Softening aging characteristics of clayey soil reinforced with cement and polypropylene fibers under water immersion
-
摘要:
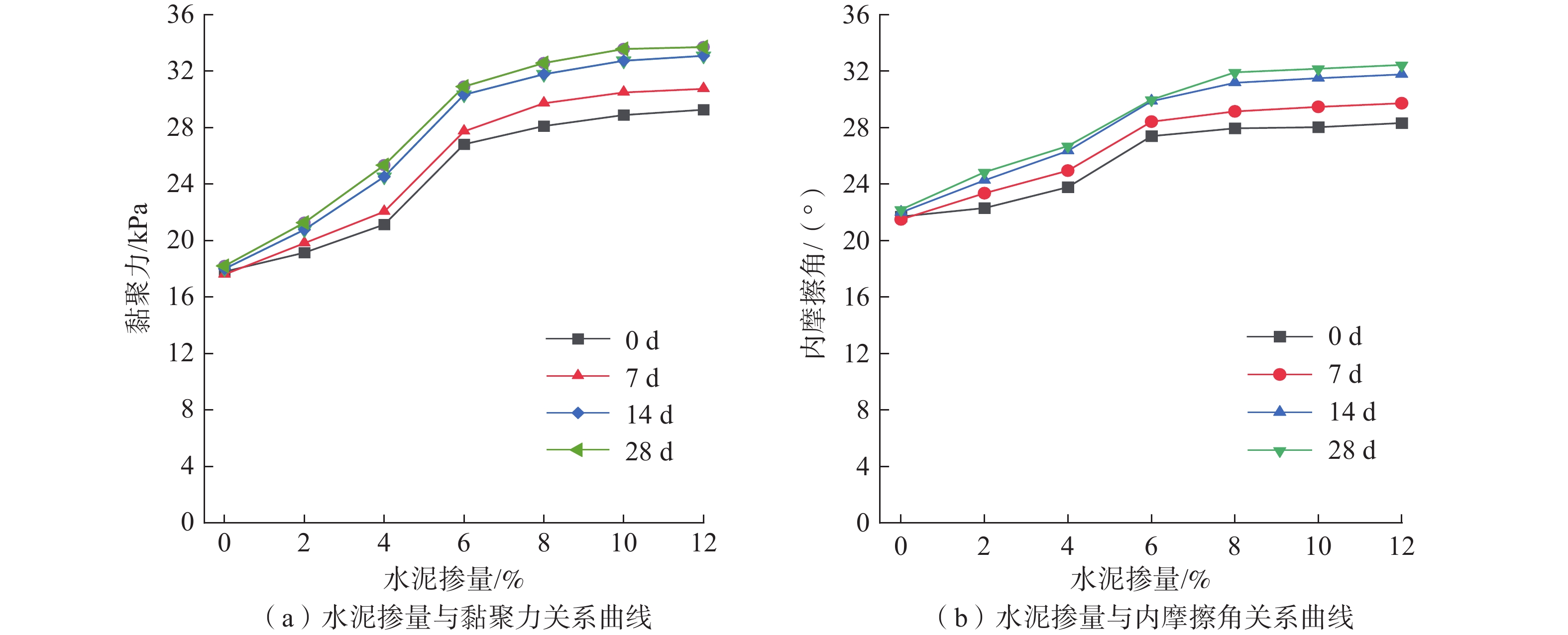
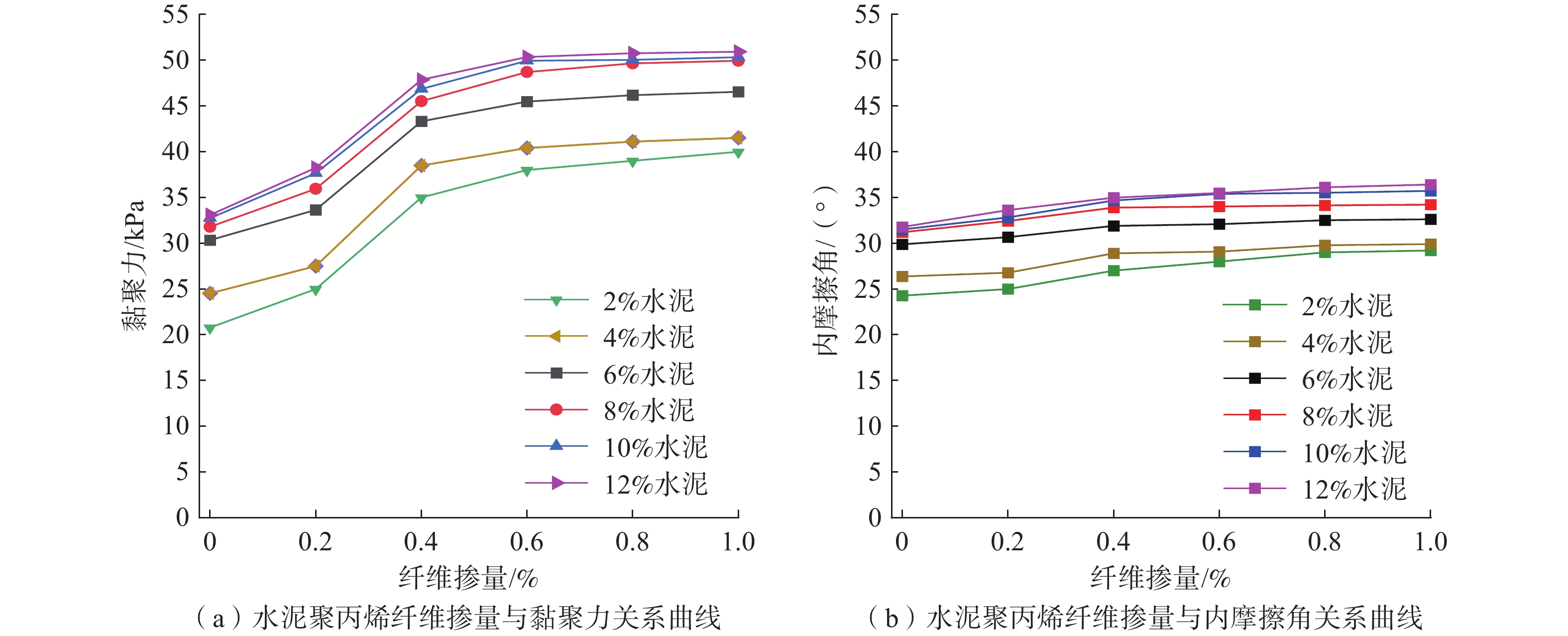
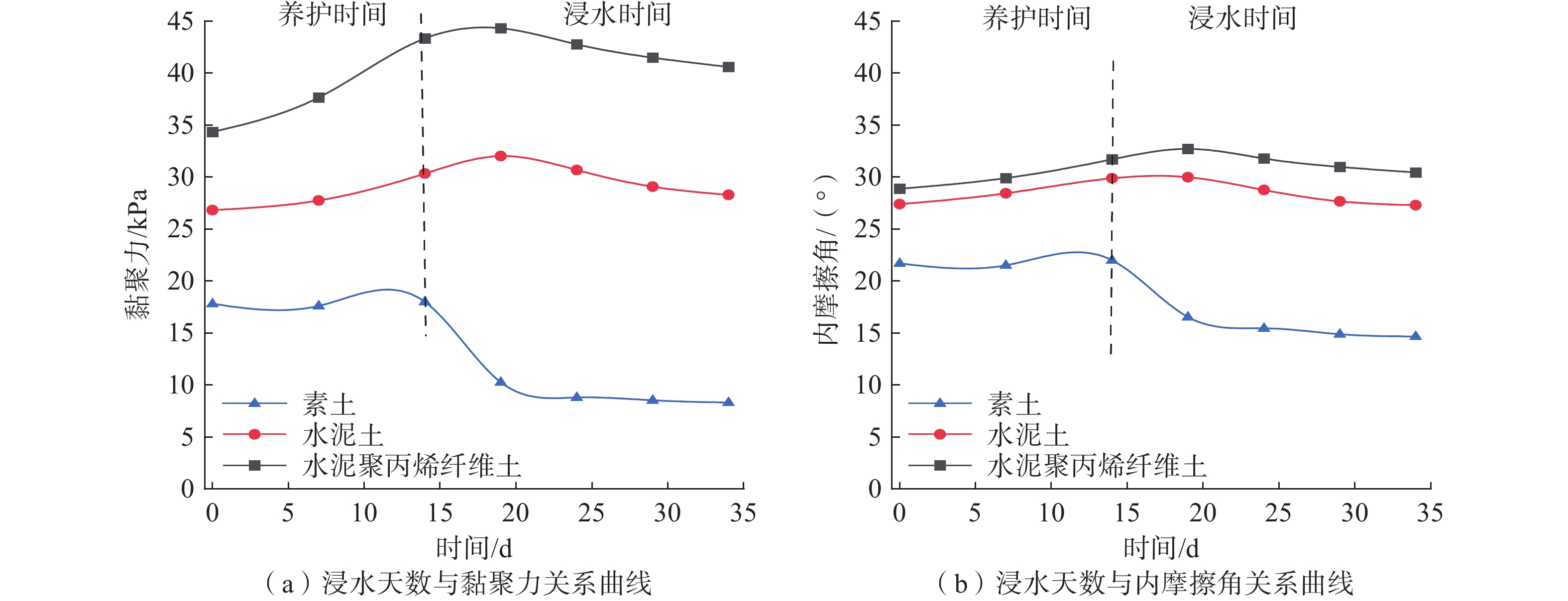
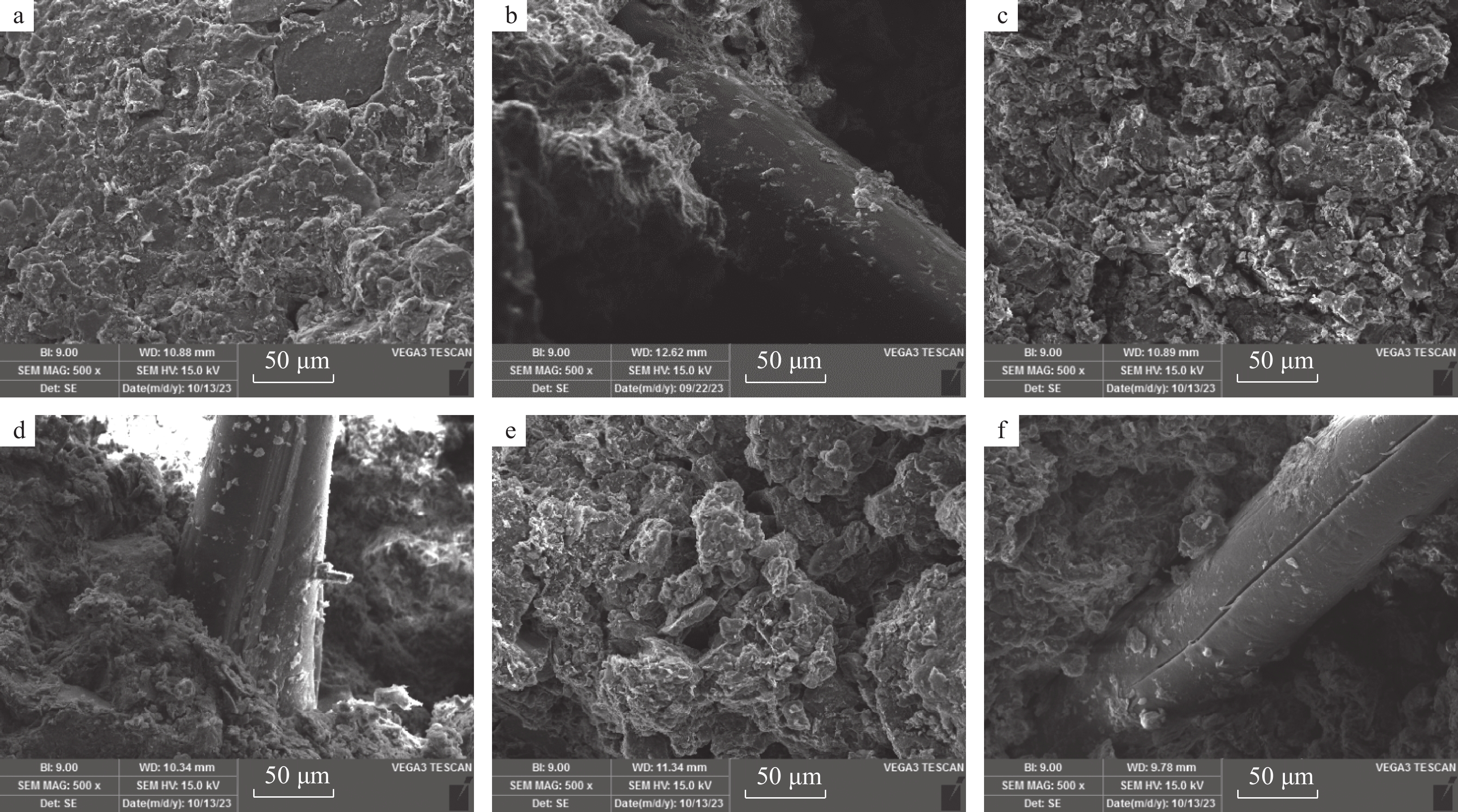
文章通过直接剪切试验,研究了水泥和聚丙烯纤维加固粉质黏土的力学特性。同时,采用浸水软化试验模拟了长期降雨对粉质黏土和加固土强度的影响,揭示试样软化后的力学性质和微观结构变化规律。研究表明,加固土的黏聚力与内摩擦角均随着水泥掺量和纤维掺量的增加而增强,但增幅在一定掺量后下降,根据增幅特征,最佳加固材料掺量为6%水泥和0.4%聚丙烯纤维。对采用该配比的试样进行浸水软化试验,发现在浸水初期阶段,由于水化水解反应,土颗粒之间的胶结性增强,土与纤维的紧密结合也进一步使土的黏聚力增加,土中土-水离子能量交换作用使黏粒结合水膜厚度减小,内摩擦角也略有增大;随着浸水时间的增加,土体中的自由水越来越多,导致土粒发生相对移动并进一步分散成块状,但由于水化产物的胶结性和纤维的包裹性较强,土体内部结构还能保持良好的完整性,因此,黏聚力和内摩擦角呈缓慢下降。研究结果可为这类黏性土加固的应用提供重要的力学参数和理论依据。
Abstract:In this paper, the mechanical properties of silty clay reinforced with cement and polypropylene fibers were studied through direct shear tests. Additionally, water immersion softening tests were conducted to simulate the effects of long-term rainfall on the strength of both plain and reinforced soils, revealing the mechanical behaviour and microstructural changes of the samples after softening. The results indicate that the cohesion and internal friction angle of the reinforced soil increase with higher cement and fiber content, but the rate of increase diminishes behind a certain threshold. Based on these findings, the optimal reinforcement composition is determined to be 6% cement and 0.4% polypropylene fibers. Water immersion softening tests conducted on samples with this composition reveal the following characteristics: In the initial stage of water immersion, due to the hydration and hydrolysis reaction, the cementation between soil particles is enhanced, and the close bonding between soil and fibers further increases the cohesion of the soil. Energy exchange between soil and water ions in the soil reduces the thickness of the water film bound to clay particles, slightly increasing the internal friction angle; as the immersion time increases, the accumulation of free water leads to relative movement and dispersion of soil particles into blocks. However, the strong cementation provided by hydration products and the encapsulating effect of fibers maintain the soil's structural integrity, resulting in a gradual decrease in cohesion and internal friction angle. These findings provide critical mechanical parameters and theoretical insights for the application of cement and polypropylene fiber reinforcement in cohesive soils.
-

-
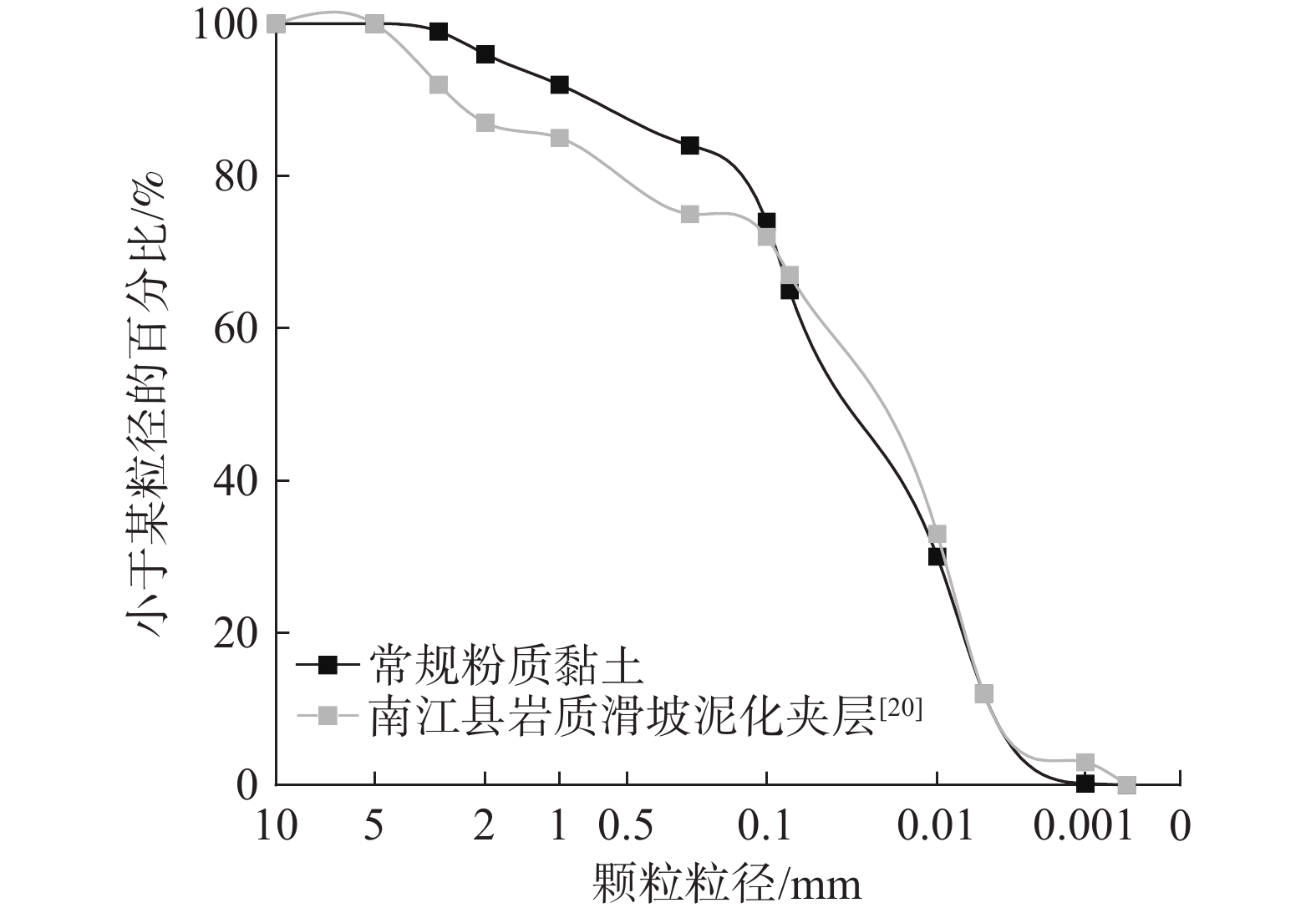
表 1 粉质黏土的物理性质
Table 1. Physical properties of silty clay
最优含水率/% 最大干密度/(g·cm−3) 液限指数/% 塑限指数/% 不同粒径(mm)颗粒分布 13 1.836 19.33 10.3 <0.005 0.005~0.075 0.075~0. 1 0.1~0.25 >0.25 12.2% 51.8% 6% 7% 23% 表 2 不同浸水天数时土样的浸出液化学成分测试结果
Table 2. Test results of chemical composition of leaching solution of soil samples under different immersion periods
浸水天数/d ρ(Ca2+)/(mg·L−1) ρ(Na+)/(mg·L−1) 粉质黏土 0 223 50 5 346 500 20 363 510 水泥聚丙烯
纤维加固土0 175 30 5 149 196 20 216 261 -
[1] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(3):433 − 454. [HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(3):433 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(3): 433 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
[2] DHANYA K A,VIBHA S,DIVYA P V. Performance of lateritic soil slopes at the onset of rainfall infiltration[J]. Indian Geotechnical Journal,2023,53(1):107 − 126. doi: 10.1007/s40098-022-00660-w
[3] 张卫雄,丁保艳,张文纶,等. 舟曲江顶崖大型滑坡成因及破坏机制分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2022,42(4):714 − 7221. [ZHANG Weixiong,DING Baoyan,ZHANG Wenlun,et al. Analysis on the cause and failure mechanism of the jiangdingya large landslide in Zhouqu,Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2022,42(4):714 − 722. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Weixiong, DING Baoyan, ZHANG Wenlun, et al. Analysis on the cause and failure mechanism of the jiangdingya large landslide in Zhouqu, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2022, 42(4): 714 − 722. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] SUN Shuwei,PANG Bo,HU Jiabing,et al. Characteristics and mechanism of a landslide at Anqian iron mine,China[J]. Landslides,2021,18(7):2593 − 2607. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01671-z
[5] WEN Haijia,XIAO Jiafeng,WANG Xiongfeng,et al. Analysis of soil–water characteristics and stability evolution of rainfall-induced landslide:A case of the Siwan Village landslide[J]. Forests,2023,14(4):808. doi: 10.3390/f14040808
[6] DOGLIONI A,CASAGLI N,NOCENTINI M,et al. The landslide of Pomarico,south Italy,occurred on January 29th 2019[J]. Landslides,2020,17(9):2137 − 2143. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01455-x
[7] SONG Kun,WANG Fawu,ZUO Qingjun,et al. Successful disaster management of the July 2020 Shaziba landslide triggered by heavy rainfall in Mazhe Village,Enshi City,Hubei Province,China[J]. Landslides,2021,18(10):3503 − 3507. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01565-6
[8] 李江,许强,王森,等. 川东红层地区降雨入渗模式与岩质滑坡成因机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(增刊2):4053 − 4062. [LI Jiang,XU Qiang,WANG Sen,et al. Study on rainfall infiltration model and formation mechanism of rock landslide in red bed area of east Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(Sup 2):4053 − 4062. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Jiang, XU Qiang, WANG Sen, et al. Study on rainfall infiltration model and formation mechanism of rock landslide in red bed area of east Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(Sup 2): 4053 − 4062. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 蔡国军,程宇航,仲闯,等. 千枚岩饱水状态下软化效应试验分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(8):3032 − 3038. [CAI Guojun,CHENG Yuhang,ZHONG Chuang,et al. Experimental on softening effect of phyllite in saturated water[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(8):3032 − 3038. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.08.007
CAI Guojun, CHENG Yuhang, ZHONG Chuang, et al. Experimental on softening effect of phyllite in saturated water[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(8): 3032 − 3038. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.08.007
[10] LIU Jie,XU Qiang,WANG Sen,et al. Formation and chemo-mechanical characteristics of weak clay interlayers between alternative mudstone and sandstone sequence of gently inclined landslides in Nanjiang,SW China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2020,79(9):4701 − 4715. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-01859-y
[11] YI Xiaoyu,FENG Wenkai,BAI Huilin,et al. Catastrophic landslide triggered by persistent rainfall in Sichuan,China:August 21,2020,Zhonghaicun landslide[J]. Landslides,2021,18(8):2907 − 2921.
[12] 彭正华,焦向阳,石长柏,等. 注浆法处理黄土坡滑坡临江崩滑堆积体深层滑移[J]. 华中科技大学学报(城市科学版),2006,23(增刊1):40 − 42. [PENG Zhenghua,JIAO Xiangyang,SHI C B,et al. Grouting method to treat deep sliding of landslide accumulation body near the river in Huangtupo landslide[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management,2006,23(Sup 1):40 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
PENG Zhenghua, JIAO Xiangyang, SHI C B, et al. Grouting method to treat deep sliding of landslide accumulation body near the river in Huangtupo landslide[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 2006, 23(Sup 1): 40 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 瞿海洋. 水泥改良黄土物理和力学特性试验研究[J]. 湖南交通科技,2021,47(3):35 − 39. [QU Haiyang. Experimental study on physical and mechanical properties of cement improved loess[J]. Hunan Communication Science and Technology,2021,47(3):35 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-844X.2021.03.008
QU Haiyang. Experimental study on physical and mechanical properties of cement improved loess[J]. Hunan Communication Science and Technology, 2021, 47(3): 35 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-844X.2021.03.008
[14] ANSOSRY,RAHMAN H A,RAMADHAN F R. Landslide mitigation of Banjir kanal Semarang,with grouting method[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2019,1387(1):012099. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1387/1/012099
[15] 孙海军. 水泥-纤维改良粉质黏土冻融循环力学特性研究[J]. 粉煤灰综合利用,2022,36(4):106 − 110. [SUN Haijun. Investigations on freeze-thaw cyclic mechanical properties of cement fiber modified silty clay[J]. Fly Ash Comprehensive Utilization,2022,36(4):106 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Haijun. Investigations on freeze-thaw cyclic mechanical properties of cement fiber modified silty clay[J]. Fly Ash Comprehensive Utilization, 2022, 36(4): 106 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 阮波,丁茴,邓威,等. 聚丙烯纤维加筋水泥砂浆土三轴压缩试验研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2021,18(2):359 − 365. [RUAN Bo,DING Hui,DENG Wei,et al. Experimental study on triaxial compression of polypropylene fiber reinforced cement mortar soil[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2021,18(2):359 − 365. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
RUAN Bo, DING Hui, DENG Wei, et al. Experimental study on triaxial compression of polypropylene fiber reinforced cement mortar soil[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(2): 359 − 365. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 庞庆庄. 聚丙烯纤维混合粘土的力学性能试验研究[J]. 吉林水利,2021(11):43 − 47. [PANG Qingzhuang. Experimental study on mechanical properties of polypropylene fiber mixed clay[J]. Jilin Water Resources,2021(11):43 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2846.2021.11.010
PANG Qingzhuang. Experimental study on mechanical properties of polypropylene fiber mixed clay[J]. Jilin Water Resources, 2021(11): 43 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2846.2021.11.010
[18] 任青阳,张勇,许虎,等. 砂浆中聚丙烯纤维掺量对预应力锚杆锚固性能影响研究[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版),2020,42(6):61 − 67. [REN Qingyang,ZHANG Yong,XU Hu,et al. Study on the influence of content of polypropylene fiber in mortar on the anchoring performance of anchor bolt[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences),2020,42(6):61 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
REN Qingyang, ZHANG Yong, XU Hu, et al. Study on the influence of content of polypropylene fiber in mortar on the anchoring performance of anchor bolt[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences), 2020, 42(6): 61 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王波,文华. 矿渣—粉煤灰地聚物注浆材料的制备及性能优化研究[J]. 金属矿山,2023(3):274 − 278. [WANG Bo,WEN Hua. Research on preparation and performance optimization of slag-fly ash geopolymer grouting material[J]. Metal Mine,2023(3):274 − 278. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Bo, WEN Hua. Research on preparation and performance optimization of slag-fly ash geopolymer grouting material[J]. Metal Mine, 2023(3): 274 − 278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 李江,许强,胡泽铭,等. 川东红层原状滑带土饱水软化试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(增刊2):4333-4342. [LI Jiang,XU Qiang,HU Zeming,et al. Experimental study on saturated softening of soil in undisturbed slip zone of red beds in eastern Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(Sup 2):4333-4342. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Jiang, XU Qiang, HU Zeming, et al. Experimental study on saturated softening of soil in undisturbed slip zone of red beds in eastern Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(Sup 2): 4333-4342. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 刘华勇,钱涛,刘聪,等. 聚丙烯纤维-水泥基稳定土抗剪强度试验研究[J]. 路基工程,2018(2):87 − 90. [LIU Huayong,QIAN Tao,LIU Cong,et al. Experimental study on shear strength of polypropylene fiber-cement based stabilized soil[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2018(2):87 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Huayong, QIAN Tao, LIU Cong, et al. Experimental study on shear strength of polypropylene fiber-cement based stabilized soil[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2018(2): 87 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 常宏,王旭升. 滑坡稳定性变化与地下水非稳定渗流初探——以三峡库区黄蜡石滑坡群石榴树包滑坡为例[J]. 地质科技情报,2004,23(1):94 − 98. [CHANG Hong,WANG Xusheng. Stability variation of a slope associated with transient groundwater flow:A case study on Shiliushu- Bao landslide in Huanglashi landslides,three gor- ges project area,China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2004,23(1):94 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHANG Hong, WANG Xusheng. Stability variation of a slope associated with transient groundwater flow: A case study on Shiliushu- Bao landslide in Huanglashi landslides, three gor- ges project area, China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2004, 23(1): 94 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 李丽华,刘文,白玉霞,等. 椰壳纤维-石灰协同作用改良黏土性能试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2025,52(1):130 − 140. [LI Lihua,LIU Wen,BAI Yuxia,et al. Experimental study on the synergistic effect of coir fiber and lime to improve soil performance[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2025,52(1):130 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Lihua, LIU Wen, BAI Yuxia, et al. Experimental study on the synergistic effect of coir fiber and lime to improve soil performance[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2025, 52(1): 130 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 袁进科,裴钻,杨森林,等. 纳米硅基固沙材料加固机理及抗冲蚀试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(6):80 − 89. [YUAN Jinke,PEI Zuan,YANG Senlin,et al. An experimental study of the reinforcement mechanism and erosion resistance of nano silicon-based sand-fixation material[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(6):80 − 89. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YUAN Jinke, PEI Zuan, YANG Senlin, et al. An experimental study of the reinforcement mechanism and erosion resistance of nano silicon-based sand-fixation material[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(6): 80 − 89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: