Analysis and risk evaluation of current land subsidence in Ningbo City
-
摘要:
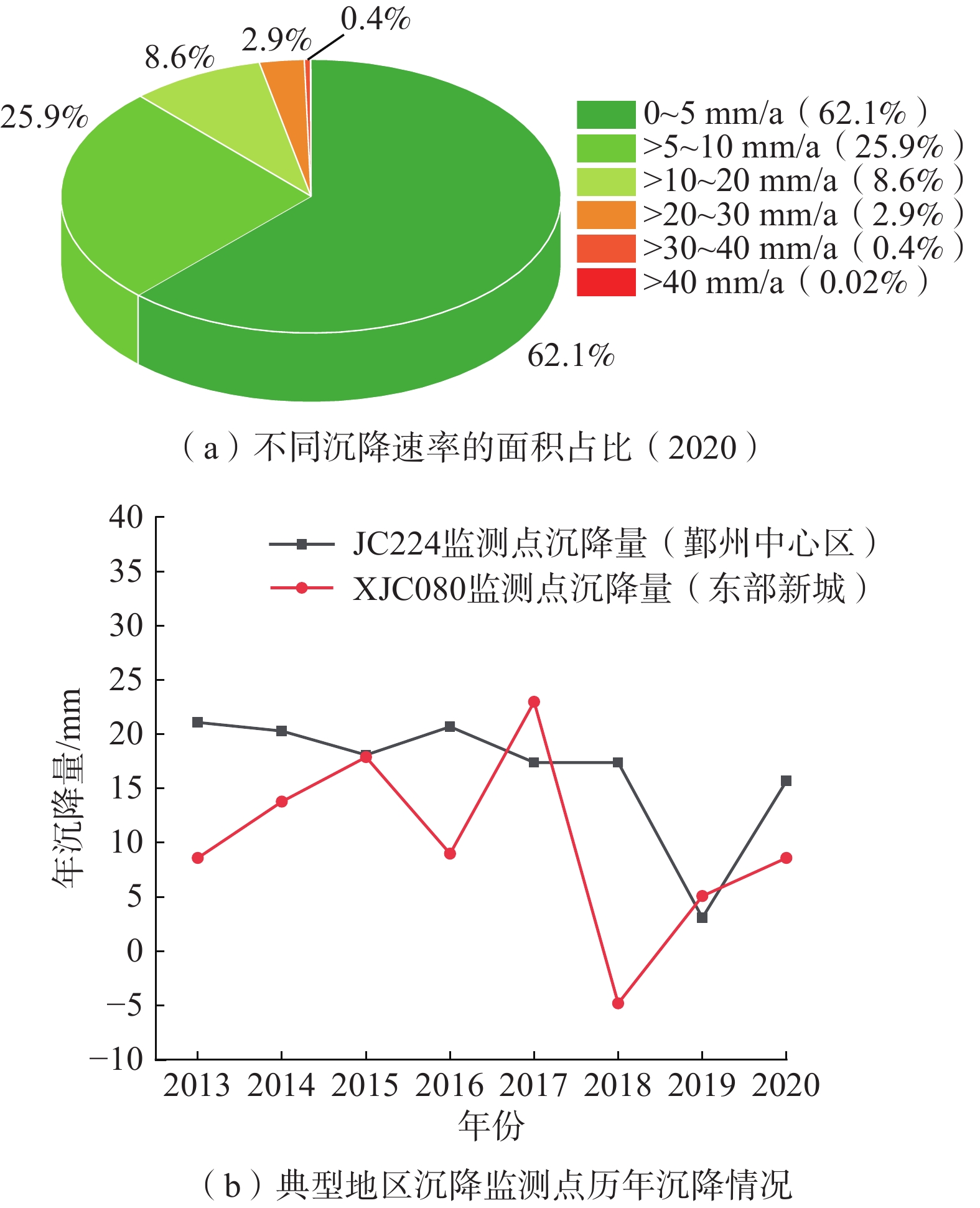
针对宁波市地面沉降发展现状及风险评价需求,结合2017—2020年的InSAR遥感监测数据与沉降点监测数据,对近年地面沉降特征进行了分析。在此基础上建立了包括地面高程、沉降易发程度、地面累计沉降量、沉降速率、城市人口密度、建设用地占比重等6个评价因子为主的地面沉降风险评价体系。其中沉降易发程度为综合考虑地质条件、水文地质条件、人为活动影响后的综合性评价因子。地面沉降风险评价结果表明:宁波市地面沉降无高易发区,中、低易发区主要与区内全新世软土层厚大、历史上大量开采地下水、局部高强度城市建设以及沿海围垦工程等因素有关。最后,划分了地面沉降中风险区、低风险区、风险防控带,并提出了相应的地面沉降风险区管控建议。
Abstract:In response to evaluating the current status and assessing the risk assessment requirements of land subsidence in Ningbo City, the characteristics of land subsidence in recent years were analyzed using InSAR remote sensing monitoring data and subsidence point monitoring data from 2017 to 2020. Based on this analysis, a land subsidence risk assessment system has been developed, primarily consisting of six evaluation factors, including ground elevation, susceptibility to subsidence, cumulative ground subsidence, subsidence rate, urban population density, and the proportion of construction land usage. The susceptibility to subsidence is a comprehensive evaluation factor that takes into account geological conditions, hydrogeological conditions, and the impact of human activities. The results of the land subsidence risk assessment indicate that there are no high-risk susceptibility zones for land subsidence in Ningbo City. Medium and low-risk susceptibility zones are primarily associated with factors such as the thick layers of the Holocene soft soil, historical excessive groundwater extraction, localized high-intensity urban development, and coastal land reclamation projects within the region. Finally, the areas were categorized into medium-risk, low-risk, and risk prevention zones, along with corresponding control recommendations for land subsidence risk management.
-

-
表 1 地面沉降风险区划影响因素数据来源
Table 1. Data sources of influencing factors for land subsidence risk zoning
序号 沉降带名称 沉降中心 1 杭州湾—泗门沉降带 前湾新区余姚泗门 2 龙山—澥浦—招宝山沉降带 镇海化工区 3 新碶—霞浦—大榭沉降带 新碶大榭沿海区域 4 瞻岐—春晓—梅山沉降带 大嵩新区、春晓梅山围填海区 5 余姚凤山—阳明—
河姆渡沉降带凤山、阳明街道 6 骆驼—庄桥—洪塘—
高桥—集士港沉降带骆驼、庄桥、洪塘街道、
高桥、集士港镇7 东部—鄞南—江口—
西坞沉降带高新区、东部新城、南部商务区、
江口、西坞街道8 环象山港沉降带 奉化莼湖、松岙、象山西周、贤庠 9 新桥—东陈—丹城—
大徐沉降带新桥、大目湾新城、大徐 10 长街—高塘—南田沉降带 南部滨海新区、象山高塘、南田 表 2 地面沉降风险区划影响因素权重及分级
Table 2. Weight and classification of factors influencing land subsidence risk zoning
影响因素 权重
(aj)影响因素分级及分值(bj) 3 2 1 地质条件 地面高程/m 0.2 <2 2~4 >4 易发程度 0.1 高易发 中易发 低易发 沉降特征 地面累计沉降量/mm 0.2 >1 000 500~1 000 <500 沉降速率/(mm·a−1) 0.3 >40 20~40 <20 社会经济
发展指标城市人口密度/(万人·km−2) 0.1 0.2 0.1~<0.2 <0.1 建设用地比重/% 0.1 >60 30~60 <30 表 3 地面沉降风险区等级划分表
Table 3. Classification table of land subsidence risk zone levels
风险区等级 高风险区 中风险区 低风险区 地面沉降综合风险指数(W) >2.5~3.0 1.5~2.5 <1.5 表 4 地面沉降风险区划影响因素数据来源
Table 4. Data sources of influencing factors for land subsidence risk zoning
数据名称 单位 数据来源 地面高程 m 2019年宁波市各区县高程数字模型
(1∶10 000 DEM)易发程度 依据《地质灾害危险性评估规范》
(DB33/T 881—2012)的计算结果地面累计
沉降量mm InSAR遥感监测数据与沉降点监测数据 沉降速率 mm·a−1 InSAR遥感监测数据与沉降点监测数据 城市人口
密度万人·km−2 宁波市统计年鉴(2020) 建设用地
比重% 第三次全国国土调查成果(2020) 表 5 宁波市地面沉降风险区管控建议一览表
Table 5. Summary of control recommendations for ground subsidence risk zones in Ningbo City
风险区等级 面积/km2 管控建议 地面沉降
中风险区132.6 ①严格执行地下水禁、限采区管理要求;
②进一步完善“空天地一体化”监测网络,提高地下水位、地面沉降监测频率,提高围填海区域的监测点密度;
③加强重大工程建设项目地面沉降综合防治方案制定;
④加强地面沉降网络和数据库建设,形成与城市线状市政工程建设、运营单位的沉降监测数据共享,各方协同防治沉降的机制地面沉降
低风险区2 214.8 ①继续严格贯彻地下水禁、限采区管理要求;
②进一步完善和优化地面沉降和地下水监测网络,加强日常监管;
③合理布局城市建设规划,加强深基坑等工程建设活动引发的地面沉降监测与管理地面沉降
风险防控带①加强高铁、轨道交通沿线两侧的地下水开发利用及邻近工程降排水管理;
②推进沿线地面沉降监测及系统预警机制建设,加强建设与重大工程密切相关的浅部含水层地下水监测井,完善地面沉降监测网络。 -
[1] 王福刚,梁秀娟,于军. 可视化地层模型信息系统在地面沉降研究中的应用[J]. 岩土工程学报,2005,27(2):219 − 223. [WANG Fugang,LIANG Xiujuan,YU Jun. The application of the information system of visualized strata model to the research of land subsidence in Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2005,27(2):219 − 223. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Fugang, LIANG Xiujuan, YU Jun . The application of the information system of visualized strata model to the research of land subsidence in Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2005 ,27 (2 ):219 −223 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 刘传正,陈春利. 中国地质灾害防治成效与问题对策[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):375 − 383. [LIU Chuanzheng,CHEN Chunli. Achievements and countermeasures in risk reduction of geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):375 − 383. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Chuanzheng, CHEN Chunli . Achievements and countermeasures in risk reduction of geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020 ,28 (2 ):375 −383 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 葛伟丽,李元杰,张春明,等. 基于InSAR技术的内蒙古巴彦淖尔市地面沉降演化特征及成因分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(4):198 − 206. [GE Weili,LI Yuanjie,ZHANG Chunming,et al. An attribution analysis of land subsidence features in the city of Bayannur in Inner Mongolia based on InSAR[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(4):198 − 206. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GE Weili, LI Yuanjie, ZHANG Chunming, et al . An attribution analysis of land subsidence features in the city of Bayannur in Inner Mongolia based on InSAR[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022 ,49 (4 ):198 −206 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] 何健辉,张进才,陈勇,等. 基于弱光栅技术的地面沉降自动化监测系统[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):146 − 153. [HE Jianhui,ZHANG Jincai,CHEN Yong,et al. Automatic land subsidence monitoring system based on weak-reflection fiber gratings[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):146 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HE Jianhui, ZHANG Jincai, CHEN Yong, et al . Automatic land subsidence monitoring system based on weak-reflection fiber gratings[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (1 ):146 −153 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 张严,朱武,赵超英,等. 佛山地铁塌陷InSAR时序监测及机理分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(4):1167 − 1177. [ZHANG Yan,ZHU Wu,ZHAO Chaoying,et al. Moniting and inversion of Foshan metro collapse with multi-temporal insar and field investigation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(4):1167 − 1177. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Yan, ZHU Wu, ZHAO Chaoying, et al . Moniting and inversion of Foshan metro collapse with multi-temporal insar and field investigation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021 ,29 (4 ):1167 −1177 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 张阿根,吴建中. 上海地面沉降管理对策与法制建设[J]. 城市地质,2006,1(2):55 − 59. [ZHANG Agen,WU Jianzhong. Management countermeasures and legal system construction for land subsidence in Shanghai[J]. City Geology,2006,1(2):55 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Agen, WU Jianzhong . Management countermeasures and legal system construction for land subsidence in Shanghai[J]. City Geology,2006 ,1 (2 ):55 −59 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] 赵团芝,侯艳声,胡新锋. 浙江宁波工程性地面沉降特征与风险区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(4):36 − 42. [ZHAO Tuanzhi,HOU Yansheng,HU Xinfeng. Characteristic analysis and risk zoning of engineering land subsidence in Ningbo City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(4):36 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Tuanzhi, HOU Yansheng, HU Xinfeng . Characteristic analysis and risk zoning of engineering land subsidence in Ningbo City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015 ,26 (4 ):36 −42 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 赵团芝,侯艳声,胡新锋. 宁波市工程性地面沉降成因分析及防治对策研究[J]. 上海国土资源,2016,37(3):60 − 64. [ZHAO Tuanzhi,HOU Yansheng,HU Xinfeng. Engineering-related land subsidence in Ningbo City:An analysis of its causes and countermeasures[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources,2016,37(3):60 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Tuanzhi, HOU Yansheng, HU Xinfeng . Engineering-related land subsidence in Ningbo City: An analysis of its causes and countermeasures[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources,2016 ,37 (3 ):60 −64 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 赵庆香,黄岁梁,杜晓燕. 天津市地面沉降风险分析研究[J]. 中国公共安全(学术版),2007(3):48 − 53. [ZHAO Qingxiang,HUANG Suiliang,DU Xiaoyan. Risk analysis on land subsidence in Tianjin[J]. China Public Security (Academy Edition),2007(3):48 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Qingxiang, HUANG Suiliang, DU Xiaoyan . Risk analysis on land subsidence in Tianjin[J]. China Public Security (Academy Edition),2007 (3 ):48 −53 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 胡蓓蓓,姜衍祥,周俊,等. 天津市滨海地区地面沉降灾害风险评估与区划[J]. 地理科学,2008,28(5):693 − 697. [HU Beibei,JIANG Yanxiang,ZHOU Jun,et al. Assessment and zonation of land subsidence disaster risk of Tianjin Binhai area[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2008,28(5):693 − 697. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HU Beibei, JIANG Yanxiang, ZHOU Jun, et al . Assessment and zonation of land subsidence disaster risk of Tianjin Binhai area[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2008 ,28 (5 ):693 −697 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 胡喜梅,马传明,邓波,等. 江苏省沿海地区地面沉降风险评价[J]. 地质科技情报,2017,36(2):222 − 228. [HU Ximei,MA Chuanming,DENG Bo,et al. Risk evaluation of land subsidence in coastal areas of Jiangsu Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2017,36(2):222 − 228. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HU Ximei, MA Chuanming, DENG Bo, et al . Risk evaluation of land subsidence in coastal areas of Jiangsu Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2017 ,36 (2 ):222 −228 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 张彭,朱邦彦,孙静雯,等. 利用多源数据分析南京市河西地面沉降风险[J]. 测绘通报,2019(11):141 − 144. [ZHANG Peng,ZHU Bangyan,SUN Jingwen,et al. Risk analysis of land subsidence in Hexi area in Nanjing based on multi-source data[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2019(11):141 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Peng, ZHU Bangyan, SUN Jingwen, et al . Risk analysis of land subsidence in Hexi area in Nanjing based on multi-source data[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2019 (11 ):141 −144 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 房浩,何庆成,徐斌,等. 沧州地区地面沉降灾害风险评价研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):159 − 164. [FANG Hao,HE Qingcheng,XU Bin,et al. A study of risk assessment of the land subsidence in Cangzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):159 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FANG Hao, HE Qingcheng, XU Bin, et al . A study of risk assessment of the land subsidence in Cangzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016 ,43 (4 ):159 −164 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 陈蓓蓓. 北京地区地面沉降监测及风险评价研究[D]. 北京:首都师范大学,2009. [CHEN Beibei. Study on land subsidence monitoring and risk assessment in Beijing area[D]. Beijing:Capital Normal University,2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Beibei. Study on land subsidence monitoring and risk assessment in Beijing area[D]. Beijing: Capital Normal University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 王齐鑫,王龙平,王泽宇. 安徽阜阳中心城区地面沉降灾害风险评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(4):32 − 39. [WANG Qixin,WANG Longping,WANG Zeyu. Risk assessment of land subsidence in central area of Fuyang City,Anhui Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(4):32 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Qixin, WANG Longping, WANG Zeyu . Risk assessment of land subsidence in central area of Fuyang City, Anhui Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019 ,30 (4 ):32 −39 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 于海若,宫辉力,陈蓓蓓,等. 京津冀地区地面沉降研究进展与思考[J]. 测绘科学,2020,45(4):125 − 133. [YU Hairuo,GONG Huili,CHEN Beibei,et al. The advance and consideration of land subsidence in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2020,45(4):125 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YU Hairuo, GONG Huili, CHEN Beibei, et al . The advance and consideration of land subsidence in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2020 ,45 (4 ):125 −133 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] 戴真印,刘岳霖,张丽平,等. 基于改进时序InSAR技术的东莞地面沉降时空演变特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(1):58 − 67. [DAI Zhenyin,LIU Yuelin,ZHANG Liping,et al. Temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of land subsidence in Dongguan based on improved time series InSAR technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(1):58 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DAI Zhenyin, LIU Yuelin, ZHANG Liping, et al . Temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of land subsidence in Dongguan based on improved time series InSAR technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (1 ):58 −67 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 李佳琦,徐佳,刘杰,等. 天津地面沉降严重区分布特征及变化规律[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(2):53 − 60. [LI Jiaqi,XU Jia,LIU Jie,et al. Distribution characteristics and evolution trend of severe land subsidence areas in Tianjin City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(2):53 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Jiaqi, XU Jia, LIU Jie, et al . Distribution characteristics and evolution trend of severe land subsidence areas in Tianjin City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (2 ):53 −60 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] 王寒梅. 上海市地面沉降风险评价体系及风险管理研究[D]. 上海:上海大学,2013. [WANG Hanmei. Study on risk assessment system and risk management of land subsidence in Shanghai[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai University,2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Hanmei. Study on risk assessment system and risk management of land subsidence in Shanghai[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 吴柯,张晓平,刘浩,等. 粉质黏土地层超大直径泥水盾构隧道地表变形与施工参数相关关系研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(5):1555 − 1566. [WU Ke,ZHANG Xiaoping,LIU Hao,et al. Correlation between surface deformation and construction parameters in silty clay ground tunneling with super large diameter slurry shield tbm[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(5):1555 − 1566. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Ke, ZHANG Xiaoping, LIU Hao, et al . Correlation between surface deformation and construction parameters in silty clay ground tunneling with super large diameter slurry shield tbm[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021 ,29 (5 ):1555 −1566 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] 苏秀婷,陈健,李明宇,等. 大直径泥水盾构隧道穿越复杂环境地层变形敏感性研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(5):1587 − 1598. [SU Xiuting,CHEN Jian,LI Mingyu,et al. Sensitivity analysis of deformation of large diameter mudwater shield through complex environment[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(5):1587 − 1598. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0528
SU Xiuting, CHEN Jian, LI Mingyu, et al . Sensitivity analysis of deformation of large diameter mudwater shield through complex environment[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021 ,29 (5 ):1587 −1598 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[22] 王小军,蒋勇,王文笛,等. 宁波滨海软土地铁盾构隧道地表沉降效应与数值模拟研究[J]. 路基工程,2018(4):61 − 68. [WANG Xiaojun,JIANG Yong,WANG Wendi,et al. Research on ground surface settlement effect and numerical simulation of shield tunnel of subway in soft soil of coast in Ningbo[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2018(4):61 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.2018.04.11
WANG Xiaojun, JIANG Yong, WANG Wendi, et al . Research on ground surface settlement effect and numerical simulation of shield tunnel of subway in soft soil of coast in Ningbo[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2018 (4 ):61 −68 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[23] 浙江省质量技术监督局. 地质灾害危险性评估规范:DB33/T 881—2012[S]. 北京:中国地质大学出版社,2012. [Code for risk assessment of geological disaster: DB33/T 881-2012[S]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences Press,2012. (in Chinese)
Code for risk assessment of geological disaster: DB33/T 881-2012[S]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences Press, 2012. (in Chinese) -




 下载:
下载: