SEISMIC REFLECTION CHARACTERISTICS OF NANWEI UPLIFT ZONE IN NANSHA AND THEIR APPLICATION TO STRUCTURAL UNIT DIVISION
-
摘要:
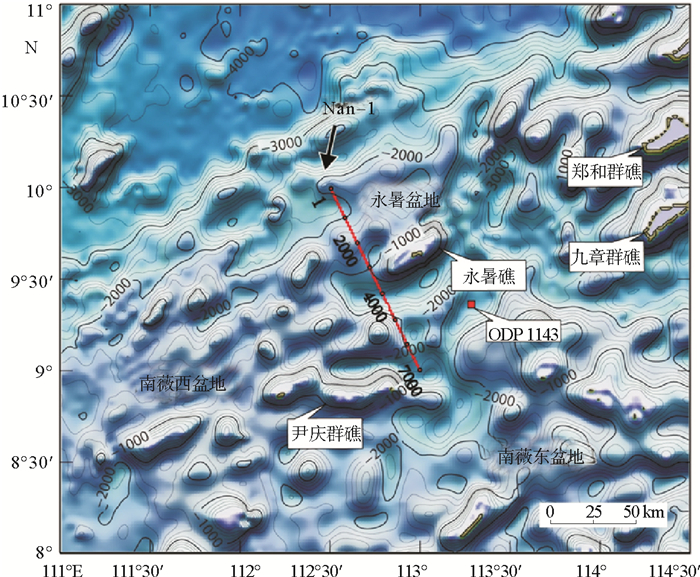
南薇隆起区地处南沙地块西北部,紧邻西南次海盆,周围发育大量陆缘裂解盆地。裂陷盆地拥有丰富的油气资源。地块经历了中生代末期至古近纪裂谷拉张,并随晚始新世的海底扩张向南漂移至现今位置。结合区域以往地震剖面和钻井数据,分析了2013年中科院南海海洋研究所“实验2号”采集的高分辨率单道地震数据(Nan-1),总结了南薇隆起区的地震反射特征。认为南薇隆起区主要由南部裂陷下沉带和北部埋藏火山隆起带两个结构单元组成。从北到南,埋藏火山隆起带跨越约63 km的范围,裂陷下沉带跨越约58 km的范围。地震剖面清晰地揭示了该区向海盆侧隆起且在SE向成带的特征。南薇区具有拉张背景,其形成与演化主要是与西南次海盆的扩张作用,以及南沙地块与婆罗洲地块的碰撞作用等有关。自上新世以来,整个南薇隆起区进入构造活动相对稳定阶段,地壳稳定性较好。
Abstract:A large number of continental margin rifting basins are well developed on the Nanwei uplift of Nansha Waters, which bears great oil and gas potentials. The region experienced a complex evolutionary history in Cenozoic period, including extensional rifting from Late Mesozoic to Paleogene and seafloor spreading in Late Eocene. A high-resolution single-channel seismic line Nan-1, acquired in the Nansha by the trial vessel "Shiyan 2" of the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology in 2013, is interpreted and analyzed in this study. As well, some previous seismic profiles and drilling data are studied. The seismic reflection characteristics of the Nanwei uplift in the southern margin are summarized and outlined briefly. Results show that the Nanwei uplift zone is mainly composed of two structural units, the southern belt of subsidence and the northern belt of buried volcanic uplift. Compared to the previous reflection seismic data in this area, some main seismic reflection layers are divided. The belt of buried volcanic uplift is about 63 km wide, and the neighboring subsidence belt 58 km wide both in SE direction. The distribution of sporadic epicenters stronger than 4 magnitude earthquakes suggest that the entire Nanwei uplift is still a relatively stable tectonic body since Pliocene.
-
Key words:
- seismic reflection /
- structural unit /
- Nanwei uplift /
- Nansha Waters /
- Yongshu Reef
-

-
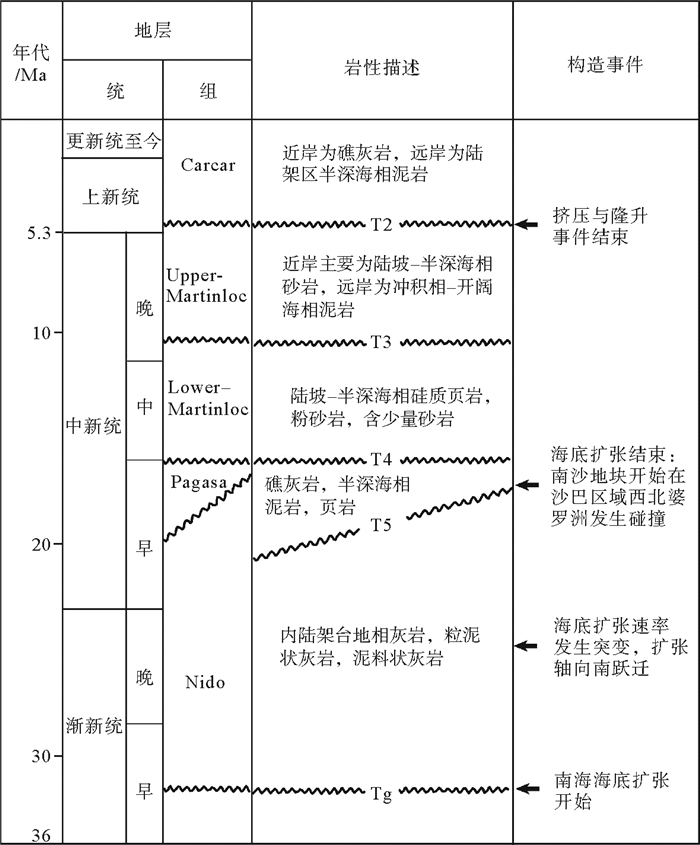
图 3 研究区主要地层界面时代、岩性及主要构造事件(据文献[8])
Figure 3.
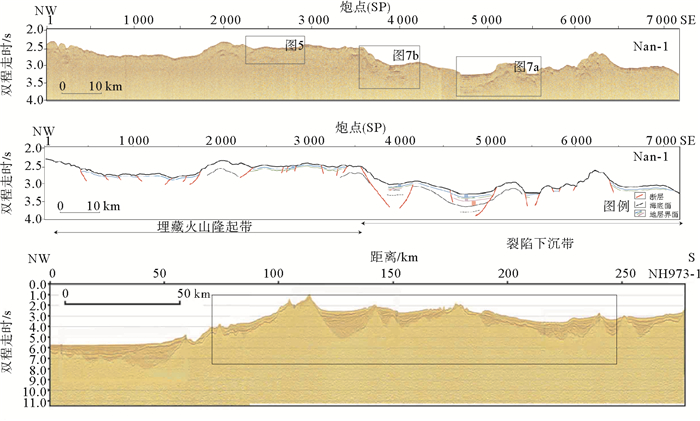
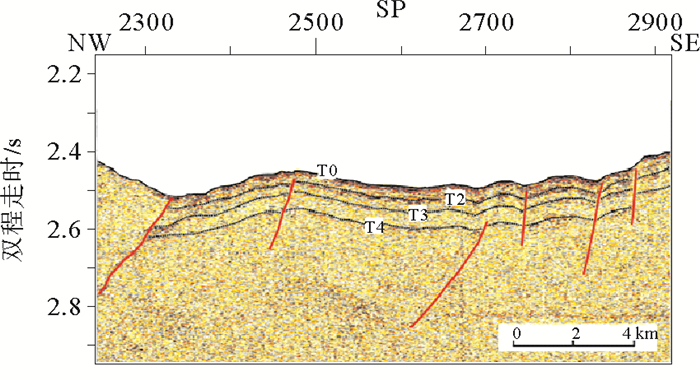
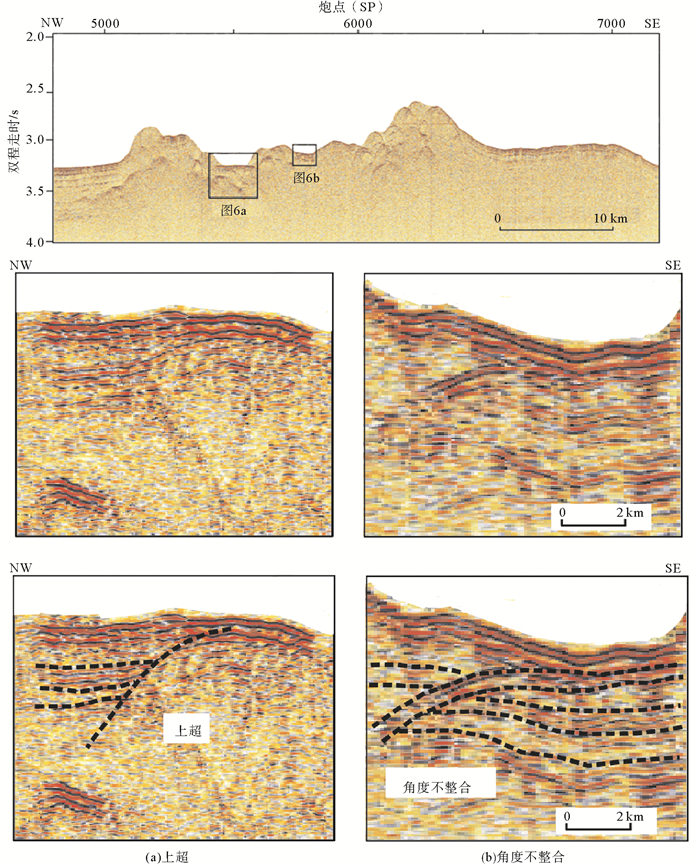
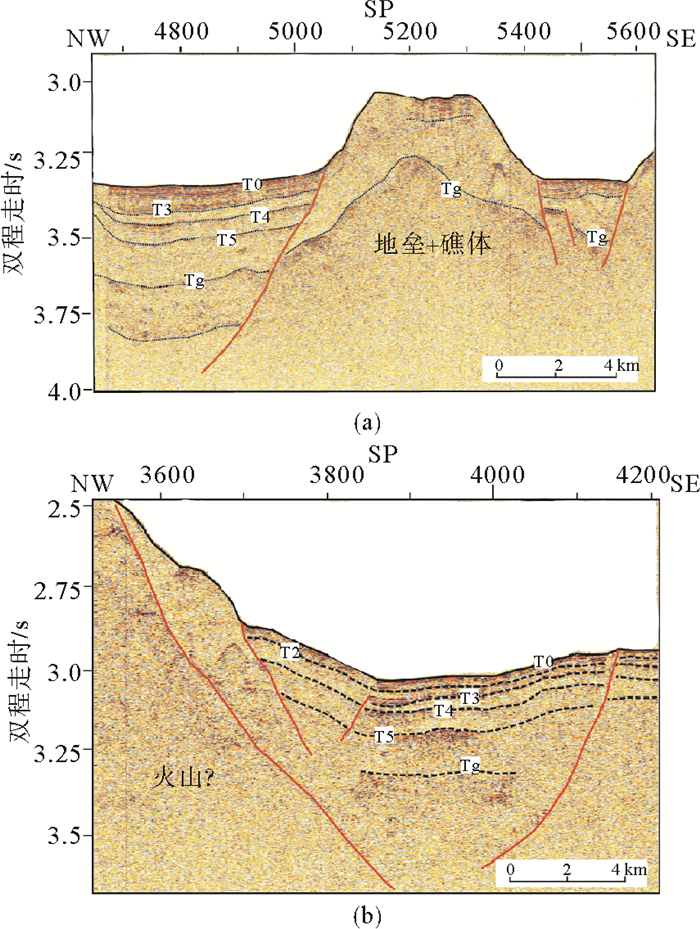
图 4 南薇隆起区的单道地震剖面Nan-1和穿越西南次海盆的NH973-1多道地震剖面(据Ding et al., 2013,修改;位置见图 1)
Figure 4.
-
[1] Brian Taylor, Dennis E. Hayes. The tectonic evolution of the South China Basin[C]//In: Dennis E. Hayes (Ed.). The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands. AGU, Washington D C 1980, 23: 89-104.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279609699_The_tectonic_evolution_of_the_South_China_Sea_Basin [2] Briais A, Patriat P, Tapponnier P. Updated interpretation of magnetic anomalies and seafloor spreading stages in the South China Sea: Implications for the Tertiary tectonics of Southeast Asia[J].Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978-2012), 1993, 98(B4): 6299-6328. doi: 10.1029/92JB02280
[3] ChunFeng Li, Xing Xu, Jian Lin, et al. Ages and magnetic structures of the South China Sea constrained by deep tow magnetic surveys and IODP Expedition 349[J]. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2014, 15: 4958-4983. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005567
[4] Brian Taylor, Dennis E. Hayes. Origin and history of the South China Basin[C]//In: Dennis E. Hayes (Ed.). The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands: Part 2. AGU, 1983, 27: 23-56.
[5] 李家彪.中国边缘海形成演化与资源效应[M].北京:海洋出版社, 2008: 148.
LI Jiabiao. Evolution of China′s Marginal Seas and its Effect of Natural Resources[M]. China Ocean Press, 2008: 148.
[6] 姚伯初, 万玲, 吴能友.大南海地区新生代板块构造活动[J].中国地质, 2004, 31(2): 113-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.02.001
YAO Bochu, WAN Ling, WU Nengyou. Cenozoic plate tectonic activities in the Great South China area[J]. Geology in China, 2004, 31(2): 113-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.02.001
[7] 姚伯初.南海新生代的构造演化与沉积盆地[C]//南海地质研究, 1998(10): 1-17.
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NHDZ199800000.htm YAO Bochu. The tectonic evolution and sedimentary basins of South China Sea in Cenozoic[C]//Geological Research of South China Sea, 1998(10): 1-17.
[8] 丁巍伟, 李家彪.南海南部陆缘构造变形特征及伸展作用:来自两条973多道地震测线的证据[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12): 3038-3056. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.006
DING Weiwei, LI Jiabiao. Seismic stratigraphy, tectonic structure and extension factors across the southern margin of the South China Sea: evidence from two regional multi-channel seismic profiles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(12): 3038-3056. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.006
[9] DING Weiwei, Franke Dieter, LI Jiabiao, et al. Seismic stratigraphy and tectonic structure from a composite multi-channel seismic profile across the entire Dangerous Grounds, South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013 (582): 162-176. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8574214
[10] 张功成, 屈红军, 刘世翔, 等.边缘海构造旋回控制南海深水区油气成藏[J].石油学报, 2015, 36(5): 533-545. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201505002
ZHANG Gongcheng, QU Hongjun, LIU Shixiang, et al. Tectonic cycle of marginal sea controlled the hydrocarbon accumulation in deep-water areas of South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(5): 533-545. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201505002
[11] 张功成, 谢晓军, 王万银, 等.中国南海含油气盆地构造类型及勘探潜力[J].石油学报, 2013, 34(4): 611-627. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201304001
ZHANG Gongcheng, XIE Xiaojun, WANG Wanyin, et al. Tectonic types of petroliferous basins and its exploration potential in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(4): 611-627. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201304001
[12] 熊莉娟, 李三忠, 索艳慧, 等.南海南部新生代控盆断裂特征及盆地群成因[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6): 113-127. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201206010
XIONG Lijuan, LI Sanzhong, SUO Yanhui, et al. Cenozoic Basin-controlling faults and their bearing on basin groups formation in the southern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 113-127. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201206010
[13] 孙福利, 王真理, 郝天珧, 等.南海南部深部结构的复杂构造地震成像[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12): 3210-3216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.020
SUN Fuli, WANG Zhenli, HAO Tianyao, et al. Seismic imaging of complicated deep structures in southern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(12): 3210-3216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.020
[14] 程子华, 丁巍伟, 董崇志, 等.南海南部地壳结构的重力模拟及伸展模式探讨[J].高校地质学报, 2014, 20(2): 239-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.02.008
CHENG Zihua, DING Weiwei, DONG Chongzhi, et al. Crustal structures inferred from gravity modeling and stretching model in the south of South China Sea [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2014, 20(2): 239-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.02.008
[15] WANG Yanlin, QIU Yan, YAN Pin, et al. Seismic evidence for Mesozoic strata in the northern Nansha waters, South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, 677-678: 190-198. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.04.003
[16] 彭学超, 郭依群, 陈玲, 等.南沙中部海域诸盆地地震地层分析[J].石油物探, 2003, 42(4): 486-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2003.04.013
PENG Xuechao, GUO Yiqun, CHEN Ling, et al. Seismic stratigraphic analysis of basins Nanweixi and Nanweidong in middle Nansha, South China Sea [J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2003, 42(4): 486-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2003.04.013
[17] YAN Pin, LIU Hailing. Tectonic-stratigraphic division and blind fold structures in Nansha Waters, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 24: 337-348. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.12.005
[18] 孙珍, 赵中贤, 李家彪, 等.南沙地块内破裂不整合与碰撞不整合的构造分析[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12): 3196-3209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.019
SUN Zhen, ZHAO Zhongxian, LI Jiabiao, et al. Tectonic analysis of the breakup and collision unconformities in the Nansha[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(12): 3196-3209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.019
[19] 孙珍, 赵中贤, 周蒂, 等.南沙海域盆地的地层系统与沉积结构[J].地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(5): 798-806. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201105003
SUN Zhen, ZHAO Zhongxian, ZHOU Di, et al. The Stratigraphy and the sequence architecture of the basins in Nansha region[J]. Earth Science - Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(5): 798-806. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201105003
[20] 李三忠, 索艳慧, 刘鑫, 等.南海的盆地群与盆地动力学[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6): 55-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201206006
LI Sanzhong, SUO Yanhui, LIU Xin, et al. Basin dynamics and basin groups of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 55-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201206006
[21] 吴世敏, 周蒂, 刘海龄.南沙地块构造格局及其演化特征[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2004, 28(1): 23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2004.01.004
WU Shimin, ZHOU Di, LIU Hailing. Tectonic framework and evolutionary characteristics of Nansha block, South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2004, 28(1): 23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2004.01.004
[22] 解习农, 任建业, 王振峰, 等.南海大陆边缘盆地构造演化差异性及其与南海扩张耦合关系[J].地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 77-87. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201501007
XIE Xinong, REN Jianye, WANG Zhenfeng, et al. Difference of tectonic evolution of continental marginal basins of South China Sea and relationship with SCS spreading [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 077-087. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201501007
[23] 高红芳.南沙中部海域南薇西盆地、南薇东盆地构造演化差异性分析[J].南海地质研究, 2002(14): 35-44. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200302177827
GAO Hongfang. Comparison study of tectonic evolution between Nanweixi basin and Nanweidong basin, South China Sea[J]. Geological Research of South China Sea, 2002(14):35-44. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200302177827
[24] Chang Jih-Hsin, Hsu Ho-Han, Liu Char-Shine, et al. Seismic sequence stratigraphic analysis of the carbonate platform, north offshore Taiping Island, Dangerous Grounds, South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.12.010.
[25] Stephan Steuera, Dieter Frankea, Florian Meresseb, et al. Oligocene-Miocene carbonates and their role for constraining the rifting and collision history of the Dangerous Grounds, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 58(Part B): 644-657. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=38e9739b3438000b8ca650b0122f3236
[26] 魏喜, 贾承造, 孟卫工, 等.西沙海域新近纪以来生物礁分布规律及油气勘探方向探讨[J].石油地球物理勘探, 2008, 43(3):308-312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2008.03.013
WEI Xi, JIA Chengzao, MENG Weigong, et al. Discussion on biogenetic reef distribution and hydrocarbon exploration direction in Xisha sea area since Neogene[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2008, 43(3): 308-312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2008.03.013
[27] 冯英辞, 詹文欢, 姚衍桃, 等.西沙群岛礁区的地质构造及其活动性分析[J].热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(3): 48-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.03.006
FENG Yingci, ZHAN Wenhuan, YAO Yantao, et al. Analysis of tectonic movement and activity in the organic reef region around the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(3): 48-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.03.006
[28] 中国科学院南沙综合科学考察队.南沙群岛永暑礁第四纪珊瑚礁地质[M].北京:海洋出版社, 1992.
Multidisciplinary Oceanographic Expedition Team of Academia Sinica to the Nansha Islands. Quaternary Coral Reef Geology of Yongshu Reef, Nansha Islands[M]. China Ocean Press, 1992.
[29] 朱袁智, 沙庆安, 郭丽芬, 等.南沙群岛永暑礁新生代珊瑚礁地质[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997.
ZHU Yuanzhi, SHA Qingan, GUO Lifen, et al. Cenozoic Coral Reef Geology of Yongshu Reef, Nansha Islands [M]. Science Press, Beijing, 1997.
[30] 汤贤赞, 唐诚, 陈木宏, 等.南沙群岛永暑礁钻井珊瑚礁和珊瑚碎屑的磁学分析[J].热带海洋学报, 2003, 22(3): 44-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.03.007
TANG Xianzan, TANG Cheng, CHEN Muhong, et al. Magnetism of drilling coral reef and coral clast from Yongshu atoll of Nansha Islands, Southern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2003, 22(3): 44-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.03.007
[31] 赵焕庭.南海诸岛珊瑚礁新构造运动的特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1998, 18(1): 37-45. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199801028456
ZHAO Huanting. Characteristics of neotectonic movement of coral reef area of the South China Sea islands[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1998, 18(1): 37-45. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199801028456
[32] 赵长煜, 宋海斌, 李家彪, 等.南海西南次海盆NH973-1测线地震解释[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12): 3258-3268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.024
ZHAO Changyu, SONG Haibin, LI Jiabiao, et al. Tectonic and seismic interpretation of line NH973-1 along southwest sub-basin in South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(12): 3258-3268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.024
[33] Hinz K, Schlueter H U. Geology of the Dangerous Grounds, South China Sea, and the continental margin off southwest Palawan: results of SONNE Cruises SO-23 and SO-27[J]. Energy, 1985, 10(3/4): 297-315. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4b2648ec7116a7122b0c581e78b88e3e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[34] Shipboard Scientific Party. Leg 184 Summary: Exploring the Asian Monsoon through Drilling in the South China Sea[R]//In: Wang P, Prell W, Blum P. eds. Proc. ODP, Initial Results, TX: IODP, College Station, 2000: 1-77.
[35] 詹文欢, 刘以宣, 钟建强, 等.南海南部活动断裂与灾害性地质初步研究[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(3): 1-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ199503000.htm
ZHAN Wenhuan, LIU Yixuan, ZHONG Jianqiang, et al. Preliminary analysis of the active faults an hazard geology in the south of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1995, 15(3): 1-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ199503000.htm
[36] 徐行, 姚永坚, 王立非.南海南部海域南薇西盆地新生代沉积特征[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(3): 170-175. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200303005
XU Xing, YAO Yongjian, WANG Lifei. Cenozoic sedimentation of Nanweixi basin, the Southern South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas(Geology), 2003, 17(3): 170-175. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200303005
[37] 刘以宣, 詹文欢.南海变质基底基本轮廓及其构造演化[J].安徽地质, 1994, 4(1-2): 82-90. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-AHDZ4Z1.010.htm
LIU Yixuan, ZHAN Wenhuan. Basin outline and tectonic evolution of the metamorphic basement in the South China Sea[J]. Geology of Anhui, 1994, 4(1-2): 82-90. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-AHDZ4Z1.010.htm
[38] 鲁宝亮, 王璞珺, 吴景富, 等.南海陆缘盆地中生界分布特征及其油气地质意义[J].石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(4): 497-503. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201404017
LU Baoliang, WANG Pujun, Wu Jingfu, et al. Distribution of the Mesozoic in the continental margin basins of the South China Sea and its petroliferous significance[J]. Petroleum exploration and Development, 2014, 41(4): 497-503. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201404017
[39] 朱俊江, 丘学林, 徐辉龙, 等.南海北部洋陆转换带地震反射特征和结构单元划分[J].热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(3): 28-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rdhy201203005
ZHU Junjiang, QIU Xuelin, XU Huilong, et al. Seismic reflection characteristic and structure unit division of a continent-ocean transition zone in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(3): 28-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rdhy201203005
[40] 施小斌, 丘学林, 夏戡原, 等.南海热流特征及其构造意义[J].热带海洋学报, 2003, 22(2): 63-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.02.007
SHI Xiaobin, QIU Xuelin, XIA Kanyuan, et al. Heat flow characteristics and its tectonic significance of South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2003, 22(2): 63-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.02.007
[41] 赵长煜, 宋海斌, 杨振武, 等.南海南部边缘沉积盆地构造—热演化历史[J].地球物理学报, 2014, 57(5): 1543-1553. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWX201405018.htm
ZHAO Changyu, SONG Haibin, YANG Zhenwu, et al. Tectonic and thermal evolution modeling for the marginal basins of the southern South China Sea[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(5): 1543-1553. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWX201405018.htm
[42] 薛晨光, 杨李东.地热监测在地震预报中的应用前景[J].科技信息, 2013, 25: 188. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kjxx201325143
XUE Chenguang, YANG Lidong. Prospects of applying geothermal monitor for the earthquake forecasting[J]. Science&Technology Information, 2013, 25: 188. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kjxx201325143
[43] Dmowska R. Connection between thermal stresses and earthquake processes[J]. Publish of the Institute of Geophysics Polish Academy of Science, 1975, 80: 1-45.
[44] 安镇文, 朱传振.地热异常和地震孕育的发生的关系[J].地震研究, 1985, 8(4): 541-549. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1985-DZYJ198504013.htm
ANZhenwen, ZHU Chuanzhen. Relationship between geothermal anomaly and earthquake development and occurrence[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 1985, 8(4): 541-549. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1985-DZYJ198504013.htm
-




 下载:
下载: