Mechanistic analysis of loess landslide reactivation in northern Shaanxi based on coupled numerical modeling of hydrological processes and stress strain evolution: A case study of the Erzhuangkelandslide in Yan’an
-
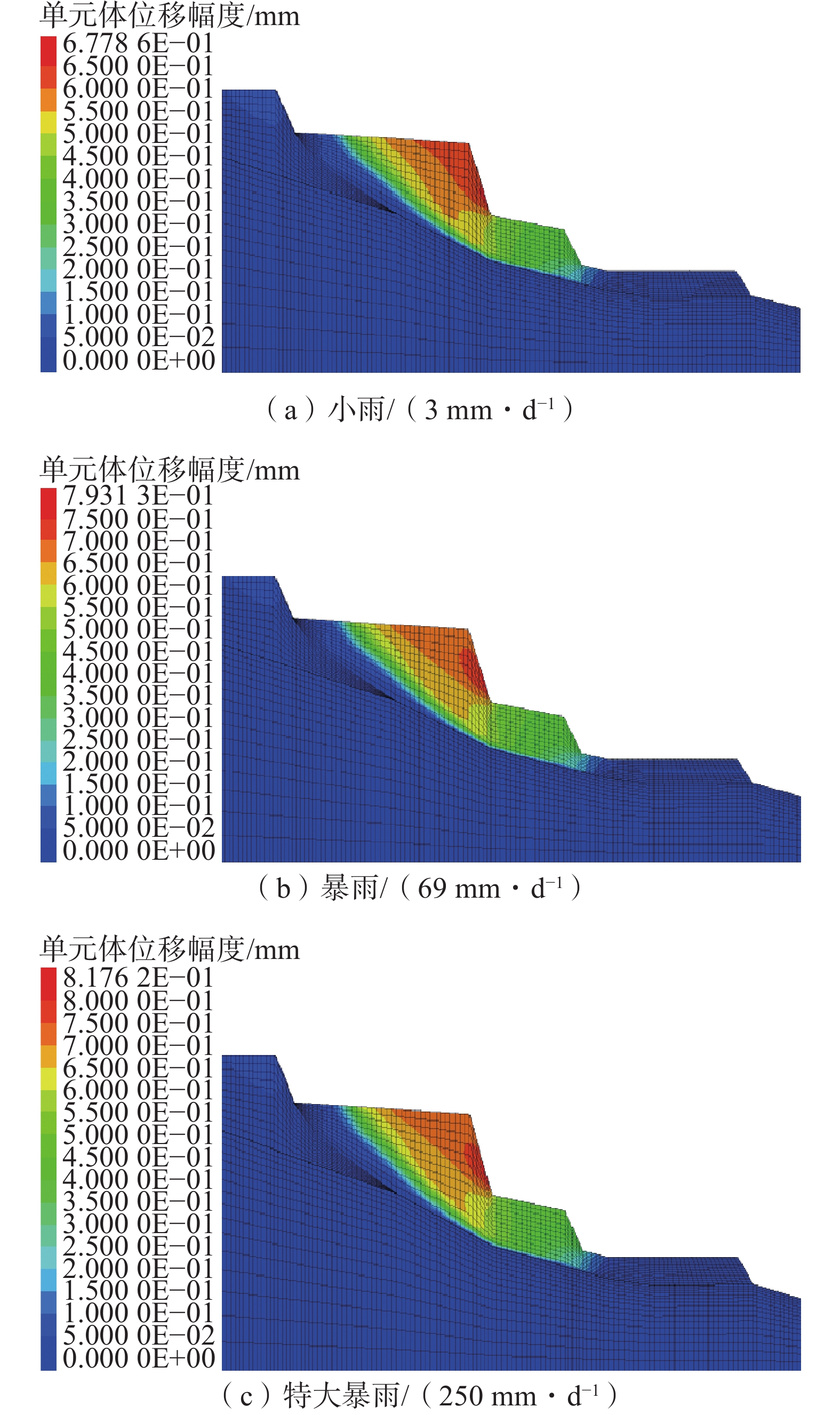
摘要:
二庄科滑坡是典型受降雨影响的滑坡,降雨改变了老滑坡的渗流场,削弱基质吸力和土体抗剪强度,导致内部产生张拉裂缝,引发整体滑动和局部大变形,但现有研究很少考虑二庄科滑坡的渗流场与应力场的相互作用。文章基于实际工程地质灾害背景,在现场监测数据和地形物理参数的基础上,建立了几何计算模型,并进行水力耦合数值模拟。通过研究滑坡内部饱和度和孔压的变化规律来探讨降雨入渗规律,从应力位移的角度探讨降雨强度对滑坡复活的影响规律。此外,为了验证方法的准确性和可行性,选取了滑坡实测点位并找到了数值模型对应位置,对位移、土压力和饱和度三个方面进行了对比分析,得出数值模型能较好地反映实际情况的结论。通过数值模拟耦合计算和降雨条件下老滑坡复活机制的研究,对实测数据进行解释并分析滑坡复活过程,为后续工程预警和减灾工作提供理论基础和技术指导。
Abstract:The Erzhuangke landslide is a typical landslide affected by the rainy season. Rainfall changes the seepage pattern with the pre-existing landslide, weakening matric suction and soil shear strength, leading to the formation of tension cracks internally. This triggers overall sliding and localized extensive deformations. Existing studies seldom considers the interaction between the seepage field and stress field of the Erzhuangke landslide. Therefore, based on the actual engineering geological disaster scenarios, supported by on-site monitoring data and terrain physical parameters, a geometric computational model is established, and hydraulic coupled numerical simulations are conducted. By investigating variations in saturation and pore pressure within the landslide, the paper explores the rainfall infiltration patterns. It examines the impact of rainfall intensity on landslide reactivation from the perspective of stress displacement. In addition, in order to validate the accuracy and feasibility of the method, selected measurement points from the landslide are matched with corresponding positions in the numerical model. Comparative analysis is performed on displacement, soil pressure, and saturation aspects, confirming that the numerical model effectively reflects the actual situation. Through coupling numerical simulations and the study of the reactivation mechanism of the old landslide under rainfall conditions, the paper interprets field data, analyzes the reactivation process, and provides theoretical foundations and technical guidance for subsequent engineering early warning and disaster mitigation works.
-

-
图 2 工程地质灾害监测点分布图[10]
Figure 2.
表 1 模型参数设置
Table 1. Table of model parameter settings
土体类型 密度/(kg∙m−3) 体积模量/Pa 孔隙率 饱和渗透系数/(m∙s−1) 内摩擦角/(°) 黏聚力/Pa 剪切模量/Pa 初始孔隙压力/Pa Qh 1900 2×108 0.40 3.9×10−4 18 3×104 — 21977 Qp 1900 2×108 0.40 3.9×10−4 18 3×104 — 21977 砂岩 2800 1×109 0.15 1×10−12 36 1.2×106 3×108 0 表 2 G6点竖向位移实际模拟数据对比
Table 2. Comparison of actual and simulated vertical displacements for monitoring point G6
日期 2021-10-28 2021-10-29 2021-10-30 2021-10-31 实际数据/mm 239.01 241.03 242.00 243.04 模拟数据/mm 202.98 209.76 214.31 219.05 误差/% 15.07 12.97 11.44 9.87 表 3 G7点竖向位移实际模拟数据对比
Table 3. Comparison of actual and simulated vertical displacements for monitoring point G7
日期 2021-10-10 2021-10-11 2021-10-12 2021-10-13 实际数据/mm −2.014 −2.991 −4.028 −4.028 模拟数据/mm 1.630 2.370 2.610 2.780 误差/% 180.93 179.24 164.80 169.02 表 4 G6点水平位移实际模拟数据对比
Table 4. Comparison of actual and simulated horizontal displacements for monitoring point G6
日期 2021-10-15 2021-10-16 2021-10-17 2021-10-18 实际数据/mm 109.50 111.35 113.32 117.00 模拟数据/mm 102.85 106.15 107.12 107.97 误差/% 6.07 4.67 5.47 7.72 表 5 G7点水平位移实际模拟数据对比
Table 5. Comparison of actual and simulated horizontal displacements for monitoring point G7
日期 2021-10-12 2021-10-13 2021-10-14 2021-10-15 实际数据/mm 9.249 14.798 20.348 24.093 模拟数据/mm 4.090 4.170 4.400 5.670 误差/% 55.7 71.82 78.38 76.47 -
[1] 刘子振. 持续降雨入渗非饱和黏土边坡失稳机理及其应用研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学,2014. [LIU Zizhen. Instability mechanism and application analysis of partially saturated clay slope under sustained rainfall infiltration[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University,2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Zizhen. Instability mechanism and application analysis of partially saturated clay slope under sustained rainfall infiltration[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 吴小策. 降雨入渗对土石混合体边坡稳定性影响机理研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2010:1 − 6. [WU Xiaoce. Study on influence mechanism of rainfall infiltration on stability of soil-rock mixture slope[D]. Changsha:Central South University,2010:1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Xiaoce. Study on influence mechanism of rainfall infiltration on stability of soil-rock mixture slope[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010: 1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] GREEN W H,AMPT G A. studies on soil physics:Flow of air and water through soils[J]. Jagr Sci,1911,4(1):1 − 24.
[4] XIAO Zhenghua,HAN Bo,TUOHUTI A,et al. Stability analysis of earth dam under unsaturated seepage[C]//Advanced Materials Research. Trans Tech Publications Ltd,2008,33:1129 − 1134.
[5] LIU Zizhen,YAN Zhixin,QIU Zhanhong,et al. Stability analysis of an unsaturated soil slope considering rainfall infiltration based on the Green-Ampt model[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2020,17(10):2577 − 2590. doi: 10.1007/s11629-019-5744-9
[6] 孙永帅,贾苍琴,王贵和. 降雨对边坡稳定性影响研究综述[J]. 施工技术,2012,41(17):63 − 66. [SUN Yongshuai,JIA Cangqin,WANG Guihe. Overview of research on stability of slope during rainfall[J]. Construction Technology,2012,41(17):63 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Yongshuai, JIA Cangqin, WANG Guihe . Overview of research on stability of slope during rainfall[J]. Construction Technology,2012 ,41 (17 ):63 −66 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] HUANG Xiaolan,XIONG Jun,LIU Jianjun. Two‐phase seepage analysis in unsaturated rock and soil slope during rainfall[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings,2010,1207(1):507 − 512.
[8] 杨国强,陶虎,雷少伟,等. 不同雨型条件下非饱和土边坡渗流及稳定分析[J]. 水电能源科学,2022,40(6):166 − 170. [YANG Guoqiang,TAO Hu,LEI Shaowei,et al. Analysis of seepage and stability of unsaturated soil slopes under different rainfall patterns[J]. Water Resources and Power,2022,40(6):166 − 170. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Guoqiang, TAO Hu, LEI Shaowei, et al . Analysis of seepage and stability of unsaturated soil slopes under different rainfall patterns[J]. Water Resources and Power,2022 ,40 (6 ):166 −170 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 蒋中明,熊小虎,曾铃. 基于FLAC3D平台的边坡非饱和降雨入渗分析[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(3):855 − 861. [JIANG Zhongming,XIONG Xiaohu,ZENG Ling. Unsaturated seepage analysis of slope under rainfall condition based on FLAC3D[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(3):855 − 861. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIANG Zhongming, XIONG Xiaohu, ZENG Ling . Unsaturated seepage analysis of slope under rainfall condition based on FLAC3D[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014 ,35 (3 ):855 −861 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 李晓科,王康,畅俊斌. 基于GNSS的滑坡监测预警技术应用——以宝塔区二庄科滑坡为例[J]. 科学技术创新,2022(12):173 − 176. [LI Xiaoke,WANG Kang,CHANG Junbin. Application of landslide monitoring and early warning technology based on GNSS:Taking erzhuangke landslide in Baota district as an example[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation,2022(12):173 − 176. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Xiaoke, WANG Kang, CHANG Junbin . Application of landslide monitoring and early warning technology based on GNSS: Taking erzhuangke landslide in Baota district as an example[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation,2022 (12 ):173 −176 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 吴梦喜. 饱和-非饱和土中渗流Richards方程有限元算法[J]. 水利学报,2009,40(10):1274 − 1279. [WU Mengxi. Finite-element algorithm for Richards’ equation for saturated-unsaturated seepage flow[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2009,40(10):1274 − 1279. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Mengxi . Finite-element algorithm for Richards’ equation for saturated-unsaturated seepage flow[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2009 ,40 (10 ):1274 −1279 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 吕雨桦,梁德贤,王莹,等. 降雨条件下非饱和土边坡渗流-应力耦合分析[J]. 桂林理工大学学报,2021,41(2):318 − 324. [LYU Yuhua,LIANG Dexian,WANG Ying,et al. Seepage-stress coupling analysis of unsaturated soil slope under rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology,2021,41(2):318 − 324. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LYU Yuhua, LIANG Dexian, WANG Ying, et al . Seepage-stress coupling analysis of unsaturated soil slope under rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology,2021 ,41 (2 ):318 −324 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 石爱红,李国庆,丁德民,等. 考虑非饱和土基质吸力的丁家坡滑坡变形机制及稳定性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):141 − 151. [SHI Aihong,LI Guoqing,DING Demin,et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):141 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SHI Aihong, LI Guoqing, DING Demin, et al . Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022 ,49 (6 ):141 −151 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 曾立峰,邵龙潭,牛庚,等. 考虑孔隙水微观赋存形态的非饱和粉土有效应力方程及其验证[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(4):37 − 46. [ZENG Lifeng,SHAO Longtan,NIU Geng,et al. An effective stress equation for unsaturated silt considering the microstructure of pore water and its verification[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(4):37 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZENG Lifeng, SHAO Longtan, NIU Geng, et al . An effective stress equation for unsaturated silt considering the microstructure of pore water and its verification[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022 ,49 (4 ):37 −46 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[15] 刘朋飞,殷跃平,李滨,等. 非饱和黄土干湿循环土水特征曲线试验及渗透系数预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(4):125 − 129. [LIU Pengfei,YIN Yueping,LI Bin,et al. The tests of soil-water characteristical curve and permeability coefficient prediction of the wetting-drying cycles for unsaturated loess[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(4):125 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2015.04.22
LIU Pengfei, YIN Yueping, LI Bin, et al . The tests of soil-water characteristical curve and permeability coefficient prediction of the wetting-drying cycles for unsaturated loess[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015 ,26 (4 ):125 −129 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 许旭堂,鲜振兴,杨枫,等. 水-力耦合及干湿循环效应对浅层残积土斜坡稳定性的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):28 − 36. [XU Xutang,XIAN Zhenxing,YANG Feng,et al. Influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet cycle effect on surficial layer stability of residual soil slopes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):28 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202102018
XU Xutang, XIAN Zhenxing, YANG Feng, et al . Influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet cycle effect on surficial layer stability of residual soil slopes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (4 ):28 −36 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -




 下载:
下载: