Spatio-temporal distribution of dust sedimentation rate of Tianshan loess since MIS3 and its implications
-
摘要:
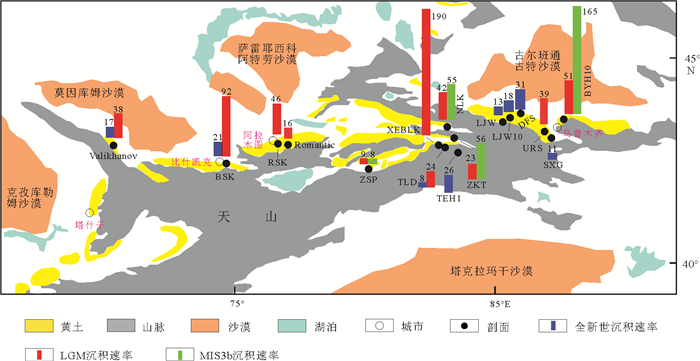
风尘堆积沉积速率的变化对揭示大气环流与古气候变化具有重要意义。基于中亚东北部天山及其周边黄土剖面已有的释光和放射性14C年代数据的分析筛选整理,初步获得了该区深海氧同位素MIS3以来黄土沉积速率的时空变化特征,并探讨了可能的原因。结果表明:(1)末次盛冰期(LGM)沉积速率总体上表现出天山西部低、伊犁盆地高的特征。这种空间变化特征可能与地形、大气环流以及伊犁盆地黄土的近源堆积有关。(2)LGM和MIS3b时期是MIS3阶段以来主要的粉尘沉积阶段。MIS3b时期沉积速率最高,LGM次之,而全新世沉积速率较低。MIS3b时期高的沉积速率可能与大规模的冰川发育有关。在全新世期间,中全新世的沉积速率相对较高,可能与中全新世气候湿润、地表捕获粉尘的能力强有关。
Abstract:Eolian loess is an important archive for understanding Quaternary environmental changes. The sedimentation rate of loess, as an important proxy to environmental changes, is helpful to revealing atmospheric circulation and paleoenvironmental changes. With the application of various dating methods especially the high-accuracy Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL), sedimentation rate has been widely applied to the orbital-scale and millennial-scale paleoclimatic changes recently in the study of Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP). Central Asia is also one of the main distribution areas of world loess. This paper is specially devoted to the spatio-temporal distribution pattern of dust sedimentation rate of the Tianshan loess in order to provide a new horizon for understanding paleoclimatic patterns in Central Asia, where sedimentation rate has been poorly studied. Therefore, we collected the available geochronological data including OSL and 14C of the last glacial loess sections from the Tianshan Mountains of Central Asia in this paper, analyzed the reliability of age data and discussed spatial and temporal distribution pattern of the sedimentation rate. The results suggest that: (1) During the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), sedimentation rate is relatively low in the west of Tianshan, but high in the Ili Basin. This spatial pattern of distribution is closely related to geographic and atmospheric conditions as well as proximal accumulation. (2) LGM and MIS3b are the main dust deposition stages since MIS3. In the Tianshan area, the sedimentation rate of MIS3b is higher than that of LGM. Since the solar insolation in the MIS3b stage is higher than that in the LGM stage, the westerly will bring more moisture from the Atlantic Ocean, Caspian Sea and Mediterranean Sea. In the Tianshan area, moisture is believed the main factor affecting glaciers. In this regard, the scale of glacier in the wetter MIS3b period is larger than that in the LGM period, and the intensified abrasion of the glaciers will bring in more fine particulate matters. (3) Sedimentation rate is low in Holocene, and the variations in sedimentation rate are similar to the 'westerly model'. We speculate that the amount of dust in the atmosphere is relatively low in Holocene. Dust is mainly deposited under wet climate since humidity is conducive to vegetation and helpful for dust to settle down. More moisture will result in higher sedimentation rate.
-
Key words:
- dust sedimentary rate /
- Holocene /
- the last glacial maximum /
- MIS3b /
- Tianshan loess
-

-
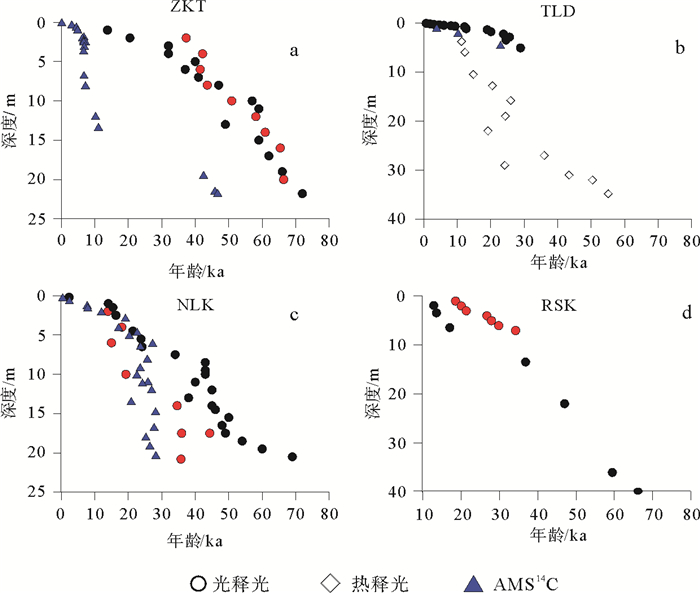
图 2 ZKT、TLD、NLK、RSK剖面年代-深度图(数据来源见表 1)
Figure 2.
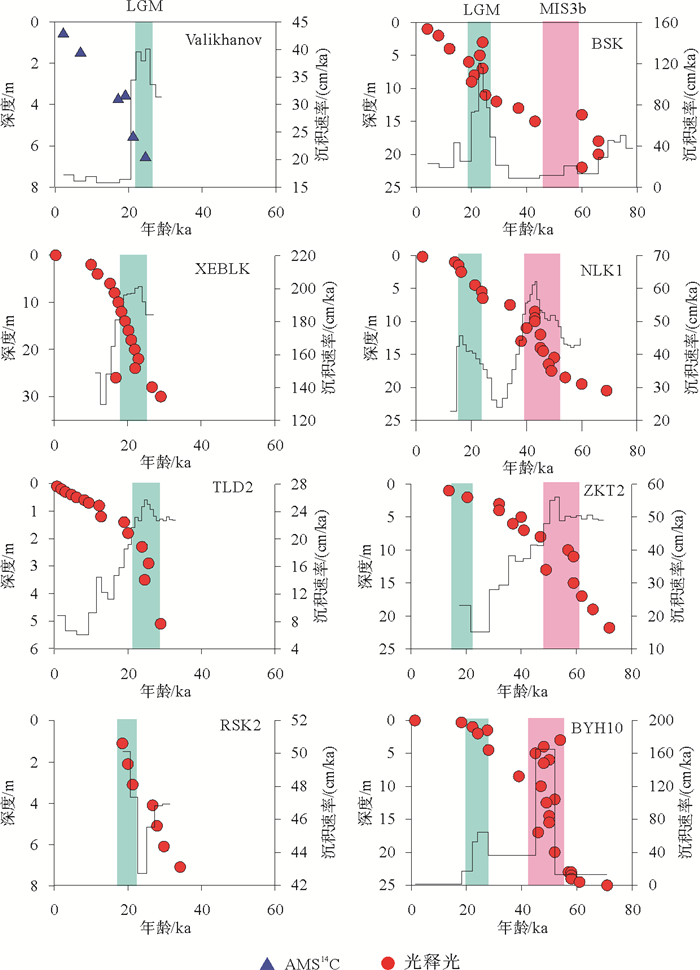
图 3 MIS3以来天山黄土沉积速率变化(数据来源见表 1)
Figure 3.
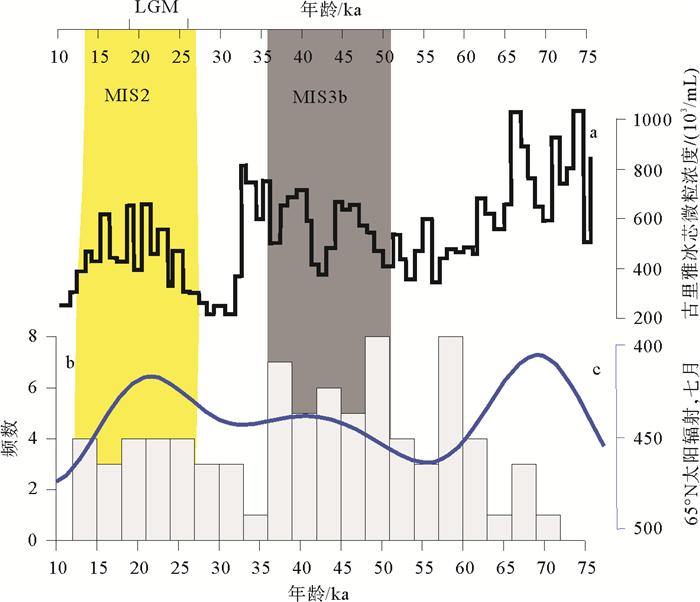
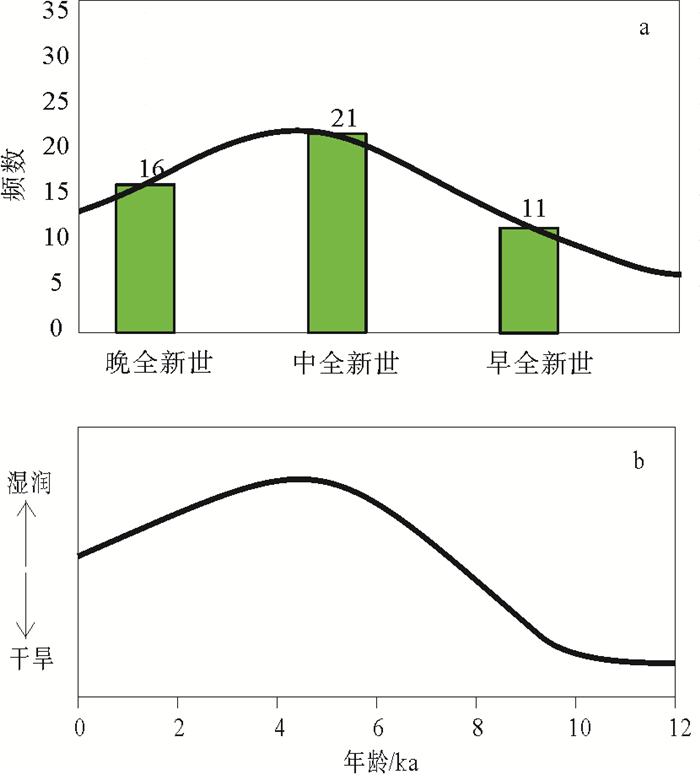
图 6 天山全新世黄土年代分布频数特征(a)及其与西风模式对比(b)(据Chen等[74])
Figure 6.
表 1 剖面位置、年代和厚度
Table 1. Locations, ages and thickness
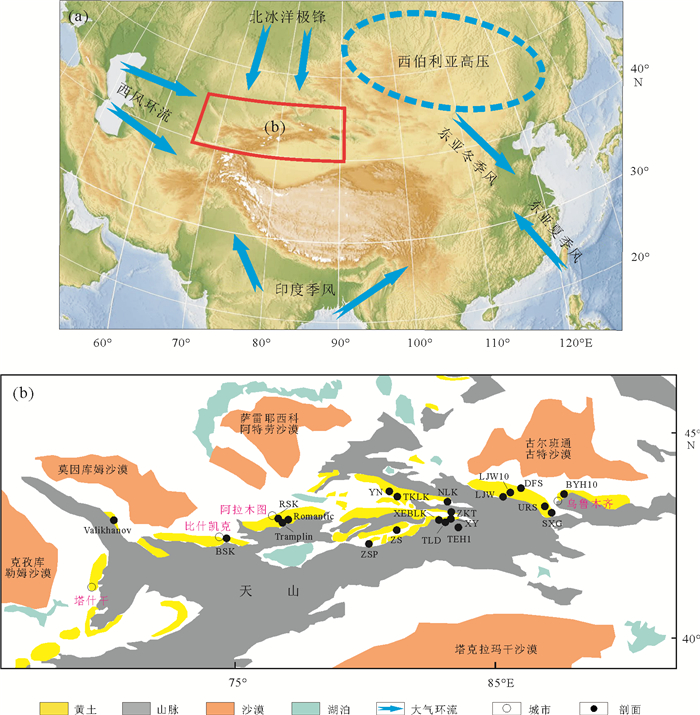
地点 剖面 经纬度坐标及海拔 厚度/m 剖面底部年龄/ka 测年材料及方法 文献来源 TLD1 43°25′N,83°03′E (12) 62.5 AMS14C有机质 [30] TLD2 43°24′5″N,83°2′13″E; 1020m 100(5.1) 29 石英(4~11μm)SAR [17] TLD3 43°25′N,83°03′E; (33.5) 55 TL [56] ZKT1 43°31′53"N,83°18′58"E; 850m 18 62.7 OSL [25] ZKT2 43°32′14"N,83°18′50"E; 900m 23 72 石英(38~63μm)SAR [47] ZKT3 43°32′25"N,83°18′10"E 22.5 46.7 AMS14C蜗牛和OSL [45] 伊犁盆地 XY 43°27′N,83°18′E; (7) 41.4 TL [25] ZSP 42°41′24″N,80°15′00″E; 1875m 6.5 67 AMS14C和石英(4~11μm)Post-IR [44] ZS 43°08′99″N,81°05′65″E; 1920m 4.5 56.9 AMS14C沉积物 [25] XEBLK 43°25′12″N,83°04′12″E; 1050m 30.7 29 石英(38~63μm)SAR [23] NLK1 43°45′36″N,83°15′00″E; 1253m 21 69 石英(38~63μm)SAR [20] NLK2 43°45′36″N,83°15′00″E; 1253m 21 35.8 石英(63~90μm)SAR [49] YN 44°00′N,82°00′E; (6) 9.4 TL [56] TEH1 42°56′N,84°E; 2400m 3.05 8.5 钾长石(150~200μm)pIRIR [55] TKLK 43°52′06″N,81°24′8″E; 636m (5) 9.4 AMS14C有机质 [56] LJW 43°50′23″N,85°07′35″E; 3641m 5(1.1) 7.1 钾长石(63~90μm)MET-pIRIR [27] SXG 43°26′46″N,87°30′27″E; 1636m 2(1.2) 8.7 钾长石(63~90μm)MET-pIRIR [27] LJW10 43°58′29″N,85°20′10"E; 1462m 2.8 12.6 钾长石(38~63μm)pIRIR [19] 天山北坡 DFS 玛纳斯河洪积扇台地,527m 1.8 7 石英(40~63μm)BLSL [48] BYH10 44°02′27"N,87°47′54"E; 622m 30 71 钾长石(63~90μm)pIRIR [22] URS 43°30′50″N,87°19′48″E; 1603m 9.4 27.4 石英(4~11μm)SMAR [28] RSK1 43°13′N,76°51′E; 1070m 80(40) 83 石英(4~11μm) IRSL [36] RSK2 43°13′N,76°51′E; 1070m 80(8) 34.2 长石(4~11μm)PIR-IRSL [21] 哈萨克斯坦和吉尔吉斯斯坦 Tramplin 43°12′31″N,76°56′01″E; 1020m 10.5 40 AMS14C蜗牛 [45] Romantic 43°12′31″N,77°01′11″E; 1000m 9(5.9) 35 AMS14C木炭、沉积物 [45] Valikhanov 43°10′30″N,69°19′02″E; 1000m 7.5 25 AMS14C沉积物 [45] BSK 42°42′15″N,74°46′51″E; 1432m 30 60 石英(90~250μm)SAR [18] 注:X(Y)表示总共X,其中上部Y作为研究对象。TLD-塔勒德,ZKT-则克台,XY-新源,ZSP-昭苏波马,ZS-昭苏,XEBLK-肖尔布拉克,NLK-尼勒克,YN-伊宁,TEH-天鹅湖,TKLK-特克拉克,LJW-鹿角湾,SXG-水西沟,DFS-大佛寺,BYH-白杨河,URS-乌鲁木齐河剖面,RSK-Remizovka,BSK-比什凯克。 -
[1] Pye K. The nature, origin and accumulation of loess[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1995, 14: 653-667. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(95)00047-X
[2] Roberts H M. The Development and Application of Luminescence Dating to Loess Deposits:a Perspective on the Past, Present and Future[J]. Boreas, 2008, 37: 484-507.
[3] Porter S C, An Z. Correlation between climate events in the North Atlantic and China during the last glaciation[J]. Nature, 1995, 375: 305-308. doi: 10.1038/375305a0
[4] 鹿化煜, 安芷生, Vandenberghe J, 等.洛川黄土地层定年的一个模式及其初步应用[J].沉积学报, 1997, 15(3): 150-152. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700005914
LU Huayu, AN Zhisheng, Vandenberghe J, et al. A dating model of loess stratigraphy in the central Chinese Loess Plateau and its preliminary application [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(3): 150-152. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700005914
[5] An Z S. The history and variability of the East Asian paleomonsoon climate[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2000, 19: 171-187. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00060-8
[6] Kohfeld K. Glacial-interglacial changes in dust deposition on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22(18-19): 1859-1878. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(03)00166-5
[7] Sun Y B, An Z S. Late Pliocene-Pleistocene changes in mass accumulation rates of eolian deposits on the central Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2005, 110: D23101. doi: 10.1029/2005JD006064
[8] Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China[J]. Nature, 2002, 416: 159-163. doi: 10.1038/416159a
[9] Stevens T, Lu H, Thomas D S G, et al. Optical dating of abrupt shifts in the Late Pleistocene East Asian Monsoon[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(5): 415. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1130-G24524A.1/
[10] Lu Y C, Wang X L, Wintle A G. A new OSL chronology for dust accumulation in the last 130000 yr for the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Research, 2007, 67(1): 152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.08.003
[11] Lai Z P, Wintle A G, Thomas D S G. Rates of dust deposition between 50ka and 20ka revealed by OSL dating at Yuanbao on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 248(3-4): 431-439. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.12.013
[12] Kang S G, Roberts H M, Wang X L, et al. Mass accumulation rate changes in Chinese loess during MIS 2, and asynchrony with records from Greenland ice cores and North Pacific Ocean sediments during the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Aeolian Research, 2015, 19: 251-258. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2015.05.005
[13] Kang S G, Wang X L, Lu Y C. Quartz OSL chronology and dust accumulation rate changes since the Last Glacial at Weinan on the southeastern Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Boreas, 2013, 42(4): 815-829. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1111/bor.12005
[14] Buylaert J P, Murray A S, Vandenberghe D, et al. Optical dating of Chinese loess using sand-sized quartz: Establishing a time frame for Late Pleistocene climate changes in the western part of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2008, 3(1-2): 99-113. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2007.05.003
[15] Stevens T, Buylaert J-P, Lu H, et al. Mass accumulation rate and monsoon records from Xifeng, Chinese Loess Plateau, Based on a luminescence age model[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2016, 31(4): 391-405. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2848
[16] 刘东生.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985:41-81.
LIU Tungsheng. Loess and Environment [M]. Science Press, Beijing, 1985: 44-81.
[17] Kang S G, Wang X L, Lu Y C, et al. A high-resolution quartz OSL chronology of the Talede loess over the past ~30ka and its implications for dust accumulation in the Ili Basin, Central Asia[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 30: 181-187. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.04.006
[18] Youn J H, Seong Y B, Choi J H, et al. Loess deposits in the northern Kyrgyz Tien Shan: Implications for the paleoclimate reconstruction during the Late Quaternary[J]. Catena, 2014, 117: 81-93. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2013.09.007
[19] Li G Q, Wen L J, Xia D S, et al. Quartz OSL and K-feldspar pIRIR dating of a loess/paleosol sequence from arid central Asia, Tianshan Mountains, NW China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 28: 40-53. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.03.011
[20] Song Y G, Lai Z P, Li Y, et al. Comparison between luminescence and radiocarbon dating of late Quaternary loess from the Ili Basin in Central Asia[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 30: 405-410. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.01.012
[21] Fitzsimmons K E, Sprafke T, Zielhofer C, et al. Loess accumulation in the Tian Shan piedmont: Implications for palaeoenvironmental change in arid Central Asia[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 469:30-43. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.07.041
[22] Li G Q, Rao Z G, Duan Y W, et al. Paleoenvironmental changes recorded in a luminescence dated loess/paleosol sequence from the Tianshan Mountains, arid central Asia, since the penultimate glaciation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 448: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.05.008
[23] Li Y, Song Y G, Lai Z P, et al. Rapid and cyclic dust accumulation during MIS 2 in central Asia inferred from loess OSL dating and grainsize analysis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 32365. doi: 10.1038/srep32365
[24] Dodonov A E, Baiguzina L L. Loess stratigraphy of central Asia: Paleoclimatic and Palaeoenvironmental aspects[J]. Quaternary Science Review, 1995, 95: 707-720.
[25] 叶玮.新疆西风区黄土沉积特征与古气候[M].北京:海洋出版社, 2001.
YE Wei. Loess Deposition Features and Paleoclimate in the Westerlies-Dominated Region of Xinjiang [M]. Ocean Press, Beijing, 2001.
[26] Li X Q, Zhao K L, Dodson J, et al. Moisture dynamics in central Asia for the last 15 kyr: New evidence from Yili Valley, Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(23-24): 3457-3466. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.09.010
[27] Zhao H, Li S-H, Li B, et al. Holocene climate changes in westerly-dominated areas of central Asia: Evidence from optical dating of two loess sections in Tianshan Mountain, China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 30: 188-193. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.04.002
[28] Lu H H, Xu Y D, Niu Y, et al. Late Quaternary loess deposition in the southern Chaiwopu Basin of the northern Chinese Tian Shan foreland and its palaeoclimatic implications[J]. Boreas, 2016, 45(2): 304-321. doi: 10.1111/bor.12152
[29] 潘燕芳.昆仑山北坡全新世黄土记录的环境变化[D].乌鲁木齐: 中国科学院新疆生态与地理研究所, 2013.
PAN Yanfang. Holocene Loess Deposits and Environmental Changes on the Northern Slope of Kunlun Mountains, Xinjiang, China [D]. Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography Chinese Academy of Sciences, Urumqi, 2013.
[30] 史正涛.伊犁黄土形成时代及环境研究[D].西安: 中国科学院地球环境研究所, 2005.
SHI Zhengtao. Age of Yili Loess in Xinjiang and Its Paleoenvironmental Implications[D]. Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005.
[31] Sun J M. Source regions and formation of the loess sediments on the high mountain regions of northwestern China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2002, 58(3): 341-351. doi: 10.1006/qres.2002.2381
[32] Ding Z L, Ranov V, Yang S L, et al. The loess record in southern Tajikistan and correlation with Chinese loess[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 200: 387-400. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00637-4
[33] Sun J M, Ye J, Wu W Y, et al. Late Oligocene-Miocene mid-latitude aridification and wind patterns in the Asian interior[J]. Geology, 2010, 38(6): 515-518. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f18074c9a90dbf63a40cf250728b485b
[34] Song Y G, Chen X L, Qian L B, et al. Distribution and composition of loess sediments in the Ili Basin, Central Asia[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 334-335: 61-73. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2013.12.053
[35] Mavlyanov G A, Academician P, Kasymov S M, et al. The Uzbekistan Loess, genesis and distribution[J]. GeoJournal, 1987, 15(2): 145-150.
[36] Machalett B, Frechen M, Hambach U, et al. The loess sequence from Remisowka (northern boundary of the Tien Shan Mountains, Kazakhstan)—Part Ⅰ: Luminescence dating[J]. Quaternary International, 2006, 152-153: 192-201. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2005.12.014
[37] Li Y, Song Y G, Yan L B, et al. Timing and spatial distribution of loess in Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(5): e0125492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125492
[38] Fang X M, Shi Z T, Yang S L, et al. Loess in the Tian Shan and its implications for the development of the Gurbantunggut Desert and drying of northern Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(6): 1381-1387.
[39] 李传想, 宋友桂, 王乐民.伊犁盆地黄土分布、年代及粉尘来源分析[J].地球与环境, 2012, 40(3): 314-320. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdqhx201203003
LI Chuanxiang, SONG Yougui, WANG Lemin. Distribution, age and dust sources of loess in the Ili Basin[J]. Earh And Environment, 2012, 40(3):314-320. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdqhx201203003
[40] 叶玮, 靳鹤龄, 赵兴有等.新疆伊犁地区黄土的粒度特征与物质来源[J].干旱区地理, 1998, 21(4): 1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199801018284
YE Wei, JIN Heling, ZHAO Xingyou, et al. Depositional features and material sources of loess in Yili region, Xinjiang[J].Arid Land Geography, 1998, 21(4): 1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199801018284
[41] 史正涛, 董铭.天山黄土粒度特征及粉尘来源[J].云南师范大学学报, 2007, 27(3): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9793.2007.03.013
SHI Zhengtao, DONG Ming. Characteristics of loess grain size and source of dust in Tianshan, China[J]. Journal of Yunnan Normal University, 2007, 27(3): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9793.2007.03.013
[42] 康树刚, 王旭龙, 王松娜.中国黄土释光测年与应用:过去、现在与未来[J].地球环境学报, 2016, 7(5): 442-467. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhjxb201605002
KANG Shugang, WANG Xulong, WANG Songna. Luminescence dating of Chinese Loess and its applications: past, present and future[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2016, 7(5):442-467. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhjxb201605002
[43] Lu Y C, Zhang J Z, Xie J. Thermoluminescence dating of loess and palaeosols from the Lantian section, Shaanxi Province, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1988, 7: 245-250. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(88)90011-X
[44] Song Y G, Li C X, Zhao J D, et al. A combined luminescence and radiocarbon dating study of the Ili loess, central Asia[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2012, 10: 2-7. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2012.04.005
[45] Feng Z D, Ran M, Yang Q L, et al. Stratigraphies and chronologies of late Quaternary loess-paleosol sequences in the core area of the central Asian arid zone[J]. Quaternary International, 2011, 240(1-2): 156-166. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.10.019
[46] Long H, Shen J, Wang Y, et al. High-resolution OSL dating of a late Quaternary sequence from Xingkai Lake (NE Asia): Chronological challenge of the "MIS 3a Mega-paleolake" hypothesis in China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 428: 281-292. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.07.003
[47] E C Y, Lai Z P, Sun Y J, et al. A luminescence dating study of loess deposits from the Yili River basin in western China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2012, 10: 50-55. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2012.04.022
[48] 葛本伟, 刘安娜.天山北麓黄土沉积的光释光年代学及环境敏感粒度组分研究[J].干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(2): 110-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqzyyhj201702019
GE Benwei, LIU Anna. Optically stimulated luminescence dating and analysis of environmentally sensitive grain-size component of loess in the northern slope of Tian Shan [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(2): 110-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqzyyhj201702019
[49] Yang S L, Forman S L, Song Y G, et al. Evaluating OSL-SAR protocols for dating quartz grains from the loess in Ili Basin, central Asia[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2014, 20: 78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2013.11.004
[50] Lai Z P. Chronology and the upper dating limit for loess samples from Luochuan section in the Chinese Loess Plateau using quartz OSL SAR protocol[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 37(2): 176-185. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.08.003
[51] Krbetschek M R, Götze J, Dietrich A, et al. Spectral information from minerals relevant for luminescence dating[J]. Radiation Measurements, 1997, 27: 695-748. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(97)00223-0
[52] 赖忠平, 欧先交.光释光测年基本流程[J].地理科学进展, 2013, 32(5): 683-693. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlkxjz201305001
LAI Zhongping, OU Xianjiao. Basic procedures of optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating[J]. Process in Geography, 2013, 32(5):683-693. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlkxjz201305001
[53] Yang H, Chen J, Thompson J A, et al. Optical dating of the 12 May 2008, Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake-related sediments: Tests of zeroing assumptions[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2012, 10: 273-279. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2012.02.022
[54] Buylaert J-P, Jain M, Murray A S, et al. A robust feldspar luminescence dating method for Middle and Late Pleistocene sediments[J]. Boreas, 2012, 41(3): 435-451. doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3885.2012.00248.x
[55] Long H, Shen J, Tsukamoto S, et al. Dry early Holocene revealed by sand dune accumulation chronology in Bayanbulak Basin (Xinjiang, NW China)[J]. The Holocene, 2014, 24(5): 614-626. doi: 10.1177/0959683614523804
[56] 史正涛.天山黄土与西北内陆干旱化[D].兰州: 兰州大学, 2002.
SHI Zhengtao. Mountains and Its Implication of Drying and Desertification in Xinjiang, Northwest China [D]. Lanzhou University, 2002.
[57] 施雅风.中国第四纪冰期划分改进建议[J].冰川冻土, 2002, 24(6): 687-692. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2002.06.001
SHI Yafeng. A suggestion to improve the chronology of Quaternary glaciations in China [J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2002, 24(6): 687-692. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2002.06.001
[58] Clark P U, Dyke A S, Shakun J D, et al. The Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Science, 2009, 325: 710-715. doi: 10.1126/science.1172873
[59] Singhvi A K, Bluszcz A, Bateman M D, et al. Luminescence dating of loess-palaeosol sequences and coversands: methodological aspects and palaeoclimatic implications[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2001, 54: 193-211. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(01)00048-4
[60] Qiang M R, Chen F H, Song L, et al. Late Quaternary aeolian activity in Gonghe Basin, northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2013, 79(3): 403-412. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2013.03.003
[61] Yu L P, Lai Z P. OSL chronology and palaeoclimatic implications of aeolian sediments in the eastern Qaidam Basin of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 337-338: 120-129. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.04.004
[62] Chen F H, Wu D, Chen J H, et al. Holocene moisture and East Asian summer monsoon evolution in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau recorded by Lake Qinghai and its environs: A review of conflicting proxies[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 154: 111-129. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.10.021
[63] Stauch G, Lai Z P, Lehmkuhl F, et al. Environmental changes during the late Pleistocene and the Holocene in the Gonghe Basin, north-eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 509:144-155. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.12.032
[64] Wang X, Yi S, Lu H, et al. Aeolian process and climatic changes in loess records from the northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Response to global temperature forcing since 30ka[J]. Paleoceanography, 2015, 30(6): 612-620. doi: 10.1002/2014PA002731
[65] Lifton N, Beel C, Hättestrand C, et al. Constraints on the late Quaternary glacial history of the Inylchek and Sary-Dzaz valleys from in situ cosmogenic 10Be and 26Al, eastern Kyrgyz Tian Shan[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 101: 77-90. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.06.032
[66] Zhao J D, Liu S Y, Wang J, et al. Glacial advances and ESR chronology of the Pochengzi Glaciation, Tianshan Mountains, China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2009, 53(3): 403-410.
[67] Zhao J D, Song Y G, King J W, et al. Glacial geomorphology and glacial history of the Muzart River valley, Tianshan Range, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(11-12): 1453-1463. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.03.004
[68] Zhao J D, Yin X F, Harbor J M, et al. Quaternary glacial chronology of the Kanas River valley, Altai Mountains, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2013, 311: 44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2013.07.047
[69] Wu G J. Microparticle record in the Guliya ice core and its comparison with polar records since the Last Interglacial[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(6): 607-611. doi: 10.1360/03wd0419
[70] Cheng H, Zhang P Z, Spötl C, et al. The climatic cyclicity in semiarid-arid central Asia over the past 500000 years[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(1): L01705.
[71] Narama C, Kondo R, Tsukamoto S, et al. OSL dating of glacial deposits during the Last Glacial in the Terskey-Alatoo Range, Kyrgyz Republic[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2007, 2(1-4): 249-254. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.06.007
[72] Mahowald N, Kohfeld K, Hansson M, et al. Dust sources and deposition during the last glacial maximum and current climate: A comparison of model results with paleodata from ice cores and marine sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1999, 104(D13): 15895-15916. doi: 10.1029/1999JD900084
[73] Reader M C, Fung I, McFarlane N. Mineral aerosols: a comparison of the last glacial maximum and preindustrial Holocene[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2000, 37: 751-767. doi: 10.1139/e99-109
[74] Chen F H, Yu Z C, Yang M l, et al. Holocene moisture evolution in arid central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2008, 27(3-4): 351-364. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.10.017
[75] An C B, Lu Y B, Zhao J J, et al. A high-resolution record of Holocene environmental and climatic changes from Lake Balikun (Xinjiang, China): Implications for central Asia[J]. The Holocene, 2011, 22(1): 43-52.
[76] Küster Y, Hetzel R, Krbetschek M, et al. Holocene loess sedimentation along the Qilian Shan (China): significance for understanding the processes and timing of loess deposition[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(1-2): 114-125. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.03.003
-



 下载:
下载: