Experimental study on long-distance shear characteristics of fully weathered granite residual soil
-
摘要:
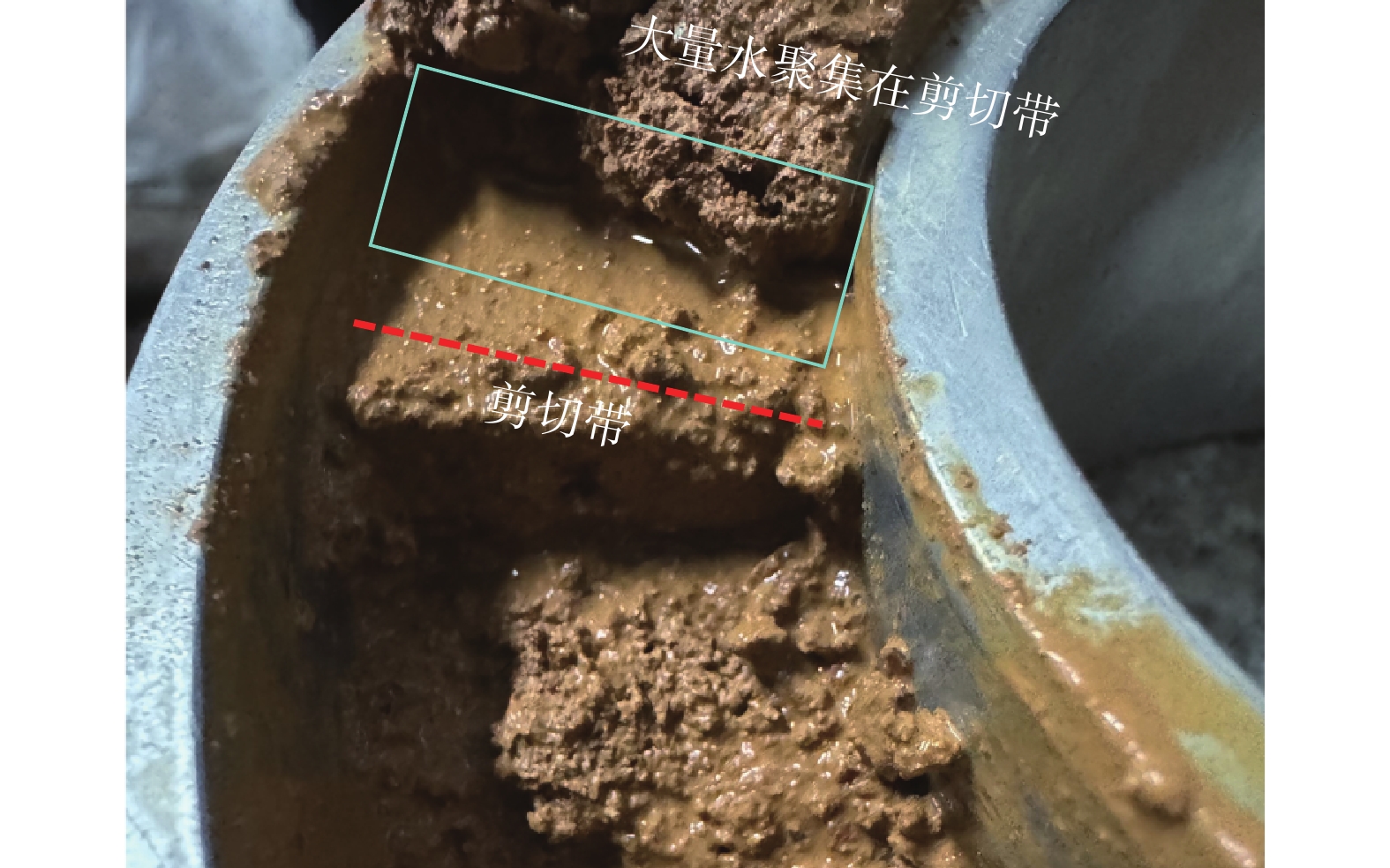
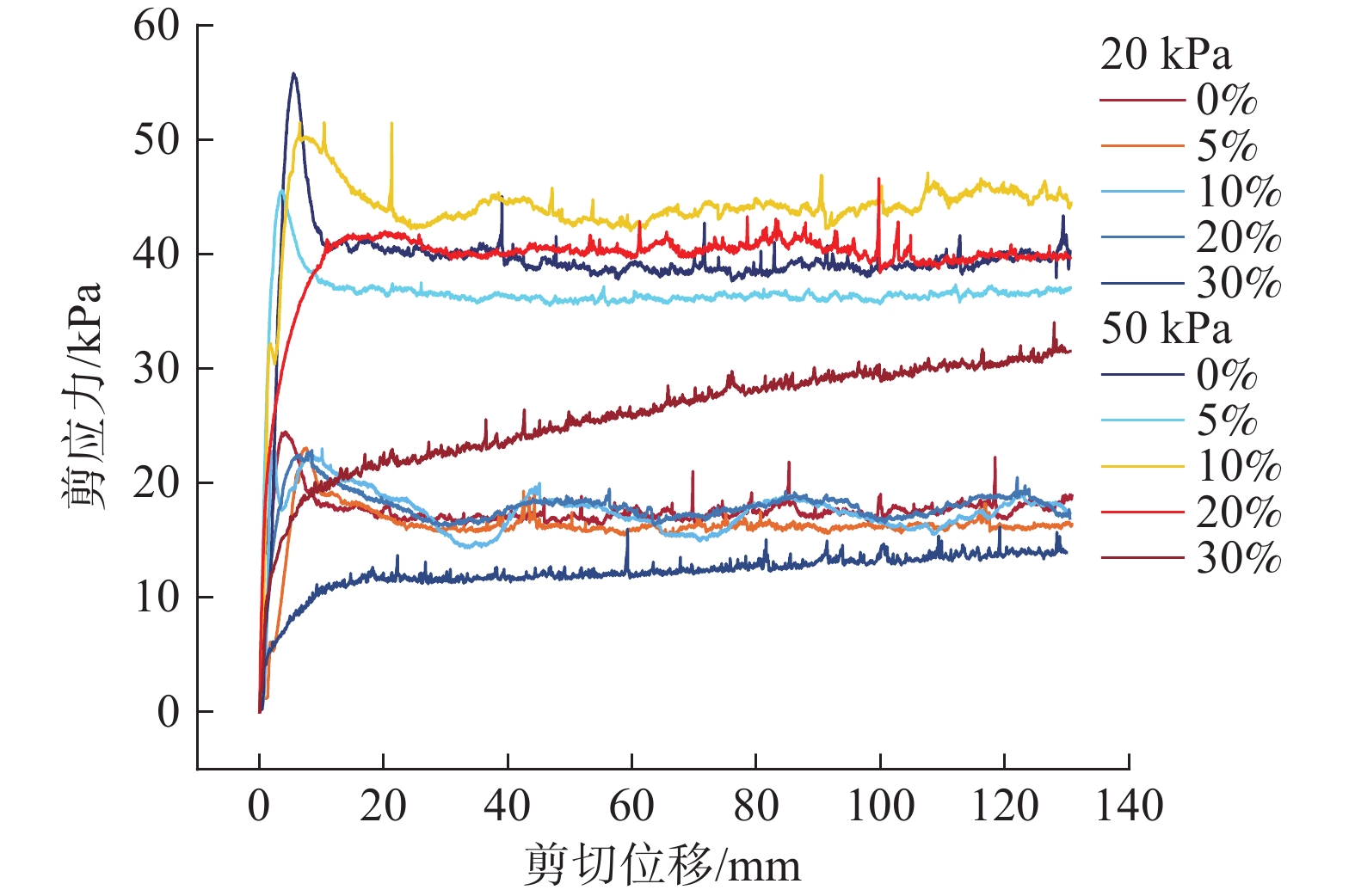
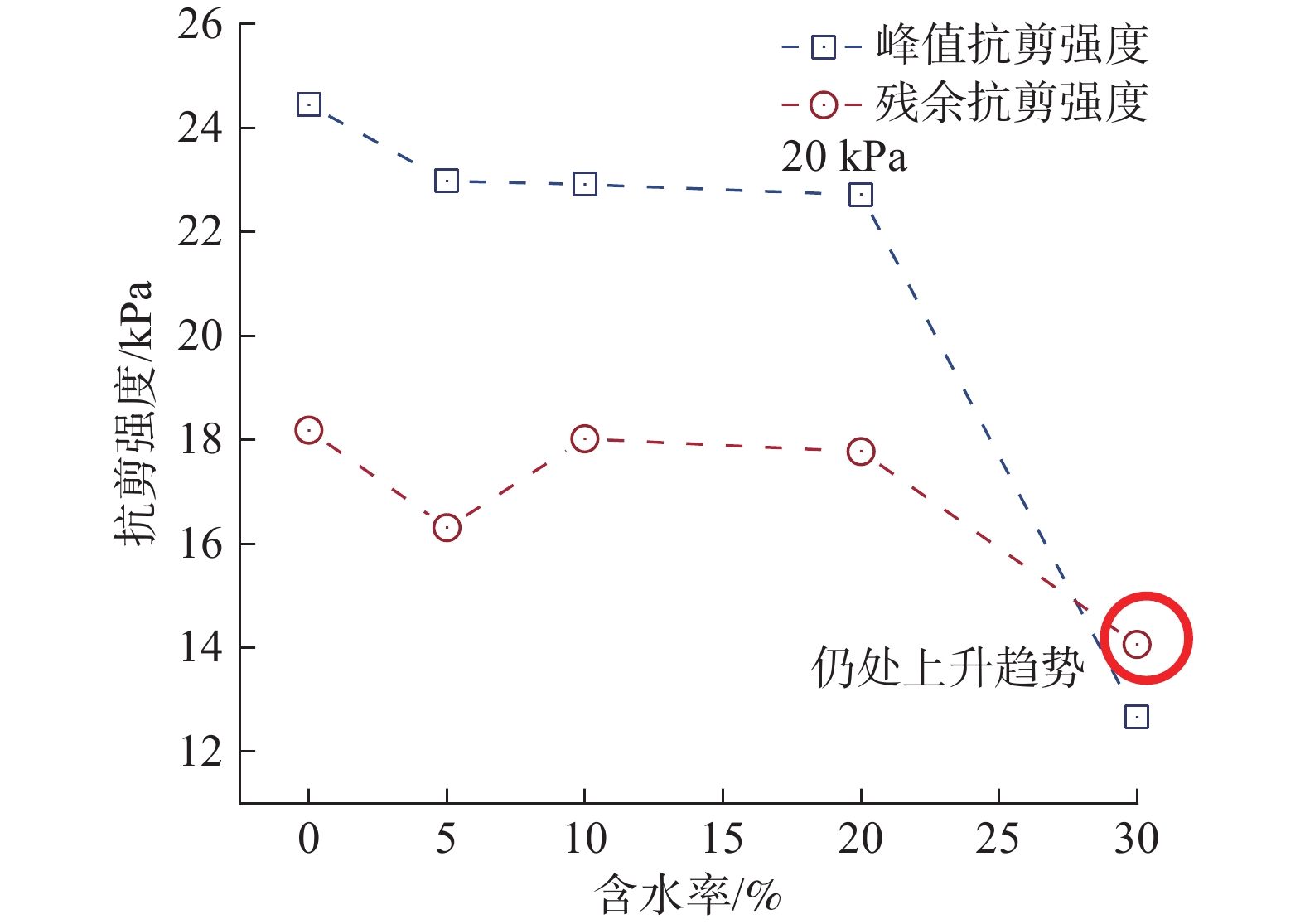
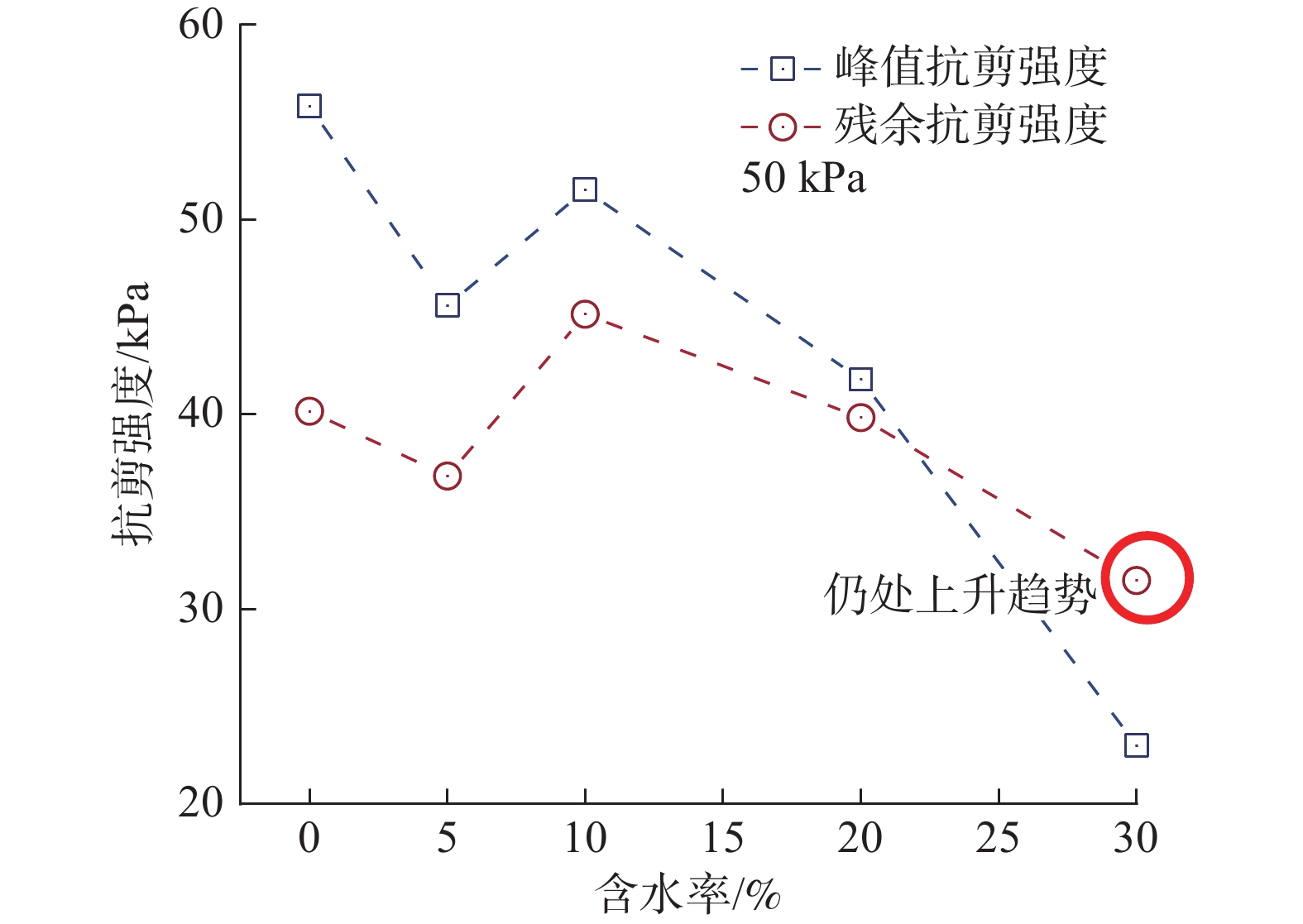
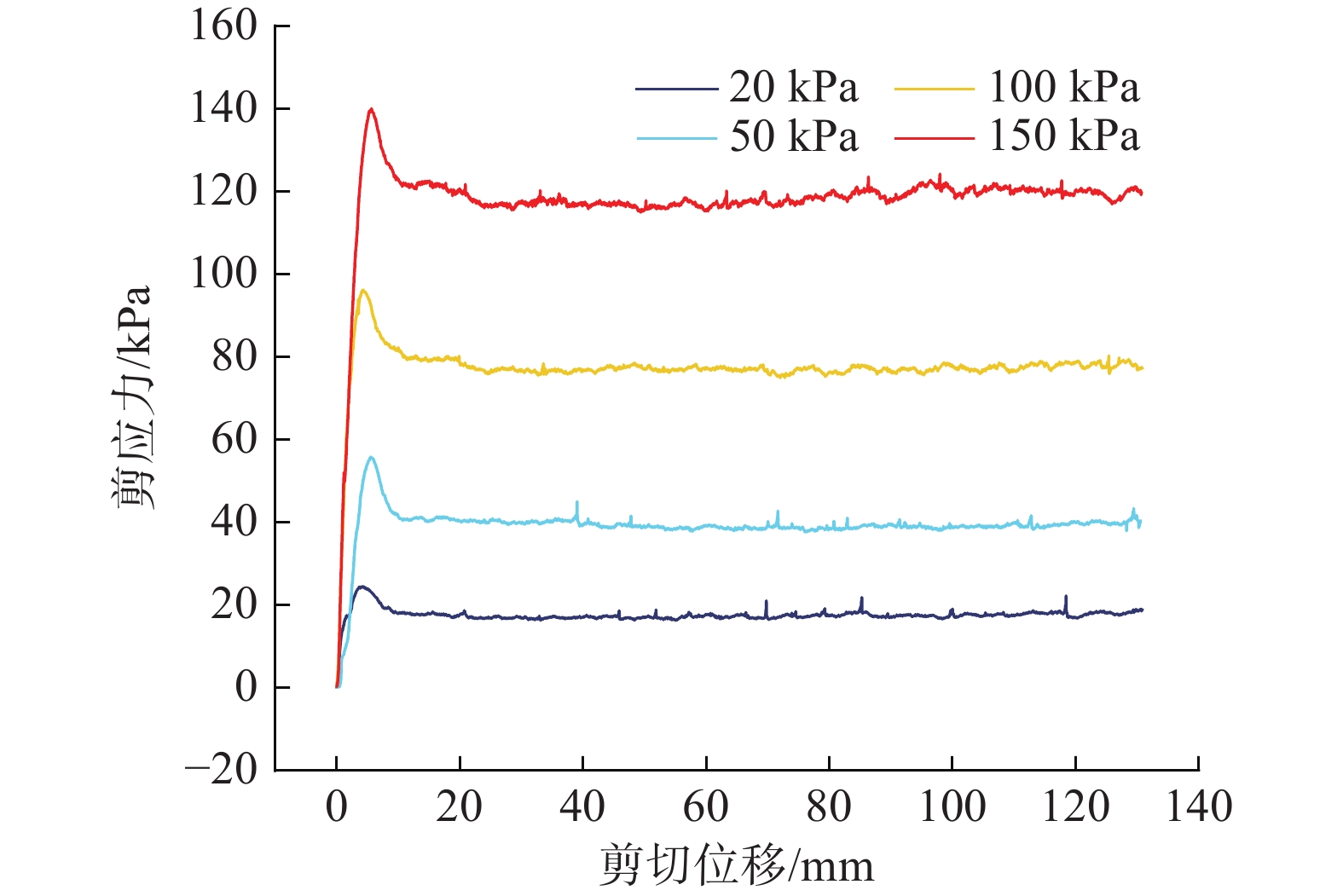
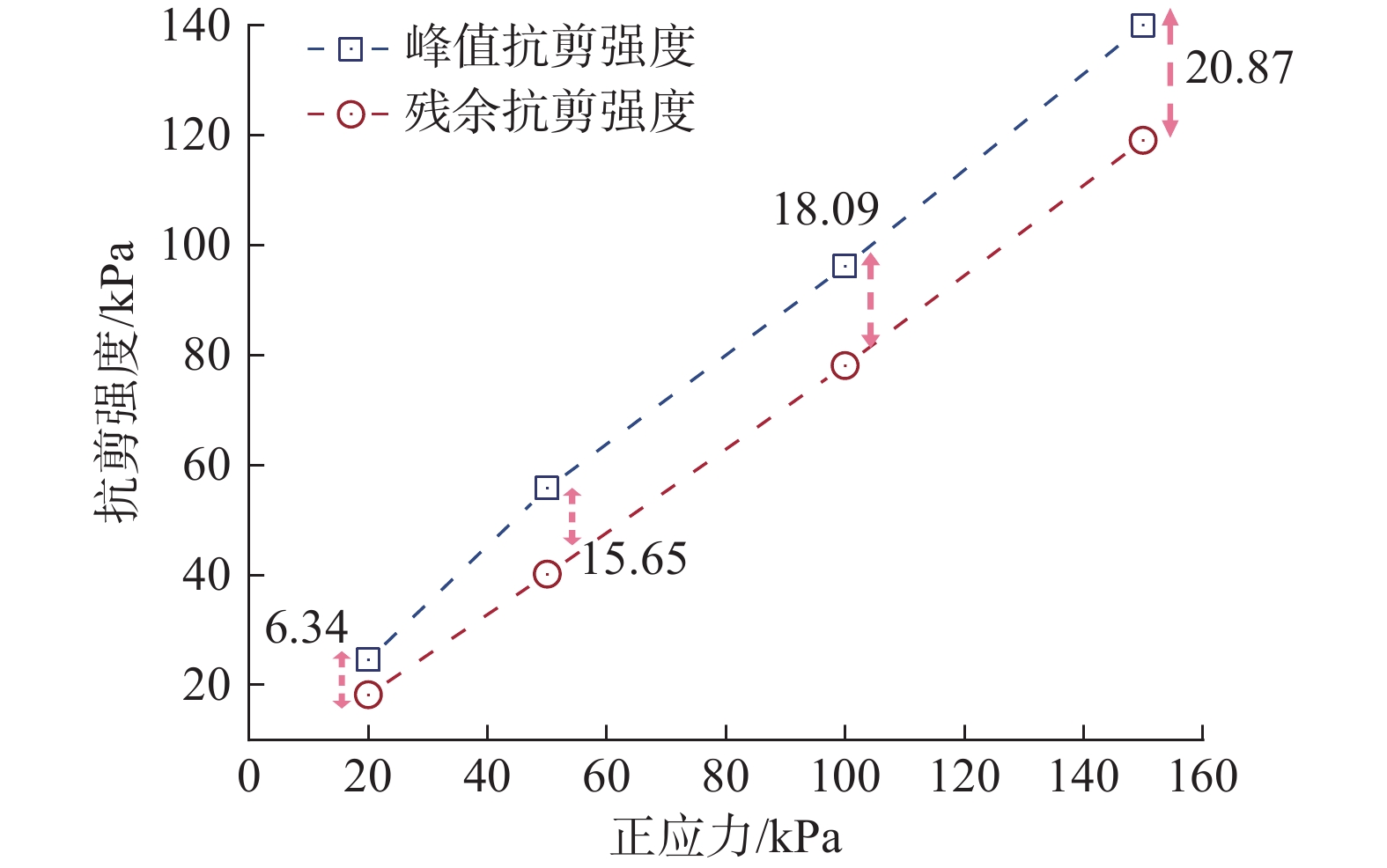
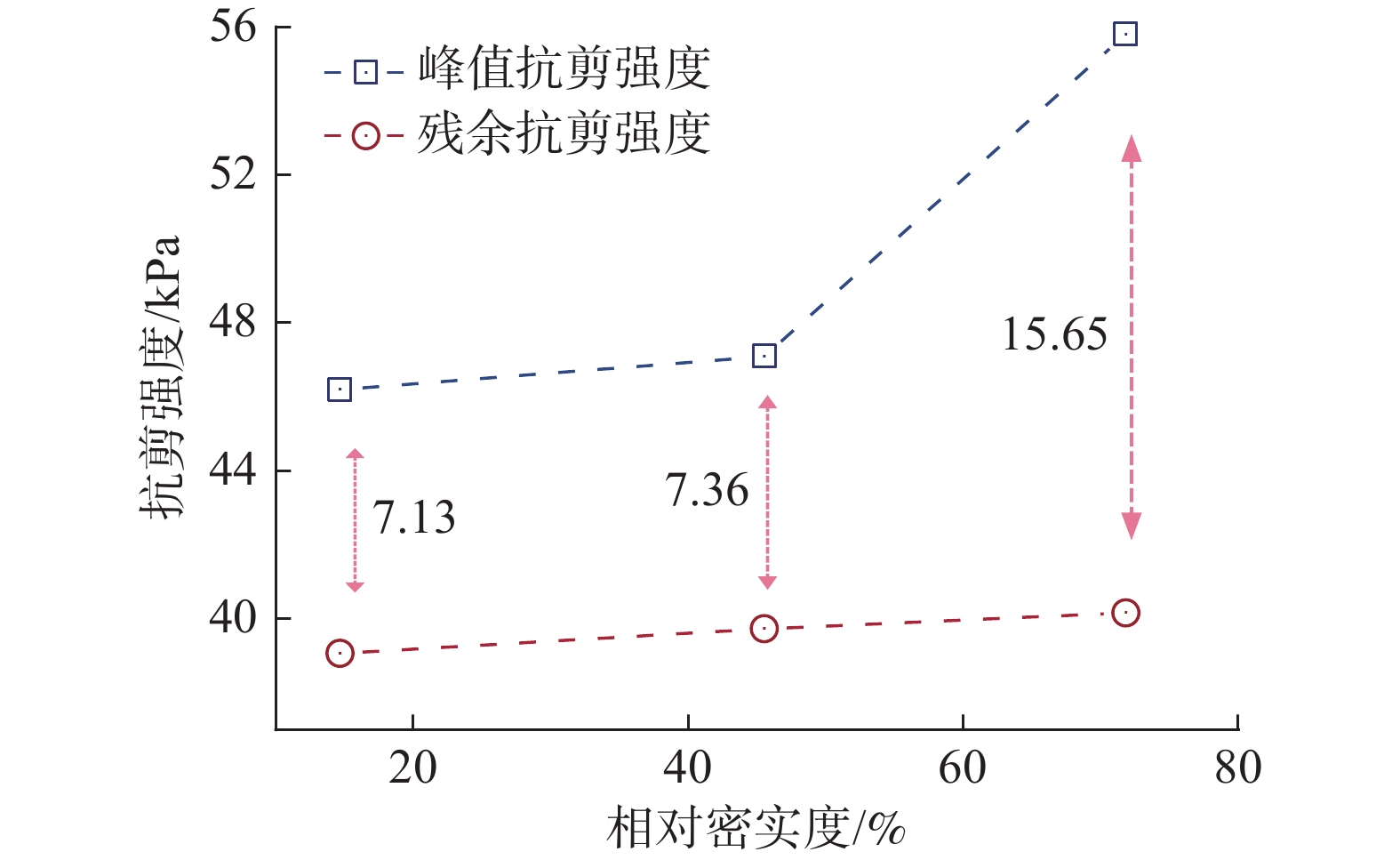
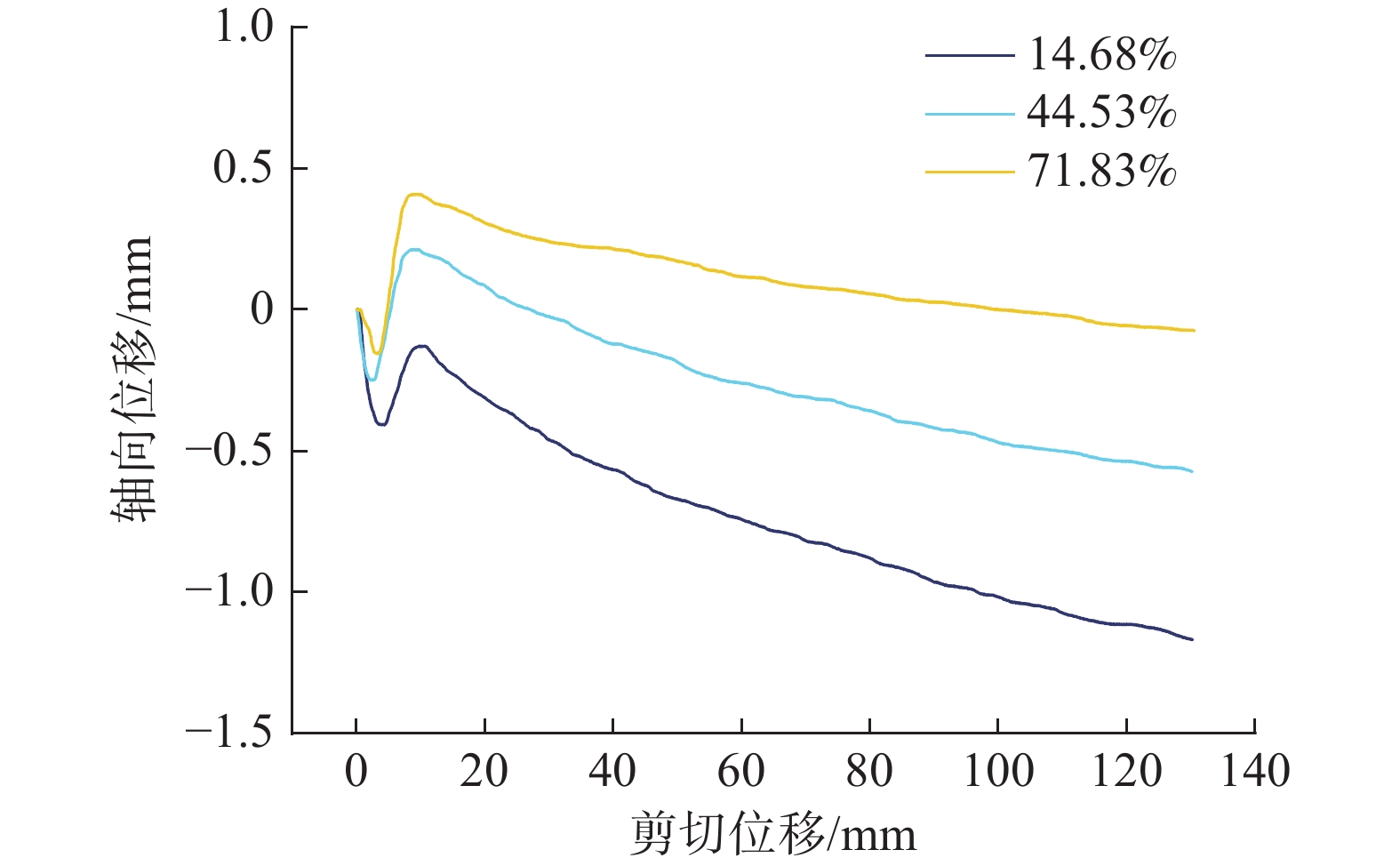
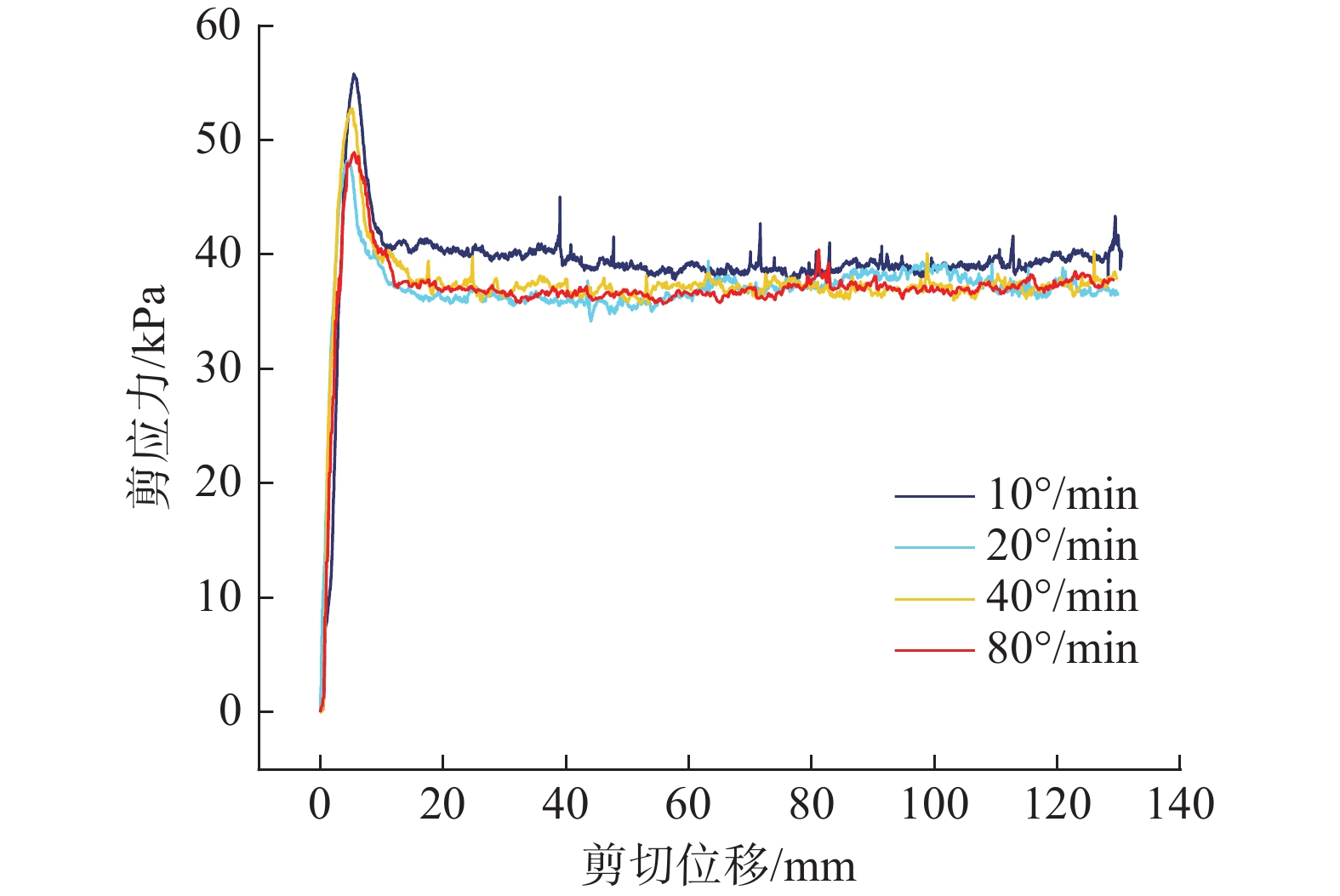
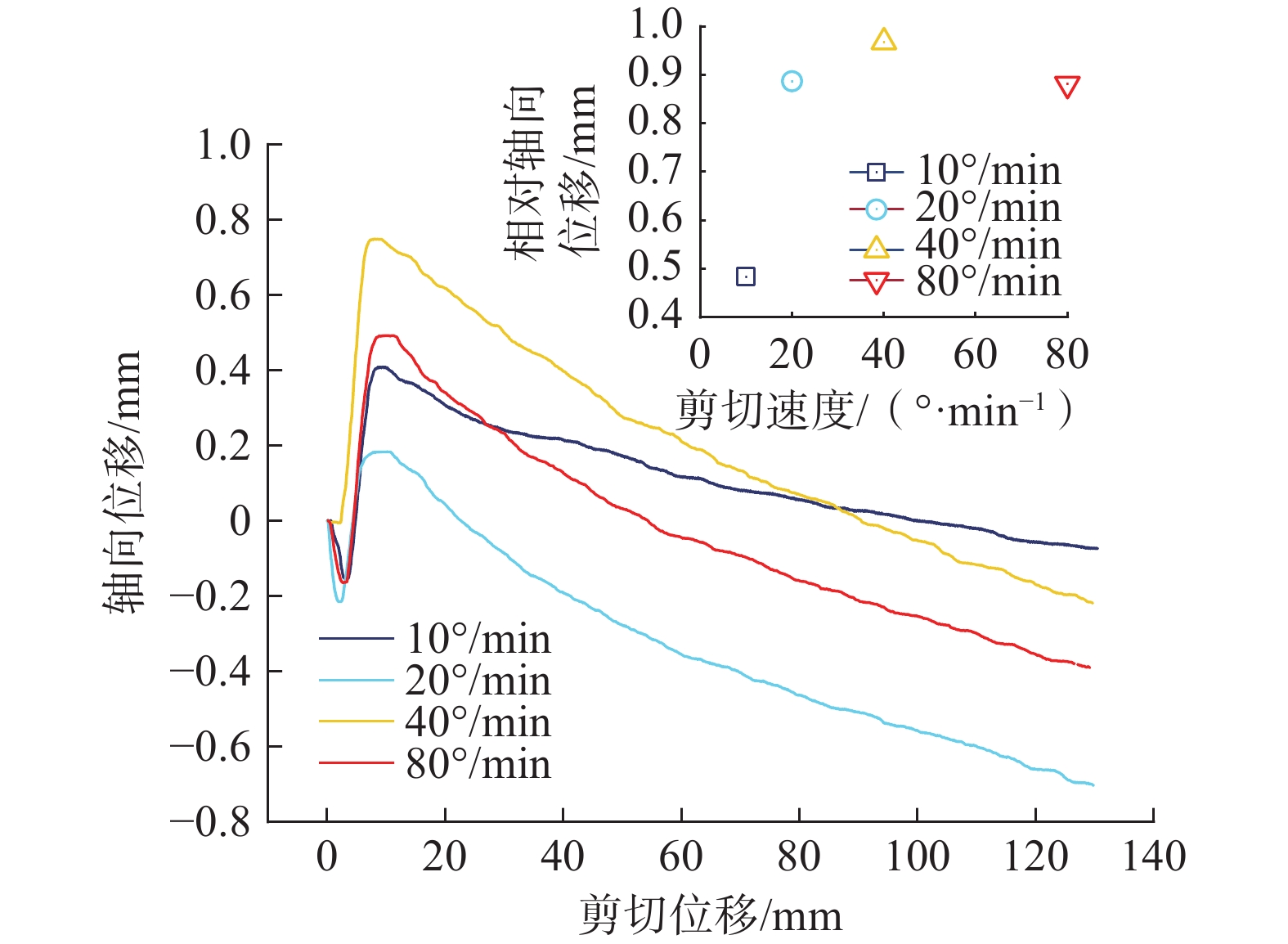
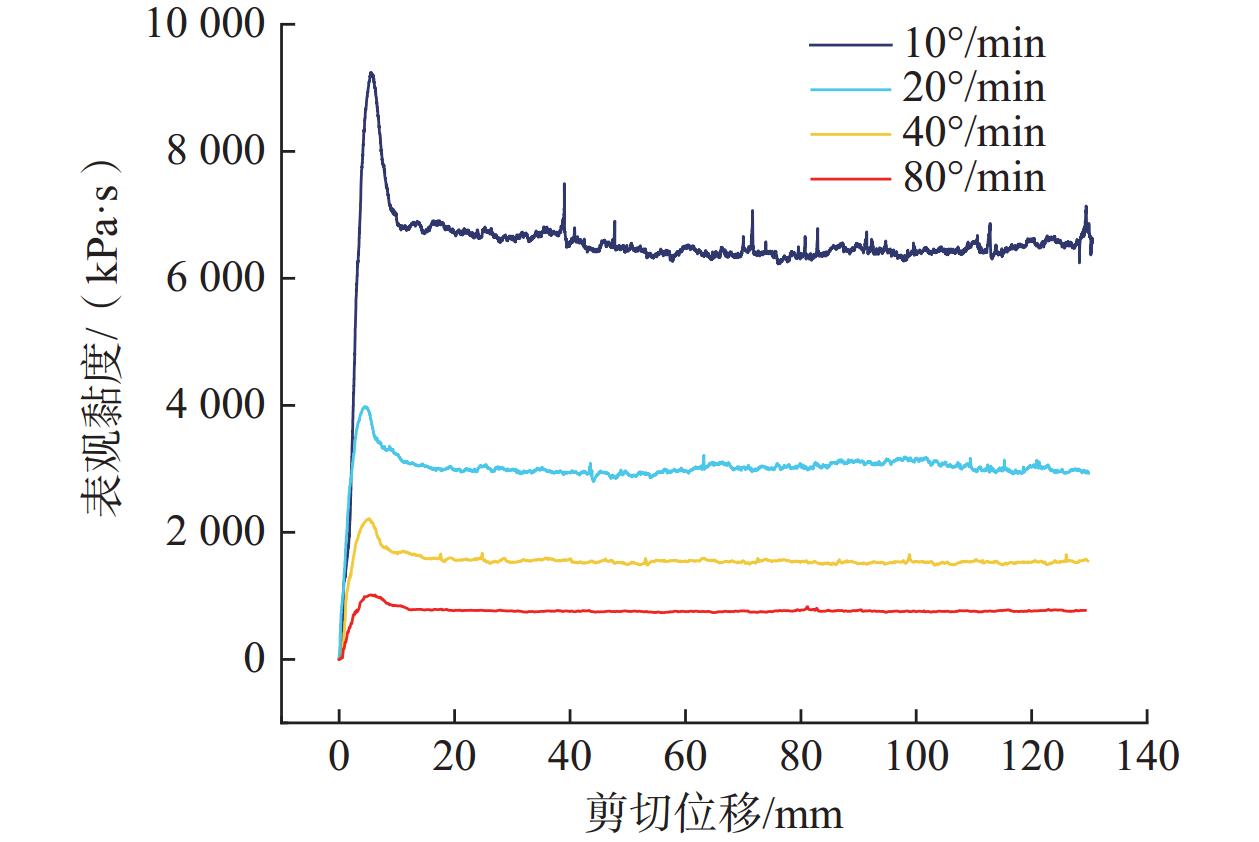
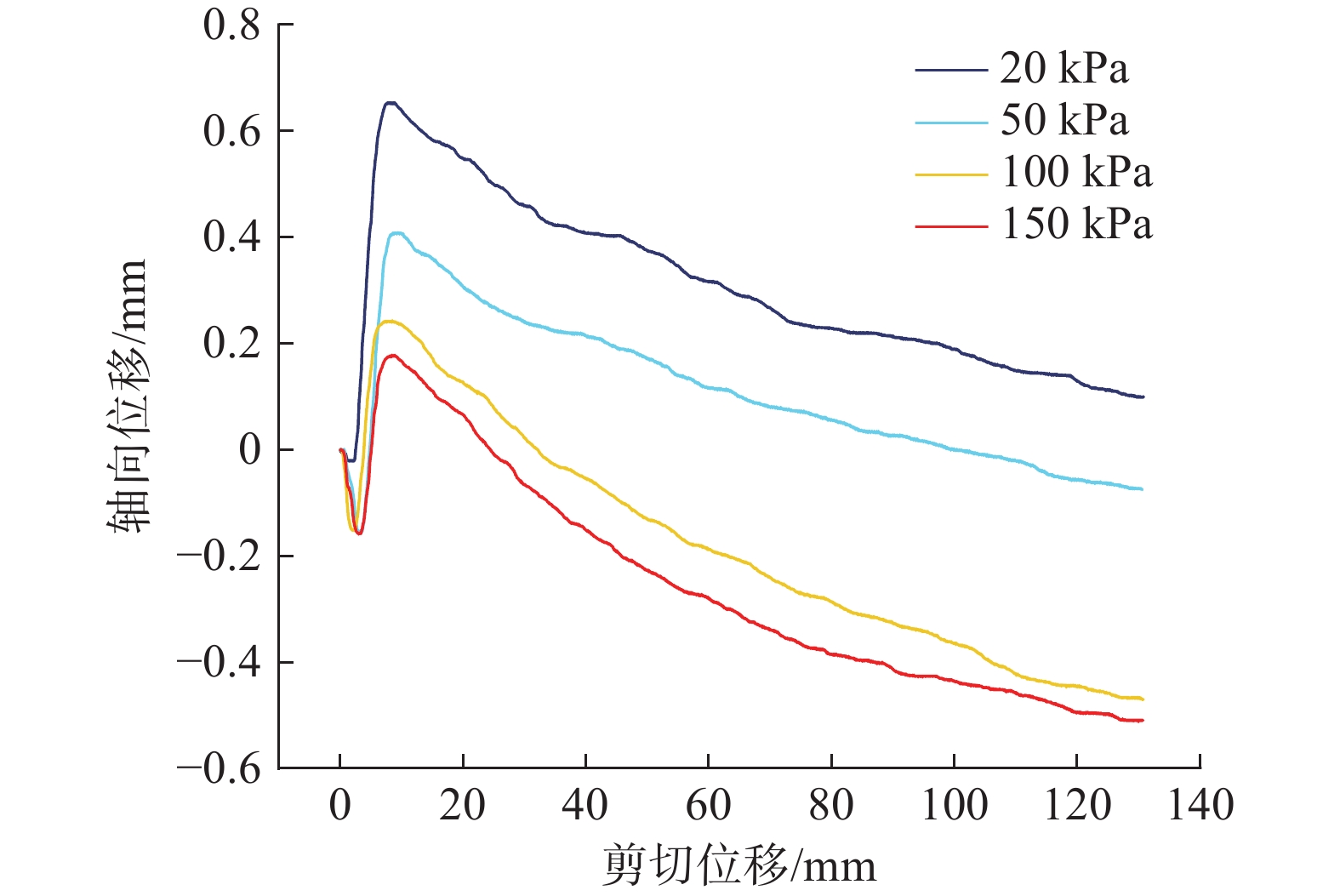
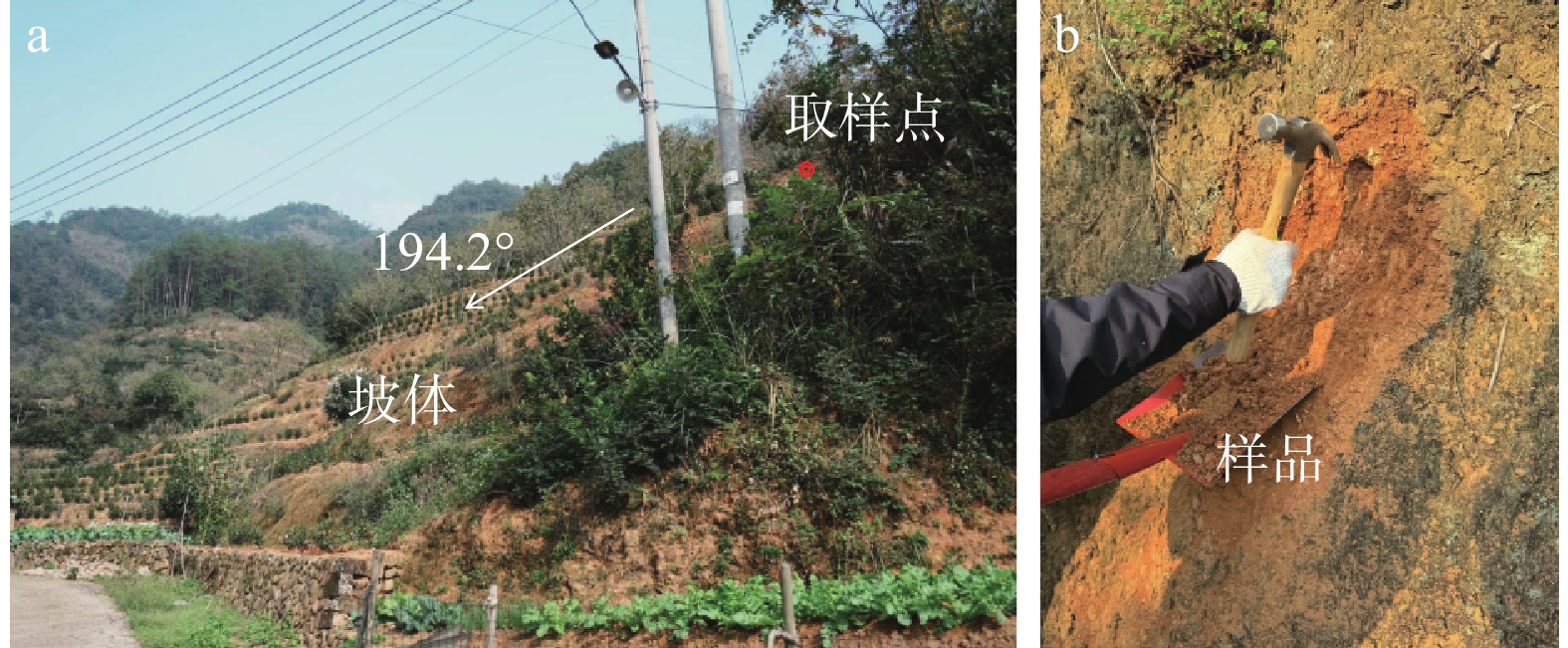
近年来,随着全球气候变化和人类工程活动的加剧,我国东南地区因降雨引发的群发性滑坡事件频发,严重威胁着人民的生命和财产安全。全风化花岗岩残积土作为这类滑坡灾害的主要地质载体,深入研究其力学特性对于揭示群发性滑坡的孕育演化机制具有重要意义。文章选取全风化花岗岩残积土为研究对象,综合考虑正应力(20 kPa,50 kPa,100 kPa,150 kPa)、含水率(0,5%,10%,20%和30%)和剪切速率(10°/min,20°/min,40°/min,和80°/min)的影响,开展了一系列环剪试验,旨在探究全风化花岗岩残积土在滑坡启动阶段及长距离运动阶段的力学行为,尤其是长距离剪切特性。试验结果表明:土体的抗剪强度与含水率有着密切关系,随着含水率的增加,抗剪强度先降低后升高再降低,当含水率达到30%时,土体会出现明显的应变硬化现象。此外,土体的抗剪强度还与正应力、剪切速率和相对密实度密切相关。具体表现为,正应力越大,土体的峰值抗剪强度和残余抗剪强度越高,且对峰值抗剪强度的影响更为显著,同时应变软化现象也更加明显;剪切速率越大,土体的峰值抗剪强度和残余抗剪强度总体呈下降趋势,对峰值抗剪强度的影响大于对残余抗剪强度的影响,且表观黏度降低。研究成果可为群发滑坡灾害防治提供重要的理论支持。
Abstract:In recent years, with the intensification of global climate change and human engineering activities, mass landslide events triggered by rainfall have become frequent in southeast China, posing serious threats to the lives and property safety of the people. Fully weathered granite residual soil, as the main geological carrier of such landslide disasters, has significant importance for revealing the mechanisms of the formation and evolution of landslide clusters through in-depth study of its mechanical properties. This paper selects fully weathered granite residual soil as the research subject and considers the effects of normal stress (20 kPa, 50 kPa, 100 kPa, 150 kPa), water content (0, 5%, 10%, 20%, and 30%), and shear rate (10°/min, 20°/min, 40°/min, and 80°/min) to conduct a series of ring shear tests. The aim is to explore the mechanical behavior of fully weathered granite residual soil during the landslide initiation and long-distance movement phases, especially its long-distance shear characteristics. Experimental results show that the shear strength of the soil is closely related to its water content; as the water content increases, the shear strength initially decreases, then increases, and decreases again. At a water content of 30%, the soil exhibits significant strain hardening. In addition, the shear strength of the soil is closely related to normal stress, shear rate, and relative density. Specifically, the higher the normal stress, the higher the peak and residual shear strengths of the soil, with a more significant effect on peak shear strength and more pronounced strain softening; the higher the shear rate, the overall downward trend in peak and residual shear strengths, with a greater effect on peak shear strength than on the residual shear strength, and lower the apparent viscosity. The findings of this study provide important theoretical support for the prevention and control of mass landslide disasters within this region.
-
Key words:
- granite residual soil /
- ring shear test /
- water content /
- normal stress /
- shear rate /
- shear strength
-

-
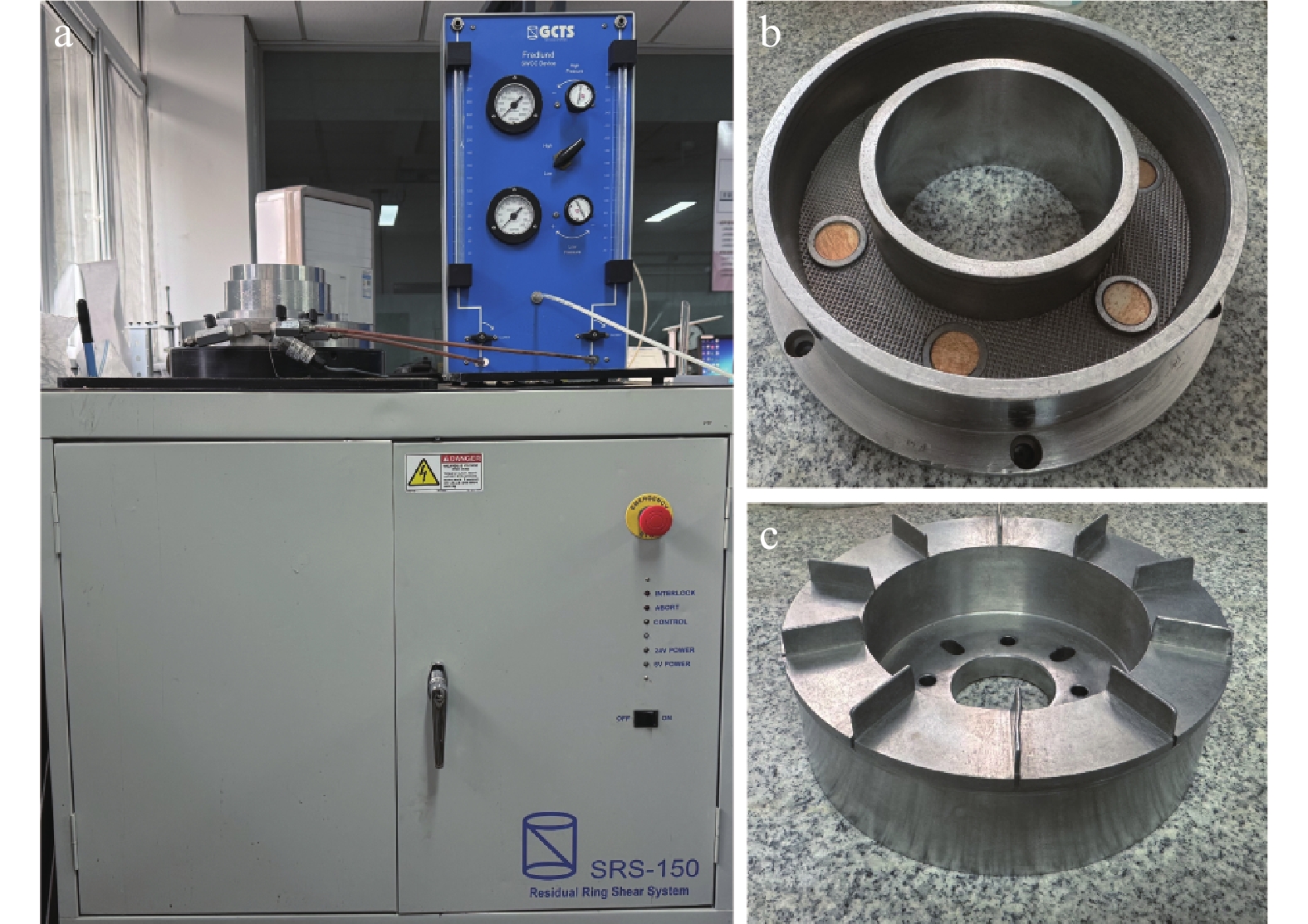
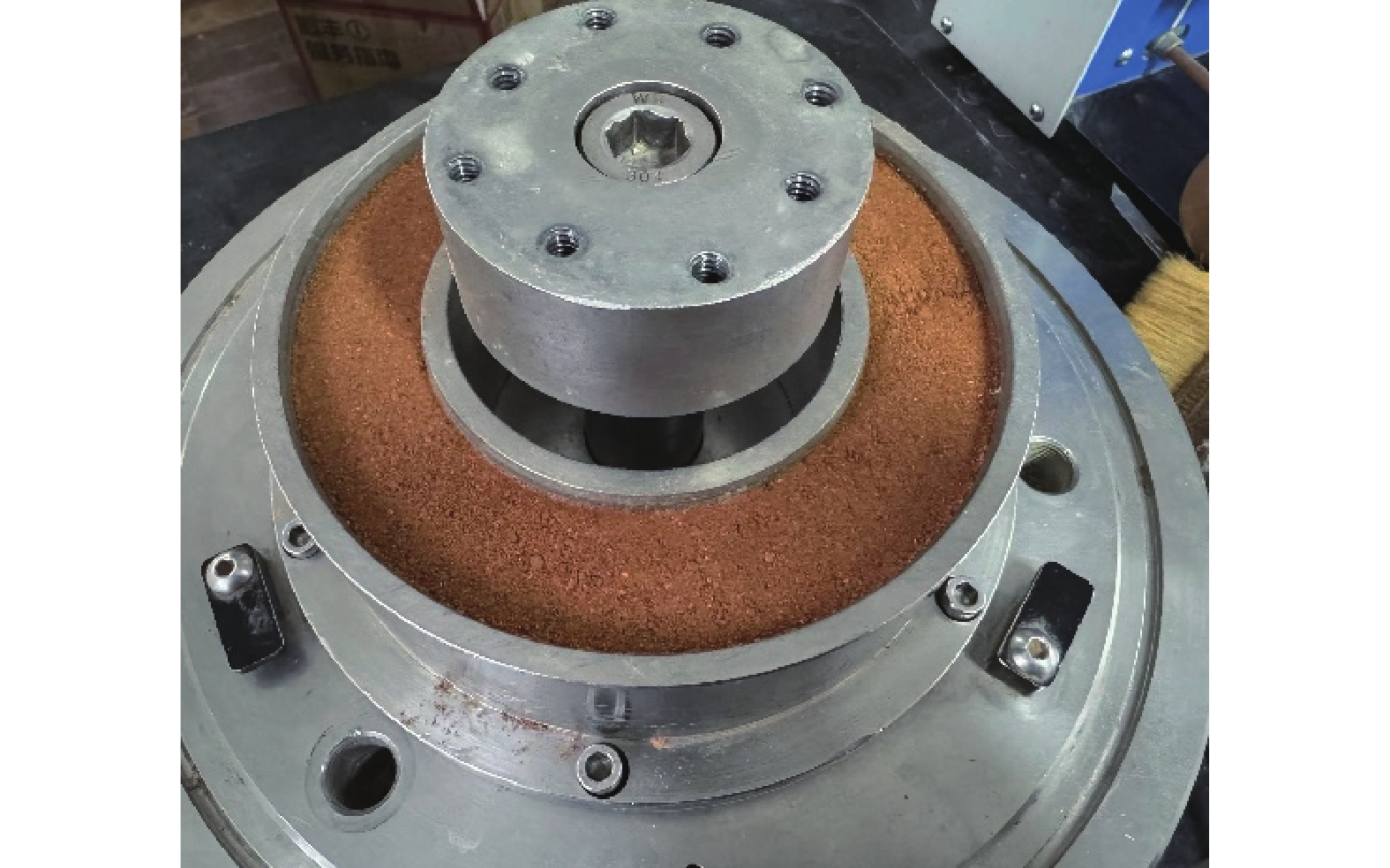
表 1 同济大学SRS−150型环剪仪主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of the SRS−150 ring shear instrument at Tongji University
主要参数 大小 剪切盒内径/mm 100 剪切盒外径/mm 150 最大装填试样高度/mm 31 有效试样面积/cm2 98 剪切速率/(°·min−1) 0.001~360 最大轴向压力/kN 10 峰值扭矩/(N·m) 250 轴向位移/mm 0~50 表 2 全风化花岗残积土物理特性
Table 2. Physical properties of the tested soil
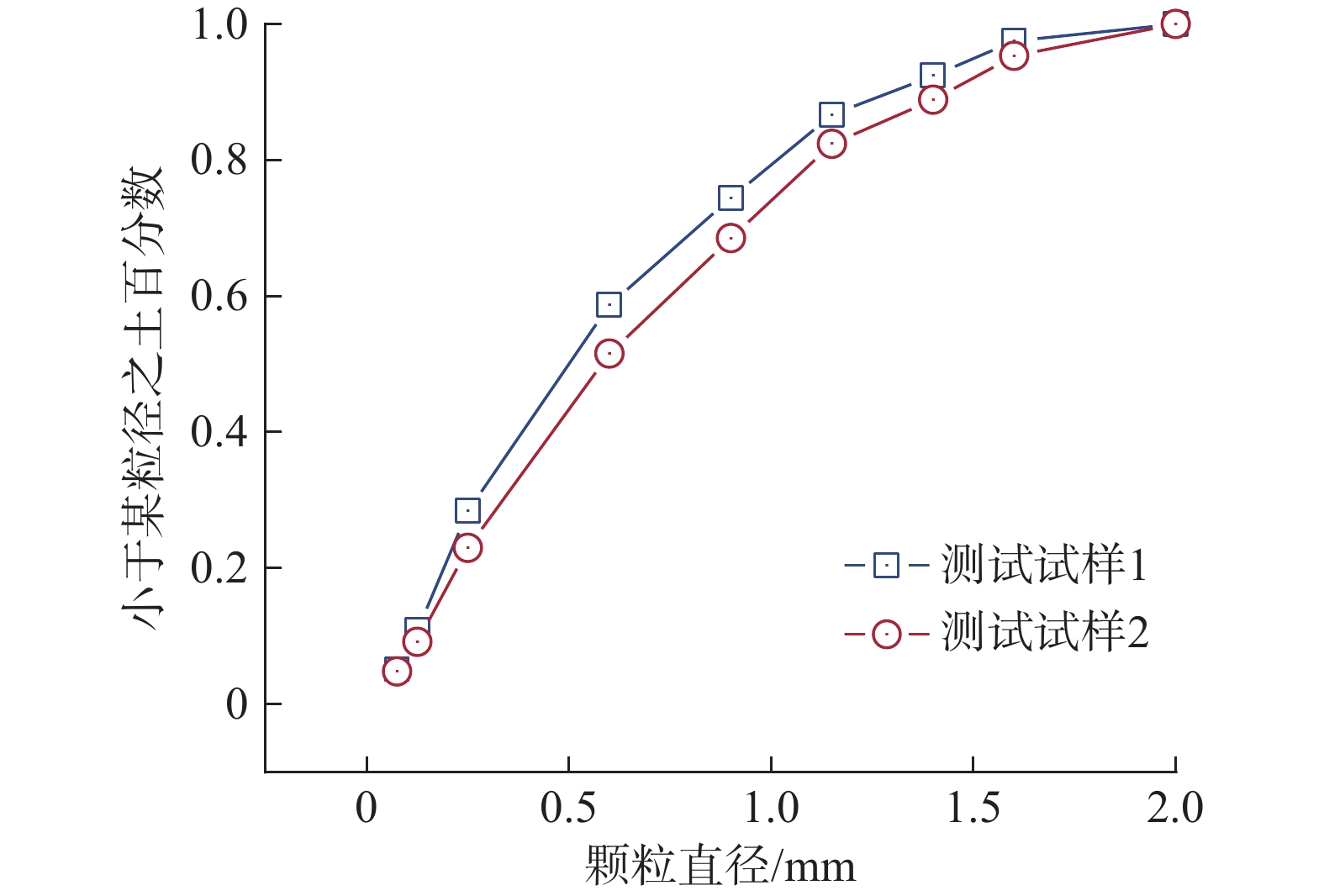
参数 密度/(g·cm−3) 天然含水率/% 比重 最大孔隙比 最小孔隙比 取值 1.066~1.698 10.451 2.644 1.4776 0.5552 表 3 环剪试验工况表
Table 3. Ring shear testing conditions
试验
编号正应力
/kPa剪切速率
/(°·min−1)剪切位移
/mm含水率
/%相对密实度
/%R1 20 10 130.8 0 71.83 R2 50 10 130.8 0 71.83 R3 100 10 130.8 0 71.83 R4 150 10 130.8 0 71.83 R5 20 10 130.8 5 71.83 R6 20 10 130.8 10 71.83 R7 20 10 130.8 20 71.83 R8 20 10 130.8 30 71.83 R9 50 10 130.8 5 71.83 R10 50 10 130.8 10 71.83 R11 50 10 130.8 20 71.83 R12 50 10 130.8 30 71.83 R13 50 20 130.8 0 71.83 R14 50 40 130.8 0 71.83 R15 50 80 130.8 0 71.83 R16 50 10 130.8 0 14.68 R17 50 10 130.8 0 44.53 -
[1] 赵建军,王思敬,尚彦军,等. 全风化花岗岩抗剪强度影响因素分析[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(4):624 − 628. [ZHAO Jianjun,WANG Sijing,SHANG Yanjun,et al. Control factors on shear strength of completely decomposed granite[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2005,26(4):624 − 628. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.04.025
ZHAO Jianjun, WANG Sijing, SHANG Yanjun, et al. Control factors on shear strength of completely decomposed granite[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(4): 624 − 628. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.04.025
[2] 高恺,段红鑫,李华,等. 不同颗粒级配对全风化花岗岩回填土抗剪强度的影响[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2024,46(5):689 − 701. [GAO Kai,DUAN Hongxin,LI Hua,et al. Effect of different particle grading on shearing strength of completely weathered granite backfill soil[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Environment,2024,46(5):689 − 701. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GAO Kai, DUAN Hongxin, LI Hua, et al. Effect of different particle grading on shearing strength of completely weathered granite backfill soil[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Environment, 2024, 46(5): 689 − 701. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 张素敏,朱永全,高炎,等. 全风化花岗岩流变特性试验研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2016,12(4):904 − 911. [ZHANG Sumin,ZHU Yongquan,GAO Yan,et al. Experimental investigation on rheological properties of completely weathered granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2016,12(4):904 − 911. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Sumin, ZHU Yongquan, GAO Yan, et al. Experimental investigation on rheological properties of completely weathered granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2016, 12(4): 904 − 911. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 颜波,汤连生,胡辉,等. 花岗岩风化土崩岗破坏机理分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2009,36(6):68 − 71. [YAN Bo,TANG Liansheng,HU Hui,et al. The mechanism of disintegration damage of granite weathered soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2009,36(6):68 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.06.015
YAN Bo, TANG Liansheng, HU Hui, et al. The mechanism of disintegration damage of granite weathered soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2009, 36(6): 68 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.06.015
[5] 王清,唐大雄,张庆云,等. 中国东部花岗岩残积土物质成分和结构特征的研究[J]. 长春地质学院学报,1991,21(1):73 − 81. [WANG Qing,TANG Daxiong,ZHANG Qingyun,et al. A study on the structure and composition of granite residual soil in the Eastern China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),1991,21(1):73 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Qing, TANG Daxiong, ZHANG Qingyun, et al. A study on the structure and composition of granite residual soil in the Eastern China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 1991, 21(1): 73 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 戴航,晏鄂川,谭延嗣,等. 通城花岗岩残积土的物理力学特性及工程安全性对比研究[J]. 安全与环境工程,2020,27(2):132 − 139. [DAI Hang,YAN Echuan,TAN Yansi,et al. Comparison of physical mechanics and engineering safety characteristics of granite residual soil in Tongcheng County[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2020,27(2):132 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DAI Hang, YAN Echuan, TAN Yansi, et al. Comparison of physical mechanics and engineering safety characteristics of granite residual soil in Tongcheng County[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2020, 27(2): 132 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] LU Yiwei,SHI Yujie,CHEN Bin,et al. Structural damage characteristics and mechanism of granite residual soil[J]. Applied Rheology,2024,34(1):20240011. doi: 10.1515/arh-2024-0011
[8] 王深法,王援高,胡珍珍. 浙江山地滑坡现状及其成因[J]. 山地学报,2000,18(4):373 − 376. [WANG Shenfa,WANG Yuangao,HU Zhenzhen. Actuality of hill sliding and its cause in the mountainous region of Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Mountain Research,2000,18(4):373 − 376. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2000.04.016
WANG Shenfa, WANG Yuangao, HU Zhenzhen. Actuality of hill sliding and its cause in the mountainous region of Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Mountain Research, 2000, 18(4): 373 − 376. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2000.04.016
[9] 詹良通,李鹤,陈云敏,等. 东南沿海残积土地区降雨诱发型滑坡预报雨强-历时曲线的影响因素分析[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(3):872 − 880. [ZHAN Liangtong,LI He,CHEN Yunmin,et al. Parametric analyses of intensity-duration curve for predicting rainfall-induced landslides in residual soil slope in southeastern coastal areas of China[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(3):872 − 880. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.03.035
ZHAN Liangtong, LI He, CHEN Yunmin, et al. Parametric analyses of intensity-duration curve for predicting rainfall-induced landslides in residual soil slope in southeastern coastal areas of China[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(3): 872 − 880. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.03.035
[10] BAI Huilin,FENG Wenkai,YI Xiaoyu,et al. Group-occurring landslides and debris flows caused by the continuous heavy rainfall in June 2019 in Mibei Village,Longchuan County,Guangdong Province,China[J]. Natural Hazards,2021,108(3):3181 − 3201. doi: 10.1007/s11069-021-04819-1
[11] BAI Huilin,FENG Wenkai,LI Shuangquan,et al. Flow-slide characteristics and failure mechanism of shallow landslides in granite residual soil under heavy rainfall[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2022,19(6):1541 − 1557. doi: 10.1007/s11629-022-7315-8
[12] SEGUÍ C,RATTEZ H,VEVEAKIS M. On the stability of deep-seated landslides. The cases of vaiont (Italy) and shuping (Three Gorges Dam,China)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2020,125(7):e2019JF005203. doi: 10.1029/2019JF005203
[13] 赵建军,王思敬,尚彦军,等. 香港全风化花岗岩饱和直剪试验中的剪胀问题[J]. 工程地质学报,2005,13(1):44 − 48. [ZHAO Jianjun,WANG Sijing,SHANG Yanjun,et al. Dilatation in direct shear tests of Hong Kong completely decomposed granite (cdg)[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2005,13(1):44 − 48. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2005.01.007
ZHAO Jianjun, WANG Sijing, SHANG Yanjun, et al. Dilatation in direct shear tests of Hong Kong completely decomposed granite (cdg)[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2005, 13(1): 44 − 48. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2005.01.007
[14] 尚彦军,岳中琦,赵建军,等. 全风化花岗岩抗剪强度试验结果对比及影响因素分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2004,12(2):199 − 207. [SHANG Yanjun,YUE Zhongqi,ZHAO Jianjun,et al. Comparison of shearing strengths of the completely decomposed granite and analysis of contributing factors[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2004,12(2):199 − 207. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.02.015
SHANG Yanjun, YUE Zhongqi, ZHAO Jianjun, et al. Comparison of shearing strengths of the completely decomposed granite and analysis of contributing factors[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2004, 12(2): 199 − 207. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.02.015
[15] 龙志东,王中文,史斌,等. 花岗岩残积土抗剪强度及其影响因素试验[J]. 长沙理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,13(3):25 − 31. [LONG Zhidong,WANG Zhongwen,SHI Bin,et al. Experimental research for shear strength and its influencing factors of granite residual soil[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science & Technology (Natural Science),2016,13(3):25 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9331.2016.03.005
LONG Zhidong, WANG Zhongwen, SHI Bin, et al. Experimental research for shear strength and its influencing factors of granite residual soil[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science & Technology (Natural Science), 2016, 13(3): 25 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9331.2016.03.005
[16] 许旭堂,简文彬,柳侃. 含水率和干密度对残积土抗剪强度参数的影响[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2015,11(2):364 − 369. [XU Xutang,JIAN Wenbin,LIU Kan. The influence of water content and dry density on shear strength parameters of residual soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2015,11(2):364 − 369. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Xutang, JIAN Wenbin, LIU Kan. The influence of water content and dry density on shear strength parameters of residual soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2015, 11(2): 364 − 369. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 郑武略,袁文俊,张富春,等. 卸荷条件下红层花岗岩残积土力学特性试验研究[J/OL]. 岩土工程技术,(2024-12-18)[2024−12−28]. [ZHENG Wulue,YUAN Wenjun,ZHANG Fuchun,et al. Mechanical properties of redbed granite residual soil under unloading conditions[J/OL]. Geotechnical Technology,(2024-12-18)[2024−12−28]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3813.TU.20241216.1509.004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHENG Wulue, YUAN Wenjun, ZHANG Fuchun, et al. Mechanical properties of redbed granite residual soil under unloading conditions[J/OL]. Geotechnical Technology, (2024-12-18)[2024−12−28]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3813.TU.20241216.1509.004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 马勤国,郭皓公,罗晓晓. 非饱和花岗岩残积土的剪切特性与抗剪强度分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2024,52(11):55 − 68. [MA Qinguo,GUO Haogong,LUO Xiaoxiao. Analysis on shear characteristics and shear strength of unsaturated granite residual soil[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2024,52(11):55 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MA Qinguo, GUO Haogong, LUO Xiaoxiao. Analysis on shear characteristics and shear strength of unsaturated granite residual soil[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(11): 55 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 陈晓平,周秋娟,蔡晓英. 高液限花岗岩残积土的物理特性和剪切特性[J]. 岩土工程学报,2011,33(6):901 − 908. [CHEN Xiaoping,ZHOU Qiujuan,CAI Xiaoying. Physical properties and shear strength characteristics of high liquid limit granite residual soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2011,33(6):901 − 908. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Xiaoping, ZHOU Qiujuan, CAI Xiaoying. Physical properties and shear strength characteristics of high liquid limit granite residual soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(6): 901 − 908. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] HU Bowen,HU Qizhi,LIU Yiming,et al. Research on the improvement of granite residual soil caused by fly ash and its slope stability under rainfall conditions[J]. Applied Sciences,2024,14(9):3734. doi: 10.3390/app14093734
[21] 路昌明,王祚鹏,吴靓,等. 基于环剪试验的蠕变型滑坡滑带力学性质——以甘肃舟曲地区锁儿头滑坡为例[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2024,46(5):677 − 688. [LU Changming,WANG Zuopeng,WU Liang,et al. Mechanical properties of creep-type landslide slip zone based on ring shear test:A case study of Suo’ertou landslide in Zhouqu area of Gansu,China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2024,46(5):677 − 688. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LU Changming, WANG Zuopeng, WU Liang, et al. Mechanical properties of creep-type landslide slip zone based on ring shear test: A case study of Suo’ertou landslide in Zhouqu area of Gansu, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2024, 46(5): 677 − 688. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 洪勇,孙涛,栾茂田,等. 土工环剪仪的开发及其应用研究现状[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(3):628 − 634. [HONG Yong,SUN Tao,LUAN Maotian,et al. Development and application of geotechnical ring shear apparatus:An overview[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2009,30(3):628 − 634. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.03.009
HONG Yong, SUN Tao, LUAN Maotian, et al. Development and application of geotechnical ring shear apparatus: An overview[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(3): 628 − 634. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.03.009
[23] 王振涛. 滑带土长距离剪切强度及对滑坡启动的影响[J]. 人民长江,2015,46(9):51 − 53. [WANG Zhentao. Long- distance shear strength of slide- zone soil and its effect on landslide initiation[J]. Yangtze River,2015,46(9):51 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Zhentao. Long- distance shear strength of slide- zone soil and its effect on landslide initiation[J]. Yangtze River, 2015, 46(9): 51 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 吴迪,简文彬,徐超. 残积土抗剪强度的环剪试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(7):2045 − 2050. [WU Di,JIAN Wenbin,XU Chao. Research on shear strength of residual soils by ring shear tests[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2011,32(7):2045 − 2050. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.07.022
WU Di, JIAN Wenbin, XU Chao. Research on shear strength of residual soils by ring shear tests[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(7): 2045 − 2050. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.07.022
[25] WANG Tengfei,YIN Kunlong,LI Yuanyao,et al. Interpretation of the reactivation of slow-moving landslides based on ring shear tests and monitoring[J]. Natural Hazards,2022,114(3):2991 − 3013. doi: 10.1007/s11069-022-05502-9
[26] RAJ BHAT D. Shear rate effect on residual strength of typical clay soils[J]. Innovative Infrastructure Solutions,2021,7(1):36.
[27] WANG Yanchao,CONG Lu. Effects of water content and shearing rate on residual shear stress[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering,2019,44(10):8915 − 8929. doi: 10.1007/s13369-019-03922-7
[28] ZHU Rongsen,XIE Wanli,LIU Qiqi,et al. Shear behavior of sliding zone soil of loess landslides via ring shear tests in the South Jingyang Plateau[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2022,81(6):244. doi: 10.1007/s10064-022-02719-7
[29] YUAN Weina,FAN Wen,JIANG Chengcheng,et al. Experimental study on the shear behavior of loess and paleosol based on ring shear tests[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,250:11 − 20. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.01.007
[30] 中华人民共和国建设部. 岩土工程勘察规范:GB 50021—2001[S]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2004. [Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Code for investigation of geotechnical engineering:GB 50021—2001[S]. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press,2004. (in Chinese)]
Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Code for investigation of geotechnical engineering: GB 50021—2001[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[31] 吴仕川. 花岗岩风化带的野外划分方法[J]. 土工基础,2013,27(6):105 − 106. [WU Shichuan. Field classification of granite weathering zone[J]. Soil Engineering and Foundation,2013,27(6):105 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Shichuan. Field classification of granite weathering zone[J]. Soil Engineering and Foundation, 2013, 27(6): 105 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 陈敬业,王钧,宫清华,等. 植被增渗效应对花岗岩残积土浅层滑坡的影响机理研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):115 − 124. [CHEN Jingye,WANG Jun,GONG Qinghua,et al. Influence mechanism of vegetation infiltration effect on shallow landslides of granite residual soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):115 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Jingye, WANG Jun, GONG Qinghua, et al. Influence mechanism of vegetation infiltration effect on shallow landslides of granite residual soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(3): 115 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 孙强,张泰丽,伍剑波,等. 植被对台风暴雨型滑坡发育的促进作用[J]. 中国地质调查,2022,9(4):66 − 73. [SUN Qiang,ZHANG Taili,WU Jianbo,et al. Promoting effect of vegetation on the landslide induced by typhoon rainstorm[J]. Geological Survey of China,2022,9(4):66 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Qiang, ZHANG Taili, WU Jianbo, et al. Promoting effect of vegetation on the landslide induced by typhoon rainstorm[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2022, 9(4): 66 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] KIMURA S,NAKAMURA S,VITHANA S B,et al. Shearing rate effect on residual strength of landslide soils in the slow rate range[J]. Landslides,2014,11(6):969 − 979. doi: 10.1007/s10346-013-0457-6
[35] LI Y R,WEN B P,AYDIN A,et al. Ring shear tests on slip zone soils of three giant landslides in the Three Gorges Project area[J]. Engineering Geology,2013,154:106 − 115. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.12.015
[36] WANG Gonghui,SUEMINE A,SCHULZ W H. Shear-rate-dependent strength control on the dynamics of rainfall-triggered landslides,Tokushima Prefecture,Japan[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2010,35(4):407 − 416. doi: 10.1002/esp.1937
[37] VALLEJO L E. Interpretation of the limits in shear strength in binary granular mixtures[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2001,38(5):1097 − 1104. doi: 10.1139/t01-029
[38] SADREKARIMI A,OLSON S M. Shear band formation observed in ring shear tests on sandy soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2010,136(2):366 − 375. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000220
[39] DOU Hongqiang,XIE Senhua,CHEN Feng,et al. Study on shear characteristics and a mechanics model of granite residual soil–rock interface[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2023,82(6):212. doi: 10.1007/s10064-023-03220-5
[40] TANG Chaosheng,SHI Bin,LIU Chun,et al. Experimental characterization of shrinkage and desiccation cracking in thin clay layer[J]. Applied Clay Science,2011,52(1/2):69 − 77.
[41] TAKE W A,BOLTON M D. Seasonal ratcheting and softening in clay slopes,leading to first-time failure[J]. Géotechnique,2011,61(9):757 − 769.
[42] MORBIDELLI R,CORRADINI C,SALTALIPPI C,et al. Initial soil water content as input to field-scale infiltration and surface runoff models[J]. Water Resources Management,2012,26(7):1793 − 1807. doi: 10.1007/s11269-012-9986-3
[43] DENG Yusong,DUAN Xiaoqian,DING Shuwen,et al. Suction stress characteristics in granite red soils and their relationship with the collapsing gully in south China[J]. Catena,2018,171:505 − 522. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.07.043
[44] 黄淙葆,代张音,高威挺,等. 贵州公路旁边坡滑带土抗剪强度特性研究[J]. 地质与资源,2023,32(3):366 − 372. [HUANG Congbao,DAI Zhangyin,GAO Weiting,et al. Shear strength characteristics of soil in the sliding zone on highway slope in Guizhou Province[J]. Geology and Resources,2023,32(3):366 − 372. (in Chinese)]
HUANG Congbao, DAI Zhangyin, GAO Weiting, et al. Shear strength characteristics of soil in the sliding zone on highway slope in Guizhou Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2023, 32(3): 366 − 372. (in Chinese)
[45] MA Penghui,PENG Jianbing,NAN Yalin,et al. The shear behavior of the slip zone loess and landslide mechanism[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2023,257:105833. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2023.105833
[46] 陈剑平,刘经,王清,等. 含水率对分散性土抗剪强度特性影响的微观解释[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(3):792 − 803. [CHEN Jianping,LIU Jing,WANG Qing,et al. Microscopic interpretation of water content influence on shear strength of dispersive soil[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(3):792 − 803. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Jianping, LIU Jing, WANG Qing, et al. Microscopic interpretation of water content influence on shear strength of dispersive soil[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2021, 51(3): 792 − 803. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[47] 刘寒冰,张互助,王静. 冻融及含水率对压实黏质土力学性质的影响[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(1):158 − 164. [LIU Hanbing,ZHANG Huzhu,WANG Jing. Effect of freeze-thaw and water content on mechanical properties of compacted clayey soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(1):158 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Hanbing, ZHANG Huzhu, WANG Jing. Effect of freeze-thaw and water content on mechanical properties of compacted clayey soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(1): 158 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[48] DAI Mingjie,CUI Deshan,CHEN Qiong,et al. Reactivated mechanism of a slow-moving landslide with two shear zones based on ring shear test and in situ monitoring[J]. Landslides,2024,21(11):2617 − 2634. doi: 10.1007/s10346-024-02320-x
[49] LI Zhe,LI Juqiang,HAN Meng,et al. Investigating the shear strength characteristics of slip zone soil based on in situ multiple shear tests[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2023,27(9):3793 − 3807. doi: 10.1007/s12205-023-2095-4
[50] XIAO Yang,YUAN Zhengxin,DESAI C S,et al. Effects of load duration and stress level on deformation and particle breakage of carbonate sands[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2020,20(7):06020014.
[51] YU Fangwei. Particle breakage and the drained shear behavior of sands[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2017,17(8):04017041.
[52] LAI Zhiqiang,VALLEJO L E,ZHOU Wei,et al. Collapse of granular columns with fractal particle size distribution:Implications for understanding the role of small particles in granular flows[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2017,44(24):12181 − 9.
[53] LIN Qiwen,CHENG Qiangong,LI Kun,et al. Contributions of rock mass structure to the emplacement of fragmenting rockfalls and rockslides:Insights from laboratory experiments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),2020,125(4):e2019JB019296. doi: 10.1029/2019JB019296
[54] DAVIES T R H. Spreading of rock avalanche debris by mechanical fluidization[J]. Rock Mechanics,1982,15(1):9 − 24. doi: 10.1007/BF01239474
-




 下载:
下载: