 8 August,2010[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2012,34(4):898 − 905. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 韩旭东,付杰,李严严,等. 舟曲江顶崖滑坡的早期判识及风险评估研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):180 − 186. [HAN Xudong,FU Jie,LI Yanyan,et al. A study of the early identification and risk assessment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):180 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202104028
[15] 戴可人,卓冠晨,许强,等. 雷达干涉测量对甘肃南峪乡滑坡灾前二维形变追溯[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(12):1778 − 1786. [DAI Keren,ZHUO Guanchen,XU Qiang,et al. Tracing the pre-failure two-dimensional surface displacements of Nanyu landslide,Gansu Province with radar interferometry[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(12):1778 − 1786. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] JI S,YU D W,SHEN C Y,et al. Landslide detection from an open satellite imagery and digital elevation model dataset using attention boosted convolutional neural networks[J]. Landslides,2020,17(6):1337 − 1352. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01353-2
[17] 郝国栋. 基于随机森林模型的商南县滑坡易发性评价[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2019
HAO Guodong. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on random forest model in Shangnan County[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] GHORBANZADEH O,BLASCHKE T,GHOLAMNIA K,et al. Evaluation of different machine learning methods and deep-learning convolutional neural networks for landslide detection[J]. Remote Sens,2019,11(2):196. doi: 10.3390/rs11020196
-



 下载:
下载: